Pain Neuroscience Education to Reduce Catastrophizing: A Parallel Randomized Trial in Youth Athletes
Abstract
1. Introduction
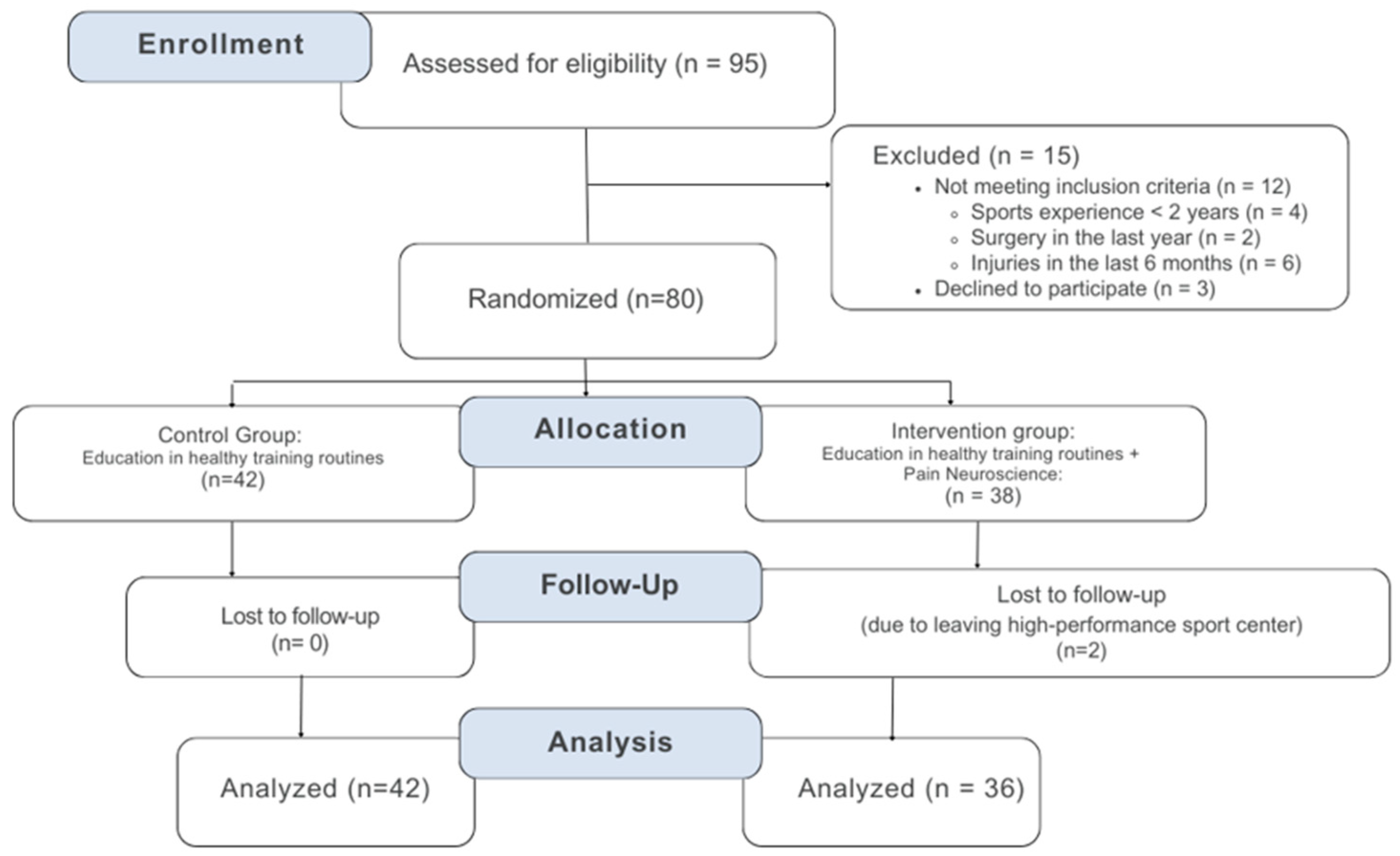
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Pain Catastrophism Scale (PCS)
2.3.2. Injury Registration
2.3.3. Educational Program
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACL | Anterior Cruciate Ligament |
| CG | Control Group |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| ES | Effect Size |
| IG | Intervention Group |
| PCS | Pain Catastrophizing Scale |
| PNE | Pain Neuroscience Education |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Gatchel, R.J.; Peng, Y.B.; Peters, M.L.; Fuchs, P.N.; Turk, D.C. The Biopsychosocial Approach to Chronic Pain: Scientific Advances and Future Directions. Psychol. Bull. 2007, 133, 581–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.L.; Tripp, D.A.; Stanish, W.; Rodgers, W.M. Catastrophizing and Pain Perception in Sport Participants. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2000, 12, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischerauer, S.F.; Talaei-Khoei, M.; Bexkens, R.; Ring, D.C.; Oh, L.S.; Vranceanu, A.M. What Is the Relationship of Fear Avoidance to Physical Function and Pain Intensity in Injured Athletes? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2018, 476, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawil, S.; Kassis, V.; Bassil, T.; Farhat, K.; Hourani, E.; Massoud, L.; Najem, C. Intermediary Role of Mental Toughness Beliefs on the Relationship between Pain Self-Efficacy and Fear Avoidance in Elite Injured Athletes. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2025, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraldsdottir, K.; Watson, A.M. Psychosocial Impacts of Sports-Related Injuries in Adolescent Athletes. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2021, 20, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartana, P.J.; Campbell, C.M.; Edwards, R.R. Pain Catastrophizing: A Critical Review. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2009, 9, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- San-Antolín, M.; Rodríguez-Sanz, D.; Becerro-De-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Casado-Hernández, I.; López-López, D.; Calvo-Lobo, C. Central Sensitization and Catastrophism Symptoms Are Associated with Chronic Myofascial Pain in the Gastrocnemius of Athletes. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 1616–1625. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/painmedicine/article/21/8/1616/5625063 (accessed on 30 June 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The Revised IASP Definition of Pain: Concepts, Challenges, and Compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fawcett, L.; Heneghan, N.R.; James, S.; Rushton, A. Perceptions of Low Back Pain in Elite Gymnastics: A Multi-Disciplinary Qualitative Focus Group Study. Phys. Ther. Sport 2020, 44, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timpka, T.; Jacobsson, J.; Bargoria, V.; Dahlström, Ö. Injury Pain in Track and Field Athletes: Cross-Sectional Study of Mediating Factors. Sports 2019, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoe, T.; Tajima, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Nagasawa, M.; Ota, T.; Morita, Y.; Chosa, E. Orthopaedic Medical Examination for Young Amateur Athletes: A Repeated Cross-Sectional Study from 2014 to 2018. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e042188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbenytė-Apolinskienė, T.; Salatkaitė, S.; Šiupšinskas, L.; Gudas, R. Prevalence of Musculoskeletal Injuries, Pain, and Illnesses in Elite Female Basketball Players. Medicina 2019, 55, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farì, G.; Fischetti, F.; Zonno, A.; Marra, F.; Maglie, A.; Bianchi, F.P.; Messina, G.; Ranieri, M.; Megna, M. Musculoskeletal Pain in Gymnasts: A Retrospective Analysis on a Cohort of Professional Athletes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre-Munar, A.; Pades-Jiménez, A.; García-Coll, N.; Molina-Mula, J.; Romero-Franco, N. Injuries, Pain, and Catastrophizing Level in Gymnasts: A Retrospective Analysis of a Cohort of Spanish Athletes. Healthcare 2022, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, M.O.; Hespanhol, L.C.; Lopes, A.D. Prevalence of musculoskeletal pain among swimmers in an elite national tournament. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 10, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moseley, G.L.; Baranoff, J.; Rio, E.; Stewart, M.; Derman, W.; Hainline, B. Nonpharmacological Management of Persistent Pain in Elite Athletes: Rationale and Recommendations. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2018, 28, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baez, S.; Jochimsen, K. Current Clinical Concepts: Integration of Psychologically Informed Practice for Management of Patients with Sport-Related Injuries. J. Athl. Train. 2023, 58, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, R.A.; Sterling, E.K.; Fenster, D.E.; Bird, M.L.; Heritage, A.J.; Woosley, V.L.; Burston, A.M.; Henry, A.L.; Huston, L.J.; Vanston, S.W.; et al. Cognitive-Behavioral-Based Physical Therapy to Enhance Return to Sport after Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: An Open Pilot Study. Phys. Ther. Sport 2020, 42, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainline, B.; Turner, J.A.; Caneiro, J.P.; Stewart, M.; Moseley, G.L. Pain in Elite Athletes—Neurophysiological, Biomechanical and Psychosocial Considerations: A Narrative Review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louw, A.; Zimney, K.; Puentedura, E.J.; Diener, I. The Efficacy of Pain Neuroscience Education on Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2016, 32, 332–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddall, B.; Ram, A.; Jones, M.D.; Booth, J.; Perriman, D.; Summers, S.J. Short-Term Impact of Combining Pain Neuroscience Education with Exercise for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain 2022, 163, E20–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Silva, D.; Pazzinatto, M.F.; Rathleff, M.S.; Holden, S.; Bell, E.; Azevedo, F.; Barton, C. Patient education for patellofemoral pain: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2020, 50, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühlmayer, L.; Birrer, D.; Röthlin, P.; Faude, O.; Donath, L. Effects of mindfulness practice on performance-relevant parameters and performance outcomes in sports: A meta-analytical review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2309–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, F.K.W.; Louie, L.H.T.; Wong, W.H.S.; Chan, K.L.; Tiwari, A.; Chow, C.B.; Ho, W.; Wong, W.; Chan, M.; Chen, E.Y.H.; et al. A sports-based youth development program, teen mental health, and physical fitness: An RCT. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochbaum, M.; Stoner, E.; Hefner, T.; Cooper, S.; Lane, A.M.; Terry, P.C. Sport psychology and performance meta-analyses: A systematic review of the literature. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myall, K.; Montero-Marin, J.; Gorczynski, P.; Kajee, N.; Syed Sheriff, R.; Bernard, R.; Harriss, E.; Kuyken, W. Effect of mindfulness-based programmes on elite athlete mental health: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczyńska, D.; Qi, W.; Jaenes, J.C.; Alarcón, D.; Arenilla, M.J.; Lipowski, M. Burnout and mental interventions among youth athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.I.; Parker, J.K. A conditional process model of the effect of mindfulness on 800-m personal best times through pain catastrophising. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, F.J.; Lefebvre, J.C.; Egert, J.R.; Affleck, G.; Sullivan, M.J.; Caldwell, D.S. The relationship of gender to pain, pain behavior, and disability in osteoarthritis patients: The role of catastrophizing. Pain 2000, 87, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorn, B.E.; Clements, K.L.; Ward, L.C.; Dixon, K.E.; Kersh, B.C.; Boothby, J.L.; Chaplin, W.F. Personality factors in the explanation of sex differences in pain catastrophizing and response to experimental pain. Clin. J. Pain 2004, 20, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugat, J.; Vila, J.; Pavesi, M.; Sanz, F. Estimación Del Tamaño de La Muestra En La Investigación Clínica y Epidemiológica. Med. Clin. 1998, 111, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Javdaneh, N.; Saeterbakken, A.H.; Shams, A.; Barati, A.H. Pain neuroscience education combined with therapeutic exercises provides added benefit in the treatment of chronic neck pain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourin, S.; Tram, J.; Sheldon, B.L.; Pilitsis, J.G. Defining Minimal Clinically Important Differences in Pain and Disability Outcomes of Patients with Chronic Pain Treated with Spinal Cord Stimulation. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 35, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, R.; Clarsen, B.; Derman, W.; Dvorak, J.; Emery, C.A.; Finch, C.F.; Hägglund, M.; Junge, A.; Kemp, S.; Khan, K.M.; et al. International Olympic Committee consensus statement: Methods for recording and reporting of epidemiological data on injury and illness in sport 2020. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmedilla Zafra, A.; Ortega Toro, E.; Abenza Cano, L. Validación de la escala de catastrofismo ante el dolor (Pain Catastrophizing Scale) en deportistas españoles. Cuad. Psicol. Deporte 2013, 13, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarsen, B.; Rønsen, O.; Myklebust, G.; Flørenes, T.W.; Bahr, R. The Oslo Sports Trauma Research Center Questionnaire on Health Problems: A New Approach to Prospective Monitoring of Illness and Injury in Elite Athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traeger, A.C.; Lee, H.; Hübscher, M.; Skinner, I.W.; Moseley, G.L.; Nicholas, M.K.; Henschke, N.; Refshauge, K.M.; Blyth, F.M.; Main, C.J.; et al. Effect of intensive patient education vs placebo patient education on outcomes in patients with acute low back pain: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, N.; Chesterton, P.; Ryan, C. The effect of pain neuroscience education on sports therapy and rehabilitation students’ knowledge, attitudes, and clinical recommendations toward athletes with chronic pain. J. Sport Rehabil. 2019, 28, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, G.L.; Butler, D.S. Fifteen Years of Explaining Pain: The Past, Present, and Future. J. Pain 2015, 16, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh, M.; Stanton, T.; George, S.; Lyng, K.D.; Vistrup, S.; Rathleff, M.S. Infographic. Pain or Injury? Why Differentiation Matters in Exercise and Sports Medicine. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Díaz, S.; Yanci, J.; Castillo, D.; Scanlan, A.T.; Raya-González, J. Effects of Nutrition Education Interventions in Team Sport Players. A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, A.; Schlarb, A.A. Let’s talk about sleep: A systematic review of psychological interventions to improve sleep in college students. J. Sleep Res. 2018, 27, e12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarz, J.; Schuster, A.K.; Hartmann, M.; Gerhardt, A.; Eich, W. Pain Perception in Athletes Compared to Normally Active Controls: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Pain 2012, 153, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; McAuley, J.H.; Hübscher, M.; Kamper, S.J.; Traeger, A.C.; Moseley, G.L. Does changing pain-related knowledge reduce pain and improve function through changes in catastrophizing? Pain 2016, 157, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.I.; Kortlever, J.T.P.; Brown, L.E.; Ring, D.; Queralt, M. Can crafted communication strategies allow musculoskeletal specialists to address health within the biopsychosocial paradigm? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2021, 479, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.A.; Ryan, C.G.; Cooper, L.; Ellington, D.; Whittle, R.; Lavender, M.; Dixon, J.; Atkinson, G.; Cooper, K.; Martin, D.J. Pain neuroscience education for adults with chronic musculoskeletal pain: A mixed-methods systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pain 2019, 20, 1140.e1–1140.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, Z.; Mansfield, C.J.; Bleacher, J.; Briggs, M. Return to Advanced Strength Training and Weightlifting in an Athlete Post-Lumbar Discec-Tomy Utilizing Pain Neuroscience Education and Proper Progression: Resident’s Case Report. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 14, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, A.; Waldecker, J.; Jacobs, C. Pain catastrophizing in college athletes. J. Sport Rehabil. 2020, 29, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, N.F.N.; Meeuwisse, W.H.; Mendonça, L.D.; Nettel-Aguirre, A.; Ocarino, J.M.; Fonseca, S.T. Complex systems approach for sports injuries: Moving from risk factor identification to injury pattern recognition. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meints, S.M.; Stout, M.; Abplanalp, S.; Hirsh, A.T. Pain-related rumination, but not magnification or helplessness, mediates race and sex differences in experimental pain. J. Pain 2017, 18, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.R.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Sullivan, M.J.; Fillingim, R.B. Catastrophizing as a mediator of sex differences in pain: Differential effects for daily pain versus laboratory-induced pain. Pain 2004, 111, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, E.J.; Fillingim, R.B. Sex differences in pain: A brief review of clinical and experimental findings. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, M.; Tousignant-Laflamme, Y.; Kloda, L.A.; Dion, D.; Dupuis, G.; Choinière, M. A systematic literature review on sex/gender and pain perception: Do biopsychosocial factors alter pain sensitivity differently in women and men? Pain 2012, 153, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepri, B.; Romani, D.; Storari, L.; Barbari, V. Effectiveness of pain neuroscience education in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain and central sensitization: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’ Sullivan, I.; Orbell, S.; Rakow, T.; Parker, R. Prospective Research in Health Service Settings: Health Psychology, Science and the Hawthorne’ Effect. J. Health Psychol. 2004, 9, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CG, All Athletes (n = 42) | GC, Male Athletes (n = 21) | CG, Female Athletes (n = 21) | IG, All Athletes (n = 36) | IG, Male Athletes (n = 18) | IG Female Athletes (n = 18) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) ¥ | 15.28 (0.97) | 15.47 (1.03) | 15.09 (0.89) | 16.08 (0.91) | 16.00 (0.90) | 16.16 (0.92) |
| Weight (kg) ¥ | 67.12 (20.83) | 69.07 (13.14) | 65.17 (26.62) | 67.76 (9.30) | 72.25 (9.79) | 63.27 (6.30) |
| Height (m) ¥ | 1.73 (0.09) | 1.78 (0.10) | 1.69 (0.07) | 1.76 (0.08) | 1.80 (0.08) | 1.72 (0.08) |
| Sport Experience (yrs) ¥ | 8.09 (3.37) | 8.85 (3.07) | 7.33 (3.55) | 9.58 (3.73) | 9.55 (4.43) | 9.61 (2.99) |
| Injury during season (%) | Yes (26.2%) | Yes (38.1%) | Yes (14.3%) | Yes (28.6%) | Yes (27.8%) | Yes (29.4%) |
| Control Group | Intervention Group | Between-Group Differences | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Athletes | PRE Mean (SD) | POST Mean (SD) | Intra-Group Differences | PRE Mean (SD) | POST Mean (SD) | Intra-Group Differences | ||||
| Mean (95%CI) | ES d (95%CI) | Mean (95%CI) | ES d (95%CI) | Mean (95%CI) | ES d (95%CI) | |||||
| Catastrophism | 11.95 (8.23) | 11.55 (8.28) | 0.40 (−2.06; 2.81) | 0.05 | 11.58 (5.97) | 9.58 (6.38) | 2.00 (0.23; 3.07) * | 0.32 | 1.96 (−1.37; 5.30) | 0.26 |
| Rumination | 4.80 (3.69) | 4.17 (3.66) | 0.62 (−0.52; 1.78) | 0.17 | 4.06 (3.17) | 3.19 (2.47) | 0.86 (−0.14; 1.86) | 0.27 | 0.98 (−0.42; 2.38) | 0.26 |
| Magnification | 2.82 (2.16) | 2.92 (2.08) | −0.10 (−0.71; 0.51) | 0.05 | 3.06 (1.97) | 2.58 (1.99) | 0.47 (−0.25; 1.19) | 0.24 | 0.34 (−0.56; 1.25) | 0.16 |
| Helplessness | 4.32 (3.43) | 4.45 (3.41) | −0.12 (−1.18; 0.93) | 0.04 | 4.47 (2.58) | 3.80 (2.72) | 0.66 (−0.23; 1.56) | 0.25 | 0.64 (−0.78; 2.07) | 0.04 |
| Males | ||||||||||
| Catastrophism | 9.95 (8.17) | 9.80 (7.63) | 0.14 (−2.98; 3.27) | 0.02 | 10.72 (6.20) | 8.11 (4.85) | 2.61 (0.11; 5.10) * | 0.47 | 1.70 (−2.53; 5.93) | 0.26 |
| Rumination | 4.00 (3.82) | 3.81 (3.80) | 0.19 (−1.27; 1.65) | 0.05 | 4.39 (3.58) | 3.00 (2.40) | 1.39 (−0.36; 3.13) | 0.38 | 0.81 (−1.29; 2.91) | 0.25 |
| Magnification | 2.52 (2.20) | 2.62 (1.96) | −0.09 (−0.89; 0.70) | 0.05 | 2.66 (2.00) | 2.17 (1.65) | 0.50 (−0.54; 1.54) | 0.26 | 0.45 (−0.73; 1.64) | 0.24 |
| Helplessness | 3.43 (3.28) | 3.38 (2.71) | 0.47 (−1.23; 1.33) | 0.02 | 3.66 (2.49) | 2.94 (1.86) | 0.72 (−0.39; 1.84) | 0.28 | 0.57 (−1.10; 1.7) | 0.19 |
| Females | ||||||||||
| Catastrophism | 13.80 (8.01) | 14.15 (8.52) | −0.35 (−4.86; 4.16) | 0.04 | 12.44 (5.77) | 11.05 (7.46) | 1.39 (1.34; 4.11) | 0.21 | 3.09 (−2.20; 8.39) | 0.38 |
| Rumination | 5.50 (3.48) | 4.95 (3.51) | 0.55 (−1.59; 2.69) | 0.16 | 3.72 (2.76) | 3.39 (2.59) | 0.33 (−0.79; 1.46) | 0.12 | 1.56 (−0.49; 3.61) | 0.44 |
| Magnification | 3.10 (2.12) | 3.50 (2.16) | −0.40 (−1.55; 0.75) | 0.19 | 3.44 (1.91) | 3.00 (2.24) | 0.44 (−0.67; 1.56) | 0.21 | 0.50 (−0.95; 1.95) | 0.22 |
| Helplessness | 5.20 (3.42) | 5.70 (3.71) | −0.50 (−2.28; 1.28) | 0.14 | 5.28 (2.47) | 4.67 (3.19) | 0.61 (−0.91; 1.13) | 0.21 | 1.03 (−1.26; 3.33) | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sastre-Munar, A.; Pades-Jiménez, A.; Romero-Franco, N. Pain Neuroscience Education to Reduce Catastrophizing: A Parallel Randomized Trial in Youth Athletes. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179701
Sastre-Munar A, Pades-Jiménez A, Romero-Franco N. Pain Neuroscience Education to Reduce Catastrophizing: A Parallel Randomized Trial in Youth Athletes. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179701
Chicago/Turabian StyleSastre-Munar, Andreu, Antonia Pades-Jiménez, and Natalia Romero-Franco. 2025. "Pain Neuroscience Education to Reduce Catastrophizing: A Parallel Randomized Trial in Youth Athletes" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179701
APA StyleSastre-Munar, A., Pades-Jiménez, A., & Romero-Franco, N. (2025). Pain Neuroscience Education to Reduce Catastrophizing: A Parallel Randomized Trial in Youth Athletes. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9701. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179701






