Prediction of Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Using Integrated Geochemistry and Three-Dimensional Electrical Resistivity Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geochemical Sample Collection and Testing
2.1. Sample Collection Method
2.1.1. Sampling Point Layout
2.1.2. Surface Sample Collection Technology
2.1.3. Deep Sample Collection Technology
2.2. Multi-Dimensional Testing Method
2.2.1. Air Drying and Grinding
2.2.2. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
2.2.3. Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (AFS)
2.2.4. Potentiometric Determination of pH
3. 3D ERT Methods and Technologies
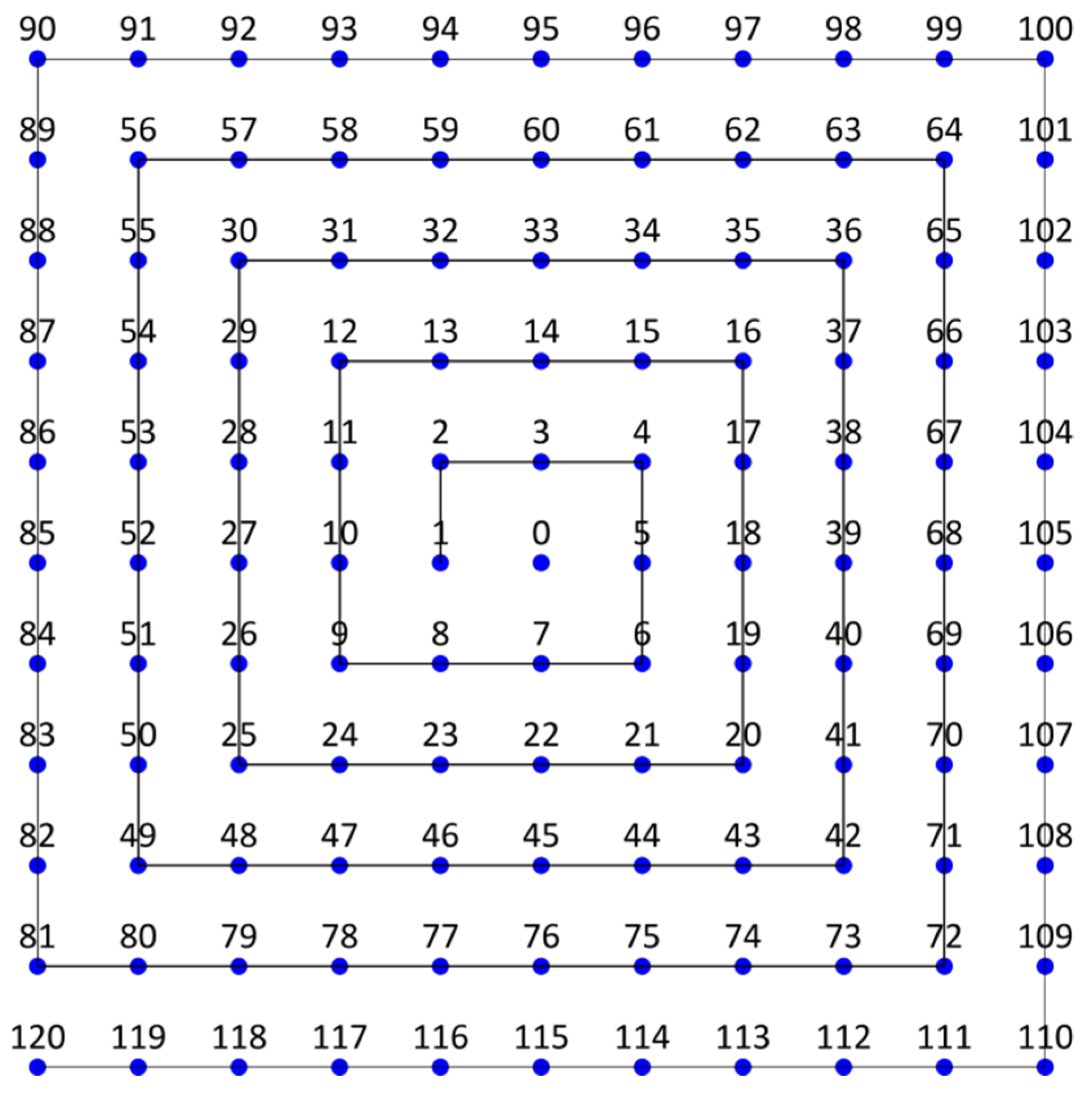
3.1. Data Collection Method
3.2. 3D Resistivity Inversion
4. Statistical Model Construction and Analysis
4.1. Site Pollution Level Assessment
4.1.1. Chemical Test Results
4.1.2. Pollution Degree Assessment
4.2. Geochemical and 3D ERT Characteristics Analysis
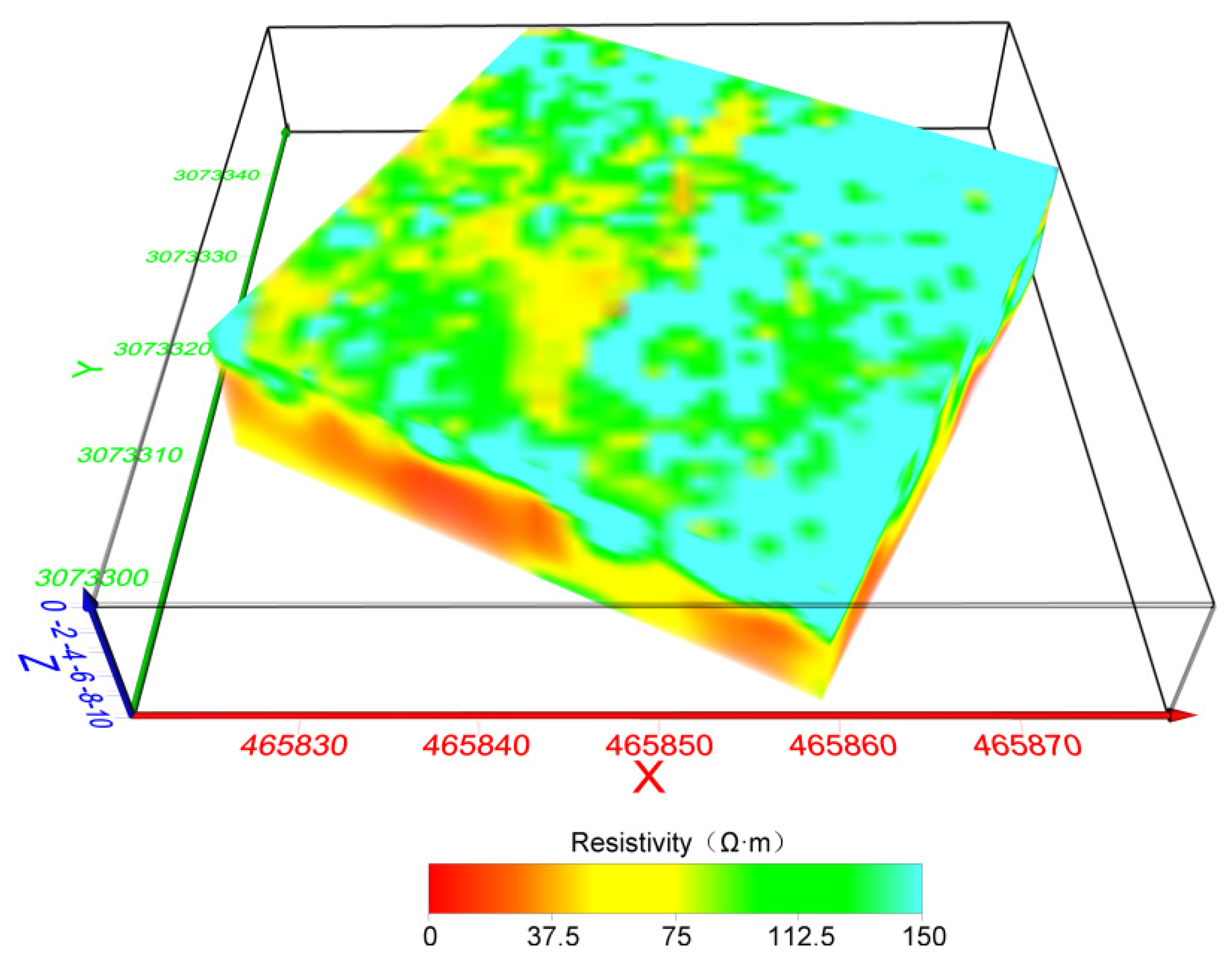
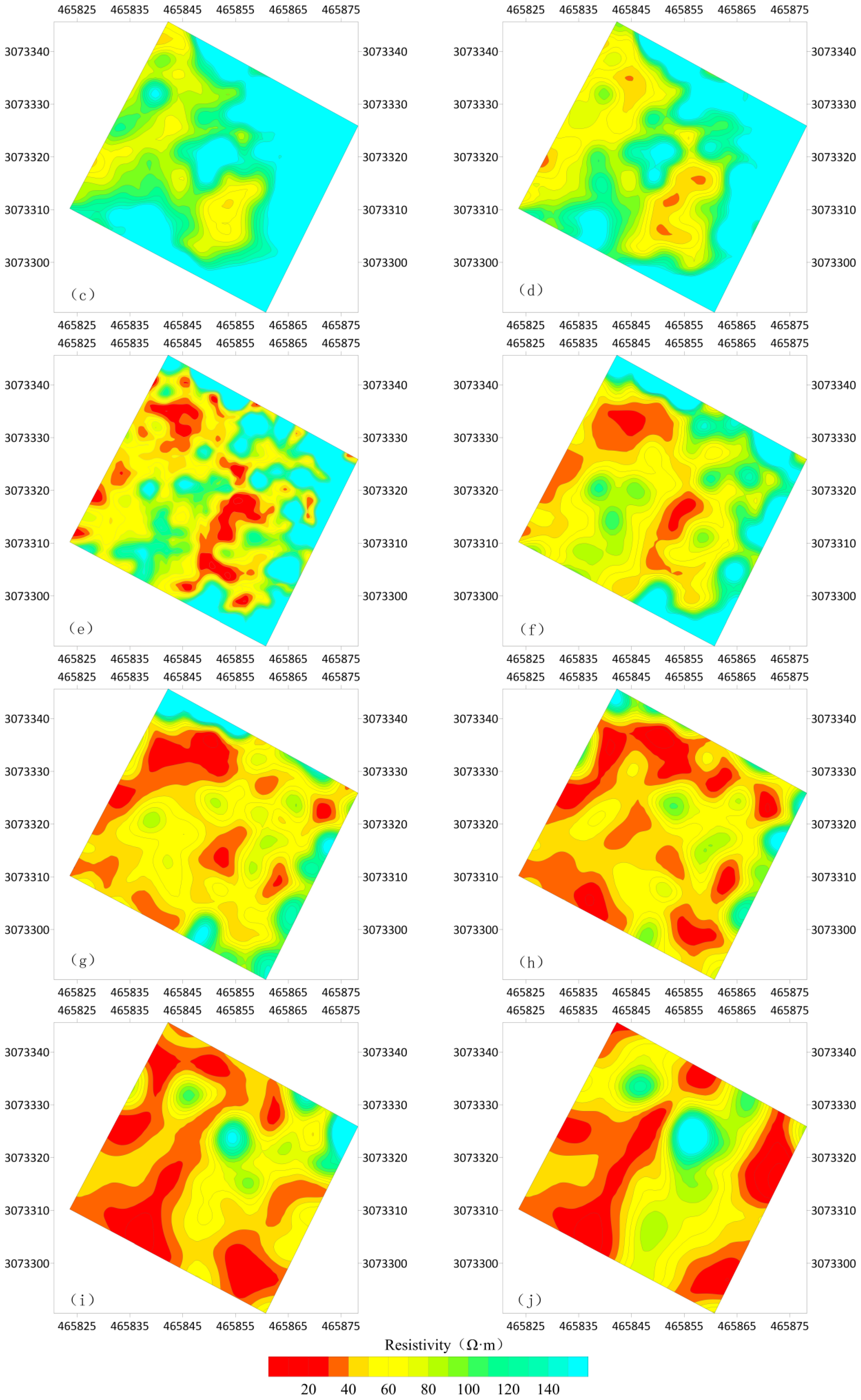
4.2.1. 3D ERT Results
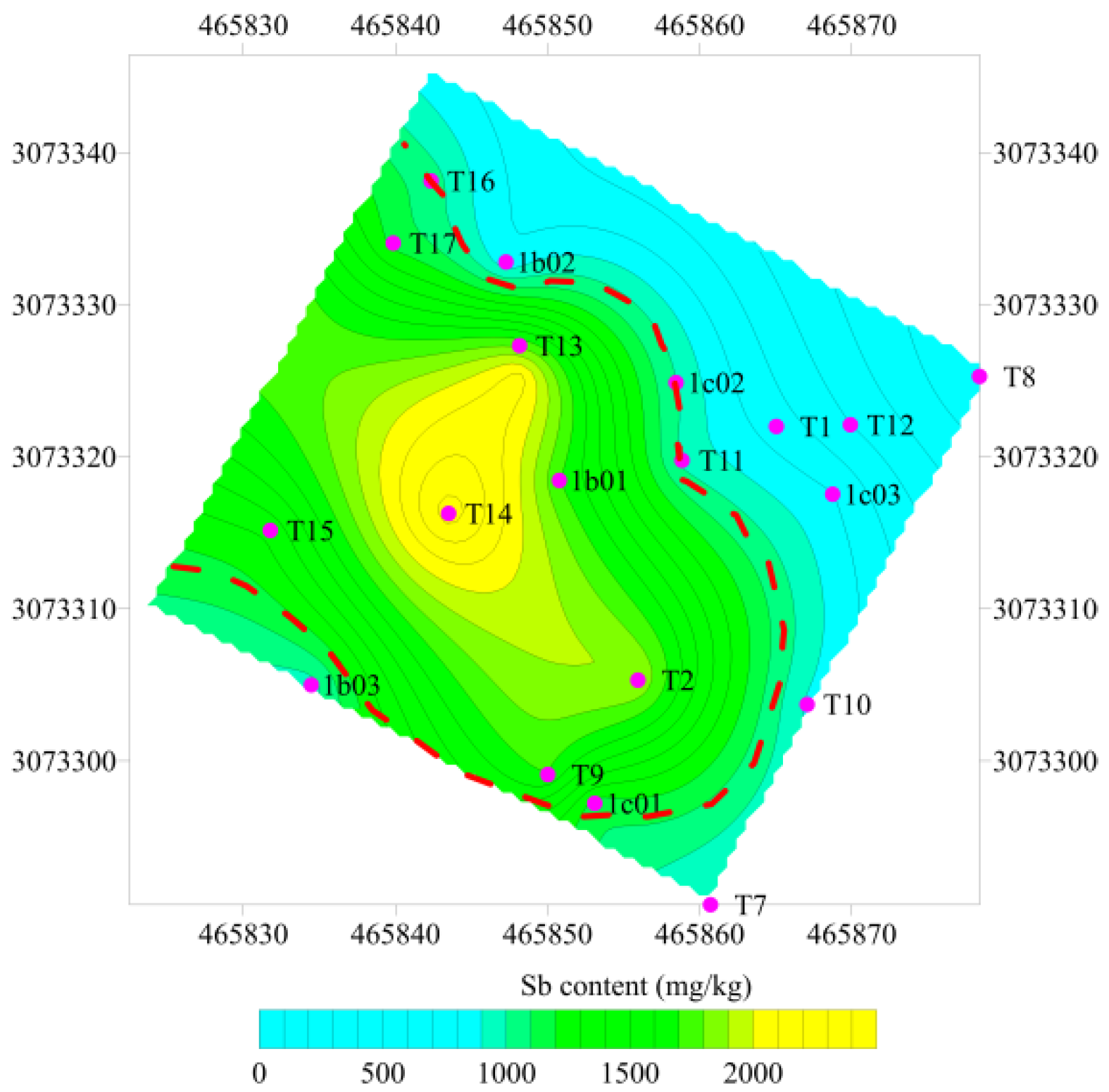
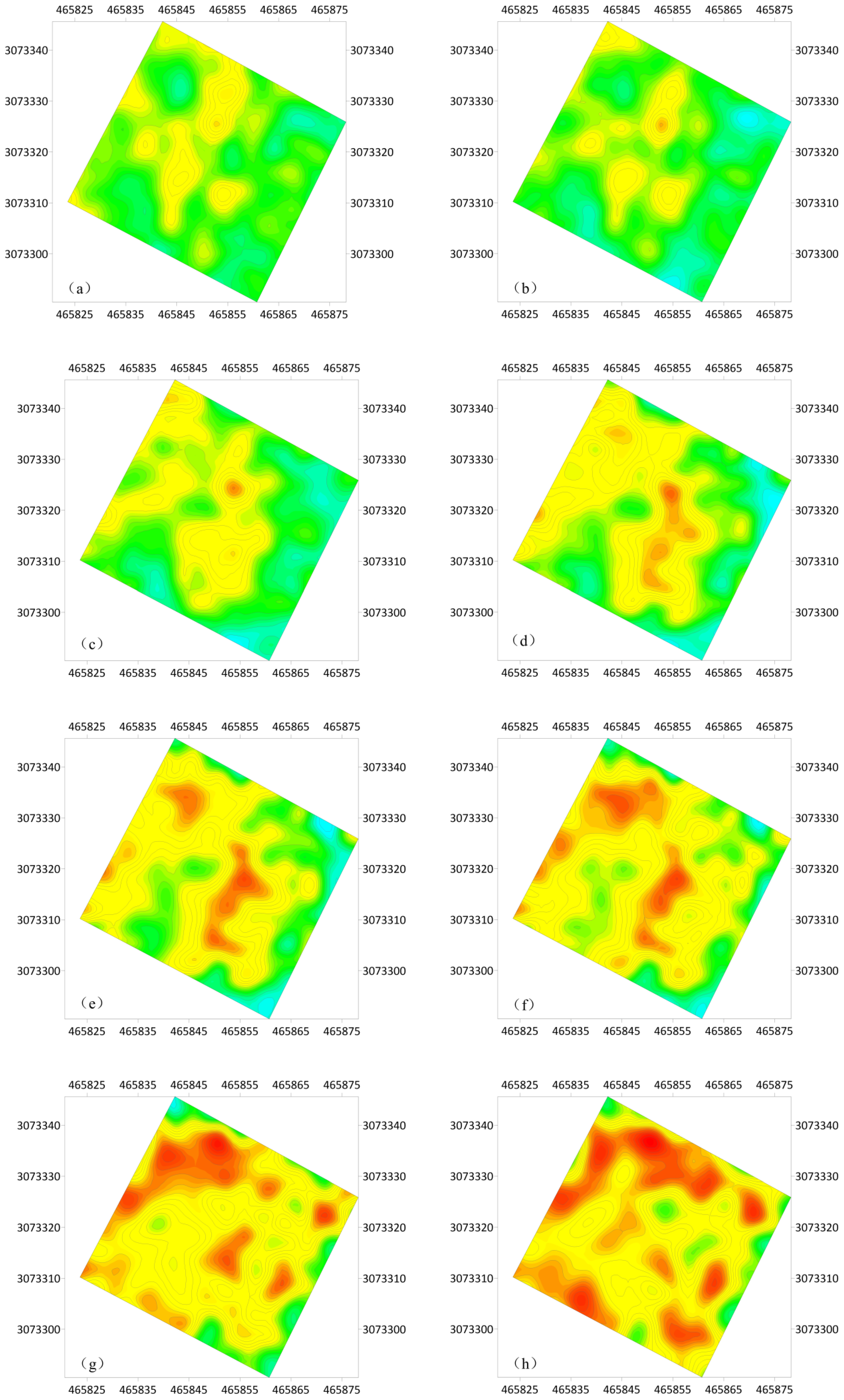
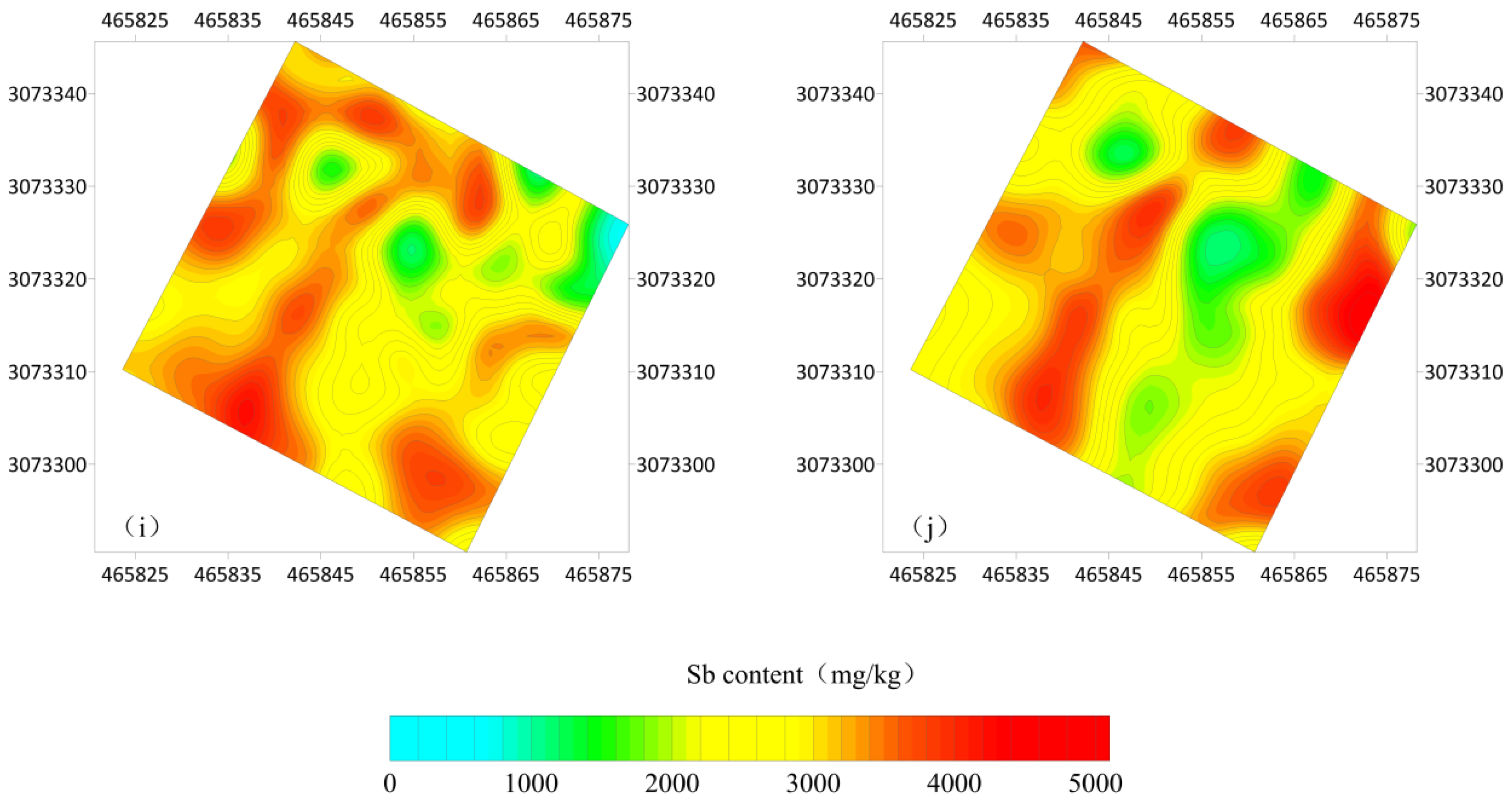
4.2.2. Analysis of Antimony Pollution Plane Characteristics
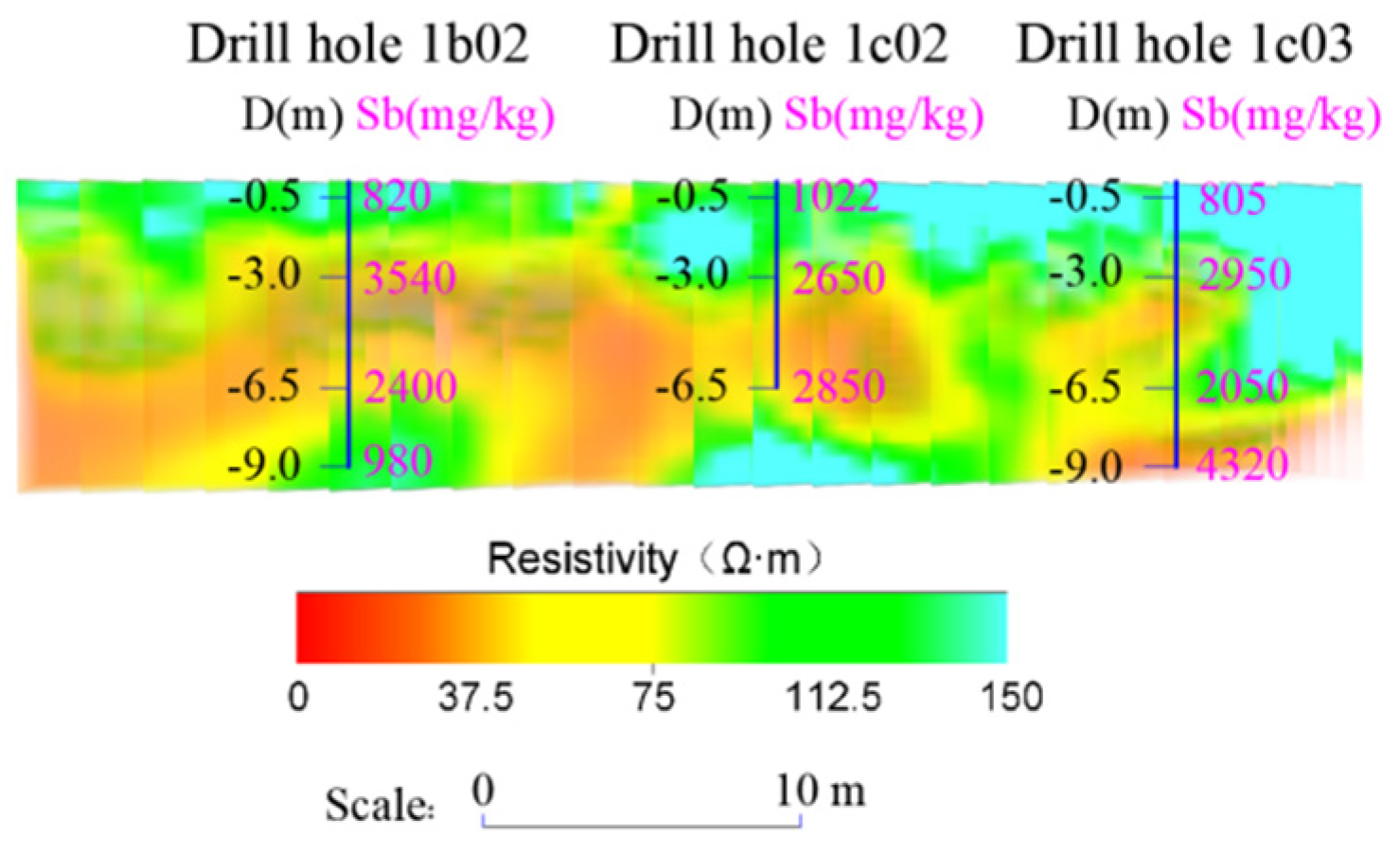
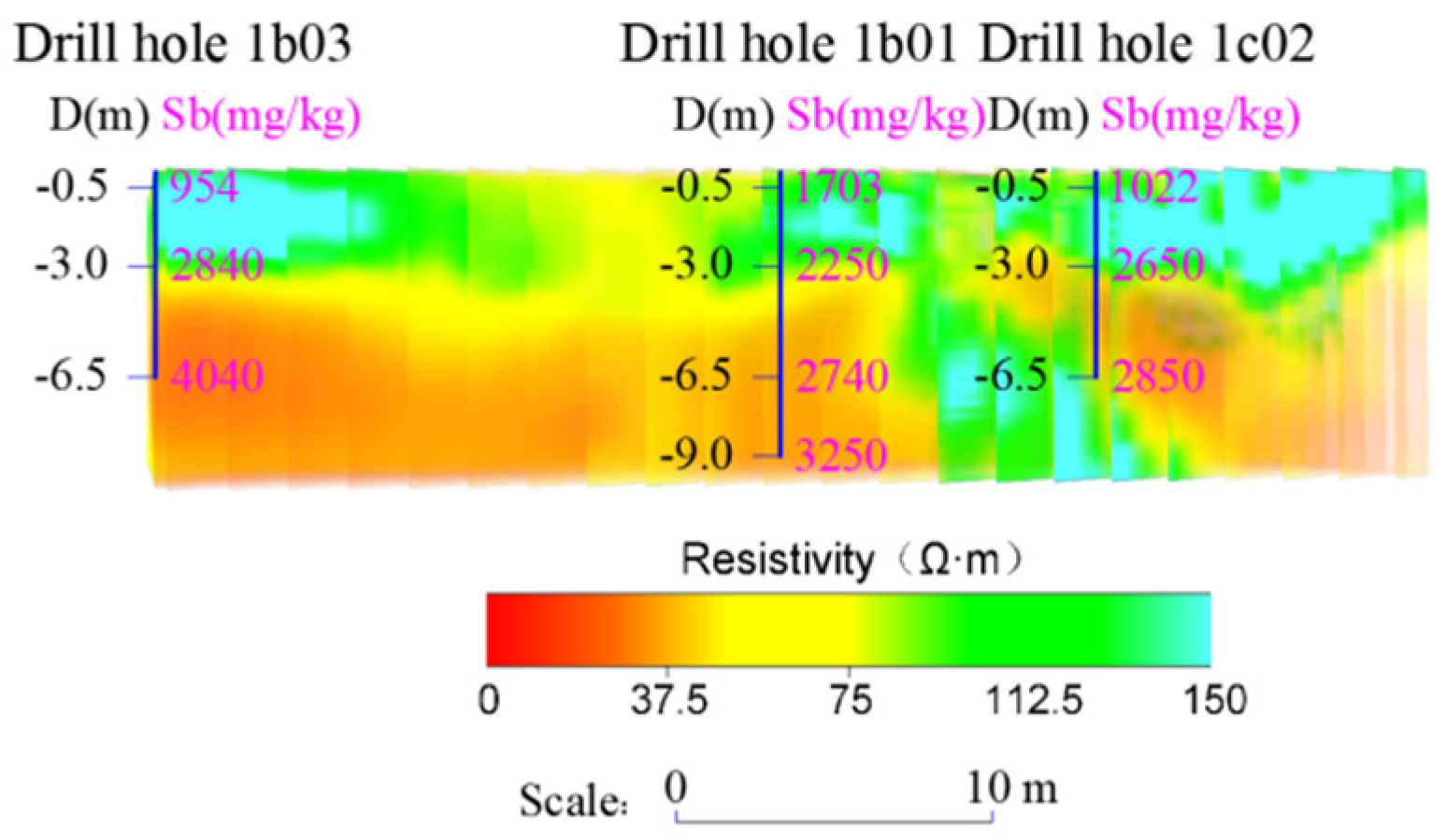
4.2.3. Analysis of Antimony Pollution Profile Characteristics
4.3. Three-Dimensional Pollution Model
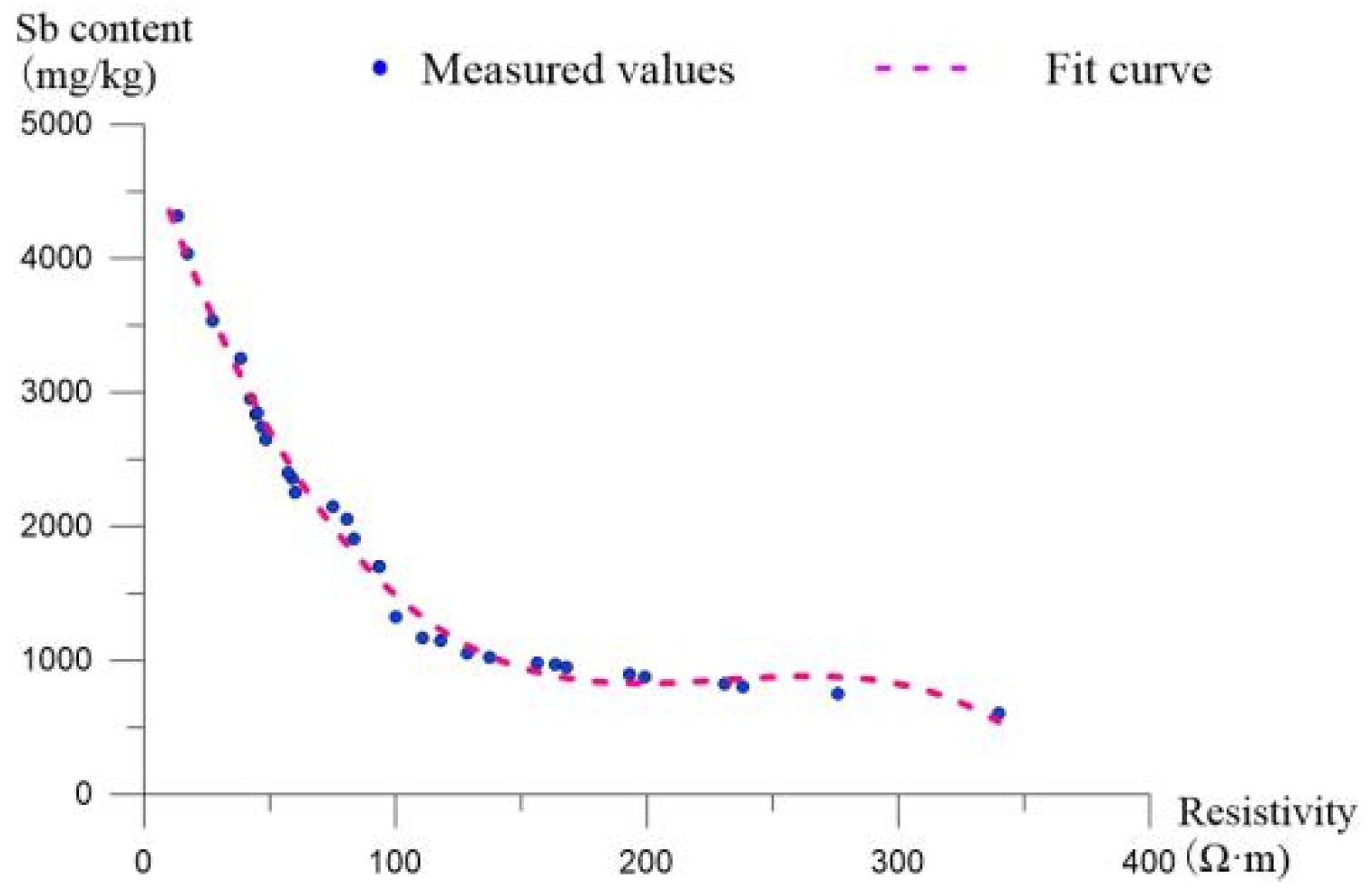
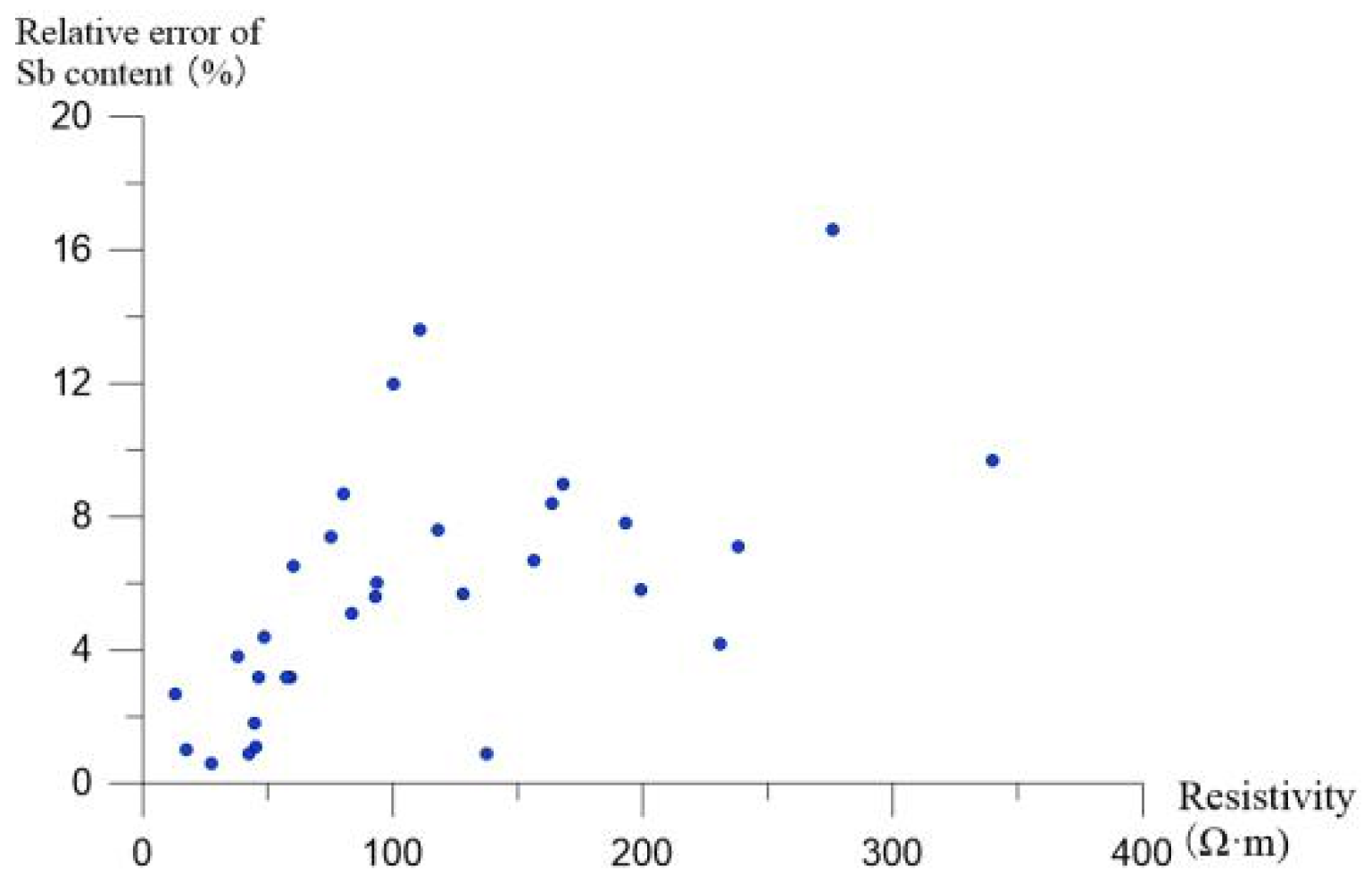
4.3.1. Mathematical Model of Resistivity and Antimony Content
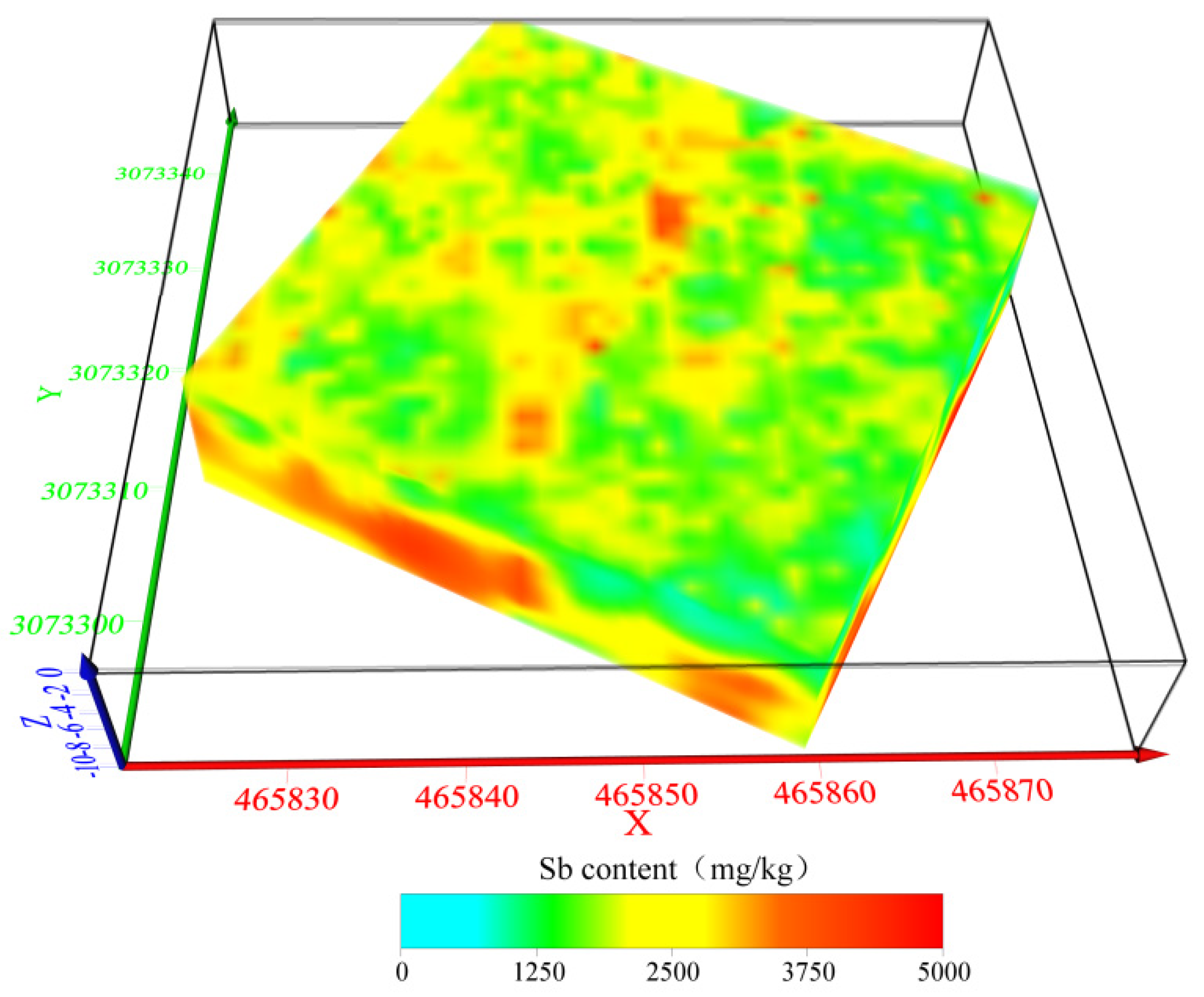
4.3.2. Analysis of the Three-Dimensional Model of Antimony Pollution on the Site
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alloway, B.J. Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and their Bioavailability, 3rd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.W.; Wen, B.; Zhou, A.G.; Liu, C.F.; Li, X.Q. Review of antimony pollution and antimony isotopic tracer in the environment. Chin. J. Nat. 2017, 39, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Li, N.; Mao, S.; Ma, R.; He, H.; Niu, Z.; Chen, X.; Xiang, H. Spatial heterogeneity of heavy metal pollution in soils: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.F.; Sun, Y.Y.; Shi, H.D.; Bai, L. Research status and progress of soil heavy metal emission inventory. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2024, 43, 2472–2486. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.S.; Graham, M.C.; Hamilton, E.M. Isotopic signatures distinguish natural vs. anthropogenic Pb sources in contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6508–6517. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.J.; Wu, D.P.; Zhang, T. Pollution Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils of a gold mining area in Beijing. Urban Geol. 2021, 16, 424–431. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.B.; Wang, C.L. Development and application of high-density electrical method. Earth Sci. Front. 2003, 10, 171–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Deng, Y.R.; Deng, D.Y.; Liu, L.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Li, Z.H. Analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban land soils using electromagnetic induction and high-density resistivity methods. J. South China Norm. Univ. 2021, 53, 15–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Qiao, C.P.; Suo, K.; Wang, B.L.; Zhao, Y. Application of integrated geophysical methods in the detection of zinc-contaminated sites. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power 2022, 43, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Birke, M.; Demetriades, A.; Filzmoser, P.; O’Connor, P. Limitations of conventional geochemical sampling for environmental studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 308–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.X.; Guo, X.J.; Sun, J.T.; Guo, E.Y. Fine characterization and quantitative analysis of leakage plumes in oil storage areas of gas stations using three-dimensional cross-hole resistivity tomography. Prog. Geophys. 2025, 40, 398–408. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Slater, L.D.; Hubbard, S.S. ERT for environmental applications: State of the art. J. Appl. Geophys. 2019, 160, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Slater, L.D.; Hubbard, S.S.; Robinson, J.; Day-Lewis, F.D.; Tiedeman, C.R.; Johnson, C.D.; Lane, J.W.; Imbrigiotta, T.E.; Lacombe, P.; et al. 3D ERT mapping of contaminant plumes in fractured bedrock. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7329–7348. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.Z.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. Deep migration of Cr and Ni in a chemical park via ERT and geochemistry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 45678–45692. [Google Scholar]
- Revil, A.; Karaoulis, M.; Johnson, T.C.; Kemma, A. Quantitative interpretation of ERT data: Challenges and solutions. Geophys. J. Int. 2022, 231, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, R.; Flores Orozco, A.; Nguyen, F.; Hermans, T. Joint inversion of geochemical and ERT data for 3D contaminant mapping. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 243, 103912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Wang, J.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y. Current status and prospects of integrated geophysical and geochemical exploration. Adv. Earth Sci. 2022, 37, 512–525. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Jin, W.; Shang, Y. Effects on the resolution of high-density electrical method by electrodes array deploying. Prog. Geophys. 2019, 34, 172–178. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V.; Kirkegaard, C.; Fiandaca, G. Advantages of integrating geophysical and geochemical data. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 1421–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Mol, G.; de Leeuw, J.; Okx, J.; Molenaar, C.; de Cleen, M.; Visser, S. Soil-related sustainable development goals: Four solutions. Sustainability 2024, 16, 56. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 25.2-2019; Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Technical Guidelines for Monitoring during Risk Control and Remediation of Soil Contamination of Land for Construction. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2019.
- HJ 166-2021; Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Technical Specification for Soil Environment Monitoring. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2021.
- HJ 1315-2023; Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Soil and Sediment-Determination of 19 Total Metal Elements-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2023.
- HJ 680-2013; Ministry of Environmental Protection. Soil and Sediment-Determination of Mercury, Arsenic, Selenium, Bismuth, Antimony-Microwave Dissolution/Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013.
- HJ 962-2018; Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Determination of Soil pH by Potentiometry. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Liu, H.F.; Liu, J.X.; Guo, R.W.; Deng, X.K.; Ruan, B.Y. Efficient inversion of 3D IP data for continuous model with complex geometry. J. Jilin Univ. 2011, 41, 1212–1218. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.F.; Guo, Z.W.; Liu, J.X.; Guo, R.W.; Ma, C.Y. 3D DCIP inversion using the finite-element approach with variable elements. Near Surf. Geophys. Environ. Prot. 2014, 27, 697–706. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.F.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, X.Q.; Zhu, D.W. Research on three-dimensional resistivity imaging for non-conventional electrode arrays in restricted exploration area. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Ruan, B.Y.; Liu, J.X. The conjugate gradient algorithm of variational damping and its capability analysis. Prog. Geophys. 2008, 23, 89–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Agricultural Land Soil Pollution Risk Control Standard. China Environmental Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2018.
- DZ/T 0295-2016; Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment. The Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wu, X.P.; Wang, T.T. Progress of Study on 3D Resistivity Inversion Method. Prog. Geophys. 2002, 17, 156–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.B.; Song, M.X.; Mei, R.; Dai, X.Q. Numerical simulation of high-density resistivity method in contaminated sites. Comput. Tech. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 47, 253–271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.Y.; Wang, M.Y. Three-dimensional resistivity imaging using integral method. Chin. J. Geophys. 2001, 44, 843–851. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liang, W.J. A new method of three-dimensional resistivity imaging and its application. J. Jilin Univ. 2005, 35, 123–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H. Numerical simulation analysis of high-density resistivity method based on contaminated site modeling. J. Geophys. Eng. 2025, 22, 1–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, E.W.; Ye, P.; Liu, L.Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.R.; Liu, Z.B. Application progress of ERT technology in environmental pollution investigation. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2025, 45, 11–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Stage | Temperature (°C) | Heating Time (min) | Holding Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Room temperature—120 | 7 | 3 |
| 2 | 120–160 | 5 | 3 |
| 3 | 160–180 | 5 | 25 |
| Point Number | Cu (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Ni (mg/kg) | Sb (mg/kg) | Tl (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 27.6 | 110 | 19.1 | 752 | 0.511 | 0.166 | 0.162 | 27.6 |
| T2 | 26.8 | 106 | 21.8 | 1905 | 0.602 | 0.225 | 0.193 | 40.1 |
| T7 | 33.6 | 104 | 24.3 | 900 | 0.551 | 0.194 | 0.047 | 22.6 |
| T8 | 36.4 | 112 | 21.5 | 301 | 0.496 | 0.211 | 0.084 | 25.4 |
| T9 | 32.4 | 147 | 20.7 | 1703 | 0.642 | 0.182 | 0.059 | 37.3 |
| T10 | 35.8 | 159 | 22.8 | 880 | 0.551 | 0.151 | 0.055 | 30.9 |
| T11 | 37.1 | 162 | 25.3 | 965 | 0.564 | 0.242 | 0.081 | 30.5 |
| T12 | 33.2 | 155 | 20.8 | 600 | 0.563 | 0.221 | 0.064 | 28.3 |
| T13 | 38.7 | 154 | 19.5 | 2150 | 0.533 | 0.264 | 0.077 | 33.2 |
| T14 | 41.9 | 142 | 20.5 | 2360 | 0.535 | 0.231 | 0.093 | 34.9 |
| T15 | 38.3 | 132 | 20.2 | 1326 | 0.491 | 0.233 | 0.123 | 41.2 |
| T16 | 31.1 | 160 | 35.1 | 1055 | 0.562 | 0.194 | 0.092 | 23.3 |
| T17 | 21.4 | 150 | 35.8 | 1166 | 0.554 | 0.111 | 0.043 | 15.6 |
| 1b01 | 31.5 | 121 | 30.8 | 1703 | 0.514 | 0.217 | 0.066 | 18.7 |
| 1b02 | 46.3 | 143 | 33.8 | 820 | 0.539 | 0.225 | 0.078 | 17.5 |
| 1b03 | 37.2 | 136 | 31.4 | 954 | 0.454 | 0.241 | 0.058 | 20.9 |
| 1c01 | 28.4 | 146 | 26.2 | 1144 | 0.469 | 0.204 | 0.093 | 23.9 |
| 1c02 | 32.7 | 118 | 22.3 | 1022 | 0.537 | 0.221 | 0.057 | 30.4 |
| 1c03 | 34.6 | 152 | 23.1 | 805 | 0.506 | 0.196 | 0.052 | 30.4 |
| Pollution Level | Pollution Index | Pollution Level |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | Pi ≤ 1 | clean |
| Ⅱ | 1 < Pi ≤ 2 | Slightly polluted |
| III | 2 < Pi ≤ 3 | Light pollution |
| IV | 3 < Pi ≤ 5 | Moderate pollution |
| Ⅴ | Pi > 5 | Severe pollution |
| Sampling Point Number | Pollution Index (Pi) | Pollution Level |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | 4.2 | Moderate pollution |
| T2 | 10.6 | Severe pollution |
| T7 | 5.0 | Moderate pollution |
| T8 | 1.7 | Slightly polluted |
| T9 | 9.5 | Severe pollution |
| T10 | 4.9 | Moderate pollution |
| T11 | 5.4 | Severe pollution |
| T12 | 3.3 | Moderate pollution |
| T13 | 11.9 | Severe pollution |
| T14 | 13.1 | Severe pollution |
| T15 | 7.4 | Severe pollution |
| T16 | 5.9 | Severe pollution |
| T17 | 6.5 | Severe pollution |
| 1b01 | 9.5 | Severe pollution |
| 1b02 | 4.6 | Moderate pollution |
| 1b03 | 5.3 | Severe pollution |
| 1c01 | 6.4 | Severe pollution |
| 1c02 | 5.7 | Severe pollution |
| 1c03 | 4.5 | Moderate pollution |
| average value | 6.6 | Severe pollution |
| Sampling Point Number | Depth (m) | Resistivity (Ω·m) | Sb (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.5 | 276.1 | 752 |
| T2 | 0.5 | 83.4 | 1905 |
| T7 | 0.5 | 192.9 | 900 |
| T8 | 0.5 | 1041.5 | 301 |
| T9 | 0.5 | 93.3 | 1703 |
| T10 | 0.5 | 199.4 | 880 |
| T11 | 0.5 | 163.4 | 965 |
| T12 | 0.5 | 339.9 | 600 |
| T13 | 0.5 | 75.4 | 2150 |
| T14 | 0.5 | 58.9 | 2360 |
| T15 | 0.5 | 100.2 | 1326 |
| T16 | 0.5 | 128.3 | 1055 |
| T17 | 0.5 | 110.7 | 1166 |
| 1b01 | 0.5 | 93.7 | 1703 |
| 1b02 | 0.5 | 230.9 | 820 |
| 1b03 | 0.5 | 168.3 | 954 |
| 1c01 | 0.5 | 117.8 | 1144 |
| 1c02 | 0.5 | 137.7 | 1022 |
| 1c03 | 0.5 | 237.9 | 805 |
| 1b01 | 3 | 60.2 | 2250 |
| 1b01 | 6.5 | 46.6 | 2740 |
| 1b01 | 9 | 38.3 | 3250 |
| 1b02 | 3 | 27.4 | 3540 |
| 1b02 | 6.5 | 57.5 | 2400 |
| 1b02 | 9 | 156.3 | 980 |
| 1b03 | 3 | 44.8 | 2840 |
| 1b03 | 6.5 | 17.5 | 4040 |
| 1c02 | 3 | 48.4 | 2650 |
| 1c02 | 6.5 | 45.1 | 2850 |
| 1c03 | 3 | 42.4 | 2950 |
| 1c03 | 6.5 | 80.5 | 2050 |
| 1c03 | 9 | 13.2 | 4320 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, M.; Zeng, B.; Xiao, X. Prediction of Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Using Integrated Geochemistry and Three-Dimensional Electrical Resistivity Tomography. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10969. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010969
Li W, Liu H, Yang S, Zhu D, Zhao Y, Luo M, Zeng B, Xiao X. Prediction of Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Using Integrated Geochemistry and Three-Dimensional Electrical Resistivity Tomography. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10969. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010969
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wangming, Haifei Liu, Shizhen Yang, Daowei Zhu, Yanglian Zhao, Min Luo, Bin Zeng, and Xiang Xiao. 2025. "Prediction of Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Using Integrated Geochemistry and Three-Dimensional Electrical Resistivity Tomography" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10969. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010969
APA StyleLi, W., Liu, H., Yang, S., Zhu, D., Zhao, Y., Luo, M., Zeng, B., & Xiao, X. (2025). Prediction of Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution Using Integrated Geochemistry and Three-Dimensional Electrical Resistivity Tomography. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10969. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010969





