Simulation Study on the Magnetic Field Characteristics of a Permanent Magnet Motor for a Rim-Driven Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of Permanent Magnet Motor for RDD
2.1. Thin-Yoke Wide-Tooth Fractional Slot Concentrated Winding Stator
2.2. Coreless Halbach Permanent Magnet Array Rotor
3. Harmonic Analysis of Air Gap Magnetic Field Based on One-Dimensional Magnetic Circuit Method
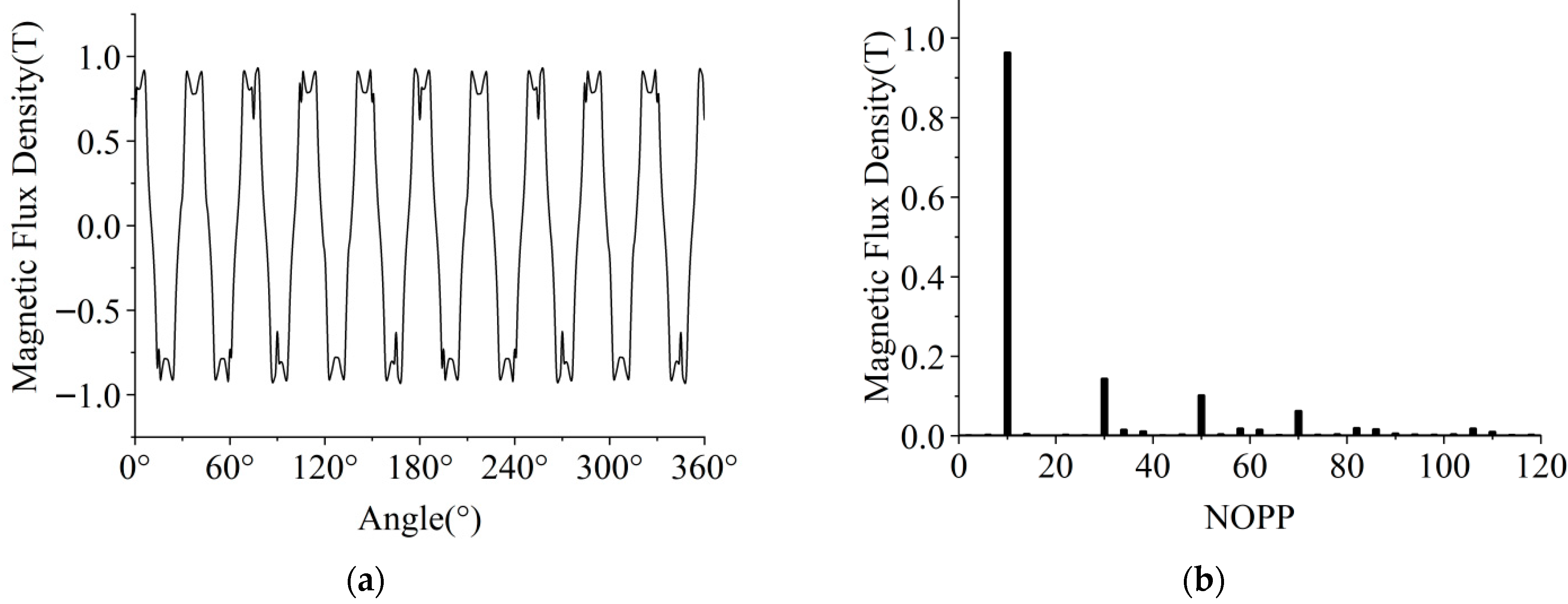
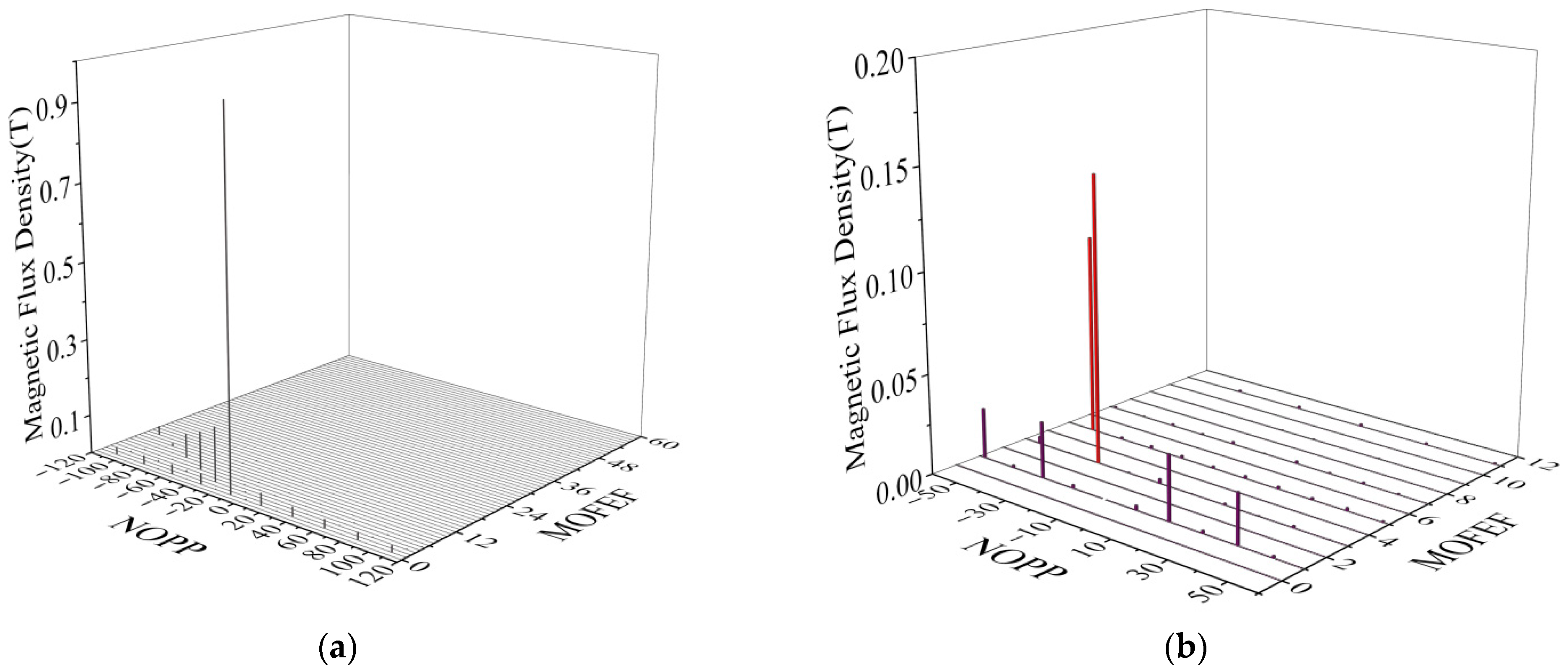
3.1. Radial Air Gap Magnetic Flux Density
3.2. Tangential Air Gap Magnetic Flux Density
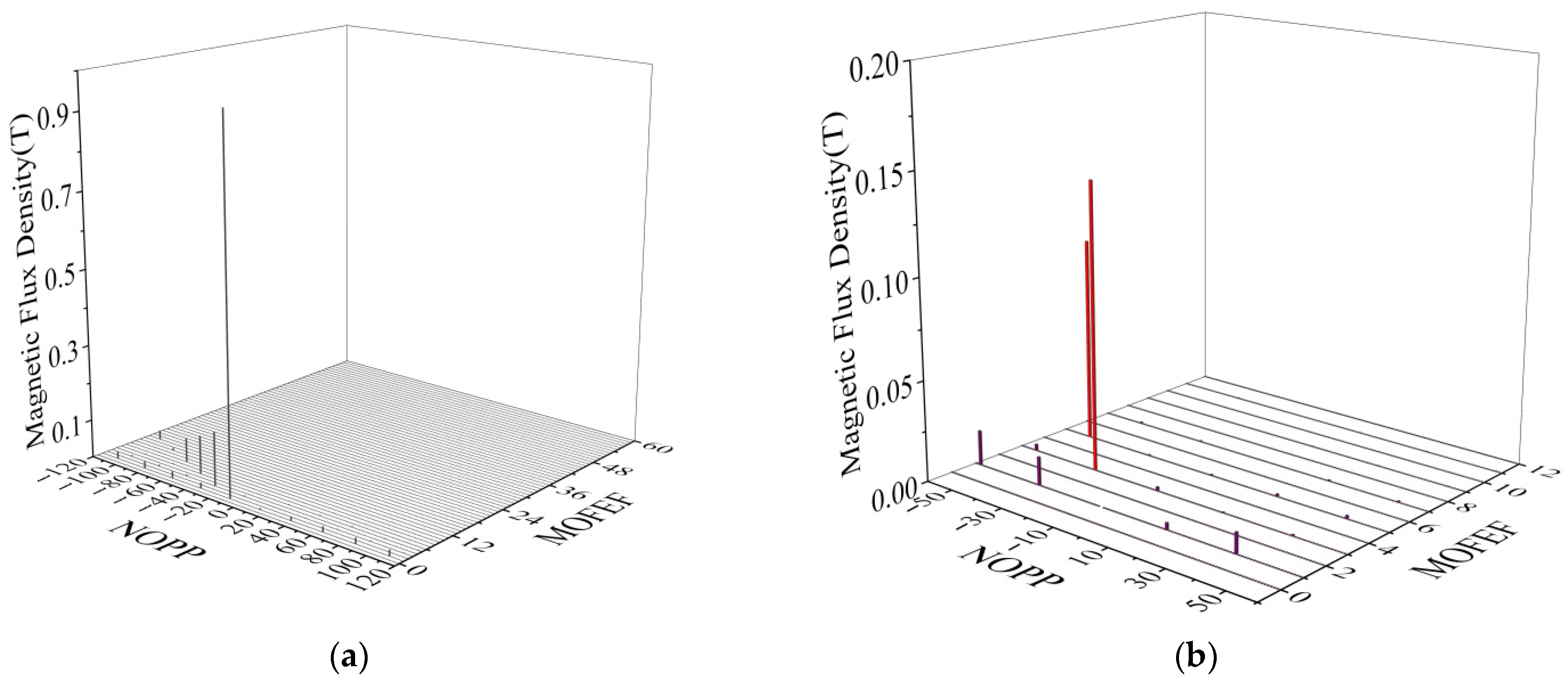
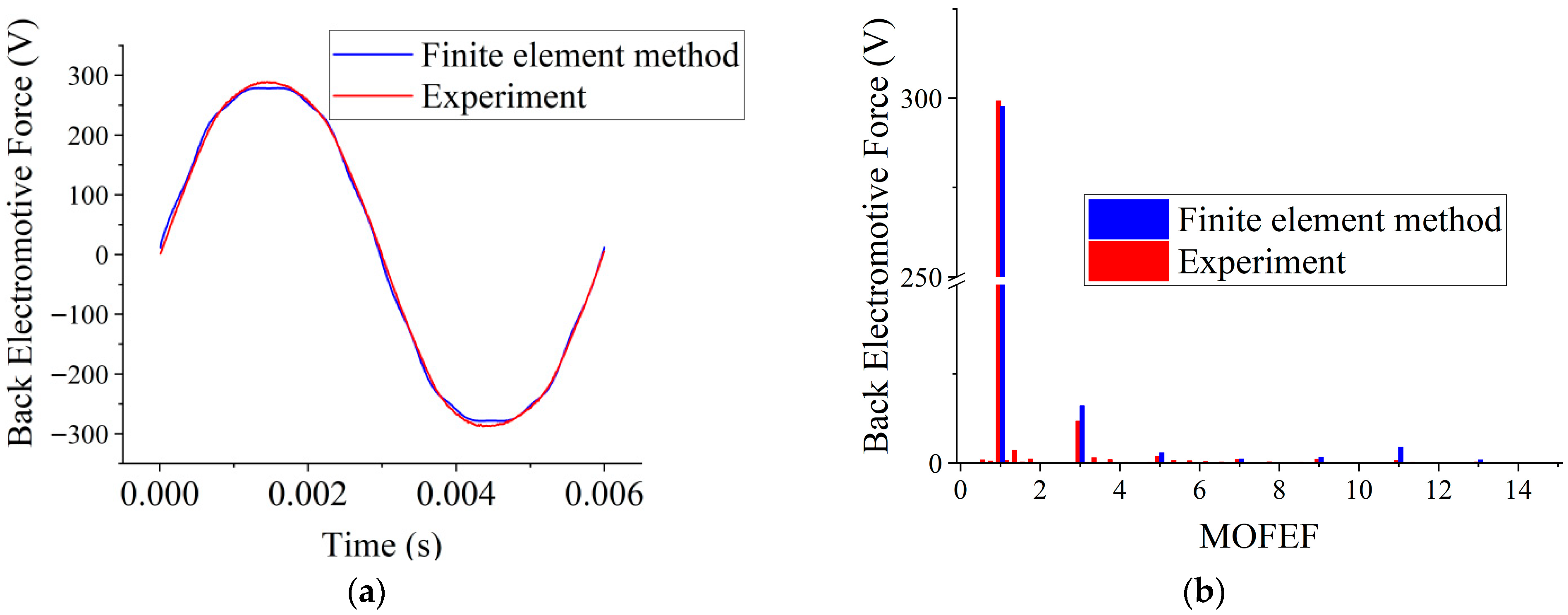
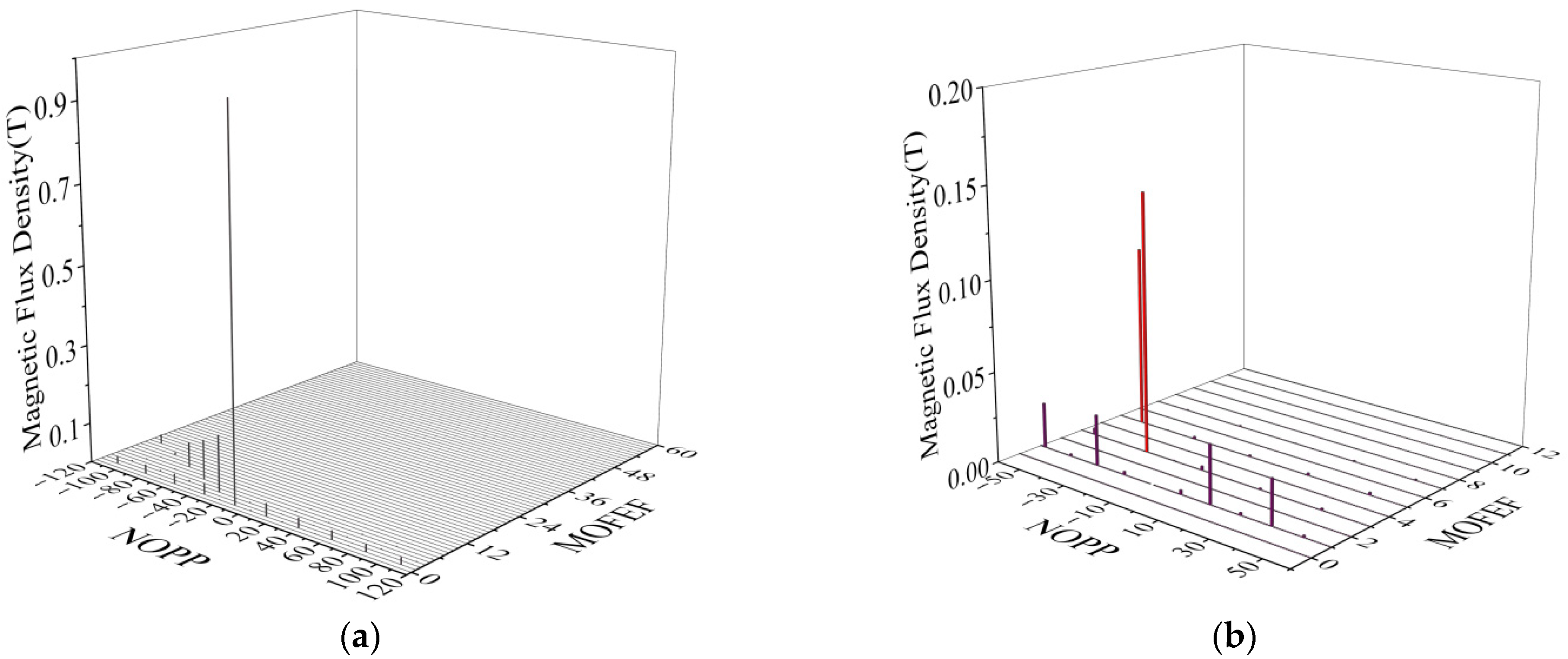
4. Simulation Analysis of Air Gap Magnetic Field Based on Two-Dimensional Finite Element Method
4.1. No-Load
4.2. Contains Only Fundamental Current
4.3. Contains Harmonic Currents
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NOPP | number of pole pairs |
| MOFEF | multiples of fundamental electrical frequency |
References
- Dubas, A.J.; Bressloff, N.W.; Sharkh, S.M. Numerical modelling of rotor–stator interaction in rim driven thrusters. Ocean Eng. 2015, 106, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassannia, A.; Darabi, A. Design and performance analysis of superconducting rim-driven synchronous motors for marine propulsion. IEEE Trans. Appl. Suppercon. 2014, 24, 5200207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohy, P.M.; Smith, A.C.; Husband, M.; Hopewell, P. Rim-drive marine thruster using a multiple-can induction motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2013, 7, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.H. Design Optimisation of a Slotless Brushless Permanent Magnet dc Motor with Helically-Wound Laminations for Underwater Rim-Driven Thrusters. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piet, V.D. Manufacture of a Prototype Advanced Permanent Magnet Motor Pod. J. Ship Prod. 2003, 19, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Vanierschot, M.; Buysschaert, F. Numerical study of scale effects on the open water performance of a rim-driven thruster. Appl. Ocean Res. 2023, 138, 103667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yan, X.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, Z. Experimental research on tribological and vibration performance of water-lubricated hydrodynamic thrust bearings used in marine shaft-less rim driven thrusters. Wear 2019, 426–427, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, M.; Zhu, P.; Cai, W.; Xia, Y.; Li, G. Optimal design and multifield coupling analysis of propelling motor used in a novel integrated motor propeller. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 5742–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, X.; Ouyang, W.; Bai, H.; Xiao, J. Multi-Parameter Fuzzy-Based Neural Network Sensorless PMSM Iterative Learning Control Algorithm for Vibration Suppression of Ship Rim-Driven Thruster. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.W.; Repp, J.R.; Taylor, O.S. Submersible outboard electric motor/propulsor. Nav. Eng. J. 1989, 101, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, K.M.; Pollock, C.; Flower, J.O. Design of a switched reluctance sector motor for an integrated motor/propeller unit. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Electrical Machines and Drives, Durham, UK, 11–13 September 1995; pp. 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkh, S.M.A.; Lai, S.H.; Turnock, S.R. A structurally integrated brushless PM motor for miniature propeller thrusters. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2004, 151, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, P.; Jin, S.; Wei, Y.; Lan, R.; Zhuang, S.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; et al. Design of novel shaftless pump-jet propulsor for multi-purpose long range and high speed autonomous underwater vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 7403304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Refaie, A.M. Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Windings Synchronous Permanent Magnet Machines: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.U.; Kim, J.M.; Koo, D.H.; Woo, B.C.; Hong, D.K.; Lee, J.Y. Fractional slot concentrated winding permanent magnet synchronous machine with consequent pole rotor for low speed direct drive. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2965–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, M.; Perriard, Y. Optimization Design of a Segmented Halbach Permanent-Magnet Motor Using an Analytical Mode. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.; Parsa, L. Multiobjective design optimization of five-phase halbach array permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J. A simple method for performance prediction of permanent magnet eddy current couplings using a new magnetic equivalent circuit model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D.; Bolte, E. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet DC motors. I. Open-circuit field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet DC motors. II. Armature-reaction field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarko, D.; Ban, D.; Lipo, T.A. Analytical calculation of magnetic field distribution in the slotted air gap of a surface permanent-magnet motor using complex relative air gap permeance. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Choi, D.; Cho, Y. Analysis of rotor eccentricity in switched reluctance motor with parallel winding using fem. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2851–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
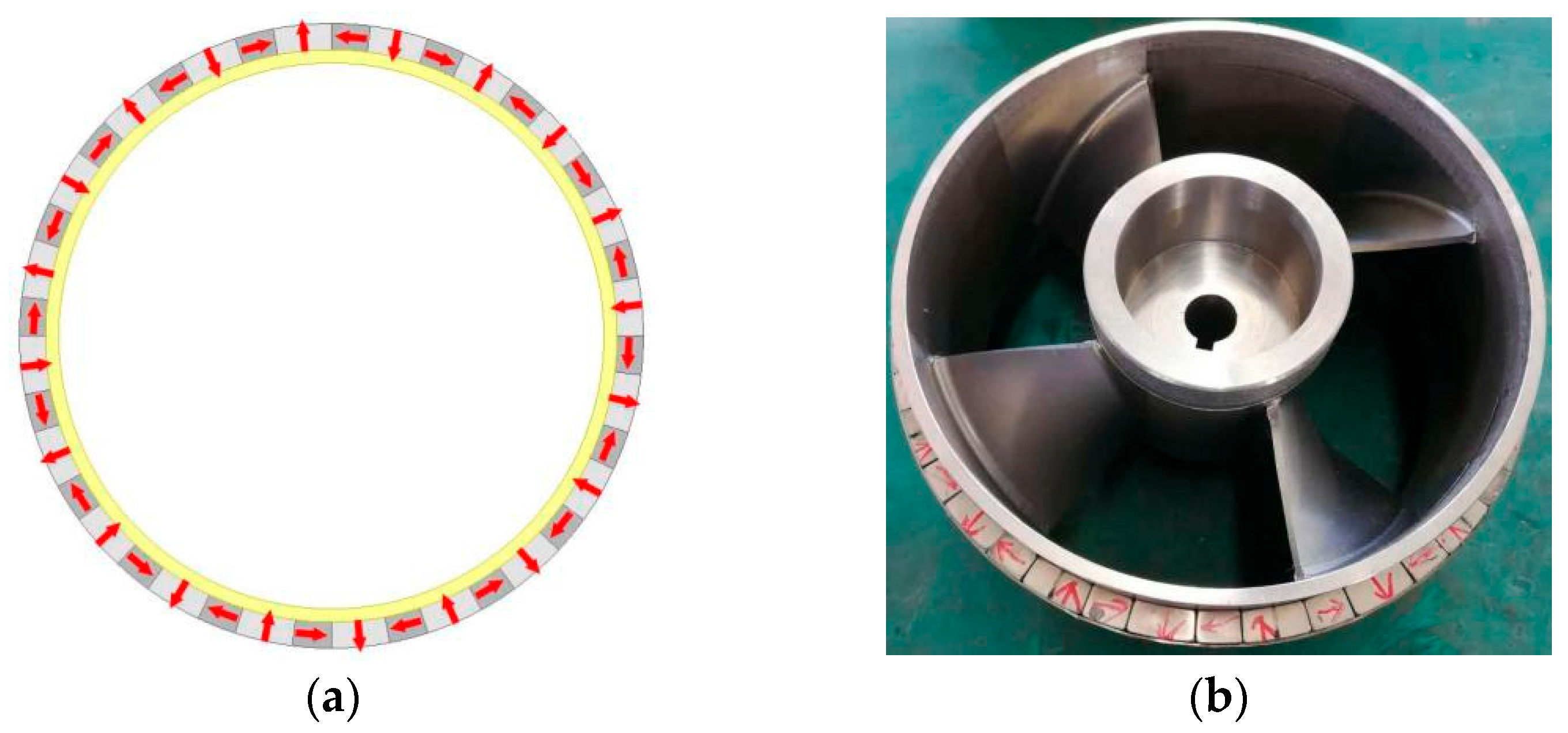

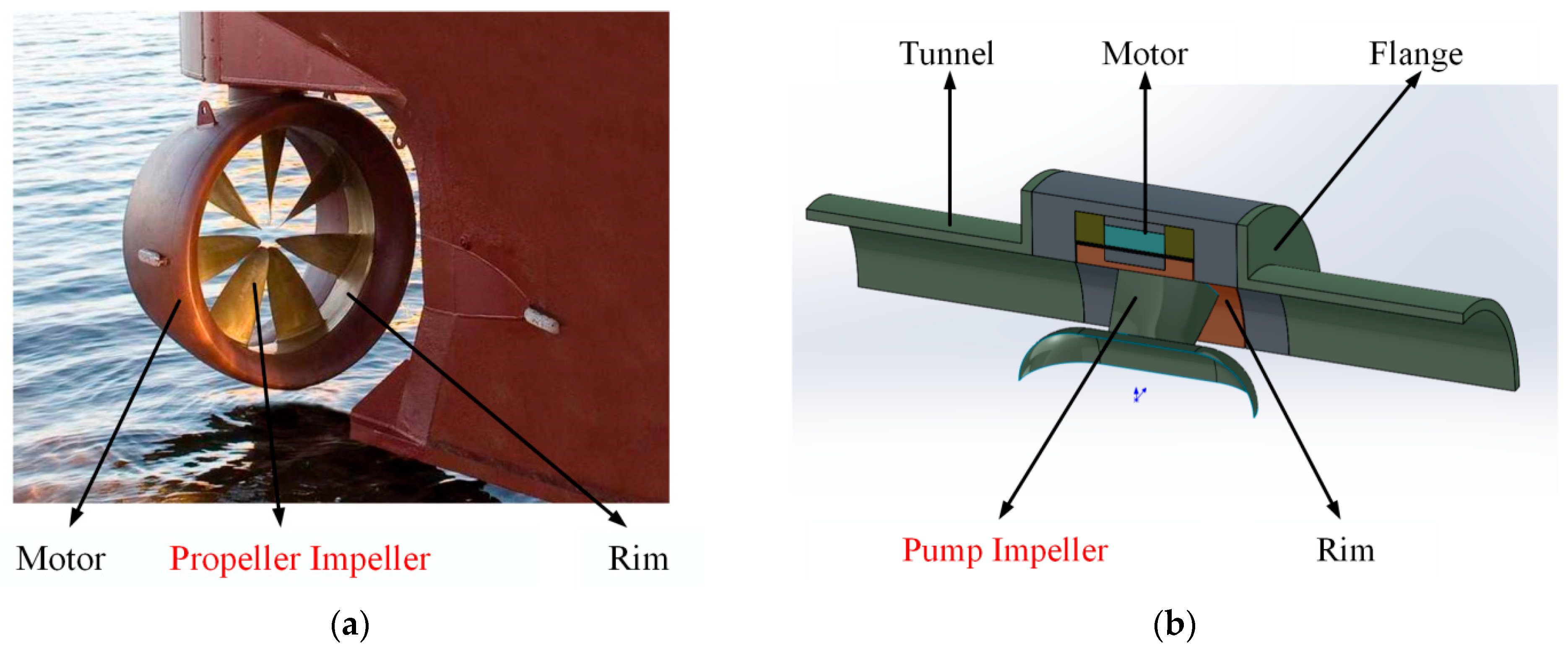
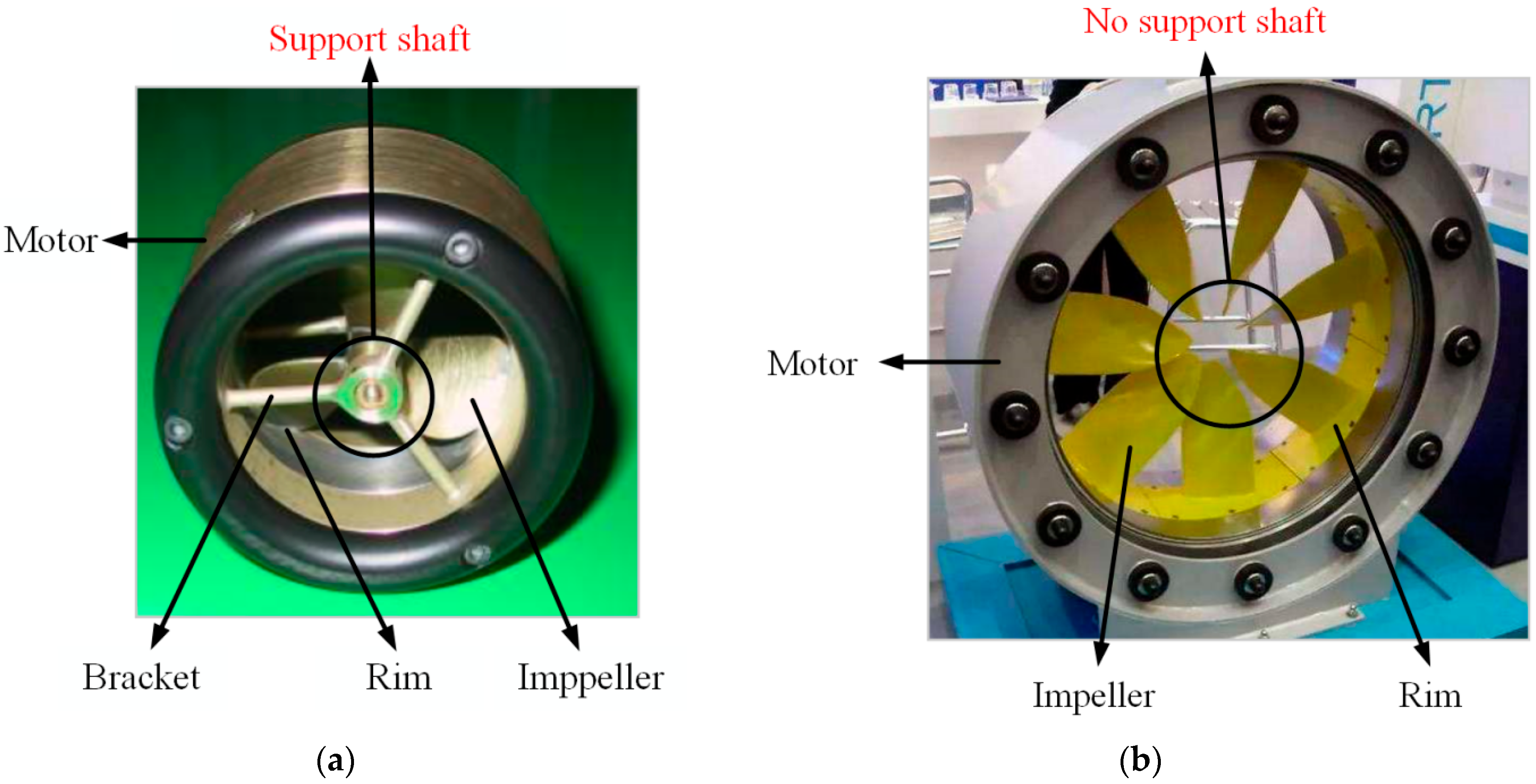

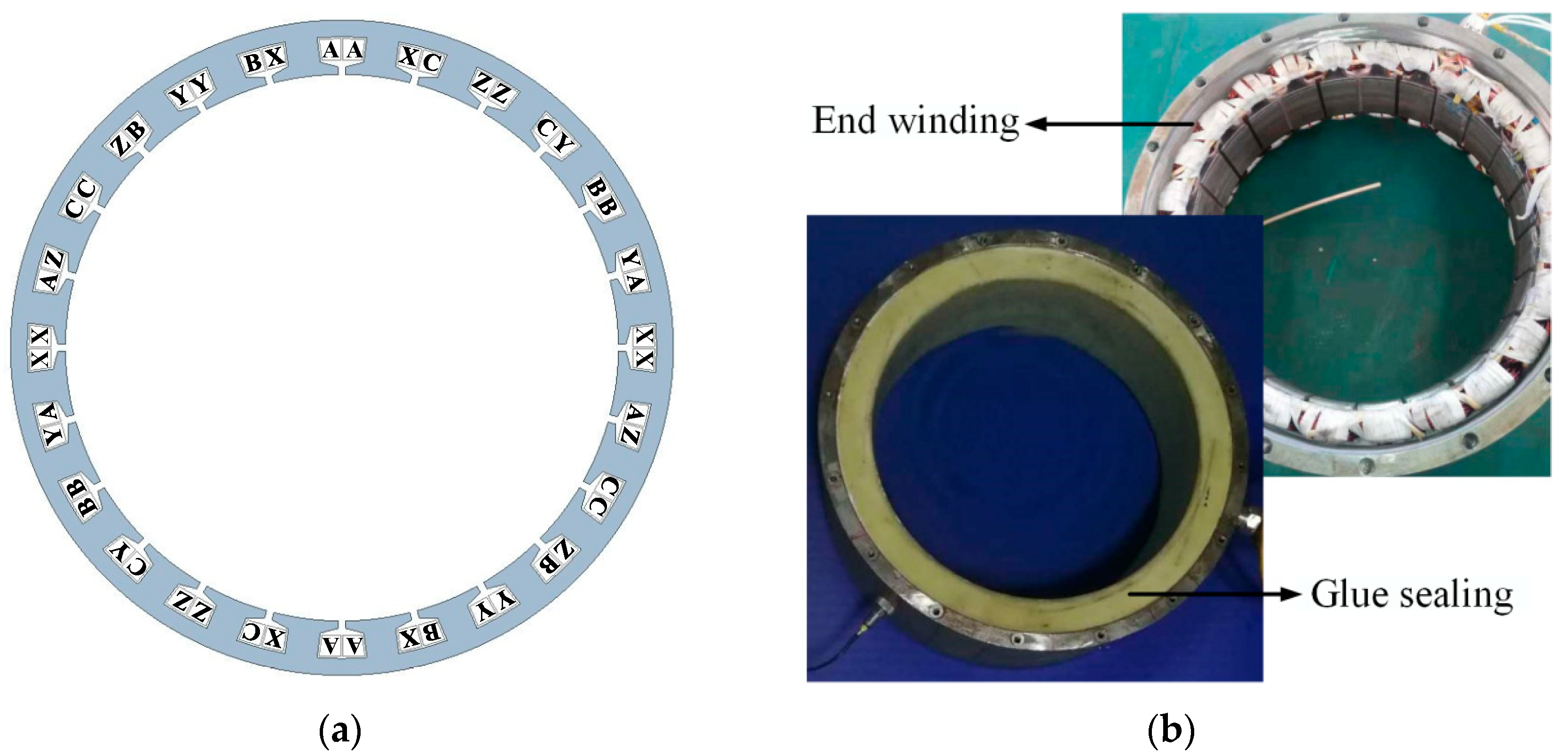
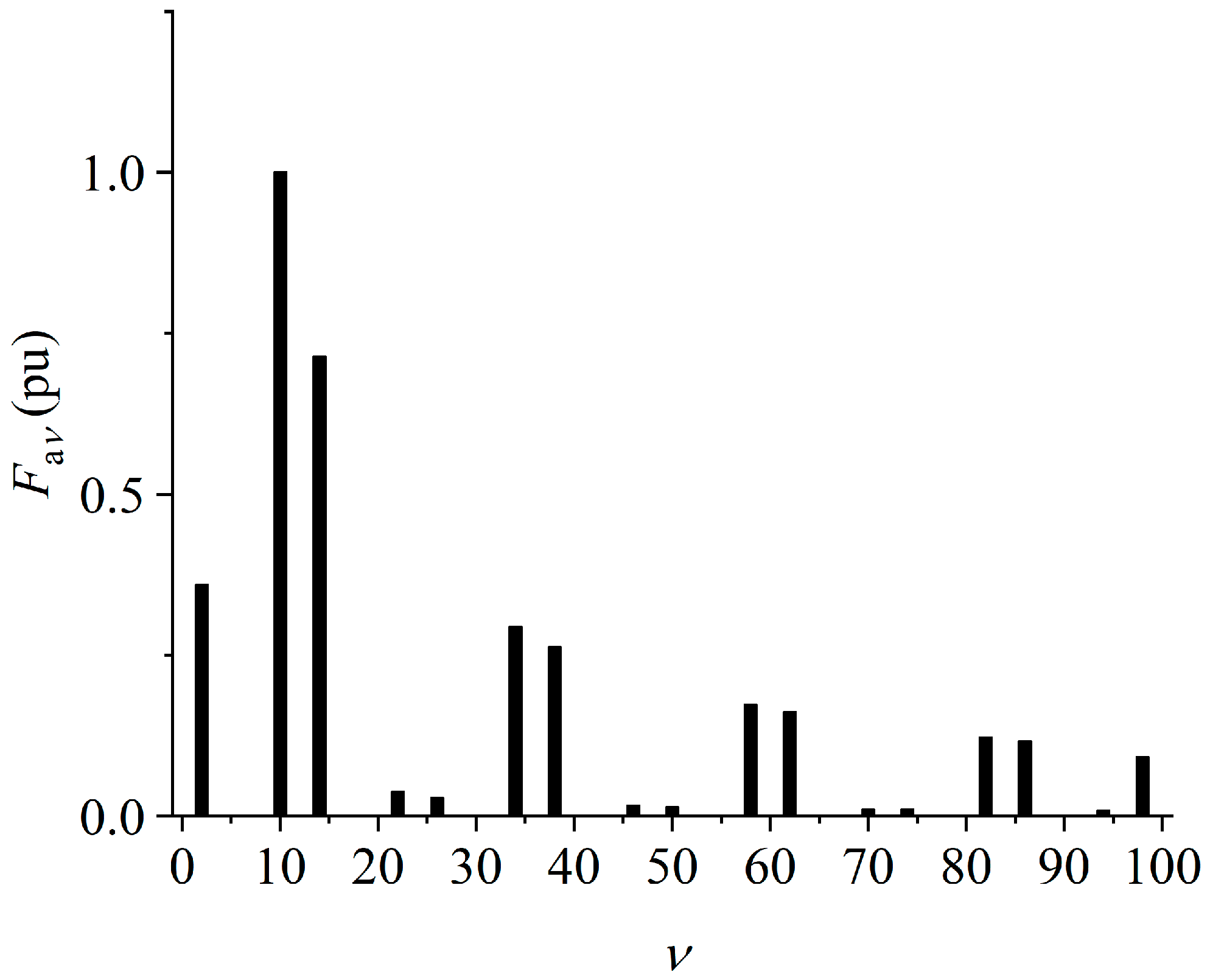








| Design Parameter | Value (Unit) |
|---|---|
| Phase number | 3 |
| Rated power | 11 kW |
| Rated (line) voltage | 380 V |
| Rated speed | 1000 r/min |
| Number of slots | 24 |
| Number of poles | 20 |
| Rated frequency | 166.67 Hz |
| Outer diameter of the stator core | 350 mm |
| Inner diameter of the stator core | 286 mm |
| Thickness of the stator epoxy resin sheath | 1 mm |
| Physical air gap | 1 mm |
| Thickness of the stainless steel sheath of the rotor | 1 mm |
| Thickness of the permanent magnet | 12 mm |
| Flange thickness | 6 mm |
| Outer diameter of the impeller | 250 mm |
| Effective axial length | 56 mm |
| Source | NOPP | MOFEF |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental magnetomotive force of the magnetic pole and constant specific magnetic permeability | 1 | |
| Harmonic magnetomotive force of the magnetic pole and constant specific magnetic permeability | ||
| Fundamental magnetomotive force of the magnetic pole and fundamental specific magnetic permeability | 1 | |
| Harmonic magnetomotive force of the magnetic pole and fundamental specific magnetic permeability |
| Source | NOPP | MOFEF |
|---|---|---|
| Harmonic magnetomotive force of the armature with fundamental current and constant specific magnetic permeability | 1 | |
| Harmonic magnetomotive force of the armature with fundamental current and fundamental specific magnetic permeability | 1 |
| Source | NOPP | MOFEF |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental magnetomotive force of the armature with harmonic current and constant specific magnetic permeability | ||
| Harmonic magnetomotive force of the armature with harmonic current and constant specific magnetic permeability | ||
| Fundamental magnetomotive force of the armature with harmonic current and fundamental specific magnetic permeability | ||
| Harmonic magnetomotive force of the armature with harmonic current and fundamental specific magnetic permeability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.; Shuai, C.; Qiao, M. Simulation Study on the Magnetic Field Characteristics of a Permanent Magnet Motor for a Rim-Driven Device. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011129
Jiang C, Shuai C, Qiao M. Simulation Study on the Magnetic Field Characteristics of a Permanent Magnet Motor for a Rim-Driven Device. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011129
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Chao, Changgeng Shuai, and Mingzhong Qiao. 2025. "Simulation Study on the Magnetic Field Characteristics of a Permanent Magnet Motor for a Rim-Driven Device" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011129
APA StyleJiang, C., Shuai, C., & Qiao, M. (2025). Simulation Study on the Magnetic Field Characteristics of a Permanent Magnet Motor for a Rim-Driven Device. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11129. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011129





