A Comparative Study of Stainless Steel and PEEK TiO2 Composite: Effects on Cell Behavior and Bacterial Adhesion in Pediatric Crowns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens
2.2. Surface Characterization
2.3. In Vitro Characterization
2.3.1. Cell Culture
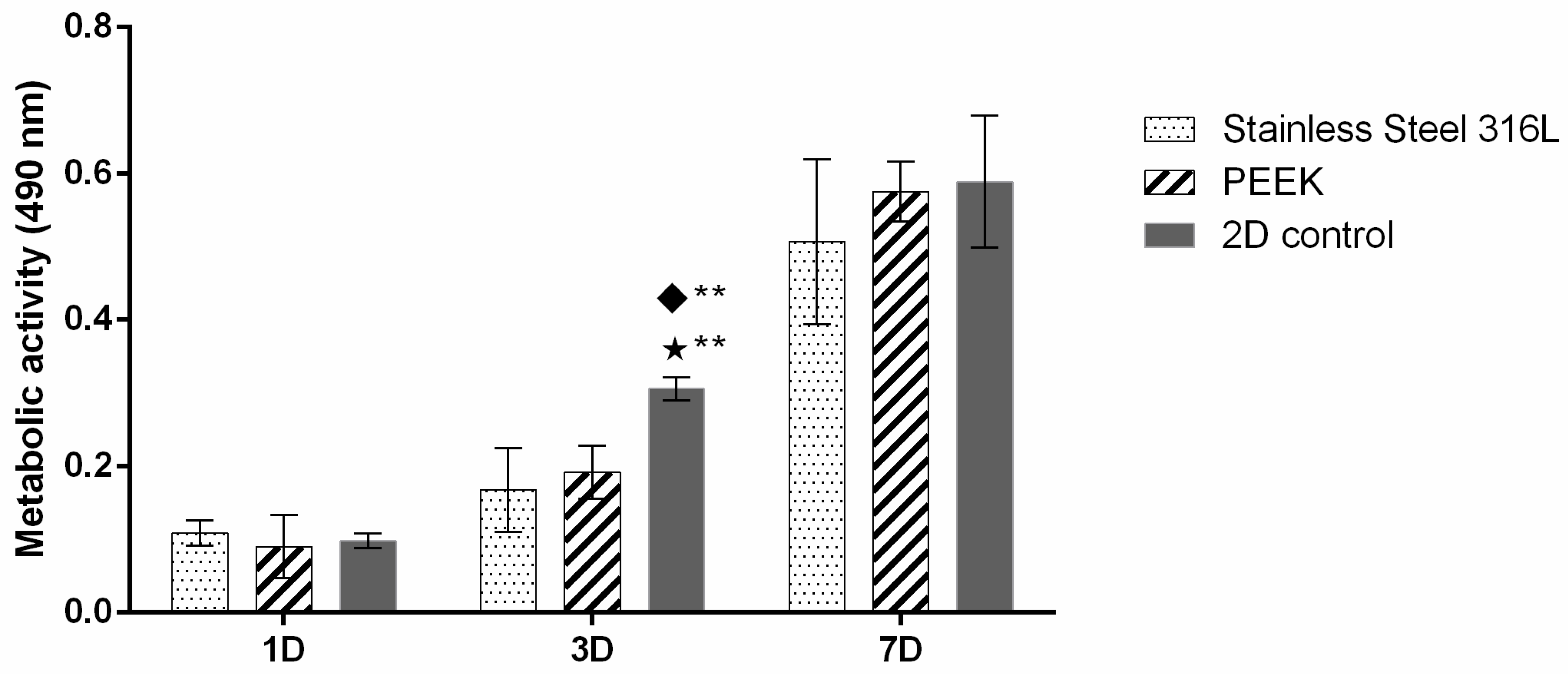
2.3.2. Metabolic Activity
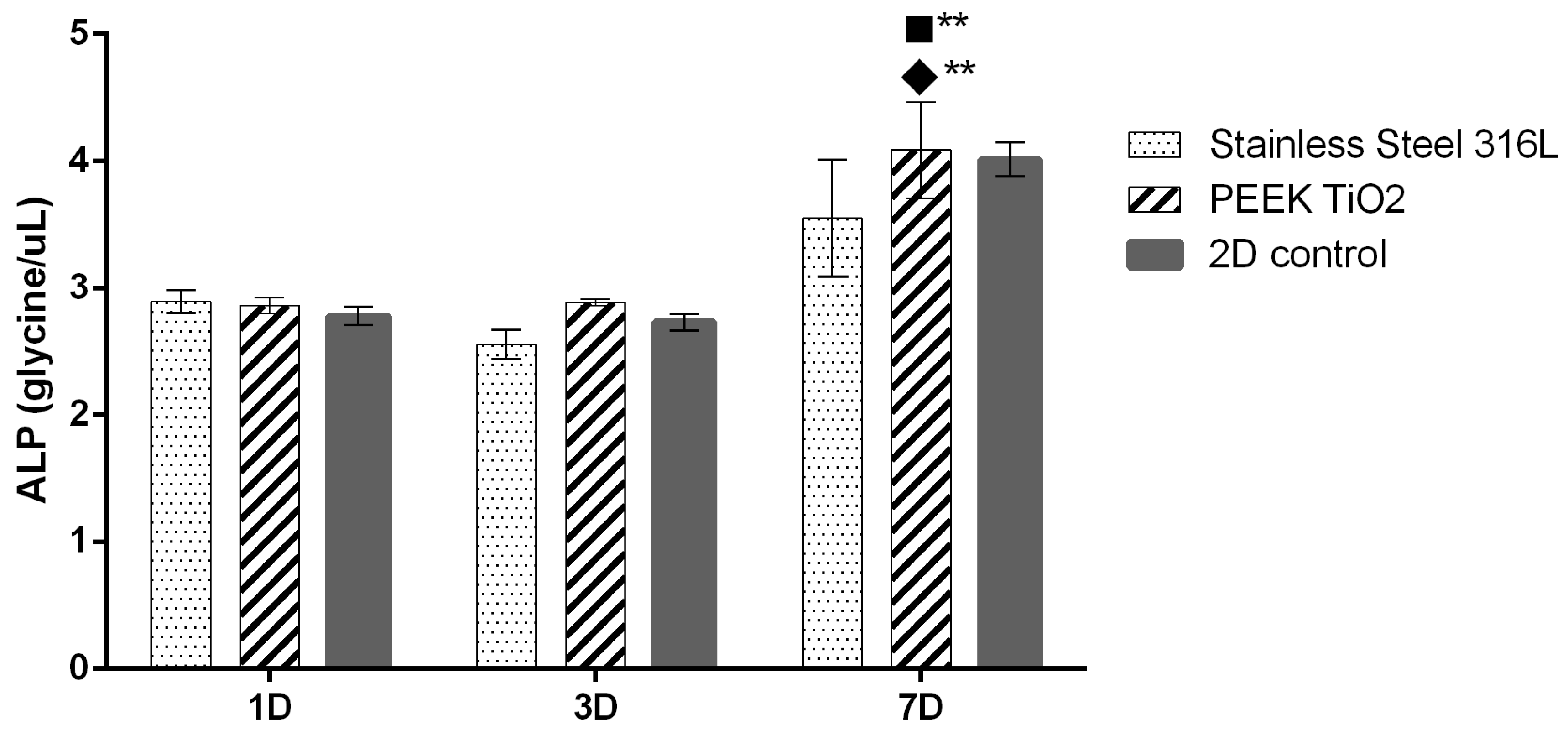
2.3.3. Alkaline Phosphatase Quantification
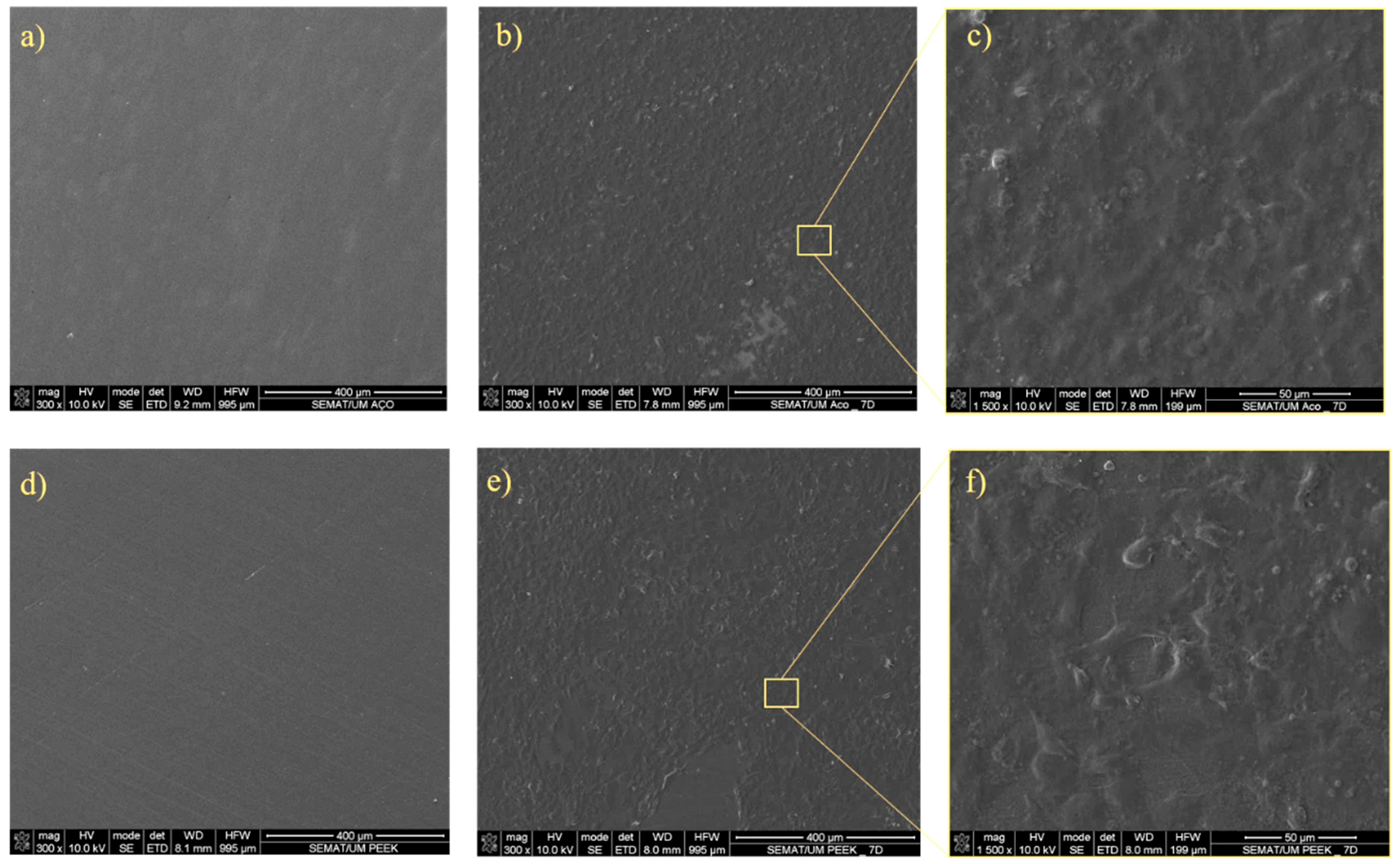
2.3.4. Cell Adhesion and Morphology by Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.5. Bacterial Adhesion Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Specimens’ Characterization
3.2. In Vitro Characterization
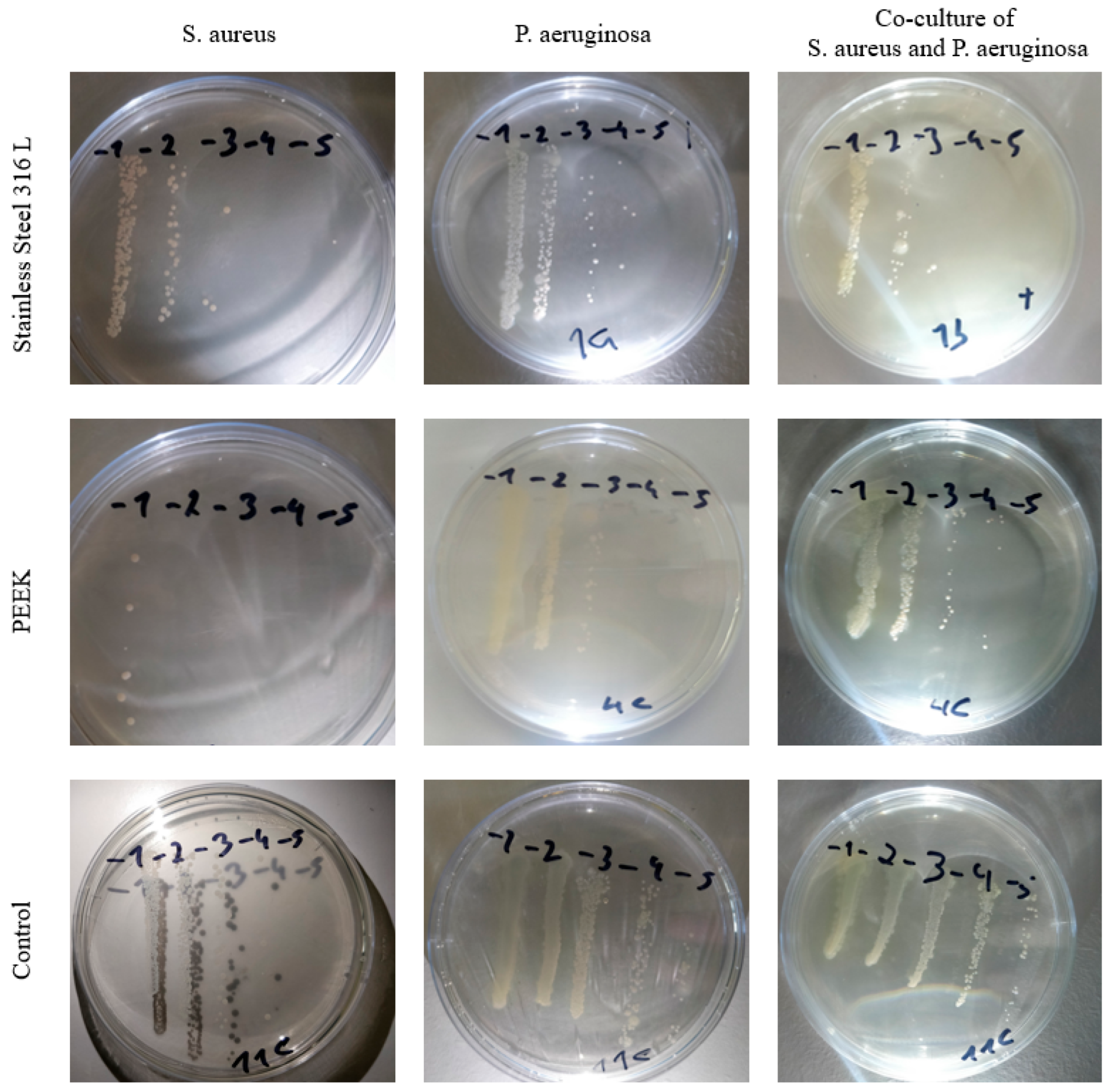
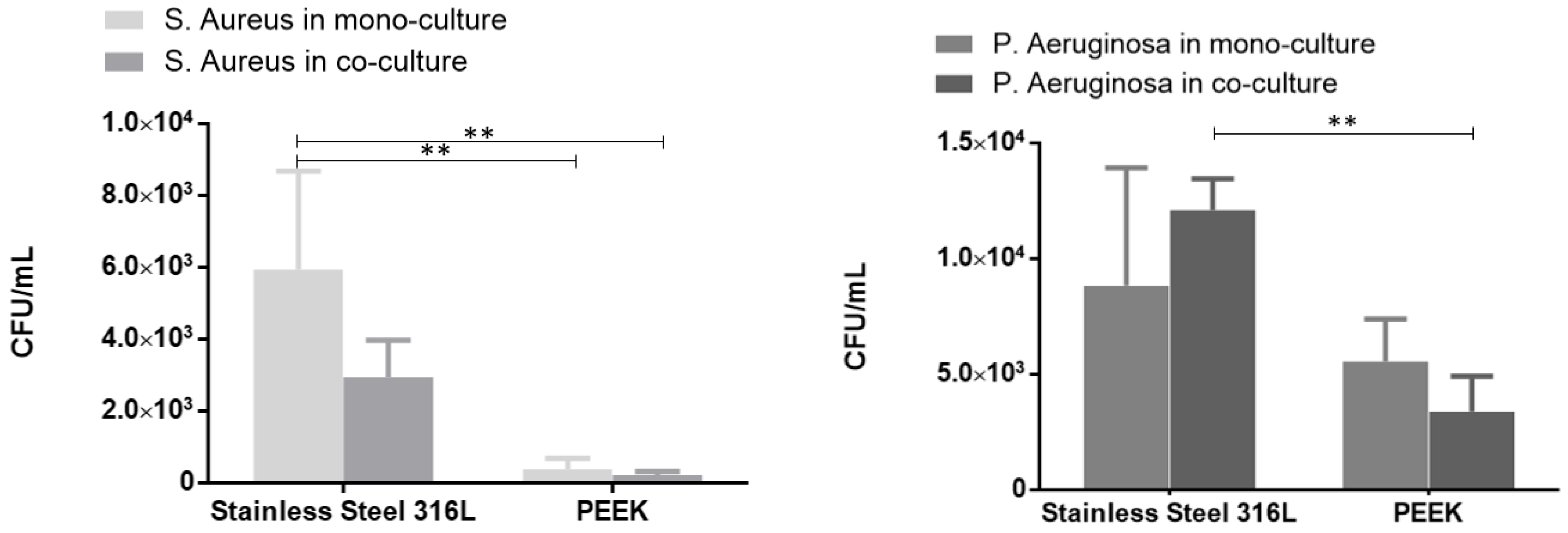
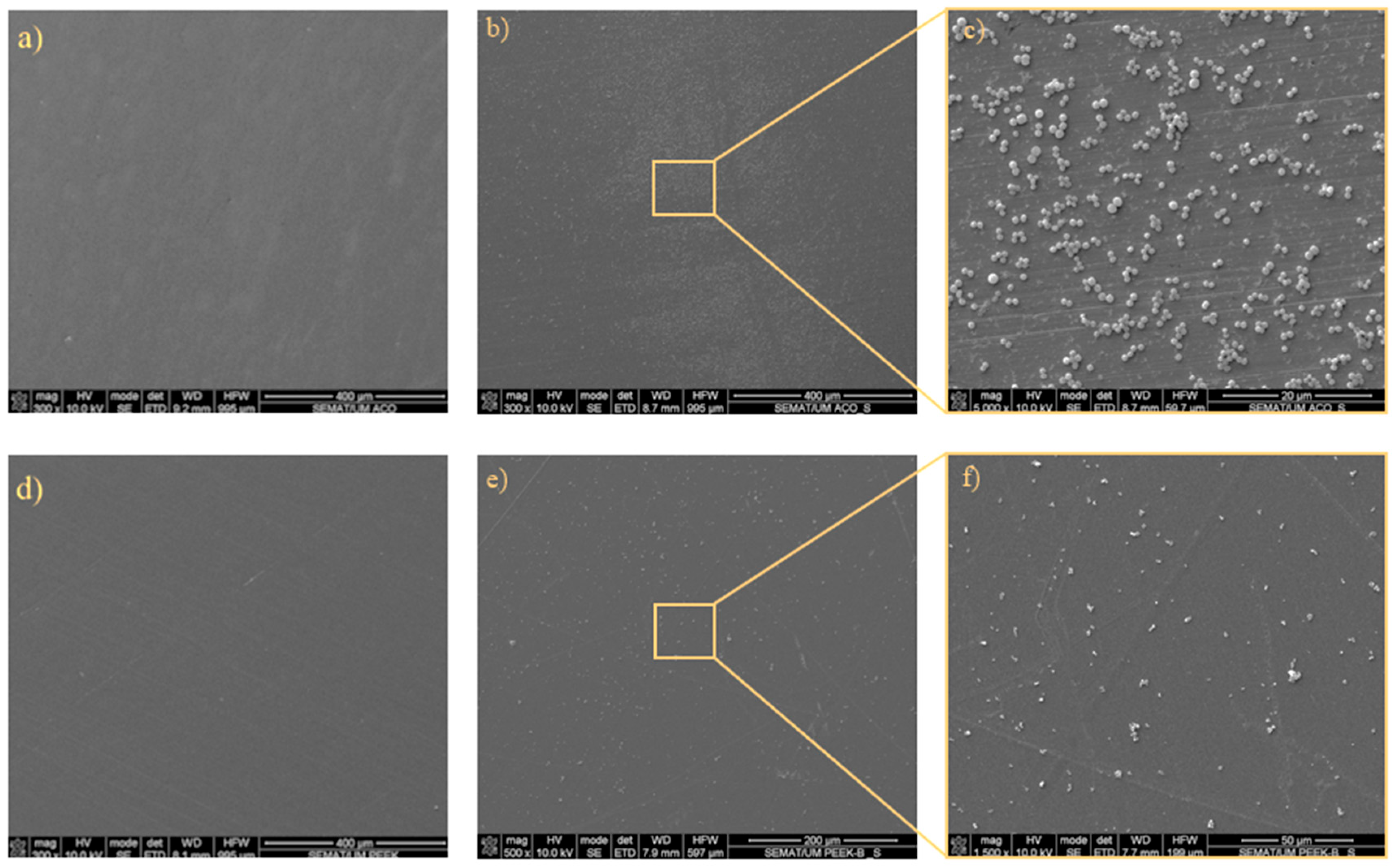
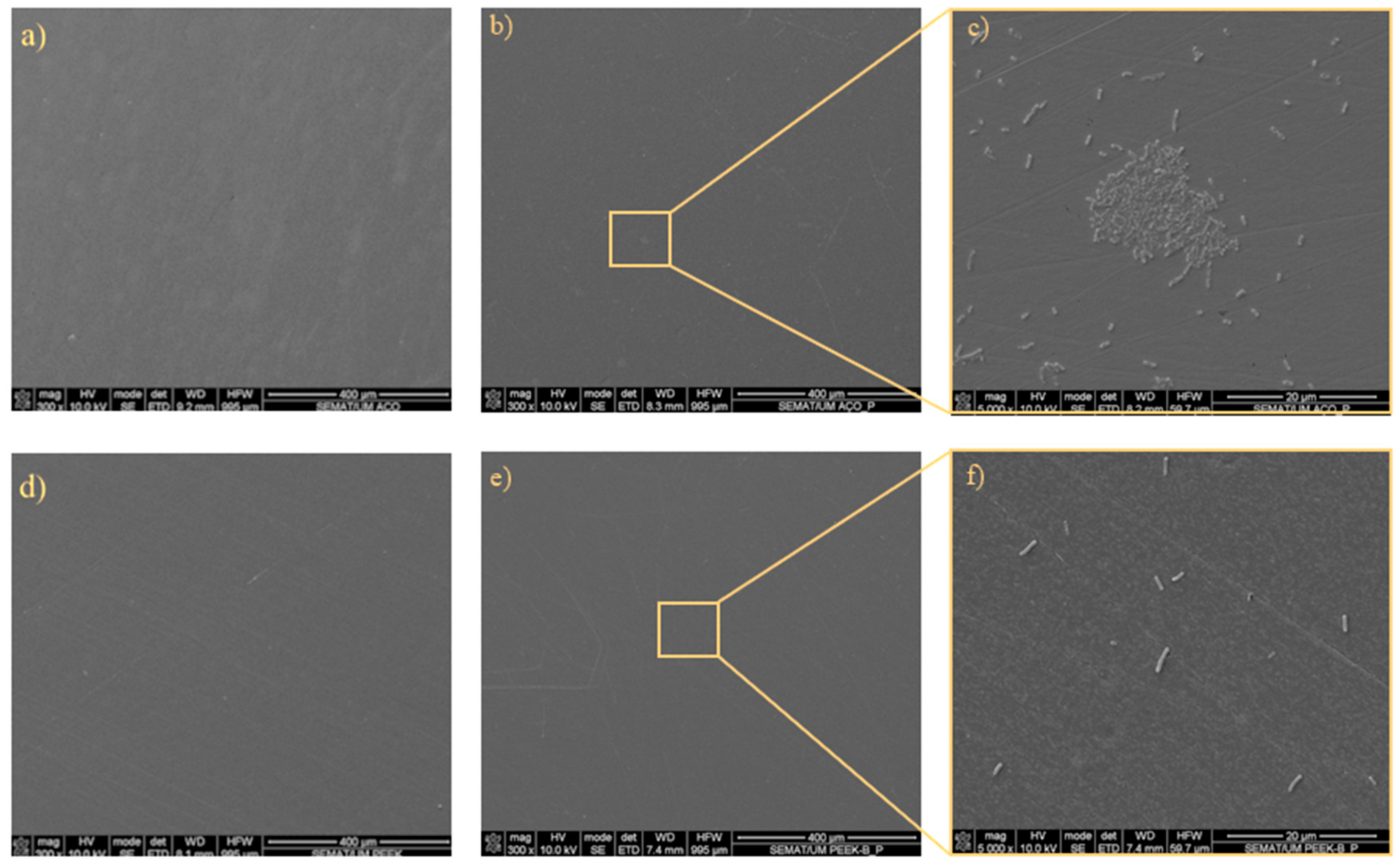
3.3. Bacterial Adhesion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding

Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marin, E. History of dental biomaterials: Biocompatibility, durability and still open challenges. Heritage Sci. 2023, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Imai, H.; Kawai, T.; Yoneyama, T. Application of titanium and titanium alloys to fixed dental prostheses. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.T.; Devi, S.P.; Krithika, C.; Raghavan, R.N. Review of metallic biomaterials in dental applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2020, 12 (Suppl. 1), S14–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.M.; Venkatesan, S. A review on application of biomaterials for medical and dental implants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2023, 237, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, N.; Yadav, S.; Ramachandran, M.; Belemkar, S. A review on surface treatment of stainless steel orthopedic implants. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2016, 36, 190–194. [Google Scholar]
- Wills, D.J.; Neville-Towle, J.; Podadera, J.; Johnson, K.A. Computed tomographic evaluation of the accuracy of minimally invasive sacroiliac screw fixation in cats. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2022, 35, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduok, U. Microbiologically induced intergranular corrosion of 316L stainless steel dental material in saliva. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaipattanawan, N.; Chompu-Inwai, P.; Nirunsittirat, A.; Phinyo, P.; Manmontri, C. Longevity of stainless steel crowns as interim restorations on young permanent first molars that have undergone vital pulp therapy treatment in children and factors associated with their treatment failure: A retrospective study of up to 8.5 years. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2022, 32, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Singh, A.; Jackson, M.J.; Coelho, R.T.; Prakash, D.; Charalambous, C.P.; Ahmed, W.; da Silva, L.R.R.; Lawrence, A.A. A comprehensive review on metallic implant biomaterials and their subtractive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1473–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, A.; Müller, W.-D. PEEK dental implants: A review of the literature. J. Oral Implant. 2013, 39, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arieira, A.; Madeira, S.; Rodrigues, F.; Silva, F. Tribological Behavior of TiO2 PEEK Composite and Stainless Steel for Pediatric Crowns. Materials 2023, 16, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Yao, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, C.; Oates, T.W.; Weir, M.D.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.H.K. Review on development and dental applications of polyetheretherketone-based biomaterials and restorations. Materials 2021, 14, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adali, U.; Sütel, M.; Yassine, J.; Mao, Z.; Müller, W.-D.; Schwitalla, A.D. Influence of sandblasting and bonding on the shear bond strength between differently pigmented polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and veneering composite after artificial aging. Dent. Mater. 2024, 40, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-F.; Lee, I.-T.; Wu, S.-H.; Chen, H.-M.; Mine, Y.; Peng, T.-Y.; Kok, S.-H. Effects of handheld nonthermal plasma on the biological responses, mineralization, and inflammatory reactions of polyaryletherketone implant materials. J. Dent. Sci. 2024, 19, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, M.; Lan, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, X. Overcoming biological inertness: Multifaceted strategies to optimize PEEK bioactivity for interdisciplinary clinical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2025, 13, 3106–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaguer-Flores, A.; Ximénez-Fyvie, L.A.; Rodil, S.E. Oral bacterial adhesion on amorphous carbon and titanium films: Effect of surface roughness and culture media. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 92, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsikogianni, M.; Missirlis, Y. Concise review of mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to biomaterials and of techniques used in estimating bacteria-material interactions. Eur. Cell Mater. 2004, 8, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W. Biofilm theory can guide the treatment of device-related orthopaedic infections. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2005, 437, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D. Periodontal microbial ecology. Periodontology 2000 2005, 38, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paster, B.J.; Boches, S.K.; Galvin, J.L.; Ericson, R.E.; Lau, C.N.; Levanos, V.A.; Sahasrabudhe, A.; Dewhirst, F.E. Bacterial diversity in human subgingival plaque. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3770–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, H.; Bigger, C.M.; Valentin, J.; Abt, D.; Qin, X.; Eberl, L.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Bacterial adhesion on soft materials: Passive physicochemical interactions or active bacterial mechanosensing? Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1801323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbourne, A.; Chapman, J.; Gelmi, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Crawford, R.J.; Truong, V.K. Bacterial-nanostructure interactions: The role of cell elasticity and adhesion forces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 546, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Allan, E.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Emergent heterogeneous microenvironments in biofilms: Substratum surface heterogeneity and bacterial adhesion force-sensing. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-J.; Chen, W.-C.; Srimaneepong, V.; Chen, C.-S.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Tung, O.-H.; Huang, H.-H. Fracture Characteristics of Commercial PEEK Dental Crowns: Combining the Effects of Aging Time and TiO2 Content. Polymers 2023, 15, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragaglia, M.; Cherubini, V.; Nanni, F. PEEK-TiO2 composites with enhanced UV resistance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 199, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.; Chu, M.; Jiang, J.; Yin, T.; Li, J.; Gao, S. Polyetheretherketone/Nano-Ag-TiO2 composite with mechanical properties and antibacterial activity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N.A.A.; Ridha, H.B.M. Investigation of tribological and mechanical properties of PEEK-TiO2 composites. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ICMAE), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–25 July 2017; pp. 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian, A.V.M.; Thanigachalam, M. Mechanical performances, in-vitro antibacterial study and bone stress prediction of ceramic particulates filled polyether ether ketone nanocomposites for medical applications. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacka, A.; Diez, M.S.; Rojo, D.; Bargiela, R.; Ciordia, S.; Zapico, I.; Albar, J.P.; Barbas, C.; dos Santos, V.A.P.M.; Fernández-García, M.; et al. Understanding the antimicrobial mechanism of TiO2-based nanocomposite films in a pathogenic bacterium. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, J.; Quinn, J.P.; Bradford, P.A.; Goering, R.V.; Nathan, C.; Bush, K.; Weinstein, R.A. Multiple antibiotic–resistant Klebsiella and Escherichia coli in nursing homes. JAMA 1999, 281, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokare, A.; Sanap, A.; Pai, M.; Sabharwal, S.; Athawale, A.A. Antibacterial activities of Nd doped and Ag coated TiO2 nanoparticles under solar light irradiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Díez-Vicente, A.L. Nano-TiO2 reinforced PEEK/PEI blends as biomaterials for load-bearing implant applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5561–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.A.; Rodríguez-Páez, J.E. Facile synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles of different crystalline phases and evaluation of their antibacterial effect under dark conditions against E. coli. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrada, M.L.; Serrano, C.; Sánchez-Chaves, M.; Fernández-García, M.; Fernández-Martín, F.; de Andres, A.; Rioboo, R.J.J.; Kubacka, A.; Ferrer, M.; Fernández-García, M. Self-sterilized EVOH-TiO2 nanocomposites: Interface effects on biocidal properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubacka, A.; Serrano, C.; Ferrer, M.; Lünsdorf, H.; Bielecki, P.; Cerrada, M.L.; Fernández-García, M.; Fernández-García, M. High-performance dual-action polymer−TiO2 nanocomposite films via melting processing. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.; Padrão, J.; da Silva, M.R.; Pinto, P.; Madeira, S.; Vaz, P.; Zille, A.; Silva, F. Bacteria co-culture adhesion on different texturized zirconia surfaces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 123, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.M.; Al-Badi, E.; Withycombe, C.; Jones, P.M.; Purdy, K.J.; Maddocks, S.E. Interaction between Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is beneficial for colonisation and pathogenicity in a mixed biofilm. Pathog. Dis. 2018, 76, fty003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhy, B.; Priyadarshini, P.; Sen, A.K. Effect of surface energy and roughness on cell adhesion and growth—Facile surface modification for enhanced cell culture. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15467–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarso; Tsuchiya, A.; Toita, R.; Tsuru, K.; Ishikawa, K. Enhanced osseointegration capability of poly(ether ether ketone) via combined phosphate and calcium surface-functionalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xiong, D.; Liu, Y. Improving surface wettability and lubrication of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) by combining with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 82, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, A.; Zaplotnik, R.; Primc, G.; Mozetič, M. Kinetics of surface wettability of aromatic polymers (PET, PS, PEEK, and PPS) upon treatment with neutral oxygen atoms from non-equilibrium oxygen plasma. Polymers 2024, 16, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea Mifsud, M.; Sachan, A.; Narayan, R.J.; Di-Silvio, L.; Coward, T. Fabrication and Characterization of a Porous TiO2-Modified PEEK Scaffold with Enhanced Flexural Compliance for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Paliwal, J.; Sharma, V.; Gupta, N.; Meena, K.K.; Singhal, P. Influence of PEEK surface modification with titanium for improving osseointegration: An in vitro study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 19801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lim, J.Y.; Donahue, H.J.; Dhurjati, R.; Mastro, A.M.; Vogler, E.A. Influence of substratum surface chemistry/energy and topography on the human fetal osteoblastic cell line hFOB 1.19: Phenotypic and genotypic responses observed in vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4535–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.-T.; Lin, D.-J.; Huang, S.; Lin, H.-T.; Chang, W.H. Osteogenic differentiation is synergistically influenced by osteoinductive treatment and direct cell–cell contact between murine osteoblasts and mesenchymal stem cells. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochford, E.; Poulsson, A.; Varela, J.S.; Lezuo, P.; Richards, R.; Moriarty, T. Bacterial adhesion to orthopaedic implant materials and a novel oxygen plasma modified PEEK surface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Hays, M.P.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Kim, J. Surface characteristics influencing bacterial adhesion to polymeric substrates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14254–14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzetti, M.; Dogša, I.; Stošicki, T.; Stopar, D.; Kalin, M.; Kobe, S.; Novak, S. The influence of surface modification on bacterial adhesion to titanium-based substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.; Boshkovikj, V.; Fluke, C.; Truong, V.; Hasan, J.; Baulin, V.; Lapovok, R.; Estrin, Y.; Crawford, R.; Ivanova, E. Bacterial attachment on sub-nanometrically smooth titanium substrata. Biofouling 2013, 29, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Yin, X.; Iglauer, S. A review on clay wettability: From experimental investigations to molecular dynamics simulations. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amshawee, S.; Yunus, M.Y.B.M.; Lynam, J.G.; Lee, W.H.; Dai, F.; Dakhil, I.H. Roughness and wettability of biofilm carriers: A systematic review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Guo, Z. Bioinspired surfaces with wettability: Biomolecule adhesion behaviors. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1502–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, C.F.; Christensen, A.-M.J.; Bojer, M.S.; Høiby, N.; Ingmer, H.; Jelsbak, L. Staphylococcus aureus alters growth activity, autolysis, and antibiotic tolerance in a human host-adapted Pseudomonas aeruginosa lineage. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 3903–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, D.B.Y.; Sircombe, K.J.; Pletzer, D. Friends or enemies? The complicated relationship between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Altenried, S.; Zogg, A.; Zuber, F.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Role of the surface nanoscale roughness of stainless steel on bacterial adhesion and microcolony formation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6456–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Specimen | Roughness, Ra (µm) |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel 316L | 0.028 ± 0.010 |
| PEEK reinforced with TiO2 | 0.083 ± 0.025 |
| Specimen | Contact Angle (θ) |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel 316L | 80.133 ± 9.860 |
| PEEK reinforced with TiO2 | 91.500 ± 8.611 |
| Condition | S. aureus on SS | S. aureus on PEEK | P. aeruginosa on SS | P. aeruginosa on PEEK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface % | 10.266 | 1.324 | 0.791 | 0.133 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, H.; Rodrigues, F.; Arieira, A.; Silva, F.; Pinto, J. A Comparative Study of Stainless Steel and PEEK TiO2 Composite: Effects on Cell Behavior and Bacterial Adhesion in Pediatric Crowns. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910809
Pereira H, Rodrigues F, Arieira A, Silva F, Pinto J. A Comparative Study of Stainless Steel and PEEK TiO2 Composite: Effects on Cell Behavior and Bacterial Adhesion in Pediatric Crowns. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910809
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Helena, Flávio Rodrigues, Ana Arieira, Filipe Silva, and João Pinto. 2025. "A Comparative Study of Stainless Steel and PEEK TiO2 Composite: Effects on Cell Behavior and Bacterial Adhesion in Pediatric Crowns" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910809
APA StylePereira, H., Rodrigues, F., Arieira, A., Silva, F., & Pinto, J. (2025). A Comparative Study of Stainless Steel and PEEK TiO2 Composite: Effects on Cell Behavior and Bacterial Adhesion in Pediatric Crowns. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10809. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910809







