Synclastic Behavior of the Auxetic Core for Furniture Panels
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Cell Properties
2.2. Poisson’s Ratios
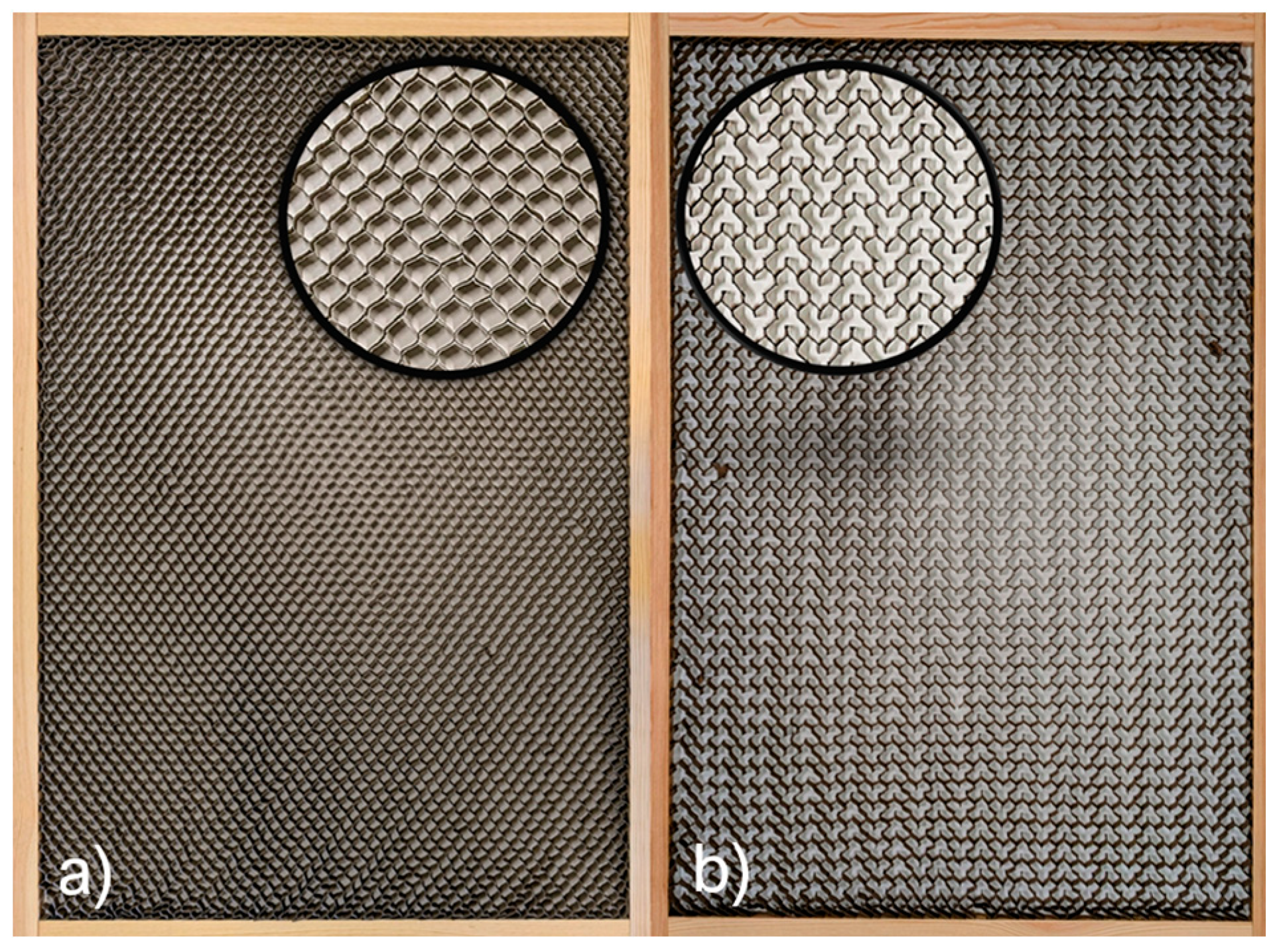
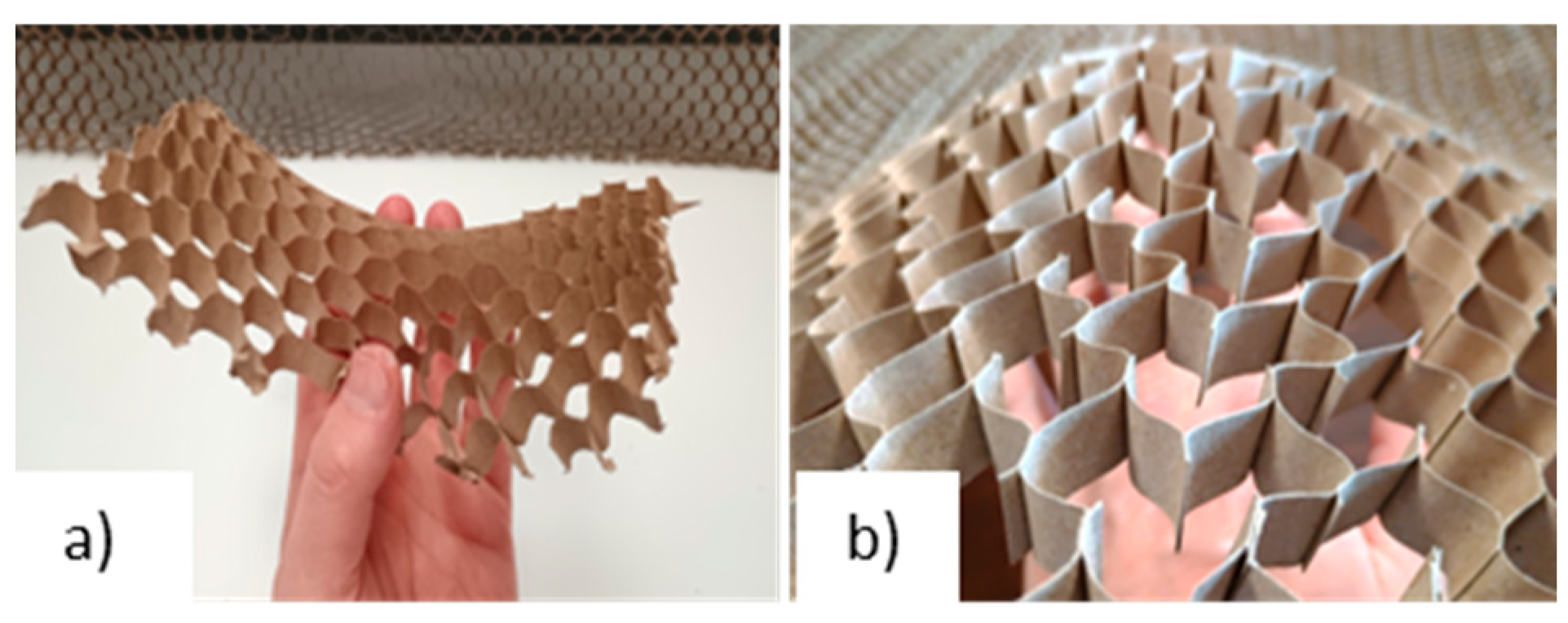
2.3. Core Samples
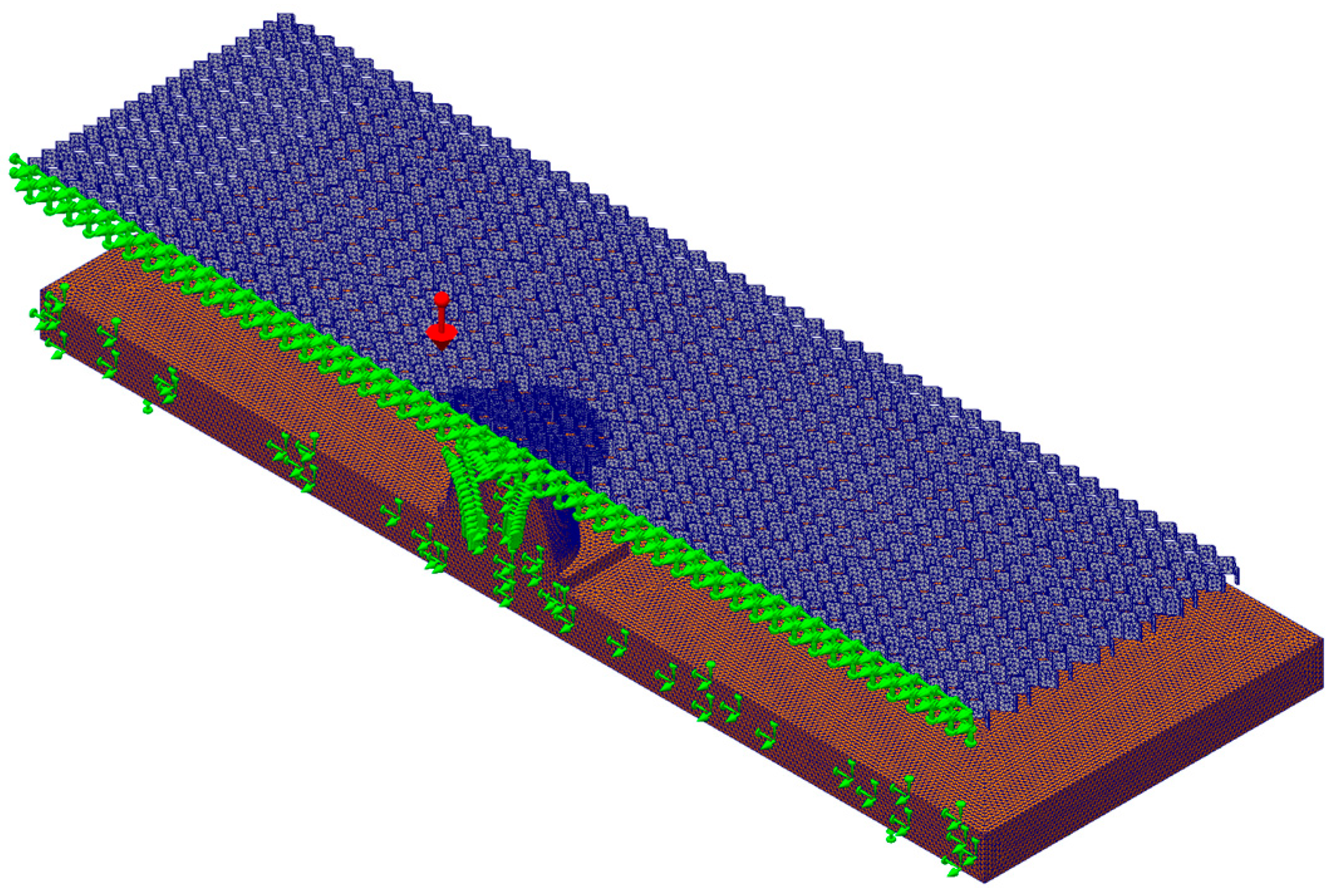
2.4. Numerical Calculations
2.4.1. Compression Tests
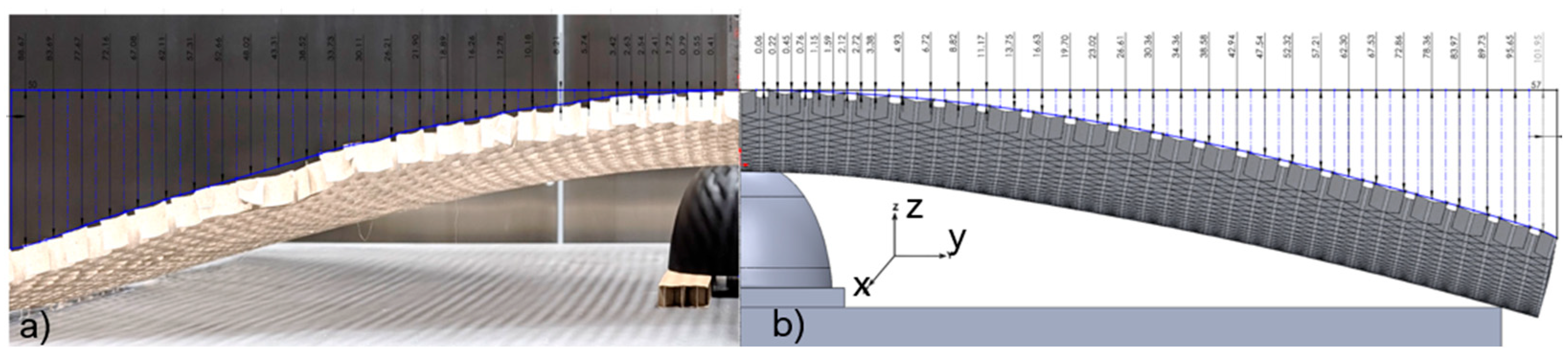
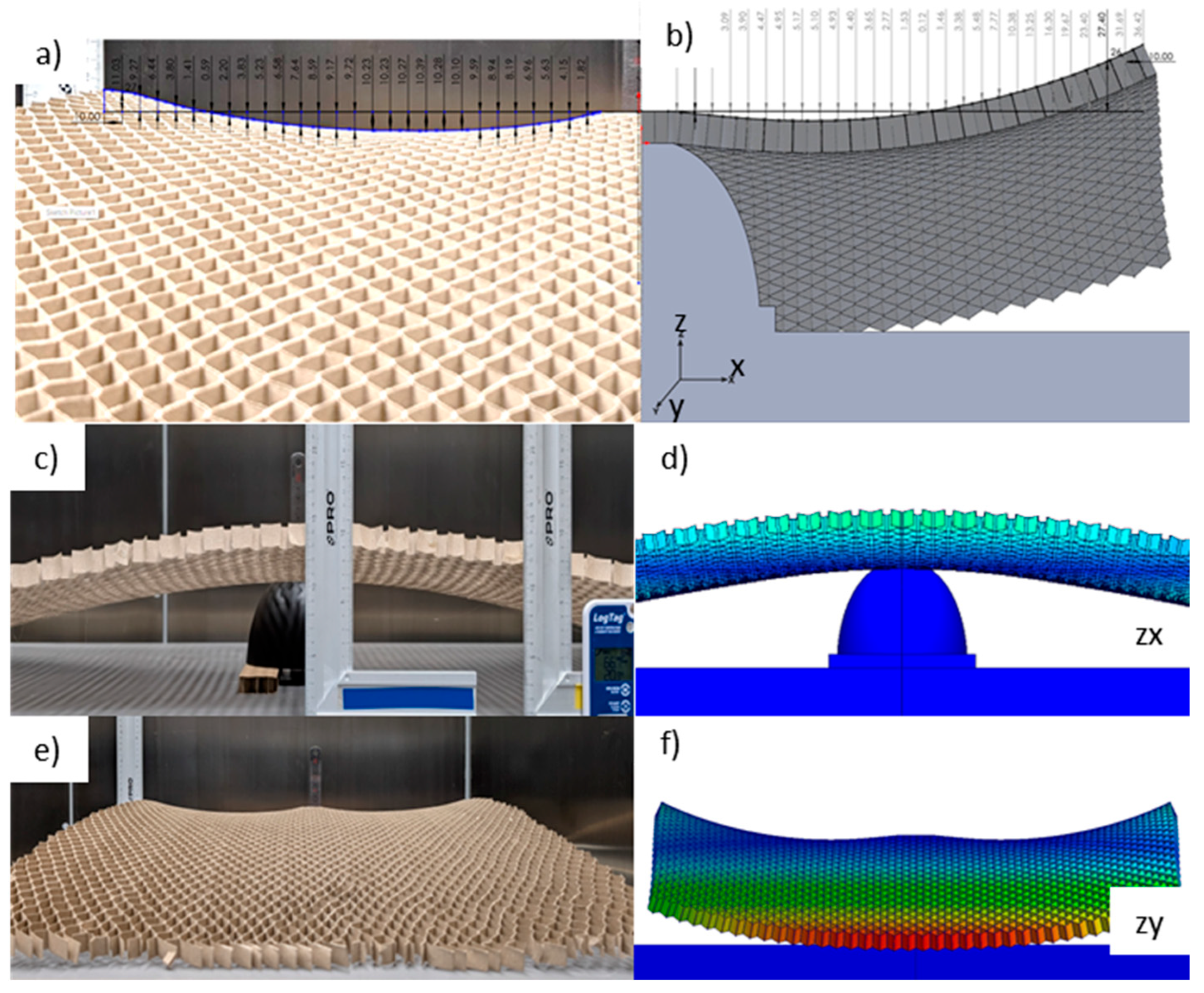
2.4.2. Bending Test
- RMSE (Root Mean Square Error)—a measure of the mean absolute error expressed in mm:
- MAX error—indicating the largest observed difference between the displacement values of the FE model and the actual measurement:
- AUC (area between curves)—defining the total geometric discrepancy between deformation curves (approximate numerical integration):
- DTW (Dynamic Time Warping)—a method of comparing curves while allowing for local X-axis shifts. The minimum sum of path-fit deviations (ω) between two sequences (X = x1, …, xn) and (Y = y1, …, ym):
3. Results
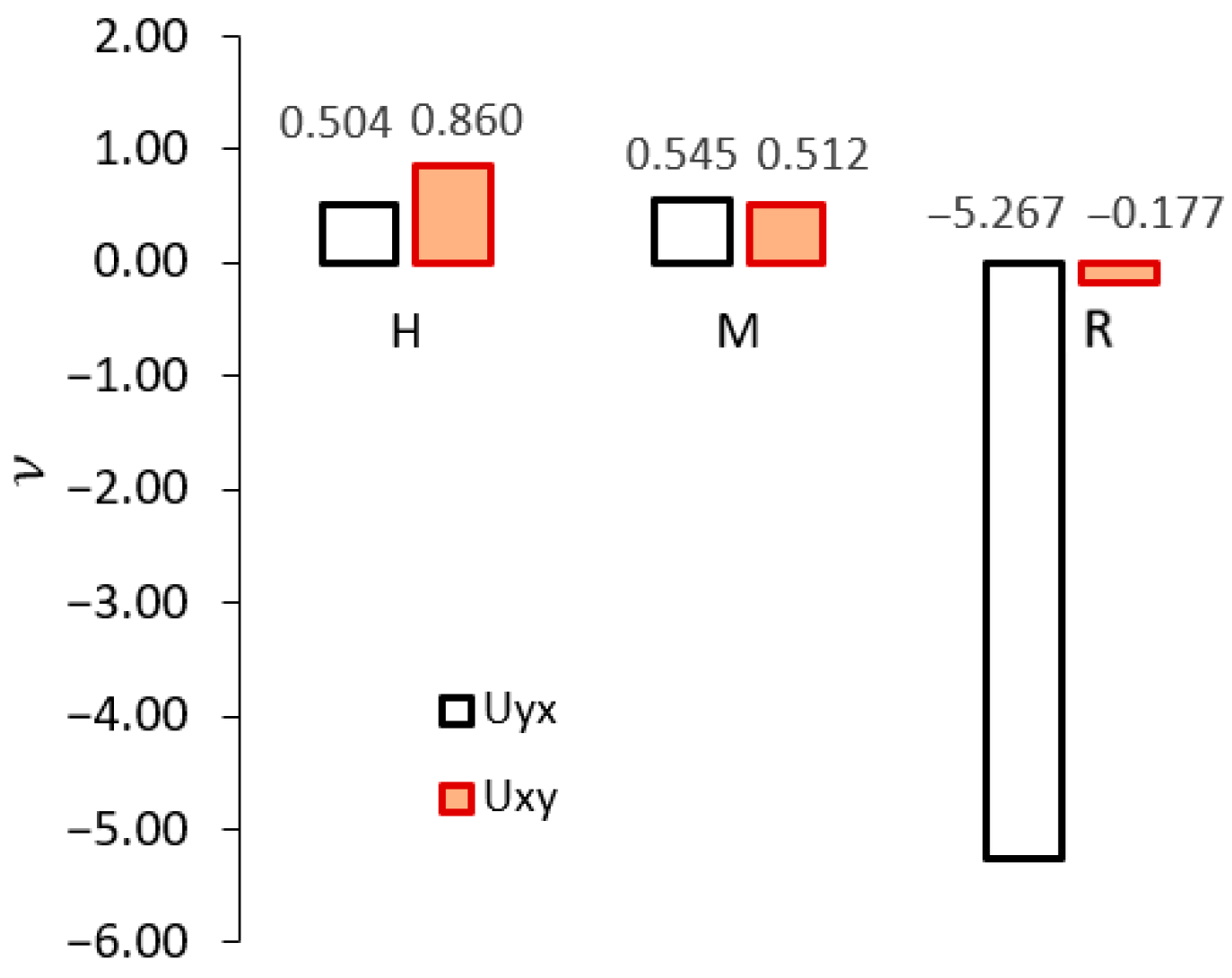
3.1. Poisson’s Ratios
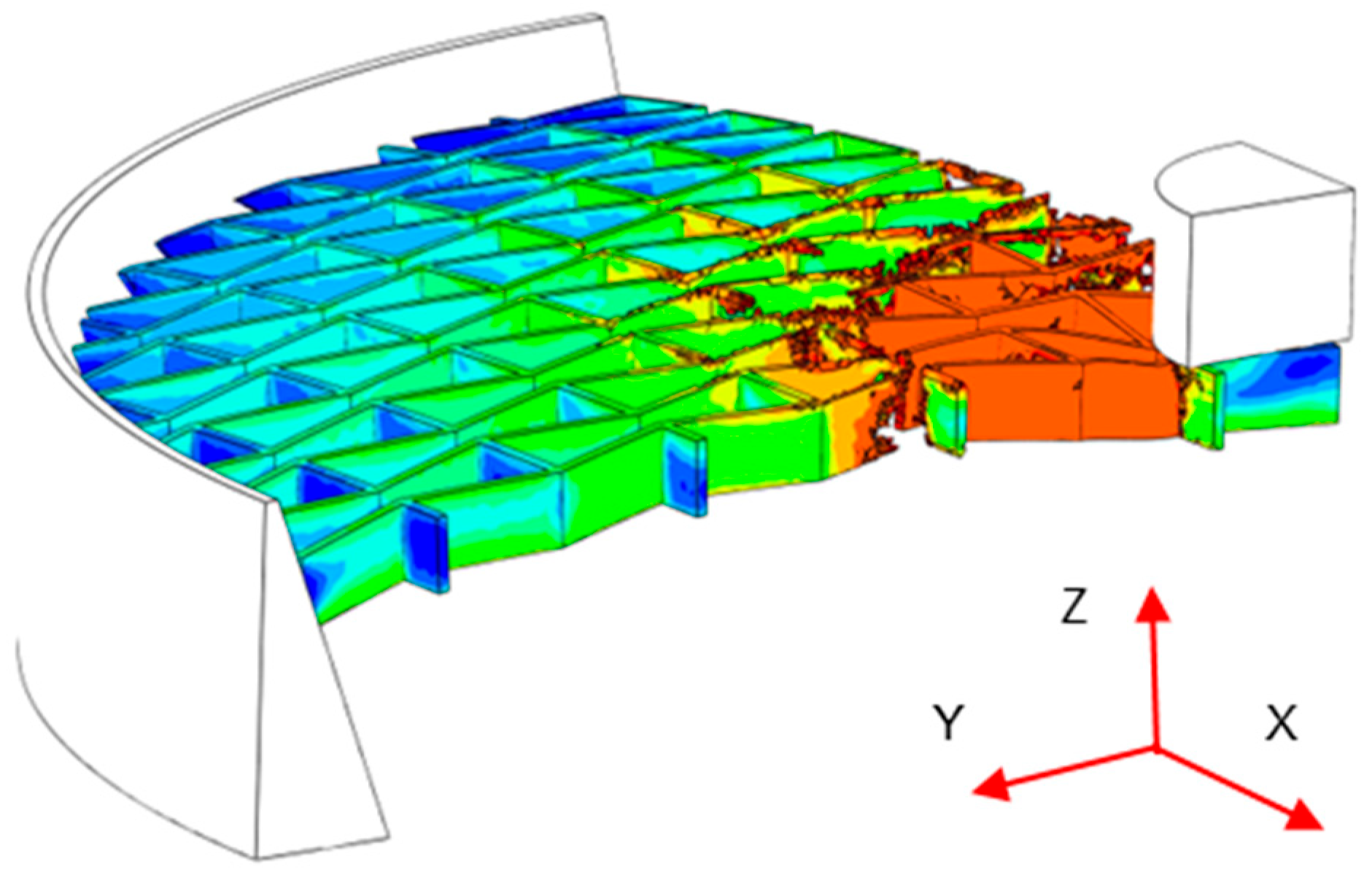
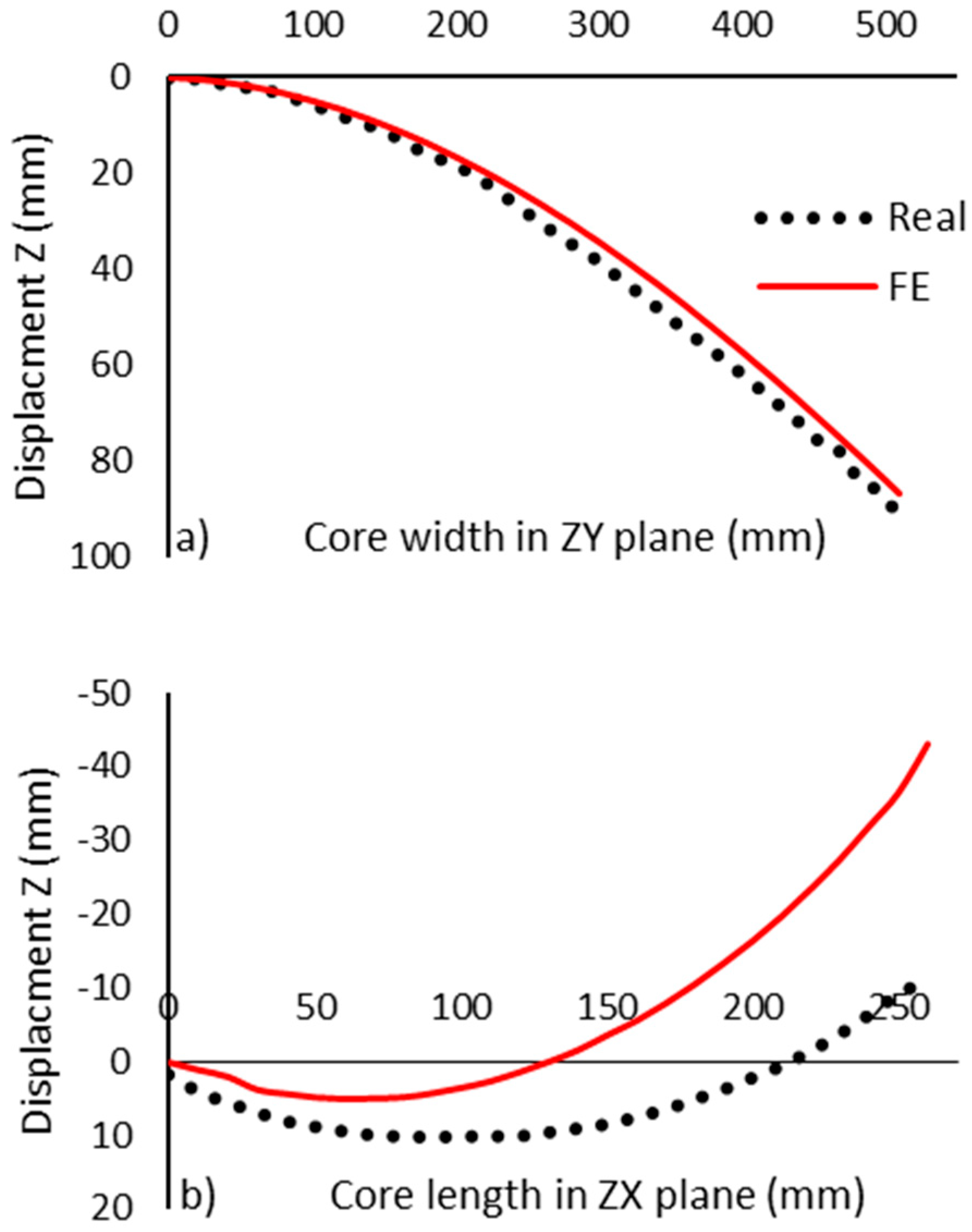
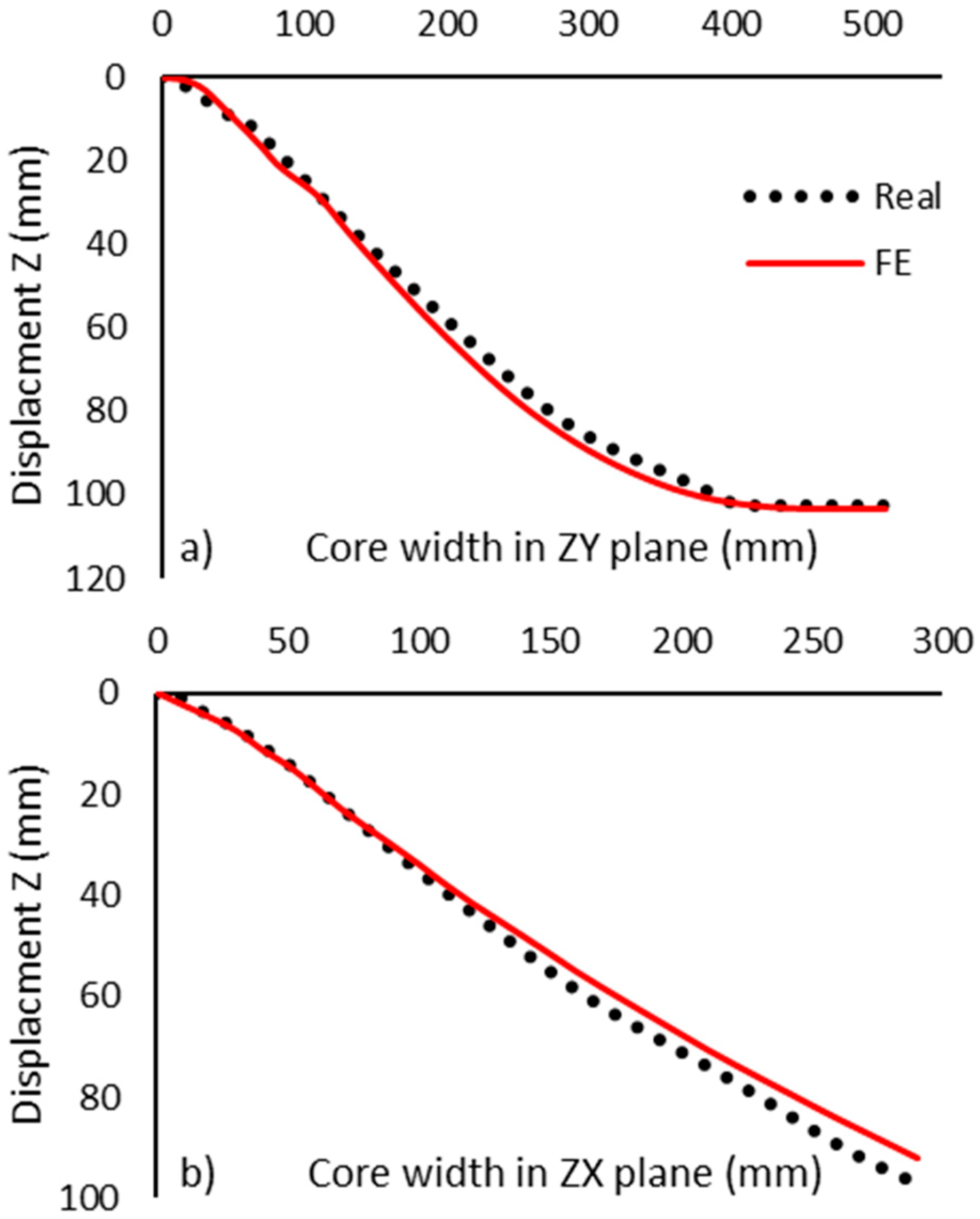
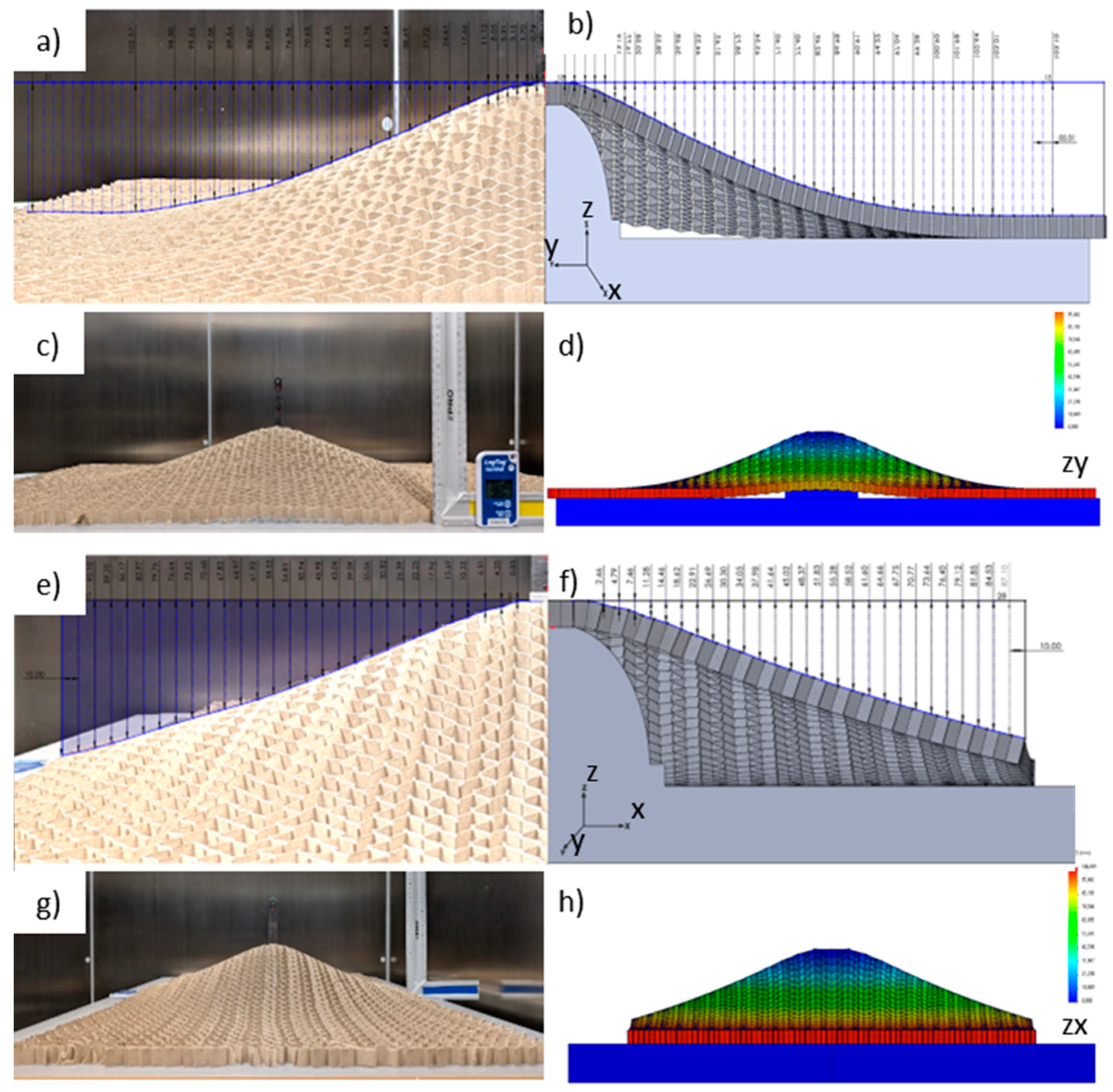
3.2. Synclastic Behaviors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The classic hexagonal core (H) confirmed the typical anticlastic behavior described in the literature—positive curvature in one direction is associated with negative curvature in the other.
- The modified core (M), despite positive Poisson’s ratio values in both orthotropy directions, clearly showed synclastic surface deformation.
- The most important factor determining the type of deformation turned out to be not the Poisson’s ratio µ itself, but the local cell topology.
- The results confirm the possibility of designing panels with synclastic properties without the need to introduce auxeticity, which opens up new perspectives for engineering applications.
- Further research will focus on modeling parametric multi-material systems and multi-scale structures composed of M-type cells. Modeling should include variable loads under variable climatic conditions, taking into account reinforcement systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heimbs, S.; Pein, M. Failure Behaviour of Honeycomb Sandwich Corner Joints and Inserts. Compos. Struct. 2009, 89, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Li, W.; Wei, K.; Duan, S.; Wen, W.; Chen, L.; Pei, Y.; Fang, D. Mechanical Properties and Energy Absorption of 3D Printed Square Hierarchical Honeycombs under In-Plane Axial Compression. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 176, 107219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanie, B.; Bouvet, C.; Ginot, M. Review of Composite Sandwich Structure in Aeronautic Applications. Compos. Part C Open Access 2020, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkati, A.; Boutagouga, D.; Harkati, E.; Bezazi, A.; Scarpa, F.; Ouisse, M. In-Plane Elastic Constants of a New Curved Cell Walls Honeycomb Concept. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 149, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.D.; Seung-Eock, K.; Tuan, N.D.; Tran, P.; Khoa, N.D. New Approach to Study Nonlinear Dynamic Response and Vibration of Sandwich Composite Cylindrical Panels with Auxetic Honeycomb Core Layer. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardzewski, J.; Kramski, D. Modelling Stiffness of Furniture Manufactured from Honeycomb Panels Depending on Changing Climate Conditions. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 137, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliński, K.; Smardzewski, J.; Narojczyk, J. Stiffness of Synclastic Wood-Based Auxetic Sandwich Panels. Phys. Status Solidi B 2020, 257, 1900749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardzewski, J.; Tokarczyk, M. Lightweight Honeycomb Furniture Panels with Discreetly Located Strengthening Blocks. Compos. Struct. 2024, 331, 117927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrówczyński, D.; Gajewski, T.; Cornaggia, A.; Garbowski, T. Impact of Temperature and Humidity on Key Mechanical Properties of Corrugated Board. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.; Khaire, N.; Tiwari, G. A Comparative Study on the Ballistic Performance of Aramid and Aluminum Honeycomb Sandwich Structures. Compos. Struct. 2022, 299, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, Q.; Sun, B. Study on the Bending Behaviors of a Novel Flexible Re-Entrant Honeycomb. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2023, 145, 041006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.E.; Alderson, A. Auxetic Materials: Functional Materials and Structures from Lateral Thinking! Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorato, A.; Innocenti, P.; Scarpa, F.; Alderson, A.; Alderson, K.L.; Zied, K.M.; Ravirala, N.; Miller, W.; Smith, C.W.; Evans, K.E. The Transverse Elastic Properties of Chiral Honeycombs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easey, N.; Chuprynyuk, D.; Musa, W.M.S.W.; Bangs, A.; Dobah, Y.; Shterenlikht, A.; Scarpa, F. Dome-Shape Auxetic Cellular Metamaterials: Manufacturing, Modeling, and Testing. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Scarpa, F.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Bending and Benchmark of Zero Poisson’s Ratio Cellular Structures. Compos. Struct. 2016, 152, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Tai, Y.H.; Lira, C.; Scarpa, F.; Yates, J.R.; Gu, B. The Bending and Failure of Sandwich Structures with Auxetic Gradient Cellular Cores. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 49, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Bao, W.; Bai, C.; Yan, Q.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Fan, H. Manufacturing and Mechanical Testing of Curved Sandwich Beams with Zero-Poisson’s Ratio Honeycomb Cores. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 8849–8856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jin, F.; Fan, H. Zero-Poisson’s-Ratio Honeycomb-Filled Braided Textile Reinforced Conical Tubes: Designing, Manufacturing and Testing. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2023, 30, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliński, K.; Smardzewski, J. Static Response of Synclastic Sandwich Panel with Auxetic Wood-Based Honeycomb Cores Subject to Compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 179, 109559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słonina, M.; Dziurka, D.; Molińska-Glura, M.; Smardzewski, J. Influence of Impregnation with Modified Starch of a Paper Core on Bending of Wood-Based Honeycomb Panels in Changing Climatic Conditions. Materials 2022, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słonina, M.; Smardzewski, J. Starch Impregnation Effect of Testliner Paper on Stiffness of Honeycomb Panels with Slender Cells. Drv. Ind. 2022, 73, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Ma, K.; Li, P.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, B.; Xiao, Y. Experimental and Numerical Studies on a Glubam Spherical Dome. Eng. Struct. 2024, 303, 117462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.C.; Ni, X.H.; Zhang, X.G.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.H.; Hao, J.; Xie, Y.M.; Ren, X. Design and Mechanical Performance of Stretchable Sandwich Metamaterials with Auxetic Panel and Lattice Core. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 192, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, H. Flexible Forming Mechanism of Curved Sandwich Shell with Flexible Honeycombs and Twill Carbon Fiber Fabrics. Compos. Struct. 2025, 354, 118779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliński, K.; Smardzewski, J. Experimental Testing of Elastic Properties of Paper and WoodEpox® in Honeycomb Panels. BioResources 2019, 14, 2977–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.E.; Nkansah, M.A.; Hutchinson, I.J.; Rogers, S.C. Molecular Network Design. Nature 1991, 353, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smardzewski, J. Transformation of Hexagonal Cells into Auxetic in Core Honeycomb Furniture Panels. In Proceedings of the ICWSE 2025: XIX. International Conference on Wood Science and Engineering, Nicosia, Cyprus, 21 August 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
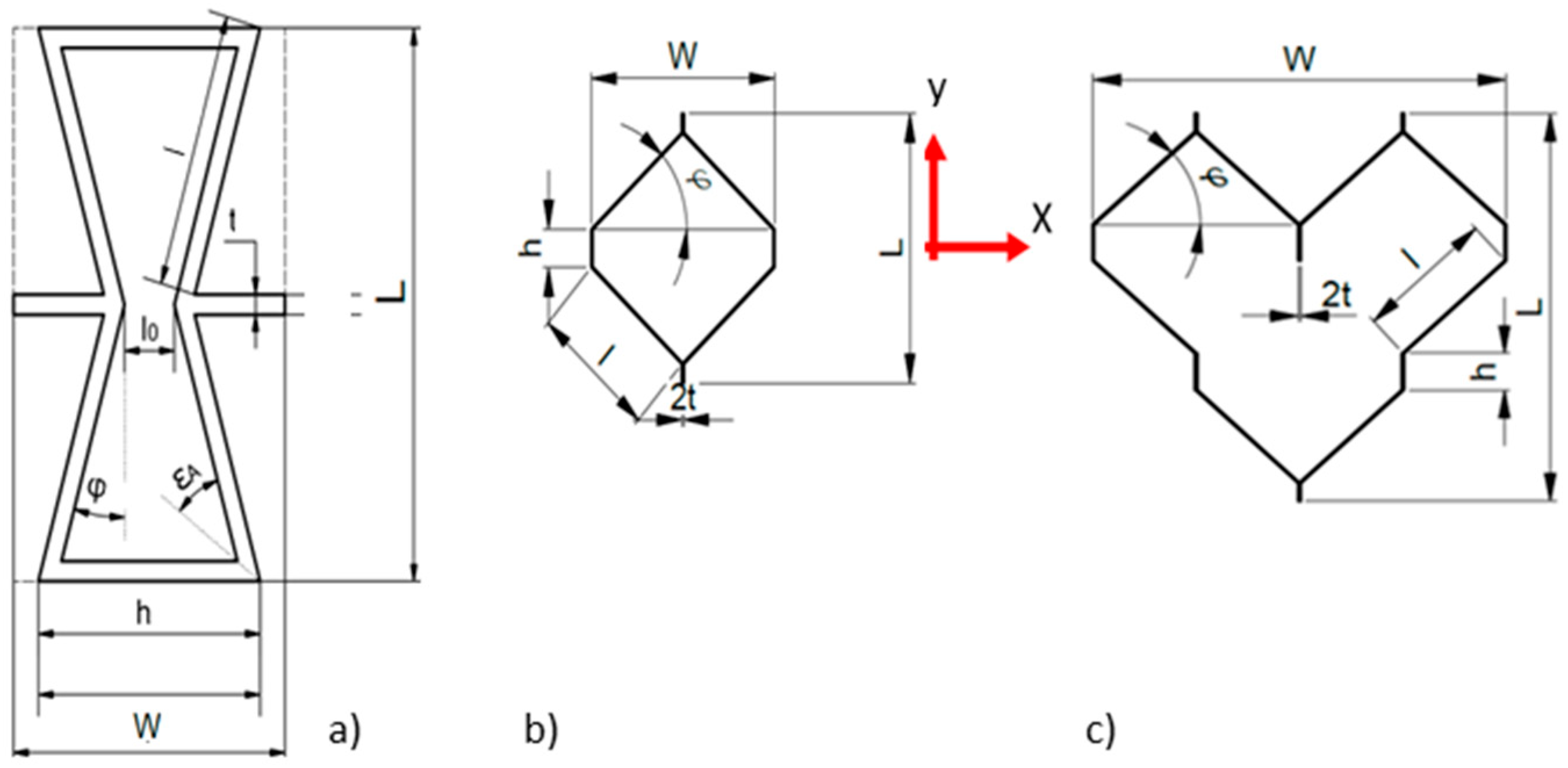
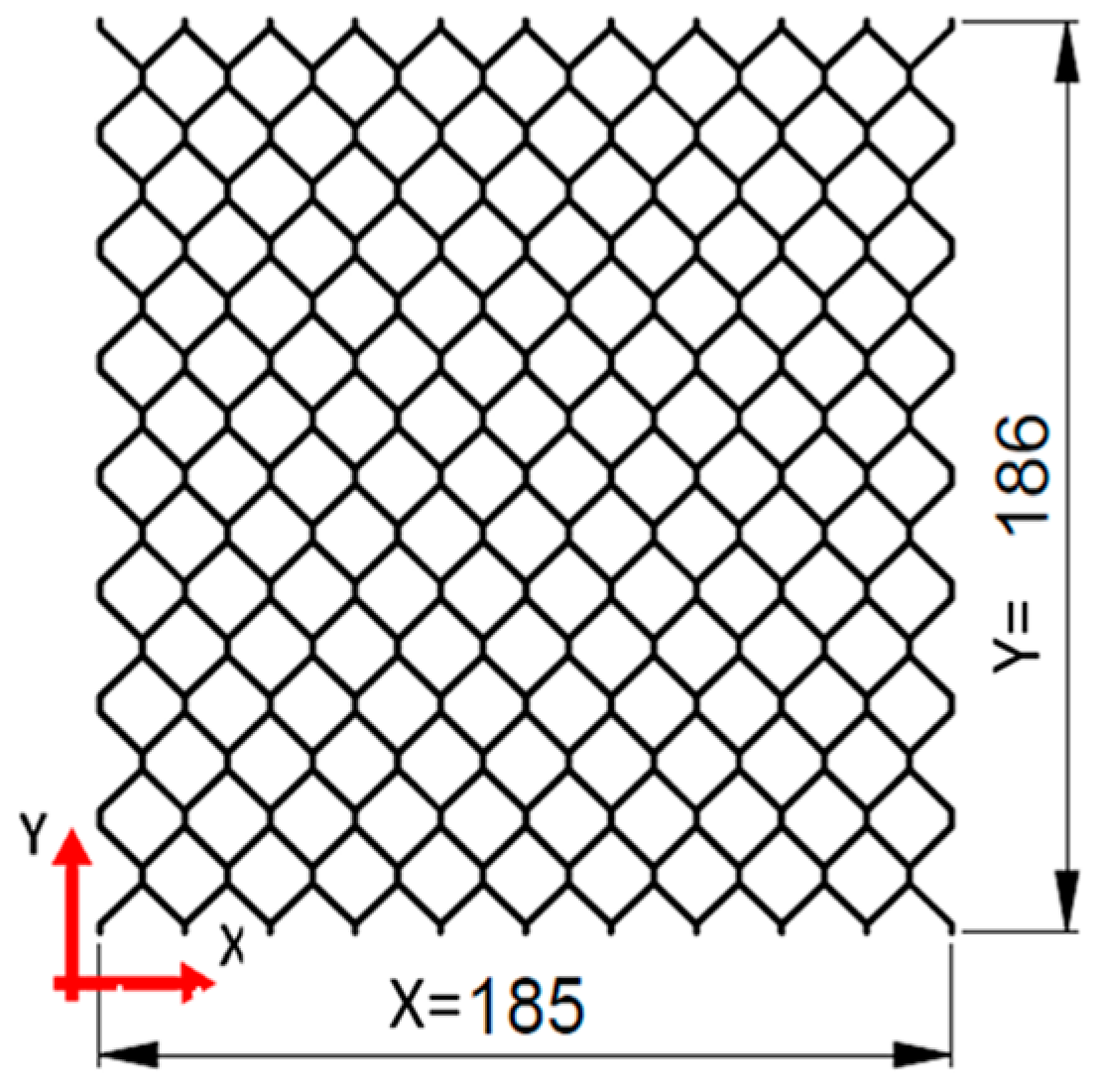
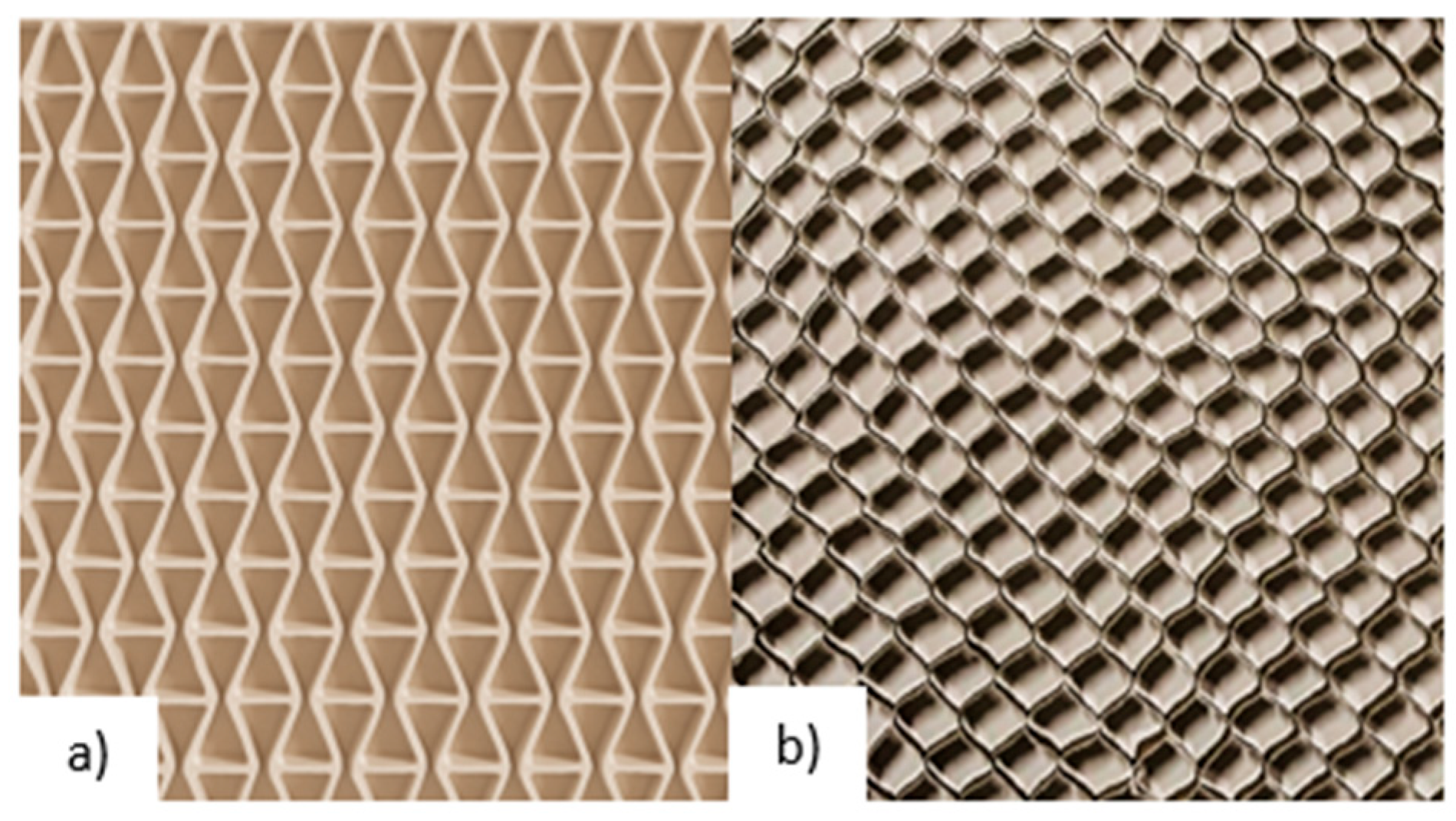
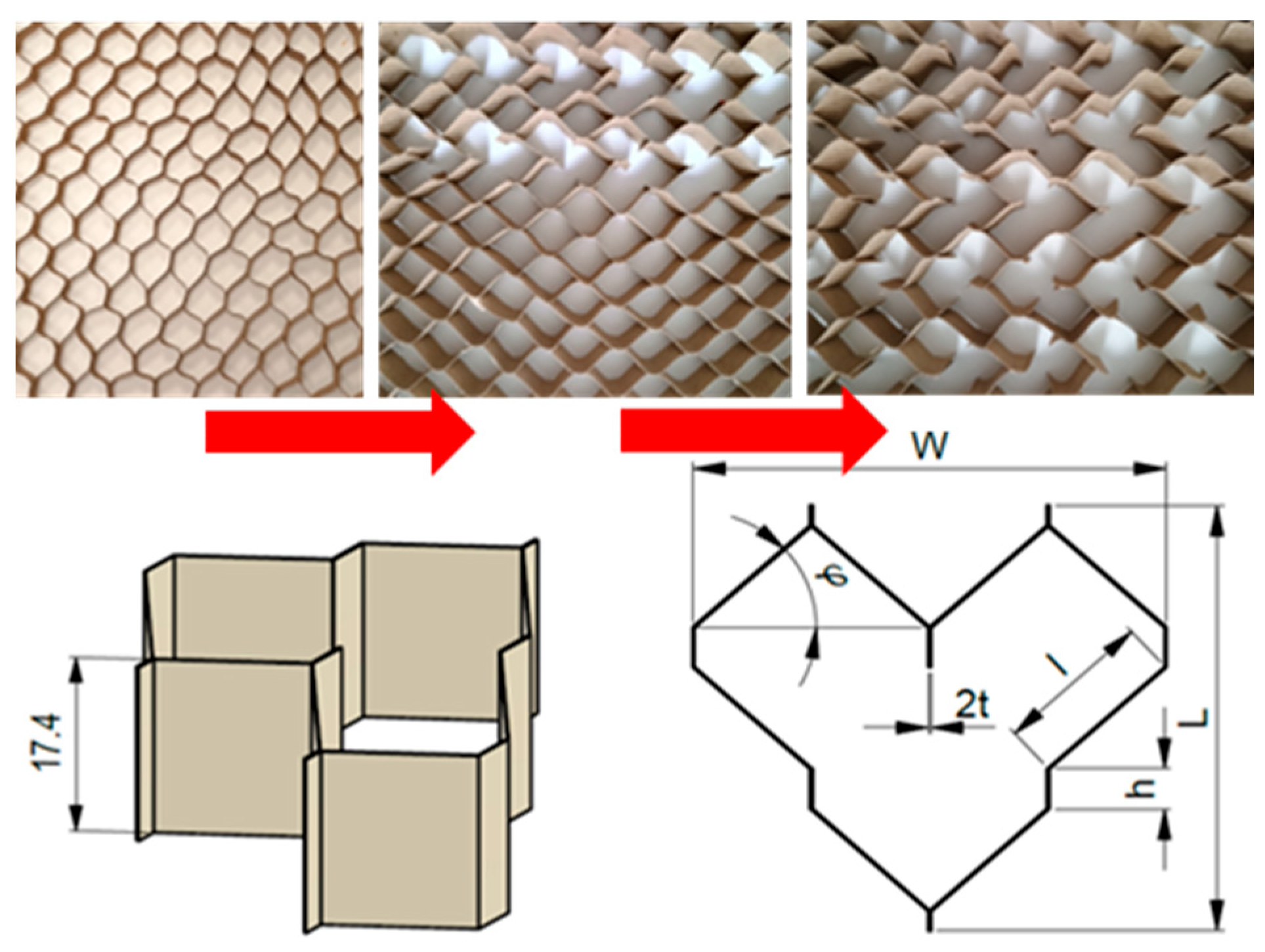


| Material | Unit | WoodEpox® | Paper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter * | Direction MD | Direction CD | ||
| kg/m3 | 630 | 686 | 686 | |
| MPa | 1045 | 5707 | 2188 | |
| - | 2022 | 954 | ||
| 4.21 | 46 | 16 | ||
| 0.31 | 0.411 | 0.147 | ||
| Symbol * | Unit | Cell Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R Re-Entrant | H Hexagonal | M Modified | ||
| - | 0.0973 | 0.0109 | 0.0161 | |
| mm | 39.8 | 23.3 | 34.9 | |
| 18.9 | 18.5 | 37.0 | ||
| 10.0 | 17.4 | 17.4 | ||
| 19.9 | 12 | 12 | ||
| 3.6 | - | - | ||
| 18.9 | 3.3 | 3.3 | ||
| 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||
| (°) | 37 | - | - | |
| 16 | 42 | 42 | ||
| Parameter | Unit | ZY | ZX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | mm | 102.09 | 21.42 |
| RMSE | 3.4 | 14.67 | |
| MAX error | 5.41 | 31.97 | |
| NRMSE | - | 3.33 | 68.48 |
| PEARSON | 0.99 | 0.94 | |
| R2 | 99.79 | 88.92 | |
| MAPE | % | 12.83 | 359.43 |
| AUC-diff | mm2 | 1039 | 2173 |
| AUC-diff | % | 5.58 | 307.67 |
| DTW | mm | 28.16 | 192.56 |
| DTWAvg | 0.45 | 4.81 | |
| Range | 102.09 | 21.42 |
| Parameter | Unit | ZY | ZX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | mm | 102.6 | 96.75 |
| RMSE | 2.4 | 2.81 | |
| MAX error | 4.07 | 5 | |
| NRMSE | - | 2.34 | 2.9 |
| PEARSON | 0.999 | 1 | |
| R2 | 99.78 | 99.97 | |
| MAPE | % | 7.81 | 11.38 |
| AUC-diff | mm2 | 478 | 470 |
| AUC-diff | % | 1.73 | 4.78 |
| DTW | mm | 34.71 | 27.48 |
| DTWAvg | 0.61 | 0.86 | |
| Range | 102.6 | 96.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smardzewski, J.; Słonina, M. Synclastic Behavior of the Auxetic Core for Furniture Panels. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910614
Smardzewski J, Słonina M. Synclastic Behavior of the Auxetic Core for Furniture Panels. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910614
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmardzewski, Jerzy, and Michał Słonina. 2025. "Synclastic Behavior of the Auxetic Core for Furniture Panels" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910614
APA StyleSmardzewski, J., & Słonina, M. (2025). Synclastic Behavior of the Auxetic Core for Furniture Panels. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910614









