Comparative Study on Prediction Methods for Water Inflow in Regional High-Intensity Water Inrush Mine Clusters: A Case Study of Xiaozhuang Coal Mine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
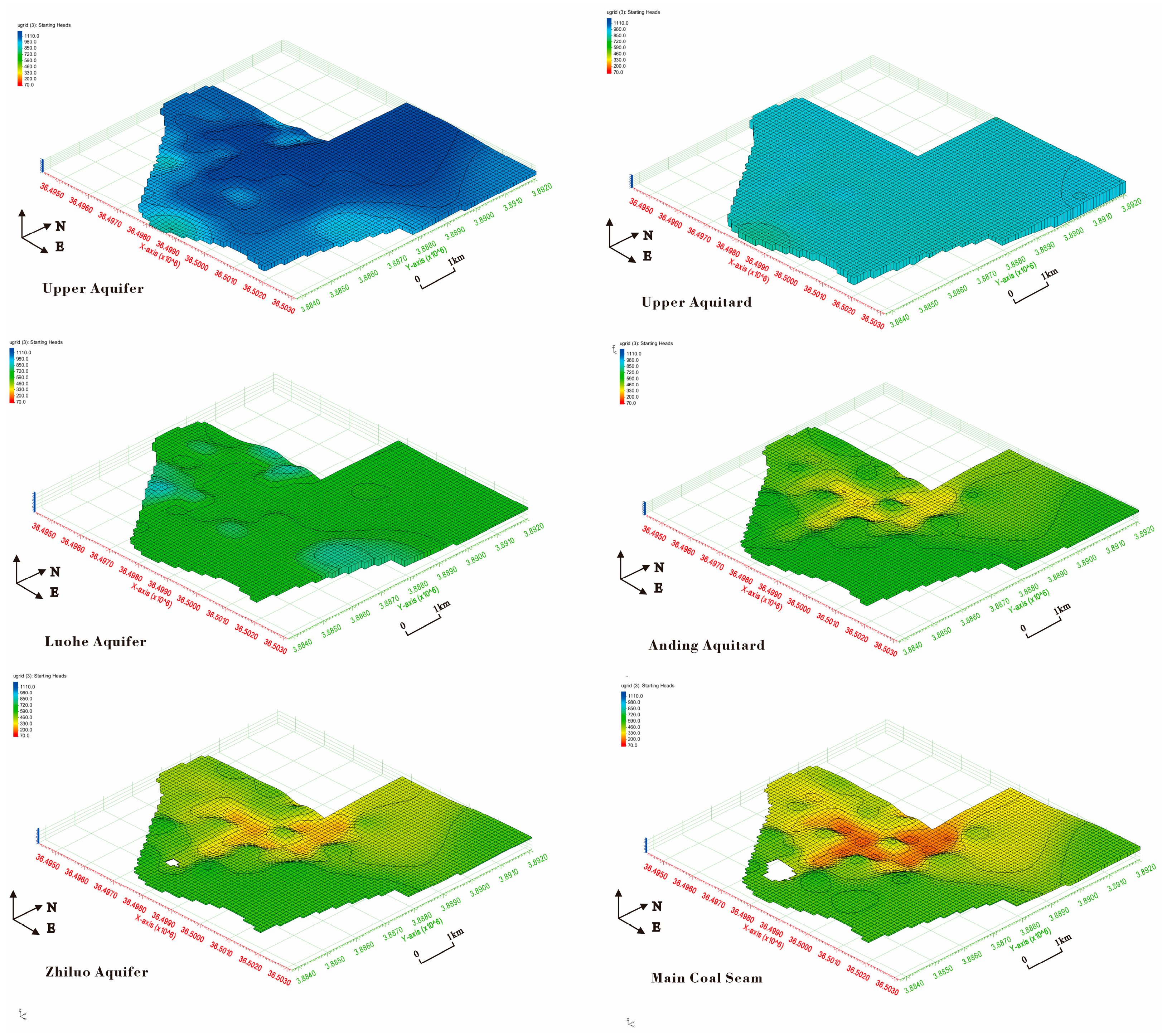
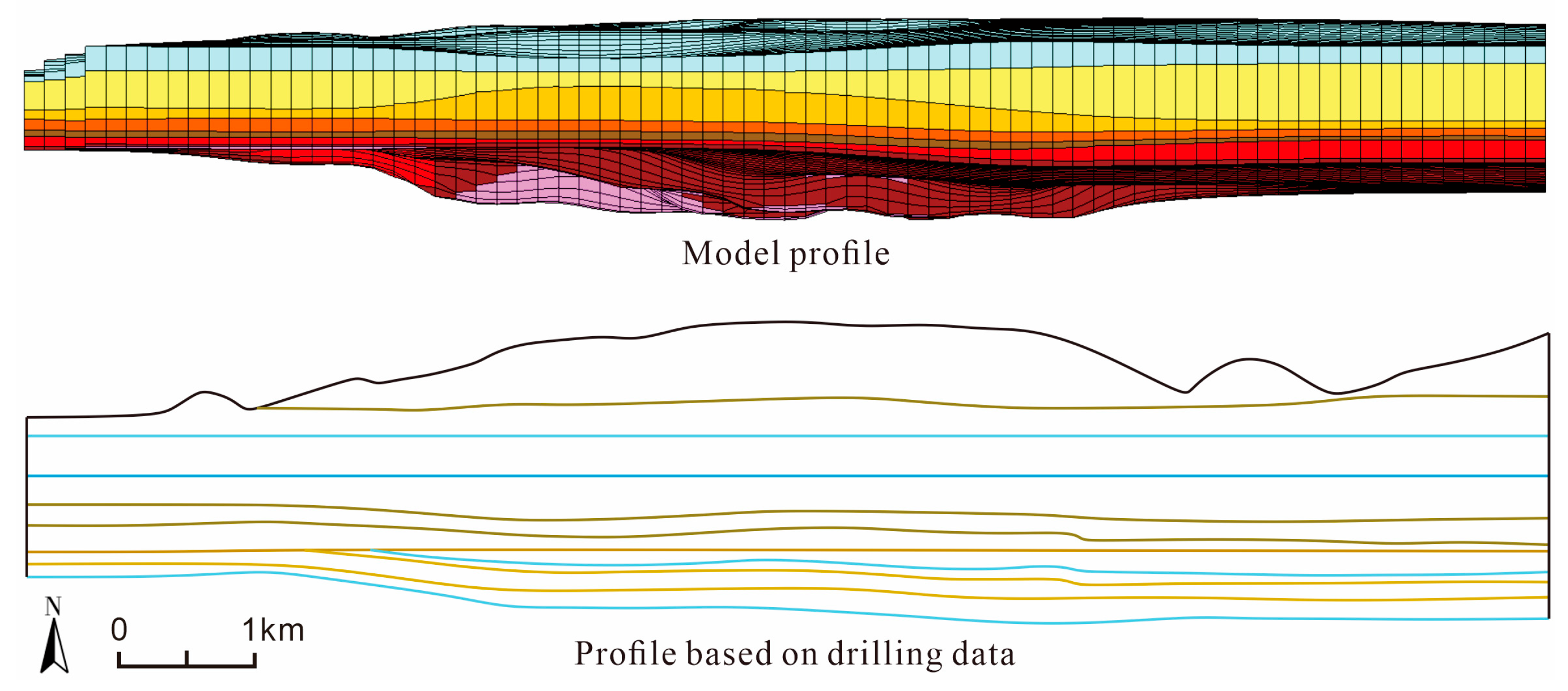
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
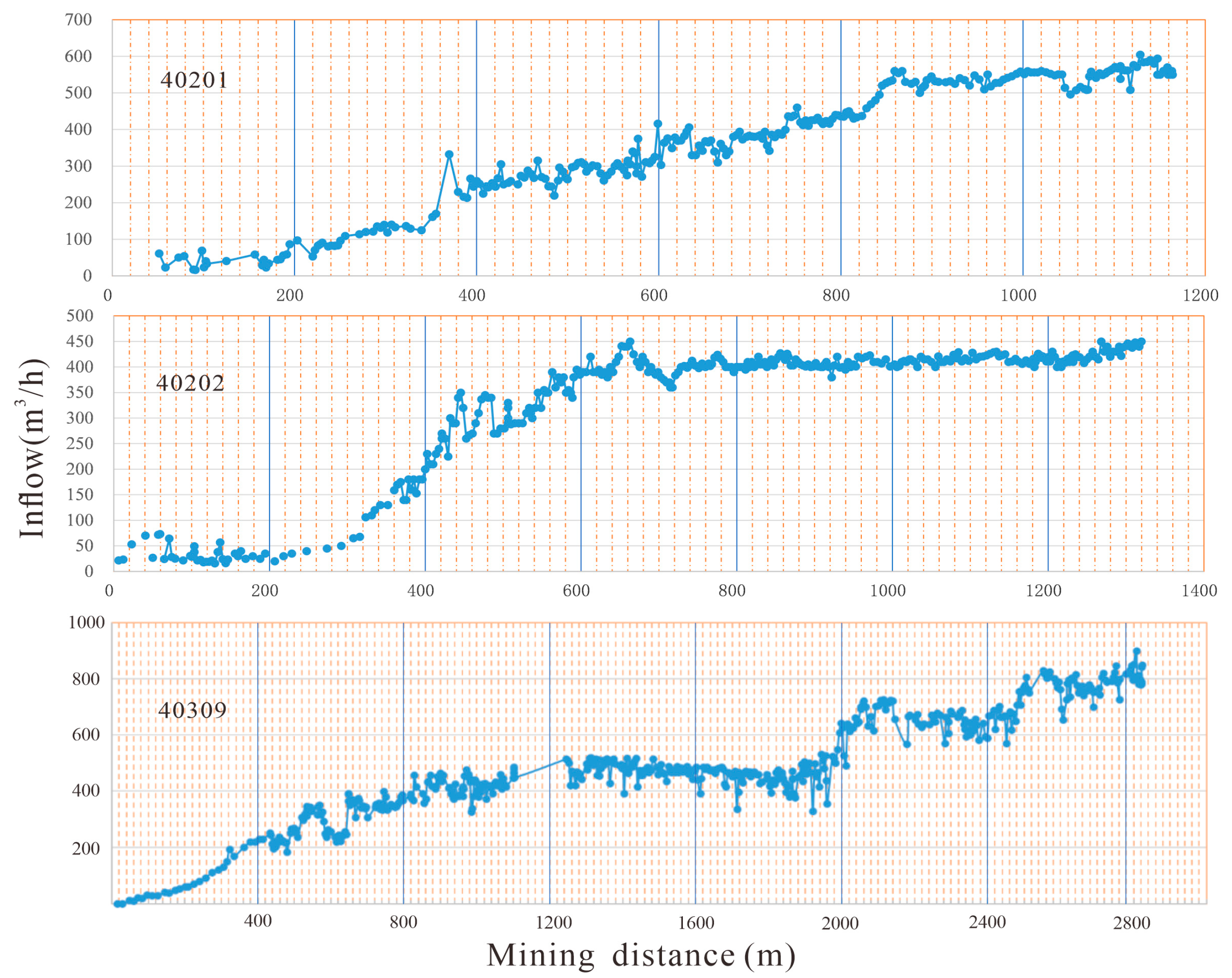
3. Results
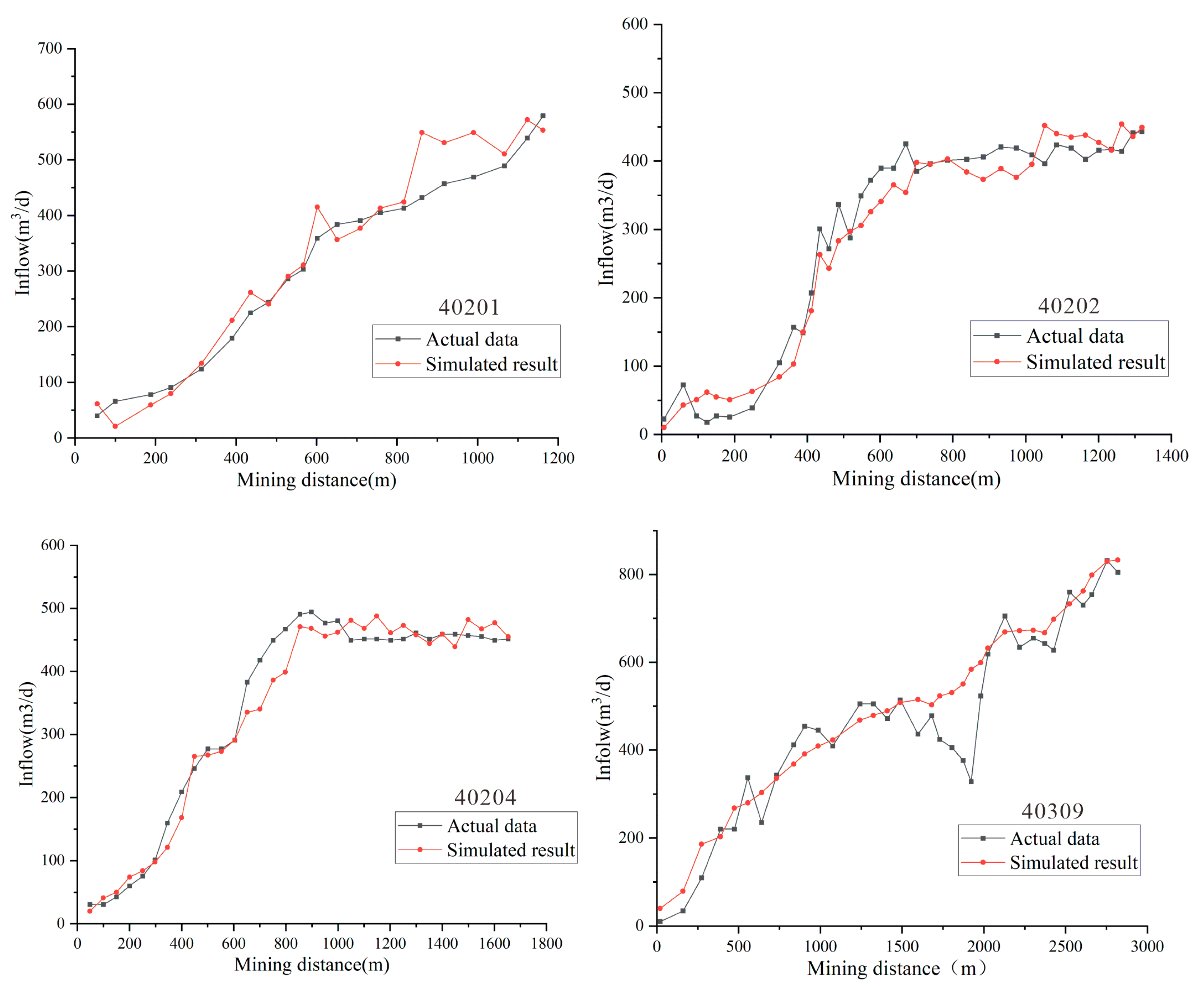
- (1)
- Hydrogeological Analogy Method
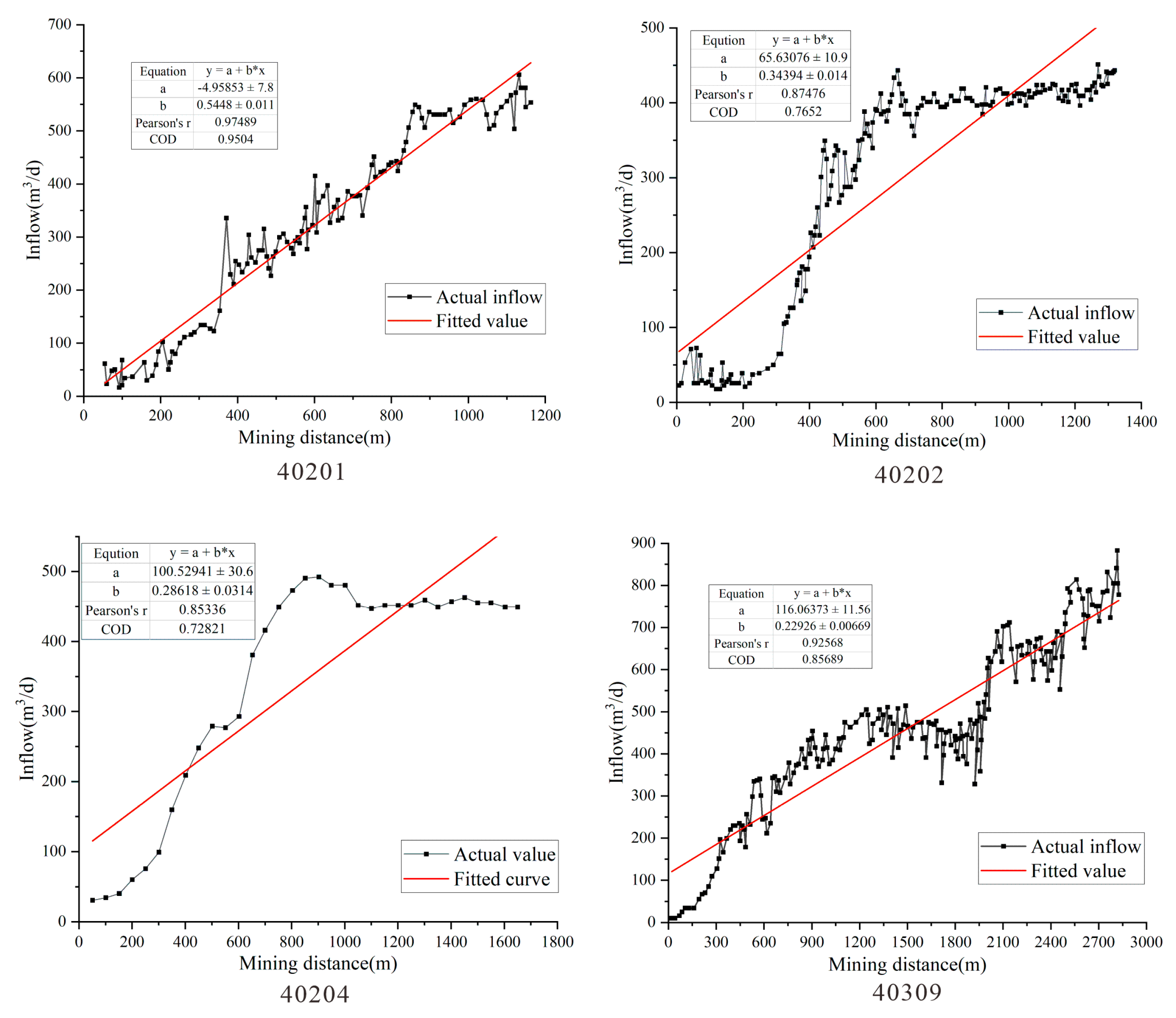
- (2)
- Dynamic Water Inflow Prediction Method
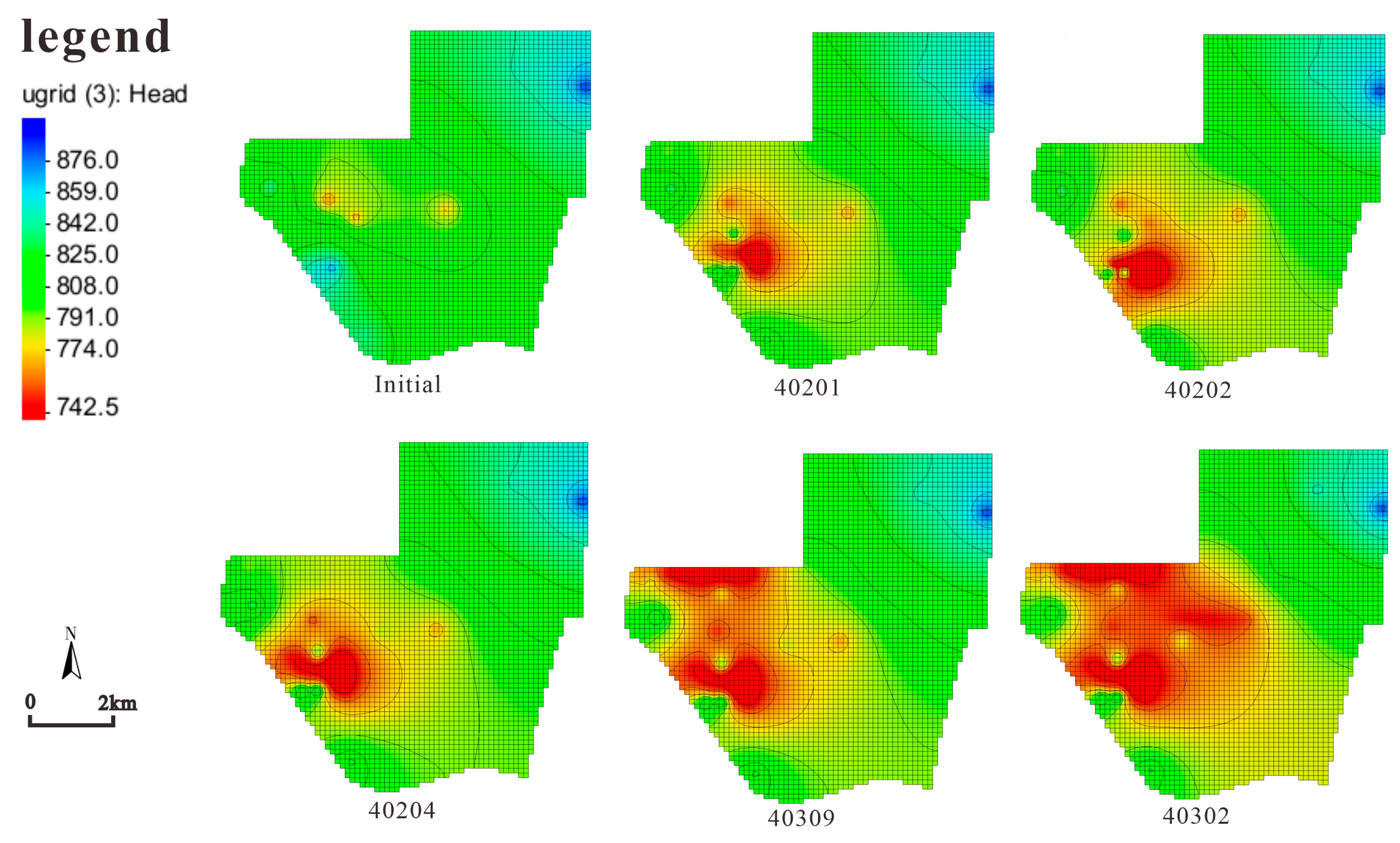
- (3)
- Numerical Simulation Method
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance Discrepancy Between Methods
4.2. Key Reasons for Performance Differences
4.3. Implications for Hazard Mitigation Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, D.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive caving water reduction mining technology for thick coal seams in extremely thick sandstone aquifers. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 88–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, V.d.O.G.; Castro, P.M.G.d.; Petesse, M.L.; Ferreira, C.M. Mining disaster in Brumadinho (Brazil): Social vulnerability from the perspective of the fisherman community. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 112, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Lai, X.; Tao, M.; Momeni, A.; Zhang, Q. Dynamic mechanical mechanism and optimization approach of roadway surrounding coal water infusion for dynamic disaster prevention. Measurement 2023, 223, 113639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, S.; Bao, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Response Characteristics and Water Inflow Prediction of Complex Groundwater Systems under High-Intensity Coal Seam Mining Conditions. Water 2023, 15, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dong, D.; Hu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wei, Z. Numerical Simulations of How Staged Dewatering and Mining Influence Surface Subsidence. Mine Water Environ. 2022, 41, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Dong, D.; Hu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, L. A Study of Interbedded Groundwater Contamination in a Mining Area and the Process of Grouting Composite Failure. Mine Water Environ. 2023, 42, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzy, A.; Malinowska, A.A. Assessment of the Impact of the Spatial Extent of Land Subsidence and Aquifer System Drainage Induced by Underground Mining. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Q.; Yin, S.; Dong, S.; Dai, Z.; Soltanian, M.R. Predicting mine water inrush accidents based on water level anomalies of borehole groups using long short-term memory and isolation forest. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Dong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Risk assessment of disaster chain in multi-seam mining beneath gully topography. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 111, 104750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yin, S.; Dai, Z.; Lian, H.; Bu, C. Multi-Factor Prediction of Water Inflow from the Working Face Based on an Improved SSA-RG-MHA Model. Water 2024, 16, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yin, H.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D.; Ding, H.; Lu, C.; Wang, Y. Quantitative prediction model and prewarning system of water yield capacity (WYC) from coal seam roof based on deep learning and joint advanced detection. Energy 2024, 290, 130200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Wu, J.; Long, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, H. Integral delay inspired deep learning model for single pool water level prediction. J. Hydrol. 2025, 659, 133328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Ghafourian, H.; Hussein Mohammed, A.; Rezaei, N.; Hashim Ibrahim, H.; Rashidi, S. Predicting tunnel water inflow using a machine learning-based solution to improve tunnel construction safety. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 40, 100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cai, M.; Dong, S.; Yin, S.; Xiao, T.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Reza Soltanian, M. An upscaling approach to predict mine water inflow from roof sandstone aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadirianniari, S.; McDougall, S.; Eberhardt, E.; Varian, J.; Llewelyn, K.; Campbell, R.; Moss, A. Statistical analysis of the impact of ore draw strategies on wet inrush hazard susceptibility in a panel cave mine. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 174, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, S.; Hu, S.; Dong, D.; Jiang, D.; Cao, C.; Lin, G.; Fu, J. Simulation of surface water–groundwater interaction in coal mining subsidence areas: A case study of the Kuye River Basin in China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 659, 133243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Mohammadi, M.; M Gharrib Noori, K.; Khishe, M.; Hashim Ibrahim, H.; Farid Hama Ali, H.; Nariman Abdulhamid, S. Presenting the best prediction model of water inflow into drill and blast tunnels among several machine learning techniques. Autom. Constr. 2021, 127, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Yin, H.; Xie, D.; Dong, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J. Prediction of dominant roof water inrush windows and analysis of control target area based on set pair variable weight—Forward correlation cloud model. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 483, 144253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wu, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Mei, A.; Yang, G.; Hua, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluating the impact of coal seam roof groundwater using variable weights theory: A special emphasis on skylight-type water inrush pattern. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, S.; Yan, T.; Yao, H.; Yang, S.; Kang, J.; Xia, X.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; et al. Integrating Microseismic Monitoring for Predicting Water Inrush Hazards in Coal Mines. Water 2024, 16, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dong, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R. Water Inflow Forecasting Based on Visual MODFLOW and GS-SARIMA-LSTM Methods. Water 2024, 16, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Xu, J.; Peng, S.; Yang, H.; Jiao, F.; Zhou, B.; Yan, F. Dynamic behavior of outburst two-phase flow in a coal mine T-shaped roadway: The formation of impact airflow and its disaster-causing effect. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jin, D.; Hu, W.; Dong, Y.; Cao, H. Research on the Dynamic Attenuation Dynamics of Double Indices of Water Gushing in the Goaf of Coal Mine Face Push Mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 2587–2594. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Sha, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X.; Ren, S.; Liu, R.; Li, S. Numerical simulation of the interaction between mine water drainage and recharge: A case study of Wutongzhuang coal mine in Heibei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Wu, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Gu, L. Enhancing mine groundwater system prediction: Full-process simulation of mining-induced spatio-temporal variations in hydraulic conductivities via modularized modeling. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 1625–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

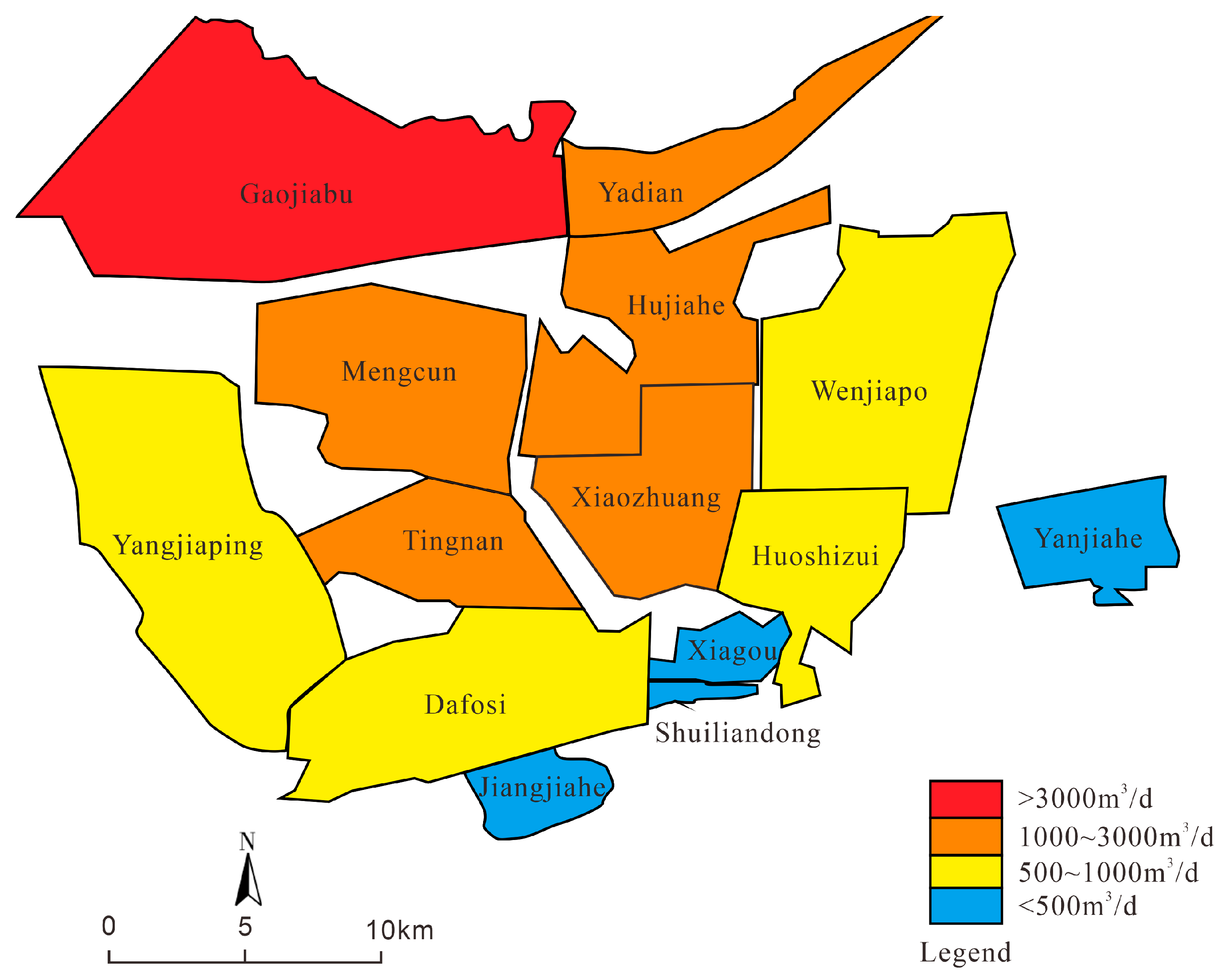
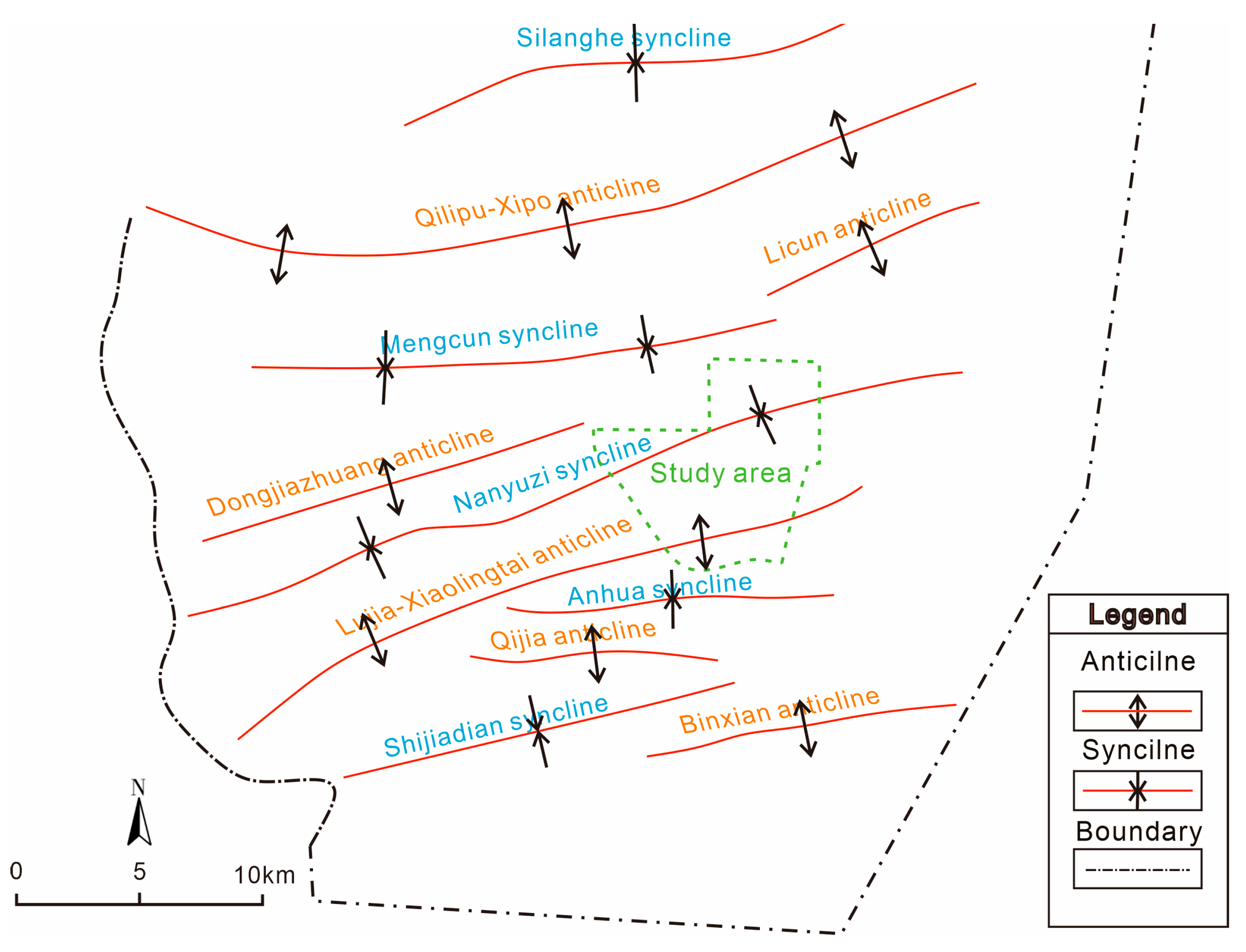
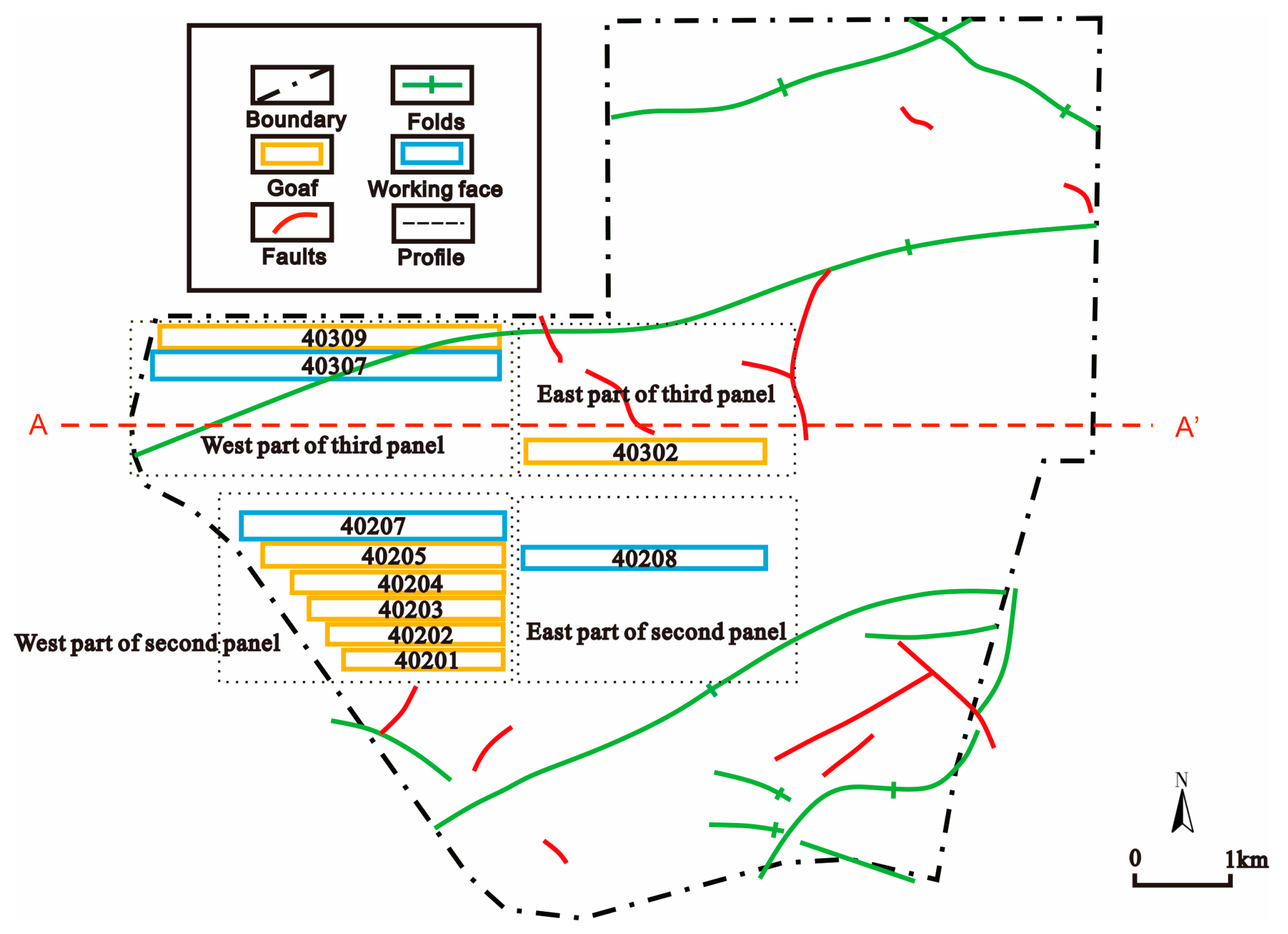



| Formation | Borehole | Water Level (m) | Permeability Coefficient (m/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luohe | 2-6 | 843.08 | 0.71567 |
| 2-5 | 847.28 | 0.787 | |
| DG3 | 844.87 | 0.16294 | |
| XZ1 | 763.06 | 0.2244 | |
| XZ2 | 748.44 | 0.05871 | |
| XZ1903 | 836.11 | 0.1667 | |
| XZ1907 | 845.69 | 0.0922 | |
| XZ1911 | 842.85 | 0.004461 | |
| XZ2101 | 748.46 | 0.104764 | |
| XZ2103 | 785.581 | 0.068186 | |
| Yijun | DG3 | 790.97 | 0.03425 |
| XZ1 | 620.95 | 0.00325 | |
| XZ2 | 617.54 | 0.00557 | |
| XZ1903 | 837.19 | 0.0007 | |
| XZ1911 | 803.3 | 0.003974 | |
| Zhiluo-Yanan | 2-6 | 809.96 | 0.00174 |
| 2-5 | 857.06 | 0.00081 | |
| DG4 | 776.69 | 0.0002 | |
| XZ1907 | 868.03 | 0.000203 |
| Working Face | Mining Period | Mining Length (m) | Mining Width (m) | Mining Thickness (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40201 | 2014.08–2015.07 | 1170 | 174 | 12.5 |
| 40202 | 2015.08–2016.09 | 1348 | 174 | 14.3 |
| 40203 | 2016.09–2017.12 | 1504 | 195 | 14.8 |
| 40204 | 2017.11–2019.03 | 1646 | 195 | 14 |
| 40309 | 2019.03–2021.03 | 2824 | 195 | 14.8 |
| 40205 | 2021.03–2022.07 | 1890 | 196 | 14 |
| 40302 | 2022.08–2023.09 | 1544 | 196 | 14 |
| Model Stratum | Corresponding Formation | Specific Yield (L/s·m) | Initial Permeability (m/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Aquifer | Quaternary Alluvial/ Pleistocene Loess | 0.0810 | 0.0589 |
| Upper Aquitard | Lower Cretaceous Huachi Formation | / | 0.0001 |
| Luohe Formation Aquifer | Lower Cretaceous Sandstone | 0.2214 | 0.0220 |
| Anding Formation | Middle Jurassic Mudstone Aquitard | / | 0.0001 |
| Zhiluo Formation Aquifer | Middle Jurassic Sandstone | 0.0026 | 0.0164 |
| Main Coal Seam | 4th Coal Seam | / | / |
| Method | R2 Range | Best For | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogeological Analogy | 0.72–0.95 | First mining faces (undisturbed conditions) | Fails for non-first mining faces |
| Dynamic Prediction | 0.88–0.96 | Non-first faces (high lateral recharge) | Requires continuous data updates |
| Numerical Simulation | 0.89–0.96 | All scenarios (mechanistic rigor) | Computationally intensive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, J.; Dong, S.; Guo, X.; Liu, B. Comparative Study on Prediction Methods for Water Inflow in Regional High-Intensity Water Inrush Mine Clusters: A Case Study of Xiaozhuang Coal Mine. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179472
Ding J, Dong S, Guo X, Liu B. Comparative Study on Prediction Methods for Water Inflow in Regional High-Intensity Water Inrush Mine Clusters: A Case Study of Xiaozhuang Coal Mine. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179472
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Jia, Shuning Dong, Xiaoming Guo, and Bo Liu. 2025. "Comparative Study on Prediction Methods for Water Inflow in Regional High-Intensity Water Inrush Mine Clusters: A Case Study of Xiaozhuang Coal Mine" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179472
APA StyleDing, J., Dong, S., Guo, X., & Liu, B. (2025). Comparative Study on Prediction Methods for Water Inflow in Regional High-Intensity Water Inrush Mine Clusters: A Case Study of Xiaozhuang Coal Mine. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9472. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179472






