Federated Load Balancing in Smart Cities: A 6G, Cloud, and Agentic AI Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
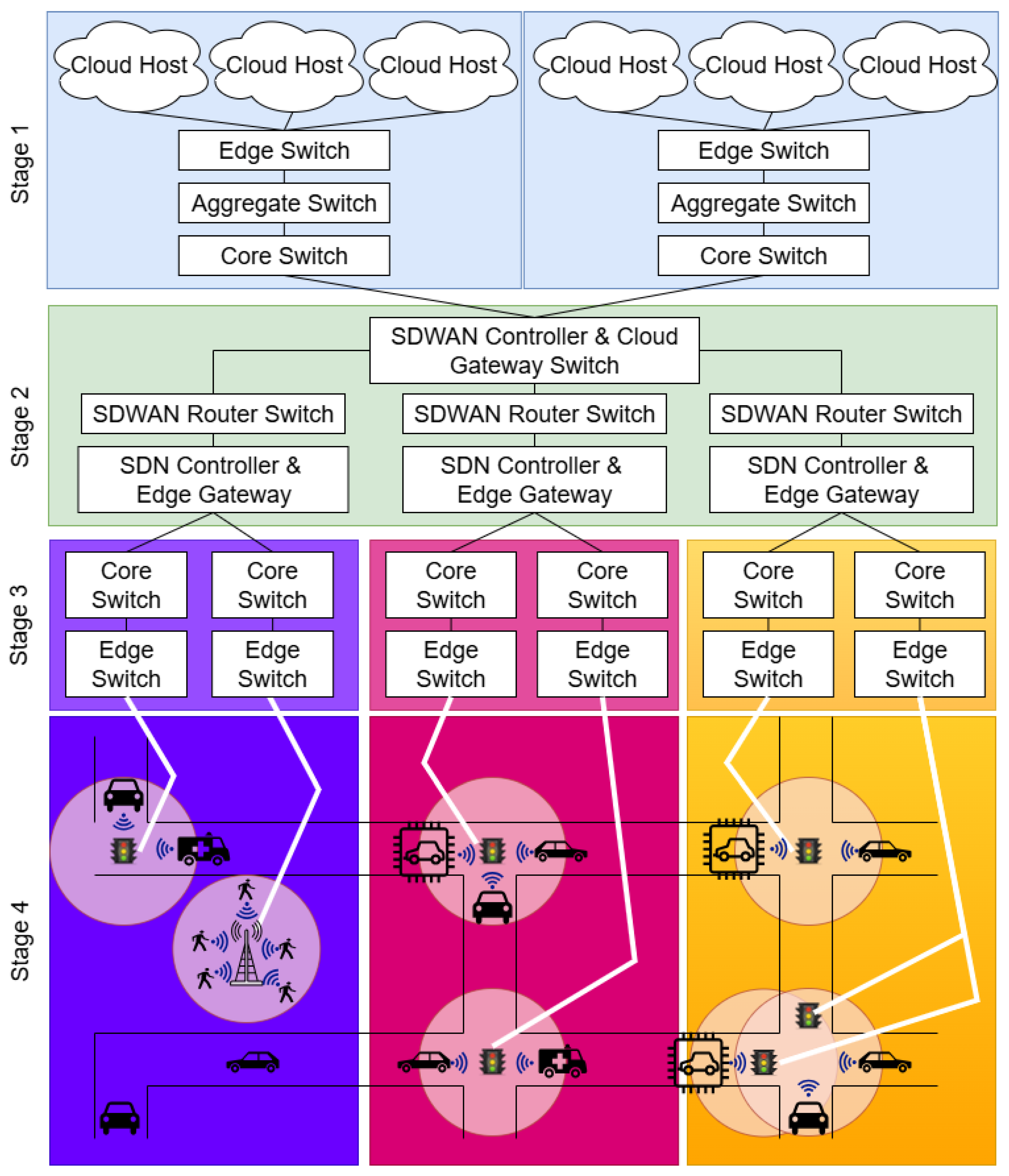
1.1. Use Case Scenario
1.2. Comparison to Other Surveys
1.2.1. IoT Simulators Survey
1.2.2. 6G Simulators Surveys
1.3. Contributions
- ResQ №1
- Which simulators are capable of supporting the simulation of entire communication infrastructures through the connection of IoT devices to the cloud through the edge?
- ResQ №2
- Which simulators are capable of simulating mobility agents and their interactions through Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms with the real world?
- ResQ №3
- Which simulators are ready to support future communication modelling through satellite communication and 6G architectures?
- ResQ №4
- Which simulators are able to model the utilisation of smart city resources?
- ResQ №5
- Which bottleneck mitigation techniques and load balancing strategies are most applicable to modern and future smart cities?
1.4. Paper Organisation
2. Network Simulators
2.1. Mobility Simulators: FedCime (FC)
Overview
Pros
Cons
2.2. Cloud Simulators
2.2.1. CloudSim (CS7G)
Overview
Pros
Cons
2.2.2. Simcan2Cloud (S2C)
Overview
Pros
Cons
2.2.3. IoTSim-SDWAN (ISDWAN)
Overview
Pros
Cons
2.3. Osmotic Simulators
2.3.1. IoTSim-Osmosis (ISO) & IoTSim-Osmosis-RES (ISOR)
Overview
Pros
Cons
2.3.2. SimulatorBridger (SB)
Overview
Pros
Cons
2.3.3. SimulatorOrchestrator (SO)
Overview
Pros
Cons
3. Cellular Network Simulation
3.1. Modern Cellular Network Simulation
3.1.1. Quality of Experience (QoE) Testing with a Remote Operated Vehicle Simulator (ROVS)
Overview
Pros
Cons
3.1.2. Stress Testing Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT)
Overview
Pros
Cons
3.2. Future 6G Architecture
3.3. 6G Simulators
3.3.1. Cell-Free 6G mMIMO Simulator (CmM)
3.3.2. Channel Simulators
BUPTCMCCCMG-IMT2030 (BC-I2)
NYUSIM (NS)
3.3.3. Satellite Technologies: UltraStar (US)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4. Bottleneck Mitigation and Load Balancing Strategies
4.1. Bottleneck Mitigation Strategies
4.1.1. Multi-Queue Bandwidth Slicing (MQBS)
Overview
- 1.
- A transmission mismatch occurs when an edge node receives incoming transmissions more quickly than it can transmit, causing a bottleneck.
- 2.
- A processing mismatch occurs when an edge node cannot process its current transmissions quickly enough, which can again lead to a bottleneck.
Pros
Cons
4.1.2. Multi-Stage Bandwidth Control Scheme (MSBCS)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.1.3. Bandwidth Forecast Service (BFS)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.2. Load Balancing Techniques
4.2.1. Weighted Load Balancing (WLB)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.2.2. Shortest Path Maximum Bandwidth (SPMB)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.2.3. Minimum Cost Flow Routing (MCFR)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.2.4. Application-Aware Dynamic Load Balancing (AADLB)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.2.5. Deep RNN SD-WAN Traffic Management (DRSTW)
Overview
Pros
Cons
4.2.6. Packet Limiter Algorithm (PLA)
Overview
Pros
Cons
5. Discussion
5.1. ResQ №1
5.2. ResQ №2
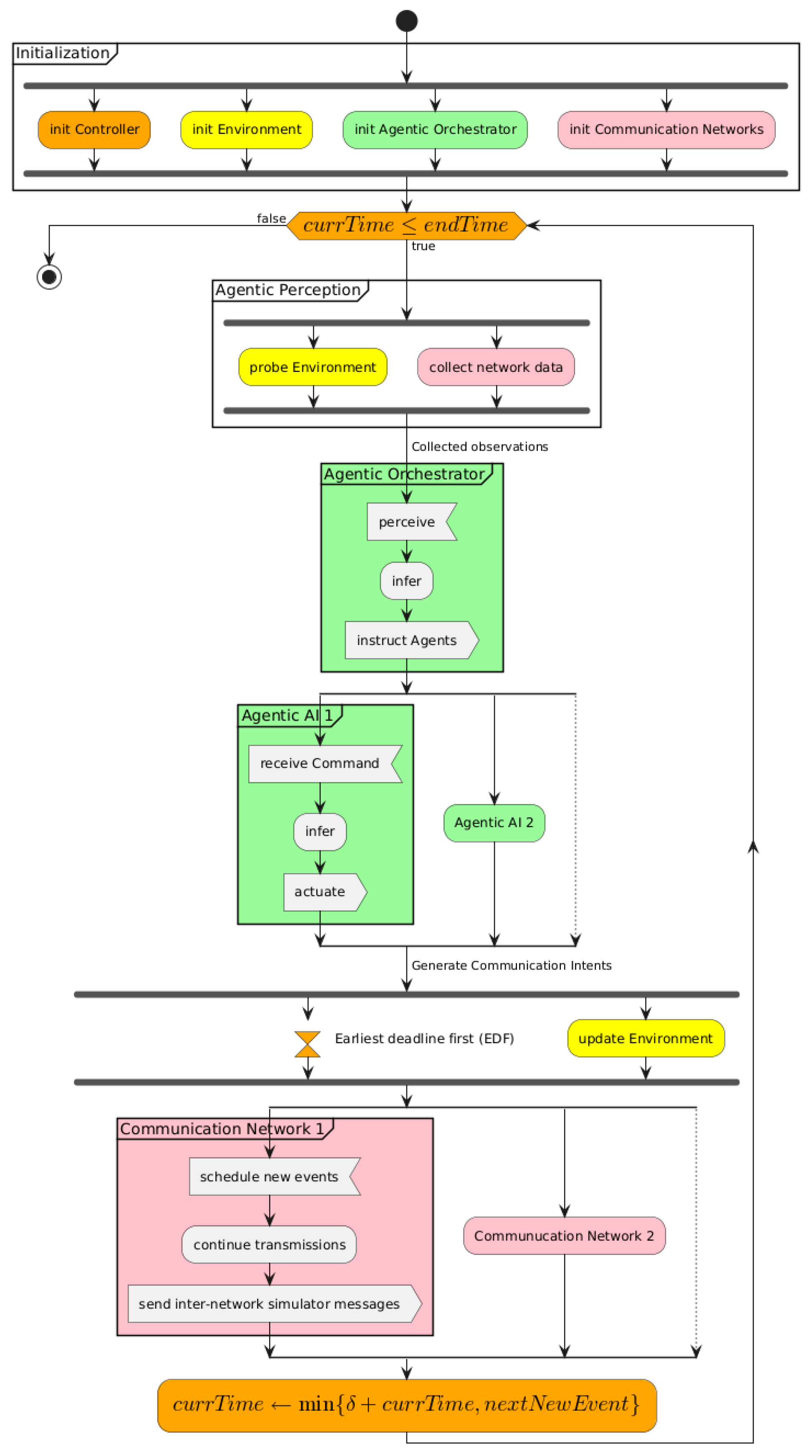
A General Framework for Orchestrating Simulators
Feasibility Study
5.3. ResQ №3
5.4. ResQ №4
5.4.1. Energy Resource Utilisation
5.4.2. Network Resource Utilisation
5.5. ResQ №5
6. Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AADLB | Application-Aware Dynamic Load Balancing |
| AP | Access Point |
| BC-I2 | BUPTCMCCCMG-IMT2030 |
| BFS | Bandwidth Forecast Service |
| C-IoT | Opt Cellular IoT Optimisation |
| CF | mMIMO Cell-Free massive Multi-Input Multi-Output |
| CmM | Cell-Free 6G mMIMO simulator |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| CS7G | CloudSim 7G |
| DRSTW | Deep RNN SD-WAN Traffic Management |
| EDT | Early Data Transmission |
| FC | FedCime |
| H2H | Human-to-Human |
| HiL | Hardware in the Loop |
| HPC | High Performance Computing |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ISDWAN | IoTSim-SDWAN |
| ISO | IoTSim-Osmosis |
| ISOR | IoTSim-Osmosis-RES |
| ISP | Internet Service Provider |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| LDCC | Lausanne Data Challenge Campaign |
| LEO | Low Earth Orbit |
| LLS | Link Level Simulator |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| LTSP | Location Time-Step Pair |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MANET | Mobile Ad-hoc NeTwork |
| MAPE | Monitor, Analyse, Plan, Execute |
| MCFR | Minimum Cost Flow Routing |
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing |
| MQBS | Multi-Queue Bandwidth Slicing |
| MQTT | Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
| MSBCS | Multi-Stage Bandwidth Control Scheme |
| NB-IoT Narrowband IoT | |
| NLS | Network Level Simulator |
| NS | NYUSIM |
| OSI | Open Systems Interconnection |
| PDR | Packet Delivery Rate |
| PLA | Packet Limiter Algorithm |
| QoE | Quality of Experience |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| RAW | Random Access Window |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| ROV | Remote Operated Vehicle |
| ROVS | Remote Operated Vehicle Simulator |
| S2C | Simcan2Cloud |
| SB | SimulatorBridger |
| SD-WAN | Software-Defined Wide Area Network |
| SDN | Software Defined Network |
| SDN-DC | Software Defined Network Data Centre |
| SLA | Service Level Agreement |
| SLS | System Level Simulator |
| SO | SimulatorOrchestrator |
| SOTA | State-Of-The-Art |
| SPMB | Shortest Path Maximum Bandwidth |
| STN | Satellite-Terrestrial Network |
| SUMO | Simulation of Urban MObility |
| UC | CF mMIMO User Centric Cell-Free massive Multi-Input Multi-Output |
| US | UltraStar |
| VANET | Vehicular Ad-hoc NeTwork |
| VM | Virtual Machine |
| WLB | Weighted Load Balancing |
References
- Syed, A.S.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Kumar, A.; Elmaghraby, A. IoT in Smart Cities: A Survey of Technologies, Practices and Challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 429–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishina, A.; Chinnici, M.; Kor, A.L.; Rondeau, E.; Georges, J.P.; De Chiara, D. Data Center for Smart Cities: Energy and Sustainability Issue. In Big Data Platforms and Applications: Case Studies, Methods, Techniques, and Performance Evaluation; Pop, F., Neagu, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawhar, I.; Mohamed, N.; Al-Jaroodi, J. Networking architectures and protocols for smart city systems. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 2018, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, E.; vom Lehn, H.; Wehrle, K. A Performance Comparison of Recent Network Simulators. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dresden, Germany, 14–18 June 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillgallon, R.; Almutairi, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G. SimulatorOrchestrator: A 6G-Ready Simulator for the Cell-Free/Osmotic Infrastructure. Sensors 2025, 25, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergami, G.; Packer, E.; Scott, K.; Del Din, S. Predicting Dyskinetic Events Through Verified Multivariate Time Series Classification. In Proceedings of the Database Engineered Applications, Bayonne, France, 26–29 August 2024; Chbeir, R., Ilarri, S., Manolopoulos, Y., Revesz, P.Z., Bernardino, J., Leung, C.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 49–62. [Google Scholar]
- Meliá, S.; Nasabeh, S.; Luján-Mora, S.; Cachero, C. MoSIoT: Modeling and Simulating IoT Healthcare-Monitoring Systems for People with Disabilities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.D.H.; Frikha, M.; Ahmed, S.; Rahebi, J. Ambulance Vehicle Routing in Smart Cities Using Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Sfax, Tunisia, 24–27 May 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, M.; Chakrabortty, R.K. An optimal ambulance routing model using simulation based on patient medical severity. Healthc. Anal. 2023, 4, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi Absardi, Z.; Javidan, R. A predictive SD-WAN traffic management method for IoT networks in multi-datacenters using deep RNN. IET Commun. 2024, 18, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Xia, Y.; Yan, Z.; Gao, H.; Qiu, D.; Guerrero, J.M.; Li, Z. Coordinated operation of multi-energy microgrids considering green hydrogen and congestion management via a safe policy learning approach. Appl. Energy 2025, 401, 126611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gu, W.; Yao, S.; Lu, S.; Zhou, S.; Wu, Z. Partitional Decoupling Method for Fast Calculation of Energy Flow in a Large-Scale Heat and Electricity Integrated Energy System. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G. Advancements and Challenges in IoT Simulators: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G.; Gillgallon, R. Platform for Energy Efficiency Monitoring Electrical Vehicle in Real World Traffic Simulation. In Proceedings of the CBI, Prague, Czech Republic, 21–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzillo, V.; Quintana, A.A. Implementation of 802.11ax and cell-free massive MIMO scenario for 6G wireless network analysis extending OMNeT++ simulator. SIMULATION 2025, 101, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgenieva, E.; Vlahov, A.; Ivanov, A.; Poulkov, V.; Manolova, A. A Comprehensive Survey of 6G Simulators: Comparison, Integration, and Future Directions. Electronics 2025, 14, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Tang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Gao, T.; Miao, H.; Chai, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Channel Measurement, Modeling, and Simulation for 6G: A Survey and Tutorial. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2305.16616. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S. Ensuring renewable energy utilization with quality of service guarantee for energy-efficient data center operations. Appl. Energy 2020, 276, 115424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Acharya, T.; DasBit, S. Quality of service in delay tolerant networks: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2018, 130, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, N.; Tafazolli, R.; Sfikas, G. Quality of service for multimedia CDMA. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2000, 38, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, S.; Uhl, T.; Nowicki, K. Influence of the jitter buffer on the quality of service VoIP. In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT), Budapest, Hungary, 5–7 October 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Li, M.; Chlamtac, I.; Prabhakaran, B. A survey of quality of service in IEEE 802.11 networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2004, 11, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademaj, F.; Bernhard, H.P. Quality-of-Service-Based Minimal Latency Routing for Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, H.; Ju, S.; Shakya, D.; Rappaport, T.S. A Tutorial on NYUSIM: Sub-Terahertz and Millimeter-Wave Channel Simulator for 5G, 6G, and Beyond. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 26, 824–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos Ramonet, A.; Pecorella, T.; Picano, B.; Kinoshita, K. Perspectives on IoT-oriented network simulation systems. Comput. Netw. 2024, 253, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szydlo, T.; Szabala, A.; Kordiumov, N.; Siuzdak, K.; Wolski, L.; Alwasel, K.; Habeeb, F.; Ranjan, R. IoTSim-Osmosis-RES: Towards autonomic renewable energy-aware osmotic computing. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2022, 52, 1698–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.; Brighente, A.; Kumar, S.A.P.; Conti, M. 5G Security Challenges and Solutions: A Review by OSI Layers. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 116294–116314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbaje, P.; Anjum, A.; Talukder, Z.; Islam, M.; Nwafor, E.; Olufowobi, H. FedCime: An Efficient Federated Learning Approach For Clients in Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Communications (EDGE), Chicago, IL, USA, 2–8 July 2023; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, R.; Zhao, J.; Cucinotta, T.; Buyya, R. CloudSim 7G: An Integrated Toolkit for Modeling and Simulation of Future Generation Cloud Computing Environments. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2024, 55, 1041–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares, P.C.; Núñez, A.; Bernal, A.; Cambronero, M.E.; Barker, A. Simcan2Cloud: A Discrete-Event-Based Simulator for Modelling and Simulating Cloud Computing Infrastructures. J. Cloud Comput. 2023, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwasel, K.; Jha, D.N.; Hernandez, E.; Puthal, D.; Barika, M.; Varghese, B.; Garg, S.K.; James, P.; Zomaya, A.; Morgan, G.; et al. IoTSim-SDWAN: A simulation framework for interconnecting distributed datacenters over Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN). J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 143, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwasel, K.; Jha, D.N.; Habeeb, F.; Demirbaga, U.; Rana, O.; Baker, T.; Dustdar, S.; Villari, M.; James, P.; Solaiman, E.; et al. IoTSim-Osmosis: A framework for modeling and simulating IoT applications over an edge-cloud continuum. J. Syst. Archit. 2021, 116, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.K.; Buyya, R. NetworkCloudSim: Modelling Parallel Applications in Cloud Simulations. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fourth IEEE International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 5–8 December 2011; pp. 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piraghaj, S.F.; Dastjerdi, A.V.; Calheiros, R.N.; Buyya, R. ContainerCloudSim: An environment for modeling and simulation of containers in cloud data centers. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2017, 47, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.N.; Alwasel, K.; Alshoshan, A.; Huang, X.; Naha, R.K.; Battula, S.K.; Garg, S.; Puthal, D.; James, P.; Zomaya, A.; et al. IoTSim-Edge: A simulation framework for modeling the behavior of Internet of Things and edge computing environments. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2020, 50, 844–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, L.; Celesti, A.; Galletta, A.; Dustdar, S.; Villari, M. From the Cloud to Edge and IoT: A Smart Orchestration Architecture for Enabling Osmotic Computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 32nd International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA), Krakow, Poland, 16–18 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheibi, O.; Weyns, D.; Quin, F. Applying Machine Learning in Self-adaptive Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. ACM Trans. Auton. Adapt. Syst. 2021, 15, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P.A.; Behrisch, M.; Bieker-Walz, L.; Erdmann, J.; Flötteröd, Y.P.; Hilbrich, R.; Lücken, L.; Rummel, J.; Wagner, P.; Wiessner, E. Microscopic Traffic Simulation using SUMO. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G. SimulatorBridgerDfT: A Real-Data Simulator for IoT-Osmotic Interactions. In Proceedings of the 2024 12th International Conference on Information Technology, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–15 December 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillgallon, R.; Bergami, G.; Almutairi, R.; Morgan, G. AI-Driven Multi-Agent Vehicular Planning for Battery Efficiency and QoS in 6G Smart Cities. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.14877. [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar, A.; Wegener, J.; Rahman, A.; Schulz-Zander, J. Towards Application Level Energy Monitoring for Green 6G Networks. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop on 5G and Beyond Network Measurements, Modeling, and Use Cases, 5G-MeMU ’24, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantoulas, I.; Loi, I.; Tsimas, D.; Sgarbas, K.; Gkamas, A.; Bouras, C. A Framework for User Traffic Prediction and Resource Allocation in 5G Networks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tealab, M.; Hassebo, A.; Dabour, A.; AbdelAziz, M. Smart Cities Digital transformation and 5G–ICT Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th IEEE Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 28–31 October 2020; pp. 0421–0425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahomed, A.S.; Saha, A.K. Unleashing the Potential of 5G for Smart Cities: A Focus on Real-Time Digital Twin Integration. Smart Cities 2025, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, C.C. Architectural Imperatives for Fog Computing: Use Cases, Requirements, and Architectural Techniques for Fog-Enabled IoT Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, C.; Gebauer, T.; Patchou, M.; Wietfeld, C. QoE Evaluation of Real-Time Remote Operation with Network Constraints in a System-of-Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Systems Conference (SysCon), Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 April 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörke, P.; Gebauer, T.; Böcker, S.; Wietfeld, C. Scaling Dense NB-IoT Networks to the Max: Performance Benefits of Early Data Transmission. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 95th Vehicular Technology Conference: (VTC2022-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 19–22 June 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, T.; Tang, Z.; Qin, X.; Zhou, H.; Shen, X.S. UltraStar: A Lightweight Simulator of Ultra-Dense LEO Satellite Constellation Networking for 6G. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, M.; Bertin, E.; Crespi, N. 5G shortcomings and Beyond-5G/6G requirements. In Proceedings of the 2022 1st International Conference on 6G Networking (6GNet), Paris, France, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Kanno, I.; Ito, M.; Chen, W.Y.; Molisch, A.F. A Realistic Path Loss Model for Cell-Free Massive MIMO in Urban Environments. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2022-2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, J.; Castanheira, D.; Silva, A.; Dinis, R.; Gameiro, A. A Review on Cell-Free Massive MIMO Systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Lv, T.; Li, W.; Ni, W.; Jamalipour, A. Joint Optimization of Beamforming and Noise Injection for Covert Downlink Transmissions in Cell-Free Internet of Things Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 10525–10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Lee, J. Edge Computing-Enabled Cell-Free Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 2884–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H.A.; Adve, R.; Shahbazpanahi, S.; Boudreau, G.; Srinivas, K.V. User-Centric Cell-Free Massive MIMO Networks: A Survey of Opportunities, Challenges and Solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 611–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Di, B.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Song, L. Beyond Cell-Free MIMO: Energy Efficient Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Aided Cell-Free MIMO Communications. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinov, I.A.; Chung, J.; Kettimuthu, R.; Bordel, B.; Alcarria, R.; Robles, T. Towards 6G Networks for Rural Environments: Vision for Improving Digital Inclusion through Open Source Hardware and Software. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 40th Central America and Panama Convention (CONCAPAN), Panama City, Panama, 9–12 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharbi, S.E.; Iturralde, M.; Dupuis, Y.; Gaugue, A. LoRaCAPS: Congestion-Aware Path Selection Protocol for Offshore LoRaWan Networking. In Proceedings of the 2024 20th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), Paris, France, 21–23 October 2024; pp. 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, K.; Tarchi, D.; Wan, S.; Kumar, N. INTERLINK: A Digital Twin-Assisted Storage Strategy for Satellite-Terrestrial Networks. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 3746–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, F.; Alwasel, K.; Noor, A.; Jha, D.N.; AlQattan, D.; Li, Y.; Aujla, G.S.; Szydlo, T.; Ranjan, R. Dynamic Bandwidth Slicing for Time-Critical IoT Data Streams in the Edge-Cloud Continuum. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8017–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, O. A bandwidth control scheme for reducing the negative impact of bottlenecks in IoT environments: Simulation and performance evaluation. Internet Things 2023, 21, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, G.; Posdorfer, W. Saving bandwidth and energy of mobile and IoT devices with link predictions. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 8229–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Li, Y.; Sugaya, M. Weighted Load Balancing Method for Heterogeneous Clusters on Hybrid Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing and Communications (EDGE), Chicago, IL, USA, 2–8 July 2023; pp. 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillgallon, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G. Testing Routing Strategies by Simulating the Mobile IoT Edge/Cloud Continuum. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Pattaya, Thailand, 29 October–1 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, T.; Vidaković, A.; Doknić, I.; Veinović, M.; Bojović, Ž. An Adaptive Application-Aware Dynamic Load Balancing Framework for Open-Source SD-WAN. Sensors 2025, 25, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, A. IOT, Smart Technologies, Smart Policing: The Impact for Rural Communities. In Smart Village Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameddah, M.A.; Das, B.; Almhana, J. Cloud-Assisted Real-Time Road Condition Monitoring System for Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 9–13 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, G.; Bade, D.; Lamersdorf, W. CloudAware: Empowering context-aware self-adaptation for mobile applications. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2018, 29, e3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, J.; Gatica-Perez, D.; Aad, I.; Blom, J.; Bornet, O.; Do, T.; Dousse, O.; Eberle, J.; Miettinen, M. From big smartphone data to worldwide research: The Mobile Data Challenge. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2013, 9, 752–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’16, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: A retrospective. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2011, 73, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, R.; Gillgallon, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G. Approximating Real-Time IoT Interaction Through Connection Counting: A QoS Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2024 20th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), Paris, France, 21–23 October 2024; pp. 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Chen, K.; Qiao, Z. A Multi-Objective Test Scenario Prioritization Method Based on UML Activity Diagram. J. Electron. Test. 2025, 41, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonica, R.; Pignataro, C.; Touch, J. A Widely Deployed Solution to the Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) Fragmentation Problem. RFC 2015, 7588, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence—A Modern Approach, Third International Edition; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Parnas, D. Scheduling processes with release times, deadlines, precedence and exclusion relations. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1990, 16, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.; Ramírez-Arroyo, A.; Sorensen, T.B. Cellular-Satellite Multi-Connectivity with Link Activation Based on Random Forest Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2024 20th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), Paris, France, 21–23 October 2024; pp. 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, E.; Gordillo, A.; Calero, C.; Ángeles Moraga, M.; García, F. Does the compiler or interpreter version influence the energy consumption of programming languages? Sci. Comput. Program. 2025, 243, 103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, A. Digital Twins for Personalized Medicine Require Epidemiological Data and Mathematical Modeling: Viewpoint. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e72411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergami, G. Towards automating microservices orchestration through data-driven evolutionary architectures. Serv. Oriented Comput. Appl. 2024, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Feature | Simulator | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC [28] | CS7G [29] | S2C [30] | ISDWAN [31] | ISO [32] | ISOR [26] | SB [14] | SO [5] | |
| Cloud Processing | - |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Cloud Workloads | - |  |  | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cloud Network Resource Management | - |  | - |  |  |  |  |  |
| Cloud Energy Resource Management | - |  | - |  |  |  |  |  |
| Federator Device Selection |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| SDWAN SDN Support | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |  |
| Edge Processing |  | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |
| Edge Network Resource Management |  | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |
| Edge Energy Resource Management | - | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |
| IoT Device Support |  | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |
| Mobility IoT Device Support |  | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| IoT Device Energy Modelling | - | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |
| Osmotic Computing Support | - | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |
| Cellular Network Support | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| 6G Infrastructure Support | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |
| AI Algorithm Support | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |
| Feature | Simulator | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROVS [46] | NBIOT [47] | CmM [15] | BC-I2 [17] | NS [24] | US [48] | SB [14] | SO [5] | |
| 3G Support | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| 4G Support | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| 5G Support |  | - | - |  |  | - |  |  |
| Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Support | - |  | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| CF mMIMO Support | - | - |  | - |  | - | - |  |
| Remote IoT Support |  | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |
| Edge Support |  |  |  | - | - |  |  |  |
| Cloud Support | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| Satellite Support | - | - | - | - | - |  | - | - |
| Feature | Algorithm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQBS [59] | MSBCS [60] | BFS [61] | WLB [62] | SPMB [31] | MCFR [63] | AADLB [64] | DRSTW [10] | PLA [63] | |
| Data Prioritisation Requirements |  |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Data Prioritisation for Bandwidth |  |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bottleneck Detection | - |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bandwidth Prediction | - |  |  | - | - | - | - |  | - |
| Dynamic Bandwidth Reallocation | - |  | - | - |  |  | - |  | - |
| Stops Working in Saturated Network |  |  | - | - | - | - |  | - | - |
| Global Synchronisation Requirements | - | - | - |  | - |  | - | - | |
| Can avoid optimal solution | - | - | - | - |  | - | - |  | - |
| Requires IoT device data | - | - | - | - | - |  | - | - | - |
| Results in data loss |  |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Works in Stage 1 from Figure 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |
| Works in Stage 2 from Figure 1 | - | - | - | - |  |  |  |  |  |
| Works in Stage 3 from Figure 1 |  | - | - |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Works in Stage 4 from Figure 1 |  |  |  | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Feature | Simulator | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC [28] | CS7G [29] | S2C [30] | ISDWAN [31] | ISO [32] | ISOR [26] | CmM [15] | US [48] | NS [24] | SB [14] | SO [5] | |
| ResQ №1 | |||||||||||
| Cloud Processing | - |  |  |  |  |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| Edge Processing |  | - | - |  |  |  | - |  | - |  |  |
| IoT Devices |  | - | - |  |  |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| SDN Support |  |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| SD-WAN Support | - | - | - |  |  |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| Osmotic Computing | - | - | - | - |  |  |  |  | |||
| 3G, 4G, 5G Support | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |  |  | |
| ResQ №2 | |||||||||||
| Agents System | - | - | - | - | - |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| RES Support | - | - | - | - | - |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| Mobility IoT Devices |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| Connection Counting Support [39] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| Real Time Data Injection | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |
| AI Enhanced Vehicular Routing [40] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |
| ResQ №3 | |||||||||||
| CF mMIMO Support | - | - | - | - | - | - |  | - |  | - |  |
| Satellite Support | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  | - | - | - |
| Resource Type Supported | Simulator | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC [28] | CS7G [29] | S2C [30] | ISDWAN [31] | ISO [32] | ISOR [26] | CmM [15] | US [48] | NS [24] | SB [14] | SO [5] | |
| ResQ №4 | |||||||||||
| Energy Resources | |||||||||||
| Cloud Energy Consumption | - |  | - |  |  | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| Edge Energy Consumption | - | - | - |  |  | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| IoT Device Battery | - | - | - |  |  | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| Vehicle Battery | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |  |  |
| Power Management | - |  | - | - | - |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| Full Cloud Energy Modelling | - |  | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Full Edge Energy Modelling | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Full IoT Energy Modelling | - | - | - | - | - |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| Network Resources | |||||||||||
| Simulated CPU Utilisation | - |  |  |  |  |  | - | - | - |  |  |
| Simulated RAM/Memory Utilisation | - |  |  |  |  | - | - | - |  |  | |
| Channel Allocation | - |  | - |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Link Bandwidth | - |  | - |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Variable Packet Size | - |  | - |  |  |  |  | - |  |  |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gillgallon, R.; Bergami, G.; Morgan, G. Federated Load Balancing in Smart Cities: A 6G, Cloud, and Agentic AI Perspective. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010920
Gillgallon R, Bergami G, Morgan G. Federated Load Balancing in Smart Cities: A 6G, Cloud, and Agentic AI Perspective. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010920
Chicago/Turabian StyleGillgallon, Rohin, Giacomo Bergami, and Graham Morgan. 2025. "Federated Load Balancing in Smart Cities: A 6G, Cloud, and Agentic AI Perspective" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010920
APA StyleGillgallon, R., Bergami, G., & Morgan, G. (2025). Federated Load Balancing in Smart Cities: A 6G, Cloud, and Agentic AI Perspective. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010920








