The Genesis of a Thin-Bedded Beach-Bar System Under the Strike-Slip Extensional Tectonic Framework: A Case Study in the Bohai Bay Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Sedimentary Characteristics and Microfacies Types
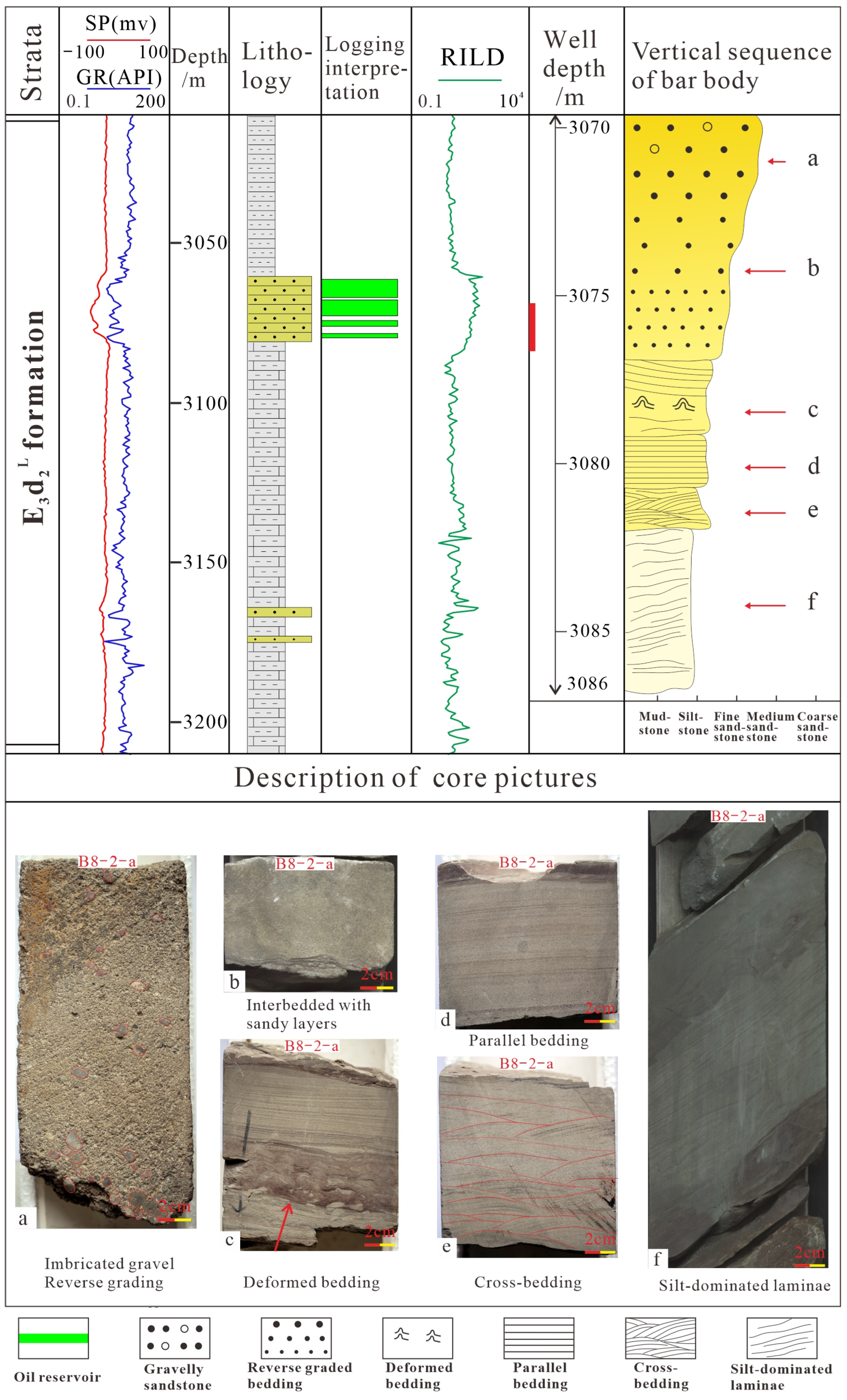
3.1.1. Bar Core
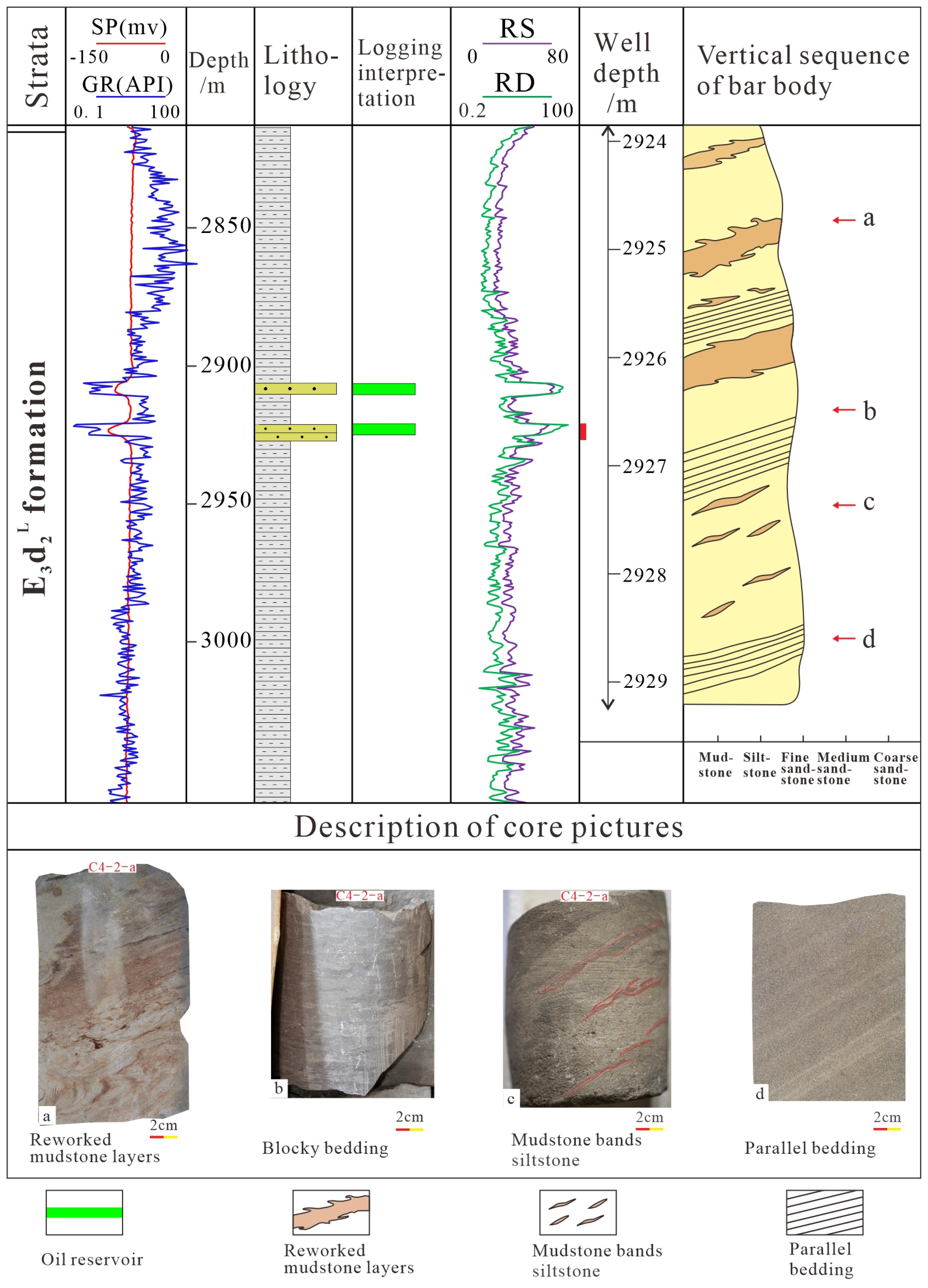
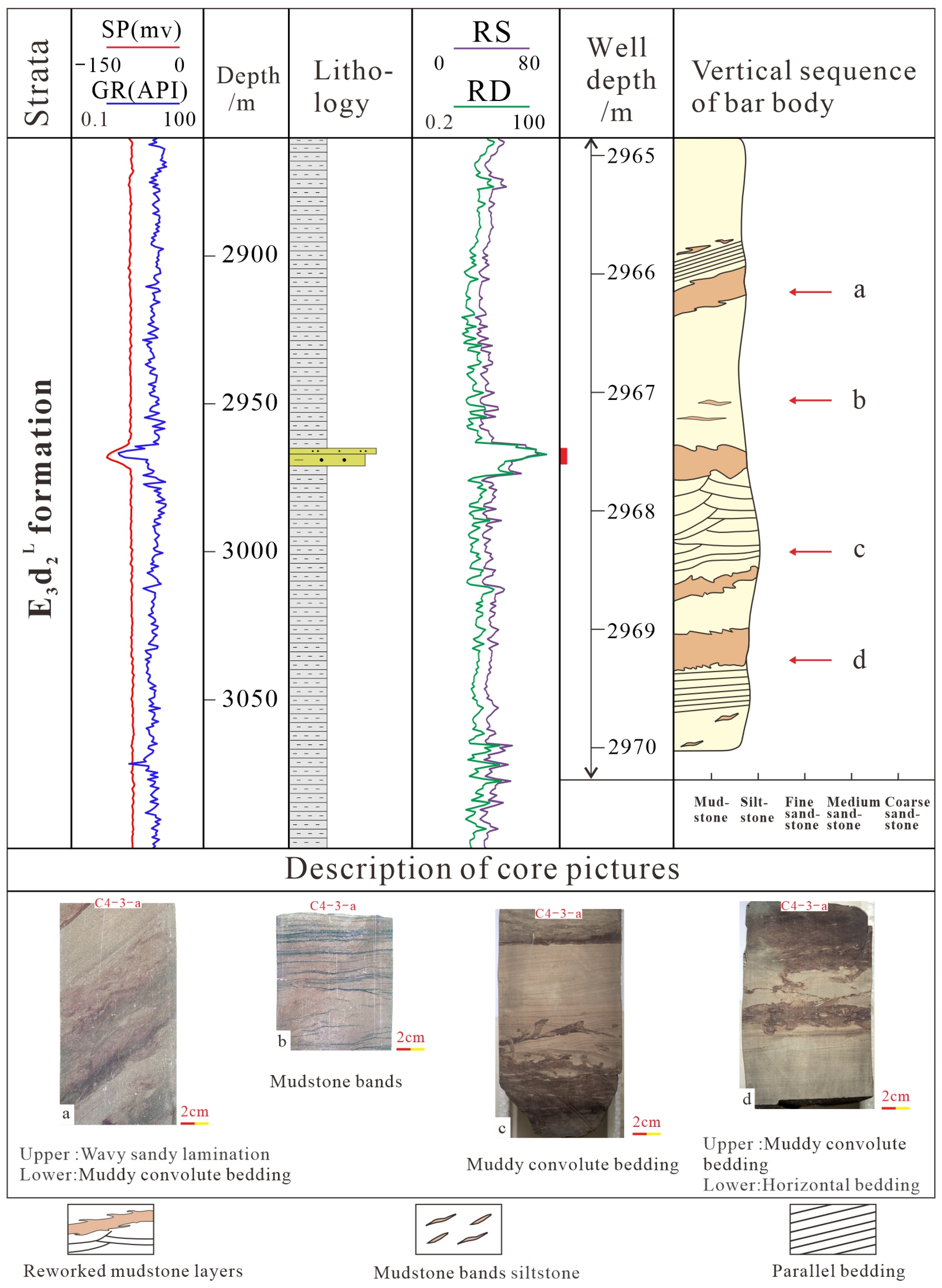
3.1.2. Beach Core
3.1.3. Beach Margin
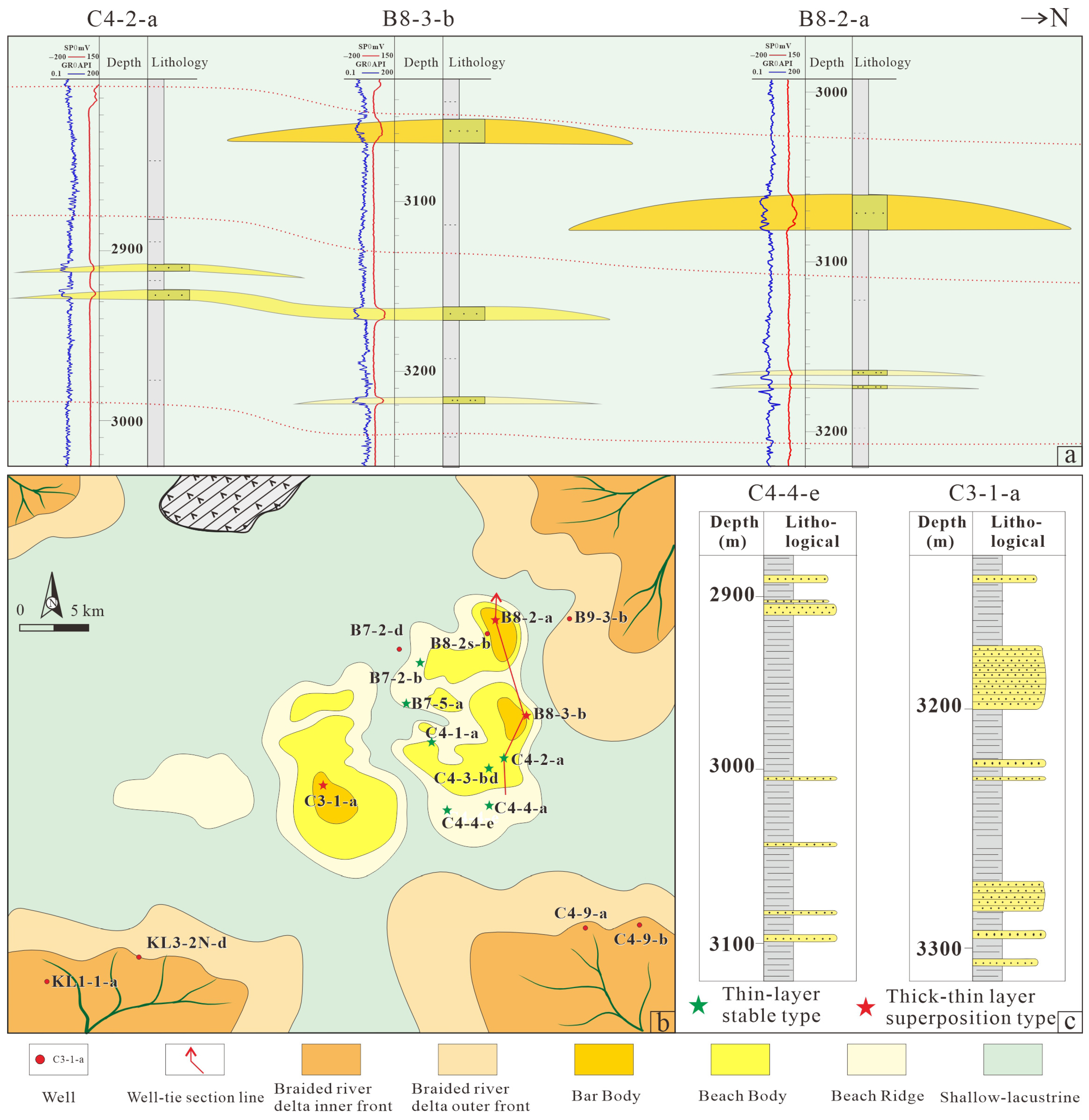
3.2. The Vertical Combination of Thin-Bedded Beach-Bar System
3.3. Genetic Analysis of Sandbodies
3.3.1. Palaeoclimate
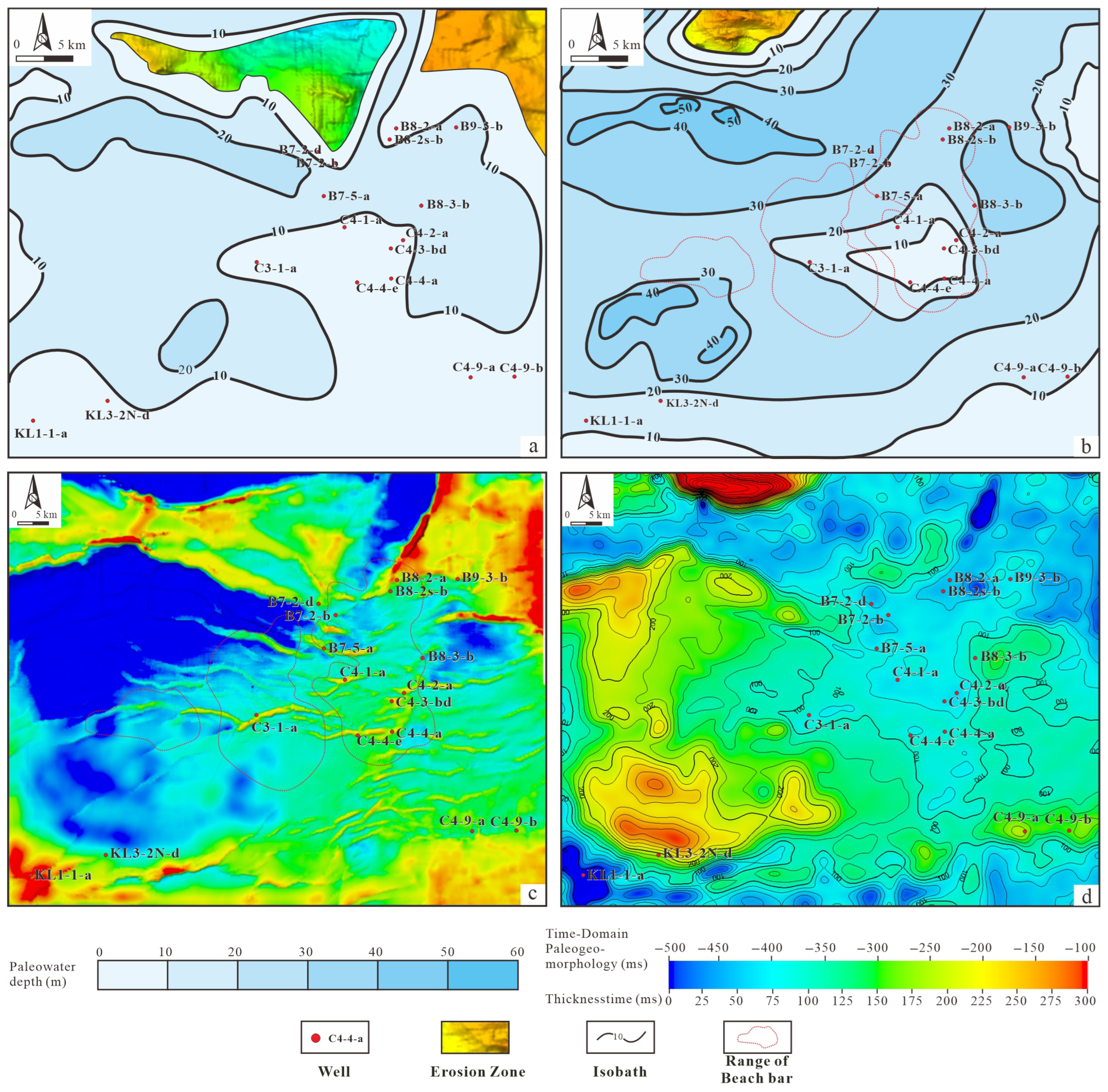
3.3.2. Paleobathymetry
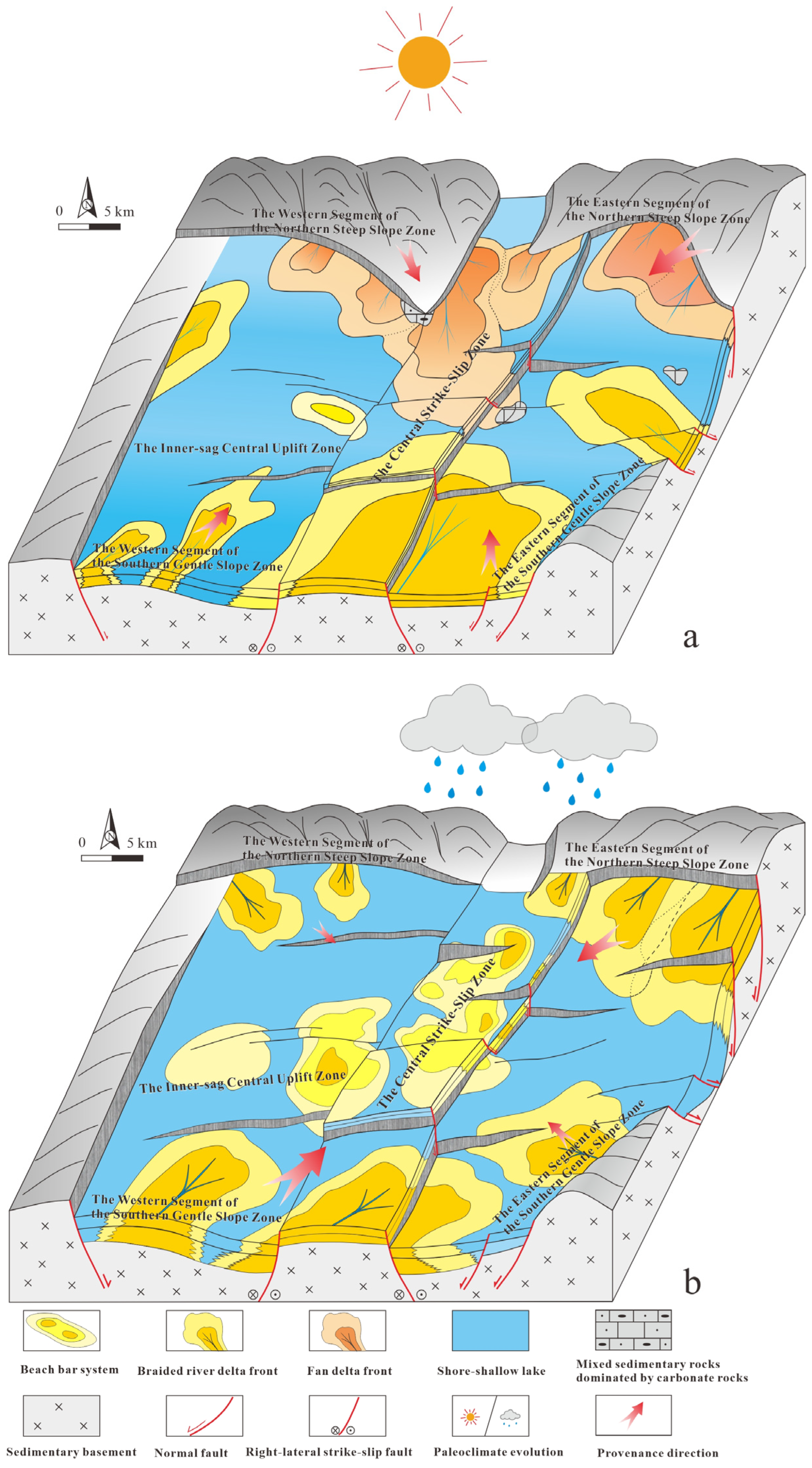
3.3.3. Tectonic Activity
3.3.4. Provenance Supply
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, X.; Zhong, D.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, S.; Sun, H.; Gao, Z.; Xian, B. Development of sedimentary geology of petroliferous basins in China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birgenheier, L.P.; Horton, B.; McCauley, A.D.; Johnson, C.L.; Kennedy, A. A depositional model for offshore deposits of the lower Blue Gate Member, Mancos Shale, Uinta Basin, Utah, USA. Sedimentology 2017, 64, 1402–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Yan, G. New fields and resource potential of tight oil and gas and shale oil exploration in the Bohai Sea area. Acta Pet. Sin. 2025, 46, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, C.; Xie, X.; Yu, X.; Huang, L.; Pan, J.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Tian, D.; Mi, H.; et al. Depositional process and sediment dispersal pattern of mass transport complex on a slope with numerous elliptical depressions, northwestern South China Sea. Sediment. Geol. 2024, 468, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Tian, M.; Tang, D. Sandbody Genesis and Hydrocarbon Accumulation Mechanism of Beach Bar Reservoir in Faulted Lacustrine Basins: A Case Study from the Upper of the Fourth Member of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Menzoul, B.; Uchman, A.; Adaci, M.; Wójcik Tabol, P.; Krzemińska, E. Provenance of the Numidian Formation deposits (Oligo–Miocene) in northern Algeria: Insights from sandstone petrography, palaeocurrent data, geochemistry, and zircon geochronology. Sediment. Geol. 2025, 477, 106808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Duan, T.; Hou, J.; Li, Y. Spatial configuration of sand and mud in the lacustrine nearshore sand bar deposits and its geological implications. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 954–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Junayed, T.R.; Rahman, N. Fluvial reservoir characterization through channel belt dimension and petrophysical analysis. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, A.; Huang, Z.L.; Jin, Z.K.; Nie, Q.H.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhao, G. Influence of structural characteristics on oil and gas distribution in block A of the Muglad Basin. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2021, 56, 172–180+11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, K.; Liu, B.; Qin, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Sinian in the Northwest Tarim Basin. Chin. J. Geol. 2014, 49, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Nanda, S. Geochemistry of a paleosol horizon at the base of the Sausar Group, central India: Implications on atmospheric conditions at the Archean–Paleoproterozoic boundary. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaofei, S.; Jiagen, H.; Yuanzhong, C.; Zhenyue, A.; Ruixiang, Y.; Yan, L. Formation Mechanism of the Thick Layer Lacustrine beach-bar and Its Geological Implications:An Example of the 2nd Member of the Shahejie Formation in Banqiao Sag. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changyin, S.; Fan, S.; Longwei, Q.; Shiqi, Z.; Qingyuan, K. Sedimentary regularities, main controlling factors, and hydrocarbon exploration potential of the beach-bars of the Member 2 of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Zhanhua sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2025, 46, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lyu, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X. Sedimentary characteristics of mixed source fine–grained gravity–flow and its significance for shale oil exploration in a lacustrine depression basin: A case study of the Chang 73 Sub-member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, NW China. Sediment. Geol. 2024, 464, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiu, L.; Fu, J.; Dong, D.; Yang, Y.; Khan, D.; Wu, Z.; Song, F.; Wen, X.; Liu, X. Architectural characteristics, evolutionary stages, and sedimentary models of clastic beach bars. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 146, 105976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Su, X.; Jiang, Z. Sedimentary characteristics of large-scale lacustrine beach-bars and their formation in the Eocene Boxing Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Sedimentology 2011, 58, 1087–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Pang, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, B. Sag, offshore Bohai Bay Basin and its control on beach-bar sands. Oil Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Shi, R.; Xie, S.; Zhang, R.; Cao, L. Sedimentary characteristics and seismic sedimentologic responses of beach-bar deposits in a downfaulted lacustrine basin: A case study of Es1 in the Palaeogene Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2022, 43, 970–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Yue, H.; Zhou, F.; Wu, Q.; Lei, Y. Characteristics and Sedimentary Models of Sheet Sand in Shallow Lacustrine Fluvial–dominated Delta Front: A case study from lower member of Minghuazhen Formation in BZ34 area, Huanghekou Sag. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2020, 38, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qian, G.; Xu, C.; Gao, Y.; Kang, R. Sandstone Distribution and Reservoir Characteristics of Shahejie Formation in Huangheko Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 3068–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Shen, A.; Hu, A.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, J. LA–ICP–MS U–Pb Age, Clumped and Stable Isotope Constraints on the Origin of Middle Permian Coarse–Crystalline Dolomite Reservoirs in Northwest Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 94, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roigé, M.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Stockli, D.F.; Teixell, A.; Boya, S.; Poyatos-Moré, M. Recycling effects in detrital zircon U–Pb signatures in a foreland basin: Identifying the multicyclic sediment sources of the Eocene–Miocene Jaca basin (southern Pyrenees, Spain). Sediment. Geol. 2023, 456, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wu, Z.P.; Li, C.R.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.Q. Structural Characteristics of Tan–Lu Fault Zone in South Area of Bohai Sea and Its Control on Basin Structure. Earth Sci. 2017, 42, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquillas, R.A.; del Papa, C.; Sabino, I.F. Sedimentary aspects and paleoenvironmental evolution of a rift basin: Salta Group (Cretaceous–Paleogene), northwestern Argentina. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2005, 94, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, G.H.; Stout, D.M. Unconventional distribution of facies in a continental rift basin: The Pliocene–Pleistocene Mangas Basin, south–western New Mexico, USA. Sedimentology 2005, 52, 1187–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Lin, C.; Wu, W.; Du, X. Sequence architecture, depositional evolution and responses to tectonic subsidence and lacustrine fluctuation in lacustrine rift basin: A case study from Cenozoic Liaodong Bay, Bohai Bay Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tim, C.; Luo, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Zhou, G.; Michael, R.S. Structural controls on facies distribution in a small half-graben basin: Luanping basin, northeast China. Basin Res. 2010, 22, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminara, S.; Pease, V.; Toro, J.; Omma, J. Provenance studies and basin evolution: Insight from the Yukon–Koyukuk Basin, Alaska. Sedimentology 2024, 72, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Bai, Q.; Ren, H.; Yan, K.; Gao, L.; Wei, L.Z. Quantitative evaluation of morphological characteristics of thin sand body: Taking the deltaic distributary channel sand body as an example in Shengtuo oil field of Dongying Depression, east of Bohai Bay Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, G.; David, C.; Oriol, O.; Edgar, B.; Jordi, I.; Xavier, D.; Albert, S.; Àngel, G.; Ramon, M. Geochemical approach for decoding the paleoenvironmental and depositional evolution of a coastal lacustrine Konservat-Lagerstätte (Early Cretaceous, south-Central Pyrenees). Sediment. Geol. 2023, 453, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gong, C.; Gearon, J.H.; Guan, D.; Wang, Q.; Qi, K.; Li, D. Increased sediment connectivity between deltas and deep-water fans in closed lake basins: A case study from Bozhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Sediment. Geol. 2024, 460, 106561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Hao, X. New insight into East Asian tectonism since the late Mesozoic inferred from erratic inversions of NW-trending faulting within the Bohai Bay Basin. Gondwana Res. 2022, 102, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.I.; Ren, J.; Lu, G.; Shi, S.; Tong, D.; Zhang, J. Cenozoic Episodic Subsidence in the Middle and North Part of Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. 2010, 35, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wei, R.; Xue, Y.; Yan, Y. Late Neogene vegetation, climate, and lake evolution in the Taiyuan Basin of China based on palynological analysis. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2025, 659, 112675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, G.R.; Ridgway, D.K. Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of fan–delta and river–delta deposystems, Pennsylvanian Minturn Formation, Colorado. AAPG Bull. 2003, 87, 1169–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Yu, F.-S.; Zhao, B.-Y.; Meng, L.-J. New model of linkage evolution for the transtensional fault systems in the Nanpu Sag of Bohai Bay Basin: Insight from seismic interpretation and analogue modelling. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 2287–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation & Shengli Oilfield Branch Exploration and Development Research Institute of Sinopec. An Integrated Quantitative Restoration Method for Paleobathymetry in Lacustrine Basins. Invention Patent CN114624775B, 7 April 2023.
- Xue, X.; Storms, J.; Zăinescu, F.; Schuster, M.; Li, W.; Hendrik May, J.; Ng, Z.L.; Van der Vegt, H.; Nutz, A.; Bozetti, G.; et al. Wind-driven hydrodynamic and depositional patterns in shallow lakes: An exploratory modelling approach based on an archetypal case of Lake Hulun. Sedimentology 2025, 72, 1040–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhu, S.; Fan, J.; Zheng, Y. Coupling Relationships between Sedimentary Microfacies, Sand Bodies, and Tectonic Fracture Characteristics in Braided River Deltas: A Case Study of the Bashijiqike Formation in the Keshen 2 Area. Minerals 2023, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Dou, L.; Kong, B. Genetic types and sedimentary model of sandbodies in a shallow–water delta: A case study of the first Member of Cretaceous Yaojia Formation in Qian’an area, south of Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. Onlin 2017, 44, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Du, X.; Wang, Q.; Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, S. Neocene Palaeontlogical Characteristics and Its Paleoenvironment Significance During the Withering Period of the Lacustrine Basin in the Southeastern BOHAI Sea, North CHINA. Acta Micropalaeontol. Sin. 2018, 35, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cao, Q.; Li, S.; Hu, S.; Zhu, K.; Ye, X.; Wan, L. Salinized lacustrine organic–rich shale influenced by marine incursions: Algal-microbial community, paleoenvironment and shale oil potential in the Paleogene Biyang Depression, East China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 580, 110621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guan, D.; Huang, X.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Liu, R.; Feng, B. Integrated SOM Multi–Attribute Optimization and Seismic Waveform Inversion for Thin Sand Body Characterization: A Case Study of the Paleogene Lower E3d2 Sub–Member in the HHK Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapkanski, S.; Ertlen, D.; Rambeau, C.; Schmitt, L. Provenance discrimination of fine sediments by mid-infrared spectroscopy: Calibration and application to fluvial palaeo-environmental reconstruction. Sedimentology 2020, 67, 1114–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, M.; Alex, W.; Mike, M.; Lidia, L. New Models for Submarine Channel Deposits on Structurally Complex Slopes: Examples from the Niger Delta System. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 129, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, D.A.; Shaw, J.B.; Mohrig, D. Topset-dominated deltas: A new model for river delta stratigraphy. Geology 2011, 39, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghali, M.A.; Shelukhina, O.; Abbasi, I.A.; Moustafa, M.S.; Hersi, O.S.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Al-Ramadan, K.; Alqubalee, A.; Bello, A.M.; Amao, A.O. Depositional and sequence stratigraphic controls on diagenesis in the Upper Cambrian-Lower Ordovician Barik Formation, central Oman: Implications for prediction of reservoir porosity in a hybrid-energy delta system. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawęda, A.; Szopa, K.; Chew, D.; O’Sullivan, G.J.; Burda, J.; Klötzli, U.; Golonka, J. Variscan post–collisional cooling and uplift of the Tatra Mountains crystalline block constrained by integrated zircon, apatite and titanite LA-(MC)-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and rare earth element analyses. Chem. Geol. 2018, 484, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.A.; Haytham, S. The Upper Neoproterozoic lacustrine–fan delta depositional systems associated with braided alluvial fans in the Nubian Shield, Egypt. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 452, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, L.; Liesa, L.C.; Simón, L.J.; Luzón, A. Sequence stratigraphy in continental endorheic basins: New contributions from the case of the northern extensional Teruel Basin. Sediment. Geol. 2025, 481, 106868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, C.; Guo, H.; Chen, Z.; Song, L.; Huang, X. Fine characterization and lithologic trap distribution patterns of delta-beach-bar sedimentary system under high-precision sequence constraints: A case study of the upper submember of the 4th member of the Shahejie Formation in the eastern segment of the southern gentle slope of Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2024, 45, 1121–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

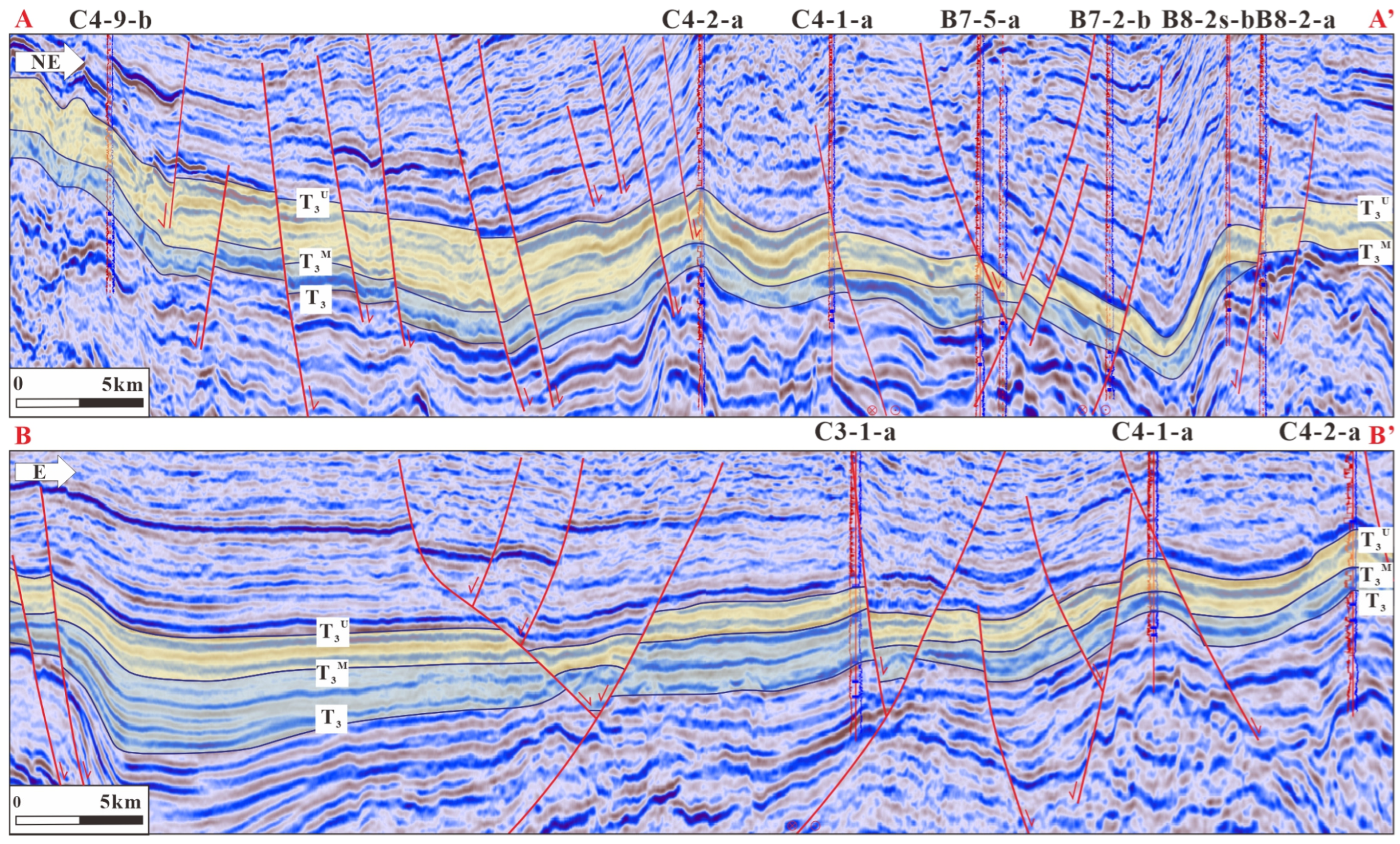
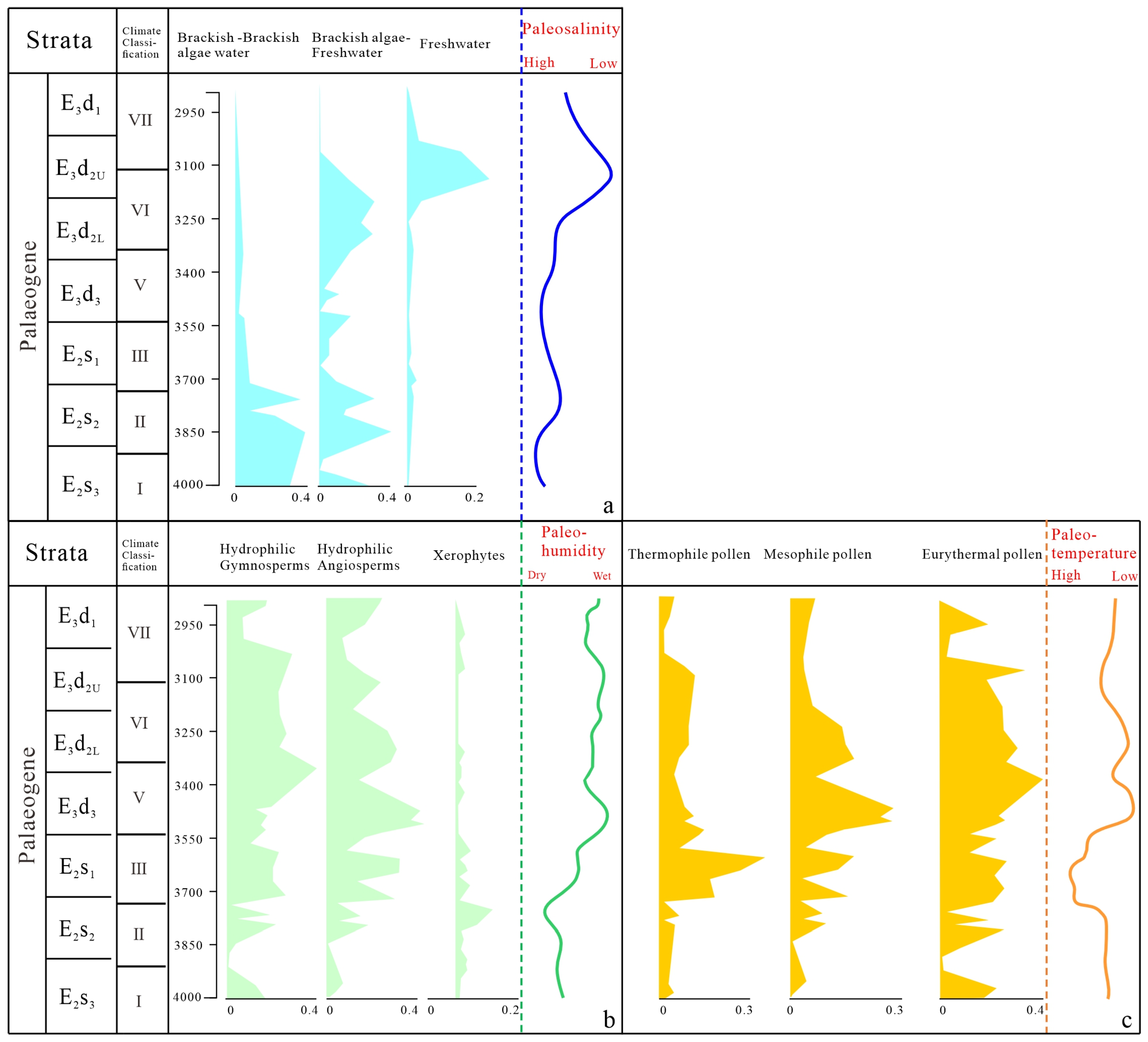

| Climate Classification | Pollen Assemblage | Climate | Strata | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VII | Gymnosperms | Pinus (two-needled pine)–Pinus (single-needled pine)–Tsuga | Warm and humid | E3d1 + E3d2 |
| Angiosperms | Juglans–Carya, with an increase in Juglans | |||
| VI | Gymnosperms | Pinus (two-needled pine)–Pinus (single-needled pine)–Tsuga–Picea | Warm and humid | E3d2 |
| Angiosperms | Juglandaceae–Juglans–Ulmus, with an increase in Juglans | |||
| V | Gymnosperms | Pinus (two–needled pine) and Pinus (single–needled pine) are relatively reduced, while the Cedrus genus is developing | Temperate and humid | E3d2 + E3d3 |
| Angiosperms | Walnut–Carya–Ulmus, with an increase in Tilia | |||
| III | Gymnosperms | Pinus (two-needled pine)–Tsuga–Picea | Subtropical and warm | E3d3 + E3s1 |
| Angiosperms | Acer–Quercus prinoides–Ulmus, with significant increases in Ulmus wislizeni, Quercus, and small-leaved Ulmus | |||
| II | Gymnosperms | Pinus (two-needled pine) continues to develop, the quantity of Tsuga increases, and the genus Ephedra shows significant growth | Subtropical and arid | E3s2 + E3s1 |
| Angiosperms | Small Heinz oak powder–Quercus–Ulmus–smaller elm, with an increase in Liquibarbar and Rutaceae | |||
| I | Gymnosperms | Pinus (two–needled pine)–Pinus (single–needled pine)–Gap pine powder | Subtropical and arid | E2s3 + E3s2 |
| Angiosperms | Quercus (medium oak)–Quercus (small Heinrich’s oak)–Quercus (small oak)–Ulmus (elm) | |||
| Well | Depth Range/m | Sampling Depth/m | Number of Concordant Points | Valid Data (Concordance > 90%) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3-1-a | 3450 | 3450 | 93 | 61 | 65.6% |
| 3515 | 3515 | 109 | 80 | 73.4% | |
| KL1-1-a | 2670 | 2670 | 92 | 70 | 76.1% |
| 2775 | 2775 | 105 | 64 | 61.0% | |
| B8-2-a | 3164–3167 | 3165 | 92 | 67 | 72.8% |
| B8-2s-b | 3190–3195 | 3190 | 123 | 101 | 82.1% |
| Sedimentary Characteristics | Bar Core | Beach Core | Beach Margin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithology | Medium-to-fine sandstone | Siltstone and argillaceous siltstone | Siltstone, silty mudstone, and mudstone |
| Thickness | >8 m | 3 to 8 m | <3 m |
| Textural Maturity | Moderate (moderately sorted; moderate to good roundness) | Moderate (moderately sorted; finer grain size) | Moderate–low (poorly sorted) |
| Sedimentary Structures | Parallel bedding, tabular cross-bedding, and wavy cross-bedding | Horizontal bedding, wavy bedding, and small-scale cross-bedding | Lenticular bedding, bioturbation structures, and wavy bedding |
| Paleogeomorphic Position | Paleogeomorphic highs | Relatively gentle paleogeomorphic highs | Margins of relatively gentle paleogeomorphic highs |
| Distribution Pattern | Localized, lobate, or irregular elliptical | Sheet-like or elongated banded around the bar core | Contiguous distribution around the beach core |
| Logging Response | Blocky/box-shaped and composite | Funnel-shaped or finger-shaped | Finger-shaped |
| Hydrodynamic Conditions | Strong | Moderate | Weak |
| Typical Wells | B8-2-a | C4-2-a | C4-3-a |
| Formation | Well | Fe/Mn | H (s) | Paleobathymetry (m) | Formation | Well | Fe/Mn | H (s) | Paleobathymetry (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E3s1 | B7-2-c | 96.9 | 1.127 | 17 | E3d2 | C4-9-d2 | 93.69 | 1.386 | 27.7 |
| E3s1 | B6-2-bD | 96.75 | 1.121 | 17.5 | E3d2 | B3-3-a | 91.92 | 1.64 | 33.6 |
| E3s1 | C4-9-d | 94.47 | 1.37 | 25.1 | E3d2 | C4-9-f | 92.37 | 1.61 | 32.1 |
| E3s1 | C4-9E-a | 95.97 | 1.22 | 20.1 | E3d2 | C4-9E-a | 91.02 | 1.73 | 36.6 |
| E3s2 | C4-9-e | 99.93 | 0.56 | 6.9 | E3d3 | B6-5-a | 92.01 | 1.63 | 33.3 |
| E3s2 | B7-2-c | 96.78 | 1.09 | 17.4 | E3d3 | C4-9-d | 93.50 | 1.46 | 28.33 |
| E3s2 | C4-9E-a | 97.92 | 0.96 | 13.6 | E3d3 | C4-9-e | 93.99 | 1.38 | 26.7 |
| Well | Sampling Depth/m | Zircon Age Range (Ma) | Geological Age | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cenozoic | Mesozoic | Paleozoic | Pt3 | Pt2/Pt1/Ar2 | |||||
| C3-1-a | 3450 | –– | 570–1000 | 1800–3100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 50 |
| 3515 | –– | 500–1000 | 1800–3100 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 16 | 59 | |
| KL1-1-a | 2670 | 65–250 | 570–1000 | 1800–3850 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 9 | 54 |
| 2775 | 135–250 | 570–1000 | 1800–3100 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 9 | 52 | |
| B8-2-a | 3165 | 65–250 | 570–1000 | 1800–3100 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 14 | 45 |
| B8-2s-b | 3190 | 65–250 | 500–800 | 1800–3100 | 0 | 11 | 2 | 15 | 73 |
| Feature | HHK E3d2ᴸ Beach-Bar System | Conventional Lacustrine Beach-Bar Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Context | Dry–hot → Warm–humid transition | Arid-dominated conditions |
| Tectonics | Strike-slip extensional tectonic framework | Simple fault-slope control |
| Sandbody Distribution | Thin-bedded (3 to 8 m) and laterally extensive | Thick–thin interbedded architecture, frequent vertical stacking, and rapid lateral variation |
| Provenance | Dual sources with paleotopographic coupling | Single dominant source |
| Innovation | Strike-slip partitioning + Paleotopography + climate transition synergy | Tectonic–sedimentary binary control |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, B.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Hou, X. The Genesis of a Thin-Bedded Beach-Bar System Under the Strike-Slip Extensional Tectonic Framework: A Case Study in the Bohai Bay Basin. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147964
Wang J, He Y, Li H, Feng B, Zhao Z, Yu X, Hou X. The Genesis of a Thin-Bedded Beach-Bar System Under the Strike-Slip Extensional Tectonic Framework: A Case Study in the Bohai Bay Basin. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147964
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Youbin He, Hua Li, Bin Feng, Zhongxiang Zhao, Xing Yu, and Xiangyang Hou. 2025. "The Genesis of a Thin-Bedded Beach-Bar System Under the Strike-Slip Extensional Tectonic Framework: A Case Study in the Bohai Bay Basin" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147964
APA StyleWang, J., He, Y., Li, H., Feng, B., Zhao, Z., Yu, X., & Hou, X. (2025). The Genesis of a Thin-Bedded Beach-Bar System Under the Strike-Slip Extensional Tectonic Framework: A Case Study in the Bohai Bay Basin. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7964. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147964







