Abstract
Dental implant components are typically fabricated using subtractive manufacturing, often involving metal materials that can be costly, inefficient, and time-consuming. This study explores the use of additive manufacturing (AM) with zirconia for dental implant overdenture bars, focusing on mechanical performance, stress distribution, and fit. Solid and lattice-structured bars were designed in Fusion 360 and produced using LithaCon 210 3Y-TZP zirconia (Lithoz GmbH, Vienna, Austria) on a CeraFab 8500 printer. Post-processing included cleaning, debinding, and sintering. A 3D-printed denture was also fabricated to evaluate fit. Thermography and optical imaging were used to assess adaptation. Custom fixtures were developed for flexural testing, and fracture loads were recorded to calculate stress distribution using finite element analysis (ANSYS R2025). The FEA model assumed isotropic, homogeneous, linear-elastic material behavior. Bars were torqued to 15 Ncm on implant analogs. The average fracture loads were 1.2240 kN (solid, n = 12) and 1.1132 kN (lattice, n = 5), with corresponding stress values of 147 MPa and 143 MPa, respectively. No statistically significant difference was observed (p = 0.578; α = 0.05). The fracture occurred near high-stress regions at fixture support points. All bars demonstrated a clinically acceptable fit on the model; however, further validation and clinical evaluation are still needed. Additively manufactured zirconia bars, including lattice structures, show promise as alternatives to conventional superstructures, potentially offering reduced material use and faster production without compromising mechanical performance.
1. Introduction
Edentulism affects about 6–10% of the world’s population [1]. With the complete loss of teeth in an arch, especially the mandible, several issues manifest themselves, such as reduced mastication forces, aged facial aesthetics, over-closure, and poor oral hygiene [2]. The main causative agent is residual ridge resorption, which is primarily due to tooth loss [3]. Although this process is irreversible, it may be mitigated with the placement of dental implants [3].
Dental implantology represents an elective phase of dentistry, in which a biocompatible screw or device is inserted into bone and osseointegrated [4]. Once integrated, the implant can help minimize bone resorption and provide an anchor for the attachment of intra-oral prosthetic components [5]. From a single implant-support crown to a full-arch hybrid denture, the implants can retain and support tooth replacements [3]. Retention implies that the implants withstand tensile forces and maintain the prosthesis in place [3]. Support implies that the implants also serve to resist the compressive forces generated by function [6]. With implant support, forces on the intraoral soft tissues are minimized, ultimately maximizing patient comfort [7]. Implant-retained prostheses provide some mitigation for the aforementioned issues [8]; however, an implant-supported prosthesis can provide a comprehensive solution to the problems related to complete edentulism [9]. Therefore, the ideal solution for an edentulous patient is an implant-supported approach [10]. Currently, there has been much progress with the fixed screw-retained hybrid denture. Although the aesthetics can be favorable, the product has limitations due to technical difficulty, cost, adjustability, and maintenance of oral hygiene [4]. The milled bar overdenture serves as an alternative approach, which provides the stability and retention of a fixed prosthesis and also offers the convenience and flexibility of a removable prosthesis [11].
With the milled bar overdenture, the bar remains attached to the implants, while the complete denture can be removed and reseated. This approach addresses some of the cost and hygiene concerns, but some technical difficulties remain [11]. A previous report showed a case report [12] illustrating a 12-year post-operative retrospective evaluation of a mandibular milled bar overdenture case, through clinical and radiological evaluation. Combining proper case selection and appropriate surgical and prosthodontic fundamentals, the treatment modality proves to be a predictable and successful option. Furthermore, the milled bar can be fabricated to compensate for misaligned implants while still supporting the denture and the patient’s occlusion [13].
Milled bars are exclusively fabricated through a reductive manufacturing process, otherwise known as subtractive manufacturing [14], which represents a costly workflow and produces a high amount of waste [15]. Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is having a significant impact on dentistry, due to a surge in efficiency and cost-effectiveness [16]. However, the process has been primarily limited to plastics and resins. Recently, additive manufacturing in zirconia has been introduced due to advances in 3D printing technology [17]. Despite this, dental implant components, including implant superstructures, are still currently fabricated through subtractive manufacturing via milling.
In summary, AM is increasingly used to fabricate surgical guides, dentures, and implant components, offering enhanced fit, reduced waste, and shorter production times [16,18,19]. Studies have shown that 3D-printed overdentures can achieve comparable masticatory performance and patient satisfaction to conventional analog methods [18,19]. However, challenges remain, particularly with ceramic materials like zirconia, which require precise shrinkage compensation and thermal processing. Despite the promising mechanical and biological properties of zirconia, its application in 3D-printed implant superstructures is still unknown.
This preliminary investigation explored the fabrication of solid dental implant bars through 3D printing using 3Y-TZP zirconia. The primary objective of this investigation is to establish a practical workflow. Additionally, a lattice-structured overdenture bar will be designed and evaluated, as this novel geometric configuration has demonstrated adequate physical properties in the field of orthopedics [20]. Lastly, an assessment of fit (using a simulated mandible and a denture) and the flexure and stress results, when subjected to a load, will be investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
A master model (Figure 1), consisting of a conventional mandibular milled implant bar fixed to a soft tissue edentulous mandibular model with four dental implants, was sourced from a commercial laboratory (Panthera Dental, Quebec City, QC, Canada). The bar was composed of commercial-grade titanium alloy and was utilized for the zirconia implant bars. The implants used were from the Nobel Biocare Replace Select 4.0 implant system (Kloten, Zurich, Switzerland). This in vitro study did not involve human participants or animal subjects and therefore did not require ethical clearance.
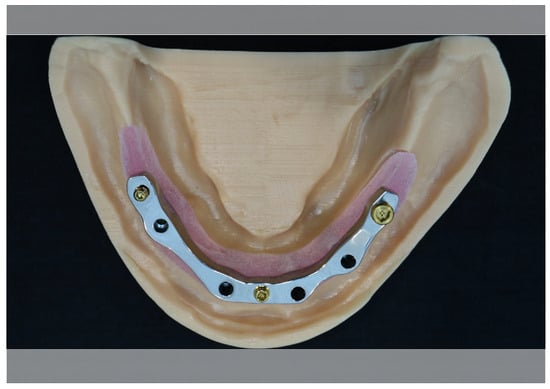
Figure 1.
Soft tissue master model with conventional milled titanium alloy mandibular implant bar.
The titanium milled bar was scanned with a commercial-grade laboratory scanner (Shining 3D, San Francisco, CA, USA). The digital implant bar was optimized using Fusion 360 software (Version v.2603.1.15) (Figure 2) (Autodesk, San Rafael, CA, USA).

Figure 2.
STL file of the dental implant bar.
The STL file of the implant bar was electronically transferred, and additive manufactured/3D printed at the Lithoz Centre (Troy, NY, USA) using LithaCon 210 3Y zirconia. The solid bar was printed/manufactured twelve (12) times (Figure 3).
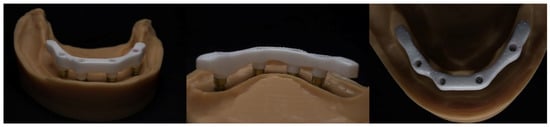
Figure 3.
3D-printed or additive-manufactured zirconia solid dental implant bar on demonstration model without soft tissue.
Complementary to the 3D printing process, all bars underwent post-processing, which included:
- Cleaning after printing and removal from the build platform.
- Thermal processing via drying (preconditioning), debinding, and sintering.
- Measurement, visual inspection, and photography.
The digital file of the 3D-printed bar was then modified and optimized to incorporate a lattice structure (Figure 4), for the printing of five (5) lattice-structured implant bars.
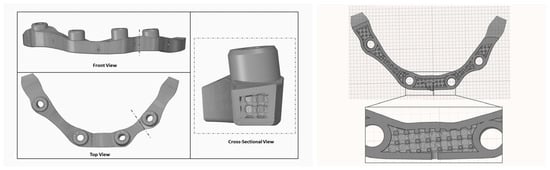
Figure 4.
Implant bar design with circular cross-section internal lattice pattern (Image provided by ADEISS Inc., London, ON, Canada).
The inclination angle during printing was set to 0°, positioning the bar parallel to the build platform. The inter-implant distances were set 7.8 mm anteriorly and 11.4 mm unilaterally, along with a cantilever length of 6.8 mm. The minimum bar height was established at 5 mm, while the lattice design incorporated a minimum solid wall thickness of 0.9 mm, aligning with the capabilities of the additive manufacturing system. The lattice structure was developed featuring a ridge-like arrangement of perpendicular struts. Both the wall thickness and the drainage hole diameter (0.75 mm) were constrained by the requirements for effective powder removal and structural integrity during the manufacturing process.
The lattice bar (Figure 5) underwent the same post-processing as mentioned above before testing.

Figure 5.
An AM mandibular zirconia lattice-structured bar.
The bars were fitted onto the master model, both with and without the simulated soft tissue (Figure 6), and were assessed using (1) standard prosthodontic objective assessments (visual inspection, stability, integrity, etc.), (2) macrophotography and (3) radiology, to assess whether the bar was clinically acceptable or unacceptable.
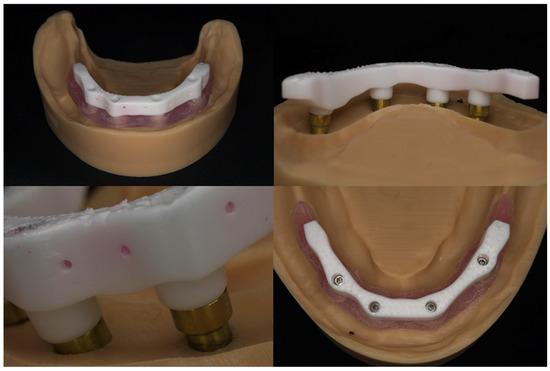
Figure 6.
An AM mandibular zirconia lattice-structured bar on a model with and without soft tissue.
The bar and soft tissue model were forwarded to a commercial dental laboratory (Alien Milling Technologies, Glendale, CA, USA) for the design and fabrication of an overdenture (Figure 7). The denture was a monolithic, single, continuous, and simultaneous print of the teeth and denture base using TrueDent, a multi-material 3D-printed denture (Stratasys, Minnetonka, MN, USA).
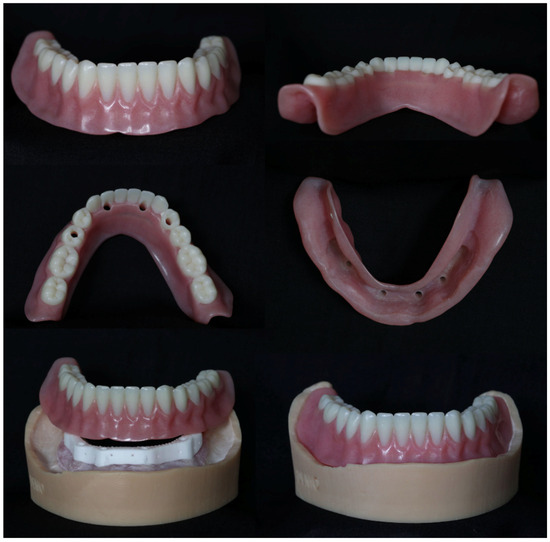
Figure 7.
3D-printed mandibular denture on AM zirconia lattice bar with soft tissue model.
Thermal imaging was conducted using the FLIR One Pro thermal camera (Teledyne FLIR, Wilsonville, OR, USA), which connects via the FLIR OneFIT™ interface to an Android-based mobile device. The camera offers a thermal image resolution of 19,200 pixels, a detection range from −20 °C to 120 °C, and a thermal sensitivity of 0.01 °C. The camera was integrated with the Dental Thermal App (version 2.6), which is downloadable via Google Play (https://play.google.com/). The FLIR One Pro camera (Wilsonville, OR, USA) was attached to the mobile device and calibrated according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. The DTA application was launched, and the thermal mode was selected. Thermal images were acquired using the Multi-Spectral Dynamic Imaging (MSX) function, enhancing contrast and spatial resolution to improve visibility of structural margins and interfaces. The temperature measurement tool within the app was used to identify maximum and minimum temperatures across the prosthesis–implant interface. To ensure consistency, all images were captured at a fixed distance and ambient room temperature [21].
Thermal patterns were assessed for asymmetries, localized heat spots, or thermal gradients across the implant–abutment interface and the intaglio surface of the superstructure. A properly fitting superstructure was expected to demonstrate uniform thermal contact with no isolated areas of temperature elevation, which could indicate micro-gaps, pressure points, or misfits [21].
The denture fit was also assessed as clinically acceptable or unacceptable based on the above-mentioned prosthodontic objective assessments.
Custom-fabricated fixtures were designed (Figure 8 and Figure 9) and manufactured (University Machine Services, Western University, London, ON, Canada) through CAD/CAM in stainless steel to support the implant bars and provide the required force for testing.
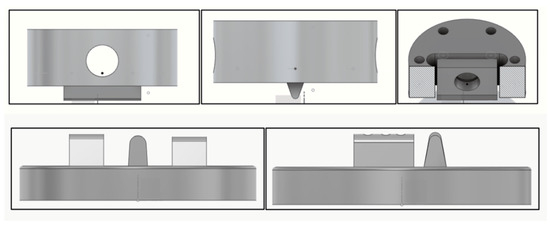
Figure 8.
Design schematics of the custom top fixture (top) and bottom fixture (bottom) for testing.
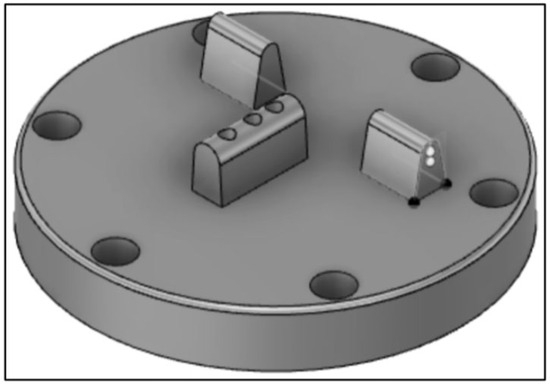
Figure 9.
Final design of the custom-fabricated bottom fixture to support the bar for testing.
All bars were submitted for flexural testing (Applied Technical Services, Marietta, GA, USA) according to ASTM D6272-17e1 [22], using the fixtures as a guide. Prior to testing, all samples were conditioned as per ASTM D618-21 [23] for at least 40 h at 23 ± 2 °C and 50 ± 10% relative humidity. Testing (Figure 10) was performed at a speed of 3 mm/min.
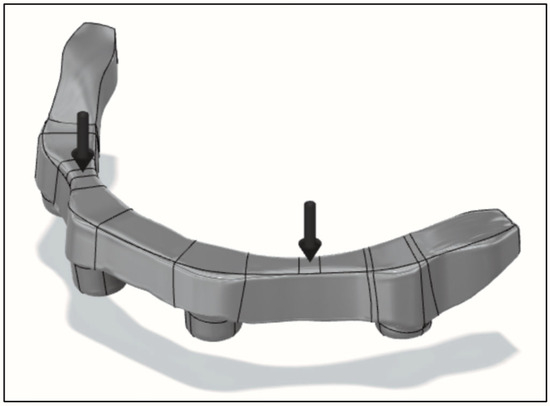
Figure 10.
Location and direction of force vectors on the bar for testing.
A finite element analysis (FEA) was conducted to compare the two previously designed bar models under fracture loading conditions (Figure 10). Both designs were imported into ANSYS R2025 and meshed using tetrahedral elements (125,685 nodes and 53,869 elements). The models were subjected to loading conditions replicating the in vitro setup, with the applied force corresponding to the previously determined fracture load. The analysis considered isotropic and linear-elastic material behavior. The simulation aimed to evaluate and compare stress distribution in each design. The maximum principal stress was calculated for both models to assess their mechanical performance and potential failure points under load.
Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics version 26 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Descriptive statistics (mean ± standard deviation) were calculated for the maximum fracture load and flexural stress of the zirconia bars. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to compare mechanical properties between the solid and lattice bar groups. The significance level was set at α = 0.05.
3. Results
All AM zirconia bars were fitted (screwed) onto the working soft tissue model and assessed as clinically acceptable, based on the following findings.
- No binding and no issues with seating onto the implants.
- No detectable tactile discrepancies between the implant and bar.
- Radiographs indicated no discernible gap between the implants and bar.
- All bars could be torqued to approximately 15 N·cm without any issues.
The bars were assessed for stability and fit using finger pressure, direct vision, tactile assessment (using an explorer), macrophotography, radiography, and thermography (Figure 11) (a novel mobile application was developed to assess the fit using surface temperature variations).
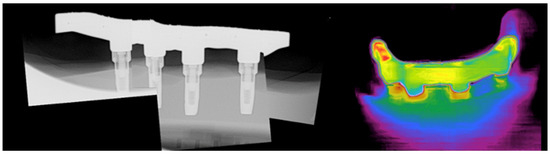
Figure 11.
AM zirconia bar and model. Composite radiograph (left) and thermography imaging (right) to assess fit.
The denture fit onto the AM implant bar with a soft tissue model was also assessed with similar criteria. The denture fit (Figure 12) all AM implant bars with proper uniform seating and appropriate retention. Fit was evaluated using a standard fit check spray. Thermography was also explored as a possible adjunct fit tool (Figure 12, right), where uniform surface temperature would signify proper fit, and higher temperatures would indicate tightness.
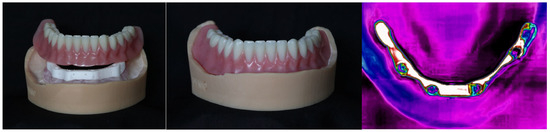
Figure 12.
The denture fits on the AM implant bar. Left photo showing the denture being attached; middle image shows the denture in place, and thermography image (right) used as a possible adjunct for fit assessment.
Applied Technical Services (Marietta, GA, USA) performed flexural testing according to ASTM D6272-17e1, using the provided fixtures as a guide. Testing was performed at a speed of 3 mm/min. The results are illustrated below.
The max load (kN) applied to the AM zirconia solid bars (Table 1) was compared to the max load (kN) applied to the AM zirconia lattice bars (Table 2). There was no statistically significant difference between the two (p = 0.578). As shown in Table 3, the flexural results indicate no statistically significant difference between the AM zirconia lattice and solid bar designs. The average maximum fracture load was 1.2240 kN for the solid bar and 1.1132 kN for the lattice bar (Figure 13). The corresponding stress values were 147 MPa and 143 MPa, respectively (p = 0.578).

Table 1.
Flexure results for solid AM zirconia bars.

Table 2.
Flexural results for the lattice AM zirconia bars.

Table 3.
Comparison of flexural results for AM zirconia lattice bar to AM zirconia solid bar: mean and standard deviation.
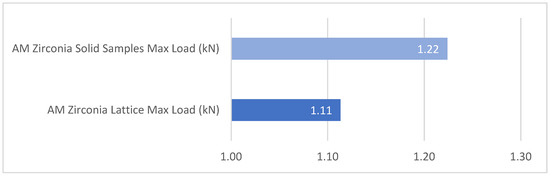
Figure 13.
Comparison of mean flexural strength between AM zirconia lattice and solid bars. The graph displays the average maximum fracture load (in kN) for each design. No statistically significant difference was found between the two groups (p = 0.578).
Finite element analysis revealed the distribution of maximum principal stress across the two zirconia bars under the simulated fracture load. The model was meshed using tetrahedral elements and subjected to boundary and loading conditions replicating an in vitro setup. The stress distribution map shows that most of the structure experienced low to moderate stress levels, predominantly in the range from 0 to 29 MPa, represented by shades of blue and green.
Localized regions near the screw holes and connecting areas between implants exhibited increased stress concentrations, with maximum principal stress values reaching up to 147 MPa (indicated by red zones). These peak stresses are critical and indicate potential areas of mechanical failure or fracture initiation under high-load conditions.
Overall, both bar designs demonstrated comparable stress distribution with limited high-stress concentrations, suggesting a mechanically stable performance under the given load and little influence of the design itself (Figure 14).
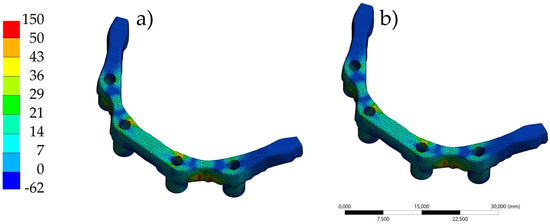
Figure 14.
Finite element analysis showing the distribution of maximum principal stress in the AM zirconia bars under simulated loading conditions. (a) The lattice bar design demonstrates localized stress concentrations near support regions with a slightly more diffuse distribution. (b) The solid bar shows similar stress localization, with peak stresses also occurring at support contact areas. Both designs exhibit fracture initiation correlating with these high-stress zones.
4. Discussion
A workflow was developed to predictably fabricate zirconia dental implant overdenture bars through additive manufacturing (AM), which was the investigation’s main aim. The trial-and-error aspect (print, post-process, assess) was challenging but necessary to formulate an appropriate algorithm for an accurate digital design, compensating for the bar’s shrinkage from sintering and debinding. Solid bars and lattice-structured bars were both fabricated, indicating that complex geometries are possible with digital design and AM utilizing zirconia.
All AM bars were deemed clinically acceptable on the simulated patient model, as assessed by (1) standard objective prosthodontic assessments (visual inspection, stability, integrity, etc.), (2) macrophotography, and (3) radiology. A novel thermography platform was also employed and indicated promise in determining fit based on surface temperature gradients.
In Figure 11 and Figure 12, the distal implants on the right side exhibited slightly higher temperatures during thermographic analysis. While this may reflect normal variability, one possible contributing factor could be manufacturing asymmetries during assembly, such as fitting, assembly sequence, or torque consistency of screw tightening. Although this hypothesis was not directly tested, it highlights the importance of standardizing these variables in future studies.
Clinically acceptable misfit values for implant superstructures are generally considered to be less than 120 µm [24]. Misfit within this range has been shown to maintain prosthetic stability and minimize biological complications [24]. Although precise quantification was not performed in this study, the observed adaptation of the AM zirconia bars was clinically acceptable based on visual assessment.
The model and bar were scanned for the fabrication of a 3D-printed denture. The denture fit on all bars and models was clinically acceptable, as determined by similar prosthodontic assessments, photography, and radiology. Thermography was also employed and showed promise in aiding fit assessment between the bar and denture.
Solid AM zirconia bars withstood an average maximum load of 1.2240 kN, which was higher than the AM zirconia lattice-structured bars, which withstood an average maximum load of 1.1132 kN, with a difference of 0.1108 kN. There was no statistical difference between the two groups (p = 0.578). An ongoing pilot study led by the first author is currently exploring a similar project involving AM solid and lattice-structured titanium alloy implant bars. The solid titanium bars withstood an average maximum load of 5.715 kN.
The bar fractures (failure) occurred in different locations but seemed to coincide with the location of the supports on the custom-fabricated fixtures (Figure 15). Future research may consider equal stress distribution fixtures or the incorporation of the soft tissue model for testing.

Figure 15.
Images depicting the fracture location on the AM solid zirconia implant bar.
The average weight of a solid bar (Table 4) was 8.03 g, while the average weight of the lattice-structured bar (Table 4) was 6.93 g. Lattice-structured bars weighed an average of 1.1 g less than solid bars. In comparison to the work currently in progress by the first author, the average weight of an AM titanium alloy solid implant bar was 5.326 g, and an AM lattice-structured titanium alloy implant bar was 4.221 g. The consistent pattern of reduced weight suggests that lattice structuring is an effective strategy for decreasing the overall mass of prosthetic components, regardless of their material composition. This weight reduction has potential clinical significance when considered in conjunction with findings from Tribst et al., who evaluated the impact of prosthesis weight and the number of implants on peri-implant bone microstrain. Their results showed a direct correlation between prosthesis weight and bone strain: heavier prostheses produced greater strain [25].

Table 4.
Weight of AM zirconia bars.
At the time of this investigation, the average cost for bar fabrication was approximately USD 570 per bar. In comparison, a milled titanium implant bar varied tremendously, but the cost averaged at USD 750 per bar. The AM zirconia bar suggests savings of USD 180/bar. The savings do not consider the fact that many AM zirconia bars can be printed at the same time. For this study, seventeen (17) bars were fabricated at the same time. Conversely, milled metal implant bars are cut from a solid disc, and each disc may provide 4–5 bars in one milling session. The AM zirconia bar avenue would ultimately result in greater cost savings, due to the ability to fabricate several bars at once. Moreover, the lattice-structured zirconia bars used less material and would therefore cost less than the solid bars. Further research is required to explore objective efficiency/sustainability metrics.
The work of Heboyan et al. [26] compared the stress–strain patterns of implants with different superstructure materials using 3D finite element analysis (FEA). The findings indicated that a stiffer superstructure reduced stress on the implants and screws, highlighting zirconia as a potential material choice. Unfortunately, zirconia’s bi-layered structure poses a fracture risk, and alternative forms should be explored [26]. The AM zirconia bars presented in this investigation can act as a zygomatic superstructure and circumvent the bilayer concern. Further research is required to explore this.
Titanium-based dental implants have been renowned for their biocompatibility and durability; however, recent studies have raised concerns about the release of titanium particles during implantation, function, and maintenance. During the surgical phase, frictional forces at the bone–implant interface may release metallic debris, ranging in size from nanometers to micrometers. Research has indicated that up to 0.5 mg of metallic particles can be introduced into surrounding tissues, contributing to local inflammation and possible disruption of osseointegration [27,28]. The micro-gap at the implant–abutment interface may facilitate biofilm formation, which accelerates corrosion and particle detachment. Corrosive conditions, such as those created by acidic environments, degrade the titanium oxide layer, leading to nanoparticle generation [27,28]. Corrosion byproducts can also alter the microenvironment of peri-implant tissues, triggering biological responses, including a higher risk of peri-implantitis [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. Implant micromovements caused by function, known as “fretting,” may result in the release of titanium particles that migrate beyond the implant site to distant organs, such as the lungs and liver [40]. The interaction between chemical, mechanical, biological, and material factors requires further investigation into material options for implant dentistry. The AM zirconia bar provides a potential alternative restorative option for those patients concerned with or opposed to titanium superstructures.
Despite these promising outcomes, certain limitations must be acknowledged. The study was conducted in a controlled in vitro environment, which does not fully replicate the complex loading conditions and long-term effects experienced in the oral cavity. Future research should incorporate fatigue testing, thermal cycling, and clinical trials to assess long-term performance. In addition, the post-processing steps (printing orientation, debinding, sintering) remain time-intensive and operator sensitive, which may impact scalability and reproducibility [41].
Additionally, intraoral factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and masticatory dynamics could significantly influence the long-term performance of zirconia superstructures. The oral cavity presents a complex environment with constant exposure to saliva and temperature variation from food and beverages [42]. Despite zirconia’s reliable strength, cyclic loading in a moist environment may contribute to low-temperature degradation and subcritical crack growth, which could lead to premature failure [43]. It is important to mention that patient-specific variations, such as bone density, ridge morphology, and implant angulation, may result in variable stress distributions across the superstructure, potentially amplifying the risk of fracture under occlusal forces. Because the lattice structure is more complex, it may be more sensitive to surface flaws or incomplete sintering. Therefore, non-destructive evaluation methods, such as CT scanning, should be used to detect internal defects before clinical use [44].
Fracture patterns observed in this study were more frequently located near the cantilever regions rather than within the inter-implant spans. This result aligns with the mechanical expectation that cantilever areas experience greater bending moments and stress concentrations, particularly in the absence of direct implant support.
The use of thermography for fit verification in this study is an innovative approach, offering a non-contact, high-resolution method to visualize thermal distribution patterns indicative of surface contact and misfit [21,45]. However, its application in the dental field remains insufficiently explored. Furthermore, unlike conventional fit-checking techniques such as pressure-indicating paste, silicone fit-checkers, or radiographic assessments, thermography lacks quantitative and standardized thresholds for a clinically acceptable fit. Its effectiveness is also limited by factors such as surface reflectivity [21]. As such, it should be considered a complementary tool, and future work should include comparative validation studies to determine its accuracy, reliability, and clinical relevance relative to established methods. In addition, a quantitative summary of temperature variation was not included due to limitations in the thermal camera’s resolution, which restricted precise extraction of consistent numerical values across all specimens. Given these limitations, the thermographic data were interpreted qualitatively.
The repeatability of the AM process is another critical consideration. Although the bars produced in this study were clinically acceptable, manufacturing consistency and shrinkage compensation must be strictly controlled. Zirconia undergoes significant shrinkage (typically ~20%) during sintering [46], and small variations in the printing or thermal debinding steps could lead to dimensional inaccuracies. In this study, compensation was integrated into the design phase using CAD software, but case-to-case variability remains a concern, and further studies should investigate this effect when producing AM dental prosthetics.
Additionally, it is important to acknowledge the limited statistical power resulting from the relatively small sample size in the lattice bar group. This limitation may affect the robustness of the comparisons made between the solid and lattice designs and should be considered when interpreting the results. Future studies with larger sample sizes are needed to confirm these findings and strengthen the statistical power.
5. Conclusions
Additive manufacturing has experienced rapid growth in recent years, with its applications in implant dentistry expanding substantially. The present study suggests that additive-manufactured zirconia is a viable option for implant-supported superstructures. The lattice design used less raw material, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
To the best of our knowledge, this study presents the first use of a 3D-printed zirconia solid and lattice-structured implant overdenture bar. Such complex geometries are not manufacturable with subtractive methods, reinforcing the advantages of additive manufacturing for alternative dental components. This novel design is a metal-free option in implant dentistry, offering high accessibility and sustainability without compromising mechanical performance.
6. Patents
USPTO: Application # 63/556,335
Utility—Provisional Application under 35 USC 111 (b)
Kalman, L. (2025). Additive Manufactured Solid and Lattice-Structured Metal and Zirconia Dental Implant Overdenture Bars, #63/556,335. Utility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.K.; methodology, L.K. and J.P.M.T.; software, L.K. and J.P.M.T.; formal analysis, L.K. and J.P.M.T.; investigation, L.K.; resources, L.K.; data curation, L.K.; writing—original draft preparation, L.K.; writing—review and editing, J.P.M.T.; visualization, L.K. and J.P.M.T.; supervision, L.K.; project administration, L.K.; funding acquisition, L.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the American Academy of Implant Dentistry Foundation grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to ADEISS for the diagram, Teresa Huynh for the administrative assistance, Alien Milling Technologies, and Lithoz for the technical support and assistance. This study was supported by a grant from the American Academy of Implant Dentistry (AAID) Foundation. The authors gratefully acknowledge the Foundation’s support in advancing research in implant dentistry.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Emami, E.; De Souza, R.F.; Kabawat, M.; Feine, J.S. The impact of edentulism on oral and general health. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 498305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asvanund, C.; Morgano, M.S. Restoration of unfavourably positioned implants for a partially edentulous patient by using an overdenture retained with a milled bar and attachments: A clinical report. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jivray, S.; Chee, W. Rationale for dental implants. Br. Dent. J. 2006, 200, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, D. The implant-supported milled-bar mandibular overdenture. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 10, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosnegutu, A.; Wismeijer, D.; Geraets, W. Implant-supported mandibular bone resorption in edentulous patients: Results of a long-term radiologic evaluation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2015, 30, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rismanchian, M.; Bajoghli, F.; Mostajeran, Z.; Fazel, A.; Eshkevari, P. Effect of implants on maximum bite force in edentulous patients. J. Oral Implantol. 2009, 35, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kok, I.J.; Chang, K.H.; Lu, T.S.; Cooper, L.F. Comparison of three-implant supported fixed dentures and two-implant-retained overdentures in the edentulous mandible: A pilot study of treatment efficacy and patient satisfaction. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacEntee, M.I.; Walton, J.N.; Glick, N. A clinical trial of patient satisfaction and prosthodontic needs with ball and bar attachments for implant-retained complete overdentures: Three-year results. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 93, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.H.; Concalves, T.M.S.V.; Garcia, R.C.M.R. Implant-supported removable partial denture improves the quality of life of patients with extreme tooth loss. Braz. Dent. J. 2015, 26, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenica, L.; Lamazza, L.; Spink, M.J.; De Biase, A. Tissue-supported dental implant prosthesis (overdenture): The search for the ideal protocol. A literature review. Ann. Stomatol. 2012, 3, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hebel, K.S.; Galindo, D.; Gajjar, R.C. Implant position record and implant position cast: Minimizing errors, procedures and patient visits in the fabrication of the milled-bar prosthesis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2000, 83, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalman, L. Implant supported milled bar overdenture. JIACD 2016, 8, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno Samper, A.; Hernández Aliaga, M.; Calvo Guirado, J.L. The implant-supported milled bar overdenture: A literature review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2010, 15, e375-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, M.; Paz, A.; Miguel, I. Fully digital workflow, integrating dental scan, smile design and CAD-CAM: Case report. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, J. The Real Cost of In-Office Milling. Available online: https://adentmag.com/the-real-cost-of-in-office-milling/ (accessed on 18 January 2019).
- Daewood, A.; Marti, B.; Sauret-Jackson, V. 3D printing in dentistry. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 219, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, L.; Tribst, J.P.M. Quality Assessment and Comparison of 3D-Printed and Milled Zirconia Anterior Crowns and Veneers: In Vitro Pilot Study. Eur. J. Gen. Dent. 2024, 13, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, M.S.; Mahanna, F.F.; Said, M.M. Evaluation of Masticatory Performance and Patient Satisfaction for Conventional and 3D-Printed Implant Overdentures: A Randomized Crossover Study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.H.; El-Khashab, M.A.; Kaddah, A.F.T. Marginal Fit of Selective Laser Melting Cobalt-Chromium Bar Versus Cast Bar on Mandibular Edentulous Casts with Two Implants Supported Over Denture: An In Vitro Study. Ahram Can. Dent. J. 2025, 4, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, L. 3D Fabrication Workflow: Solid & Lattice-Structured Titanium Alloy Dental Implant Overdenture Bars. Oral Health 2022, 112. Available online: https://www.oralhealthgroup.com/features/3d-fabrication-workflow-solid-lattice-structured-titanium-alloy-dental-implant-overdenture-bars/ (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Kalman, L. Development of a Novel Dental Thermal Imaging Application. Med. Res. Innov. 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D6272-17e1; Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials by Four-Point Bending. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D618-21; Standard Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Beuer, F. Marginal and Internal Fit of Zirconia Based Fixed Dental Prostheses Fabricated with Different Concepts. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2010, 2, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tribst, J.P.M.; Dal Piva, A.M.D.O.; Borges, A.L.S.; Rodrigues, V.A.; Bottino, M.A.; Kleverlaan, C.J. Does the Prosthesis Weight Matter? 3D Finite Element Analysis of a Fixed Implant-Supported Prosthesis at Different Weights and Implant Numbers. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2020, 12, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heboyan, A.; Lo Giudice, R.; Kalman, L.; Zafar, M.S.; Tribst, J.P.M. Stress Distribution Pattern in Zygomatic Implants Supporting Different Superstructure Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E.; Fischer, G.A.; Delgado-Ruiz, R. Titanium wear of dental implants from placement, under loading and maintenance protocols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential causes of titanium particle and ion release in implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, Z.D.; Patel, A.; Eraldo, B. Dental Implant Failure and the Association with Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs). 2022. Available online: https://www.oralhealthgroup.com/features/dental-implant-failure-and-the-association-with-proton-pump-inhibitors-ppis-and-selective-serotonin-reuptake-inhibitors-ssris/ (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Siverino, C.; Freitag, L.; Arens, D.; Styger, U.; Richards, R.G.; Moriarty, T.F.; Stadelmann, V.A.; Thompson, K. Titanium Wear Particles Exacerbate S. epidermidis-Induced Implant-Related Osteolysis and Decrease Efficact of Antibiotic Therapy. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, R.S.; Hanssen, A.D.; Osmon, D.R.; Illstrup, D. Metal-backed patellar component failure in total knee arthroplasty: A possible risk for late infection. Am. J. Orthop. 1998, 27, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chisari, E.; Magnuson, J.A.; Ong, C.B.; Parvizi, J.; Krueger, C.A. Ceramic-onpolyethylene hip arthroplasty reduces the risk of postoperative periprosthetic joint infection. J. Orthop. Res. 2021, 40, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Dadar, M.; Aaseth, J. Delayed-type hypersensitivity to metals in connective tissue decreases and fibromyalgia. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liow, M.H.L.; Kwon, Y.M. Metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty: Risk factors for pseudotumours and clinical systematic evaluation. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; Ebramzadeh, E.; Nelson, S.; Takamura, K.; De Smet, K.; Amstutz, H.C. Histological Features of Pseudotumor-like Tissues From Metal-on-Metal Hips. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, G.; Pandit, H.; Kliskey, K.; Murray, D.; Gill, H.S.; Athanasou, N. Necrotic and inflammatory changes in metal-on-metal resurfacing hip arthroplasties. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Kwon, Y.M.; Mehmood, S.; Downing, C.; Jurkschat, K.; Murray, D.W. Characterization of metal-wear nanoparticles in pseudotumor following metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, J.P.; Gililland, J.M.; Peters, C.L.; Archibeck, M.J.; Anderson, L.A.; Pelt, C.E. Metallosis and Corrosion Associated With Revision Total Knee Arthroplasties with Metaphyseal Sleeves. Arthroplast. Today 2023, 22, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagay, B.E.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Barao, V.A. Insight into corrosion of dental implants: From biochemical mechanisms to designing corrosion-resistant materials. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2022, 9, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaroop, A.K. Can titanium material for dental implants cause allergy? iCliniq. 2024. Available online: https://www.icliniq.com/articles/dental-oral-health/allergy-and-titanium-dental-implants (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Lu, Y.; van Steenoven, A.; Dal Piva, A.M.D.O.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Wang, L.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Feilzer, A.J. Additive-Manufactured Ceramics for Dental Restorations: A Systematic Review on Mechanical Perspective. Front. Dent. Med. 2025, 6, 1512887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielle, P.; Tarrega, A.; Sémon, E.; Maratray, J.; Gorria, P.; Liodenot, J.J.; Liaboeuf, J.; Andrejewski, J.-L.; Salles, C. From Human to Artificial Mouth, from Basics to Results. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lughi, V.; Sergo, V. Low Temperature Degradation-Aging-of Zirconia: A Critical Review of the Relevant Aspects in Dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, S.F.; Norley, C.J.; Pollmann, S.I.; Holdsworth, D.W. Cost-Effective Micro-CT System for Non-Destructive Testing of Titanium 3D Printed Medical Components. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, T.A.; Alfaifi, A.; Alghamdi, Y.; Nassar, M.; Abuljadyel, R.A. Thermal Sensing of Photo-Activated Dental Resin Composites Using Infrared Thermography. Polymers 2023, 15, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, C.E.E.; Borges, A.F.S.; Macedo, R.M.; Rubo, J.H.; Griggs, J.A. Dimensional Changes from the Sintering Process and Fit of Y-TZP Copings: Micro-CT Analysis. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, e405–e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).