Exposure Pathways, Systemic Distribution, and Health Implications of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
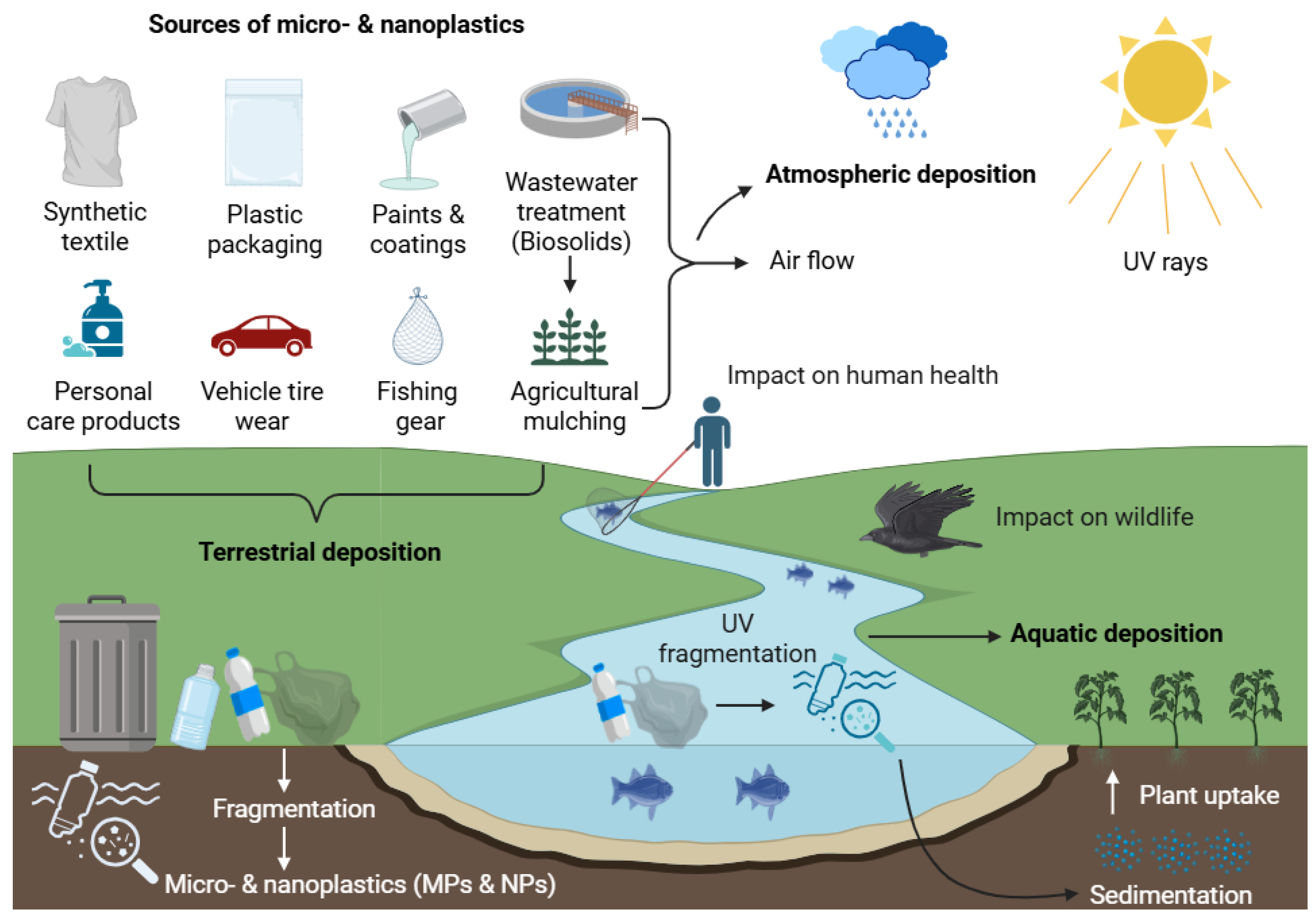
2. Sources, Transport, and Environmental Distribution of MNPs
2.1. Aquatic Transport
2.2. Atmospheric Transport
2.3. Soil and Terrestrial Transport
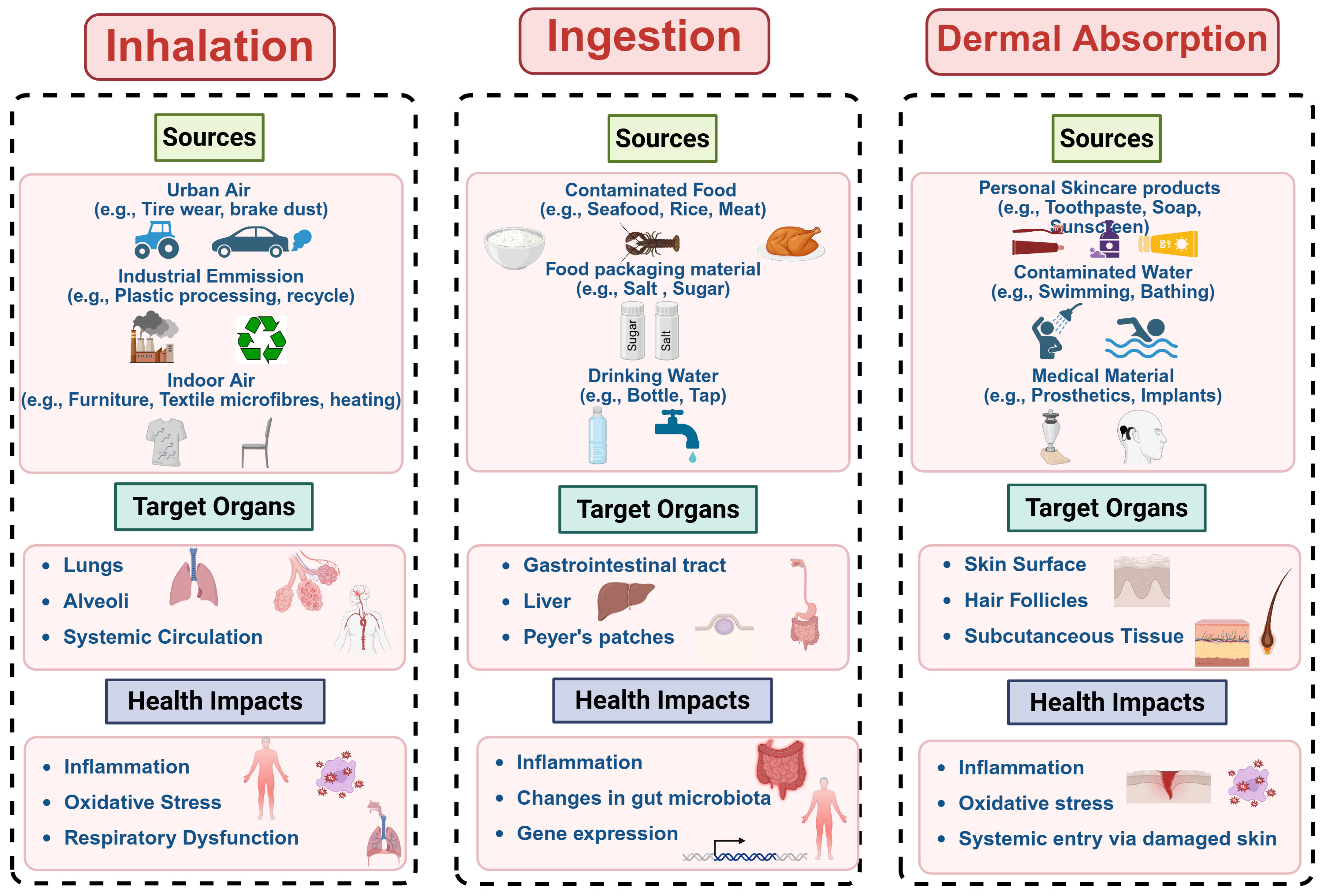
3. Human Exposure Pathways to MNPs
3.1. Inhalation of Airborne MNPs
3.2. Ingestion of MNPs Through Dietary Intake
3.3. MNP Exposure Through Dermal Contact
3.4. Disparities in Exposure and Vulnerability
4. MNPs’ Toxicity to Humans
4.1. Cellular Uptake, Translocation Pathways, and Accumulation Mechanisms of MNPs
4.1.1. Cellular Uptake of MNPs
4.1.2. Translocation and Systemic Distribution
4.1.3. Accumulation and Persistence
| Sample | Polymer Type(s) | Size Range | Concentration/ Abundance (n = number of particles) | Detection Method | Study Population | Key Finding on Accumulation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | PET, PE, PS, PMMA, and PP | 0.7–700 nm | 1.6 μg/mL | Py-GC/MS | 22 healthy adults (Netherlands) | Systemic circulation; binds to plasma proteins | [9] |
| Body fluids | PP, PS, PTFE, PVB, PA, LDPE, and PVA | 2.15–103.27 μm | 702 n/L | Raman micro-spectroscopy | 104 adults (24–96 years) | Higher in individuals with vascular disease | [84] |
| Placenta | PP, PE, PET, PS, PVC, PC, POM, and acrylic | 5–307 μm | 0.029–18 n/g | μFTIR, LD-IR, and Raman | Pregnant women (Italy, China, Germany, and Iran) | Fetal–maternal barrier penetration | [10,85,86,87] |
| Breast Milk | PA, PU, PE, PVC, PP, PET, and PMMA | 2–50 μm | 0.53–20.2 n/g | LD-IR, Raman | Lactating women (Italy, China) | Transfer to infants via lactation | [10,87] |
| Lung | PP, PE, PET, PVC, PS, rayon, and cotton | 1.6–2475 μm | 0.56–1.42 n/g | μFTIR, Raman | Adults (Brazil, UK, and China) | Fibres trapped in alveoli; higher in urban residents | [43,44,88] |
| Sputum | PU, PVC, PE, alkyd varnish, and acrylates | 20–500 μm | 3.95–39.5 n/mL | FTIR, LD-IR | 22 respiratory disease patients (China) | Correlated with occupational exposure | [89] |
| Colon | PC, PA, PP, PS, and PET | 800–1600 μm (fibres) | 28.1 ± 15.4 n/g | FTIR | 11 adults (Malaysia) | Accumulation in the inflamed mucosa (IBD link) | [90] |
| Feces (Adult) | PET, PP, PE, PA, PVC, and PS | 20–1800 μm | 1–41.8 n/g | μFTIR, Raman, and Py-GC/MS | Adults (China, Indonesia, USA, and Germany) | Higher in IBD patients vs. healthy | [91,92,93,94,95] |
| Feces (Infant) | PET, PC, PA, PU, and PE | >20 μm | 26.6–54.1 n/g | μFTIR, LD-IR | Newborns/infants (China, Germany) | Early-life exposure via ingestion | [87,96] |
| Liver | PET, PP, PS, POM, PMMA, and PVC | 4–30 μm | 0.70 (non-cirrhotic); 6.9 (cirrhotic) n/g | Raman | 11 adults (Germany) | Higher accumulation in cirrhotic livers | [97] |
| Thrombi | LDPE, PS, PVC, PET, PMMA, and POM | 1–26 μm | 5 n/thrombi | Raman, SEM | 26 cardiovascular patients (China) | Associated with vascular pathology | [98] |
| Urine | PE, PS, PTFE, PVA, PVC, and PP | 3–15 μm | 1–3 n/L | Raman, μFTIR | Adults (Italy, UK) | Renal filtration evidence | [99,100] |
| Saliva | PE, PET, PS, PVC, PA, POM, PC, and PU | 1.5–500 μm | 0.33–2 n/individual/day | μRaman | 2000 adults (Iran) | Oral cavity retention; daily shedding | [101] |
| Seminal Fluid/Testis | PET, PP, PS, PE, and PVC | 20–286 μm | 0.23–11.6 n/g | Py-GC/MS, LD-IR | 30 semen/6 testis samples | Gonadal accumulation | [102,103,104] |
4.2. Toxicodynamic Responses of MNPs: Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Cytotoxic Effects
4.2.1. Oxidative Stress
4.2.2. Inflammation
4.2.3. Cytotoxicity
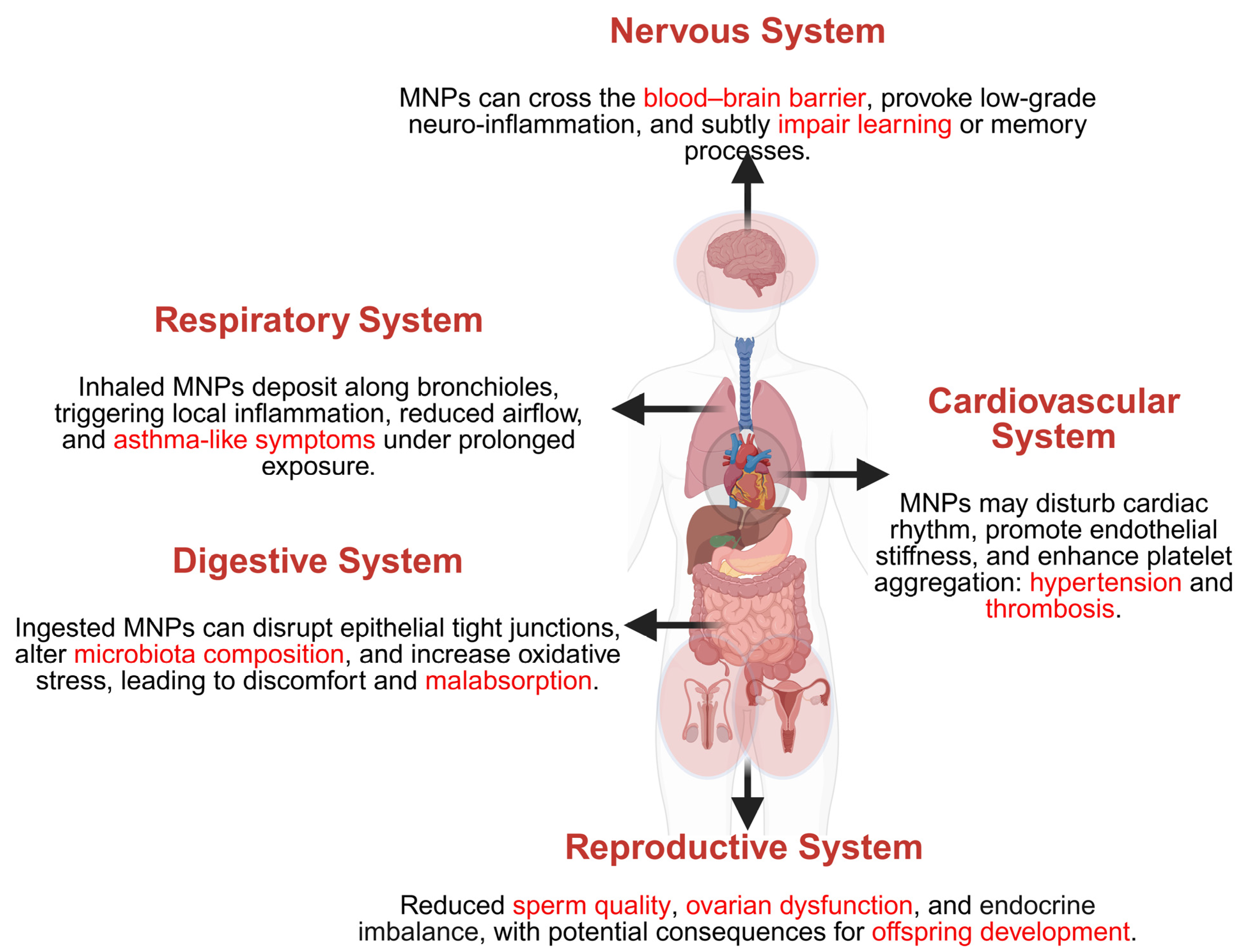
5. Health Effects of MNPs on Human Physiological Systems
5.1. Respiratory System
5.2. Digestive System
5.3. Cardiovascular System
5.4. Nervous System
5.5. Reproductive System
6. Challenges and Future Research Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MNPs | Micro- and nanoplastics |
| MP | Microplastic |
| NP | Nanoplastics |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PVB | Polyvinyl butyral |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| POM | Polyoxymethylene |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| Py-GC/MS | Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| LD-IR | Laser Direct Infrared Imaging |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| TBBPA | Tetrabromobisphenol A |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| GST | Glutathione S-Transferase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| NOAELs | No Observed Adverse Effect Levels |
| FaSTE-MPA | Fast, Single, Tissue Extraction for Multiplexed Plastic Analysis |
| AURORA | Actionable eUropean ROadmap for early-life health Risk Assessment |
| POLYRISK | Polymers of Low Concern Risk Assessment Framework |
References
- Galloway, T.S.; Cole, M.; Lewis, C. Interactions of Microplastic Debris throughout the Marine Ecosystem. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the Marine Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.; Pulicharla, R.; Rezai, P.; Brar, S.K. Microplastics in Wastewaters: Pretreatment to Detection Trail. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliszewicz, A.; Panteleeva, N.; Karaban, K.; Runka, T.; Winczek, M.; Beck, E.; Poniatowska, A.; Olejniczak, I.; Boniecki, P.; Golovanova, E.V.; et al. First Evidence of Microplastic Occurrence in the Marine and Freshwater Environments in a Remote Polar Region of the Kola Peninsula and a Correlation with Human Presence. Biology 2023, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.; Allen, S.; Abbasi, S.; Baker, A.; Bergmann, M.; Brahney, J.; Butler, T.; Duce, R.A.; Eckhardt, S.; Evangeliou, N.; et al. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in the Marine-Atmosphere Environment. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and Fragmentation of Plastic Debris in Global Environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, G.; Wankhede, L.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K. Microplastic-Associated Biofilms in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Mechanisms and Impacts. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 72, 107582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human Consumption of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and Quantification of Plastic Particle Pollution in Human Blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First Evidence of Microplastics in Human Placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental Exposure to Microplastics: An Overview on Possible Human Health Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirinzi, G.F.; Pérez-Pomeda, I.; Sanchís, J.; Rossini, C.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Cytotoxic Effects of Commonly Used Nanomaterials and Microplastics on Cerebral and Epithelial Human Cells. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyedibe, V.; Kakar, F.L.; Okoye, F.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Hamza, R. Chapter 2—Sources and Occurrence of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in the Environment. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Tyagi, R.D., Pandey, A., Drogui, P., Yadav, B., Pilli, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 33–58. ISBN 978-0-323-99908-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D.M.; Johnston, H.J.; Gaiser, B.; Pinna, N.; Caputo, G.; Culha, M.; Kelestemur, S.; Altunbek, M.; Stone, V.; Roy, J.C.; et al. A Cross-Species and Model Comparison of the Acute Toxicity of Nanoparticles Used in the Pigment and Ink Industries. NanoImpact 2018, 11, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, N.; Nikolaidis, N.F.; Barmpalexis, P. Microplastics (MPs) in Cosmetics: A Review on Their Presence in Personal-Care, Cosmetic, and Cleaning Products (PCCPs) and Sustainable Alternatives from Biobased and Biodegradable Polymers. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Dixon, S.J. Microplastics: An Introduction to Environmental Transport Processes. WIREs Water 2018, 5, e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Passananti, M. Atmospheric Micro and Nanoplastics: An Enormous Microscopic Problem. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetuyi, B.O.; Mathew, J.T.; Inobeme, A.; Falana, Y.O.; Adetunji, C.O.; Shahnawaz, M.; Oyewole, O.A.; Eniola, K.I.T.; Yerima, M.B.; Popoola, O.A. Tyres, Bitumen Wear and Plastic Bottles, Other Single Used Plastic as Major Sources of Microplastic. In Microplastic Pollution; Shahnawaz, M., Adetunji, C.O., Dar, M.A., Zhu, D., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 141–160. ISBN 978-981-9983-57-5. [Google Scholar]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.; Bhardwaj, G.; Pulicharla, R.; Rezai, P.; Brar, S.K. Innovating Ferro-Sonication Approach for Extracting Microplastics from Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matavos-Aramyan, S. Addressing the Microplastic Crisis: A Multifaceted Approach to Removal and Regulation. Environ. Adv. 2024, 17, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aransiola, S.A.; Victor-Ekwebelem, M.O.; Daza, B.X.; Oladoye, P.O.; Alli, Y.A.; Bamisaye, A.; Aransiola, A.B.; Oni, S.O.; Maddela, N.R. Micro- and Nano-Plastics Pollution in the Marine Environment: Progresses, Drawbacks and Future Guidelines. Chemosphere 2025, 374, 144211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, G.; Mohammadiun, M.; Osorio Gonzalez, C.S.; Kaur Brar, S.; Karimpour, S. Wastewater-Induced Microplastic Biofouling in Freshwater: Role of Particle Size and Flow Velocity. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2025, 4, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Majeed, L.R.; Mehta, N.; Radu, T.; Martín-Fabiani, I.; Bhat, M.A. Microplastics in Terrestrial Ecosystems: Sources, Transport, Fate, Mitigation, and Remediation Strategies. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2025, 10, 2633–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtene-Jones, W.; Quinn, B.; Ewins, C.; Gary, S.F.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Microplastic Accumulation in Deep-Sea Sediments from the Rockall Trough. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, G.; Revell, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, C.; Wang, D.; Le Ru, E.C.; Wu, G.; Mitrano, D.M. Long-Range Atmospheric Transport of Microplastics across the Southern Hemisphere. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Mützel, S.; Primpke, S.; Tekman, M.B.; Trachsel, J.; Gerdts, G. White and Wonderful? Microplastics Prevail in Snow from the Alps to the Arctic. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurkschat, L.; Gill, A.J.; Milner, R.; Holzinger, R.; Evangeliou, N.; Eckhardt, S.; Materić, D. Using a Citizen Science Approach to Assess Nanoplastics Pollution in Remote High-Altitude Glaciers. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, S.; Kumar, M.; Singh, L.; Bolan, N.S.; Saha, M. Microplastics as an Emerging Source of Particulate Air Pollution: A Critical Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Kloas, W.; Zarfl, C.; Hempel, S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to Terrestrial Ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Wang, P.-Y.; Saqib, S.; Zhao, L.; Ashraf, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, W.; Khan, A.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, Y.-C. Toxicological Complexity of Microplastics in Terrestrial Ecosystems. iScience 2025, 28, 111879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa’adu, I.; Farsang, A. Plastic Contamination in Agricultural Soils: A Review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, Y.; Marshall, M.R.; Zhao, J.; Gui, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Jones, D.L.; Zang, H. Microplastics as an Emerging Threat to Plant and Soil Health in Agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zuo, R.; Shang, J.; Wu, G.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Nano- and Micro-Plastic Transport in Soil and Groundwater Environments: Sources, Behaviors, Theories, and Models. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Riksen, M.J.P.M.; Sirjani, E.; Sameni, A.; Geissen, V. Wind Erosion as a Driver for Transport of Light Density Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Microplastics in Drinking-Water. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241516198 (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Banaee, M.; Multisanti, C.R.; Impellitteri, F.; Piccione, G.; Faggio, C. Environmental Toxicology of Microplastic Particles on Fish: A Review. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 287, 110042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheraz, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Nano/Microplastics in Indoor Air: A Critical Review of Synthesis Routes for Toxicity Testing and Preventative Measure Strategies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 180, 274–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A First Overview of Textile Fibers, Including Microplastics, in Indoor and Outdoor Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, A.; Jensen, R.L.; Liu, L.; Vollertsen, J. Simulating Human Exposure to Indoor Airborne Microplastics Using a Breathing Thermal Manikin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne Microplastics: Consequences to Human Health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Shruti, V.C.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D. Microplastic Diagnostics in Humans: “The 3Ps” Progress, Problems, and Prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Júnior, G.R.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of Airborne Microplastics in Human Lung Tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of Microplastics in Human Lung Tissue Using μFTIR Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atis, S.; Tutluoglu, B.; Levent, E.; Ozturk, C.; Tunaci, A.; Sahin, K.; Saral, A.; Oktay, I.; Kanik, A.; Nemery, B. The Respiratory Effects of Occupational Polypropylene Flock Exposure. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 25, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.; Wang, W.-X. Human Exposure to Microplastics and Its Associated Health Risks. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Stone, V.; Gilmour, P.; Brown, D.; MacNee, W. Ultrafine Particles: Mechanisms of Lung Injury. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 358, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Wilson, M.R.; MacNee, W.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Size-Dependent Proinflammatory Effects of Ultrafine Polystyrene Particles: A Role for Surface Area and Oxidative Stress in the Enhanced Activity of Ultrafines. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 175, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hoet, P.H.; Nemery, B. In Vitro Toxicity Assessment of Polyvinyl Chloride Particles and Comparison of Six Cellular Systems. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2002, 65, 1141–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danopoulos, E.; Twiddy, M.; West, R.; Rotchell, J.M. A Rapid Review and Meta-Regression Analyses of the Toxicological Impacts of Microplastic Exposure in Human Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, R.; Wu, D.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Luo, Y. A Systematic Review of the Impacts of Exposure to Micro- and Nano-Plastics on Human Tissue Accumulation and Health. Eco-Environ. Health 2023, 2, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahedi, F.; Fard, N.J.H. Micro- and Nanoplastic Toxicity in Humans: Exposure Pathways, Cellular Effects, and Mitigation Strategies. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 102043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Shi, H. A Review of Microplastics in Table Salt, Drinking Water, and Air: Direct Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, B.; Özçifçi, Z.; Kanbur, E.D.; Akçay, H.T.; Gül, S.; Bektaş, Y.; Aytan, Ü. Microplastics in Honey from Türkiye: Occurrence, Characteristic, Human Exposure, and Risk Assessment. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 135, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Zhao, T.; Tan, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Yan, M.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Zheng, P. Microplastics in Tea from Planting to the Final Tea Product: Traceability, Characteristics and Dietary Exposure Risk Analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 455, 139636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessì, C.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Gallen, M.; Samanipour, S.; Kaserzon, S.; Rauert, C.; Wang, X.; Thomas, K.V. Plastics Contamination of Store-Bought Rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierski, M.; Lechat, B.; Sire, O.; Le Maguer, G.; Le Tilly, V.; Bruzaud, S. Microplastic Contamination of Packaged Meat: Occurrence and Associated Risks. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic Contamination of Tap Water, Beer, and Sea Salt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.A.; Welch, V.G.; Neratko, J. Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danopoulos, E.; Twiddy, M.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastic Contamination of Drinking Water: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aristizabal, M.; Jiménez-Orrego, K.V.; Caicedo-León, M.D.; Páez-Cárdenas, L.S.; Castellanos-García, I.; Villalba-Moreno, D.L.; Ramírez-Zuluaga, L.V.; Hsu, J.T.S.; Jaller, J.; Gold, M. Microplastics in Dermatology: Potential Effects on Skin Homeostasis. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, C.; Negi, S.; Nagarkoti, S.; Daverey, A. Mechanistic Insight into Potential Toxic Effects of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, T.; Roche, N.; Lohmann, R.; Hodges, G. A Thermodynamic Approach for Assessing the Environmental Exposure of Chemicals Absorbed to Microplastic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, Quantity and Sorptive Properties of Microplastics Extracted from Cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Katsouli, J.; Marczylo, E.L.; Gant, T.W.; Wright, S.; de la Serna, J.B. The Potential Impacts of Micro-and-Nano Plastics on Various Organ Systems in Humans. EBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Du, L.; Sima, L.; Zou, D.; Qiu, X. Effects of Micro (Nano) Plastics on the Reproductive System: A Review. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; You, F. Microplastic Human Dietary Uptake from 1990 to 2018 Grew across 109 Major Developing and Industrialized Countries but Can Be Halved by Plastic Debris Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 8709–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E.S.; Olagbaju, O.A.; Okoye, C.O.; Addey, C.I.; Chukwudozie, K.I.; Okoro, J.O.; Deme, G.G.; Ewusi-Mensah, D.; Igun, E.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; et al. Microplastic Burden in Africa: A Review of Occurrence, Impacts, and Sustainability Potential of Bioplastics. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 12, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; van Dijk, F.; Vasse, G.F.; Liu, Q.; Gosselink, I.F.; Weltjens, E.; Remels, A.H.V.; de Jager, M.H.; Bos, S.; Li, C.; et al. Inhalable Textile Microplastic Fibers Impair Airway Epithelial Differentiation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashov, V.; Geraci, C.L.; Schulte, P.A.; Howard, J. Nano- and Microplastics in the Workplace. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2021, 18, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarus, G.M.; Muianga, C.; Brenner, S.; Stallings, K.; Casillas, G.; Pohl, H.R.; Mumtaz, M.M.; Gehle, K. Worker Studies Suggest Unique Liver Carcinogenicity Potential of Polyvinyl Chloride Microplastics. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jia, Z. Recent Insights into Uptake, Toxicity, and Molecular Targets of Microplastics and Nanoplastics Relevant to Human Health Impacts. iScience 2023, 26, 106061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Iachetta, G.; Tussellino, M.; Carotenuto, R.; Prisco, M.; De Falco, M.; Laforgia, V.; Valiante, S. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Internalization in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2016, 31, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Nayyar, D.; Hwang, Y.S.; Bartucci, R.; Salvati, A. Effect of Positive Charges on Liposome Stability, Uptake Efficacy and Impact on Cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 681, 125881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, V.; Böhmert, L.; Lisicki, E.; Block, R.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Pack, L.K.; Selb, R.; Lichtenstein, D.; Voss, L.; Henderson, C.J.; et al. Uptake and Effects of Orally Ingested Polystyrene Microplastic Particles in Vitro and in Vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 1817–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Chen, Y.; Ling, Z.; Xiang, P. Microplastics in the Human Body: A Comprehensive Review of Exposure, Distribution, Migration Mechanisms, and Toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; DeLoid, G.M.; Zarbl, H.; Baw, J.; Demokritou, P. Micro- and Nanoplastics (MNPs) and Their Potential Toxicological Outcomes: State of Science, Knowledge Gaps and Research Needs. NanoImpact 2023, 32, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, J.A.; Wang, S.W.J.; Knemeyer, I.W.; Wirth, M.A.; Alton, K.B. Intestinal Lymphatic Transport for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, H.; Busch, M.; Yang, S.; Venus, T.; Aalderink, G.; Crespo, J.F.F.; Villacorta, A.; Hernández, A.; Estrela-Lopis, I.; Boeren, S.; et al. Toxicity of True-to-Life Microplastics to Human iPSC-Derived Intestinal Epithelia Correlates to Their Protein Corona Composition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue Accumulation of Microplastics in Mice and Biomarker Responses Suggest Widespread Health Risks of Exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic Level Transfer of Microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Cui, W.; et al. The Landscape of Micron-Scale Particles Including Microplastics in Human Enclosed Body Fluids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amereh, F.; Amjadi, N.; Mohseni-Bandpei, A.; Isazadeh, S.; Mehrabi, Y.; Eslami, A.; Naeiji, Z.; Rafiee, M. Placental Plastics in Young Women from General Population Correlate with Reduced Foetal Growth in IUGR Pregnancies. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.; Ehrlich, L.; Henrich, W.; Koeppel, S.; Lomako, I.; Schwabl, P.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Microplastic in Human Placenta and Meconium in a Clinical Setting. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. Detection of Various Microplastics in Placentas, Meconium, Infant Feces, Breastmilk and Infant Formula: A Pilot Prospective Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, J.; Yu, H.; Su, H.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, Y.; Hollert, H.; Shi, H.; et al. An Emerging Role of Microplastics in the Etiology of Lung Ground Glass Nodules. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Bi, R.; Guo, Q.; Yu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Detection and Analysis of Microplastics in Human Sputum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.S.; Anuar, S.T.; Azmi, A.A.; Khalik, W.M.A.W.M.; Lehata, S.; Hamzah, S.R.; Ismail, D.; Ma, Z.F.; Dzulkarnaen, A.; Zakaria, Z.; et al. Detection of Microplastics in Human Colectomy Specimens. JGH Open 2021, 5, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Y.B.; He, H.R.; Zhang, J.F.; Ma, G.S. You Are What You Eat: Microplastics in the Feces of Young Men Living in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luqman, A.; Nugrahapraja, H.; Wahyuono, R.A.; Islami, I.; Haekal, M.H.; Fardiansyah, Y.; Putri, B.Q.; Amalludin, F.I.; Rofiqa, E.A.; Götz, F.; et al. Microplastic Contamination in Human Stools, Foods, and Drinking Water Associated with Indonesian Coastal Population. Environments 2021, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-W.; Lim, J.Y.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Chiou, J.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Lai, K.P.; Li, L.; Chan, P.K.S.; Fang, J.K.-H. Preliminary Findings of the High Quantity of Microplastics in Faeces of Hong Kong Residents. Toxics 2022, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, A.T.; Nugrahapraja, H.; Wahyuono, R.A.; Islami, I.; Haekal, M.H.; Fardiansyah, Y.; Sugiyo, P.W.W.; Putro, Y.K.; Fauzia, F.N.; Santoso, H.; et al. Microplastic Contamination in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract and Daily Consumables Associated with an Indonesian Farming Community. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Microplastics in Human Feces Reveals a Correlation between Fecal Microplastics and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Status. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Trasande, L.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of Polyethylene Terephthalate and Polycarbonate Microplastics in Infant and Adult Feces. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatits, T.; Tamminga, M.; Liu, B.; Sebode, M.; Carambia, A.; Fischer, L.; Püschel, K.; Huber, S.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastics Detected in Cirrhotic Liver Tissue. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Feng, Y.; Wang, R.; Jiang, J.; Guan, Q.; Yang, X.; Wei, H.; Xia, Y.; Luo, Y. Pigment Microparticles and Microplastics Found in Human Thrombi Based on Raman Spectral Evidence. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 49, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Notarstefano, V.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Giorgini, E.; Montano, L. First Evidence of Microplastics in Human Urine, a Preliminary Study of Intake in the Human Body. Toxics 2023, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotchell, J.M.; Austin, C.; Chapman, E.; Atherall, C.A.; Liddle, C.R.; Dunstan, T.S.; Blackburn, B.; Mead, A.; Filart, K.; Beeby, E.; et al. Microplastics in Human Urine: Characterisation Using μFTIR and Sampling Challenges Using Healthy Donors and Endometriosis Participants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 274, 116208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Turner, A. Human Exposure to Microplastics: A Study in Iran. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codrington, J.; Varnum, A.A.; Hildebrandt, L.; Pröfrock, D.; Bidhan, J.; Khodamoradi, K.; Höhme, A.-L.; Held, M.; Evans, A.; Velasquez, D.; et al. Detection of Microplastics in the Human Penis. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2025, 37, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Weng, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Detection and Characterization of Microplastics in the Human Testis and Semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano, L.; Giorgini, E.; Notarstefano, V.; Notari, T.; Ricciardi, M.; Piscopo, M.; Motta, O. Raman Microspectroscopy Evidence of Microplastics in Human Semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Ośko, J.; Knez, E.; Grembecka, M. Microplastics and Oxidative Stress—Current Problems and Prospects. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Ni, B.-J. Toxicity of Micro/Nanoplastics in the Environment: Roles of Plastisphere and Eco-Corona. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Jung, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. Potential Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastic Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Hepatotoxicity and Disrupt Lipid Metabolism in the Liver Organoids. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Basak, S. Human Exposure to Micro- and Nanoplastics: A Mechanistic Perspective of Health Risks Associated with Metabolic and Reproductive Functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 989, 179879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, X. Combined Exposure to Polyvinyl Chloride and Polystyrene Microplastics Induces Liver Injury and Perturbs Gut Microbial and Serum Metabolic Homeostasis in Mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, F.; Sarker, D.B.; Jocelyn, J.A.; Sang, Q.-X.A. Molecular and Cellular Effects of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Focus on Inflammation and Senescence. Cells 2024, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Bao, T.T.; Lan, H. Long-Term Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics Triggers Premature Testicular Aging. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2023, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Fu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Internalization and Toxicity: A Preliminary Study of Effects of Nanoplastic Particles on Human Lung Epithelial Cell. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Lin, H.; Liu, S.; Sui, G. Assessment of Cancer-Related Signaling Pathways in Responses to Polystyrene Nanoplastics via a Kidney-Testis Microfluidic Platform (KTP). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Shi, W.; Hu, F.; Song, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, J. Prolonged Oral Ingestion of Microplastics Induced Inflammation in the Liver Tissues of C57BL/6J Mice through Polarization of Macrophages and Increased Infiltration of Natural Killer Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chiu, I.-J.; Huang, C.C.-Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Chia, Z.-C.; Lee, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chiu, H.-W. The Kidney-Related Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Human Kidney Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells HK-2 and Male C57BL/6 Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 57003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Lin, C.-H. Polystyrene Microplastic Particles: In Vitro Pulmonary Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, P.; Doyle, D.; Mojarad, N.; Taherkhani, S.; Janzadeh, A.; Honardoost, M.; Gholami, M. Effects of Micro- and Nanoplastic Exposure on Macrophages: A Review of Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2025, 35, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Cytotoxicity and Efflux Pump Inhibition in Human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, A.; Vecchiotti, G.; Colafarina, S.; Zarivi, O.; Aloisi, M.; Arrizza, L.; Chichiriccò, G.; Di Carlo, P. In Vitro Genotoxicity of Polystyrene Nanoparticles on the Human Fibroblast Hs27 Cell Line. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. In Vitro Evaluation of Nanoplastics Using Human Lung Epithelial Cells, Microarray Analysis and Co-Culture Model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, E.; Leveque, M.; Ruiz, P.; Ratel, J.; Durif, C.; Chalancon, S.; Amiard, F.; Edely, M.; Bezirard, V.; Gaultier, E.; et al. Microplastics: What Happens in the Human Digestive Tract? First Evidences in Adults Using in Vitro Gut Models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, A.; Molinero, N.; Reinosa, J.J.; Alcolea-Rodriguez, V.; Portela, R.; Bañares, M.A.; Fernández, J.F.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. PET Microplastics Affect Human Gut Microbiota Communities during Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion, First Evidence of Plausible Polymer Biodegradation during Human Digestion. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yin, H.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Influence of the Co-Exposure of Microplastics and Tetrabromobisphenol A on Human Gut: Simulation in Vitro with Human Cell Caco-2 and Gut Microbiota. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojic, S.; Falco, M.M.; Stojkovic, P.; Ljujic, B.; Gazdic Jankovic, M.; Armstrong, L.; Markovic, N.; Dopazo, J.; Lako, M.; Bauer, R.; et al. Platform to Study Intracellular Polystyrene Nanoplastic Pollution and Clinical Outcomes. Stem Cells 2020, 38, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshtein, G.; Arbell, D.; Yedgar, S. Hemolytic Effect of Polymeric Nanoparticles: Role of Albumin. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2011, 10, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-Y.; Li, H.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X. Size-Dependent Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Autophagy Response in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.; Kiran, S.; Li, Y.; Sang, Q.-X.A. Microplastics Exposure Affects Neural Development of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cortical Spheroids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fu, X.; Hou, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Induced Female Reproductive Toxicity in Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruder, A.M.; Bertke, S.J. Cancer Incidence among Boat-Building Workers Exposed to Styrene. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2017, 60, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinan, P.; McGavin, C.R.; Kreiss, K.; Nicholson, A.G.; Maher, T.M.; Howell, T.; Banks, J.; Taylor, A.J.N.; Chen, C.-H.; Tsai, P.-J.; et al. Obliterative Bronchiolitis in Fibreglass Workers: A New Occupational Disease? Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenco, L.F.; Oliveira, R.C.; Junior, G.R.; Galvao, L.D.S.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Microplastics Inhalation: Evidence in Human Lung Tissue. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, PA1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, T.; Ge, Y.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. Inhalation Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Induces Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-like Lung Injury in Mice through Multi-Dimensional Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Cao, Y.; Chai, X.; Zhao, Q.; Geng, Y.; Liu, D.; Tian, S. Potential Health Risks of the Interaction of Microplastics and Lung Surfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, R.; Jo, J.; Acharya, M.; Maharjan, A.; Lee, D.; Bahadur, K.C.P.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Heo, Y. Evaluation of Potential Toxicity of Polyethylene Microplastics on Human Derived Cell Lines. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolstad, H.A.; Juel, K.; Olsen, J.; Lynge, E. Exposure to Styrene and Chronic Health Effects: Mortality and Incidence of Solid Cancers in the Danish Reinforced Plastics Industry. Occup. Environ. Med. 1995, 52, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddone, E.; Modonesi, C.; Gatta, G. Occupational Exposures and Colorectal Cancers: A Quantitative Overview of Epidemiological Evidence. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12431–12444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Size-Dependent Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics on the Gastrointestinal Tract: Oxidative Stress Related-DNA Damage and Potential Carcinogenicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Feng, X.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nie, P.; Xu, H. Co-Exposure with Cadmium Elevates the Toxicity of Microplastics: Trojan Horse Effect from the Perspective of Intestinal Barrier. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Acedo, A.; García-Recio, E.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J. Evidence from in Vitro and in Vivo Studies on the Potential Health Repercussions of Micro- and Nanoplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Chen, G.; Guo, X. Dietary Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics Exacerbates Liver Damage in Fulminant Hepatic Failure via ROS Production and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Lai, W.; Bian, L.; Yan, J.; Xi, Z. Exposure to Polypropylene Microplastics via Oral Ingestion Induces Colonic Apoptosis and Intestinal Barrier Damage through Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfella, R.; Prattichizzo, F.; Sardu, C.; Fulgenzi, G.; Graciotti, L.; Spadoni, T.; D’Onofrio, N.; Scisciola, L.; Grotta, R.L.; Frigé, C.; et al. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Gao, Q.; Xu, M.; Fang, N.; Mu, L.; Han, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Microplastics and Nanoplastics Increase Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Myocardial Infarction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 489, 137624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Ni, S.; Yue, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. Microplastics in Three Types of Human Arteries Detected by Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (Py-GC/MS). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Amarakoon, D.; Wei, C.; Choi, K.Y.; Smolensky, D.; Lee, S.-H. Adverse Effect of Polystyrene Microplastics (PS-MPs) on Tube Formation and Viability of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Cause Cardiac Fibrosis by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Promoting Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Rats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, W. Low-Dose of Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Cardiotoxicity in Mice and Human-Originated Cardiac Organoids. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulukan, E.; Şenol, O.; Baran, A.; Kankaynar, M.; Yıldırım, S.; Kızıltan, T.; Bolat, İ.; Ceyhun, S.B. Nano-Sized Polystyrene Plastic Particles Affect Many Cancer-Related Biological Processes Even in the next Generations; Zebrafish Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Hwang, J.; Bang, J.; Han, S.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. In Vitro Toxicity from a Physical Perspective of Polyethylene Microplastics Based on Statistical Curvature Change Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lett, Z.; Hall, A.; Skidmore, S.; Alves, N.J. Environmental Microplastic and Nanoplastic: Exposure Routes and Effects on Coagulation and the Cardiovascular System. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werder, E.J.; Engel, L.S.; Richardson, D.B.; Emch, M.E.; Gerr, F.E.; Kwok, R.K.; Sandler, D.P. Environmental Styrene Exposure and Neurologic Symptoms in U.S. Gulf Coast Residents. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihart, A.J.; Garcia, M.A.; El Hayek, E.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Kingston, J.D.; Castillo, E.F.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Howard, T.; Bleske, B.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Microplastics in Decedent Human Brains. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, T.; Zhao, X. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Penetrate across the Blood-Brain Barrier and Induce Activation of Microglia in the Brain of Mice. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Han, B.; Wang, T.; Dong, H.; Chen, L. Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Nanoplastics on Embryonic Brain Development Using Brain Organoids Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Hsu, L.-F.; Wu, I.-L.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, W.-C.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, L.-T.; Tan, C.-L.; Luo, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; et al. Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics Impairs Hippocampus-Dependent Learning and Memory in Mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tan, S.; Xie, D.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Dang, Y.; Xiang, M. Photoaged Microplastics Induce Neurotoxicity Associated with Damage to Serotonergic, Glutamatergic, Dopaminergic, and GABAergic Neuronal Systems in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Xing, M. Secondary Brain Injury after Polystyrene Microplastic-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage Is Associated with Inflammation and Pyroptosis. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.S.; Bai, Y.L.; Jin, C.H.; Na, J.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Pan, G.W.; Yan, L.J.; Sun, W. Evidence on Invasion of Blood, Adipose Tissues, Nervous System and Reproductive System of Mice After a Single Oral Exposure: Nanoplastics versus Microplastics. BES 2022, 35, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Gong, D. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Swine Testis Cells via ROS/MAPK/HIF1α Pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Sui, M.; Wang, T.; Teng, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, M. Detection and Quantification of Various Microplastics in Human Endometrium Based on Laser Direct Infrared Spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Cause Granulosa Cells Apoptosis and Fibrosis in Ovary through Oxidative Stress in Rats. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guan, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Fu, F. Polystyrene Microplastics Induced Ovarian Toxicity in Juvenile Rats Associated with Oxidative Stress and Activation of the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP Signaling Pathway. Toxics 2023, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Yu, R.; Liu, J.; Su, J. Reproductive Toxicity of Microplastics in Female Mice and Their Offspring from Induction of Oxidative Stress. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.-J.; Han, J.-S.; Park, E.-J.; Seong, E.; Lee, G.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Son, H.-Y.; Han, H.-Y.; Lee, B.-S. Repeated-Oral Dose Toxicity of Polyethylene Microplastics and the Possible Implications on Reproduction and Development of the next Generation. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 324, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene Translocation and Fetal Deposition after Acute Lung Exposure during Late-Stage Pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Physiological System | Human Model/Sample | MNPs Type and Size | Exposure | Key Health Effects | Mechanistic Pathways | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | Alveolar epithelial cells (A549) | PS-NPs (25 nm, 70 nm) | 1.14–25 μg/mL, 24–48 h | ↓ Cell viability; ↑ apoptosis; ↑ IL-8, TNF-α, and NF-κB | Caspase activation, cytochrome c release, and pro-inflammatory signalling | [113] |
| Lung epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) | PS-MPs (1 μm) | 1–1000 μg/cm2, 24–48 h | ROS-induced cytotoxicity; ↓ transepithelial resistance; and ↑ COPD risk | Oxidative stress; barrier dysfunction | [117,121] | |
| Pulmonary alveolar cells (HPAEpIC) | PS-NPs (40 nm) | 24 h | ↓ Cell viability; ↑ MMP-9; and surfactant protein A dysregulation | Redox imbalance; apoptotic pathway activation | [121] | |
| Digestive | Colon adenocarcinoma cells (Caco-2, HT29) | PE-MPs (1–10 μm) | 21 mg/8 mL, 14 days | ↑ Pathobionts (e.g., Enterobacteriaceae); ↓ beneficial bacteria (e.g., Akkermansia) | Gut dysbiosis, biofilm formation, and intestinal homeostasis loss | [122] |
| Simulated gastrointestinal model | PET-MPs | Single dose (0.166 g), 72 h | PET biotransformation; altered colonic microbiota | Microbial adhesion, polymer degradation | [123] | |
| Colon cells + gut microbiota | PE-MPs | 100–1000 mg/L, 24–48 h | ↓ Gut diversity and metabolic disruption | ROS-induced barrier dysfunction; immune activation | [124] | |
| Cardiovascular | Embryonic stem cells (hiPSCs) | PS-NPs (40 nm) | 1 × 109/mL, 24 h | Impaired heart valve development; ↓ LEFTY1/2; and ↑ CA4, OCLM | Developmental gene dysregulation | [125] |
| Red blood cells (RBCs) | PS-NPs (50–250 nm) | 50–500 μg/mL, 1 h | Hemolysis (plasma-free medium) | Membrane disruption | [126] | |
| Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) | PS-NPs (100 nm, 500 nm) | 5–100 μg/mL | ↑ LDH release, membrane damage, and autophagy | ER stress; autophagosome formation | [127] | |
| Nervous | Forebrain cortical spheroids (3D model) | PS-MPs (1 μm, 10 μm) | 5–100 μg/mL, 4–30 days | ↓ Neuronal maturation; ↓ cortical layer VI markers | Altered Nestin, PAX6, and HOXB4 expression | [128] |
| Reproductive | Placenta/meconium (mother–infant pairs) | PA, PU MPs (>20 μm) | Clinical detection | Microbiota dysbiosis (Proteobacteria ↑); inverse PE-microbiota correlation | Epigenetic modulation, microbial translocation | [129] |
| Testicular cells (NTE) | PS-MPs (50 nm) | 200 μg/mL, 24 h | ↑ JNK1/2/3, TNF-α; dysregulated PI3K-AKT pathway | Oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory signalling | [114] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhardwaj, G.; Abdulkadhim, M.; Joshi, K.; Wankhede, L.; Das, R.K.; Brar, S.K. Exposure Pathways, Systemic Distribution, and Health Implications of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Humans. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168813
Bhardwaj G, Abdulkadhim M, Joshi K, Wankhede L, Das RK, Brar SK. Exposure Pathways, Systemic Distribution, and Health Implications of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Humans. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168813
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhardwaj, Gaurav, Mustafa Abdulkadhim, Khyati Joshi, Lachi Wankhede, Ratul Kumar Das, and Satinder Kaur Brar. 2025. "Exposure Pathways, Systemic Distribution, and Health Implications of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Humans" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168813
APA StyleBhardwaj, G., Abdulkadhim, M., Joshi, K., Wankhede, L., Das, R. K., & Brar, S. K. (2025). Exposure Pathways, Systemic Distribution, and Health Implications of Micro- and Nanoplastics in Humans. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168813







