LightMFF: A Simple and Efficient Ultra-Lightweight Multi-Focus Image Fusion Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
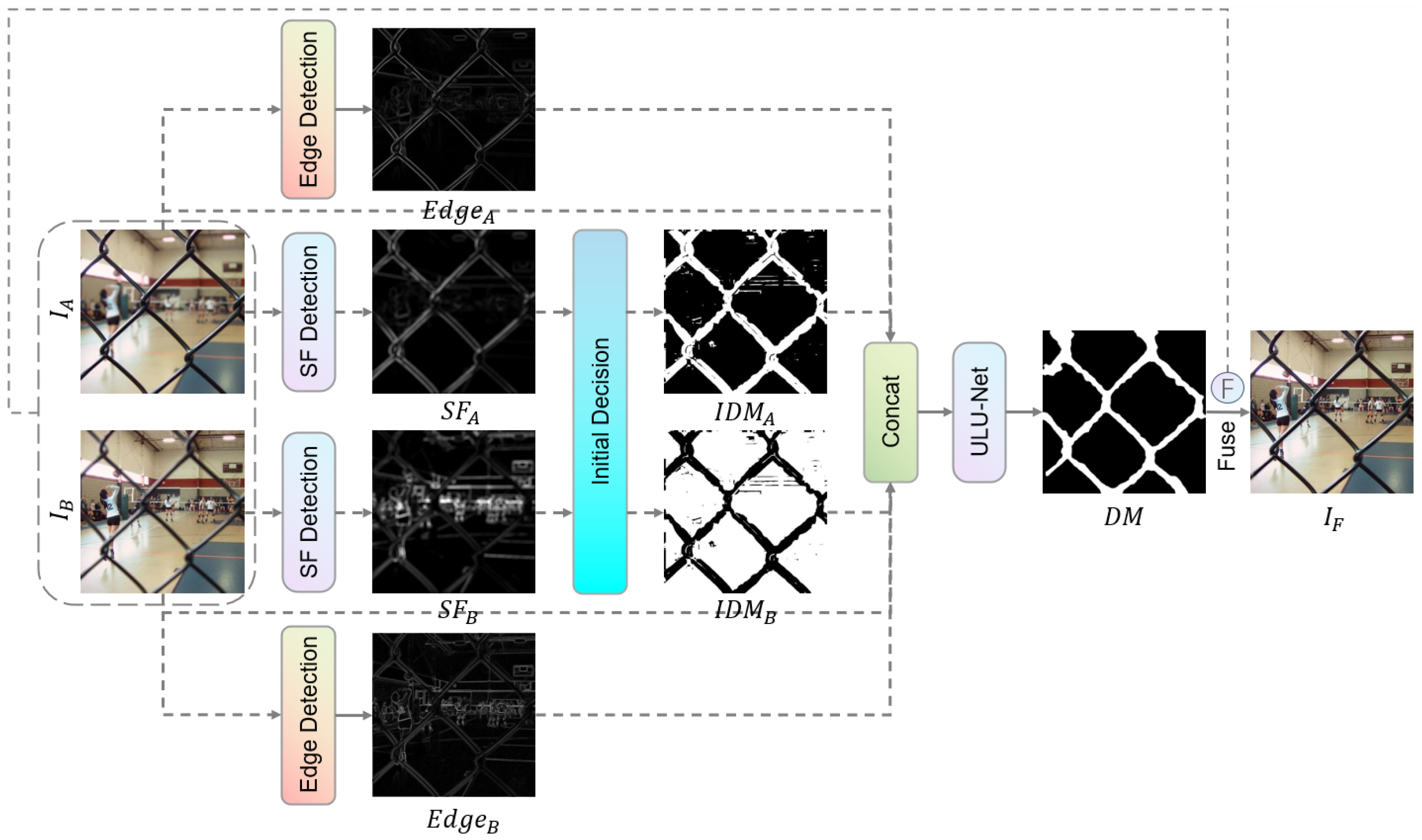
- We introduce a novel task transformation paradigm that reframes MFF from direct focus classification to a decision map refinement process. By providing an initial coarse decision map and explicit edge maps as prior guidance and boundary cues, our approach simplifies network optimization and improves fusion quality.
- We present ULU-Net, a novel U-Net variant designed specifically for MFF. This architecture achieves competitive performance with an ultra-low parameter count, significantly reducing model complexity.
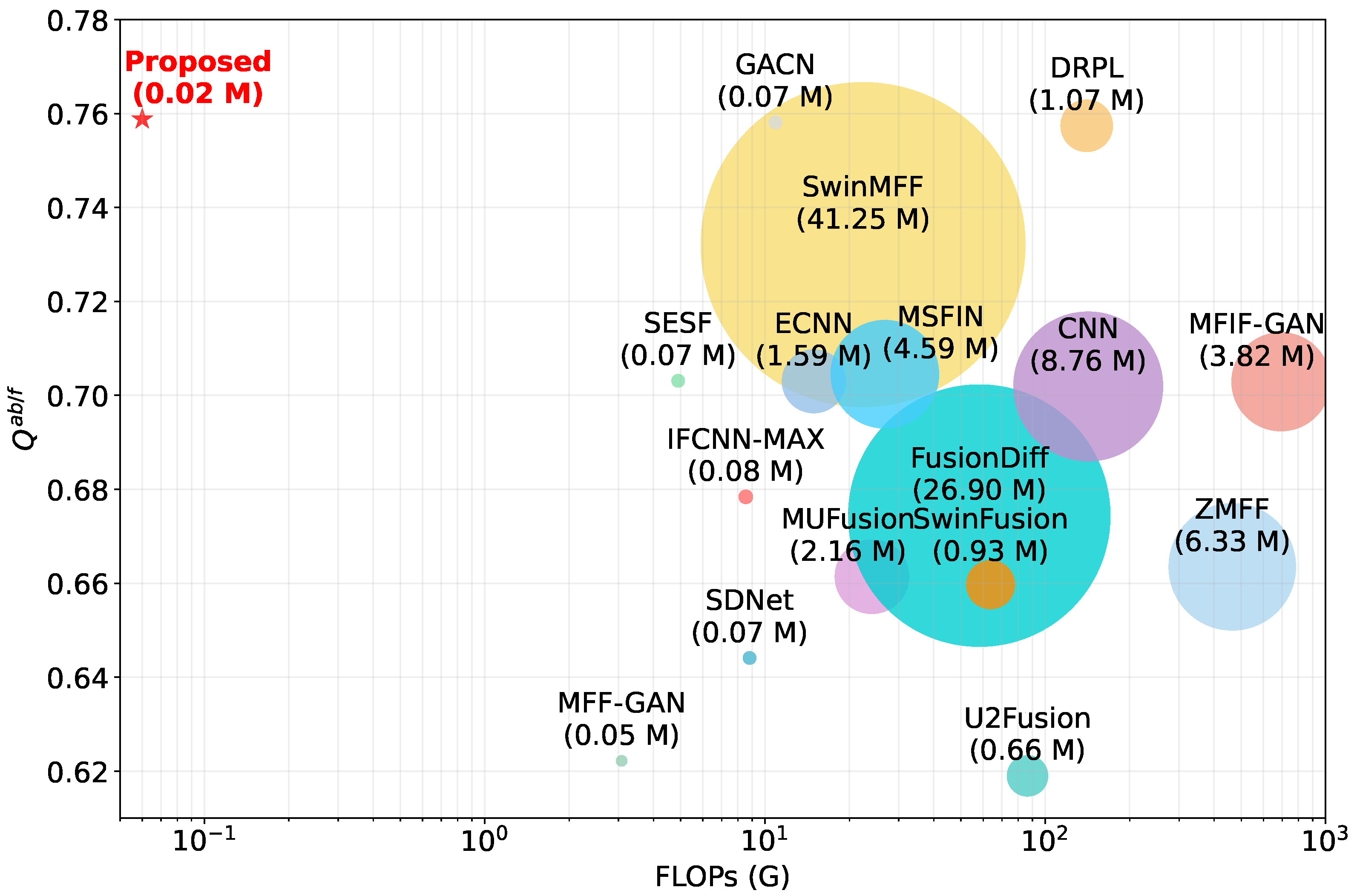
- We propose LightMFF, an ultra-lightweight MFF framework that combines our novel task transformation paradigm with the ULU-Net architecture. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that LightMFF achieves state-of-the-art fusion quality while requiring significantly fewer parameters and computational resources than existing methods.
2. Related Works
2.1. Decision Map-Based Deep Learning Methods
2.2. End-to-End Deep Learning Methods
2.3. Lightweight Multi-Focus Image Fusion Networks
3. Method
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Focus Property and Edge Detection
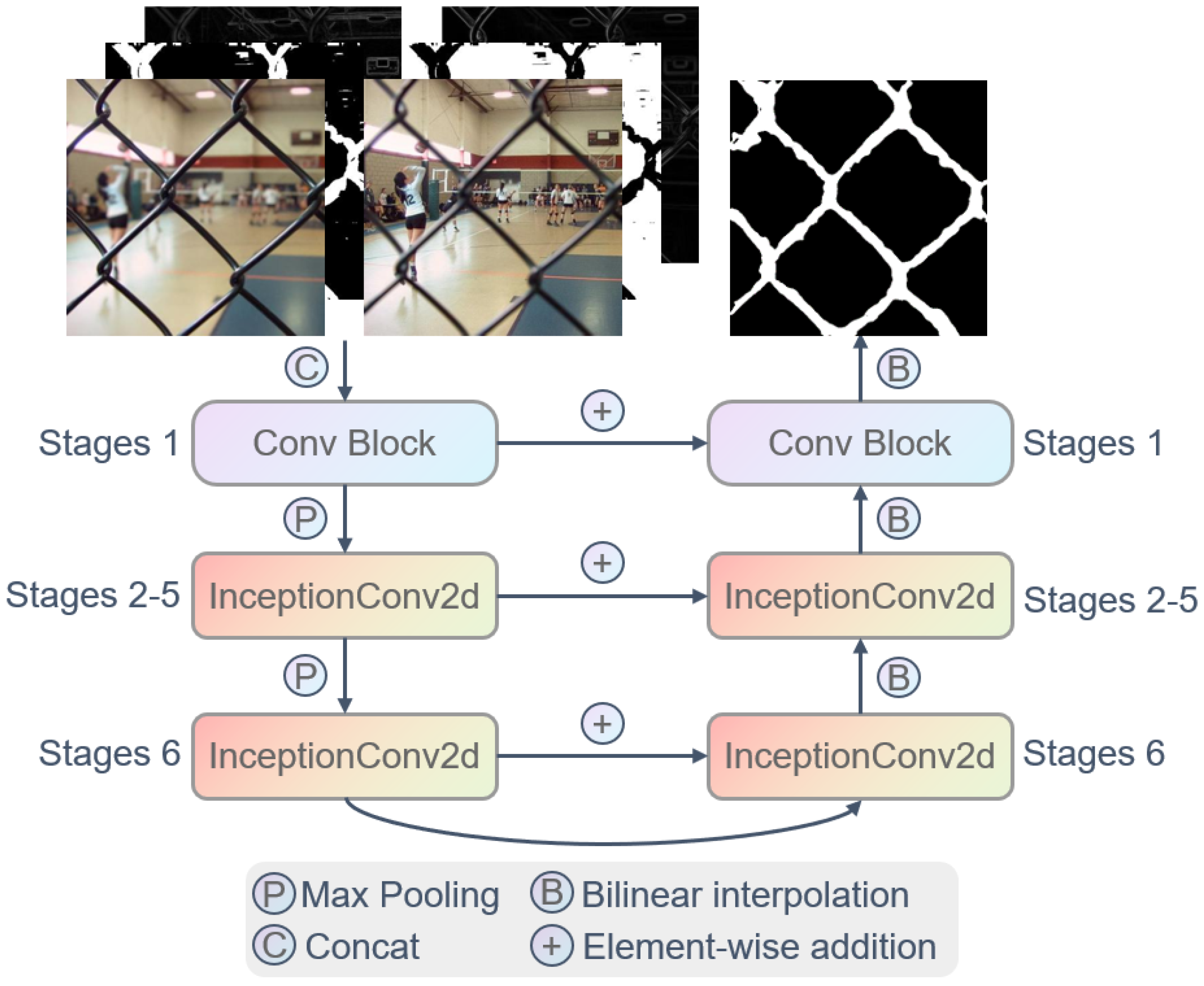
3.3. Network Architecture
3.4. Loss Function
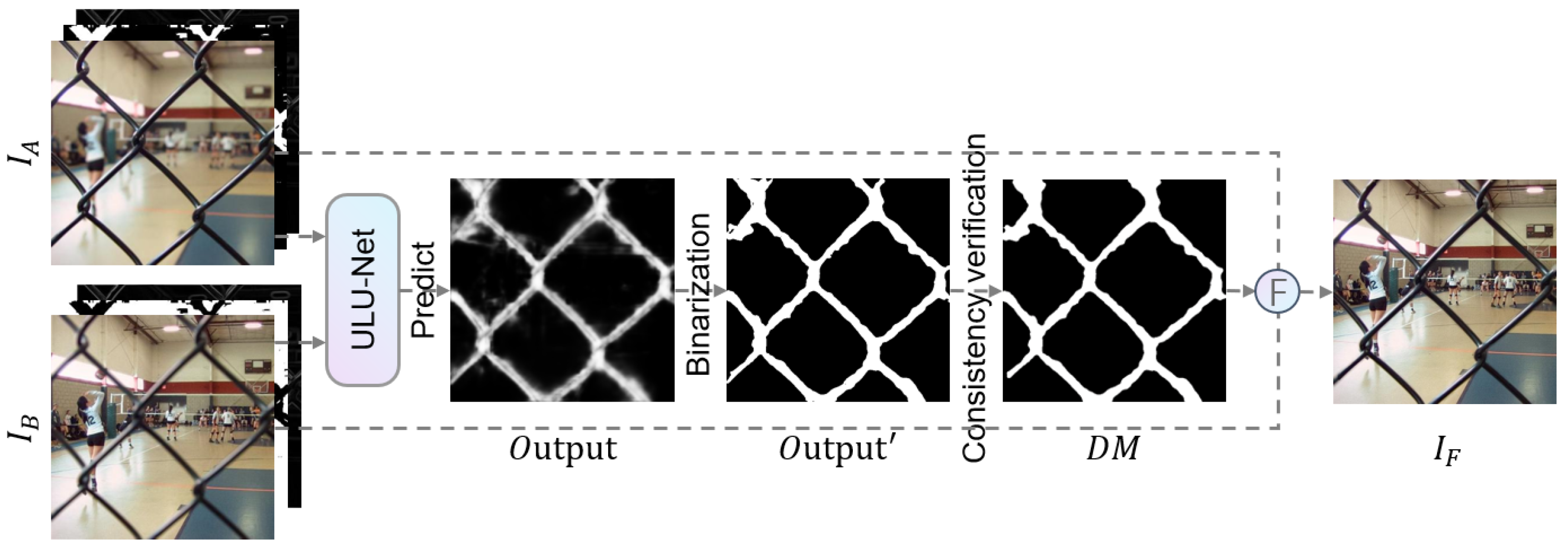
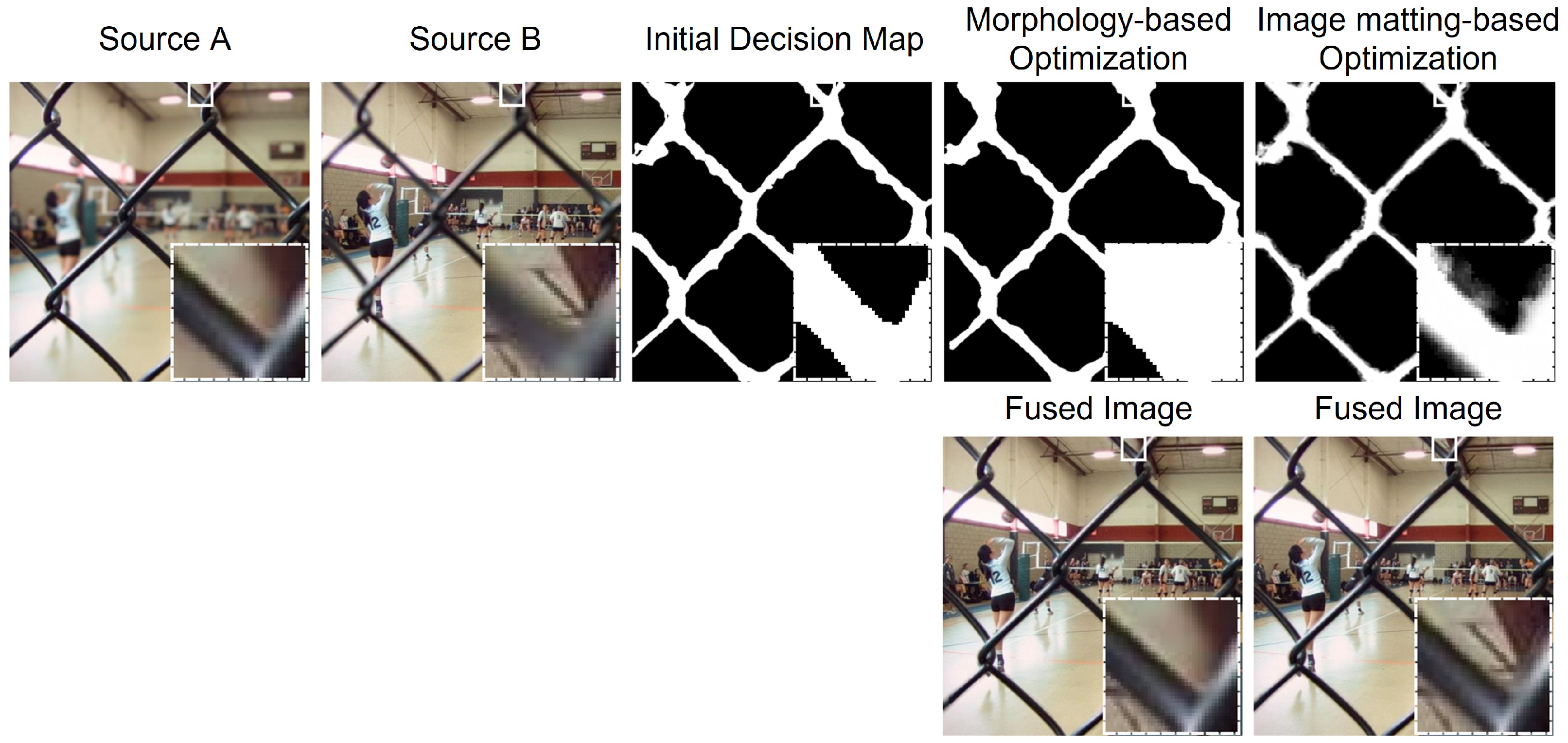
3.5. Fusion Scheme
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
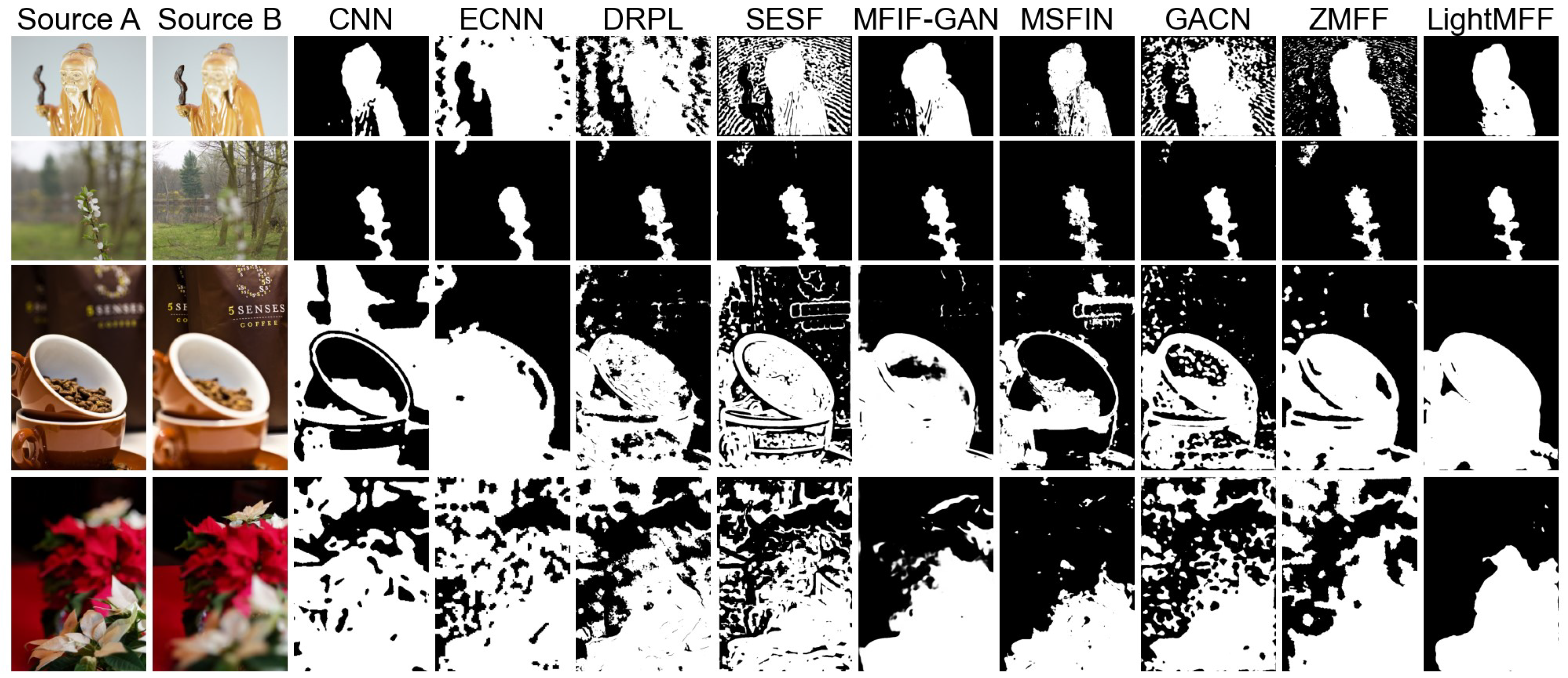
4.2. Experimental Results
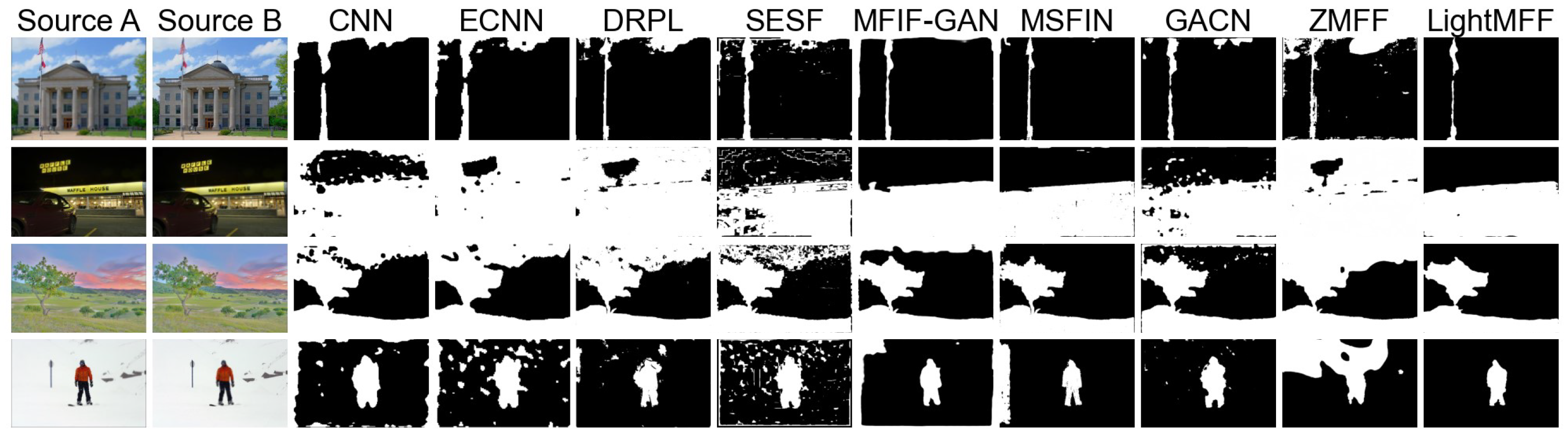
4.3. Performance Under Extreme Conditions
4.4. Performance in Real-World Scenarios
4.5. Performance Under Image Degradation
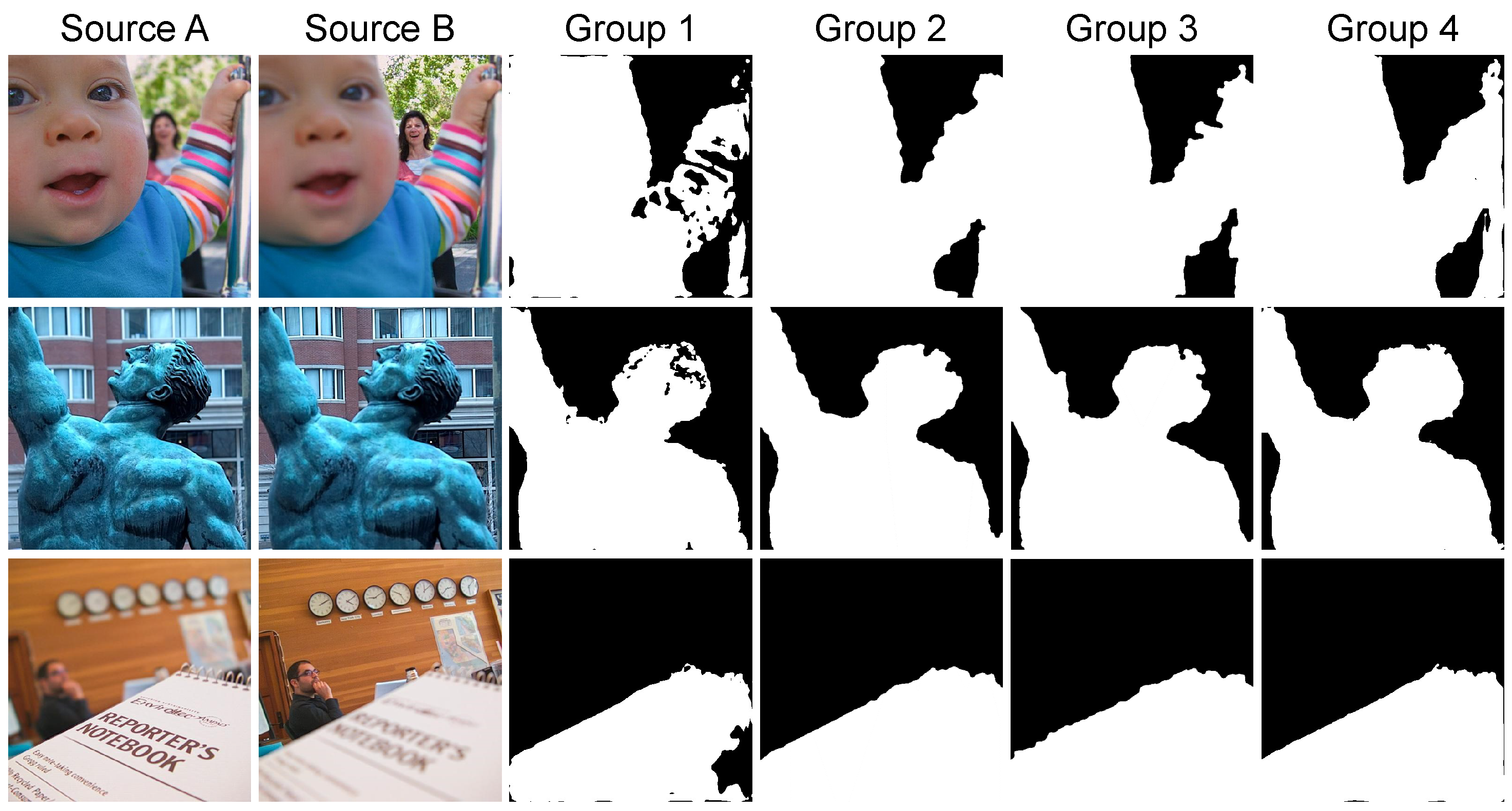
4.6. Ablation Study
- Group 1 (Baseline): Only source images are fed into the network, representing the conventional approach where the network directly learns to distinguish focused from defocused regions.
- Group 2 (w/Decision Map): Source images and the initial decision map are used as input. This setting evaluates the effectiveness of our proposed paradigm shift from direct classification to decision map refinement.
- Group 3 (w/Edge Map): Source images are complemented with edge maps. This setting examines the impact of explicit boundary information without decision map guidance.
- Group 4 (Full Model): Our complete model, incorporating both the initial decision map and edge information, demonstrates the synergistic effect of all components.
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, X.; Guo, B.; Li, P.; Jiang, Q. Underwater Three-Dimensional Microscope for Marine Benthic Organism Monitoring. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2024-Singapore, Singapore, 15–18 April 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, N.; Xin, B.J.; Xing, W.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y. Structural characterization and measurement of nonwoven fabrics based on multi-focus image fusion. Measurement 2019, 141, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Tan, H.; Li, J. SAMF: Small-area-aware multi-focus image fusion for object detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024–2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 3845–3849. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. In Readings in Computer Vision; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, P.J.; Kolczynski, R.J. Enhanced image capture through fusion. In Proceedings of the 1993 (4th) International Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 11–14 May 1993; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.J.; O’Callaghan, R.J.; Nikolov, S.G.; Bull, D.R.; Canagarajah, N. Pixel-and region-based image fusion with complex wavelets. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Manjunath, B.; Mitra, S.K. Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph. Model. Image Process. 1995, 57, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, S.; Sun, F. Image fusion using nonsubsampled contourlet transform. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Image and Graphics (ICIG 2007), Chengdu, China, 22–24 August 2007; pp. 719–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, B.L. Multifocus image fusion using the nonsubsampled contourlet transform. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X. Multiscale feature interactive network for multifocus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, J. ZMFF: Zero-shot multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 92, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, K.; Shalini Punithavathani, D. Optimized ensemble decision-based multi-focus imagefusion using binary genetic Grey-Wolf optimizer in camera sensor networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 1735–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, N.; Majid, A.; Javed, S.G. A novel ensemble approach using individual features for multi-focus image fusion. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 54, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, M.; Liu, Z. Algebraic multi-grid based multi-focus image fusion using watershed algorithm. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 47082–47091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.P. Multifocus image fusion with enhanced linear spectral clustering and fast depth map estimation. Neurocomputing 2018, 318, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, N.; Thepade, S. High-quality image multi-focus fusion to address ringing and blurring artifacts without loss of information. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 4353–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Lei, Y. Multi-focus image fusion using biochemical ion exchange model. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 51, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhang, T. Combining transformers with CNN for multi-focus image fusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 235, 121156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, X.; Lu, G.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, D. DRPL: Deep regression pair learning for multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4816–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, M. New insights into multi-focus image fusion: A fusion method based on multi-dictionary linear sparse representation and region fusion model. Inf. Fusion 2024, 105, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J. Multi-focus image fusion with parameter adaptive dual channel dynamic threshold neural P systems. Neural Netw. 2024, 179, 106603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2017, 36, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin-Naji, M.; Aghagolzadeh, A.; Ezoji, M. Ensemble of CNN for multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 51, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Yan, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 54, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Guo, B.; Li, P.; He, S.; Zhou, S. SwinMFF: Toward high-fidelity end-to-end multi-focus image fusion via swin transformer-based network. Vis. Comput. 2024, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. SwinFusion: Cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.J.; Kittler, J. DDBFusion: An unified image decomposition and fusion framework based on dual decomposition and Bézier curves. Inf. Fusion 2025, 114, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Pei, R.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W. FusionDiff: Multi-focus image fusion using denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, X.; Ban, X.; Huang, H.; Mukeshimana, M. Sesf-fuse: An unsupervised deep model for multi-focus image fusion. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 5793–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. MFIF-GAN: A new generative adversarial network for multi-focus image fusion. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2021, 96, 116295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Q.; Miao, S.; Wang, P.; Chu, X. Multi-focus image fusion based on transformer and depth information learning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 119, 109629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Wan, X.; Tang, Z.; Liang, J.; Ji, H. Multi-Focus Image Fusion via Explicit Defocus Blur Modelling. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2025, 39, 6657–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, Z.; Fang, A. LSKN-MFIF: Large selective kernel network for multi-focus image fusion. Neurocomputing 2025, 635, 129984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J. SDNet: A versatile squeeze-and-decomposition network for real-time image fusion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2761–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Le, Z.; Shao, Z.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. MFF-GAN: An unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2021, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.J. MUFusion: A general unsupervised image fusion network based on memory unit. Inf. Fusion 2023, 92, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Qingyan, J.; Chen, D.; Guo, B.; Li, P.; Zhou, S. StackMFF: End-to-end multi-focus image stack fusion network. Appl. Intell. 2025, 55, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Zhao, J.; Pan, Z.; Li, H.; Li, Y. MMAE: A universal image fusion method via mask attention mechanism. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 158, 111041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, D.; Yu, H.; Gui, G.; Gui, W. LFDT-Fusion: A latent feature-guided diffusion Transformer model for general image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2025, 113, 102639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Hou, J.; Nie, R.; Yao, S.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, Q.; He, K. A lightweight scheme for multi-focus image fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 23501–23527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, K.; Dou, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jeon, G.; Yang, X. LNMF: Lightweight network for multi-focus image fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 22335–22353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Hu, B.; Gao, X. MLNet: A multi-domain lightweight network for multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 5565–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Gong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, G. A lightweight GAN-based image fusion algorithm for visible and infrared images. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Computer Science and Blockchain (CCSB), Shenzhen, China, 6–8 September 2024; pp. 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, D.; Ouyang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhou, H.; Ling, B.W.K.; Teo, K.L. MACTFusion: Lightweight cross transformer for adaptive multimodal medical image fusion. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024, 29, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, M.; Samavi, S.; Shirani, S. Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 25, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, I.; Feldman, G. A 3x3 isotropic gradient operator for image processing. Stanf. Artif. Intell. Proj. (Sail) 1968, 1968, 271–272. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, P.; Yan, S.; Wang, X. Inceptionnext: When inception meets convnext. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5672–5683. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, T.Y.; Dollár, G. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Sudre, C.H.; Li, W.; Vercauteren, T.; Ourselin, S.; Jorge Cardoso, M. Generalised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: Third International Workshop, DLMIA 2017, and 7th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Québec City, QC, Canada, 14 September 2017; Proceedings 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, D.; Yin, B.; Ruan, X. Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Wei, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. MFFW: A new dataset for multi-focus image fusion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.04780. [Google Scholar]
- Rockinger, O. Image sequence fusion using a shift-invariant wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 26–29 October 1997; Volume 3, pp. 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighat, M.B.A.; Aghagolzadeh, A.; Seyedarabi, H. Multi-focus image fusion for visual sensor networks in DCT domain. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2011, 37, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Olshausen, B.A.; Field, D.J. Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images. Nature 1996, 381, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous image fusion and denoising with adaptive sparse representation. IET Image Process. 2015, 9, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, B. Multi-scale weighted gradient-based fusion for multi-focus images. Inf. Fusion 2014, 20, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Sevcenco, I.S.; Agathoklis, P. Multi-exposure and multi-focus image fusion in gradient domain. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2016, 25, 1650123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Yan, J.; Qu, X. High quality multi-focus image fusion using self-similarity and depth information. Opt. Commun. 2015, 338, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, I.; Chanda, B. Multi-focus image fusion using a morphology-based focus measure in a quad-tree structure. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X. Guided filter-based multi-focus image fusion through focus region detection. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 72, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Miao, L.; Zong, H. Multi-focus image fusion using boosted random walks-based algorithm with two-scale focus maps. Neurocomputing 2019, 335, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Kong, L.; Liu, B.; He, Y. Multimodal image seamless fusion. J. Electron. Imaging 2019, 28, 023027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Yin, X.; Wu, D.; Shen, H.; Ban, X.; Wang, Y. End-to-end learning for simultaneously generating decision map and multi-focus image fusion result. Neurocomputing 2022, 470, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xydeas, C.S.; Petrovic, V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron. Lett. 2000, 36, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Laganiere, R.; Liu, Z. Performance assessment of combinative pixel-level image fusion based on an absolute feature measurement. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2007, 3, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Piella, G.; Heijmans, H. A new quality metric for image fusion. In Proceedings of the 2003 International Conference on Image Processing (Cat. No. 03CH37429), Barcelona, Spain, 14–17 September 2003; Volume 3, pp. 3–173. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Blum, R.S. A new automated quality assessment algorithm for image fusion. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Lischinski, D.; Weiss, Y. A closed-form solution to natural image matting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 30, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
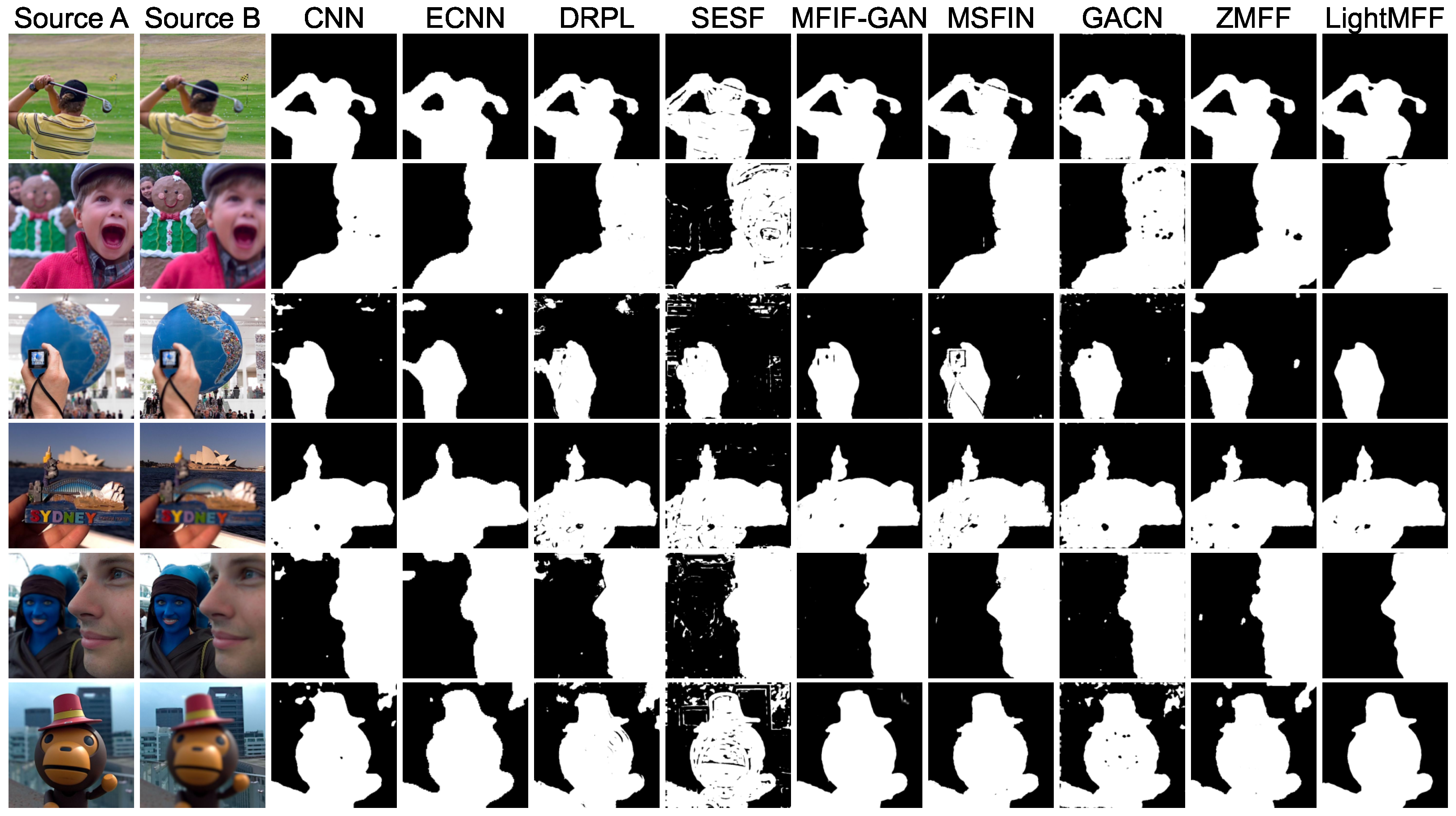
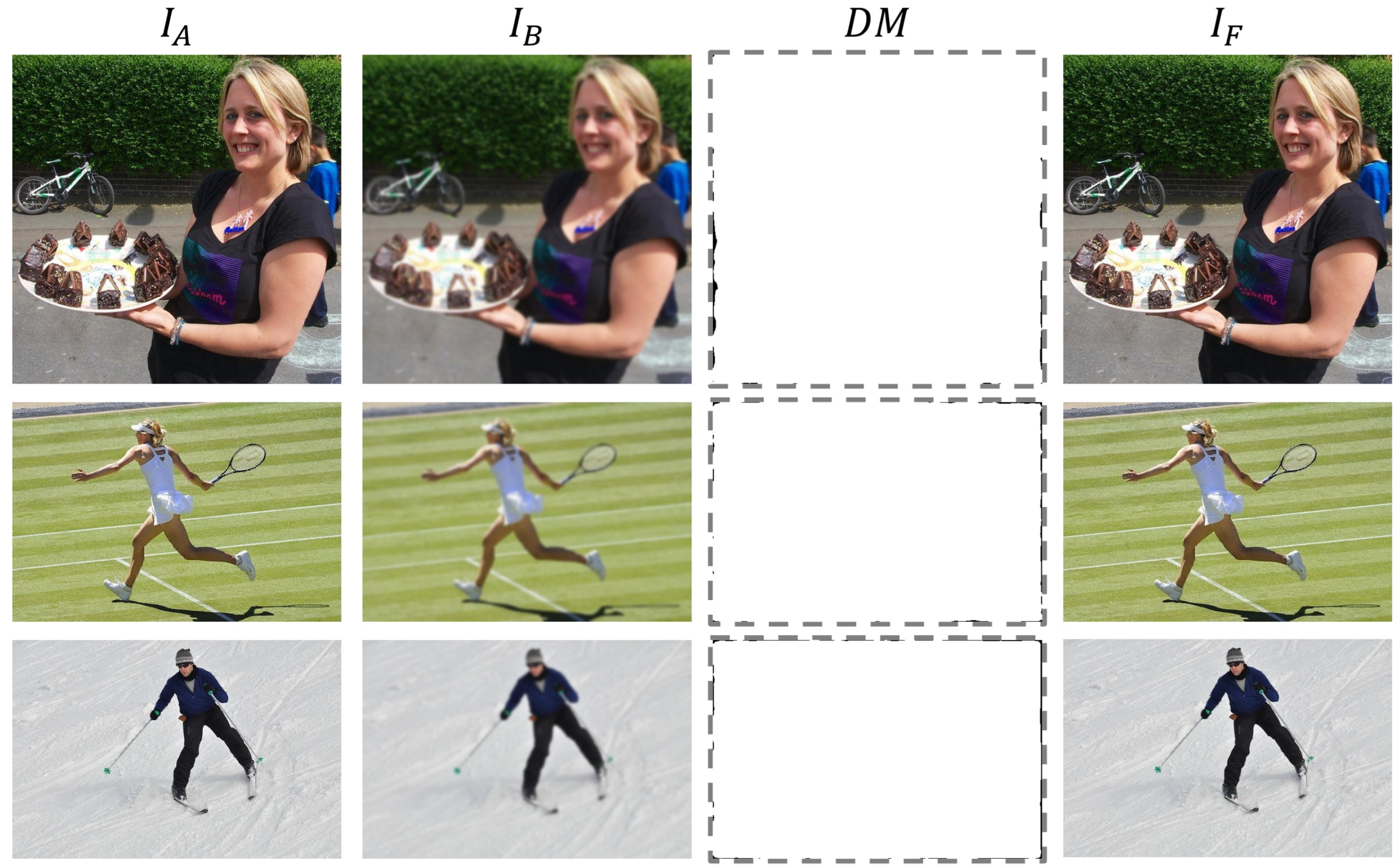
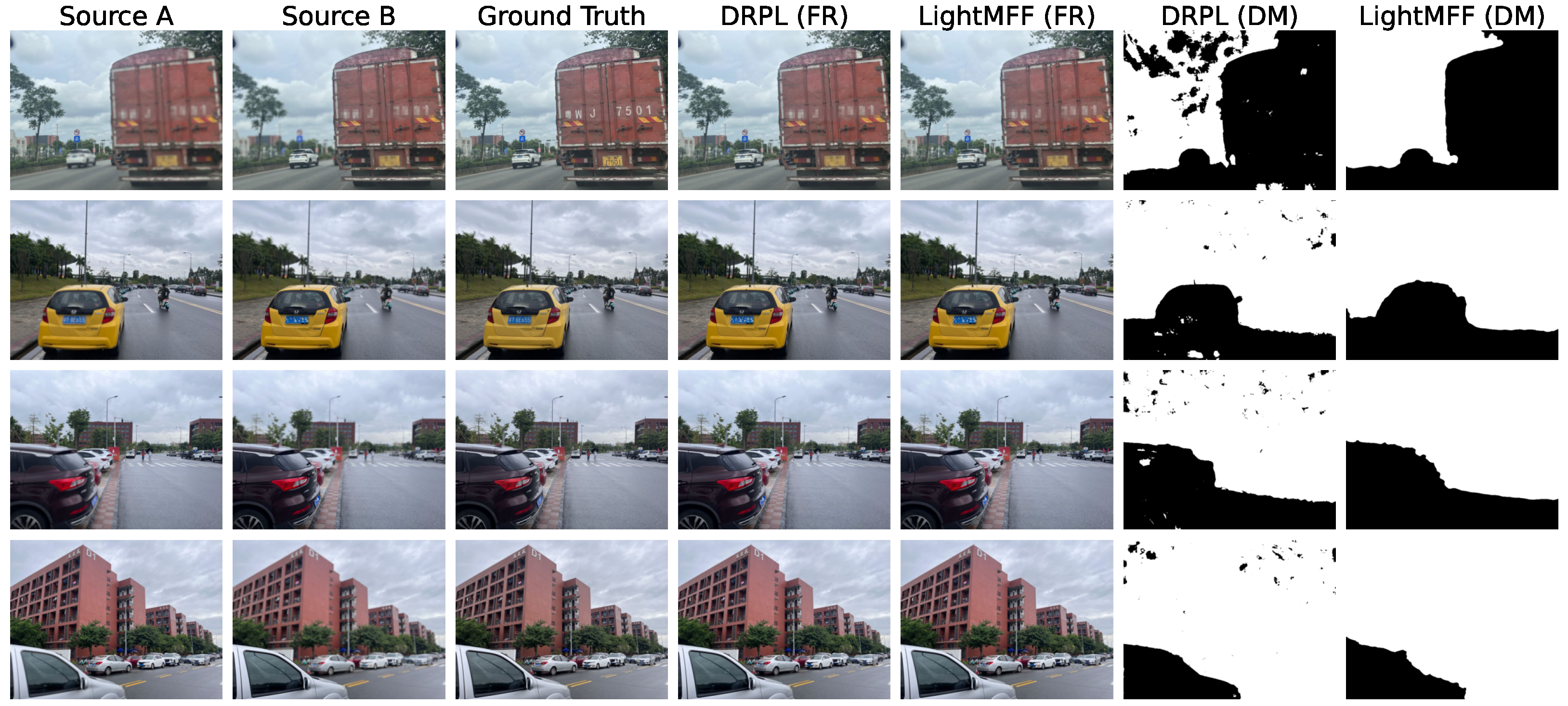





| Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods based on image transform domain | ||||||
| DWT [7] | 0.6850 | 0.8677 | 0.2878 | 0.8977 | 0.8356 | 0.6117 |
| DTCWT [54] | 0.6929 | 0.8992 | 0.2925 | 0.8987 | 0.8408 | 0.6234 |
| NSCT [8] | 0.6901 | 0.9039 | 0.2928 | 0.9030 | 0.8413 | 0.6174 |
| CVT [55] | 0.7243 | 0.8968 | 0.7966 | 0.9388 | 0.9023 | 0.7277 |
| DCT [7] | 0.7031 | 0.9383 | 0.7825 | 0.9093 | 0.8073 | 0.6624 |
| GFF [56] | 0.6998 | 1.0020 | 0.2952 | 0.8982 | 0.8351 | 0.6518 |
| SR [57] | 0.6944 | 1.0003 | 0.2921 | 0.8984 | 0.8309 | 0.6406 |
| ASR [58] | 0.6951 | 1.0024 | 0.2926 | 0.8986 | 0.8308 | 0.6413 |
| MWGF [59] | 0.7037 | 1.0545 | 0.3176 | 0.8913 | 0.8107 | 0.6758 |
| ICA [60] | 0.6766 | 0.8687 | 0.2964 | 0.9084 | 0.8219 | 0.5956 |
| NSCT-SR [61] | 0.6995 | 1.0189 | 0.2949 | 0.9000 | 0.8385 | 0.6501 |
| Methods based on image spatial domain | ||||||
| SSSDI [62] | 0.6966 | 1.0351 | 0.2915 | 0.8961 | 0.8279 | 0.6558 |
| QUADTREE [63] | 0.7027 | 1.0630 | 0.2940 | 0.8962 | 0.8265 | 0.6681 |
| DSIFT [61] | 0.7046 | 1.0642 | 0.2954 | 0.8977 | 0.8354 | 0.6675 |
| SRCF [46] | 0.7036 | 1.0590 | 0.2954 | 0.8978 | 0.8369 | 0.6669 |
| GFDF [64] | 0.7049 | 1.0524 | 0.2974 | 0.8989 | 0.8399 | 0.6657 |
| BRW [65] | 0.7040 | 1.0516 | 0.2964 | 0.8984 | 0.8371 | 0.6650 |
| MISF [66] | 0.6984 | 1.0391 | 0.2945 | 0.8929 | 0.8063 | 0.6607 |
| MDLSR_RFM [20] | 0.7518 | 1.1233 | 0.8294 | 0.9394 | 0.9021 | 0.8064 |
| End-to-end methods based on deep learning | ||||||
| IFCNN-MAX [24] | 0.6784 | 0.8863 | 0.2962 | 0.9013 | 0.8324 | 0.5986 |
| U2Fusion [25] | 0.6190 | 0.7803 | 0.2994 | 0.8909 | 0.7108 | 0.5159 |
| SDNet [35] | 0.6441 | 0.8464 | 0.3072 | 0.8934 | 0.7464 | 0.5739 |
| MFF-GAN [36] | 0.6222 | 0.7930 | 0.2840 | 0.8887 | 0.7660 | 0.5399 |
| SwinFusion [27] | 0.6597 | 0.8404 | 0.3117 | 0.9011 | 0.7460 | 0.5745 |
| MUFusion [37] | 0.6614 | 0.8030 | 0.7160 | 0.9089 | 0.8036 | 0.6758 |
| FusionDiff [29] | 0.6744 | 0.8692 | 0.2900 | 0.8980 | 0.8261 | 0.5747 |
| SwinMFF [26] | 0.7321 | 0.9605 | 0.8222 | 0.9390 | 0.8986 | 0.7543 |
| DDBFusion [28] | 0.5026 | 0.8152 | 0.5610 | 0.8391 | 0.4947 | 0.6057 |
| Decision map-based methods using deep learning | ||||||
| CNN [22] | 0.7019 | 1.0424 | 0.2968 | 0.8976 | 0.8311 | 0.6628 |
| ECNN [23] | 0.7030 | 1.0723 | 0.2945 | 0.8946 | 0.8169 | 0.6698 |
| DRPL [19] | 0.7574 | 1.1405 | 0.8435 | 0.9397 | 0.9060 | 0.8035 |
| SESF [30] | 0.7031 | 1.0524 | 0.2950 | 0.8977 | 0.8353 | 0.6657 |
| MFIF-GAN [31] | 0.7029 | 1.0618 | 0.2960 | 0.8982 | 0.8395 | 0.6660 |
| MSFIN [10] | 0.7045 | 1.0601 | 0.2973 | 0.8990 | 0.8436 | 0.6664 |
| GACN [67] | 0.7581 | 1.1334 | 0.8443 | 0.9405 | 0.9013 | 0.8024 |
| ZMFF [11] | 0.6635 | 0.8694 | 0.2890 | 0.8951 | 0.8253 | 0.6136 |
| LightMFF | 0.7588 | 1.1462 | 0.8450 | 0.9400 | 0.9061 | 0.8067 |
| Method | Model Size (M) | FLOPs (G) | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| End-to-end methods based on deep learning | |||
| IFCNN-MAX [24] | 0.08 | 8.54 | 0.09 |
| U2Fusion [25] | 0.66 | 86.40 | 0.16 |
| SDNet [35] | 0.07 | 8.81 | 0.10 |
| MFF-GAN [36] | 0.05 | 3.08 | 0.06 |
| SwinFusion [27] | 0.93 | 63.73 | 1.79 |
| MUFusion [37] | 2.16 | 24.07 | 0.72 |
| FusionDiff [29] | 26.90 | 58.13 | 81.47 |
| SwinMFF [26] | 41.25 | 22.38 | 0.46 |
| DDBFusion [28] | 10.92 | 184.93 | 1.69 |
| Decision map-based methods using deep learning | |||
| CNN [22] | 8.76 | 142.23 | 0.06 |
| ECNN [23] | 1.59 | 14.93 | 125.53 |
| DRPL [19] | 1.07 | 140.49 | 0.22 |
| SESF [30] | 0.07 | 4.90 | 0.26 |
| MFIF-GAN [31] | 3.82 | 693.03 | 0.32 |
| MSFIN [10] | 4.59 | 26.76 | 1.10 |
| GACN [67] | 0.07 | 10.89 | 0.16 |
| ZMFF [11] | 6.33 | 464.53 | 165.38 |
| LightMFF | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Reduction (%) | 60.00% | 98.05% | 66.67% |
| Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 0.7578 | 1.1448 | 0.8437 | 0.9363 | 0.9021 | 0.8036 |
| Group 2 | 0.7587 | 1.1460 | 0.8447 | 0.9389 | 0.9055 | 0.8060 |
| Group 3 | 0.7584 | 1.1459 | 0.8443 | 0.9373 | 0.9053 | 0.8057 |
| Group 4 | 0.7588 | 1.1462 | 0.8450 | 0.9400 | 0.9061 | 0.8067 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Lin, Z.; Guo, B.; He, S.; Gu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, P. LightMFF: A Simple and Efficient Ultra-Lightweight Multi-Focus Image Fusion Network. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137500
Xie X, Lin Z, Guo B, He S, Gu Y, Bai Y, Li P. LightMFF: A Simple and Efficient Ultra-Lightweight Multi-Focus Image Fusion Network. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137500
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xinzhe, Zijian Lin, Buyu Guo, Shuangyan He, Yanzhen Gu, Yefei Bai, and Peiliang Li. 2025. "LightMFF: A Simple and Efficient Ultra-Lightweight Multi-Focus Image Fusion Network" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137500
APA StyleXie, X., Lin, Z., Guo, B., He, S., Gu, Y., Bai, Y., & Li, P. (2025). LightMFF: A Simple and Efficient Ultra-Lightweight Multi-Focus Image Fusion Network. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7500. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137500







