Penumbra Shadow Representation in Photovoltaics: Comparing Dynamic and Constant Intensity
Abstract
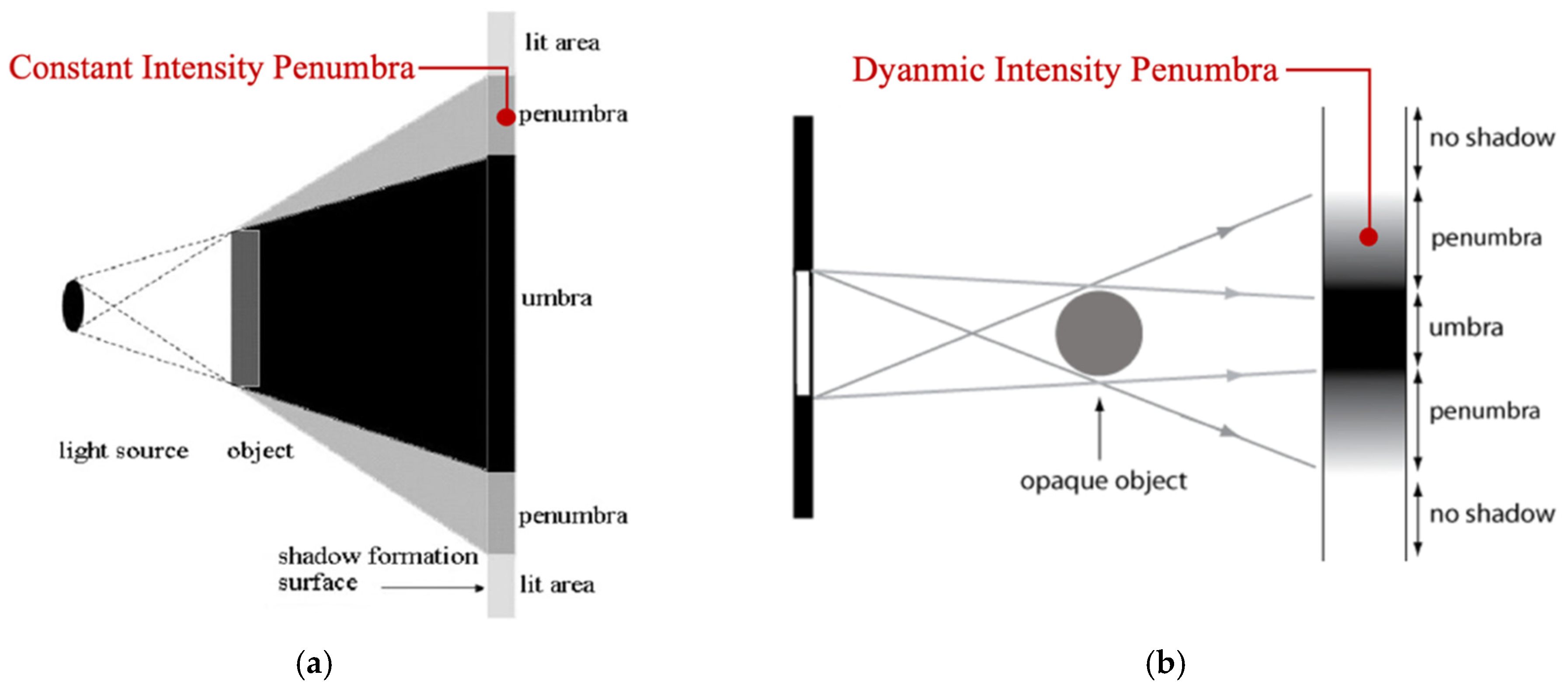
1. Introduction
2. Research Work and the Shading Process
3. Materials and Methods
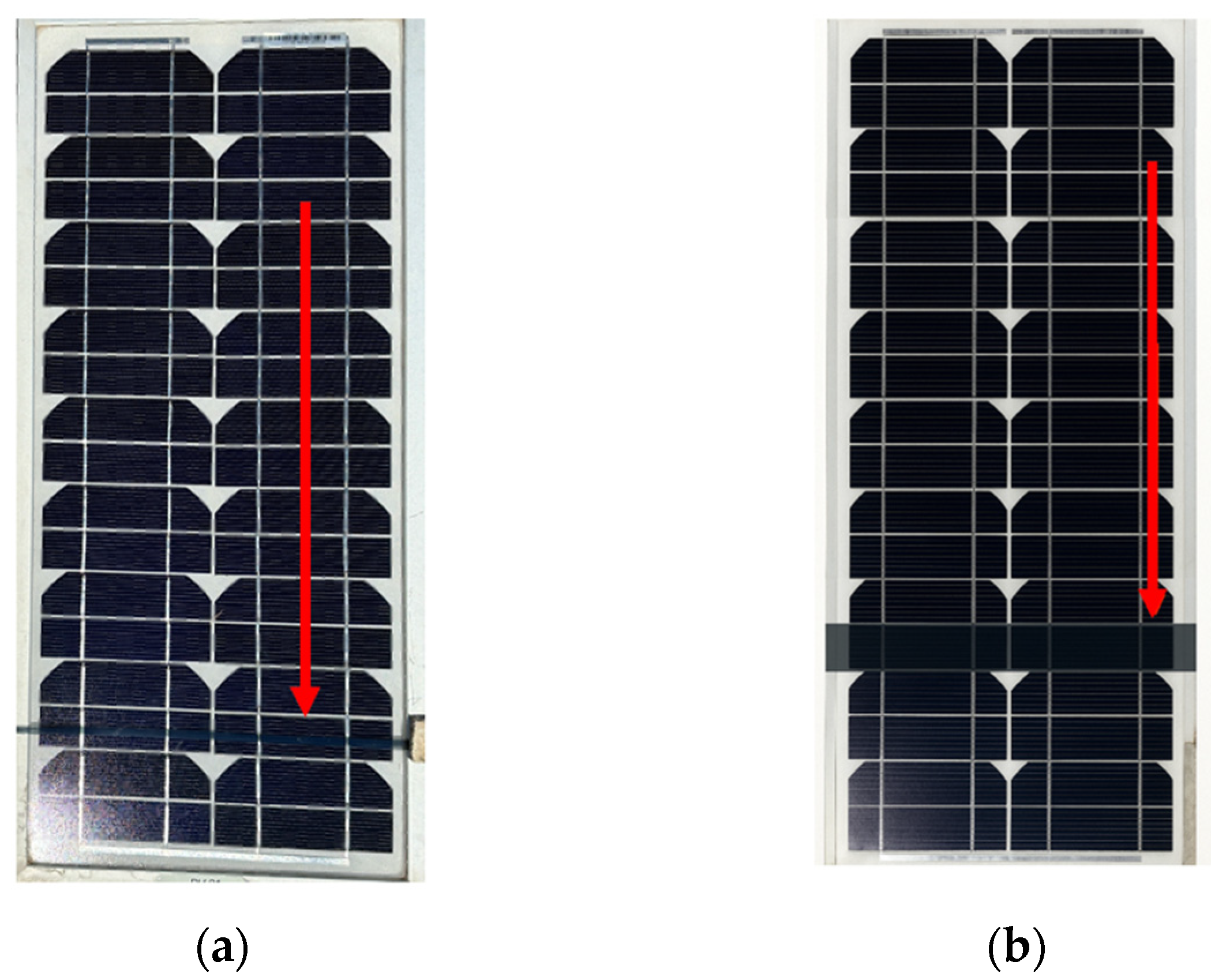
3.1. Choosing the Appropriate Material to Replicate a Dynamic-Intensity Penumbra-Only Shadow
3.2. Setup Conditions and PV Sources Utilised
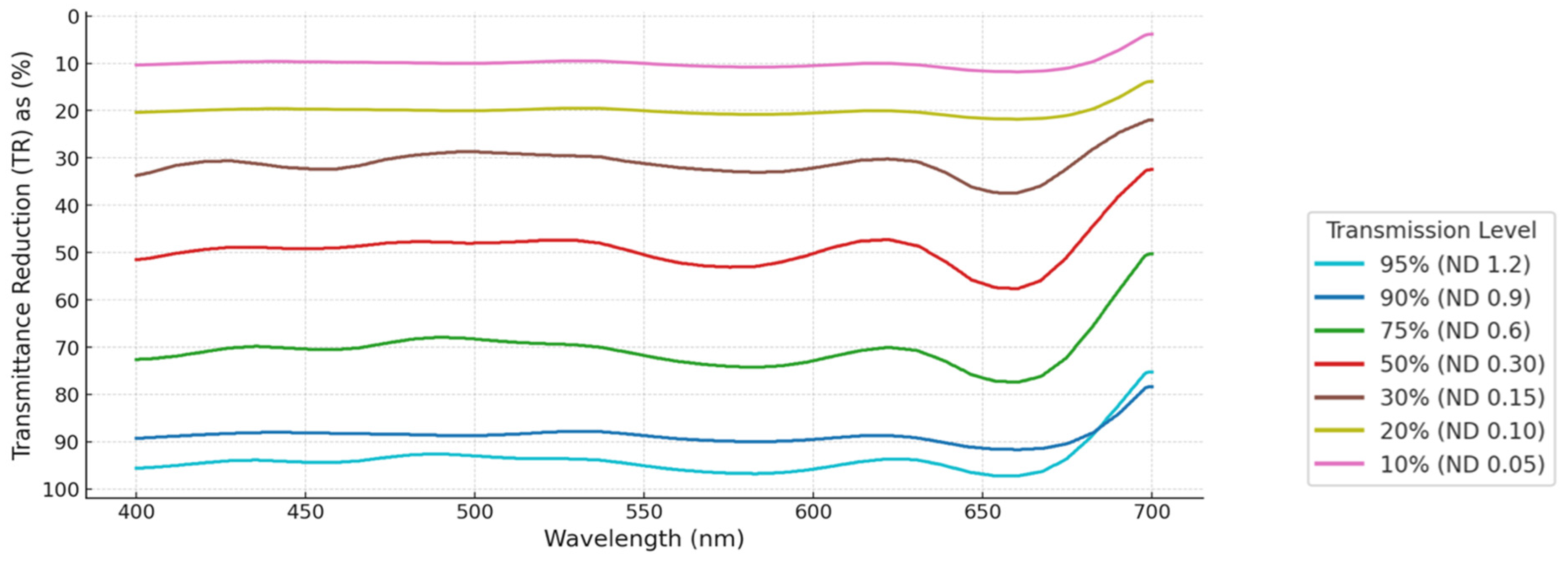
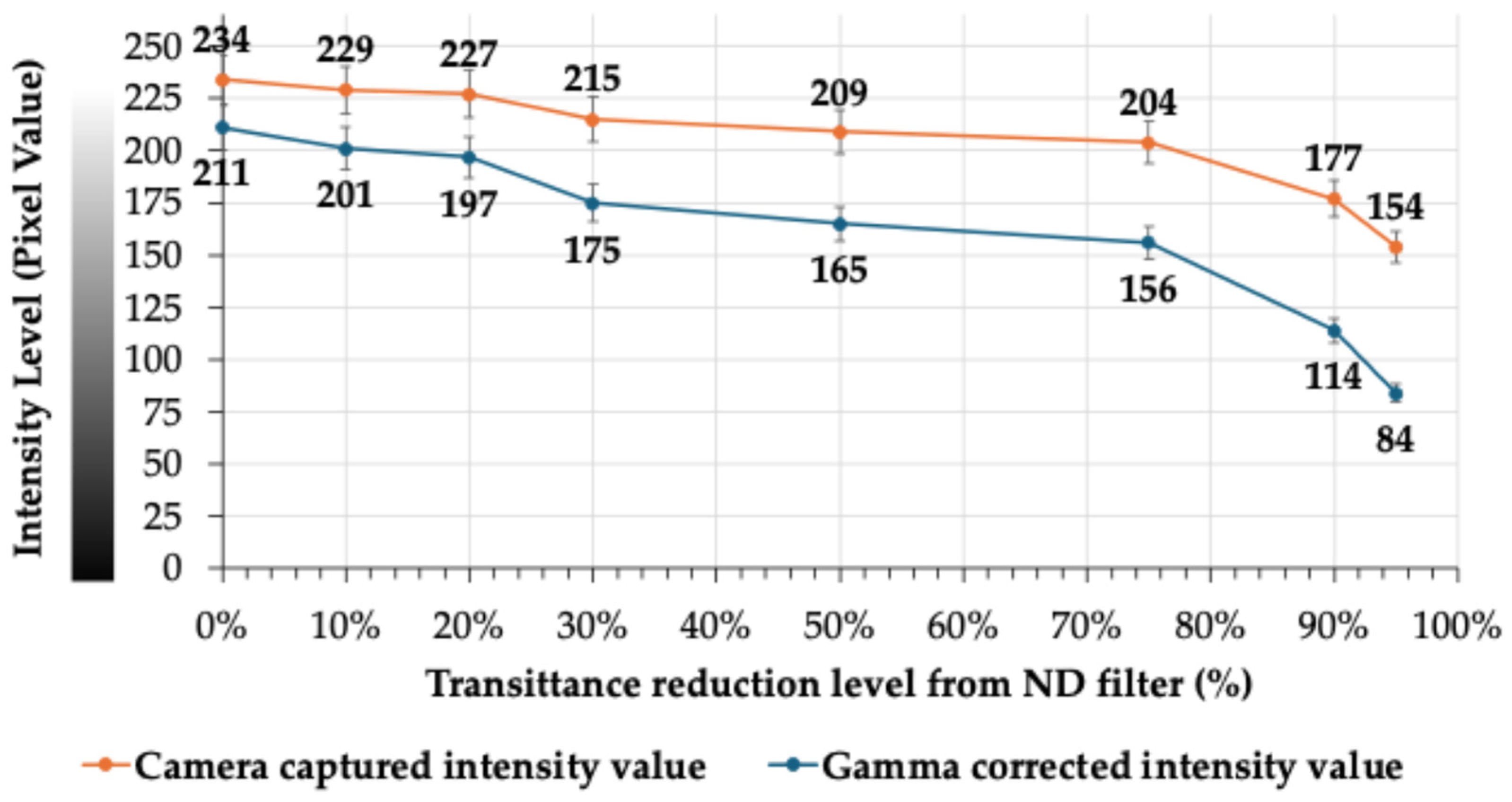
3.3. Quantifying the Intensity Associated with Each ND Filter
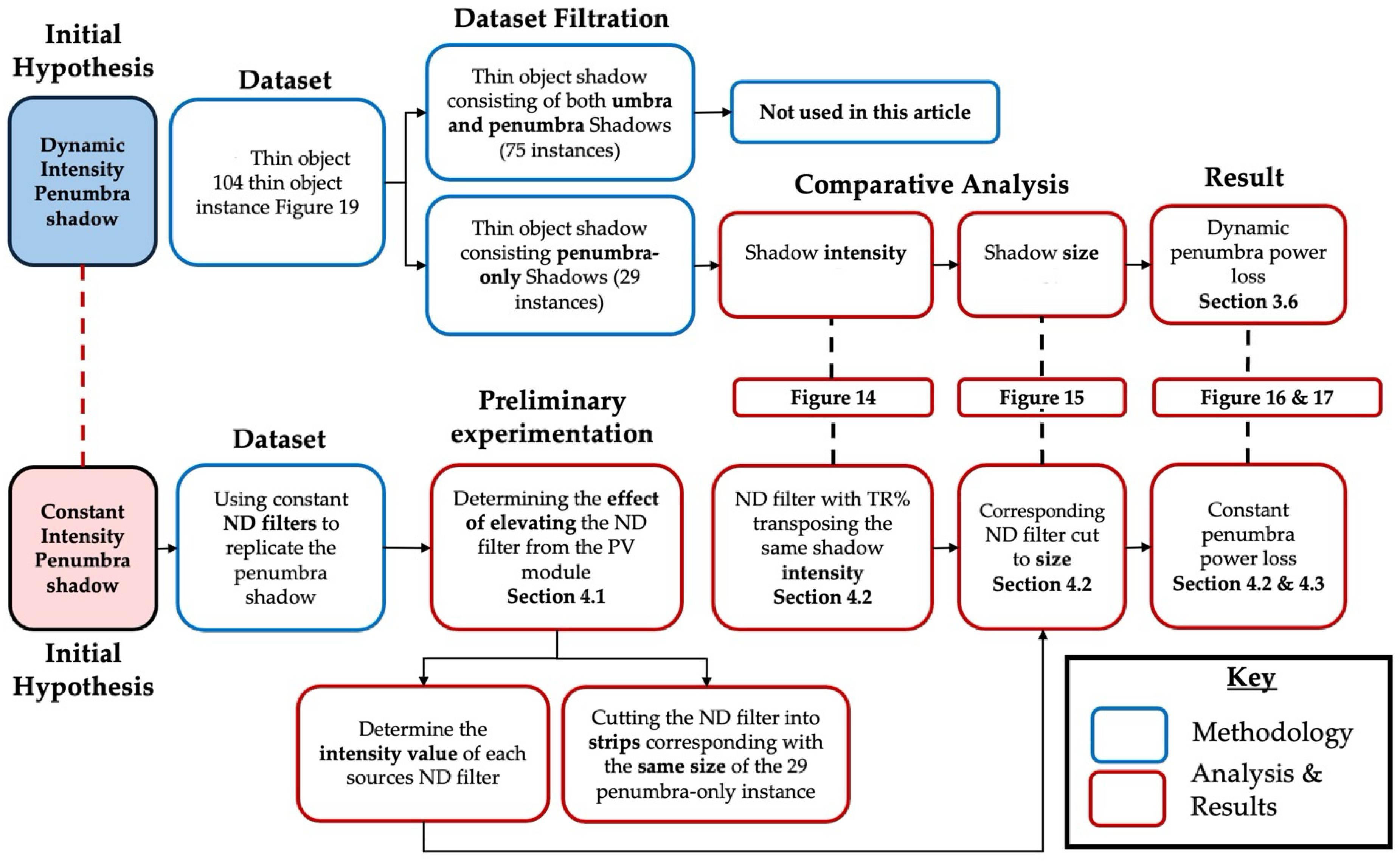
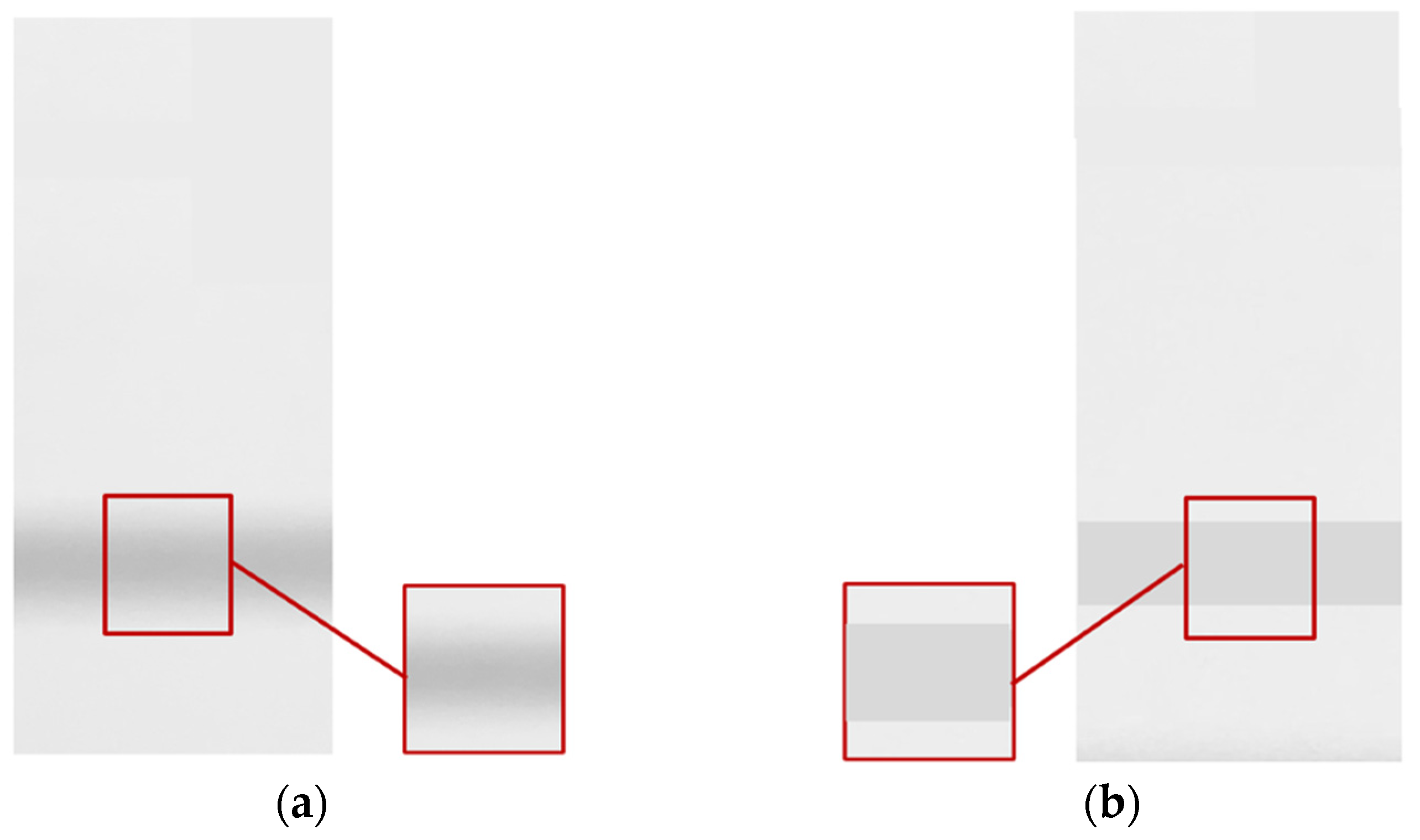
3.4. Direct Comparable Method Used Between a Dynamic-Intensity Penumbra Shadow and Constant-Intensity Shadow
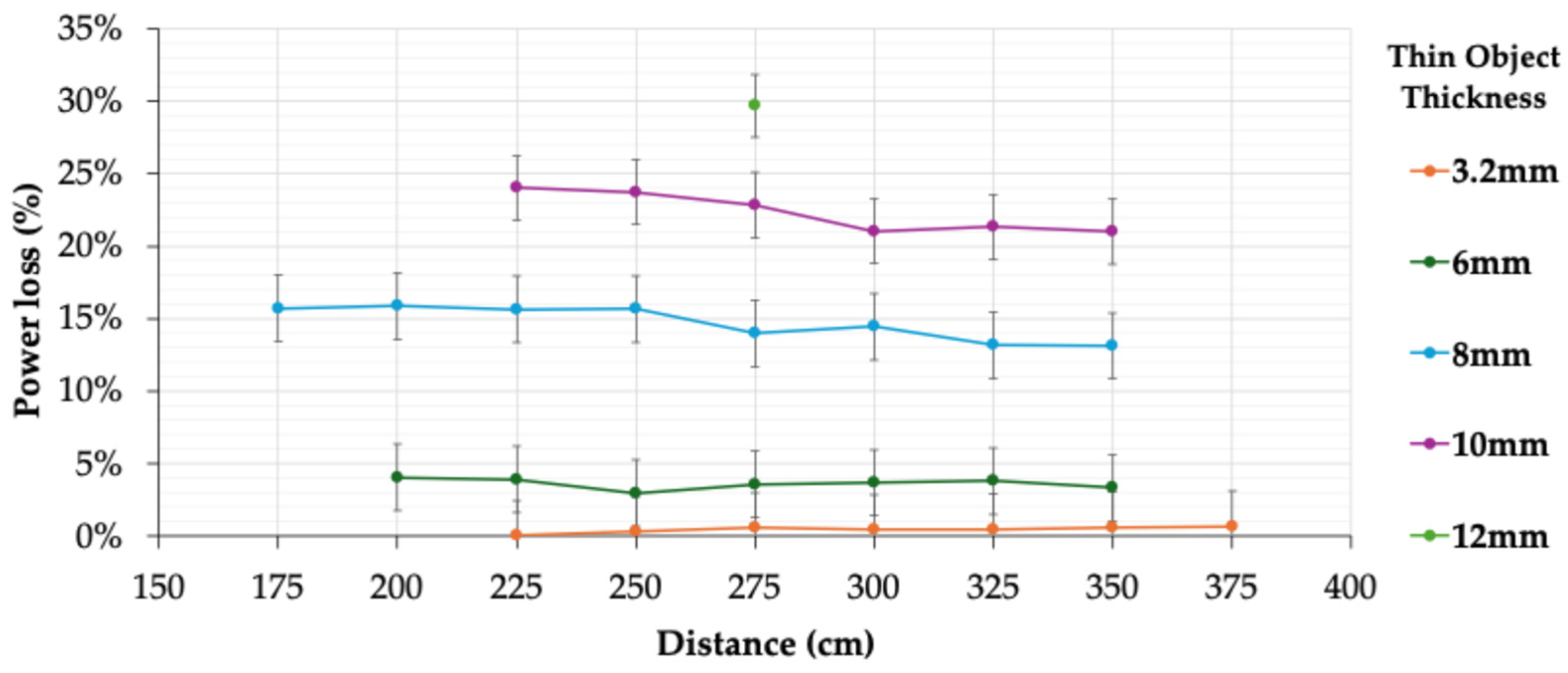
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Preliminary Experimental Measurements
4.1.1. Determining the Effect of Elevating the ND Filter from the PV Module
4.1.2. Determining the Intensity Value for the Range of ND Filters (on the White Surface Sheet)
4.2. Experimental Procedure
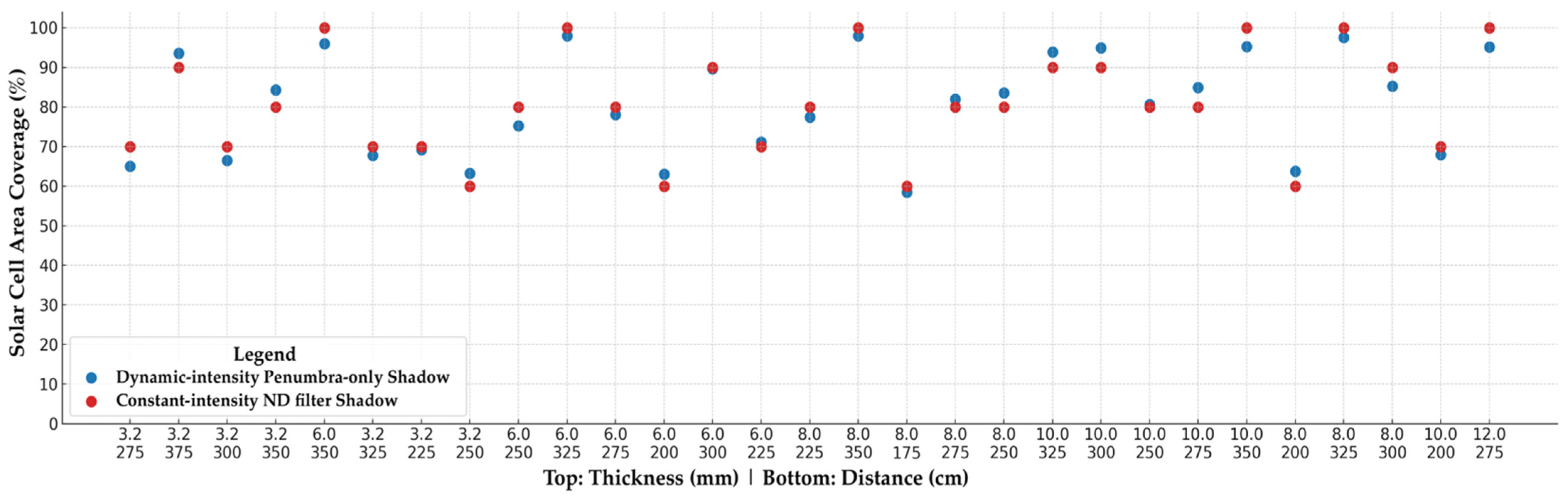
4.3. Results and Interpretation
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aljumaili, M.; Abdalkafor, A.; Taha, M. Analysis of the Hard and Soft Shading Impact on Photovoltaic Module Performance Using Solar Module Tester. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2019, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, A.H.; Dawood, Z.S.; Hussein, H.A. Theoretical and experimental analysis of photovoltaic module characteristics under different partial shading conditions. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teneta, J.; Kreft, W.; Janowski, M. Partial Shading of Photovoltaic Modules with Thin Linear Objects: Modelling in MATLAB Environment and Measurement Experiments. Energies 2024, 17, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolara, A.; Lazaroiu, G.C.; Leva, S.; Manzolini, G. Experimental investigation of partial shading scenarios on pv (photovoltaic) modules. Energy 2013, 55, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinapis, K.; Litjens, G.; Donker, M.; Folkerts, W.; Sark, W. Outdoor characterization and comparison of string and mlpe under clear and partially shaded conditions. Energy Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhimish, M.; Theristis, M.; d’Alessandro, V. Photovoltaic hotspots: A mitigation technique and its thermal cycle. Optik 2024, 300, 171627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numan, A.; Hussein, H.A.; Dawood, Z.S. Hot Spot Analysis of Photovoltaic Module under Partial Shading Conditions by Using IR-Imaging Technology. Eng. Technol. J. 2021, 39, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fri, A.; El Bachtiri, R.; El Ghzizal, A. Improved MPPT Algorithm for Controlling a PV System Grid Connected for Rapid Changes of Irradiance. Int. Rev. Autom. Control IREACO 2016, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, N.; SaravanaKumar, N. Reduced Partial shading effect in Multiple PV Array configuration model using MPPT based Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization Technique. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2020, 103287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.A.; Adil, N.L.J.; Yan, F.Y.; Amaludin, N.; Bohari, N.; Sar-ee, S. Analysis of the Effects of Hard Shading Pattern on I–V Performance Curve. Appl. Sol. Energy 2023, 59, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klugmann-Radziemska, E. Shading, Dusting and Incorrect Positioning of Photovoltaic Modules as Important Factors in Performance Reduction. Energies 2020, 13, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, K.; Tan, T.; Wang, L. Cast Shadow Removal with GMM for Surface Reflectance Component. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; p. 730. [Google Scholar]
- Hernán, J. Calculation of the shadow-penumbra relation and its application on efficient architectural design. Sol. Energy 2014, 110, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Wu, Y.; Su, X.; Zou, W.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, L. Influence and characteristic of shading on photovoltaic performance of bifacial modules and method for estimating bifacial gain. In Building Simulation; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Jee, H.; Park, Y.; Lee, J. Simulation-Based Shading Loss Analysis of a Shingled String for High-Density Photovoltaic Modules. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ma, T. Solar Photovoltaic system under partial shading and perspectives on maximum utilization of the shaded land. Int. J. Green Energy 2023, 20, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, Z.; Mazinan, A.H. Maximum power point tracking of the solar power plants in shadow mode through artificial neural network. Complex Intell. Syst. 2019, 5, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Galeano, A.; Bressan, M.; Jiménez Vargas, F.; Alonso, C. Shading Ratio Impact on Photovoltaic Modules and Correlation with Shading Patterns. Energies 2018, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Qin, G.; Zhu, J. Shadow Detection and Reconstruction of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images in Mountainous and Hilly Environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Govindan, V.K.; Kalady, S. A Survey on Shadow Detection Techniques in a Single Image. Inf. Technol. Control 2018, 47, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendrinos, D. On the Fuzzy Nature of Shadows. 2017. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dimitrios-Dendrinos/publication/317433717_ON_THE_FUZZY_NATURE_OF_SHADOWS/links/593aa58ba6fdcc17a9898705/ON-THE-FUZZY-NATURE-OF-SHADOWS.pdf (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Geometrical Optics Laboratory. Available online: https://www.animations.physics.unsw.edu.au/labs/geometrical-optics/geometrical-optics-lab.html (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Ramanath, R.; Drew, M.S. Penumbra and Umbra. In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Ikeuchi, K., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 589–590. ISBN 978-0-387-31439-6. [Google Scholar]
- Axisa, M.; Demicoli, M.; Mule’Stagno, L. Analysing the Effects of Thin Object Shading on PV Sources: A Dual Approach Combining Outdoor and Laboratory Solar Simulator Experimentation. Energies 2024, 17, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axisa, M.; Mule’Stagno, L.; Demicoli, M. Quantifying the effect of shadow formation on photovoltaic sources under thin object shading: An image analysis approach. EPJ Photovolt. 2025, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axisa, M.; Mule’Stagno, L.; Demicoli, M. Correlating field experimentation and image analysis for the assessment of induced losses from thin object shading on photovoltaic sources. In Proceedings of the EU PVSEC 2024, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- De Rosa, A.; Bortot, A.; Bergamo, F. Praise of Penumbra; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; ISBN 1-119-98396-7. [Google Scholar]
- Štampfl, V.; Gabrijelčič, H.; Ahtik, J. The Role of Light and Shadow in the Perception of Photographs. Teh. Vjesn. 2023, 30, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.-A.; Moreno, J.C. Spectral transmission of solar radiation by plastic and glass materials. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 208, 111894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.; Rotter, A.; Malvestiti, A.; Hafner, M. The role of glass as a barrier against the transmission of ultraviolet radiation: An experimental study. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2009, 25, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohn, B.; Heeger, K.; Wise, T.; Gettrust, E.; Lyman, M. UV degradation of the optical properties of acrylic for neutrino and dark matter experiments. J. Instrum. 2009, 4, T09001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonot, L.; Hébert, M.; Mazauric, S.; Hersch, R.D. Assessing the proper color of translucent materials by an extended two-flux model from measurements based on an integrating sphere. Electron. Imaging 2017, 2017, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, V.; Sharma, V. Different types of Optical Filters and their Realistic Application. J. Manag. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2016, 3, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, E.Y.; Fung, G.S.K. Automatic white balancing in digital photography. In Single-Sensor Imaging: Methods and Applications for Digital Cameras; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Heron, G.; Dutton, G.N. The Pulfrich phenomenon and its alleviation with a neutral density filter. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 73, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami Color Research Laboratory. ND Filter. Available online: https://www.mcrl.co.jp/english/products/p_standard/detail/NDfilters.html (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Kase Filters. Using Graduated ND Filters. Available online: https://kasefilters.eu/nice-to-know/guides/using-graduated-nd-filters/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Willey, R. Designing Metallic Neutral Density Filters with Constant Optical Density Versus Wavelength. Space Sci. J. 2024, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo Ramos, C.A.; Alcaso, A.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) technology: Review and case study. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 354, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, J.E. OPTICAL MATERIALS|Color Filter and Absorption Glasses. In Encyclopedia of Modern Optics; Guenther, R.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 440–446. ISBN 978-0-12-369395-2. [Google Scholar]
- Luciani, S.; Coccia, G.; Tomassetti, S.; Pierantozzi, M.; Di Nicola, G. Correction Procedures for Temperature and Irradiance of Photovoltaic Modules: Determination of Series Resistance and Temperature Coefficients by Means of an Indoor Solar Flash Test Device. Tec. Ital.-Ital. J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 65, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60904-1:2020; Part 1: Measurement of Photovoltaic Current-Voltage Characteristics. International Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Understanding Neutral Density Filters|Edmund Optics. Available online: https://www.edmundoptics.com/knowledge-center/application-notes/optics/understanding-neutral-density-filters/?srsltid=AfmBOorwBdA2g5zdwLEDddyzul6popAOdCHe_N_jGyJezKwTqgpO72Dj (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Sinapis, K.; Tzikas, C.; Litjens, G.; van den Donker, M.; Folkerts, W.; van Sark, W.G.J.H.M.; Smets, A. A comprehensive study on partial shading response of c-Si modules and yield modeling of string inverter and module level power electronics. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, Á.; Loonen, R.C.G.M.; Valckenborg, R.M.E.; Hensen, J.L.M. An unsupervised method for identifying local PV shading based on AC power and regional irradiance data. Sol. Energy 2018, 174, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khobragade, K. A Comparative study of Converting Coloured Image to Gray-scale Image using Different Technologies. Master’s Thesis, Fergusson College, Pune, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, S.; Singh, P.; Waoo, A. Review of gamma correction techniques in digital imaging. ShodhKosh J. Vis. Perform. Arts 2024, 5, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singnoo, J.; Finlayson, G. Understanding the Gamma Adjustment of Images. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 8–12 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, J.; Fernandes, J.C. Linear versus Non-Linear Digital Image Processing Methods. In Proceedings of the Congresso Luso-Moçambicano de Engenharia, Maputo, Moçambique, 29 July–2 August 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, H. Blind inverse gamma correction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A. Implementation of Curve Fitting using Polynomial Regression in Python. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2024, 186, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyub, B.; Mccuen, R. Curve Fitting and Regression Analysis. In Numerical Analysis for Engineers; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 331–394. ISBN 978-0-429-16212-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rezagholizadeh, M.; Clark, J. Image Sensor Modeling: Color Measurement at Low Light Levels. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 3–7 November 2014; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Udo, O.C.; Idochi, O. Simple Regression Models: A Comparison using Criteria Measures. Afr. J. Math. Stat. Stud. 2024, 7, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.M. Best practice in statistics: Use the Welch t-test when testing the difference between two groups. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 58, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oti, E.U.; Olusola, M.O.; Esemokumo, P.A. Statistical Analysis of the Median Test and the Mann-Whitney U Test. Int. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2021, 7, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Fang, H. A New Nonlinear Model-Based Fault Detection Method Using Mann–Whitney Test. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 10856–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size—Or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, A.; Khosla, A.; Joshi, D. Design and simulation of 20MW photovoltaic power plant using PVSyst. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2020, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chedid, R.; Tajeddine, R.; Chaaban, F.; Ghajar, R. Modeling and simulation of PV arrays under varying conditions. In Proceedings of the MELECON 2014-2014 17th IEEE Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, Beirut, Lebanon, 13–16 April 2014; p. 542. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, A. Rooftop solar PV system planning with 3D visualization using PVSOL (Case study in Syria). J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2024, 11, 66–77. [Google Scholar]







| Description | Symbol | Outdoor Calibrated at STC | Image Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Applicable Experiment No. | Section 4.1 |  | |
| Cell Technology | Mono Si | ||
| No. of Series cells | 36 | ||
| Size of Cells (mm) | 52 × 31 | ||
| Bypass diodes | 0 | ||
| Rated Power Output | P | 10 W | |
| Short circuit current | ISC | 0.60 A | |
| Open circuit voltage | VOC | 21.1 V | |
| MPP current | TMPP | 0.55 V | |
| MPP voltage | VMPP | 17.2 V |
| ND (OD Value) | TR (%) |
|---|---|
| ND 1.20 | ≈95% |
| ND 0.90 | ≈90% |
| ND 0.60 | ≈75% |
| ND 0.30 | ≈50% |
| ND 0.15 | ≈30% |
| ND 0.10 | ≈20% |
| ND 0.05 | ≈10% |
| Unshaded | 0% |
| Variable | Value Source | |
|---|---|---|
| Extracted Penumbra-only instances (29) from [25] | Thickness | Ref. [25], Section 3.2, Figure 19 * |
| Distance | Ref. [25], Section 3.2, Figure 19 * | |
| Power Loss | Ref. [25], Section 3.2, Figure 19 * | |
| Maintaining Size | Dynamic-intensity penumbra shadow | Ref. [25], Section 3.2, Figures 21 and 22 * |
| Constant-intensity shadow | This article, Section 4.2, Figure 15 | |
| Maintaining Intensity | Dynamic-intensity penumbra shadow | Ref. [25], Section 3.2 * |
| Constant-intensity shadow | This article, Section 4.2, Figure 14 |
| Filter Utilised: 95% TR | ||
|---|---|---|
| Distance Between ND Filter and White Surface (cm) | Intensity (Pixel Value) | Power Loss (%) |
| 10 | 154 | 93.57 |
| 20 | 154 | 93.54 |
| 30 | 154 | 93.52 |
| 40 | 154 | 93.17 |
| 50 | 154 | 93.14 |
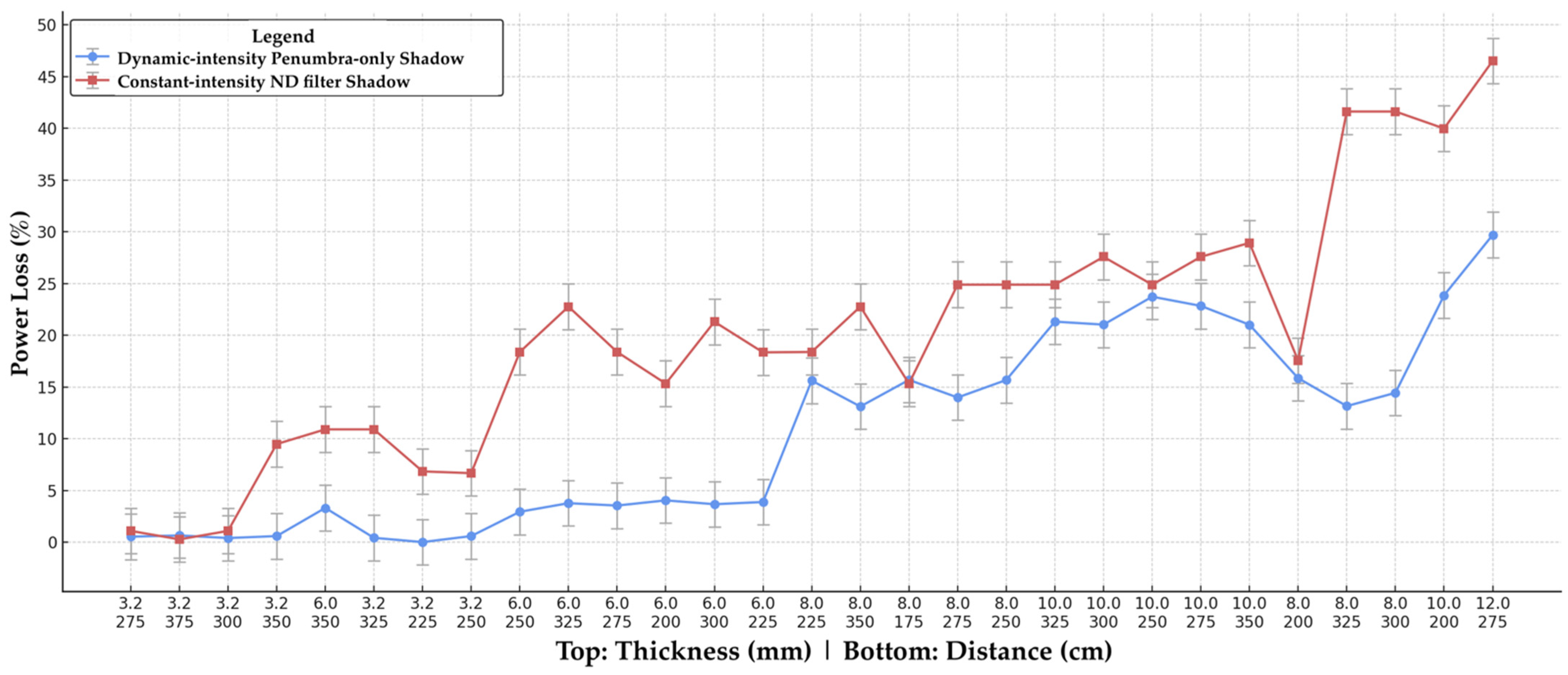
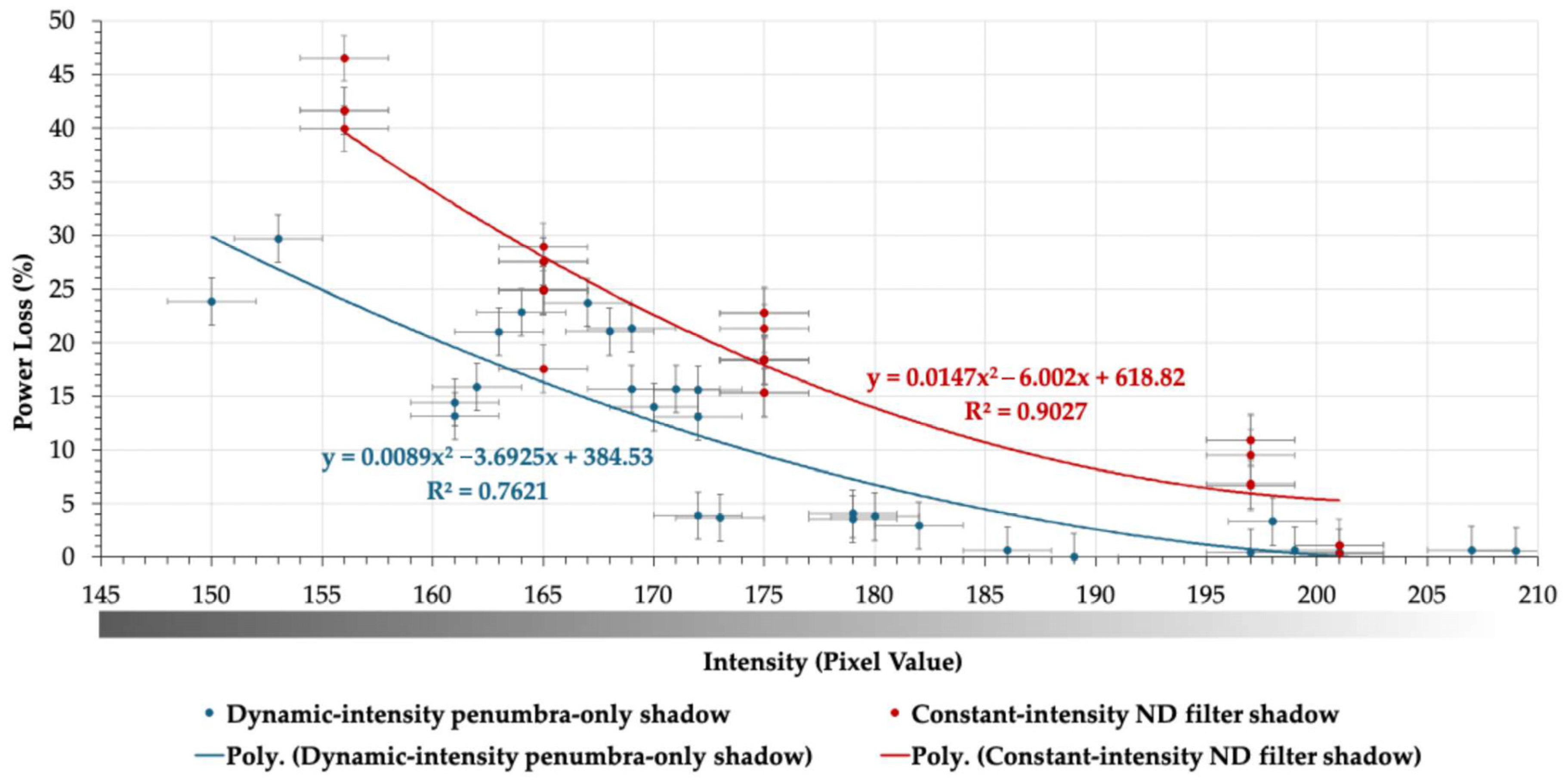
| Category | Metric | Dynamic-Intensity Penumbra-Only Shadow | Constant-Intensity ND Filter Shadow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction error | MAE (Mean Absolute Error) (%) | 3.74 | 2.92 |
| RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) (%) | 4.43 | 3.72 | |
| Relationship between the second-degree polynomial regression model | R2 (Individual model) | 0.762 | 0.903 |
| Adjusted R2 (Individual model) | 0.743 | 0.895 | |
| Testing for normality of the distribution | Shapiro–Wilk Test (p-value) | 0.0032 | |
| Comparative statistical test | Mann–Whitney U-test (p-value) | 0.00229 | |
| Cohen’s d (Effect Size) | −0.893 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Axisa, M.; Mule’ Stagno, L.; Demicoli, M. Penumbra Shadow Representation in Photovoltaics: Comparing Dynamic and Constant Intensity. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179820
Axisa M, Mule’ Stagno L, Demicoli M. Penumbra Shadow Representation in Photovoltaics: Comparing Dynamic and Constant Intensity. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179820
Chicago/Turabian StyleAxisa, Matthew, Luciano Mule’ Stagno, and Marija Demicoli. 2025. "Penumbra Shadow Representation in Photovoltaics: Comparing Dynamic and Constant Intensity" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179820
APA StyleAxisa, M., Mule’ Stagno, L., & Demicoli, M. (2025). Penumbra Shadow Representation in Photovoltaics: Comparing Dynamic and Constant Intensity. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9820. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179820







