Abstract
As styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used and tends to age, the performance improvement in aging resistance is greatly important to rubber industrial fields. To this end, this study considered using layered double hydroxides (LDHs) as inorganic fillers and subsequently modified them by silane coupling agent KH−580 to obtain organically functionalized LDHs (m−LDHs) for solving the compatibility and aging concerns. The modified fillers were incorporated into styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR) to prepare m−LDHs/SBR composites. To evaluate their aging resistance, both SBR and m−LDHs/SBR samples were subjected to ultraviolet (UV) accelerated aging tests. Comprehensive characterizations were carried out using Fourier−transform infrared spectroscopy (FT−IR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and standard mechanical property testing. FT−IR confirmed the successful grafting of KH−580 onto LDHs surfaces, while TGA demonstrated a ~50 °C increase in decomposition temperature of the modified SBR compared to the pristine sample, indicating enhanced thermal stability. Mechanical performance, including tensile strength, elongation at break, and hardness, was better retained in m−LDHs/SBR after aging, revealing the role of m−LDHs as both UV shielding and interfacial reinforcing agents. These findings highlight the potential of surface−functionalized LDHs as multifunctional fillers to enhance the durability and service lifetime of rubber materials.
1. Introduction
Styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used in tire manufacturing, seals, shock absorbers, and various engineering materials due to its excellent abrasion resistance, elasticity, and cost−effectiveness [1]. However, as an unsaturated rubber, molecular chains of SBR contain numerous double bonds, making it highly susceptible to degradation from a combination of heat, oxygen, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation [2,3]. This thermo−oxidative and photo−oxidative aging leads to rubber chain scission, changes in the cross−linking structure, and free radical reactions. Consequently, SBR exhibits a decline in mechanical properties, increased hardness, and enhanced brittleness, which significantly restricts its long−term performance and applications [4,5]. Therefore, improving the aging resistance of SBR represents a critical scientific challenge for enhancing its long−term durability and broadening its practical applications.
To enhance the durability and service life of rubber materials, researchers commonly incorporate inorganic fillers into the polymer matrix. Mathew et al. [6] found that talc can significantly improve the indentation hardness, flexural properties, and tear strength of rubber, thereby enhancing the material’s durability. Abbas et al. [7] demonstrated that inorganic fillers such as silica and carbon black can significantly enhance the mechanical properties of rubber, thereby extending its service life. Previous studies have demonstrated that the incorporation of certain fillers can improve the durability and anti−aging properties of polymers. Nevertheless, challenges remain regarding ultraviolet protection, gas barrier capability, and environmental sustainability [8,9]. Consequently, the development of novel green functional fillers has emerged as a prominent research focus.
In recent years, layered double hydroxides (LDHs) have gradually become a highly regarded type of new filler in polymer composites due to their tunable chemical composition, low cost, excellent flame retardancy, good gas barrier properties, and outstanding ultraviolet shielding ability [10,11]. Yu et al. [12] introduced a coating of LDH nanosheets onto a PET film and found a significant reduction in its oxygen transmission rate, demonstrating that LDHs can serve as an efficient gas barrier material. Delorme et al. [13] confirmed the role of LDHs in enhancing the photostability of polymers. Gao et al. [14] revealed the critical role of the layered structure and ionic composition of LDHs in UV absorption and scattering. Li et al. [15] demonstrated that incorporating functionalized LDHs into nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) not only improved their dispersion but also imparted thermo−oxidative aging resistance to the rubber. Basu et al. [16] reported that unmodified LDHs were used as a reinforcing agent in carboxylated nitrile butadiene rubber (XNBR), which not only improved its mechanical properties but also imparted flame retardancy. Xiao et al. [17] introduced lignin−LDH into SBR and found the dispersion of LDH in SBR improved, interfacial stress transfer was enhanced, mechanical properties were significantly improved, and thermal stability was increased. These findings suggest that the incorporation of LDH can effectively suppress the aging of rubber induced by ultraviolet radiation and oxygen, thereby improving its long−term durability and structural stability.
However, the surface of unmodified LDHs is highly hydrophilic, resulting in poor interfacial compatibility with hydrophobic polymers such as SBR. This often leads to agglomeration within the matrix, causing insufficient interfacial bonding and inefficient stress transfer, thereby limiting their reinforcing and protective performance [18,19,20]. To address this issue, researchers have proposed various surface modification methods, including organic intercalation, ion exchange, and surface grafting [21]. Among them, surface functionalization with silane coupling agents has been proven to be an effective strategy [22].
Over decades, some relevant researchers have closely focused on investigating the performance benefits of silane modification of LDHs to polymeric matrix. For example, Tonder et al. [18] stated that the modification of dodecyl sulfate magnesium−aluminum LDH (DS−LDH) with γ−aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APS) can significantly improve mechanical properties and damping characteristics of polyurethane (PU) in association with the enhanced interfacial strength between LDH and PU. Zhang et al. [23] found that surface modification of LDHs with KH560 can significantly inhibit the degradation of asphalt binder with the improved aging resistance, particularly anti−UV aging. Zhang et al. [24] discovered that KH550−modified LDHs can make contributions to giving superior UV aging resistance to asphalt binder. These limited studies have shown that silane modification can significantly improve the interfacial characteristic between LDHs and polymer or organic materials. However, it is still unknown if the silane works better to help LDHs to optimally enhance the aging resistance of SBR.
Silane molecules possess both organic functional groups and inorganic groups. The organic end can engage in chemical or physical interactions with rubber chains, while the inorganic end can condense and bond with hydroxyl groups on the surface of LDH. This dual action mechanism not only significantly improves the dispersibility of the filler but also enhances its interfacial adhesion in the polymer matrix [25,26]. Based on this, this study selected KH−580 as a silane coupling agent to modify LDHs, thereby preparing surface−modified LDHs (m−LDHs)/SBR composites. Through a systematic investigation of the structure of composites, thermal stability, and mechanical properties before and after UV aging, this study aims to elucidate the reinforcing and anti−aging mechanisms of m−LDHs in the SBR matrix. This research provides a theoretical basis and experimental support for enhancing the durability and green functionalization of rubber materials. As detailed, the technical flowchart of this study is displayed in Figure 1.
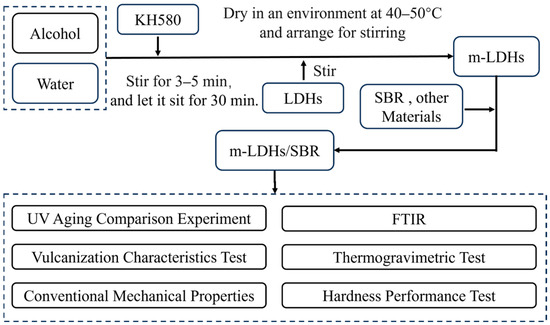
Figure 1.
Technical flowchart of this study.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH)
The LDH, supplied by Shanghai Qiao Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), was adopted as an anti−aging modifier in this study. The chemical structure of the used LDH is Mg4Al2(OH)12CO3·3H2O, specifically containing cations of Mg2+ and Al3+ and anions of CO32−. Figure 2 shows the general layered structure diagram of LDH with cations and anions [27]. Compared with conventional inorganic fillers such as silica and carbon black, LDHs possess abundant surface −OH groups, which, upon surface modification, can establish stronger interfacial interactions with rubber molecular chains.
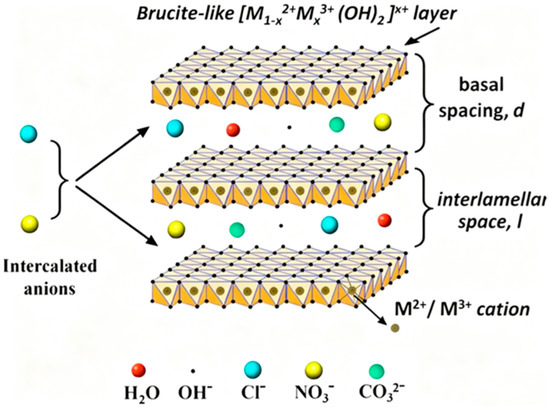
Figure 2.
General layered structure diagram of LDH with cations and anions [27].
2.1.2. Styrene–Butadiene Rubber (SBR1502)
SBR is a white synthetic rubber made from the copolymerization of styrene and butadiene, and it is one of the most widely used synthetic rubbers today. In this study, SBR was obtained from PetroChina Lanzhou Petrochemical Company (Lanzhou, China). Compared to other rubbers, SBR has good compatibility with fillers such as carbon black, silica, and LDH. Figure 3a displays the appearance and molecular structure of SBR.
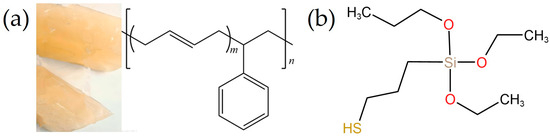
Figure 3.
Appearance and molecular structure of SBR (a) and molecular formula of KH580 (b).
2.1.3. Silane Coupling Agent (KH−580)
KH−580, a yellow transparent liquid, is a commonly used silane coupling agent. In this study, KH−580, obtained from Shanghai Linchen Chemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), was used as a surface modifier. Compared to KH560 and KH−550, KH−580 can chemically bond with the double bonds in the rubber chain. This can enhance the interfacial adhesion between the inorganic fillers and the rubber matrix. Figure 3b displays the molecular structure of KH−580.
2.1.4. Other Materials
Stearic acid (SA, analytically pure) was purchased from Tianjin Bodi Chemical Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Zinc oxide (ZnO, chemically pure), tetramethylthiuram disulfide (TMTD, chemically pure), N−cyclohexyl−2−benzothiazolesulfenamide (CZ, chemically pure), sulfur (chemically pure), and ethanol (chemically pure) were supplied by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). White carbon black (WCB, JF−666) was obtained from Chongqing Jianfeng Industrial Group Co., Ltd. (Chongqing, China).
For deionized water, it was derived from tap water by removing ions like Ca2+, Na+, Cl−, etc., using a lab−use deionized water machine equipped with an ion exchange system, which was satisfactory with a resistivity of more than 10 MΩ·cm.
2.2. Preparation of Organically Modified Hydrotalcite (m−LDHs)
First of all, the hydrolysis solution was prepared by mixing silane coupling agent (KH−580) into an alcohol–water solution at a mass ratio of 20:72:8 for 3–5 min and then staying at room temperature for 30 min. Subsequently, a certain amount of LDHs was placed in a beaker, and the hydrolyzed solution was added while constantly stirring to ensure complete impregnation. Afterwards, the resulting m−LDHs were then dried in an oven at 40–50 °C with intermittent stirring to facilitate uniform drying. Once fully dried, the m−LDHs were sealed in a bag for future use.
2.3. Preparation of m−LDHs Modified SBR (m−LDHs/SBR)
The fabrication of the SBR vulcanizates began by compounding all raw materials on a two−roll mill. For this formulation it is referenced to the typical mixes used in the preparation of rubber composites. As determined from studies, it was preliminarily known that the formulation, consisting of 100 SBR, 1.5 stearic acid, 5 zinc oxide, 15 carbon black, 3 m−LDHs, 1.5 sulfur, 0.5 TMTD, and 0.2 CZ, can be optimally adopted to prepare well−dispersed SBR composite. The resulting compound was stored at room temperature for 24 h to allow for maturation. Subsequently, the compound was compression molded in a hot press at 150 °C under a pressure of 10 MPa for 15 min. Finally, the modified SBR (m−LDH/SBR) specimens were obtained for tests. The Pristine samples (SBR) were prepared without the addition of m−LDHs, while all other components remained identical to those used in the m−LDH/SBR samples. Both the SBR and m−LDH/SBR sheets were then cut using a standard cutter to produce dumbbell−shaped samples for tensile strength analysis.
2.4. Ultraviolet Aging Process
Both SBR and m−LDHs/SBR samples were subjected to accelerated aging in a UV aging chamber. The chamber’s conditions were set to an air environment, a temperature of 40 °C, and a UV intensity of 1500 μW/cm2. The samples were aged for various durations: 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 d. At each time interval, the corresponding samples were removed from the chamber and stored in separate bags for subsequent tensile property testing.
2.5. Testing and Characterization
2.5.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT−IR) Detection
The FT−IR spectra of LDH and m−LDHs were recorded using a BH−40 Fourier transform infrared spectrometer that was manufactured by Beijing Beifen−Ruili Analytical Instrument (Group) Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). The samples were ground into fine powders and dried under an infrared lamp for 2 h to remove moisture. The dried powders were then thoroughly mixed with pre−dried KBr at a mass ratio of 1:100, uniformly ground, and pressed into pellets with a diameter of 13 mm for analysis. The spectra were collected in the range of 400–4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1, and 32 scans were accumulated for each sample, following the similar test conditions published in previous studies [28,29].
2.5.2. Vulcanization Characteristics Test
The vulcanization behavior of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR compounds was evaluated using a Brookfield DV−II+ Pro rotorless rheometer that was manufactured by Brookfield Engineering Laboratories (Middleborough, MA, USA). The measurements were carried out at 170 °C under a pressure of 10 MPa for 20 min. The minimum torque (ML), maximum torque (MH), and optimum cure time (t90) were determined, and each test was repeated three times to ensure reproducibility.
2.5.3. Thermogravimetric Test
The thermal stability of the samples was analyzed using a NETZSCH STA409EP thermogravimetric analyzer (NETZSCH Gerätebau GmbH, Selb, Germany) under a nitrogen atmosphere (99.99% purity) with a flow rate of 50 mL/min. Approximately 5 ± 0.5 mg of each sample was placed in an aluminum crucible and heated from 40 to 800 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min. The instrument was calibrated using magnesium oxide and calcium carbonate standards, and data were collected and processed with Proteus STA 7.1 software. Each sample was measured three times to ensure reproducibility, and both the weight loss temperature and residual mass were recorded.
2.5.4. Conventional Mechanical Properties Testing
(1) Tensile Testing
The tensile properties were measured using a WDW electronic universal testing machine. The specimens were prepared in a standard dumbbell shape with a width of 6 mm, and the thickness was determined by the three−point method using an HD−10 precision thickness gauge to ensure uniform dimensions. The testing speed was set at 500 mm/min, and the procedure was conducted in accordance with the GB/T 528−2009 standard [30]. Each group of samples was tested at least five times, and the average value was reported as the final result, with outliers excluded to ensure accuracy and reliability.
(2) Tear Testing
The tear strength was measured using right−angle tear specimens, which were prepared with an automatic cutting machine to ensure standardized shape and dimensions. The specimen thickness was determined by the three−point method using an HD−10 precision thickness gauge that was manufactured by Nanjing Huade Soil Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China). to ensure accuracy and uniformity. The tests were conducted on a WDW electronic universal testing machine at a stretching speed of 500 mm/min. Each group of samples was tested at least five times, and the average value was reported as the final result, with outliers excluded to improve data reliability.
2.5.5. Hardness Performance Test
The Shore A hardness of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR was measured using a TYLX−A Shore hardness tester that was manufactured by Changchun Tianyuan Test Machine Co., Ltd. (Changchun, China). The tests were conducted in strict accordance with the GB/T 23651−2009 standard [31]. The specimens were prepared as flat, defect−free sheets without bubbles or cracks, with a thickness of not less than 6 mm to minimize substrate effects. During the test, the indenter was vertically pressed into the specimen surface under the specified loading conditions, and the stabilized hardness values were recorded. For each sample, measurements were taken at least five different positions, and the average value was reported as the final result, with outliers excluded to improve reliability.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FT−IR Analysis
Figure 4 displays the FT−IR spectra of KH−580, LDH, and m−LDH. As illustrated in Figure 4a, it is easy to capture that the characteristic bands identifying the attached structures of C−H stretching vibration in −CH2− at 2934 cm−1 and 2838 cm−1, S−H stretching vibration in −SH at 2560 cm−1, as well as Si−O−C at 1809 cm−1 and Si−C at 1188 cm−1 and 802 cm−1. For its use, it will be hydrolyzed to own large amounts of −OH, in response to having wide bands approximately between 3550 cm−1 and 3200 cm−1. As it was adopted to modify the surface of LDH, it leads to significant changes in molecular structure, as observed in Figure 4b. Comparatively, for pristine LDH, the absorption peak, corresponding to the stretching vibration of O–H, can be observed at around 3450 cm−1, and for m−LDHs, some changes occur at 3550 cm−1~3200 cm−1, coming from the modification of hydrolyzed KH−580, indicating that the modification alters the interfacial structure rather than merely physically shielding the hydroxyl groups. An absorption band at 1639 cm−1 is assigned to the stretching vibration of C=O in carboxyl groups, while the peak at 1376 cm−1 corresponds to CO32− in LDH, which also contributes to low−frequency vibrations in the 1639–500 cm−1 region.
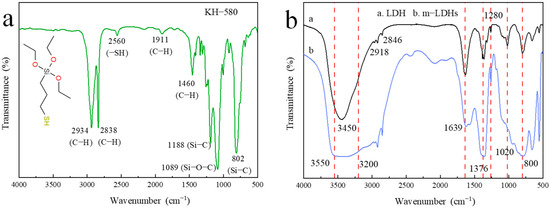
Figure 4.
FT−IR spectra: (a) KH−580; (b) LDH and m−LDH.
Other than this, the absorption peaks at 1280 cm−1, 1020 cm−1, and 800 cm−1, associated with Si–O–M, Si–O, and Si–O–C vibrations, closely corresponding to the locations observed from the FT−IR spectrum of KH580 shown in Figure 4a, are significantly enhanced and slightly shifted relative to the original LDH peaks, confirming that the silane coupling agent condenses with surface hydroxyls to form covalent Si–O–M bonds. No notable changes are observed in the 2500–1800 cm−1 region, indicating that the layered lattice and interlayer ions remain intact, and the modification predominantly occurs at the surface. Overall, the weakening of the O–H absorption, the appearance of new Si–O/Si–O–C vibration bands, and the presence of C–H signals collectively provide strong evidence that KH−580 chemically condenses with LDH, achieving effective organic surface modification.
3.2. UV−vis Spectroscopy Analysis
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the UV−vis absorption curves and UV−vis diffuse reflectance curves of the modified SBR, respectively. As shown in Figure 5, within the 400 nm ultraviolet light region, the absorbance decreases with increasing wavelength but fluctuates and declines around approximately 330 nm for the m−LDHs/SBR. After reaching the 440 nm visible light region, the absorbance gradually decreases and stabilizes. As shown in Figure 6, within the 400 nm ultraviolet light region, the reflectance increases with increasing wavelength but fluctuates and declines around approximately 330 nm for the m−LDHs/SBR. After reaching the 440 nm visible light region, the reflectance gradually increases and stabilizes. From Figure 5 and Figure 6, it can be concluded that after modification, m−LDHs/SBR exhibits excellent UV absorption and reflection effects. The LDHs provide both physical shielding and chemical absorption effects, thereby enhancing the anti−UV aging performance of the SBR.
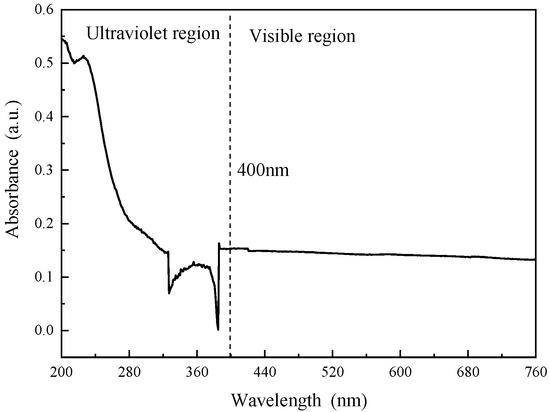
Figure 5.
UV−vis absorption curve of m−LDHs/SBR.
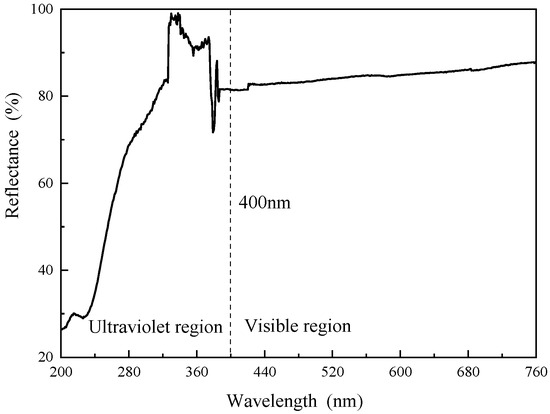
Figure 6.
UV−vis diffuse reflectance curve of m−LDHs/SBR.
3.3. Vulcanization Characteristics Analysis
Figure 7 shows the vulcanization curves of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR. During the scorch stage, no crosslinking reaction occurs in the rubber compound. As the vulcanization time increases, the corresponding functional groups in SBR and m−LDHs/SBR are relatively dispersed within this range, and the torque gradually decreases. In the pre−vulcanization stage, crosslinking begins in both SBR and m−LDHs/SBR. As the reaction progresses, the degree of crosslinking increases, forming a network structure. The torque values in this figure indicate that the torque for m−LDHs/SBR (0.80 N·m) is higher than that for SBR (0.78 N·m), suggesting that the m−LDHs/SBR has better resistance to deformation than the SBR. In the curing stage, once the crosslinking reaction reaches a certain degree, both SBR and m−LDHs/SBR maintain a constant torque or exhibit only minor variations after reaching the maximum torque.
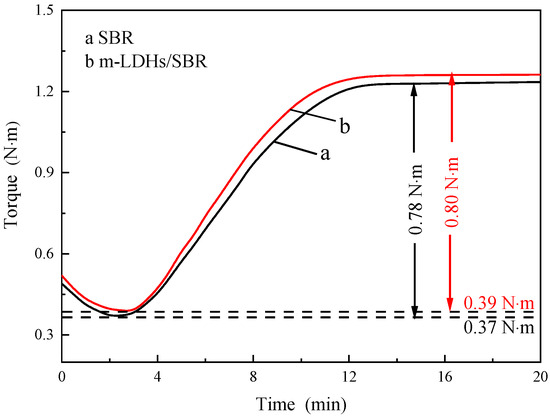
Figure 7.
Vulcanization curves of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR.
Overall, the addition of m−LDHs did not significantly affect the vulcanization rate or process of SBR. Moreover, at the same time point, the torque of m−LDHs/SBR was always higher than that of SBR. This can be attributed to the role of m−LDHs as a “bridge,” enhancing the interfacial bonding between the inorganic fillers and the organic rubber matrix. Additionally, the m−LDHs powder, as a rigid particulate filler, increased the material’s torque and improved its resistance to deformation.
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
Figure 8 presents the thermogravimetric curves of the four samples. It can be observed that the weight loss rates of the four samples are essentially identical, indicating that the incorporation of m−LDHs has minimal impact on the overall decomposition rate of SBR, although slight differences in decomposition temperatures are noted. Following UV aging, the decomposition temperatures of all samples decrease. Comparison of curves c and d reveals that the m−LDHs/SBR exhibits a decomposition temperature of approximately 450 °C, which is 50 °C higher than that of pure SBR. This enhancement can be attributed to the inherent heat resistance of the inorganic LDHs, which, after modification, inhibit the thermal decomposition of the resin and thereby improve its thermal stability. It should be noted that the m−LDHs/SBR shows only a single major weight loss step. This is primarily due to the low loading of m−LDHs (3% by weight of SBR), which is insufficient to produce a distinct secondary step in the TG curve. Therefore, the single weight loss does not necessarily indicate the formation of a copolymer; rather, it reflects that the thermal decomposition behavior is dominated by the SBR matrix. Nonetheless, the FTIR result confirmed that the silane modification promotes the particle surface of LDHs from inorganic towards organic, supporting better compatibility between them.
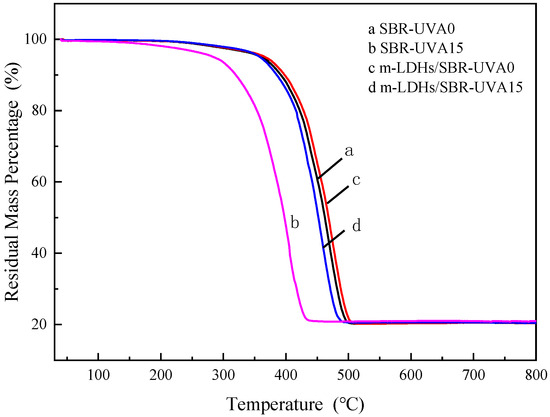
Figure 8.
TGA curves of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR samples before and after UV aging.
3.5. Mechanical Properties Analysis
3.5.1. Tensile Strength
Figure 9 and Figure 10 illustrate the tensile strength at 100% and 300% elongations for SBR and m−LDHs/SBR, respectively. The strength of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR exhibits a decreasing trend as the aging time increases. From the data in Figure 9, the change rates of tensile strength at 100% and 300% after aging for 3 d and 15 d were calculated and are presented in Table 1. The change rate of the tensile strength at 100% for m−LDHs/SBR is 15%, which is significantly lower than the 55% change rate observed for SBR over the same period. Similarly, using the data from Figure 10, the change rates of tensile strength at 300% on day 3 and day 15 were calculated, as shown in Table 1. The change rate of the tensile strength at 300% for m−LDHs/SBR is 10%, which is notably lower than the 103% change rate for SBR in the corresponding period.
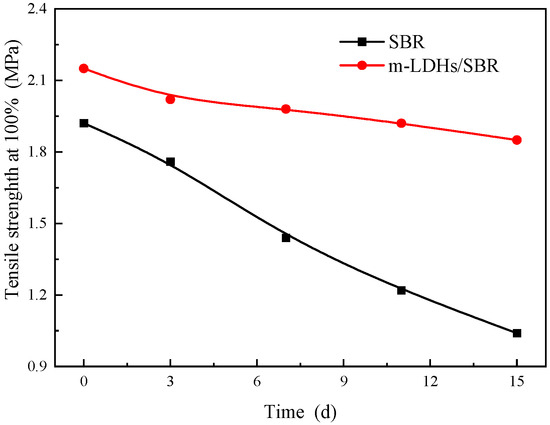
Figure 9.
Tensile strength at 100%, showing the effect of m−LDHs on the aging behavior of SBR.
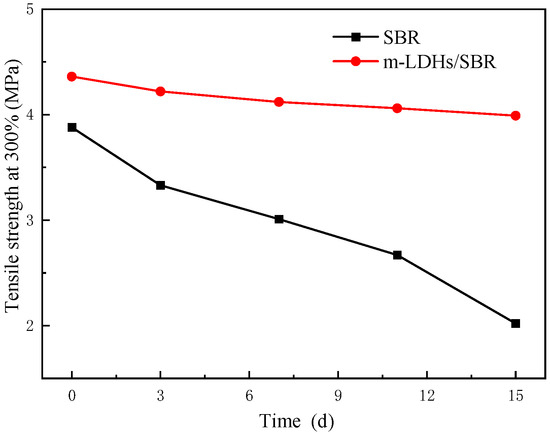
Figure 10.
Tensile strength at 300% showing the effect of m−LDHs on the aging behavior of SBR.

Table 1.
Change rate in tensile strength at 100,% and 300% for SBR and m−LDHs/SBR.
Figure 11 shows the tensile strength at break curve for SBR and m−LDHs/SBR. It can be observed that, with prolonged aging time, the tensile strength at break for both SBR and m−LDHs/SBR decreases. This reduction may be attributed to aging−induced reactions or changes in the internal functional groups of SBR, which alter its structural properties and consequently decrease both elongation at break and tensile strength at break.
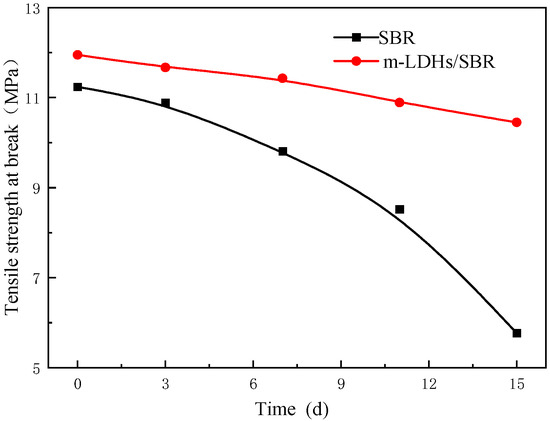
Figure 11.
Tensile strength at break of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR.
The change rate of tensile strength at break between day 3 and day 15 was calculated and is shown in Table 2. The change rate for m−LDHs/SBR is 9%, which is significantly lower than the 41% change rate observed for SBR during the same period.

Table 2.
Change rate of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR tensile strength at break.
In summary, as aging time increases, the changes in tensile strength and tensile strength at break for the m−LDHs/SBR are less pronounced than those for the SBR. This can be attributed to two factors: First, the m−LDHs powder within the modified SBR acts as both a partial filler and a “bridge”, enhancing the material’s mechanical properties. Second, the UV shielding effect of LDHs slows the aging process of SBR, leading to smaller variations in the corresponding mechanical parameters.
3.5.2. Elongation at Break
Figure 12 shows the elongation at break for SBR and m−LDHs/SBR. As shown in Figure 13, with prolonged aging time, both the elongation at break and tensile strength at break of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR decrease. This can be attributed to aging−induced reactions or changes in the internal functional groups of SBR, which alter its structural properties, leading to a reduction in elongation at break and tensile strength at break.
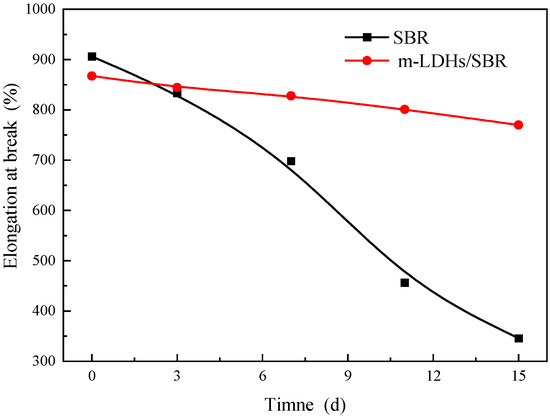
Figure 12.
Elongation at break of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR.
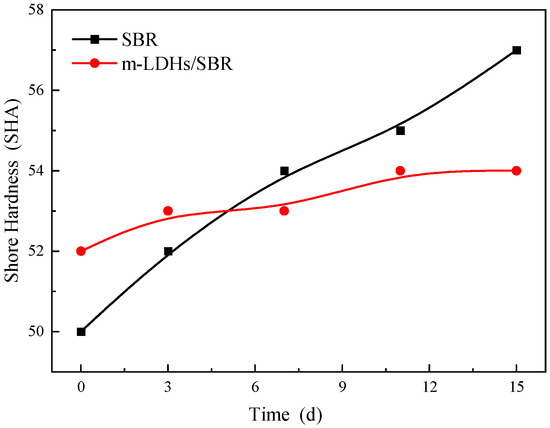
Figure 13.
Hardness change curve of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR after UV aging.
From the elongation at break curve of SBR, the change rate between day 3 and day 15 was calculated, as shown in Table 3. The change rate for m−LDHs/SBR is 7%, which is significantly lower than the 48% change rate for unmodified SBR during the same period.

Table 3.
Change rate of SBR elongation at break.
In conclusion, with increasing aging time, the change in elongation at break for the modified SBR is smaller than that of the SBR, due to the same reasons as those for the changes in tensile strength.
3.5.3. Shore Hardness Analysis
Figure 13 shows the hardness change curves for SBR before and after modification. As a general trend, with prolonged aging time, the hardness values of both SBR and m−LDHs/SBR increase. This is due to aging−induced reactions or changes in the internal functional groups of SBR, which, influenced by environmental factors, gradually degrade the material’s mechanical properties. However, calculating the hardness change rate between day 3 and day 15 from the hardness change curve, as shown in Table 4, the change rate for m−LDHs/SBR is 8%, significantly lower than the 52% change rate for SBR during the same period.

Table 4.
Change rate of SBR and m−LDHs/SBR hardness.
In summary, with increasing aging time, the change in hardness of the m−LDHs/SBR is smaller than that of the SBR, for reasons consistent with the analysis of changes in tensile strength and elongation at break.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- FTIR analysis showed that the addition of silane coupling agent KH−580 successfully achieved the surface organic modification of LDHs, generating m−LDHs.
- (2)
- Vulcanization characteristic analysis stated that the addition of m−LDHs does not affect the vulcanization speed and process of SBR. m−LDHs act as a “bridge,” promoting the interfacial bonding between the filler and the rubber matrix. Moreover, the added m−LDHs powder acts as a rigid particle filler in the material, thereby increasing the torque of m−LDHs/SBR and enhancing the anti−deformation ability of the modified SBR.
- (3)
- TGA demonstrated that the thermal stability of the m−LDHs/SBR is better than before modification, with the decomposition temperature increased by about 50 °C.
- (4)
- Mechanical properties illustrated that with increasing aging time, the change rates of tensile strength, elongation at break, and hardness of the m−LDHs/SBR are smaller than those of the SBR. On one hand, this is because the m−LDHs powder inside the m−LDHs/SBR acts as a partial filler and “bridge”. On the other hand, the UV shielding effect of LDH slows down the aging rate of SBR, resulting in enhanced corresponding mechanical properties.
Overall, the proposed treatment method for LDHs can provide new insights into improving the aging resistance of SBR for pushing more durable applications of rubber composites. In spite of this, some works still need to be identified in the future, including tire aging in practice, benefit comparisons with other common anti−aging fillers, and performance−enhancing mechanisms. Based on this, it will have more evidence to understand why LDHs can give such benefits to rubbers. In addition, future work will incorporate XRD and possibly TEM analysis to further clarify the structural changes and dispersion mechanism of modified LDHs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.X.; Data curation, J.H. and N.Y.; Formal analysis, N.Y.; Investigation, J.H., N.Y. and X.X.; Methodology, J.H.; Project administration, X.X.; Resources, X.X.; Software, J.H. and N.Y.; Writing—original draft, J.H.; Writing—review and editing, J.H. and X.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Plan Project of the Department of Housing and Urban–Rural Development of Hubei Province, grant number 2023200.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Wuhan Institute of Technology for providing test conditions to completion of all works.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Um, G.; Kwon, T.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H. The Influence of Styrene Content in Solution Styrene Butadiene Rubber on Silica−Filled Tire Tread Compounds. Polymers 2023, 15, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamouda, I.; Tayefi, M.; Eesaee, M.; Hassanipour, M.; Nguyen−Tri, P. Kinetic Analysis of Thermal Degradation of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber Compounds Under Different Aging Conditions. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Li, G. Thermogravimetric studies of styrene–butadiene rubber (SBR) after accelerated thermal aging. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Bai, F.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Lin, J.; Wei, G.; Du, X. Aging properties of styrene−butadiene rubber nanocomposites filled with carbon black and rectorite. Polym. Test. 2017, 64, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Q.; Hu, D.; Jiang, X.; Wang, R. Molecular dynamics simulation of ultraviolet aging effects on the mechanical and physical properties of natural rubber. Polym. Bull. 2025, 82, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Malu, K.M.; Varghese, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vaishak, N. Effect of inorganic fillers on natural rubber latex foam vulcanisates. J. Rubber Res. 2024, 27, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, S.A.; Alobad, Z.K.; Albozahid, M.A. The Effecting of Physical Properties of Inorganic Fillers on Swelling Rate of Rubber Compound: A review Study. Univ. Babylon Eng. Sci. 2019, 27, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, S.; Hussain, M.; Zheng, Q.; Song, Y. Thermo−soil weathering and life cycle assessment of carbon black, silica and cellulose nanocrystal filled rubber nanocomposites. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrollahi, A.; Razzaghi−Kashani, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Habibi, N. Carbon black/silica hybrid filler networking and its synergistic effects on the performance of styrene−butadiene rubber composites. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Xie, D.; Zeng, Q.; Xu, H.; Ge, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Dai, J.; et al. UV stabilizer intercalated layered double hydroxide to enhance the thermal and UV degradation resistance of polypropylene fiber. Polym. Test. 2023, 121, 107979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.X.; Zhu, H. Flame Retardant Properties of Polymer/Layered Double Hydroxide N Nanocomposites. In Handbook of Polymernanocomposites. Processing, Performance and Application: Volume A: Layered Silicates; Pandey, J.K., Reddy, K.R., Mohanty, A.K., Misra, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 389–414. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Ruengkajorn, K.; Crivoi, D.-D.; Chen, C.; Buffet, J.-C.; O’Hare, D. High gas barrier coating using non−toxic nanosheet dispersions for flexible food packaging film. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.E.; Radusin, T.; Myllytie, P.; Verney, V.; Askanian, H. Enhancement of Gas Barrier Properties and Durability of Poly(butylene succinate−co−butylene adipate)−Based Nanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Gui, H.; Xu, J.; Shen, R.; Wei, L.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, S.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Yao, C. ZnTi layered double hydroxide/dealkaline lignin 2D/2D nanosheets for ultraviolet shielding poly(ethylene terephthalate) nanocomposites. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 212, 106249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, Z.; He, X.; Jiang, P.; Lu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. Aging−Resistant Functionalized LDH-SAS/Nitrile−Butadiene Rubber Composites: Preparation and Study of Aging Kinetics/Anti−Aging Mechanism. Materials 2018, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, D.; Das, A.; George, J.J.; Wang, D.-Y.; Stöckelhuber, K.W.; Wagenknecht, U.; Leuteritz, A.; Kutlu, B.; Reuter, U.; Heinrich, G. Unmodified Ldh as Reinforcing Filler for Xnbr and the Development of Flame−Retardant Elastomer Composites. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2014, 87, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Feng, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Yi, C.; Su, S. Preparation and characterization of lignin−layered double hydroxide/styrene−butadiene rubber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tonder, L.; Labuschagné, F. Systematic Literature Review of the Effect of Layered Double Hydroxides on the Mechanical Properties of Rubber. Polymers 2021, 13, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Sun, C.; Zheng, L.; Wen, S. Enhanced Gas Barrier and Mechanical Properties of Styrene−Butadiene Rubber Composites by Incorporating Electrostatic Self−Assembled Graphene Oxide @ Layered Double Hydroxide Hybrids. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 39846–39855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameliya, J.; Verma, A.; Dutta, P.; Arora, C.; Vyas, S.; Varma, R.S. Layered Double Hydroxide Materials: A Review on Their Preparation, Characterization, and Applications. Inorganics 2023, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, M.; Szerlauth, A.; Muráth, S.; Varga, G.; Szilagyi, I. Surface modification of two−dimensional layered double hydroxide nanoparticles with biopolymers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 191, 114590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminifazl, A.; Karunarathne, D.J.; Golden, T.D. Synthesis of Silane Functionalized LDH−Modified Nanopowders to Improve Compatibility and Enhance Corrosion Protection for Epoxy Coatings. Molecules 2024, 29, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, J.; Xue, L.; Sun, Y. Investigation of γ−(2,3−Epoxypropoxy)propyltrimethoxy Silane Surface Modified Layered Double Hydroxides Improving UV Ageing Resistance of Asphalt. Materials 2017, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Sun, Y.B.; Feng, K. Effect of Silane Coupling Agent Surface Modified Layered Double Hydroxides on Properties of Bitumen. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 847, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, J.; Parathodika, A.R.; Hu, G.-H.; Naskar, K. Functional rubber composites based on silica−silane reinforcement for green tire application: The state of the art. Funct. Compos. Mater. 2022, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrabito, G.; Bonasera, A.; Prestopino, G.; Orsini, A.; Mattoccia, A.; Martinelli, E.; Pignataro, B.; Medaglia, P.G. Layered Double Hydroxides: A Toolbox for Chemistry and Biology. Crystals 2019, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Leng, Z.; Lan, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Bai, Y.; Sreeram, A.; Hu, J. Sustainable Practice in Pavement Engineering through Value−Added Collective Recycling of Waste Plastic and Waste Tyre Rubber. Engineering 2021, 7, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, G.; Huang, X.; Alam, G.M.B.; Chen, X.; Sreeram, A. Material characterization and engineering performance evaluation of phosphogypsum as a high−performance filler for bituminous pavements. Fuel 2025, 393, 134977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 528−2009; Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Determination of Tensile Stress−Strain Properties. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 23651−2009; Rubber Vulcanized or Thermoplastic—Hardness Testing—Introduction and Guide. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).