Biflavonoid Profiling of Juniperus Species: The Influence of Plant Part and Growing Location
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
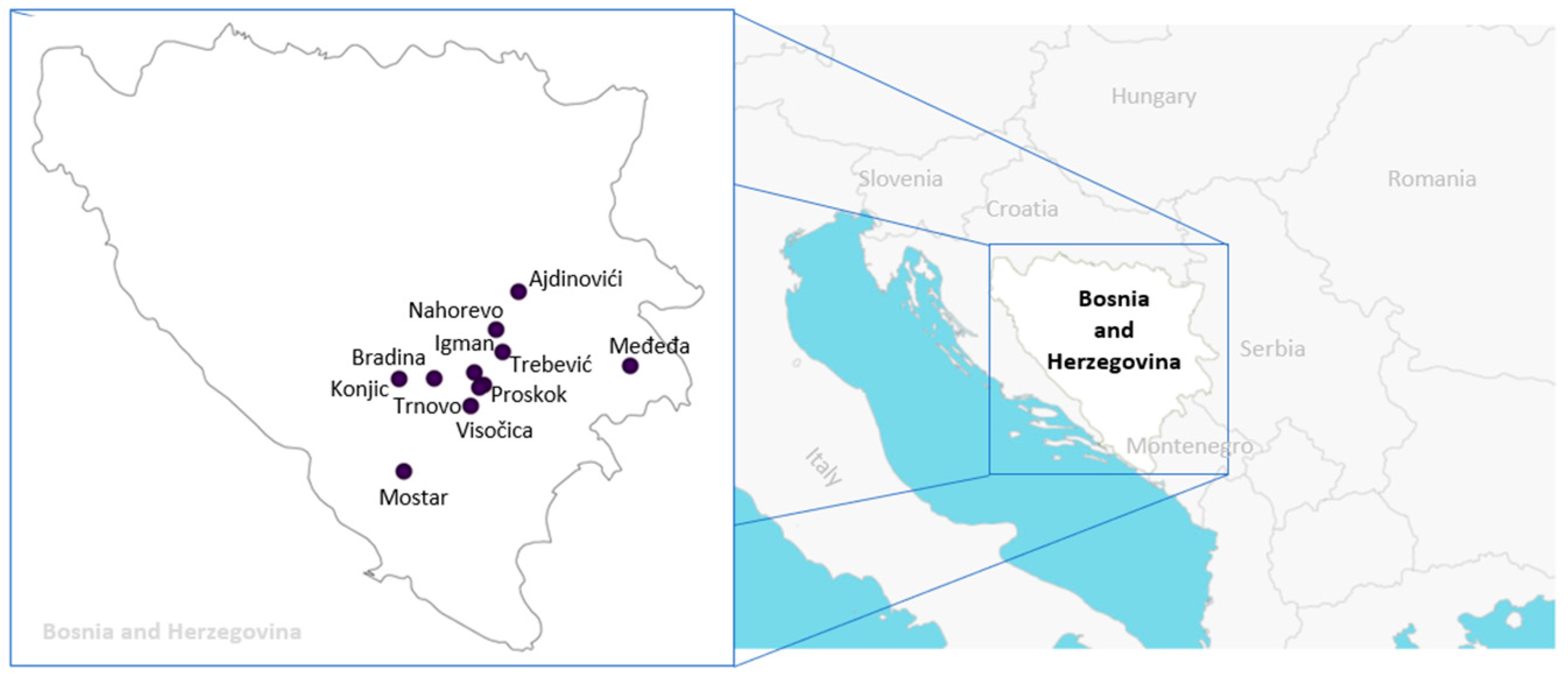
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Extraction
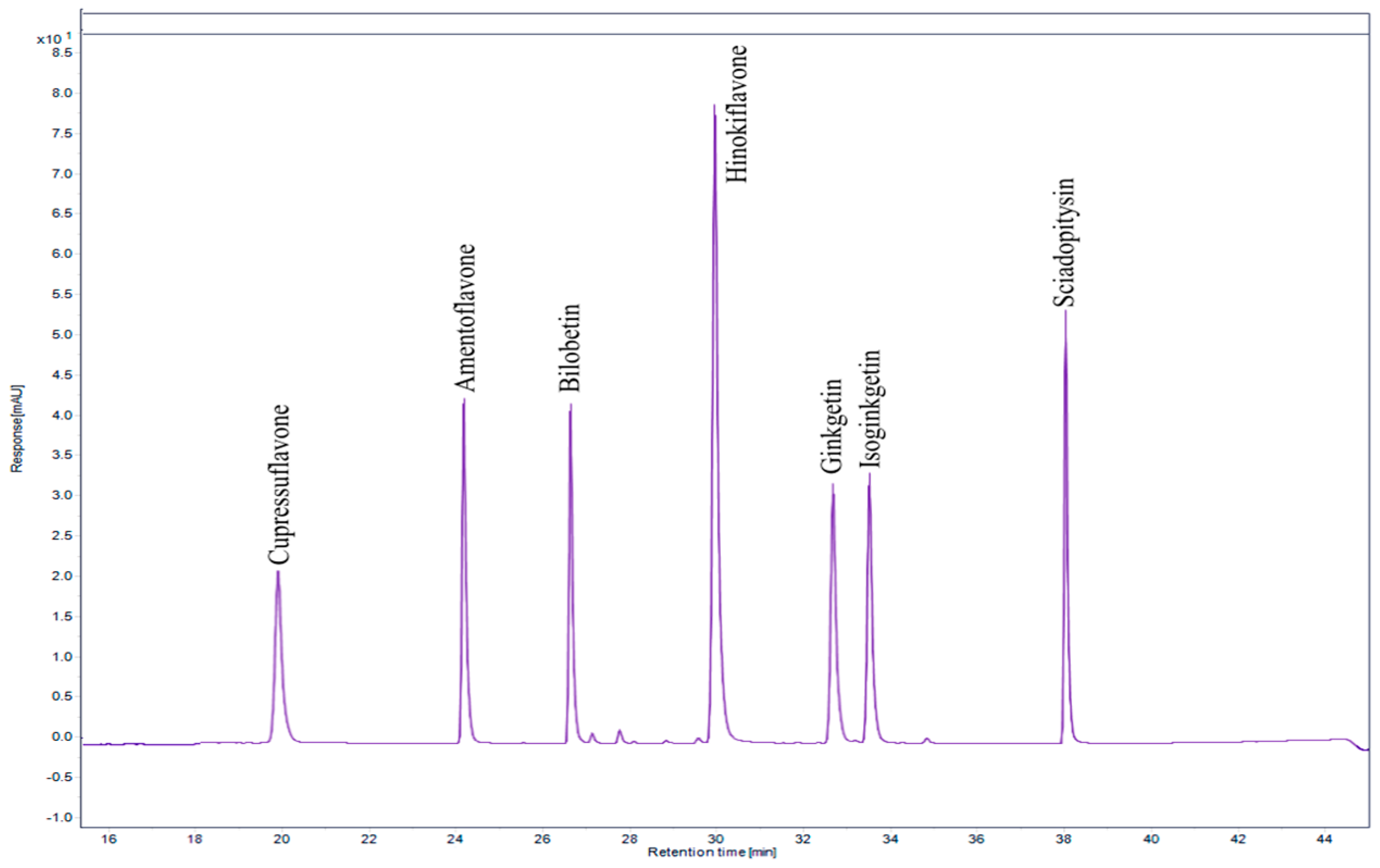
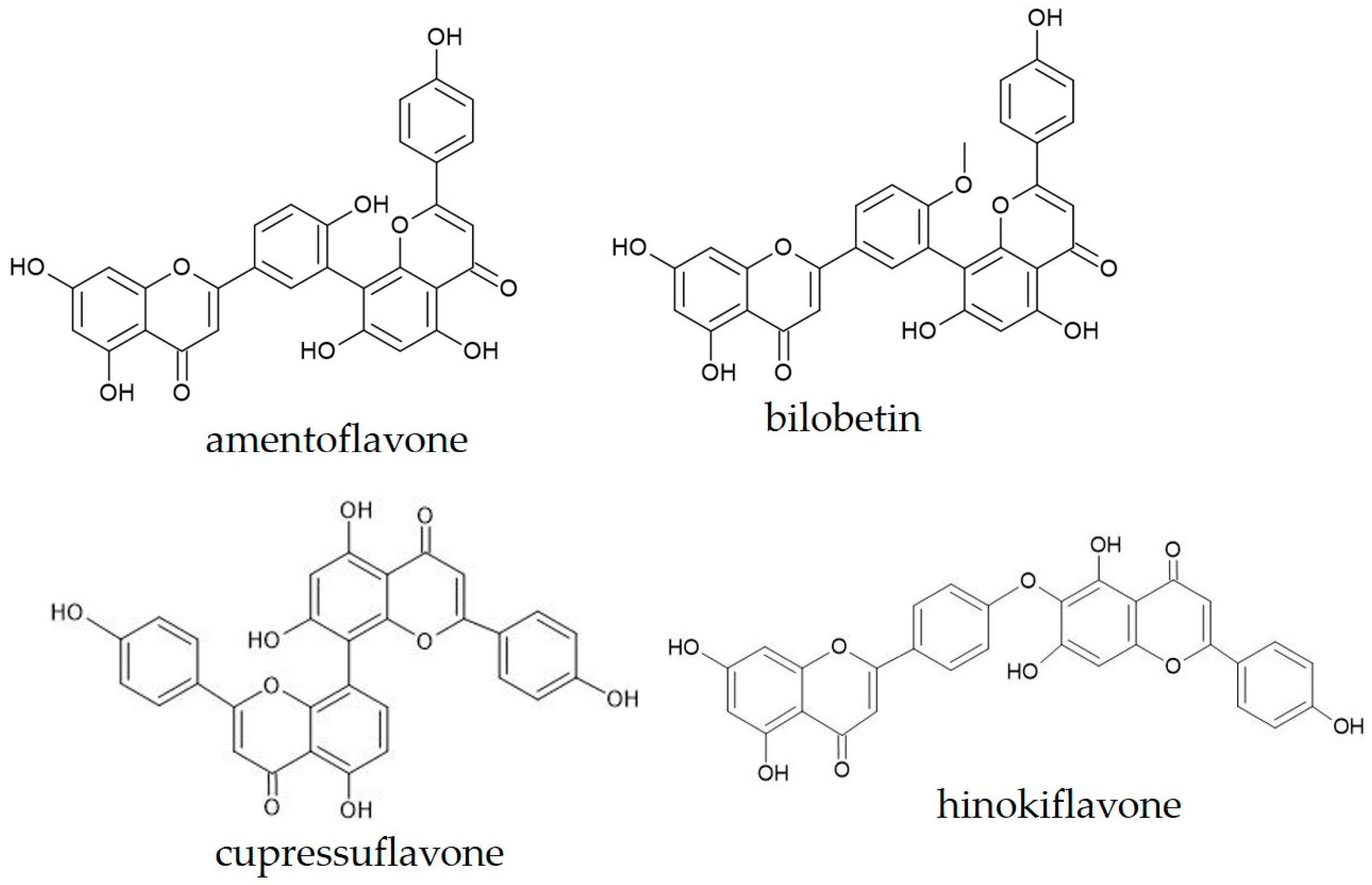
2.3. Biflavonoid Profiling
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
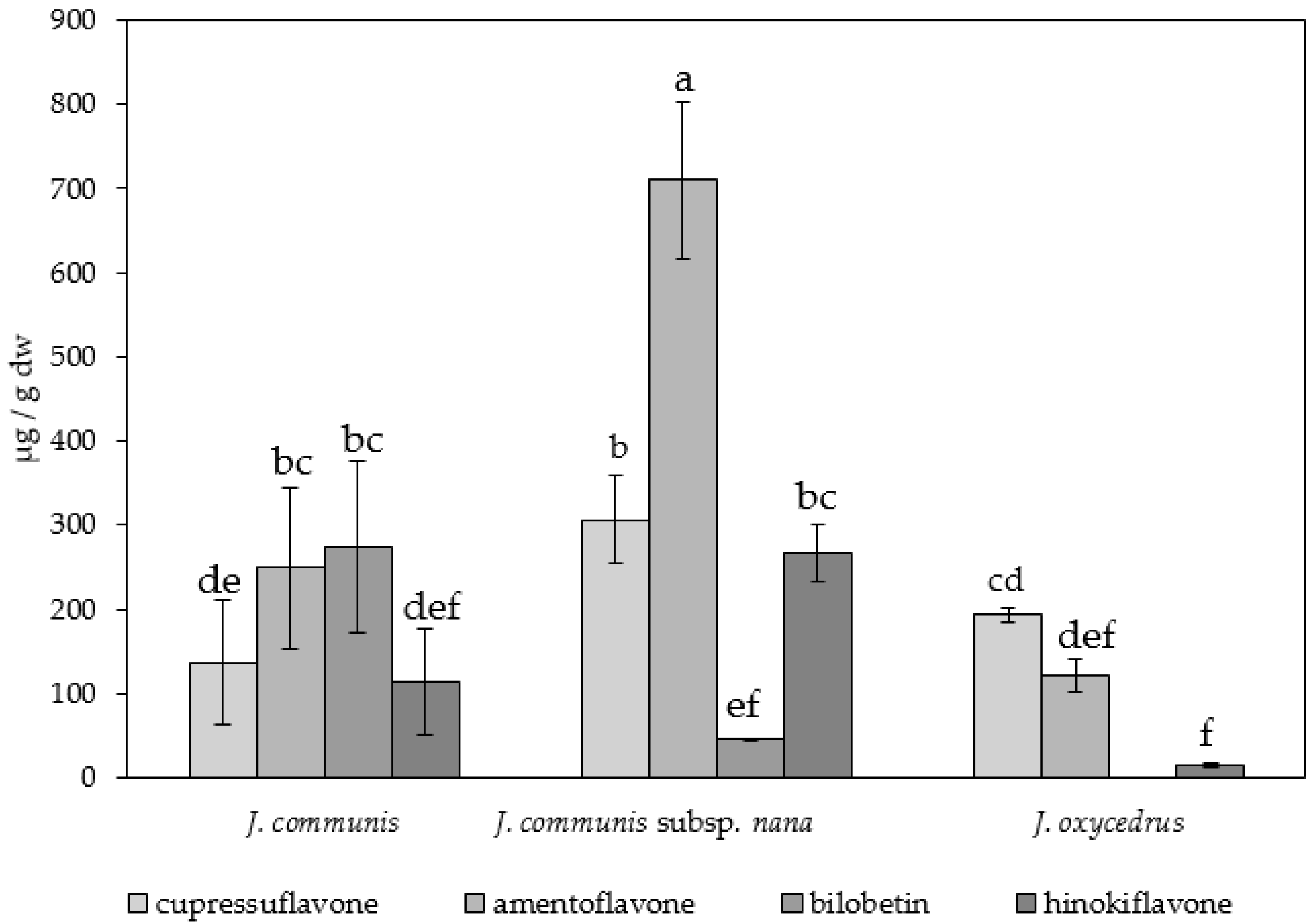
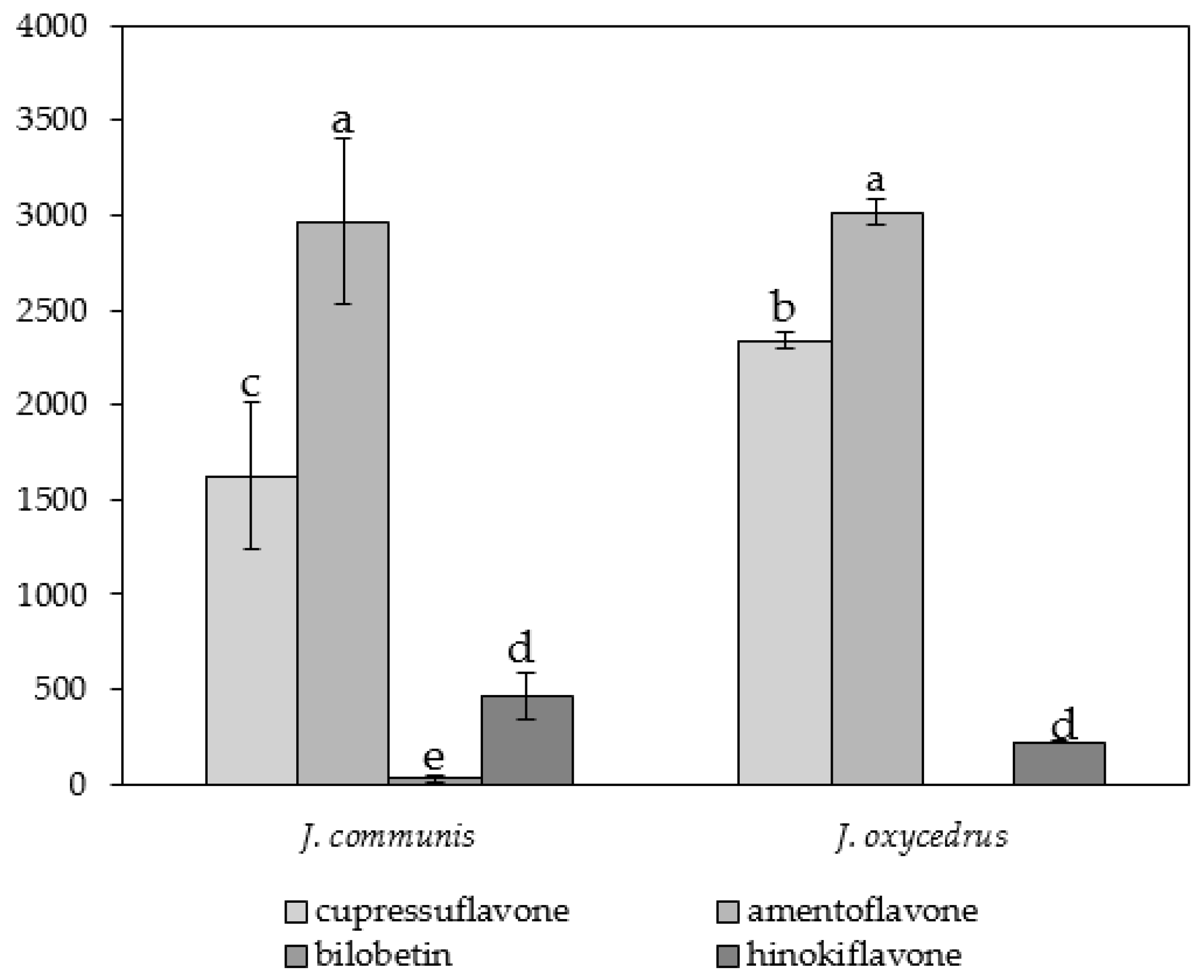
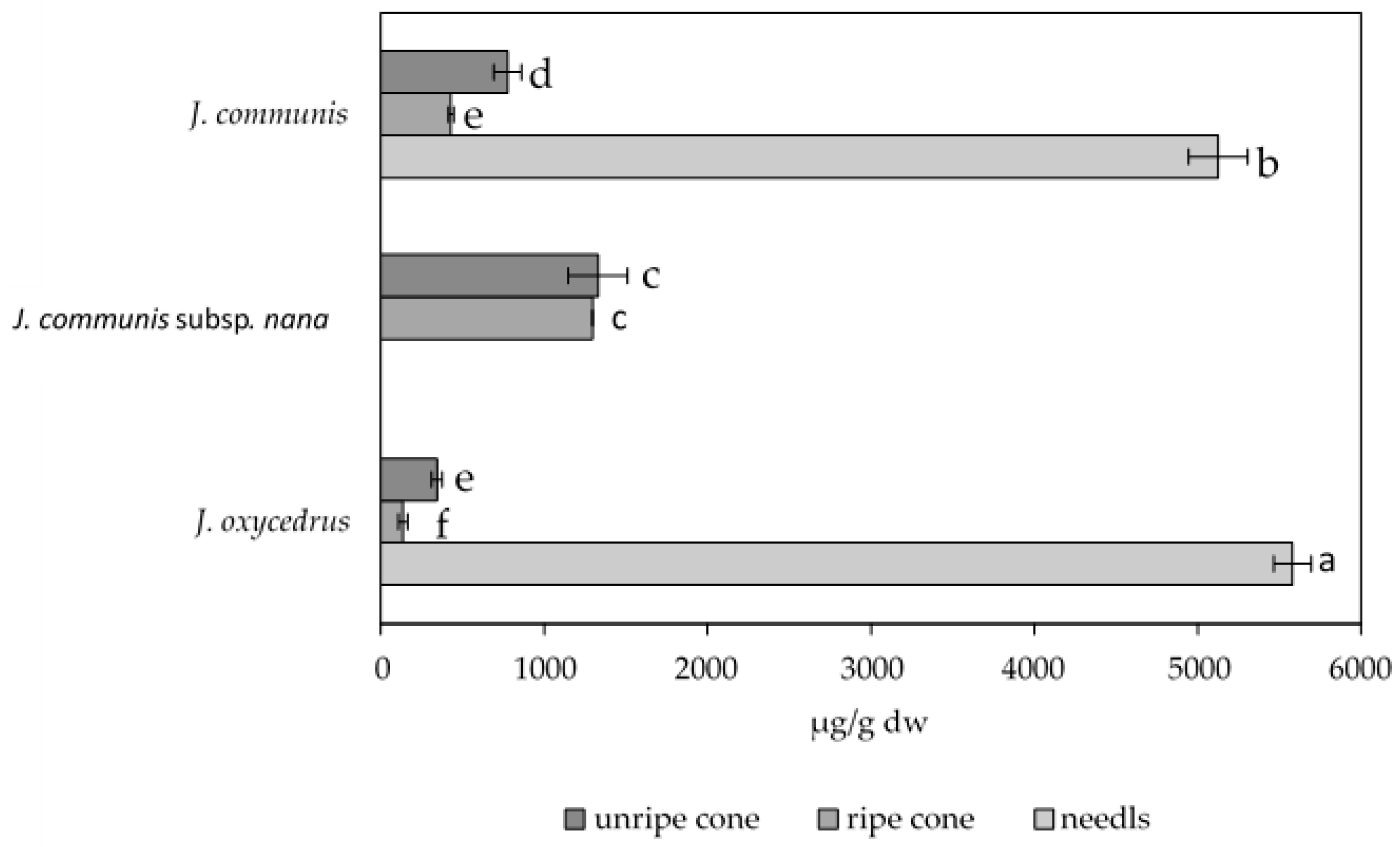
3.1. Species-Specific and Organ-Specific Biflavonoid Accumulation
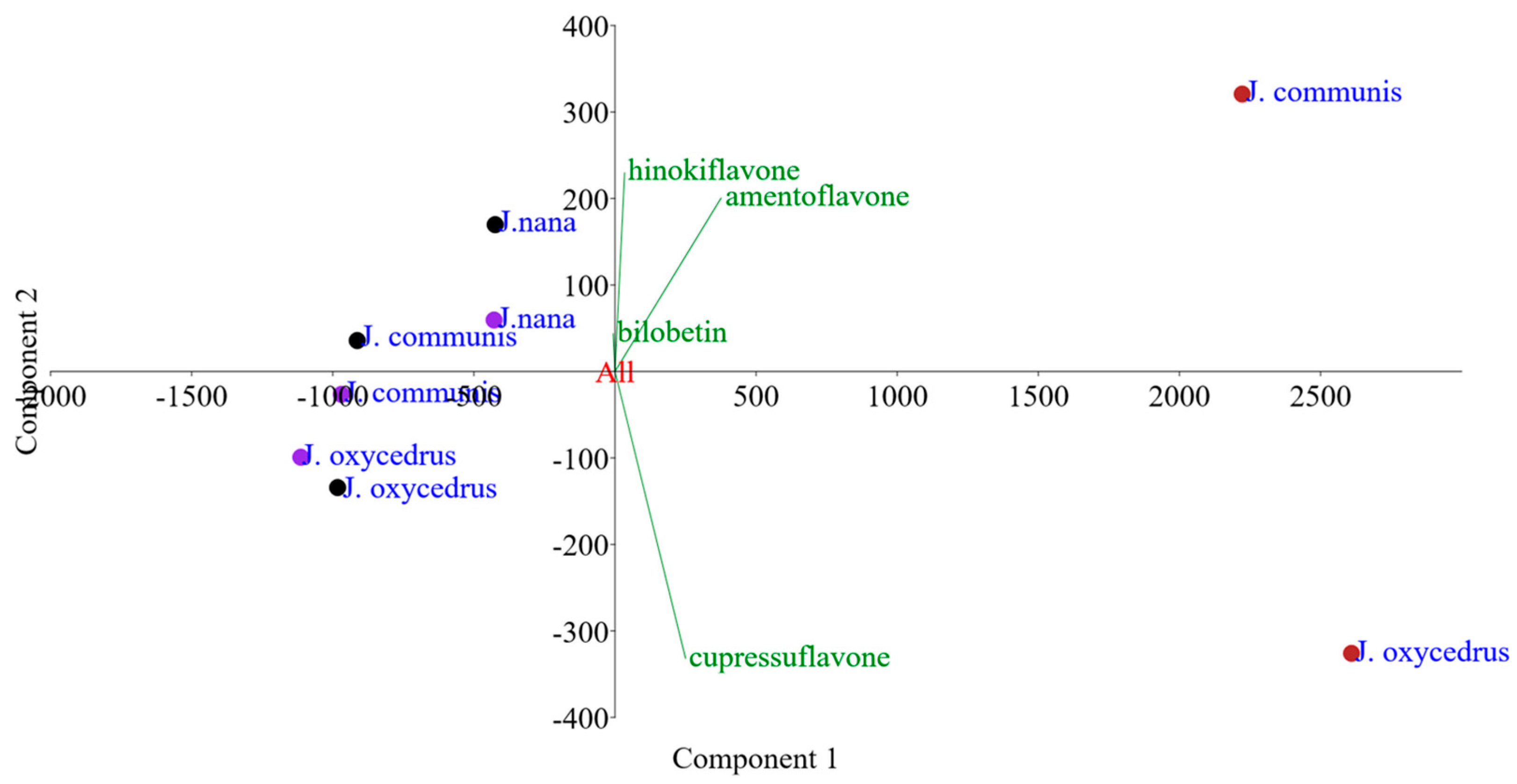
3.2. Geography-Dependent Biflavonoid Accumulation in J. communis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raina, R.; Verma, P.K.; Peshin, R.; Kour, H. Potential of Juniperus Communis L. as a Nutraceutical in Human and Veterinary Medicine. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemnezhad, A.; Ghorbanzadeh, A.; Sarmast, M.K.; Ghorbanpour, M. A Review on Botanical, Phytochemical, and Pharmacological Characteristics of Iranian Junipers (Juniperus spp.). In Plant-Derived Bioactives; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 493–508. [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti, M.; Michelozzi, M.; Giaccherini, C.; Ieri, F.; Vincieri, F.F.; Mulinacci, N. Flavonoids and Biflavonoids in Tuscan Berries of Juniperus communis L.: Detection and Quantitation by HPLC/DAD/ESI/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6596–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, N.; Trovato, A.; Dugo, P.; Cacciola, F.; Donato, P.; Marino, A.; Bellinghieri, V.; La Barbera, T.M.; Güvenç, A.; Taviano, M.F. Comparative Analysis of Flavonoid Profile, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of the Berries of Juniperus communis L. var. Communis and Juniperus communis L. var. saxatilis Pall. from Turkey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6570–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.; Zielińska, M.; Boratyńska, K.; Romo, A.; Salva-Catarineu, M.; Marcysiak, K.; BoratyŃski, A. Taxonomic and Geographic Differentiation of Juniperus phoenicea agg. Based on Cone, Seed, and Needle Characteristics. Syst. Biodivers. 2018, 16, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, W.R.; Seca, A.M.L. The Current Status of the Pharmaceutical Potential of Juniperus L. Metabolites. Medicines 2018, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bais, S.; Gill, N.S.; Rana, N.; Shandil, S. A Phytopharmacological Review on a Medicinal Plant: Juniperus communis. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 634723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojić, A.A.; Liga, S.; Uţu, D.; Ruse, G.; Suciu, L.; Motoc, A.; Şoica, C.M.; Tchiakpe-Antal, D.-S. Beyond Essential Oils: Diterpenes, Lignans, and Biflavonoids from Juniperus communis L. as a Source of Multi-Target Lead Compounds. Plants 2024, 13, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, F.; Huang, X. Proceedings of Chemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Synthesis of Biflavonoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamec, D.; Jurčević Šangut, I.; Karalija, E.; Šarkanj, B.; Zelić, B.; Šalić, A. 3′-8″- Biflavones: A Review of Their Structural Diversity, Natural Occurrence, Role in Plants, Extraction and Identification. Molecules 2024, 29, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šamec, D.; Karalija, E.; Dahija, S.; Hassan, S.T.S. Biflavonoids: Important Contributions to the Health Benefits of Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.). Plants 2022, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mërtiri, I.; Păcularu-Burada, B.; Stănciuc, N. Phytochemical Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of Albanian Juniperus communis and Juniperus oxycedrus Berries and Needle Leaves Extracts. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Živić, N.; Milošević, S.; Dekić, V.; Dekić, B.; Ristić, N.; Ristić, M.; Sretić, L. Phytochemical and Antioxidant Screening of Some Extracts of Juniperus communis L. and Juniperus oxycedrus L. Czech J. Food Sci. 2019, 37, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Mrid, R.; Bouchmaa, N.; Bouargalne, Y.; Ramdan, B.; Karrouchi, K.; Kabach, I.; El Karbane, M.; Idir, A.; Zyad, A.; Nhiri, M. Phytochemical Characterization, Antioxidant and In Vitro Cytotoxic Activity Evaluation of Juniperus oxycedrus Subsp. Oxycedrus Needles and Berries. Molecules 2019, 24, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. LC-ESI-QTOF/MS Characterization of Phenolic Compounds from Medicinal Plants (Hops and Juniper Berries) and Their Antioxidant Activity. Foods 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.; Botoran, O.; Cristea, R.; Mihăescu, C.; Șuțan, N. Effects of Geographical Area and Harvest Times on Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Juniperus communis L. Pseudo-Fruits Extracts: A Statistical Approach. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.M.; Al-Qurainy, F.; Nadeem, M.; Tarroum, M.; Khan, S.; Shaikhaldein, H.O.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Alfagham, A.; Alkahtani, J. Optimization Method for Phenolic Compounds Extraction from Medicinal Plant (Juniperus procera) and Phytochemicals Screening. Molecules 2021, 26, 7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elboughdiri, N.; Ghernaout, D.; Kriaa, K.; Jamoussi, B. Enhancing the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Juniper Berries Using the Box-Behnken Design. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27990–28000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.K. Variation in Ripening Years of Seed Cones of Juniperus communis L. Watsonia 2010, 28, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jurčević Šangut, I.; Pavličević, L.; Šamec, D. Influence of Air Drying, Freeze Drying and Oven Drying on the Biflavone Content in Yellow Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.) Leaves. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Taviano, M.F.; Marino, A.; Trovato, A.; Bellinghieri, V.; Melchini, A.; Dugo, P.; Cacciola, F.; Donato, P.; Mondello, L.; Güvenç, A.; et al. Juniperus oxycedrus L. Subsp. Oxycedrus and Juniperus oxycedrus L. Subsp. Macrocarpa (Sibth. & Sm.) Ball. “Berries” from Turkey: Comparative Evaluation of Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moumou, M.; Mokhtari, I.; Tayebi, A.; Milenkovic, D.; Amrani, S.; Harnafi, H. Juniperus oxycedrus L. Fruit, Leaves, and Essential Oil: A Systematic Literature Review on Bioactive Compounds, Pharmacological Properties and Toxicology. Phytochem. Rev. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, N.; Marino, A.; Köroğlu, A.; Cacciola, F.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Taviano, M.F. Comparative Study of the Phenolic Profile, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Leaf Extracts of Five Juniperus L. (Cupressaceae) Taxa Growing in Turkey. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurčević Šangut, I.; Šamec, D. Seasonal Variation of Polyphenols and Pigments in Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.) Leaves: Focus on 3′,8″-Biflavones. Plants 2024, 13, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovač Tomas, M.; Jurčević, I.; Šamec, D. Tissue-Specific Profiling of Biflavonoids in Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.). Plants 2022, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalija, E.; Šamec, D. Amentoflavone: Structure, Resources, Biosynthetic Pathway and Bioactivity and Pharmacology. In Handbook of Dietary Flavonoids; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, P.; Dasila, K.; Singh, M.; Kuniyal, J.C. Influence of Environmental Factors on Phytochemical Compositions and Antioxidant Activity of Juniperus communis L. Discov. Environ. 2025, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Plant Part | Location | Cupressuflavone [µg/g dw] | Amentoflavone [µg/g dw] | Bilobetin [µg/g dw] | Hinokiflavone [µg/g dw] | Total Biflavonoids [µg/g dw] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unripe cones | Nahorevo | 136.29 ± 32.56 ghi | 342.63 ± 61.14 d | 358.63 ± 43.00 a | 166.83 ± 16.24 e | 1004.38 ± 152.93 d |
| Trebević | 264.02 ± 5.93 e | 291.89 ± 13.09 d | 388.01 ± 116.81 a | nd | 943.91 ± 135.83 de | |
| Visočica | 97.62 ± 2.14 ghi | 111.18 ± 1.86 d | 139.41 ± 14.81 c | 72.07 ± 3.59 fgh | 420.28 ± 22.39 fg | |
| Bradina | 108.15 ± 0.33 ghi | 309.47 ± 17.61 d | 219.25 ± 17.09 b | 167.43 ± 11.22 e | 804.30 ± 46.25 def | |
| Konjic | 76.65 ± 6.44 hi | 189.06 ± 22.22 d | 263.43 ± 14.97 b | 49.15 ± 7.27 gh | 594.00 ± 50.91 defg | |
| ripe cones | Proskok | 118.63 ± 19.89 ghi | 239.01 ± 41.03 d | 43.15 ± 4.17 d | 94.90 ± 10.13 fg | 495.69 ± 66.88 efg |
| Igman | 162.29 ± 70.95 fg | 233.70 ± 95.64 d | 36.87 ± 12.90 d | 85.95 ± 39.07 fg | 518.80 ± 218.56 efg | |
| Trnovo | 219.52 ± 4.69 ef | 245.64 ± 0.91 d | nd | 108.82 ± 0.86 f | 573.97 ± 4.63 defg | |
| Nahorevo | 4.69 ± 0.55 fghi | 205.84 ± 5.69 d | nd | 99.90 ± 1.08 fg | 442.93 ± 6.22 fg | |
| Ajdinovici | 101.51 ± 43.47 ghi | 141.53 ± 38.52 d | nd | 50.48 ± 15.76 gh | 293.52 ± 97.75 g | |
| Međeđa | 134.32 ± 24.57 ghi | 206.27 ± 14.70 d | nd | 15.76 ± 7.02 fgh | 408.93 ± 46.30 fg | |
| Trebević | 120.24 ± 0.89 ghi | 159.17 ± 4.55 d | 27.17 ± 1.79 d | 68.33 ± 1.29 fgh | 374.91 ± 4.16 fg | |
| Visočica | 139.43 ± 28.49 fgh | 107.29 ± 14.22 d | nd | 69.07 ± 8.80 fgh | 315.79 ± 51.50 g | |
| Bradina | 86.45 ± 0.10 ghi | 238.32 ± 1.29 d | nd | 97.82 ± 0.09 fg | 422.59 ± 1.29 fg | |
| Konjic | 51.40 ± 16.14 i | 116.52 ± 30.69 d | nd | 33.11 ± 11.46 h | 201.03 ± 58.29 g | |
| needles | Trnovo | 1987.54 ± 88.24 a | 3267.78 ± 319.03 a | 23.94 ± 0.98d | 528.39 ± 42.23 b | 6033.24 ± 448.52 a |
| Nahorevo | 1825.59 ± 9.27 b | 3486.68 ± 91.71 a | nd | 602.58 ± 9.11 a | 5914.86 ± 91.55 a | |
| Visočica | 2059.95 ± 90.38 a | 2790.53 ± 139.81 b | 52.62 ± 28.56 d | 433.29 ± 6.35 c | 5336.39 ± 14.52 b | |
| Bradina | 1360.87 ± 9.14 c | 2998.96 ± 382.28 b | 21.79 ± 4.13 d | 548.66 ± 45.76 b | 4930.28 ± 433.04 b | |
| Trebević | 1385.09 ± 80.91 c | 3030.85 ± 496.13 b | 21.62 ± 2.47 d | 445.61± 62.07 c | 4883.18 ± 636.63 b | |
| Konjic | 1124.42 ± 7.91 d | 2218.14 ± 290.28 c | nd | 250.80 ± 41.57 d | 3593.36 ± 339.76 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medvedec, B.; Jurčević Šangut, I.; Macanović, A.; Karalija, E.; Šamec, D. Biflavonoid Profiling of Juniperus Species: The Influence of Plant Part and Growing Location. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137082
Medvedec B, Jurčević Šangut I, Macanović A, Karalija E, Šamec D. Biflavonoid Profiling of Juniperus Species: The Influence of Plant Part and Growing Location. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137082
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedvedec, Barbara, Iva Jurčević Šangut, Armin Macanović, Erna Karalija, and Dunja Šamec. 2025. "Biflavonoid Profiling of Juniperus Species: The Influence of Plant Part and Growing Location" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137082
APA StyleMedvedec, B., Jurčević Šangut, I., Macanović, A., Karalija, E., & Šamec, D. (2025). Biflavonoid Profiling of Juniperus Species: The Influence of Plant Part and Growing Location. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7082. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137082











