Open-Pit Slope Stability Analysis Integrating Empirical Models and Multi-Source Monitoring Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Empirical Model
2.2. Method for Displacement Detection of DTMs
2.2.1. Monitoring Measurements to Construct DTM
- (1)
- SAR monitoring
- (2)
- GNSS monitoring
- (3)
- Video monitoring
2.2.2. Transforming SAR Data to the GNSS Coordinate System
2.2.3. Transforming Video Data to the GNSS Coordinate System
- (1)
- Spatiotemporal Synchronization and Geometric Correction of Video Data
- (2)
- Multi-Scale Feature Extraction and Sparse 3D Reconstruction
- (3)
- Coarse and Fine Registration for Coordinate Unification
2.3. Constructing the DTM
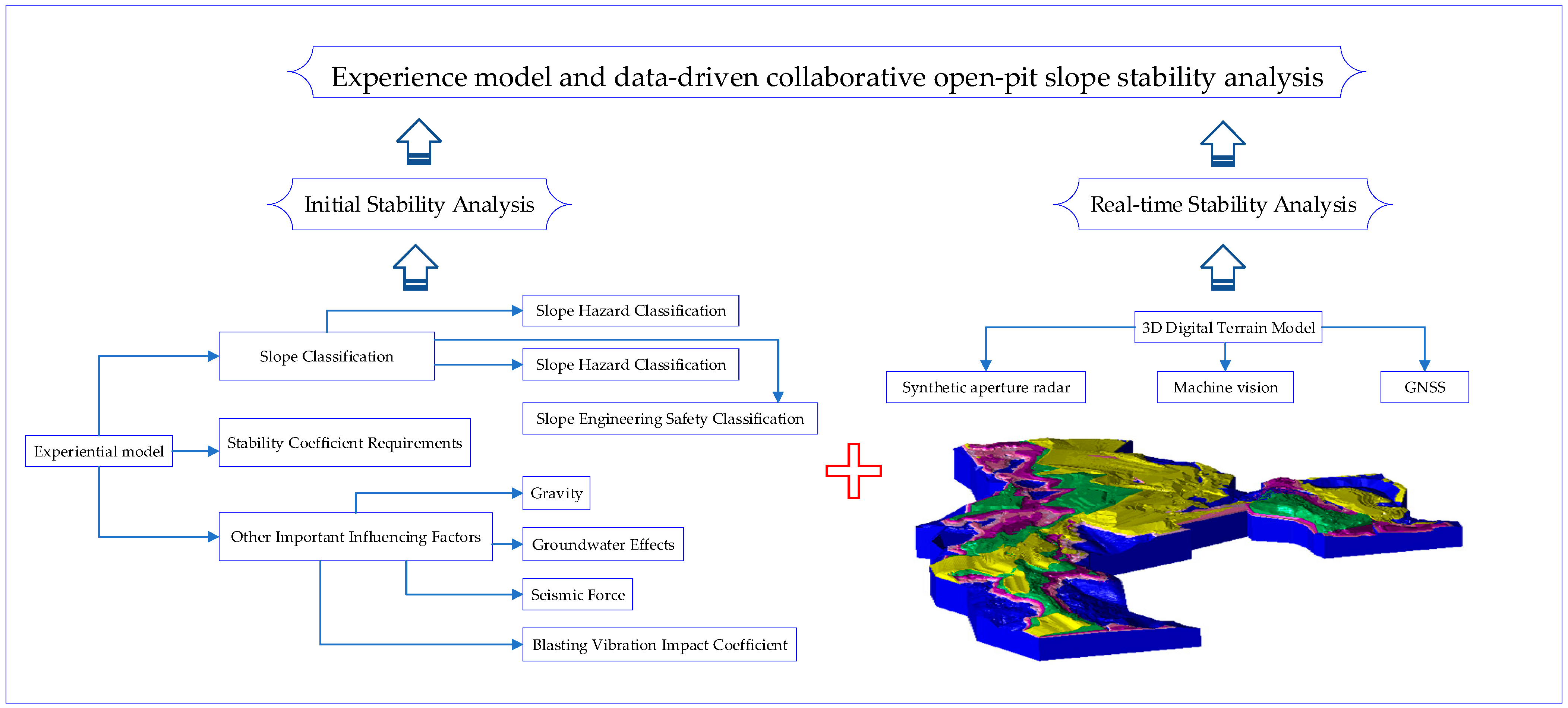
2.4. Main Contributions of the Proposed Method
- (1)
- Multi-source fusion-based dynamic 3D modeling and feature-driven sensitive area identification: This paper constructs a mine-specific DTM by fusing SAR (subsurface tomography), a GNSS (precision positioning), and machine vision (surface micro-deformation); reconstructs discrete monitoring points into continuous 3D geological entities through stratum profile inversion; proposes a convex hull-displacement dual-criterion identification method to extract terrain skeletons; captures primary peak points in 3D topography; and enables dynamic real-time identification of sensitive monitoring zones.
- (2)
- Sensitive-area-driven targeted reconstruction of traditional mechanical methods: This paper establishes an “entire-domain scanning and focused breakthrough” analysis paradigm, concentrating precision analysis on sensitive areas and enhancing analytical efficiency. It also optimizes stability analysis for sensitive regions to reduce computational costs for large-scale mine slope monitoring and overcome resource bottlenecks in conventional methods.
3. Data
3.1. Mining Area
3.2. Block Density Test
3.3. Single-Axis Compression Deformation Test
3.4. Split Tensile Test
3.5. Shear Strength Test
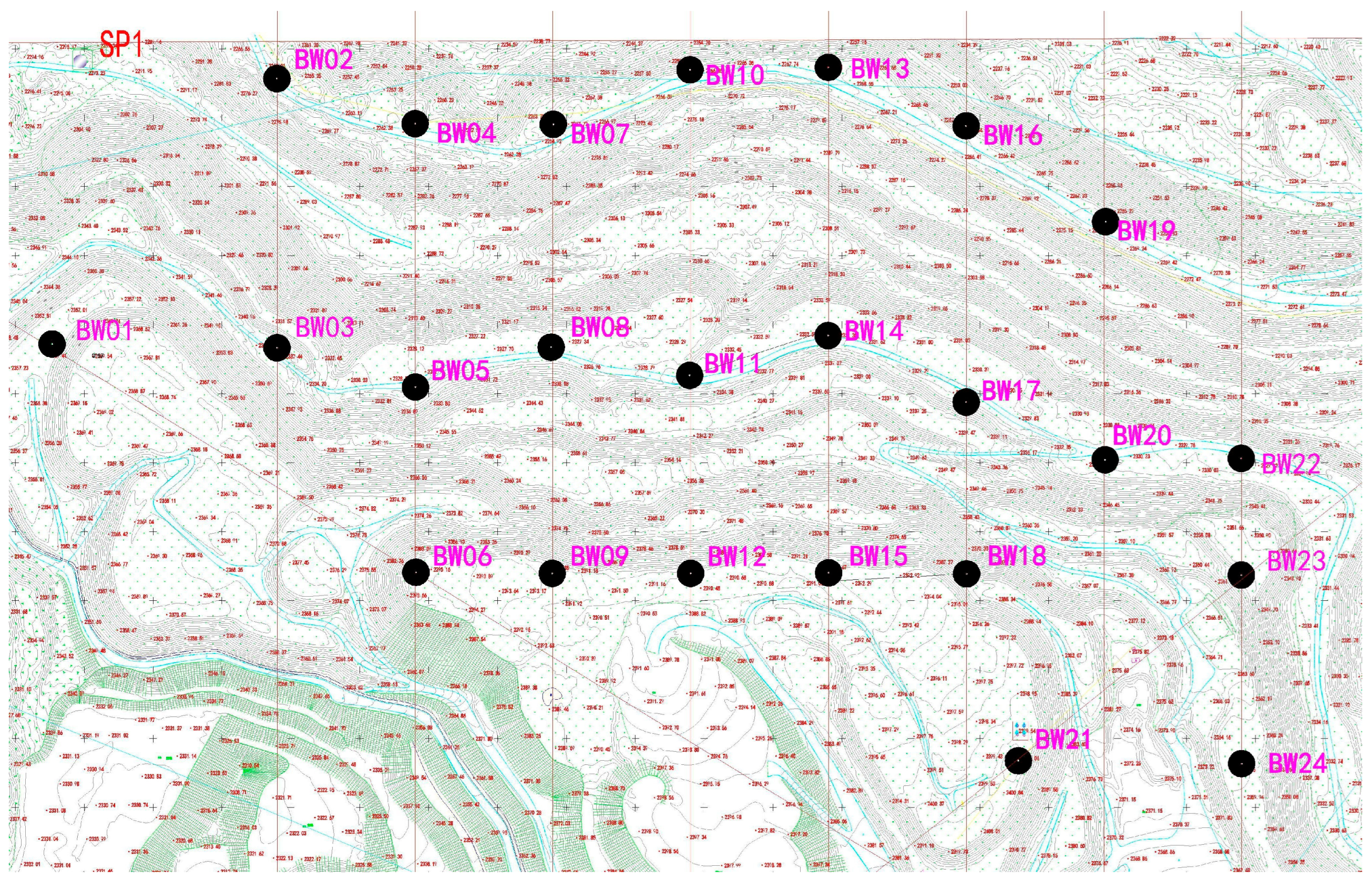
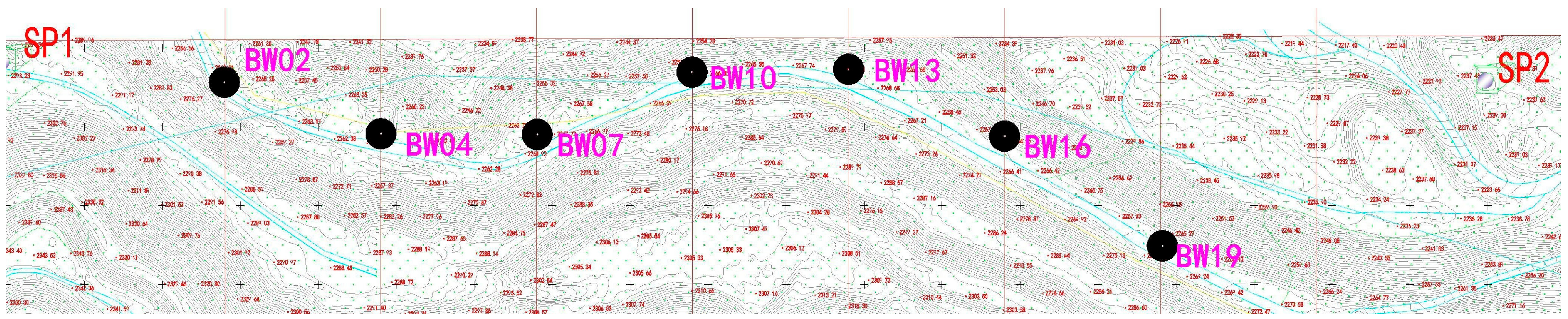
3.6. GNSS Monitoring Setting
3.7. Video Monitoring Setting
3.8. SAR Monitoring Setting
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Results of the Empirical Model Discrimination Method
4.1.1. Calculation of Empirical Model Parameters
- (1)
- (2)
- Groundwater Conditions
- (3)
- Comprehensive Horizontal Seismic Coefficient
- (4)
- Blasting Vibration Impact Coefficient
4.1.2. Stability Analysis Results of the Experience Model
- (1)
- Slope Stability Analysis of the Current Situation in the First Mining Area
- (2)
- Slope Stability Analysis of the Current Situation in the Second Mining Area
- (3)
- Slope Stability Analysis of the Current Situation in the Third Mining Area
- (4)
- Slope Stability Analysis of the Current Situation in the Fourth Mining Area
- (5)
- Slope Stability Analysis of the Current Situation in the Southern Area
4.2. Stability Analysis Results of the DTM
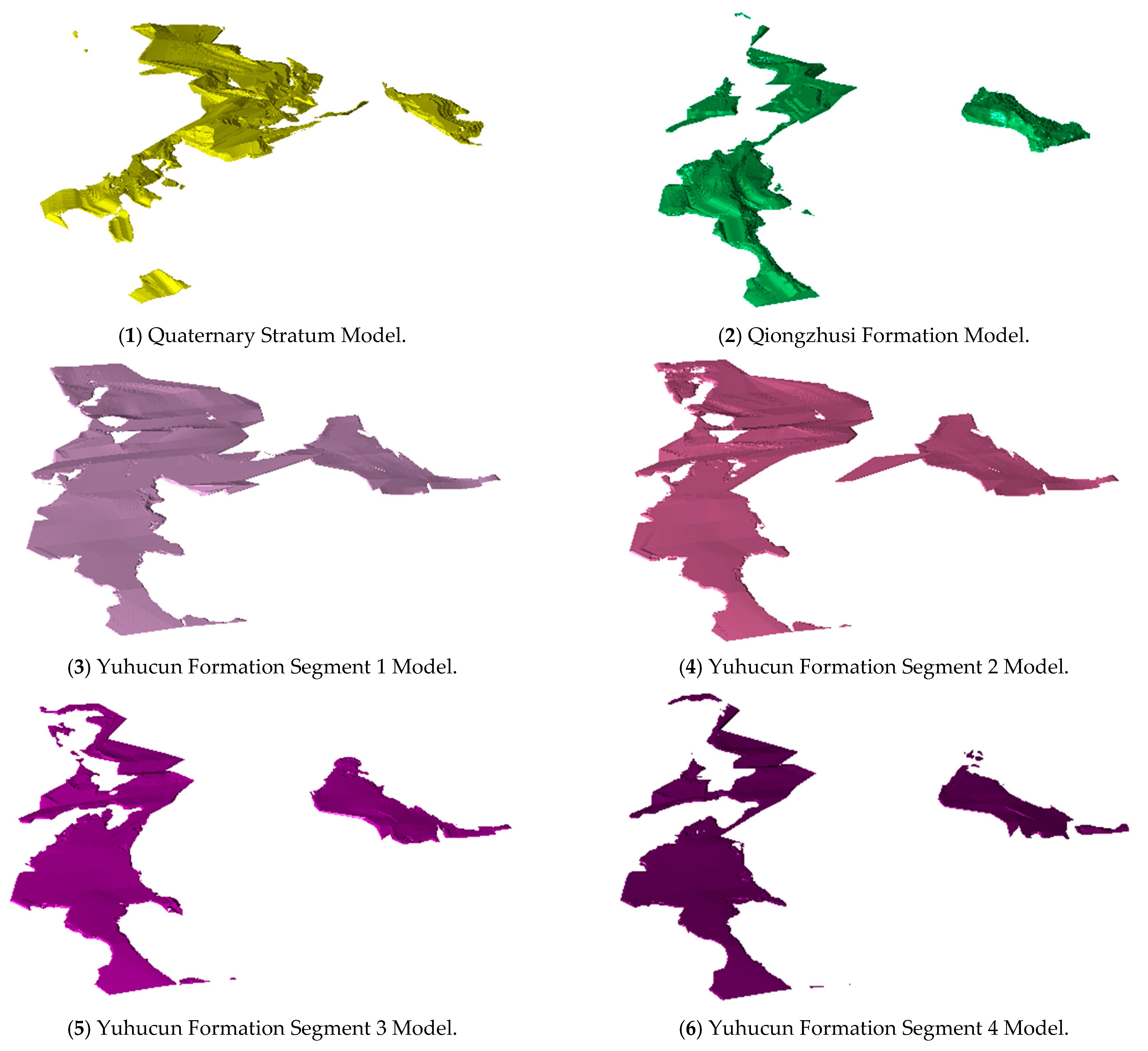
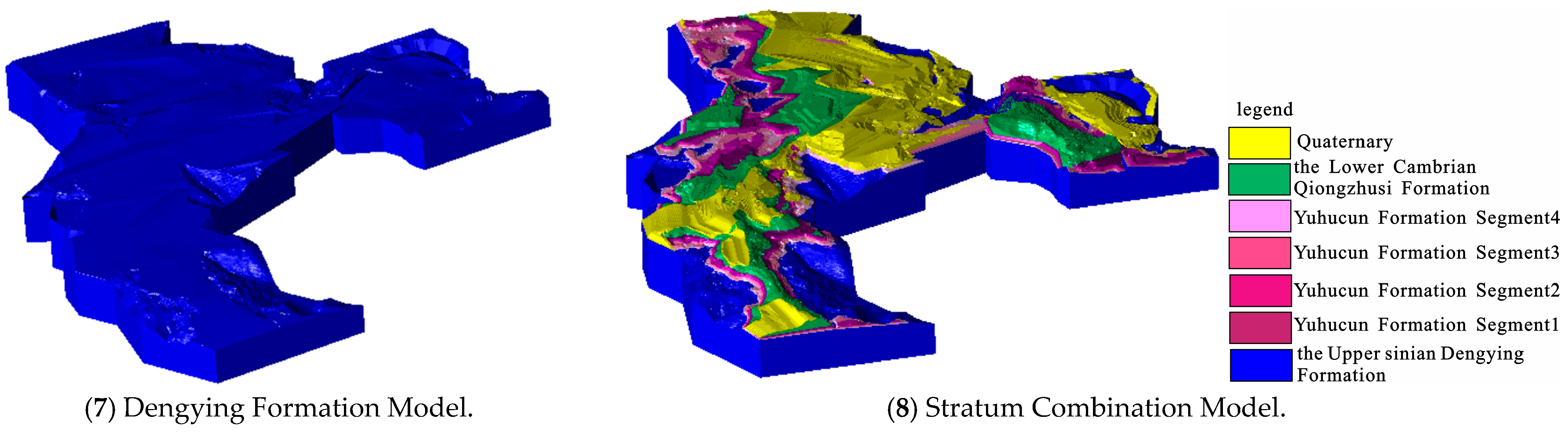
4.2.1. Stratigraphic Model Visualization
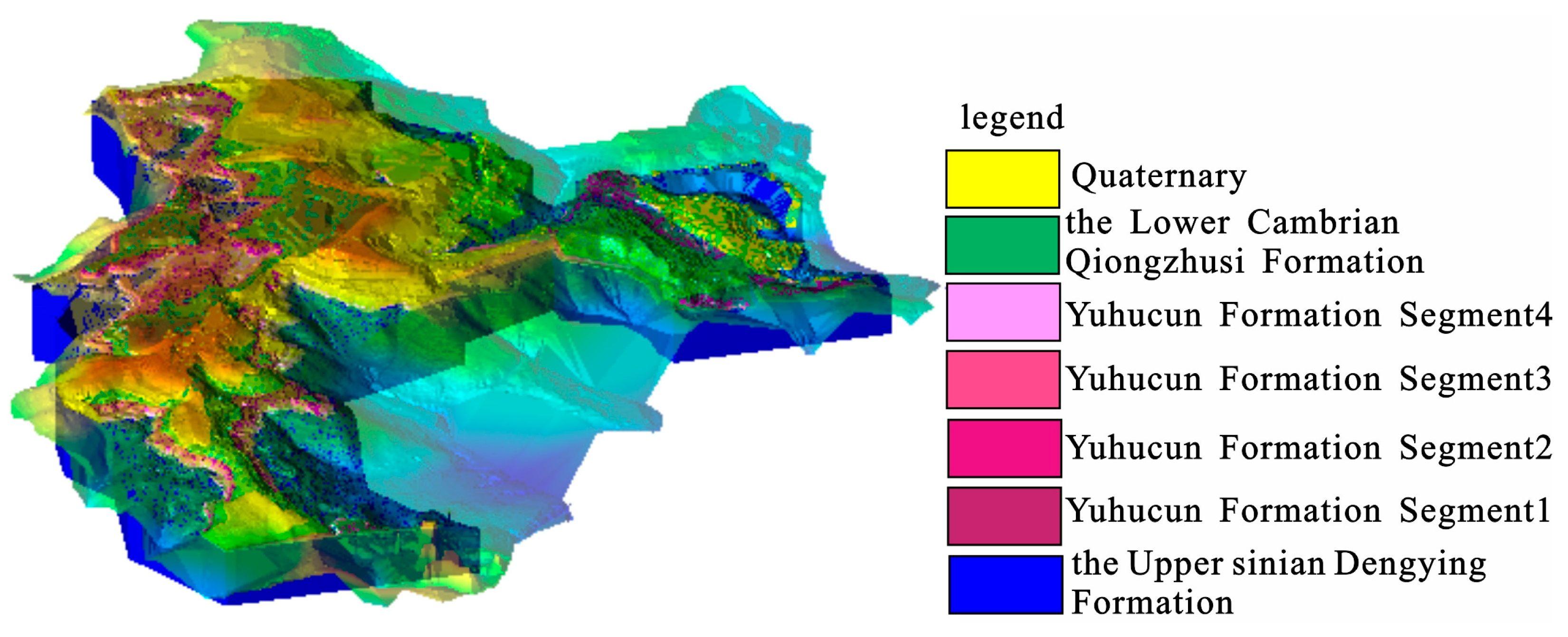
4.2.2. Overall DTM Visualization and Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Critical Slip Surface Characteristics and Stability Mechanisms
5.2. Parametric Uncertainty and Sensitivity
5.3. Temporal Dynamics from Integrated Monitoring
5.4. Geomechanical Implications of Stratigraphic Heterogeneity
5.5. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Gentle and symmetrical anticline structure: The mining area generally exhibits a gently inclined and symmetrical anticline structure. This geological structure inherently possesses good stability. The arcuate structure of the anticline helps distribute and resist stresses on the slope, reducing the risk of slope sliding.
- (2)
- Consistency between the orebody (layer) and ore-bearing rock series: The basic morphology and occurrence of the orebody (layer) are consistent with the ore-bearing rock series, which means that the mechanical properties of the orebody and surrounding rocks are similar, contributing to the overall stability of the slope.
- (3)
- Complex morphology of the outcrop line: Although the outcrop line of the orebody (layer) presents a complex morphology due to surface weathering erosion, topographic cutting, and mining activities, these morphological changes increase the roughness of the slope surface to some extent, which helps enhance the friction between the slope and soil or rock, thereby improving slope stability.
- (4)
- Development of folds in the shallow outcrops of the orebody (layer): The development of folds in the shallow outcrops of the orebody (layer) increases the complexity of the orebody morphology but also provides more support points vertically along the slope, helping distribute stresses on the slope and reducing the risk of landslides.
- (5)
- Mechanical properties of phosphatic rock: Phosphatic rocks within the phosphorus-bearing rock series generally exhibit good mechanical properties, such as high compressive and shear strengths. These properties help resist stresses and deformations on the slope, thereby enhancing slope stability.
- (6)
- Impact of layered structure: The phosphorus-bearing rock series is divided into multiple layers, such as the siliceous dolomite section of the roof, the upper ore layer of phosphatic rock, etc. These layered structures form multiple potential support surfaces within the slope, contributing to increased slope stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Empirical Model
Appendix A.1.1. Slope Classification
- (1)
- Slope Height Classification
- Ultra-high slopes: H > 500 m;
- High slopes: 300 m < H ≤ 500 m;
- Slopes: 100 m < H ≤ 300 m;
- Low slopes: H ≤ 100 m.
- (2)
- Slope Hazard Classification
| Slope Hazard Classification | I | II | III | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Possible casualties | Casualties involved | Injuries reported | No casualties | |
| Potential economic losses (USD) | Direct | ≥1,000,000 | 500,000~1,000,000 | ≤500,000 |
| Indirect | ≥10,000,000 | 5,000,000~10,000,000 | ≤5,000,000 | |
| Comprehensive assessment | Very serious | Serious | Not serious | |
- (3)
- Slope Engineering Safety Classification
| Slope Engineering Safety Classification | Slope Height H (m) | Slope Hazard Classification |
|---|---|---|
| I | H > 500 m | I, II, III |
| 300 m < H ≤ 500 m | I, II | |
| 100 m < H ≤ 300 m | I | |
| II | 300 m < H ≤ 500 m | III |
| 100 m < H ≤ 300 m | II, III | |
| H ≤ 100 m | I | |
| III | 100 m < H ≤ 300 m | III |
| H ≤ 100 m | II, III |
Appendix A.1.2. Stability Coefficient Requirements
| Slope Engineering Safety Classification | The Safety Factor Slope Engineering | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Combination I | Load Combination II | Load Combination III | |
| I | 1.25–1.20 | 1.23–1.18 | 1.20–1.15 |
| II | 1.20–1.15 | 1.18–1.13 | 1.15–1.10 |
| III | 1.15–1.10 | 1.13–1.08 | 1.10–1.05 |
Appendix A.1.3. Other Important Influencing Factors
- (1)
- Gravity
- (2)
- Groundwater Effects
- (3)
- Seismic Force
- (4)
- Blasting Vibration Impact Coefficient
Appendix A.1.4. Calculating the Safety Factor
- (1)
- Bishop Method
- (2)
- Morgenstern–Price (M-P) Method
Appendix A.2. Basic Test Results
| Zoning | Profile Number | Top Elevation (m) | Bottom Elevation (m) | Slope Height (m) | Slope Angle (°) | Main Lithology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | I-1 | 2405 | 2326 | 79 | 36 | Sandstone, Phosphate Rock, Dolomite |
| II | II-1 | 2373 | 2308 | 65 | 15 | |
| III | III-1 | 2403 | 2317 | 86 | 16 | Quaternary, Sandstone, Phosphate Rock, Dolomite |
| IV | IV-1 | 2405 | 2265 | 140 | 22 | Sandstone, Phosphate Rock, Dolomite |
| IV-2 | 2437 | 2385 | 52 | 16 | ||
| V | V-1 | 2358 | 2255 | 103 | 16 | |
| V-2 | 2328 | 2206 | 122 | 29 | Quaternary, Sandstone, Phosphate Rock, Dolomite |
| Rock Texture and Condition | Sample Number | Diameter (cm) | Height (cm) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Destruction Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite (Saturated) | B1 | 4.85 | 10.7 | 30.3 | Longitudinal splitting |
| B2 | 4.87 | 9.7 | 18.3 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B3 | 4.85 | 9.2 | 47.2 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B4 | 4.85 | 10.3 | 34.5 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B5 | 4.85 | 10.3 | 33.8 | Local longitudinal splitting | |
| B6 | 4.85 | 10.3 | 27.7 | Local longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 32.0 | / | |||
| Dolomite (Natural) | B1 | 4.85 | 9.9 | 44.0 | Longitudinal splitting |
| B2 | 4.85 | 9.6 | 63.1 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B3 | 4.85 | 9.0 | 39.5 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B4 | 4.88 | 9.6 | 68.4 | Local longitudinal splitting | |
| B5 | 4.87 | 7.2 | 26.2 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B6 | 4.85 | 7.0 | 29.1 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 45.1 | / | |||
| Phosphorite (Saturated) | L1 | 4.86 | 10.3 | 40.9 | Longitudinal splitting |
| L2 | 4.85 | 8.9 | 36.0 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L3 | 4.88 | 9.6 | 48.0 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L4 | 4.88 | 9.6 | 36.3 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L5 | 4.88 | 9.1 | 46.2 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L6 | 4.88 | 9.1 | 28.2 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 39.3 | / | |||
| Phosphorite (Natural) | L1 | 4.85 | 9.1 | 43.7 | Longitudinal splitting |
| L2 | 4.84 | 8.4 | 65.7 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L3 | / | / | / | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L4 | 4.85 | 10.3 | 46.8 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L5 | 4.87 | 10.3 | 61.0 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L6 | 4.87 | 10.3 | 44.0 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 52.2 | / | |||
| Sandstone (Saturated) | S1 | 4.88 | 10.2 | 46.2 | Longitudinal splitting |
| S2 | 4.87 | 10.2 | 31.1 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| S3 | 4.87 | 10.2 | 37.9 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 38.4 | / | |||
| Sandstone (Natural) | S1 | 4.88 | 10.0 | 60.9 | Local longitudinal splitting |
| S2 | 4.88 | 9.9 | 56.6 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| S3 | 4.85 | 10.2 | 66.0 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 61.2 | / | |||
| Rock Texture or Lithology | Sample Number | Shear Modulus of Elasticity E50 (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio μ50 | Tangent Modulus of Elasticity Ee (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio μe | Destruction Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite | B1 | 29.0 | 0.25 | 30.2 | 0.36 | Longitudinal splitting |
| B2 | 22.6 | 0.32 | 23.4 | 0.40 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B3 | 38.4 | 0.22 | 35.3 | 0.24 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B4 | 42.7 | 0.29 | 38.9 | 0.41 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| B5 | 38.5 | 0.23 | 42.8 | 0.24 | Local longitudinal splitting | |
| B6 | 40.5 | 0.19 | 34.0 | 0.16 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 35.3 | 0.25 | 34.1 | 0.31 | / | |
| Phosphorite | L1 | 31.9 | 0.23 | 30.4 | 0.24 | Longitudinal splitting |
| L2 | 50.4 | 0.19 | 52.1 | 0.22 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L3 | 24.3 | 0.22 | 24.4 | 0.26 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L4 | 64.6 | 0.25 | 54.3 | 0.23 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L5 | 48.1 | 0.22 | 65.5 | 0.27 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| L6 | 19.0 | 0.22 | 28.7 | 0.25 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 39.7 | 0.22 | 42.57 | 0.24 | / | |
| Quartz Sandstone | S1 | 46.2 | 0.20 | 28.2 | 0.24 | Longitudinal splitting |
| S2 | 31.1 | 0.26 | 33.8 | 0.24 | Longitudinal splitting | |
| S3 | 37.9 | 0.25 | 37.7 | 0.34 | Local longitudinal splitting | |
| Mean | 38.4 | 0.24 | 33.23 | 0.27 | / |
| Lithology | Sample Number | Diameter (cm) | Height (cm) | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite (Natural) | B1 | 4.88 | 4.52 | 6.27 |
| B2 | 4.85 | 4.30 | 8.41 | |
| B3 | 4.85 | 2.96 | 7.01 | |
| Mean | 4.86 | 3.93 | 7.23 | |
| Dolomite (Saturated) | B1 | 4.85 | 4.70 | 5.10 |
| B2 | 4.85 | 3.00 | 5.95 | |
| B3 | 4.85 | 4.25 | 5.34 | |
| Mean | 4.85 | 3.98 | 5.46 | |
| Phosphate Rock (Natural) | L1 | 4.86 | 4.65 | 1.35 |
| L2 | 4.85 | 4.28 | 1.85 | |
| L3 | 4.85 | 4.30 | 1.67 | |
| L4 | 4.87 | 2.96 | 7.47 | |
| L5 | 4.88 | 4.25 | 7.34 | |
| L6 | 4.88 | 3.02 | 7.03 | |
| Mean | 4.87 | 3.91 | 4.45 | |
| Phosphate Rock (Saturated) | L1 | 4.85 | 2.96 | 1.22 |
| L2 | 4.88 | 4.25 | 1.06 | |
| L3 | 4.85 | 3.02 | 1.34 | |
| L4 | 4.85 | 3.50 | 6.06 | |
| L5 | 4.85 | 4.80 | 6.62 | |
| L6 | 4.85 | 3.42 | 6.83 | |
| Mean | 4.86 | 3.66 | 3.85 | |
| Sandstone (Natural) | S1 | 4.88 | 4.04 | 7.28 |
| S2 | 4.88 | 3.98 | 9.36 | |
| S3 | 4.88 | 3.98 | 8.92 | |
| Mean | 4.88 | 4.00 | 8.52 | |
| Sandstone (Saturated) | S1 | 4.85 | 4.55 | 5.66 |
| S2 | 4.88 | 4.80 | 5.95 | |
| S3 | 4.88 | 4.50 | 5.91 | |
| Mean | 4.87 | 4.62 | 5.84 |
| Lithology | Sample Number | Length (cm) | Width (cm) | Shear Area (cm2) | Shear Stress τ (kPa) | Internal Friction Angle φ (°) | Cohesion C (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolomite | B1 | 5.18 | 5.28 | 27.35 | 58.81 | 40.2 | 3.36 |
| 5.30 | 5.30 | 28.09 | 44.58 | ||||
| B2 | 4.90 | 5.28 | 25.87 | 28.38 | |||
| 5.10 | 5.30 | 27.03 | 30.62 | ||||
| B3 | 5.28 | 5.30 | 27.98 | 13.70 | |||
| 5.30 | 5.30 | 28.09 | 17.24 | ||||
| B4 | 5.32 | 5.28 | 28.09 | 30.54 | |||
| 5.30 | 5.30 | 28.09 | 28.82 | ||||
| B5 | 4.92 | 5.25 | 25.83 | 16.54 | |||
| 5.27 | 5.34 | 28.14 | 20.11 | ||||
| B6 | 5.30 | 5.30 | 28.09 | 11.34 | |||
| 5.25 | 5.30 | 27.82 | 9.62 | ||||
| Phosphate Rock | L4 | 5.30 | 5.35 | 28.35 | 150.09 | 42.7 | 8.90 |
| 5.30 | 5.40 | 28.62 | 137.34 | ||||
| L5 | 5.30 | 5.35 | 28.35 | 126.22 | |||
| 5.30 | 5.32 | 28.20 | 64.62 | ||||
| L6 | 5.35 | 5.38 | 28.78 | 87.76 | |||
| 5.35 | 5.35 | 28.62 | 71.57 | ||||
| Sandstone | S1 | 5.30 | 5.30 | 28.09 | 69.59 | 41.3 | 6.09 |
| 5.28 | 5.25 | 27.72 | 88.51 | ||||
| S2 | 5.32 | 5.30 | 28.20 | 50.35 | |||
| 5.30 | 5.32 | 28.20 | 44.73 | ||||
| S3 | 5.32 | 5.32 | 28.30 | 20.16 | |||
| 5.32 | 5.32 | 28.30 | 27.54 | ||||
| 5.28 | 5.25 | 27.72 | 88.51 | ||||
| S2 | 5.32 | 5.30 | 28.20 | 50.35 | |||
| 5.30 | 5.32 | 28.20 | 44.73 | ||||
| S3 | 5.32 | 5.32 | 28.30 | 20.16 | |||
| 5.32 | 5.32 | 28.30 | 27.54 |
| Slope Location | Division Method | Grade | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southwest Slope of First Mining Area | Slope Height Grade | Low Slope | Slope Height 79 m |
| Slope Hazard Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned | |
| Slope Engineering Safety Grade | II | Based on Comprehensive Slope Height Grade, Slope Hazard Grade and Mine Site Conditions, Grade II is Assigned | |
| Southwest Slope of Second Mining Area | Slope Height Grade | Low Slope | Slope Height 92 m |
| Slope Hazard Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned | |
| Slope Engineering Safety Grade | II | Based on Comprehensive Slope Height Grade, Slope Hazard Grade and Mine Site Conditions, Grade II is Assigned | |
| South Slope of Third Mining Area | Slope Height Grade | Low Slope | Slope Height 85 m |
| Slope Hazard Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned | |
| Slope Engineering Safety Grade | II | Based on Comprehensive Slope Height Grade, Slope Hazard Grade and Mine Site Conditions, Grade II is Assigned | |
| South Slope of Fourth Mining Area | Slope Height Grade | Middle Slope | Slope Height 140 m |
| Slope Hazard Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned | |
| Slope Engineering Safety Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Slope Height Grade, Slope Hazard Grade and Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned | |
| Southern Area Slope | Slope Height Grade | Middle Slope | Slope Height 147 m |
| Slope Hazard Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned | |
| Slope Engineering Safety Grade | I | Based on Comprehensive Slope Height Grade, Slope Hazard Grade and Mine Site Conditions, Grade I is Assigned |
| Slope Area (m2) | Slope Engineering Safety Grade | Safety Factor for Slope Engineering Design | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Combination I | Load Combination II | Load Combination III | ||
| Southwest Slope of First Mining Area (76,497) | II | 1.20–1.15 | 1.18–1.13 | 1.15–1.10 |
| Southwest Slope of Second Mining Area (159,903) | II | 1.20–1.15 | 1.18–1.13 | 1.15–1.10 |
| South Slope of Third Mining Area (425,903) | II | 1.20–1.15 | 1.18–1.13 | 1.15–1.10 |
| South Slope of Fourth Mining Area (390,941) | I | 1.25–1.20 | 1.23–1.18 | 1.20–1.15 |
| Southern Area Slope (273,289) | I | 1.25–1.20 | 1.23–1.18 | 1.20–1.15 |
| Point | ∆X | ∆Y | ∆Z | ∑X | ∑Y | ∑Z | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW12 | −0.22 | −0.24 | −0.66 | −0.143 | 3.327 | 0.55 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW06 | −0.45 | −0.43 | −1.24 | −0.113 | 3.932 | 1.072 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW07 | 0.92 | −0.84 | −1.87 | −1.198 | 5.475 | 3.994 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW11 | 0.03 | −0.63 | −1.04 | −0.488 | 3.899 | 1.825 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW10 | 1.21 | −0.33 | −2.71 | −1.809 | 5.85 | 4.346 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW04 | 1.34 | −0.51 | −1.82 | −0.672 | 4.316 | 4.077 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW09 | −0.12 | −0.54 | −0.46 | 0.472 | 1.437 | −0.249 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW13 | 0.35 | −2.3 | −1.39 | 3.166 | 9.144 | 4.517 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW15 | −0.59 | −0.62 | −0.13 | 0.408 | 2.189 | −0.249 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW05 | 0.56 | −0.87 | −1.44 | −0.667 | 3.718 | 2.626 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW23 | −0.53 | −0.83 | −0.51 | 1.545 | 0.357 | −0.84 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW01 | −0.25 | −0.73 | −0.46 | 0.743 | 2.218 | 0.208 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW02 | 1.06 | −0.41 | −2.98 | −3.344 | 8.604 | 6.217 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW22 | 0.13 | −0.2 | −1.17 | −0.82 | 2.159 | 1.719 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW03 | −0.27 | −1.15 | −1.55 | −0.016 | 3.168 | 0.874 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW20 | 0.55 | 0.37 | −2.83 | −2.577 | 6.867 | 3.615 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW24 | −0.28 | −0.44 | −0.22 | −0.025 | 0.827 | 0.103 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW18 | −0.29 | 0.46 | −1.13 | −0.74 | 1.301 | −0.312 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW16 | 0.64 | −0.73 | −0.88 | −0.385 | 4.547 | 2.556 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW08 | 0.6 | −0.59 | −1.99 | 0.065 | 3.708 | 3.298 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW17 | 0.2 | −0.1 | −1.74 | −1.296 | 5.33 | 2.669 | 2024/11/3 0:00 |
| BW06 | 0.1 | 0.38 | −0.67 | −0.641 | −0.938 | 0.1 | 2024/11/3 1:00 |
| BW24 | −0.15 | −0.06 | −0.74 | −1.039 | 2.322 | 1.215 | 2024/11/3 1:00 |
Appendix A.3. Implementation Details and Software Environment
Appendix A.3.1. Software and Programming Languages
Appendix A.3.2. Script Availability
Appendix A.3.3. Hardware Specifications
Appendix A.3.4. Reproducibility Note
References
- Lumbroso, D.; Davison, M.; Body, R.; Petkovšek, G. Modelling the Brumadinho tailings dam failure, the subsequent loss of life and how it could have been reduced. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, L.; Carraro, E.; Reyes-Carmona, C.; Puliero, S.; Bhuyan, K.; Rosi, A.; Monserrat, O.; Floris, M.; Meena, S.R.; Galve, J.P. Landslide displacement forecasting using deep learning and monitoring data across selected sites. Landslides 2023, 20, 2111–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, N.; Yang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Mei, G. Machine learning approaches for slope deformation prediction based on monitored time-series displacement data: A comparative investigation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, G.; Kishore, N. Numerical modelling-based stability analysis of waste dump slope structures in open-pit mines-a review. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. D 2021, 102, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, L.; Lehikoinen, A.; Helle, I.; Myrberg, K. An overview of methods to evaluate uncertainty of deterministic models in decision support. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 63, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchsteiger, C. On the use of probabilistic and deterministic methods in risk analysis. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 1999, 12, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, R.; van Westen, C.J. Slope instability recognition, analysis, and zonation. In Landslides, Investigation and Mitigation; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 129–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Khan, M.U.; Rehman, G. A brief review of the slope stability analysis methods. Geol. Behav 2020, 4, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Ugai, K. Numerical analysis of rainfall effects on slope stability. Int. J. Geomech. 2004, 4, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tang, C.; Zhu, W.; Liang, Z. Numerical analysis of slope stability based on the gravity increase method. Comput. Geotech. 2009, 36, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuric, A.; Nuric, S.; Kricak, L.; Husagic, R. Numerical methods in analysis of slope stability. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Investig. 2013, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kainthola, A.; Verma, D.; Thareja, R.; Singh, T. A review on numerical slope stability analysis. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 2, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt, E. Rock slope stability analysis–utilization of advanced numerical techniques. Earth Ocean Sci. UBC 2003, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, E.F.; Hosseinzadeh, S. Slope stability assessment using both empirical and numerical methods: A case study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabinová, S.; Kotrasová, K.; Kormaníková, E.; Hegedüsová, I. Analysis of slope stability. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2021, 17, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostić, S.; Vasović, N.; Sunarić, D. Slope stability analysis based on experimental design. Int. J. Geomech. 2016, 16, 04016009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zaman, M.M. Analytical method for analysis of slope stability. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1999, 23, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Ge, S. A comprehensive review of slope stability analysis based on artificial intelligence methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 239, 122400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, T.; Dai, M. Reliability analysis method for slope stability based on sample weight. Water Sci. Eng. 2009, 2, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Alonso, E.; Tabba, M. Application of risk analysis to the prediction of slope instability. Can. Geotech. J 1977, 14, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, L. Area failure probability method for slope system failure risk assessment. Comput. Geotech. 2019, 107, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z. Probabilistic slope stability analysis by risk aggregation. Eng. Geol. 2014, 176, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Vigliorolo, E. Risk-Based Slope Hazard Evaluation System. In Geo-Risk 2017; ASCE Press: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Fredlund, D.; Stolte, W. A probabilistic slope stability analysis using deterministic computer software. In Probabilistic Methods in Geotechnical Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, A.P.; Tolooiyan, A. Comparative approaches to probabilistic finite element methods for slope stability analysis. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2020, 100, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Saroglou, C.; Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Yong, R. A new approach for evaluation of slope stability in large open-pit mines: A case study at the Dexing Copper Mine, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xue, Y. Probabilistic prediction of slope failure time. Eng. Geol. 2020, 271, 105586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qiu, C.; Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Mugahed, A.-S.Q.; Tan, J. Stability analysis of a high-steep dump slope under different rainfall conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, X.; Shang, Y. Study on the influence of rainfall infiltration on the stability of dump slope. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wei, C.; Sha, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; Cao, L. Study on the influence of water–rock interaction on the stability of schist slope. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, C.; Barla, M.; Pieraccini, M.; Antolini, F. Early warning monitoring of natural and engineered slopes with ground-based synthetic-aperture radar. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2015, 48, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, R.; Sepehri, M.; Khaksar, S.; Murray, I. Slope Stability Monitoring Methods and Technologies for Open-Pit Mining: A Systematic Review. Mining 2025, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Hu, H.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X. Determination of the stability of high-steep slopes by global navigation satellite system (GNSS) real-time monitoring in long wall mining. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.; Fenton, G.A. Probabilistic slope stability analysis by finite elements. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ran, B.; Gu, X.; Sun, G.; Zou, Y. Probabilistic stability analysis of a layered slope considering multi-factors in spatially variable soils. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 11209–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alganci, U.; Besol, B.; Sertel, E. Accuracy assessment of different digital surface models. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.B.; Dobkin, D.P.; Huhdanpaa, H. The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 1996, 22, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, A. Ground-penetrating radar and its use in sedimentology: Principles, problems and progress. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 66, 261–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.A.; Sun, J. Revealing stratigraphy in ground-penetrating radar data using domain filtering. Geophysics 1999, 64, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, M.; Mitri, R.S.; Gai, I.; Brighi, G.; Tortora, P. Spectral properties of bistatic radar signals using the ray tracing technique and a facet approach. Aerospace 2024, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2423.8-1995; Environmentaltesting for Electric and Electronic Products—Part 2:Test Methods—Test Ed:Free Fall. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1995.
- GB 35114; Technical Requirements for Information Security of Video Surveillance Network System for Public Security. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB 18306-2015; Seismic Ground Motion Parameter Zonation Map of China. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB 50330-2013; Technical Code for Building Slope Engineering. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB 6722-2014; Safety Regulations for Blasting. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB 51016-2014; Technical Code for Non-Coal Open-Pitmine Slope Engineering. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Romana, M.R. A geomechanical classification for slopes: Slope mass rating. In Rock Testing and Site Characterization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 575–600. [Google Scholar]
- Pantelidis, L. Rock slope stability assessment through rock mass classification systems. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2009, 46, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loáiciga, H.A. Groundwater and earthquakes: Screening analysis for slope stability. Eng. Geol. 2015, 193, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Calculation Parameters | Coefficient K | Total Amount of Explosive Charge for Simultaneous Blasting Q (kg) | Safety Distance (m) | Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculation Values | 250 | 500 | 60 | 1.5 |
| Profile | Slope Angle (°) | Slope Height (m) | Load Combination | Safety Factor | Slope Grade | Standard Required Values | Compliance with Standards | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Arc Failure Analysis Method | Slip-Wedge Method | |||||||||
| Bishop | M-P | Bishop | M-P | |||||||
| I-1 | 36 | 79 | I | 3.175 | 3.167 | 3.006 | 3.110 | II | 1.20–1.15 | Yes |
| II | 3.060 | 3.052 | 2.899 | 3.000 | II | 1.18–1.13 | Yes | |||
| III | 2.741 | 2.735 | 2.605 | 2.693 | II | 1.15–1.10 | Yes | |||
| Profile | Slope Angle (°) | Slope Height (m) | Load Combination | Safety Factor | Slope Grade | Standard Required Values | Compliance with Standards | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Arc Failure Analysis Method | Slip-Wedge Method | |||||||||
| Bishop | M-P | Bishop | M-P | |||||||
| II-1 | 15 | 65 | I | 3.838 | 3.835 | 3.320 | 3.541 | II | 1.20–1.15 | Yes |
| II | 3.802 | 3.797 | 3.292 | 3.519 | II | 1.18–1.13 | Yes | |||
| III | 3.440 | 3.431 | 3.159 | 3.341 | II | 1.15–1.10 | Yes | |||
| Profile | Slope Angle (°) | Slope Height (m) | Load Combination | Safety Factor | Slope Grade | Standard Required Values | Compliance with Standards | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Arc Failure Analysis Method | Slip-Wedge Method | |||||||||
| Bishop | M-P | Bishop | M-P | |||||||
| III-1 | 16 | 86 | I | 2.501 | 2.493 | 2.354 | 2.432 | II | 1.20–1.15 | Yes |
| II | 2.386 | 2.379 | 2.254 | 2.324 | II | 1.18–1.13 | Yes | |||
| III | 2.077 | 2.074 | 1.971 | 2.034 | II | 1.15–1.10 | Yes | |||
| Profile | Slope Angle (°) | Slope Height (m) | Load Combination | Safety Factor | Slope Grade | Standard Required Values | Compliance with Standards | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Arc Failure Analysis Method | Slip-Wedge Method | |||||||||
| Bishop | M-P | Bishop | M-P | |||||||
| IV-1 | 22 | 140 | I | 1.861 | 1.857 | 1.774 | 1.813 | I | 1.25–1.20 | Yes |
| II | 1.801 | 1.796 | 1.717 | 1.755 | I | 1.23–1.18 | Yes | |||
| III | 1.631 | 1.628 | 1.554 | 1.606 | I | 1.20–1.15 | Yes | |||
| IV-2 | 16 | 52 | I | 3.631 | 3.627 | 3.351 | 3.476 | I | 1.25–1.20 | Yes |
| II | 3.567 | 3.563 | 3.298 | 3.418 | I | 1.23–1.18 | Yes | |||
| III | 2.952 | 2.949 | 2.757 | 2.860 | I | 1.20–1.15 | Yes | |||
| Profile | Slope Angle (°) | Slope Height (m) | Load Combination | Safety Factor | Slope Grade | Standard Required Values | Compliance with Standards | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Arc Failure Analysis Method | Slip-Wedge Method | |||||||||
| Bishop | M-P | Bishop | M-P | |||||||
| V-1 | 16 | 103 | I | 1.688 | 1.688 | 1.477 | 1.537 | I | 1.25–1.20 | Yes |
| II | 1.638 | 1.637 | 1.439 | 1.498 | I | 1.23–1.18 | Yes | |||
| III | 1.493 | 1.491 | 1.400 | 1.416 | I | 1.20–1.15 | Yes | |||
| V-2 | 29 | 122 | I | 1.631 | 1.626 | 1.532 | 1.585 | I | 1.25–1.20 | Yes |
| II | 1.589 | 1.584 | 1.492 | 1.546 | I | 1.23–1.18 | Yes | |||
| III | 1.467 | 1.463 | 1.379 | 1.432 | I | 1.20–1.15 | Yes | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Hou, K. Open-Pit Slope Stability Analysis Integrating Empirical Models and Multi-Source Monitoring Data. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9278. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179278
Cheng Y, Hou K. Open-Pit Slope Stability Analysis Integrating Empirical Models and Multi-Source Monitoring Data. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9278. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179278
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yuyin, and Kepeng Hou. 2025. "Open-Pit Slope Stability Analysis Integrating Empirical Models and Multi-Source Monitoring Data" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9278. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179278
APA StyleCheng, Y., & Hou, K. (2025). Open-Pit Slope Stability Analysis Integrating Empirical Models and Multi-Source Monitoring Data. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9278. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179278





