EEG-Powered UAV Control via Attention Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods for Detecting Attention with BCI
2.1. EEG-Based Attention Assessment
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.3. Support Vector Machine
3. Experimental Validation of Attention Assessment Framework
3.1. System Architecture
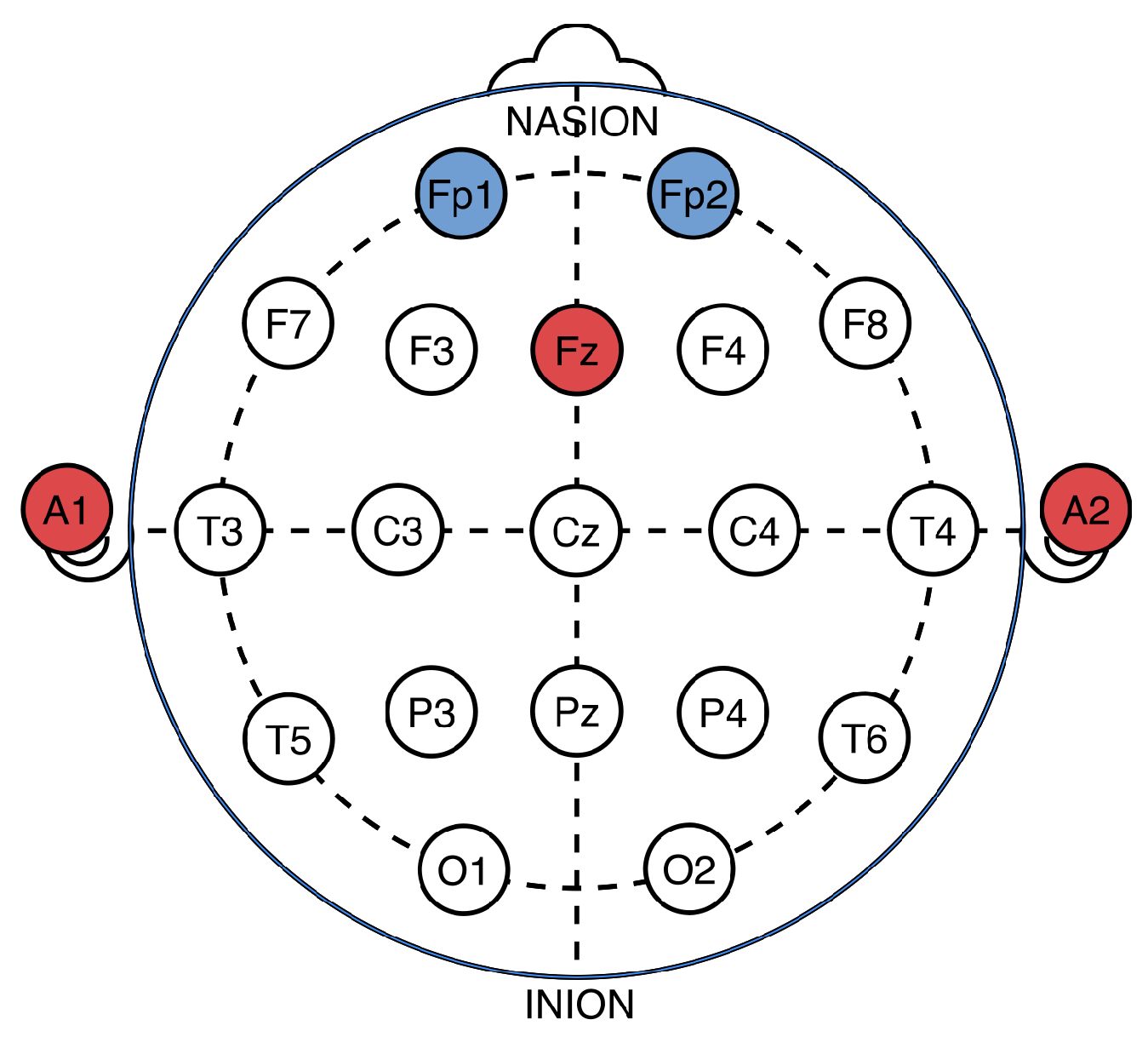
3.2. EEG Data Acquisition and Analysis
3.2.1. Focused Attention Collection Method
3.2.2. Relaxation Collection Method
3.3. Data Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
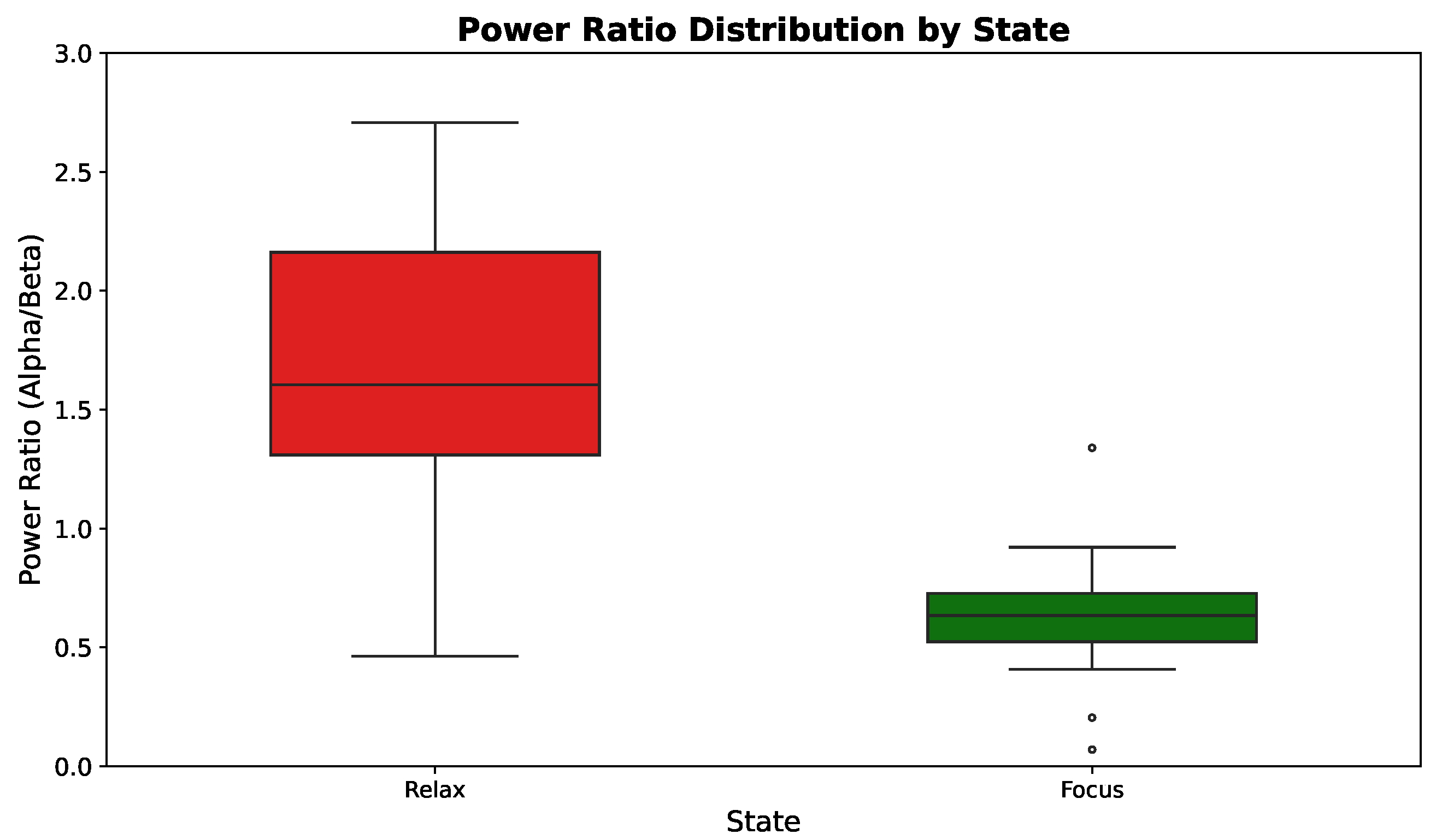
3.4. Experimental Results
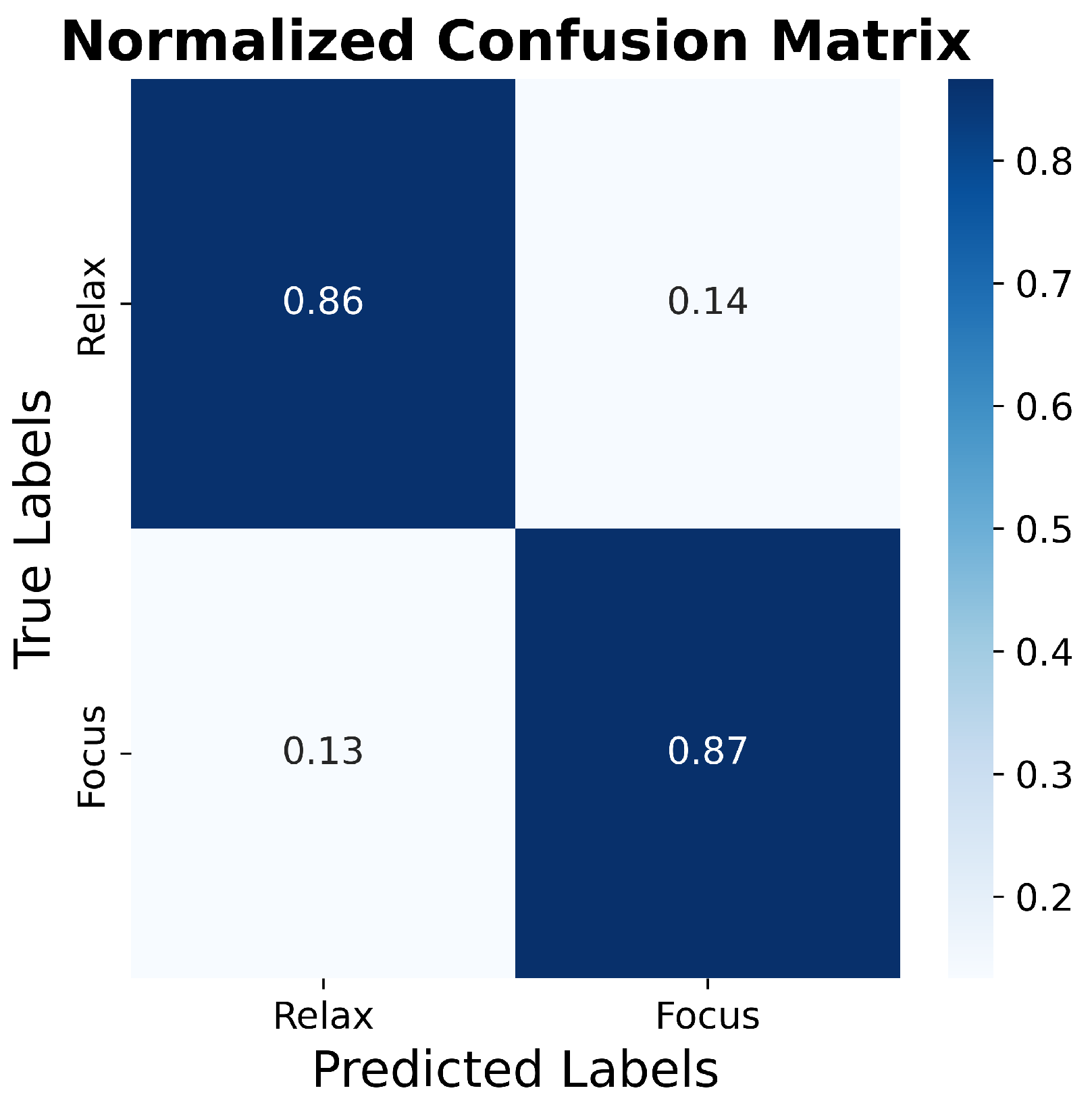
3.5. SVM Classification Analysis
3.6. Comparison with Additional Classifiers
3.7. System Interface and Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costello, E.J.; Egger, H.; Angold, A. 10-year research update review: The epidemiology of child and adolescent psychiatric disorders: I. Methods and public health burden. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2005, 44, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Cui, X.; Gao, Z.; Gu, Z. Frontal EEG-based multi-level attention states recognition using dynamical complexity and extreme gradient boosting. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 673955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.G.; Lee, T.S.; Guan, C.; Fung, D.S.S.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, S.S.W.; Zhang, H.; Krishnan, K.R.R. A brain-computer interface-based attention training program for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guze, S.B. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Ed. (DSM-IV). Am. J. Psychiatry 1995, 152, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, J.J.S.; Huss, M.; Asherson, P.; Akehurst, R.; Beusterien, K.; French, A.; Sasané, R.; Hodgkins, P. Distinguishing comorbidity and successful management of adult ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2012, 16 (Suppl. 5), 3S–19S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattfeld, A.T.; Gabrieli, J.D.; Biederman, J.; Spencer, T.; Brown, A.; Kotte, A.; Kagan, E.; Whitfield-Gabrieli, S. Brain differences between persistent and remitted attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Brain 2014, 137, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.R.; Popovic, D.P.; Olmstead, R.E.; Stikic, M.; Levendowski, D.J.; Berka, C. Drowsiness/alertness algorithm development and validation using synchronized EEG and cognitive performance to individualize a generalized model. Biol. Psychol. 2011, 87, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, C. A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 1998, 2, 121–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinterberger, T.; Nijboer, F.; Kübler, A.; Matuz, T.; Furdea, A.; Mochty, U.; Jordan, M.; Lal, T.N.; Hill, N.J.; Mellinger, J.; et al. Brain-Computer Interfaces for Communication in Paralysis: A Clinical Experimental Approach; Unpublished; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wijdicks, E.F. Brain death worldwide: Accepted fact but no global consensus in diagnostic criteria. Neurology 2002, 58, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szurhaj, W.; Lamblin, M.D.; Kaminska, A.; Sediri, H. EEG guidelines in the diagnosis of brain death. Neurophysiol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 45, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.S.; Goh, S.J.A.; Quek, S.Y.; Phillips, R.; Guan, C.; Cheung, Y.B.; Feng, L.; Teng, S.S.W.; Wang, C.C.; Chin, Z.Y.; et al. A brain-computer interface-based cognitive training system for healthy elderly: A randomized control pilot study for usability and preliminary efficacy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acı, Ç.İ.; Kaya, M.; Mishchenko, Y. Distinguishing mental attention states of humans via an EEG-based passive BCI using machine learning methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 134, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.H.; Chiang, C.Y.; Chu, H.C. Recognizing the degree of human attention using EEG signals from mobile sensors. Sensors 2013, 13, 10273–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.D. Classification of relaxation and concentration mental states with EEG. Information 2021, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothe, C.; Shirazi, S.Y.; Stenner, T.; Medine, D.; Boulay, C.; Grivich, M.I.; Makeig, S. The lab streaming layer for synchronized multimodal recording. Imaging Neurosci. 2025, 3, IMAG.a.136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, S.; Hölle, D.; Bleichner, M.G.; Debener, S. Pocketable labs for everyone: Synchronized multi-sensor data streaming and recording on smartphones with the lab streaming layer. Sensors 2021, 21, 8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornhege, G.; Blankertz, B.; Krauledat, M.; Losch, F.; Curio, G.; Müller, K.R. Combined optimization of spatial and temporal filters for improving brain-computer interfacing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, D.J.; Wolpaw, J.R. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Commun. ACM 2011, 54, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C.; Birbaumer, N. Human brain-computer interface. In Motor Cortex in Voluntary Movements; Sporns, O., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 367–402. [Google Scholar]
- McFarland, D.J.; Krusienski, D.J. Brain-Computer Interfaces: Principles and Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fatourechi, M.; Bashashati, A.; Ward, R.K.; Birch, G.E. EMG and EOG artifacts in brain computer interface systems: A survey. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, J. Comparison of an open-hardware electroencephalography amplifier with medical grade device in brain-computer interface applications. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02438. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Bian, G.B.; Tian, Z. Removal of artifacts from EEG signals: A review. Sensors 2019, 19, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvinage, M.; Castermans, T.; Petieau, M.; Hoellinger, T.; Cheron, G.; Dutoit, T. Performance of the Emotiv Epoc headset for P300-based applications. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahani, H.; Safaei, A.A. Efficient deep learning approach for diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children based on EEG signals. Cogn. Comput. 2024, 16, 2315–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.S.; Hsiao, K.L.; Liu, L.C. EEG-based detection model for evaluating and improving learning attention. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2018, 38, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezaei, M.; Sardouie, S.H. Detection of human attention using EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 24th National and 2nd International Iranian Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME), Tehran, Iran, 30 November–1 December 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguerza, J.M.; Muñoz, A. Support vector machines with applications. Stat. Sci. 2006, 21, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearst, M.A.; Dumais, S.T.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, H.; Burges, C.J.; Kaufman, L.; Smola, A.; Vapnik, V. Support vector regression machines. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Huang, H.; Bao, X.; Pan, J.; Li, Y. An EEG-based attention recognition method: Fusion of time domain, frequency domain, and non-linear dynamics features. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1194554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, R.; Zhou, T.; Xu, T.; Hu, H. A subject-specific attention index based on the weighted spectral power. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Shi, C.; Yan, L. Driving attention state detection based on GRU-EEGNet. Sensors 2024, 24, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramoser, H.; Müller-Gerking, J.; Pfurtscheller, G. Optimal spatial filtering of single-trial EEG during imagined hand movement. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotte, F.; Guan, C. Regularizing common spatial patterns to improve BCI designs: Unified theory and new algorithms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirrmeister, R.T.; Springenberg, J.T.; Fiederer, L.D.J.; Glasstetter, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Tangermann, M.; Hutter, F.; Burgard, W.; Ball, T. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 5391–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Safont, G.; Vergara, L.; Vidal, E. Graph regularization methods in soft detector fusion. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 138507–138520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, K.K.; Chin, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, C. Filter bank common spatial pattern (FBCSP) algorithm on BCI Competition IV datasets 2a and 2b. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barachant, A.; Bonnet, S.; Congedo, M.; Jutten, C. Classification of covariance matrices using a Riemannian-based kernel for BCI applications. Neurocomputing 2012, 90, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







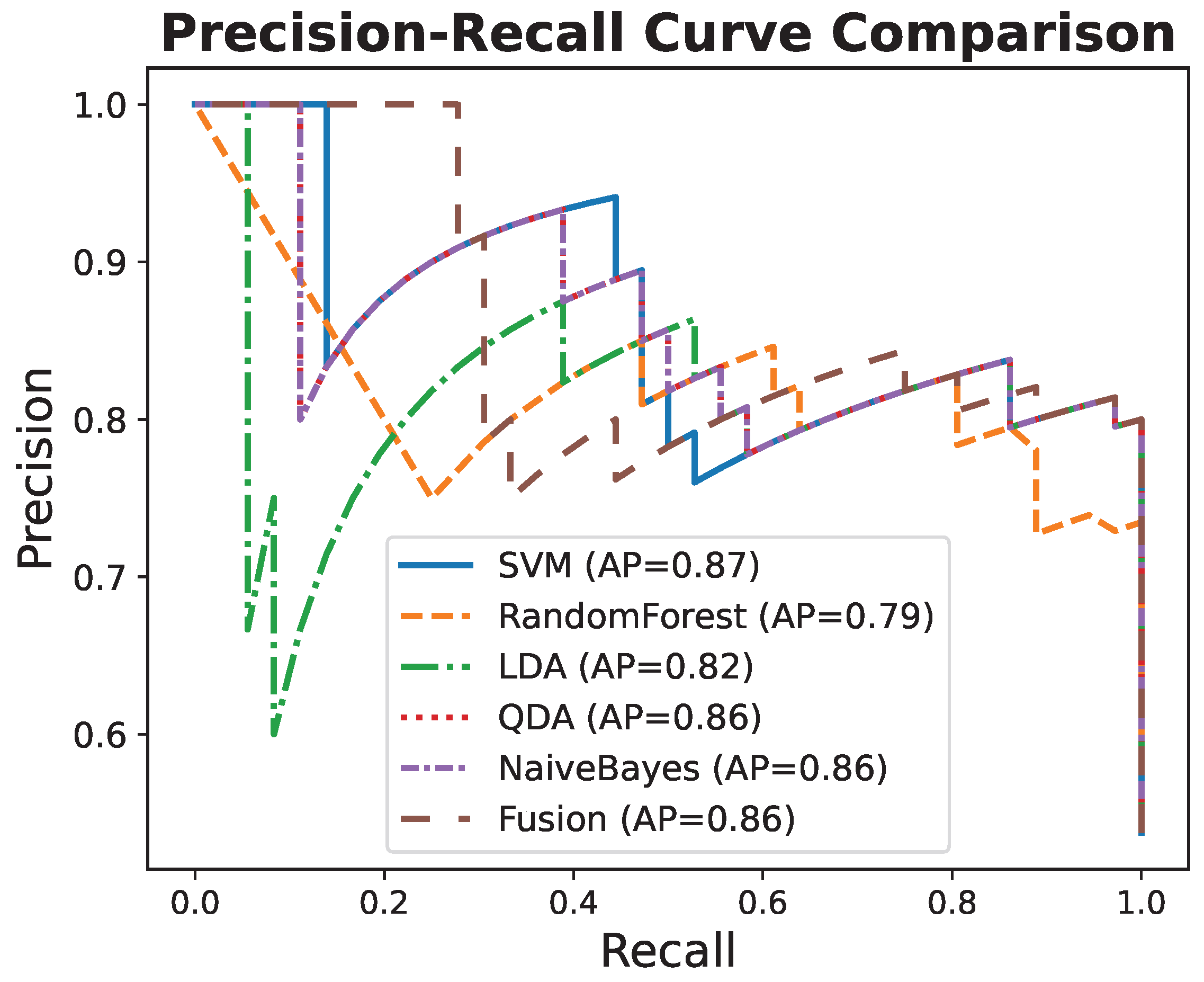
| Classifier | ACC | AUC | AP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fusion | 0.881 | 0.918 | 0.899 |
| SVM | 0.881 | 0.895 | 0.853 |
| LDA | 0.866 | 0.894 | 0.870 |
| Naive Bayes | 0.851 | 0.894 | 0.850 |
| Random Forest | 0.806 | 0.891 | 0.867 |
| QDA | 0.821 | 0.887 | 0.819 |
| Comparison | ACC | AUC | AP |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVM vs. RF | 0.044 */0.047 * | ns | ns |
| SVM vs. LDA | ns | ns | ns |
| SVM vs. QDA | **/0.0049 ** | 0.025 */0.0166 * | 0.011 */0.0166 * |
| SVM vs. Naive Bayes | **/0.0049 ** | ns | 0.025 */0.0093 * |
| Fusion vs. SVM | 0.011 */0.0256 * | ns | ns |
| Subject ID | Accuracy (%) | Response Time (s) | Control Success Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 87.2 | 1.25 | 94.8 |
| S2 | 84.5 | 1.42 | 90.3 |
| S3 | 86.1 | 1.30 | 92.7 |
| S4 | 83.6 | 1.47 | 88.9 |
| Mean | 85.4 | 1.36 | 91.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, J.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; Maeda, T.; Cao, J. EEG-Powered UAV Control via Attention Mechanisms. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910714
Gong J, Liu H, Zhao L, Maeda T, Cao J. EEG-Powered UAV Control via Attention Mechanisms. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910714
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Jingming, He Liu, Liangyu Zhao, Taiyo Maeda, and Jianting Cao. 2025. "EEG-Powered UAV Control via Attention Mechanisms" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910714
APA StyleGong, J., Liu, H., Zhao, L., Maeda, T., & Cao, J. (2025). EEG-Powered UAV Control via Attention Mechanisms. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10714. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910714







