PET Radiomics Signatures and Artificial Intelligence for Decoding Immunotherapy Response in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Single-Center Study
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. PET/CT Imaging
2.3. Imaging Post-Processing and Feature Extraction
2.4. Assessment of Immunotherapy Response
2.5. Follow-Up
2.6. Model Building
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. Response to Immunotherapy
3.3. Radiomic Analysis
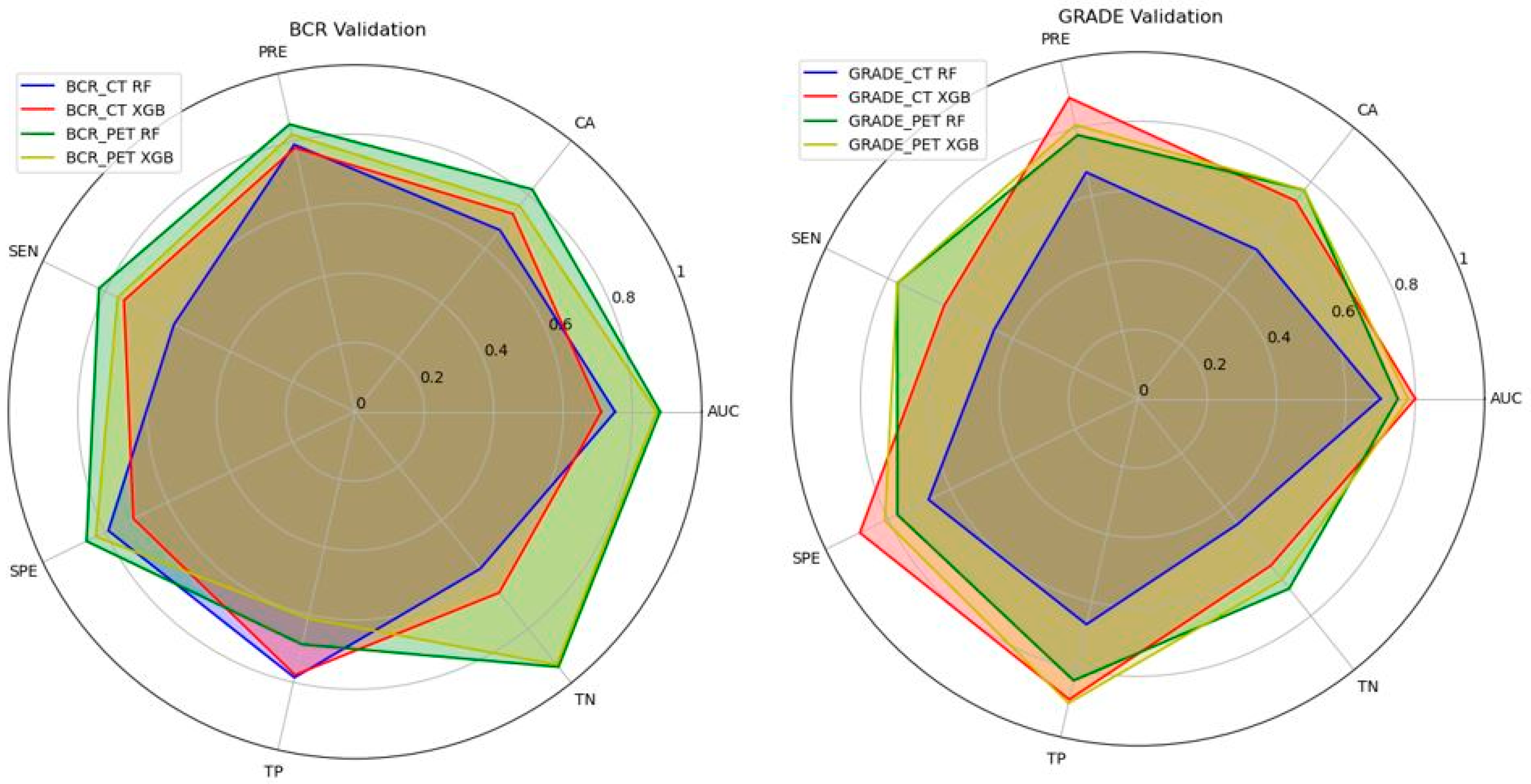
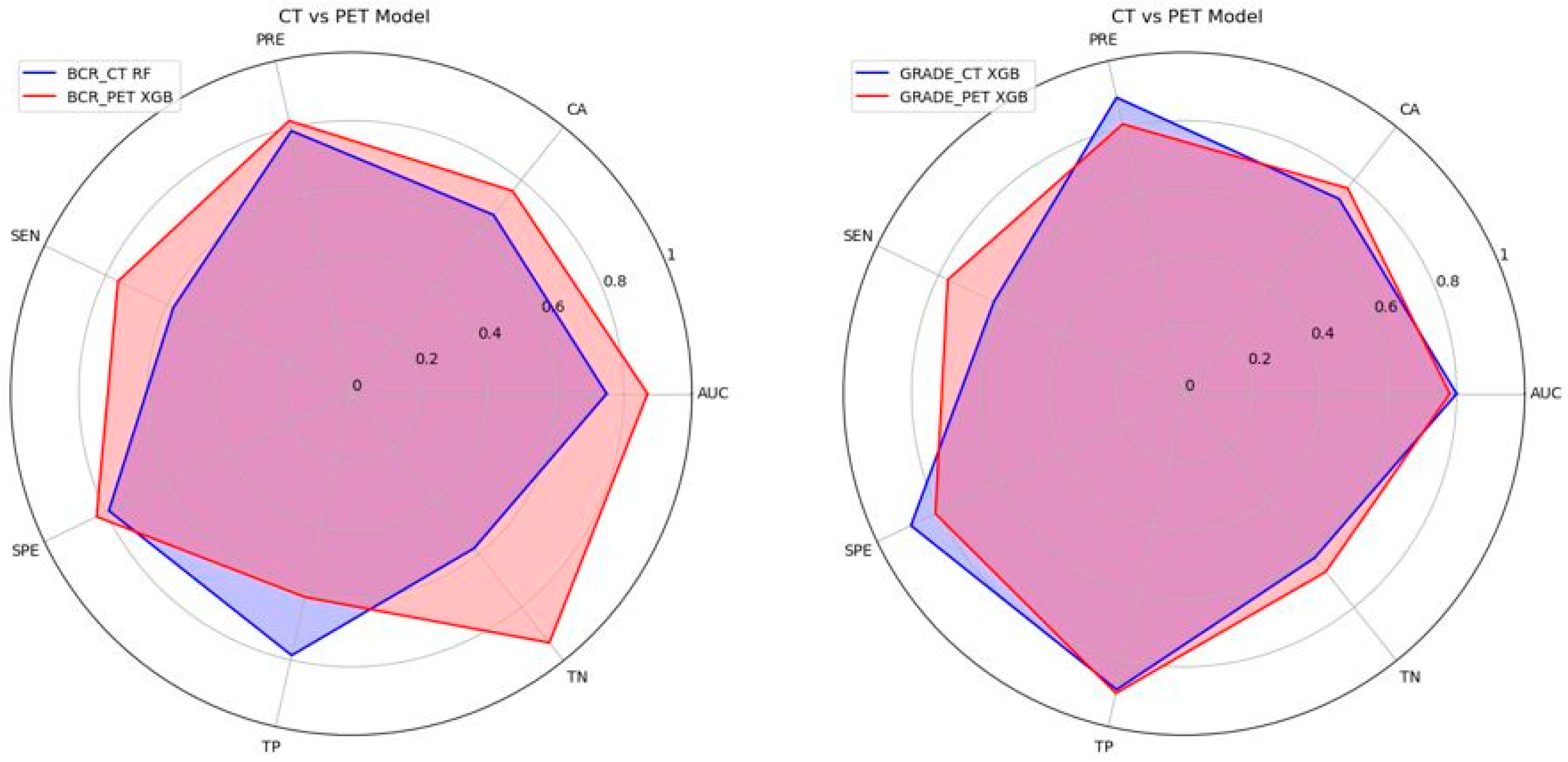
3.4. Performance of the Machine Learning Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffin, L.L.; Ali, F.R.; Lear, J.T. Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Bue, E.; Paracampo, C.; Dolci, L.; Portonero, I.; Colonna, S.; Navissano, M.; Garbossa, D.; Massa Micon, B. Surgical Management of Cutaneous Carcinomas Invading the Scalp: A Case Series and Proposal of a Therapeutical Algorithm. World Neurosurg. 2025, 198, 123964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, S.; Boncimino, F.; Todorova, K.; Waszyn, S.E.; Mandinova, A. Therapeutic Approaches for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Standard of Care and Emerging Modalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Zhu, D. Clinical Cancer Immunotherapy: Current Progress and Prospects. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 961805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat Hossain, M. A Comprehensive Review of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Cancer Treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, K.; Roudaia, L.; Buhlaiga, N.; Del Rincon, S.V.; Papneja, N.; Miller, W.H. A Review of Cancer Immunotherapy: From the Past, to the Present, to the Future. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, S87–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.P.; Ming, L.C.; Dhaliwal, J.S.; Gupta, M.; Ardianto, C.; Goh, K.W.; Hussain, Z.; Shafqat, N. Role of Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.S.; Patel, T.; DiGiovanni, J.; Nathan, C.-A.O.; Khandelwal, A.R. Current Efficacy and Safety and Survival Outcomes of Cemiplimab in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, S0022202X25003793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challapalli, A.; Stewart, G.; Shaw, H.; Davies, P.J.; Lopez-Baez, J.C.; Ottley, E.C.; Kelly, S. Real-World Evidence Study on the Early Use of Cemiplimab in the UK: REACT-CEMI (Real World Evidence of Advanced CSCC Treatment with Cemiplimab). Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1408667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksienski, D.; Truong, P.T.; Bone, J.N.; Egli, S.; Clarkson, M.; Patterson, T.; Lesperance, M.; Lakkunarajah, S. Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Impact of Age on the Safety and Efficacy of Cemiplimab and the Prognostic Significance of Blood Biomarkers. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2024, 15, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, J.E.; Rack, S.; Yan, R.; Babu, S.; Donnelly, O.; Walter, H.; Faust, G.; Bhagani, S.; Isola, P.; Metcalf, R. Evaluation of Clinical Parameters Associated with Response and Resistance to Cemiplimab in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Cohort Study. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Proietti, I.; Petrozza, V.; Potenza, C.; Bagni, O.; Schillaci, O. The Prognostic Role of [18F]FDG PET/CT in Patients with Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Submitted to Cemiplimab Immunotherapy: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2024, 39, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The Bridge between Medical Imaging and Personalized Medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Bianconi, F.; Schillaci, O.; Spanu, A.; Palumbo, B. The Role and Potential of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Malignant Melanoma: Prognostication, Monitoring Response to Targeted and Immunotherapy, and Radiomics. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, L.; Manco, L.; Cittanti, C.; Adamantiadis, S.; Szilagyi, K.E.; Scribano, G.; Mindicini, N.; Carnevale, A.; Bartolomei, M.; Giganti, M. 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomic Analysis and Artificial Intelligence to Predict Pathological Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Radiol. Med. 2025, 130, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, L.; Cittanti, C.; Manco, L.; Ortolan, N.; Borgia, F.; Malorgio, A.; Scribano, G.; Mastella, E.; Guidoboni, M.; Stefanelli, A.; et al. ML Models Built Using Clinical Parameters and Radiomic Features Extracted from 18F-Choline PET/CT for the Prediction of Biochemical Recurrence after Metastasis-Directed Therapy in Patients with Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallardo, D.; Sparano, F.; Vitale, M.G.; Trojaniello, C.; Fordellone, M.; Cioli, E.; Esposito, A.; Festino, L.; Mallardo, M.; Vanella, V.; et al. Impact of Cemiplimab Treatment Duration on Clinical Outcomes in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2024, 73, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, O.A.; Westgate, D.; Saadaie Jahromi, B.; Shebrain, A.; Zhang, T.; Ashour, H.M. PD-L1 Inhibitor Cosibelimab for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Comprehensive Evaluation of Efficacy, Mechanism, and Clinical Trial Insights. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.; Shim, H.S.; Hong, T.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, C.Y.; Park, B.J.; et al. Deciphering the Intratumoral Histologic Heterogeneity of Lung Adenocarcinoma Using Radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural Topuz, Ö.; Bağbudar, S.; Aksu, A.; Söylemez Akkurt, T.; Akkaş, B.E. Radiomic Signatures Derived from Baseline 18F FDG PET/CT Imaging Can Predict Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Values in Patients with Primary Breast Cancer. Nuklearmedizin 2025, 64, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanduleanu, S.; Woodruff, H.C.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.E.; Jochems, A.; Dubois, L.; Lambin, P. Tracking Tumor Biology with Radiomics: A Systematic Review Utilizing a Radiomics Quality Score. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Wahid, K.A.; van Dijk, L.V.; Farahani, K.; Thompson, R.F.; Fuller, C.D. Radiomic Biomarkers of Tumor Immune Biology and Immunotherapy Response. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 28, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallardo, D.; Simeone, E.; Festino, L.; Tuffanelli, M.; Vanella, V.; Trojaniello, C.; Vitale, M.G.; Ottaviano, M.; Capone, M.; Madonna, G.; et al. IL-6 as New Prognostic Factor in Patients with Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Cemiplimab. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, D.; Napolitano, F.; Maresca, D.C.; Scala, M.; Amato, A.; Belli, S.; Ascione, C.M.; Vallefuoco, A.; Attanasio, G.; Somma, F.; et al. Early Assessment of IL8 and PD1+ Treg Predicts Response and Guides Treatment Monitoring in Cemiplimab-Treated Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e010421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, B.G.M.; Guminski, A.; Bowyer, S.; Migden, M.R.; Schmults, C.D.; Khushalani, N.I.; Chang, A.L.S.; Grob, J.-J.; Lewis, K.D.; Ansstas, G.; et al. A Phase 2 Open-Label Study of Cemiplimab in Patients with Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (EMPOWER-CSCC-1): Final Long-Term Analysis of Groups 1, 2, and 3, and Primary Analysis of Fixed-Dose Treatment Group 6. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2025, 92, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, L.S.; Cavanagh, K.; Hicks, R.J.; Callahan, J.; Xie, J.; Cardin, A.; Lim, A.M.; Rischin, D. FDG-PET/CT Imaging for Evaluating Durable Responses to Immune Check Point Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in Medical Imaging-”how-to” Guide and Critical Reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.; Cavinato, L.; Fiz, F.; Sollini, M.; Chiti, A.; Torzilli, G.; Ieva, F.; Viganò, L. Mapping Tumor Heterogeneity via Local Entropy Assessment: Making Biomarkers Visible. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.A.S.; Kelahan, L.C.; Magnetta, M.; Savas, H.; Agrawal, R.; Avery, R.J.; Aouad, P.; Liu, B.; Xue, Y.; Chae, Y.K.; et al. A Framework for Harmonization of Radiomics Data for Multicenter Studies and Clinical Trials. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2022, 6, e2200023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novruzov, E.; Peters, H.A.; Jannusch, K.; Kobbe, G.; Dietrich, S.; Fischer, J.C.; Rox, J.; Antoch, G.; Giesel, F.L.; Antke, C.; et al. The Predictive Power of Baseline Metabolic and Volumetric [18F]FDG PET Parameters with Different Thresholds for Early Therapy Failure and Mortality Risk in DLBCL Patients Undergoing CAR-T-Cell Therapy. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2025, 14, 100619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boellaard, R.; Buvat, I.; Nioche, C.; Ceriani, L.; Cottereau, A.-S.; Guerra, L.; Hicks, R.J.; Kanoun, S.; Kobe, C.; Loft, A.; et al. International Benchmark for Total Metabolic Tumor Volume Measurement in Baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT of Lymphoma Patients: A Milestone Toward Clinical Implementation. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behdenna, A.; Colange, M.; Haziza, J.; Gema, A.; Appé, G.; Azencott, C.-A.; Nordor, A. pyComBat, a Python Tool for Batch Effects Correction in High-Throughput Molecular Data Using Empirical Bayes Methods. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewski, M.R.; Gillies, R.J. The Biological Meaning of Radiomic Features. Radiology 2021, 298, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, L.; Manco, L.; Filippi, L. Synthetic Imaging for Research and Education in Nuclear Medicine: Who’s Afraid of the Black Box? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Erdim, C.; Ates, E.; Kaya, O.K.; Kilickesmez, O. Radiomics of Renal Masses: Systematic Review of Reproducibility and Validation Strategies. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, B.; Bagci, U.; Mansoor, A.; Xu, Z.; Mollura, D.J. A Review on Segmentation of Positron Emission Tomography Images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 50, 76–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesdorp, N.J.; Zeeuw, J.M.; Postma, S.C.J.; Roor, J.; van Waesberghe, J.H.T.M.; van den Bergh, J.E.; Nota, I.M.; Moos, S.; Kemna, R.; Vadakkumpadan, F.; et al. Deep Learning Models for Automatic Tumor Segmentation and Total Tumor Volume Assessment in Patients with Colorectal Liver Metastases. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2023, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.; Ahmad, N.; Nasir, A.; Ahmad Tariq, Z. Hybrid Deep Learning EfficientNetV2 and Vision Transformer (EffNetV2-ViT) Model for Breast Cancer Histopathological Image Classification. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 184119–184131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Vendt, B.; Smith, K.; Freymann, J.; Kirby, J.; Koppel, P.; Moore, S.; Phillips, S.; Maffitt, D.; Pringle, M.; et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository. J. Digit. Imaging 2013, 26, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
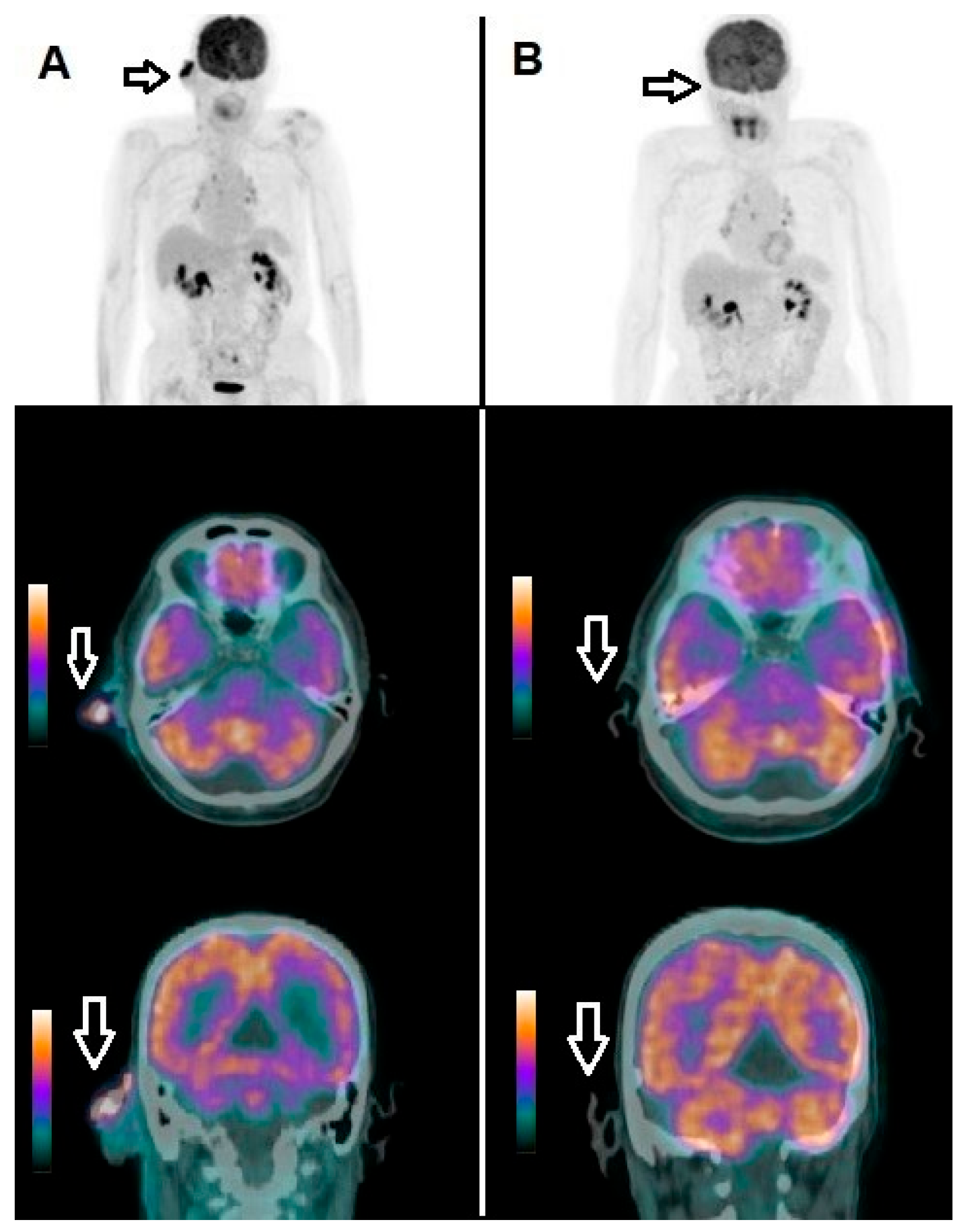
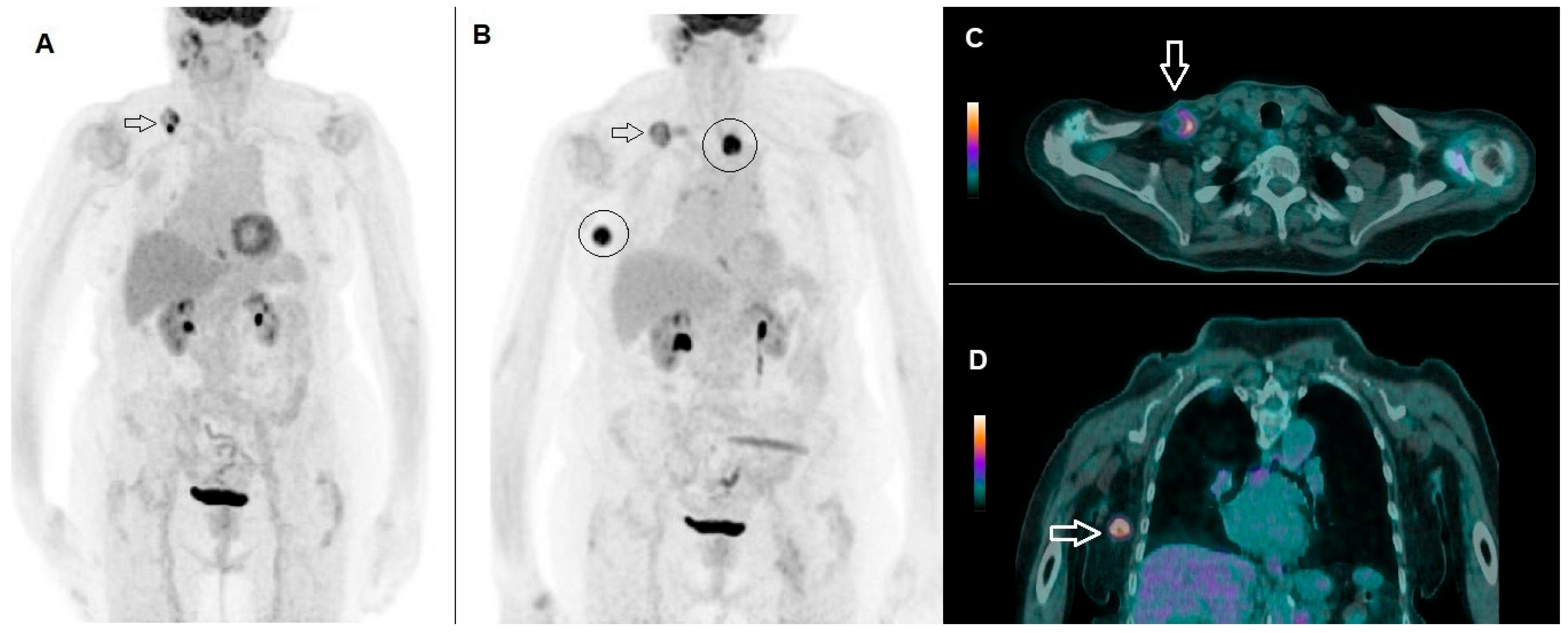
| Characteristics | N (Percentage) |
|---|---|
| Patients | 59 |
| Male sex | 51 (86.4%) |
| Median age y (interquartile range) | 86 (84–89) |
| ECOG | |
| 0–1 | 47 |
| ≥2 | 12 |
| Tumor Location | |
| Head/neck | 52 (88.1%) |
| Trunk | 4 (6.7%) |
| Lower limbs | 3 (5%) |
| Tumor grade | |
| G1–G2 | 38 (64.4%) |
| G3 | 21 (35.6%) |
| Metastatic patients | 8 (13.5%) |
| Nodal metastases | 6 (10.1%) |
| Distant metastases | 2 (3.3%) |
| Immunotherapy with respect to other therapies | |
| As 1st line | 46 (77.9%) |
| After upfront surgery | 12 (20.3%) |
| After upfront RT | 1 (1.7%) |
| PET-based response after 12 weeks (PERCIST) | |
| CMR | 5 (8.4%) |
| PMR | 39 (66.1%) |
| SMD | 2 (3.3%) |
| PMD | 13 (22%) |
| Best clinical response (BCR) to immunotherapy | |
| CB | 46 (77.9%) |
| NCB | 13 (22.1%) |
| Immunotherapy-related toxicity | |
| Cardiovascular toxicity | 1 (1.7%) |
| Therapeutic-switch after immunotherapy failure | |
| Chemotherapy | 2 (3.3%) |
| Radiotherapy | 3 (5%) |
| Palliative treatments | 8 (13.5%) |
| Progression-free survival (median, months) | 14.7 |
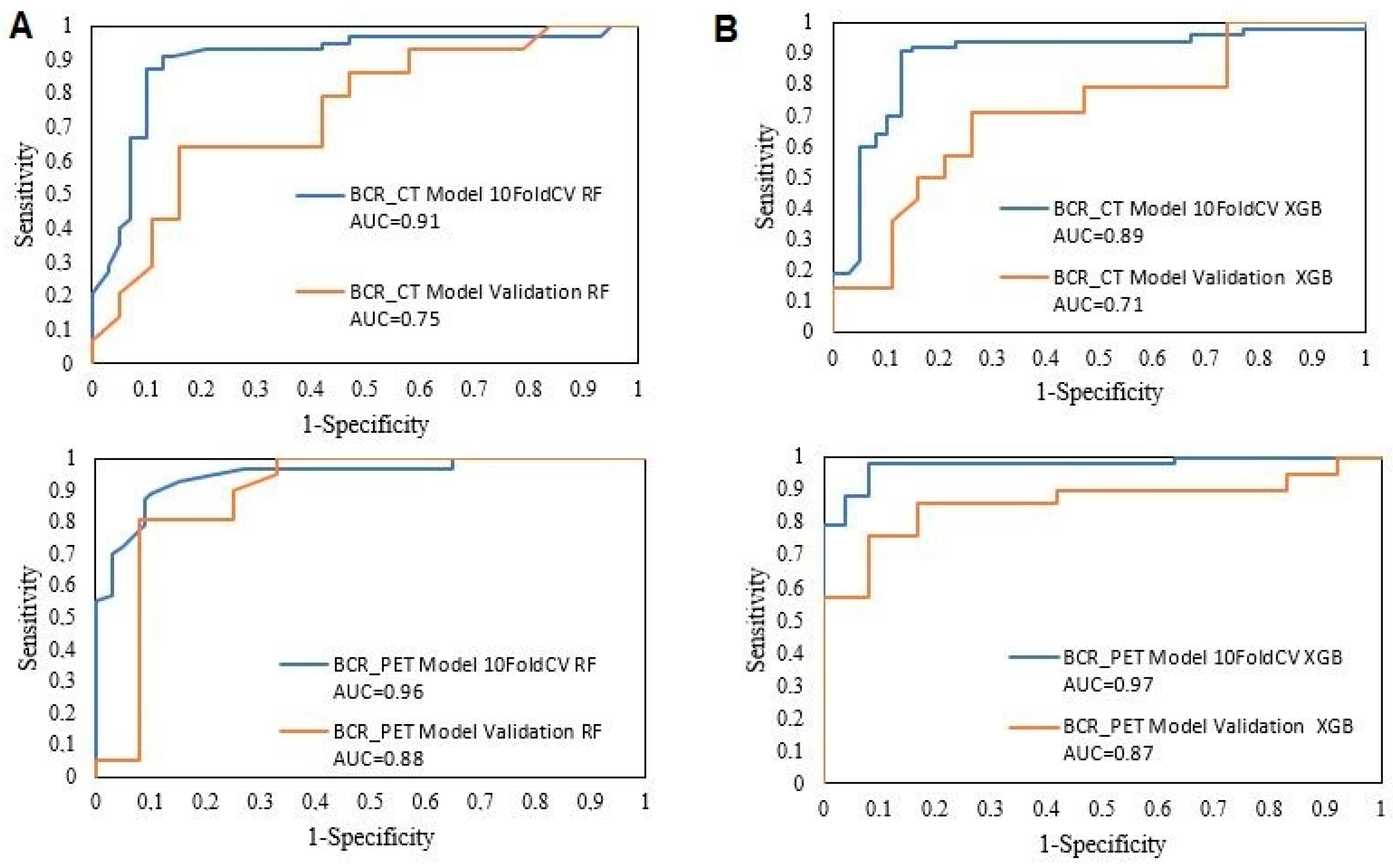
| Training 10FoldCV | AUC | CA | PRE | SEN | SPE | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCR_CT Model | RF | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 82.90% | 90.20% |
| XGB | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 85.00% | 90.40% | |
| BCR_PET Model | RF | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 93.60% | 88.90% |
| XGB | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 91.80% | 90.70% |
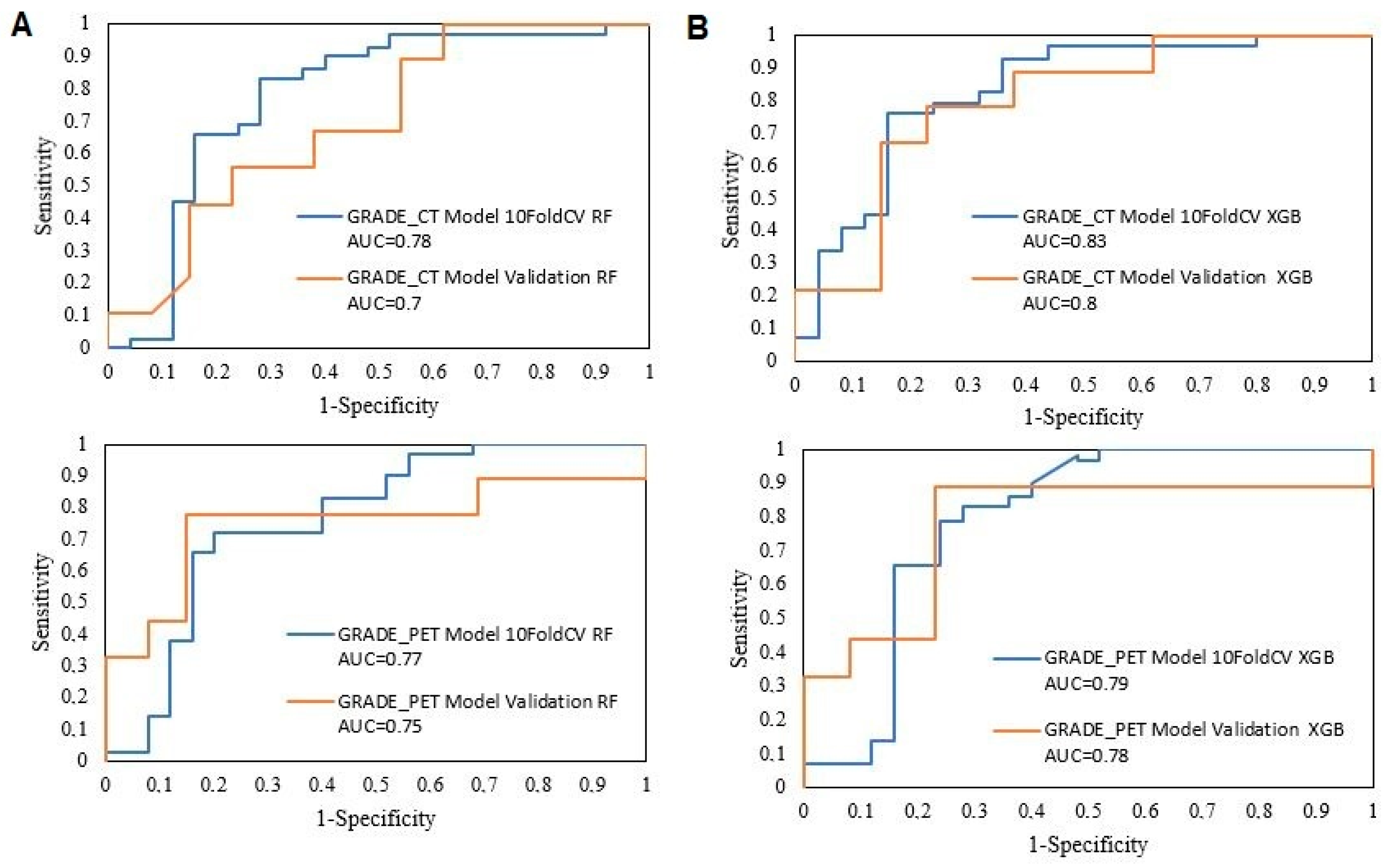
| Training 10-Fold CV | AUC | CA | PRE | SEN | SPE | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRADE_CT Model | RF | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 80.00% | 73.50% |
| XGB | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 77.30% | 75.00% | |
| GRADE_PET Model | RF | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 71.40% | 69.70% |
| XGB | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 78.30% | 77.40% |
| Internal Validation | AUC | CA | PRE | SEN | SPE | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCR_CT Model | RF | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 78.60% | 57.90% |
| XGB | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 77.80% | 66.70% | |
| BCR_PET Model | RF | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 68.80% | 94.10% |
| XGB | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 61.10% | 93.30% | |
| GRADE_CT Model | RF | 0.70 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.46 | 0.67 | 66.70% | 46.20% |
| XGB | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 0.89 | 88.90% | 61.50% | |
| GRADE_PET Model | RF | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 83.30% | 70.00% |
| XGB | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 90.00% | 66.70% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manco, L.; Proietti, I.; Scribano, G.; Pirisino, R.; Bagni, O.; Potenza, C.; Pellacani, G.; Filippi, L. PET Radiomics Signatures and Artificial Intelligence for Decoding Immunotherapy Response in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126453
Manco L, Proietti I, Scribano G, Pirisino R, Bagni O, Potenza C, Pellacani G, Filippi L. PET Radiomics Signatures and Artificial Intelligence for Decoding Immunotherapy Response in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126453
Chicago/Turabian StyleManco, Luigi, Ilaria Proietti, Giovanni Scribano, Riccardo Pirisino, Oreste Bagni, Concetta Potenza, Giovanni Pellacani, and Luca Filippi. 2025. "PET Radiomics Signatures and Artificial Intelligence for Decoding Immunotherapy Response in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Single-Center Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126453
APA StyleManco, L., Proietti, I., Scribano, G., Pirisino, R., Bagni, O., Potenza, C., Pellacani, G., & Filippi, L. (2025). PET Radiomics Signatures and Artificial Intelligence for Decoding Immunotherapy Response in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6453. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126453








