Lightweight Detection Method of Wheelset Tread Defects Based on Improved YOLOv7
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
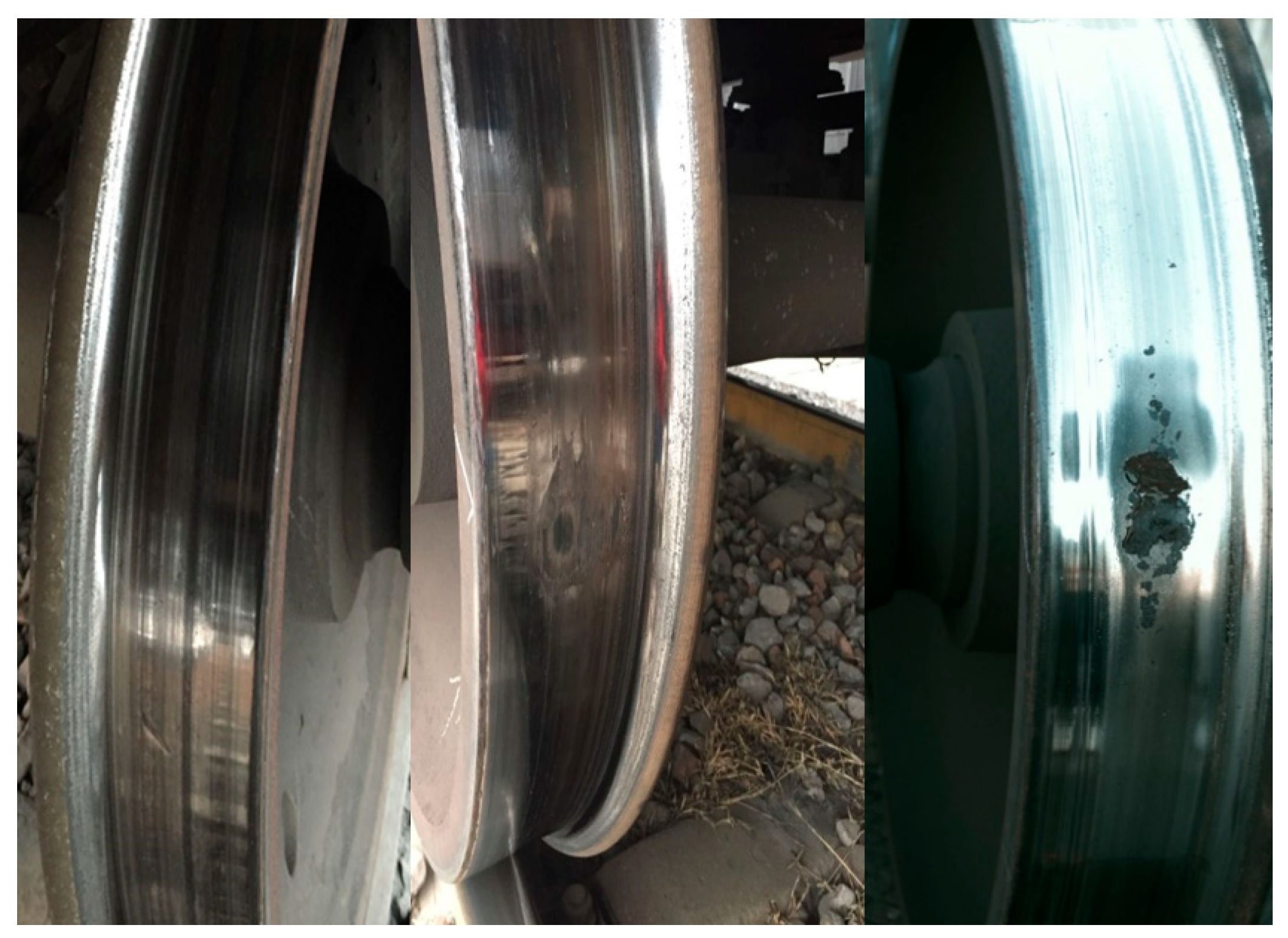
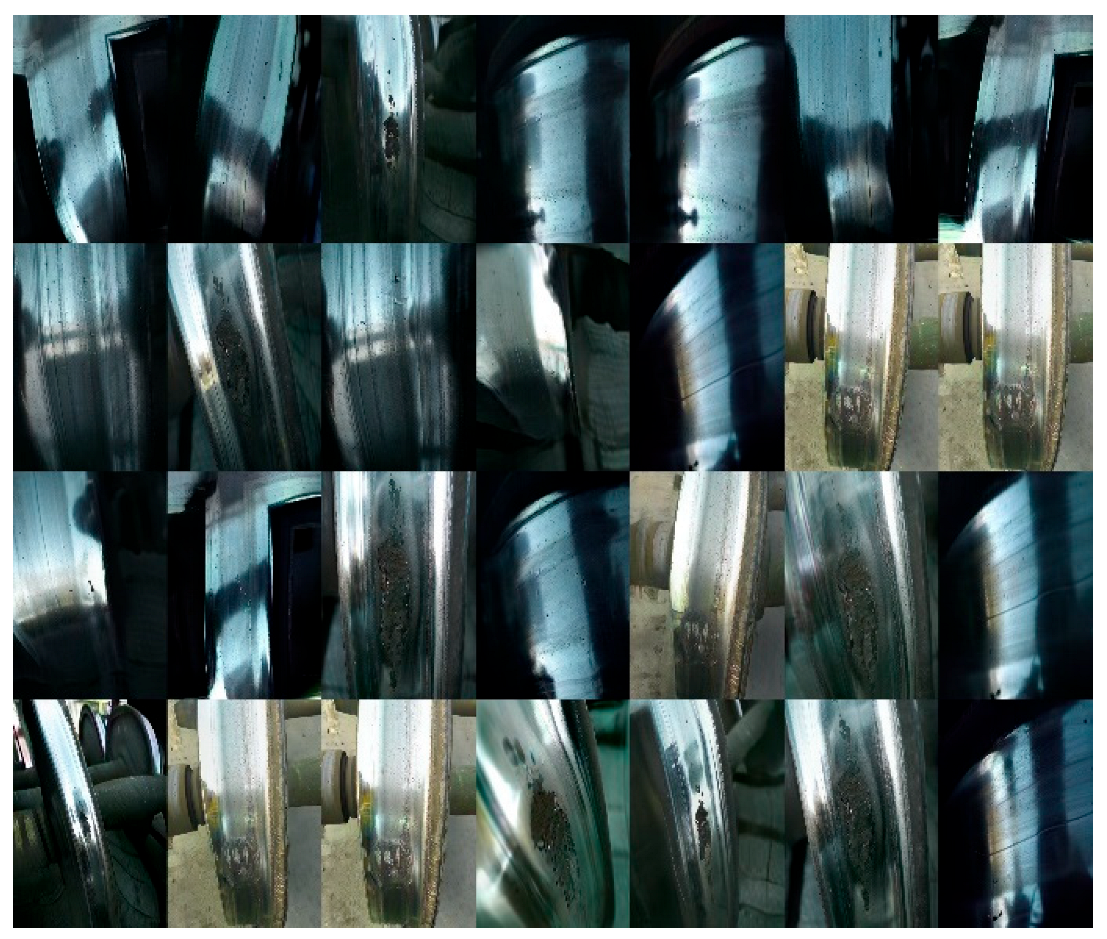
2.1. Dataset, Environment, and Parameters
2.2. Loss Function and Model Evaluation Metrics
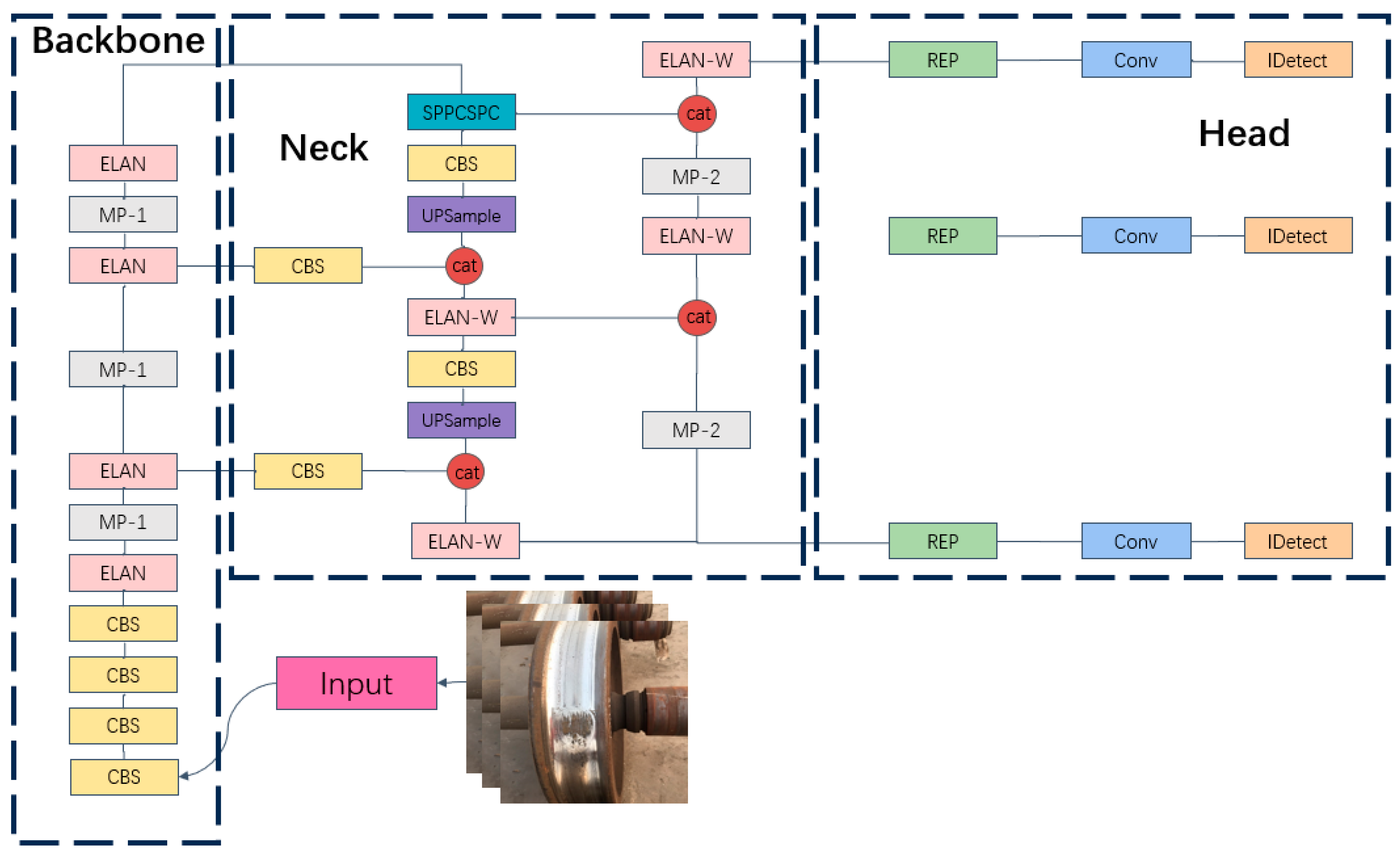
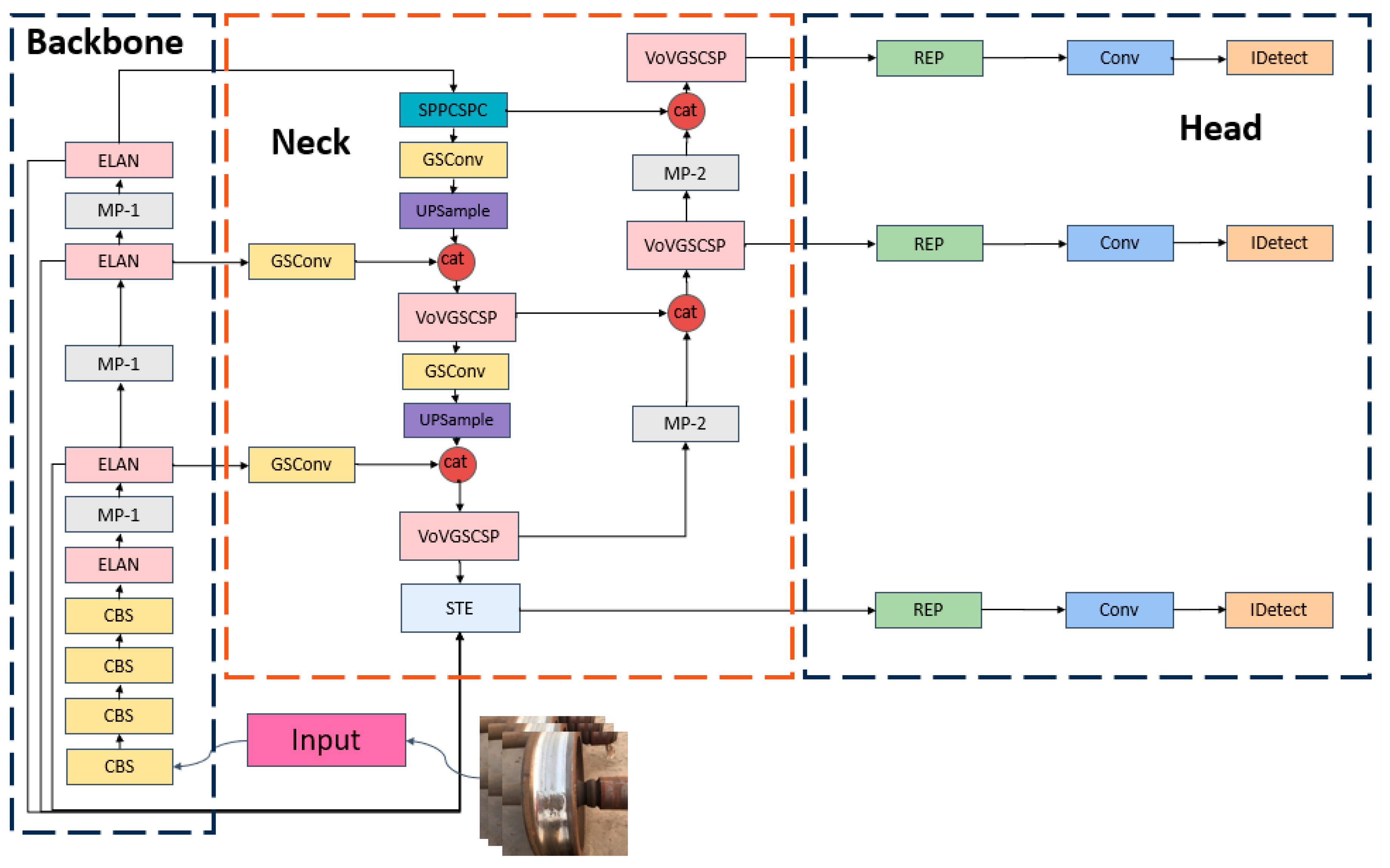
2.3. Improved YOLOv7 Network Architecture
2.3.1. YOLOv7 Network Architecture
2.3.2. YOLOv7-STE
2.3.3. Loss Function
2.4. Discussion on the Innovations in the Improved YOLOv7 Model
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparative Experimental Results Analysis
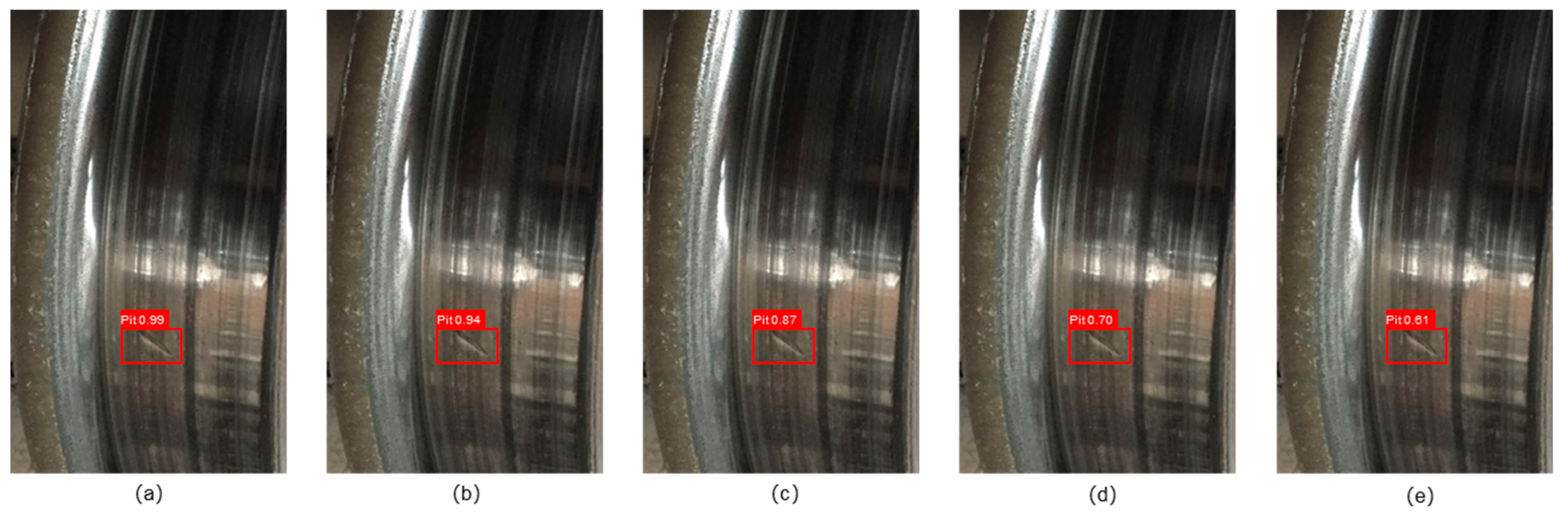
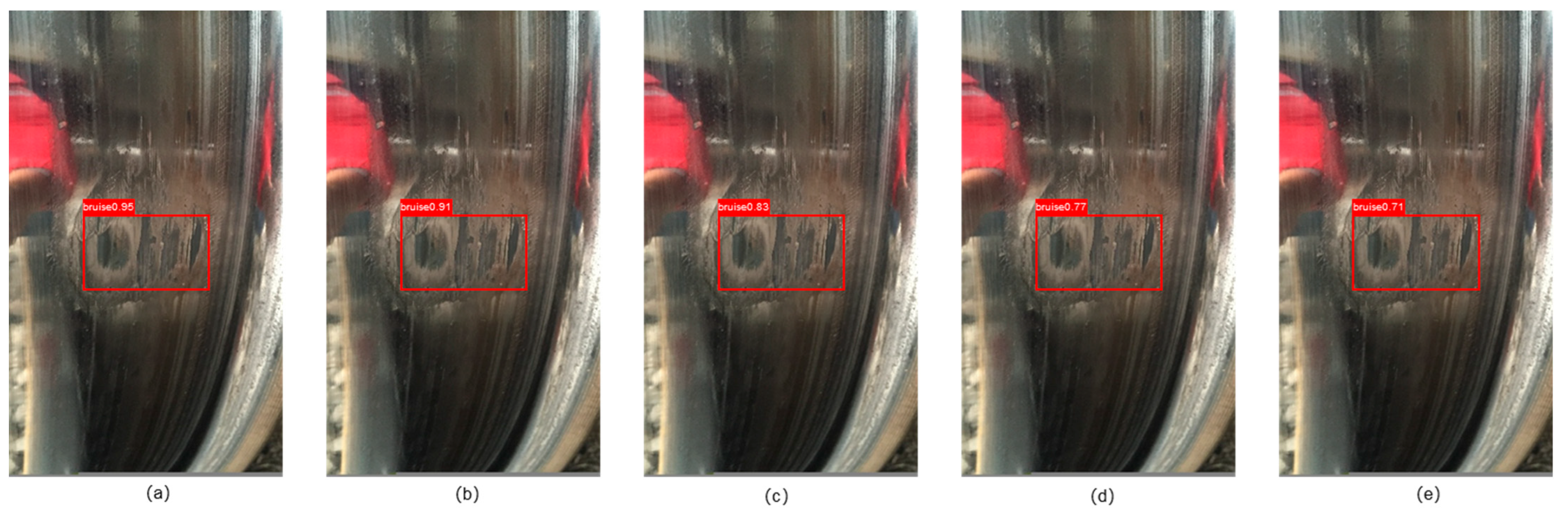
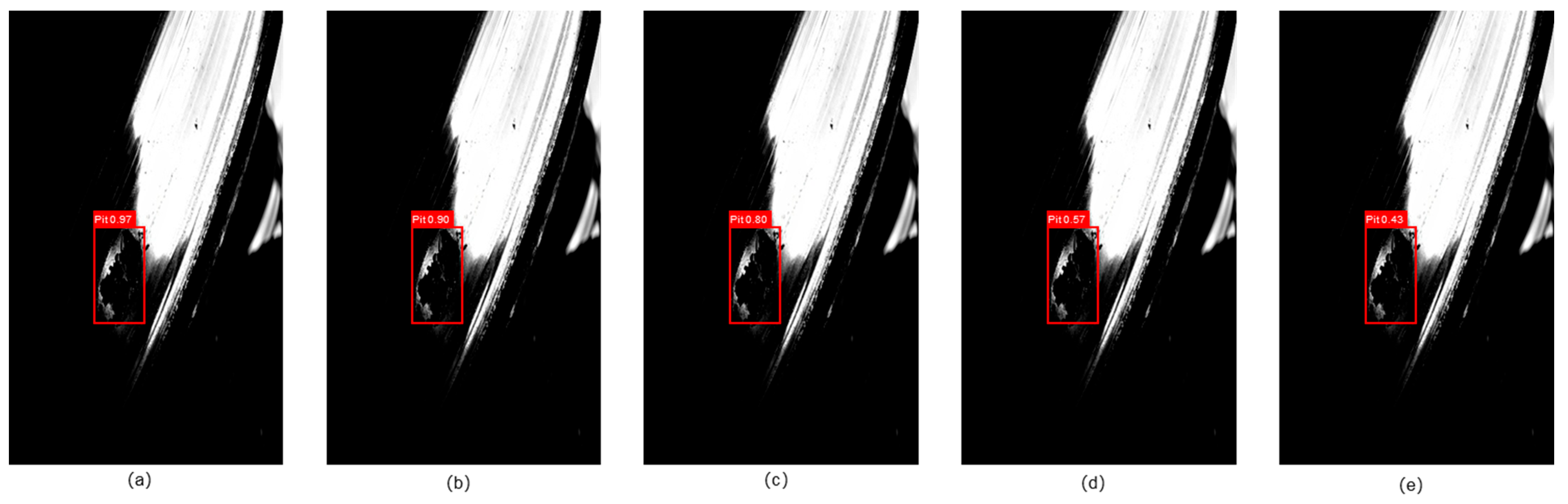
3.2. Detailed Error Analysis and Security Discussion
3.3. Ablation Experiments
3.4. Comparison of Different Models by Defect Type
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.; He, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C. LLD-MFCOS: A Multiscale anchor-free detector based on label localization distillation for wheelset tread defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 500385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ji, Z.; Guo, X.; Hsu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yin, S. A comprehensive laser image dataset for real-time measurement of wheelset geometric parameters. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Detection of Train Wheelset Tread Defects with Small Samples Based on Local Inference Constraint Network. Electronics 2024, 13, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Yin, H.L. Deformable residual attention network for defect detection of train wheelset tread. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, J. Integrated intelligent system for rail flaw detection vehicle. Electr. Drive Locomot. 2021, 1, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yu, X.; Cao, J.; Du, W. Intelligent rail flaw detection system based on deep learning and support vector machine. Electr. Drive Locomot. 2021, 2, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, Z. A new method of wavelet and support vector machine for detection of the train wheel bruise. China Mech. Eng. 2004, 15, 1641–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, J. Tread profile of wheel detection method based image processing and Hough transform. Electron. Meas. Technol. 2017, 40, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Z.; Wang, G. Fast method of detecting packaging bottle defects based on ECA-EfficientDet. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 9518910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzetti, L.; Rangarajan, A.K.; Dinca, A.; Boom, B.; Popescu, D.; Offermans, P.; Pinotti, C.M. The hawk eye scan: Halyomorpha halys detection relying on aerial tele photos and neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 226, 109365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.H.; Yang, H.F.; Cai, J.H.; Zhou, L.C.; He, Y.T.; Su, M.H.; Zhao, X.-J.; Xun, Y.-L. A Survey of Galaxy Pairs in the SDSS Photometric Images based on Faster-RCNN. Astron. J. 2024, 168, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wu, T.; Gao, G.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, H. Lightweight safflower cluster detection based on YOLOv5. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Sui, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, X. Real-time detection and counting of wheat ears based on improved YOLOv7. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Huang, W.H. A two-stage road sign detection and text recognition system based on YOLOv7. Internet Things 2024, 27, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qian, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, P.; Hu, Z.; Chai, Y. Fs-yolo: Fire-smoke detection based on improved YOLOv7. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, B.; He, H.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z. Helmet wearing detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv5. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Yuan, X.; Yao, X.; Yan, K.; Zeng, Q.; Xie, X.; Han, J. Towards large-scale small object detection: Survey and benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13467–13488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Ren, J.; Yang, J. LightRay: Lightweight network for prohibited items detection in X-ray images during security inspection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 103, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, E.; Yang, G.; Liang, Z.; Tan, M. MD-YOLO: Multi-scale Dense YOLO for small target pest detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.; Luo, J.; Liu, G.; Luo, H. A real-time small target detection network. SIViP 2021, 15, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, H.; Wen, J. Classification of flower image based on attention mechanism and multi-loss attention network. Comput. Commun. 2021, 179, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Qin, W.; Xiao, J.; Huang, X.; Pan, J.; Feng, H. Rapid detection of fish with SVC symptoms based on machine vision combined with a NAM-YOLO v7 hybrid model. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Ting, C.M.; Ting, F.F.; Phan, R.C.W. ASF-YOLO: A novel YOLO model with attentional scale sequence fusion for cell instance segmentation. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 147, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Yue, X. Lightweight object detection algorithm for automotive fuse boxes based on deep learning. J. Electron. Imaging 2025, 34, 013031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Huang, Y.; Dai, L.; Xu, F.; Hu, H. Railway obstacle intrusion warning mechanism integrating YOLO-based detection and risk assessment. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 38, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, G.; Cui, Y.; Srinivas, A.; Qian, R.; Lin, T.Y.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V.; Zoph, B. Simple copy-paste is a strong data augmentation method for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2918–2928. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aittala, M.; Laine, S.; Härkönen, E.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Alias-free generative adversarial networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 852–863. [Google Scholar]
- Abayomi-Alli, O.O.; Damaševičius, R.; Misra, S.; Maskeliūnas, R. Cassava disease recognition from low-quality images using enhanced data augmentation model and deep learning. Expert Syst. 2021, 38, e12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Bai, S. Improving machine learning based phase and hardness prediction of high-entropy alloys by using Gaussian noise augmented data. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 223, 112140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, P.; Li, Y. Scgan: Semi-centralized generative adversarial network for image generation in distributed scenes. Inf. Fusion 2024, 112, 102556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Song, C. Research on a small target object detection method for aerial photography based on improved YOLOv7. Vis. Comput. 2024, 41, 3487–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengde, C.; Junyu, L.; Xiaojie, X.; Jianzhou, G.; Shiyun, H.; Zhiyan, Z.; Yubin, L. Detection and tracking of agricultural spray droplets using GSConv-enhanced YOLOv5s and DeepSORT. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 235, 110353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huillcen Baca, H.A.; Palomino Valdivia, F.L.; Gutierrez Caceres, J.C. Efficient human violence recognition for surveillance in real time. Sensors 2024, 24, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Automatic recognition of pavement cracks from combined GPR B-scan and C-scan images using multiscale feature fusion deep neural networks. Autom. Constr. 2023, 146, 104698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Categories | Number of Targets | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set | |
| Pit | 1280 | 160 | 160 |
| Bruise | 1280 | 160 | 160 |
| Peel | 1280 | 160 | 160 |
| Total | 3840 | 480 | 480 |
| Hardware and Software | Configuration Parameter |
|---|---|
| Computer | Operating System: Windows 10 |
| CPU: Intel(R) Core (TM) i9-9900K CPU@3.60GHz | |
| GPU: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 | |
| RAM: 16 GB | |
| Video memory: 24 GB | |
| Software version | Python3.9.12 + PyTorch1.9.1 + CUDA11.7 + cuDNN8.2.1 + Opencv4.5.5 + Visual Studio Code2022 (1.69.1) |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch size | 64 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 |
| Warm-up epochs | 3 |
| Number of iterations | 120 |
| Momentum parameter | 0.937 |
| Image size | 640 × 640 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Model | Parameter size (MB) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5:0.95(%) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7-STE | 61.09 | 98.1 | 65.3 | 75.9 |
| YOLOv8 | 63.1 | 96.5 | 56.8 | 81.1 |
| YOLOv7 | 135 | 96.9 | 55.2 | 75.4 |
| YOLOv5 | 155.78 | 88.5 | 51.2 | 73.6 |
| SSD | 183.2 | 51.9 | 40.7 | 33.1 |
| Faster R-CNN | 216 | 60.5 | 35.9 | 8.3 |
| Model | Pit | Bruise | Peel | Macro-Avg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv7-STE | 97.3 | 97.5 | 99.6 | 98.1 |
| YOLOv7 | 86.5 | 94.1 | 98.8 | 93.1 |
| YOLOv8 | 87.8 | 94.5 | 98.9 | 93.7 |
| YOLOv5 | 80.1 | 89.3 | 95.2 | 88.2 |
| Defect Category | Precision | Recall | AP@0.5 | False Negative Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pit | 92.1 | 92.5 | 90.2 | 7.5 |
| Bruise | 96.8 | 95.9 | 95.3 | 4.1 |
| Peel | 99.2 | 98.8 | 99.0 | 1.2 |
| All categories | 96.0 | 95.7 | 94.8 | 4.3 |
| Loss Function | Model Volume | mAP@0.5:0.95 | mAP@0.5(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MB) | (%) | All Classes | Pit | Peel | Bruise | |
| CIoU | 135 | 51.33 | 93.9 | 91.6 | 97.3 | 92.9 |
| WIoU | 135 | 51.44 | 94.1 | 90 | 99.5 | 93 |
| SIoU | 135 | 51.34 | 93.9 | 91.5 | 97.3 | 93 |
| DIoU | 135 | 51.69 | 94.6 | 91.1 | 99.2 | 93.6 |
| EIoU | 135 | 52.77 | 95.7 | 92.6 | 99.5 | 95.1 |
| GSConv | STE | EIoU | Model Volume | mAP@0.5:0.95 | mAP@0.5(%) | FPS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MB) | (%) | All Classes | Pit | Peel | Bruise | ||||
| √ | 135 | 52.9 | 96.0 | 92.8 | 99.5 | 95.8 | 73.9 | ||
| √ | √ | 51 | 50.3 | 92.7 | 83.3 | 99.6 | 95.5 | 86.7 | |
| √ | √ | 149 | 53.1 | 96.1 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 94.1 | 61 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 61.09 | 65.3 | 98.1 | 97.3 | 99.6 | 97.5 | 75.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, P.; Gao, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z. Lightweight Detection Method of Wheelset Tread Defects Based on Improved YOLOv7. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010903
Yang P, Gao F, Yang X, Wang C, Yang H, Zhang Z. Lightweight Detection Method of Wheelset Tread Defects Based on Improved YOLOv7. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010903
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Peng, Fan Gao, Xinwen Yang, Caidong Wang, Hongjun Yang, and Zhifeng Zhang. 2025. "Lightweight Detection Method of Wheelset Tread Defects Based on Improved YOLOv7" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010903
APA StyleYang, P., Gao, F., Yang, X., Wang, C., Yang, H., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Lightweight Detection Method of Wheelset Tread Defects Based on Improved YOLOv7. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10903. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010903





