Musculoskeletal Pain and Compensatory Mechanisms in Posture and Adaptation to Sport in Players from the Polish Men’s Goalball National Team—Cross Sectional Study
Abstract
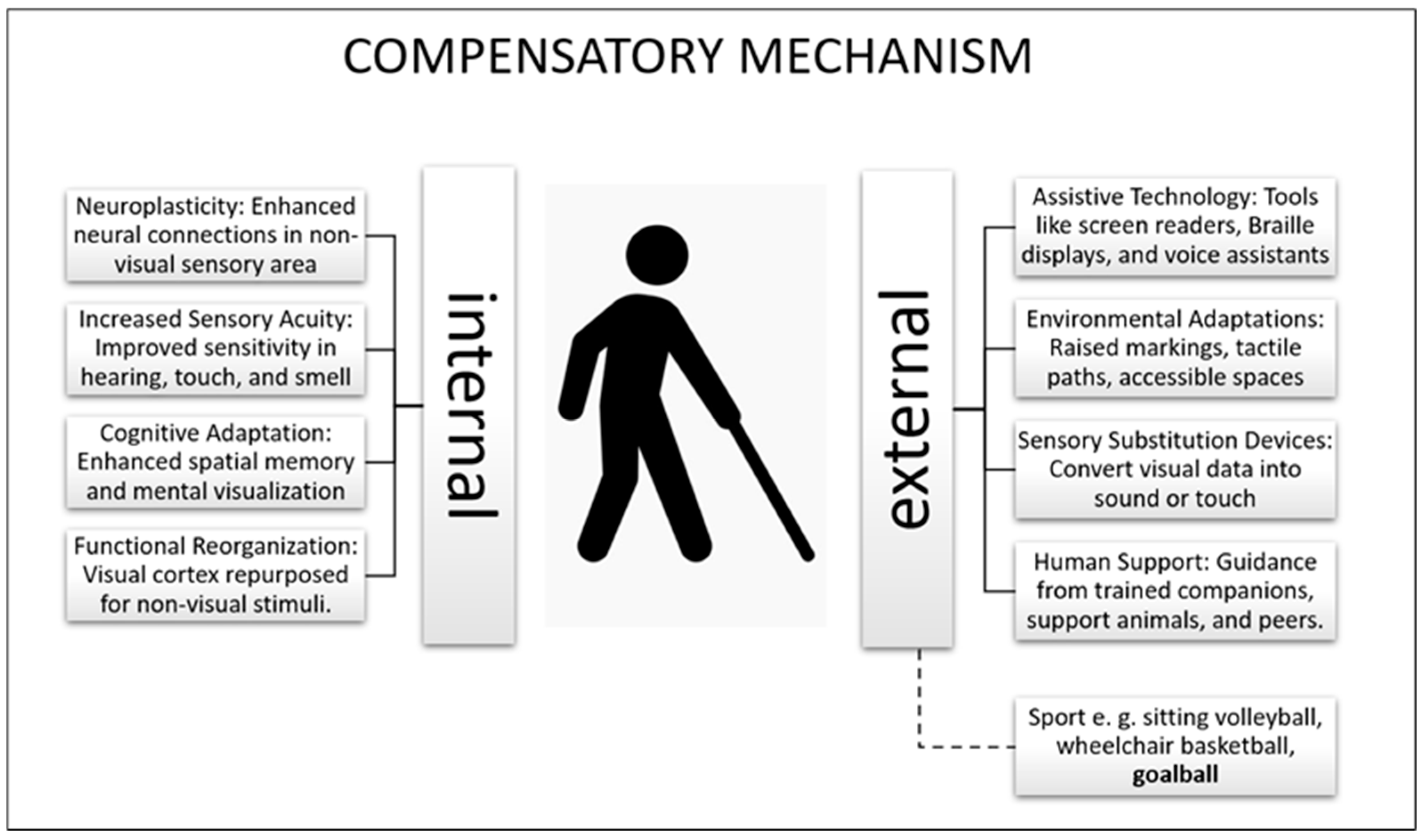
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Protocol of the Study
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fadian, U.F.L.; Hidayatullah, M.F.; Riyadi, S.; Umar, F. Development of Paralympic Sport 2008-2022 through Systematic Literature Review. KnE Soc. Sci. 2024, 9, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzchowska, A.; Gaweł, E.; Rosołek, B. Determinants of the prevalence and location of musculoskeletal pain in elite Para athletes. Medicine 2022, 101, e31268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzchowska, A.; Gawel, E.; Celebanska, D.; Rosolek, B. Musculoskeletal pain as the effect of internal compensatory mechanisms on structural and functional changes in body build and posture in elite Polish sitting volleyball players. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzchowska, A.; Gaweł, E.; Gómez, M.A.; Żebrowska, A. Prediction of injuries, traumas and musculoskeletal pain in elite Olympic and Paralympic volleyball players. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, L.R.D.S.; Gomes, J.F.M.; Belache, F.A.T.C.; Meziat Filho, N.A.M.; Vigário, P.D.S. Musculoskeletal Pain, Mood, and Sports Injury in Wheelchair Power Soccer Players. J. Sport. Rehabil. 2024, 33, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzchowska, A.; Gaweł, E.; Maszczyk, A.; Roczniok, R. The importance of extrinsic and intrinsic compensatory mechanisms to body posture of competitive athletes a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł, E.; Zwierzchowska, A. Effect of Compensatory Mechanisms on Postural Disturbances and Musculoskeletal Pain in Elite Sitting Volleyball Players: Preparation of a Compensatory Intervention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorud, H.S.; Mork, R.; Bjørset, C.O.; Gilson, S.J.; Hagen, L.A.; Langaas, T.; Pedersen, H.R.; Svarverud, E.; Vikesdal, G.H.; Baraas, R.C. Laboured reading and musculoskeletal pain in school children—The role of lifestyle behaviour and eye wear: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierzchowska, A.; Gawel, E.; Karpinski, J.; Maszczyk, A.; Zebrowska, A. The effect of swimming on the body posture, range of motion and musculoskeletal pain in elite para and able-bodied swimmers. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.T.; Horvat, M.; Croce, R.; Mason, R.C.; Wolf, S.L. The impact of vision loss on postural stability and balance strategies in individuals with profound vision loss. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.S.; Fischer, G.; da Rosa, R.G.; Schons, P.; Teixeira, L.; Hoogkamer, W.; Peyré-Tartaruga, L.A. Gait and functionality of individuals with visual impairment who participate in sports. Gait Posture 2018, 62, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Pádua, M.; Sauer, J.F.; João, S. Quantitative Postural Analysis of Children with Congenital Visual Impairment. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2018, 41, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallemans, A.; Ortibus, E.; Meire, F.; Aerts, P. Low vision affects dynamic stability of gait. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bair, W.N.; Barela, J.A.; Whitall, J.; Jeka, J.J.; Clark, J.E. Children with developmental coordination disorder benefit from using vision in combination with touch information for quiet standing. Gait Posture 2011, 34, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa Porcellis da Silva, R.; Marques, A.C.; Reichert, F.F. Objectively measured physical activity in Brazilians with visual impairment: Description and associated factors. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Schrack, J.A.; Wang, H.; E, J.Y.; Wanigatunga, A.A.; Agrawal, Y.; Urbanek, J.K.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Swenor, B.K. Visual Impairment and Objectively Measured Physical Activity in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 2194–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Paralympic Committee. Available online: https://www.paralympic.org/goalball (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- International Blind Sports Federation. Goalball Rules and Regulations 2022–2024. Available online: https://goalball.sport/about-goalball/rules-and-downloads/ (accessed on 6 August 2024).
- Hirschmüller, A.; Kosel, J.; Südkamp, N.P.; Kubosch, E.J. Epidemiology of Injuries and Illnesses in Handicapped Athletes Competing at the Paralympic Games. Ger. J. Sports Med. 2005, 66, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottesen, T.; Mashkovskiy, E.; Gentry, M.; Jensen, D.; Webborn, N.; Tuakli-Wosornu, Y. Acute and chronic musculoskeletal injury in para-sport: A systematic review. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 29, 205–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willick, S.E.; Webborn, N.; Emery, C.; Blauwet, C.A.; Pit-Grosheide, P.; Stomphorst, J.; Van de Vliet, P.; Patino Marques, N.A.; Martinez-Ferrer, J.O.; Jordaan, E.; et al. The epidemiology of injuries at the London 2012 Paralympic Games. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuorinka, I.; Jonsson, B.; Kilbom, A.; Vinterberg, H.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Andersson, G.; Jørgensen, K. Standardised Nordic questionnaires for the analysis of musculoskeletal symptoms. Appl. Ergon. 1987, 18, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio: Report of a WHO Expert Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, R.N.; Stefanovski, D.; Buchanan, T.A.; Sumner, A.E.; Reynolds, J.C.; Sebring, N.G.; Xiang, A.H.; Watanabe, R.M. A better index of body adiposity. Obesity 2011, 19, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Gencbas, D.; Tosun, B.; Bebis, H.; Sinan, O. Musculoskeletal Pain, Related Factors, and Posture Profiles Among Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study from Turkey. Pain. Manag. Nurs. 2021, 22, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.C.M.; Vigário, P.S.; Mainenti, M.R.M.; Silva, D.T.R.; Lima, T.R.L.; Lemos, T. Computerized photogrammetric assessment of postural alignment in visually impaired athletes. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo Hoo, J.A.; Kim, H.; Fram, J.; Lin, Y.S.; Page, C.; Easthausen, I.; Jayabalan, P. Shoulder pain and ultrasound findings: A comparison study of wheelchair athletes, nonathletic wheelchair users, and nonwheelchair users. PM&R 2022, 14, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabara, M. A comparison of the posture between young female handball players and non-training peers. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2014, 27, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Mengibar, J.M.; Sainz-de-Baranda, P.; Santonja-Medina, F. Training intensity and sagittal curvature of the spine in male and female artistic gymnasts. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 58, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginés-Díaz, A.; Martínez-Romero, M.T.; Cejudo, A.; Aparicio-Sarmiento, A.; Sainz de Baranda, P. Sagittal Spinal Morphotype Assessment in Dressage and Show Jumping Riders. J. Sport. Rehabil. 2019, 29, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz de Baranda, P.; Cejudo, A.; Moreno-Alcaraz, V.J.; Martinez-Romero, M.T.; Aparicio-Sarmiento, A.; Santonja-Medina, F. Sagittal spinal morphotype assessment in 8 to 15 years old Inline Hockey players. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.D.N.; Carvalho, T.L.D.; Felício, L.R.; Mainenti, M.R.M.; Vigário, P.D.S. Postural control in athletes with different degrees of visual impairment. J. Phys. Educ. 2018, 29, e2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrysomallis, C. Relationship between balance ability, training and sports injury risk. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magno e Silva, M.; Bilzon, J.; Duarte, E.; Gorla, J.; Vital, R. Sport injuries in elite paralympic swimmers with visual impairment. J. Athl. Train. 2013, 48, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magno e Silva, M.; Morato, M.P.; Bilzon, J.L.; Duarte, E. Sports injuries in brazilian blind footballers. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Jiménez, J.; Gámez-Calvo, L.; Rojas-Valverde, D.; León, K.; Gamonales, J.M. Analysis of Injuries and Wellness in Blind Athletes during an International Football Competition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwierzchowska, A.; Rosołek, B.; Celebańska, D.; Gawlik, K.; Wójcik, M. The Prevalence of Injuries and Traumas in Elite Goalball Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Mean ± SD | Min-Max | Qualitative Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| BM (kg) | 81.4 ± 14.1 | 57.2–108.7 | - |
| BH (cm) | 177,0; 17 | 170.0–195.3 | - |
| WC (cm) | 86.9 ± 9.9 | 70.5–106.0 | <90 n = 9; >90 ** n = 3 |
| HC (cm) | 102.5 ± 8.1 | 87.0–119.0 | - |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.6 ± 3.1 | 19.1–29.9 | <25 n = 7; ≥25 and <30 ** n = 5 |
| BAI | 23.9 ± 2.8 | 19.9–28.3 | <21 n = 3; >21 ** n = 9 |
| FAT (%) * | 21.8 ± 7.1 | 12.3–37.7 | - |
| FfST (%) * | 74.2 ± 6.8 | 59.2–83.4 | - |
| Body Parts | NMQ7 n/% | NMQ6 n/% |
|---|---|---|
| neck/nape of the neck | 1/8.3 | 3/25 |
| arms | 4/33.3 | 5/41.7 |
| upper back | 1/8.3 | 4/33.3 |
| elbows | 0 | 4/33.3 |
| wrists/hands | 6/50 | 6/50 |
| lower back | 5/41.7 | 5/41.7 |
| hips/thighs | 2/16.7 | 3/25 |
| knees | 2/16.7 | 3/25 |
| ankles/feet | 3/25 | 5/41.7 |
| Player Number | TKA, HP (°) Value Reference Range | LLA, HP (°) Value Reference Range | Pelvic Alignment in HSP Value Reference Range | Qualitative Assessment of Body Posture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Player 1 | 53 ↑ 28–48 | 42 ↑ 18–30 | 23 ↑ 8–16 | Hyperkyphosis, hyperlordosis, anterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 2 | 52 • 39–55 | 29 • 23–31 | 9 ↓ 10–16 | Normal kyphosis, normal lordosis, posterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 3 | 47 • 34–52 | 33 • 21–35 | 20 ↑ 8–18 | Normal kyphosis, normal lordosis, anterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 4 | 57 ↑ 28–48 | 41 ↑ 18–30 | 23 ↑ 8–16 | Hyperkyphosis, hyperlordosis, anterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 5 | 46 • 35–55 | 27 • 17–31 | 11 • 6–16 | Normal kyphosis, normal lordosis, pelvis aligned correctly |
| Player 6 | 42 • 39–55 | 19 ↓ 23–31 | 9 ↓ 10–16 | Normal kyphosis, hypolordosis, posterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 7 | 54 ↑ 34–52 | 42 ↑ 21–35 | 20 ↑ 8–18 | Hyperkyphosis, hyperlordosis, anterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 8 | 36 • 34–52 | 29 • 21–35 | 18 • 8–18 | Normal kyphosis, normal lordosis, pelvis aligned correctly |
| Player 9 | 47 • 34–52 | 19 ↓ 21–35 | 2 ↓ 8–18 | Normal kyphosis, hypolordosis, posterior pelvic tilt |
| Player 10 | 41 • 34–52 | 24 • 21–35 | 8 • 8–18 | Normal kyphosis, normal lordosis, pelvis aligned correctly |
| Player 11 | 51 • 34–52 | 32 • 21–35 | 15 • 8–18 | Normal kyphosis, normal lordosis, pelvis aligned correctly |
| Player 12 | 48 • 28–48 | 10 ↓ 18–30 | 5 ↓ 8–16 | Normal kyphosis, hypolordosis, posterior pelvic tilt |
| All players ± SD (min–max) | 47.8 ± 6.0 36.0–57.0 | 28.9 ± 9.9 10.0–42.0 | 13.6 ± 7.2 2.0–23.0 | - |
| Player Number | Range of Motion (Flexion) | Range of Motion (Extension) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TK Value Reference Range | LL Value Reference Range | TK Value Reference Range | LL Value Reference Range | |
| Player 1 | 31 • 11–33 | 60 • 60–76 | 1 • −17–5 | −14 • −27–(−9) |
| Player 2 | 6 • 2–24 | 63 • 55–69 | −12 • −23–(−3) | −15 • −24–(−8) |
| Player 3 | 17 • 6–28 | 67 • 56–74 | 14 ↑ −22–6 | −20 • −28–(−10) |
| Player 4 | 7 ↓ 11–33 | 75 • 60–76 | 1 • −17–5 | −7 ↓ −27–(−9) |
| Player 5 | 15 • 9–25 | 60 • 45–61 | 14 ↑ −23–(−7) | −11 • −20–4 |
| Player 6 | 2 • 2–24 | 69 • 55–69 | −13 • −23–(3) | −3 ↓ −24–(−8) |
| Player 7 | 11 • 6–28 | 70 • 56–74 | −9 • −22–6 | −13 ↓ −28–(−20) |
| Player 8 | 22 • 6–28 | 70 • 56–74 | −8 • −22–6 | 1 ↓ −28–(−10) |
| Player 9 | 7 • 6–28 | 67 • 56–74 | 13 ↑ −22–6 | −20 • −28–(−10) |
| Player 10 | 4 ↓ 6–28 | 76 • 56–74 | −5 • −22–6 | −3 ↓ −28–(−10) |
| Player 11 | 14 • 6–28 | 51 ↓ 56–74 | 0 • −22–6 | −10 • −28–(−10) |
| Player 12 | 10 ↓ 11–33 | 58 ↓ 60–76 | −7 • −17–5 | −28 ↑ −27–(−9) |
| All players ± SD (min–max) | 12.2 ± 8.3 (2–31) | 65.6 ± 7.3 (51–76) | −0.9 ± 9.9 (−13–14) | −11.9 ± 8.3 (−28–1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosołek, B.; Alexe, D.I.; Celebańska, D.; Zwierzchowska, A. Musculoskeletal Pain and Compensatory Mechanisms in Posture and Adaptation to Sport in Players from the Polish Men’s Goalball National Team—Cross Sectional Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116363
Rosołek B, Alexe DI, Celebańska D, Zwierzchowska A. Musculoskeletal Pain and Compensatory Mechanisms in Posture and Adaptation to Sport in Players from the Polish Men’s Goalball National Team—Cross Sectional Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116363
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosołek, Barbara, Dan Iulian Alexe, Diana Celebańska, and Anna Zwierzchowska. 2025. "Musculoskeletal Pain and Compensatory Mechanisms in Posture and Adaptation to Sport in Players from the Polish Men’s Goalball National Team—Cross Sectional Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116363
APA StyleRosołek, B., Alexe, D. I., Celebańska, D., & Zwierzchowska, A. (2025). Musculoskeletal Pain and Compensatory Mechanisms in Posture and Adaptation to Sport in Players from the Polish Men’s Goalball National Team—Cross Sectional Study. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6363. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116363








