Comparing Virtual Reality and Robotic Training Effects on Balance Ability and Confidence in Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Robotics for Balance Training
1.2. Virtual Reality (VR) and Robotic-VR Combined Balance Training
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
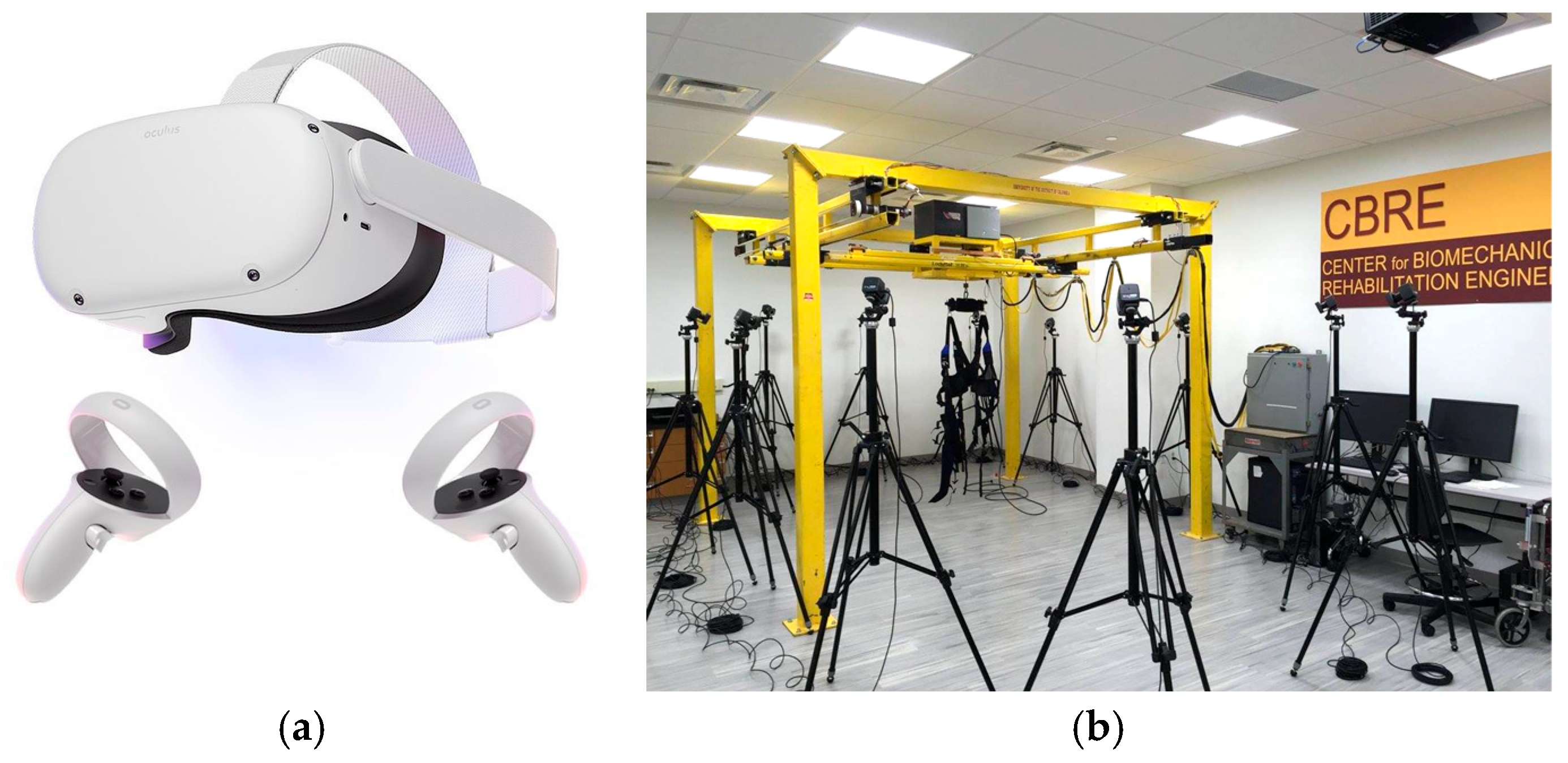
2.2. Training
2.3. Balance Assessment
2.4. Data Analysis
- AP COP time series without offset:
- ML COP time series without offset:where APo/MLo: AP/ML COP path relative to the origin of the force platform coordinate system AP/ML and N = number of data points.
- AP Root Mean Square (RMSAP):
- ML Room Mean Square (RMSML):where
- N is the total number of data points,
- ∑ represents the summation over all data points.
- AP Peak-to-peak Displacement (MAXDAP):MAXDAP = max(AP) − min(AP)
- ML Peak-to-peak Displacement (MAXDML):MAXDML = max(ML) − min(ML)
3. Results
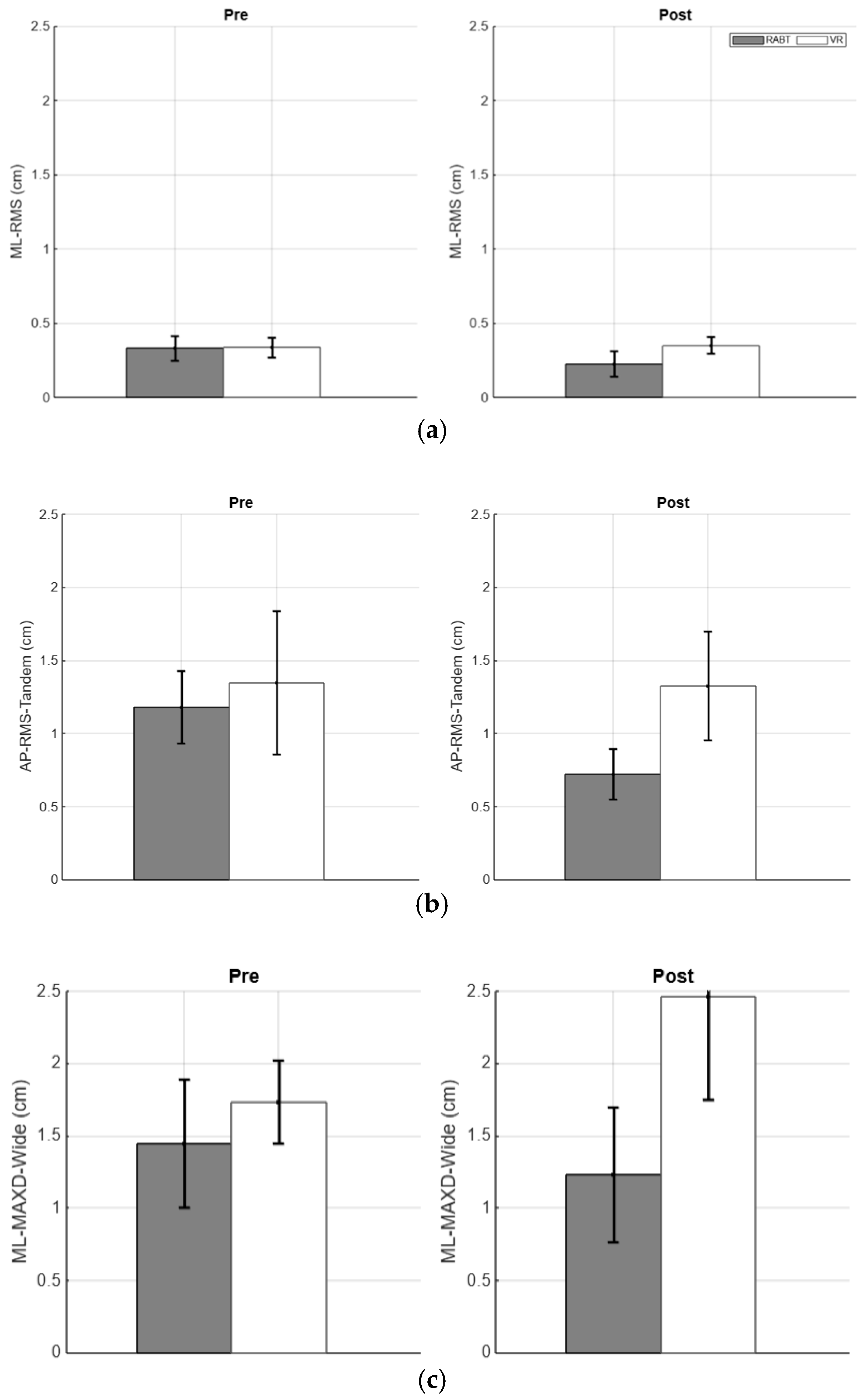
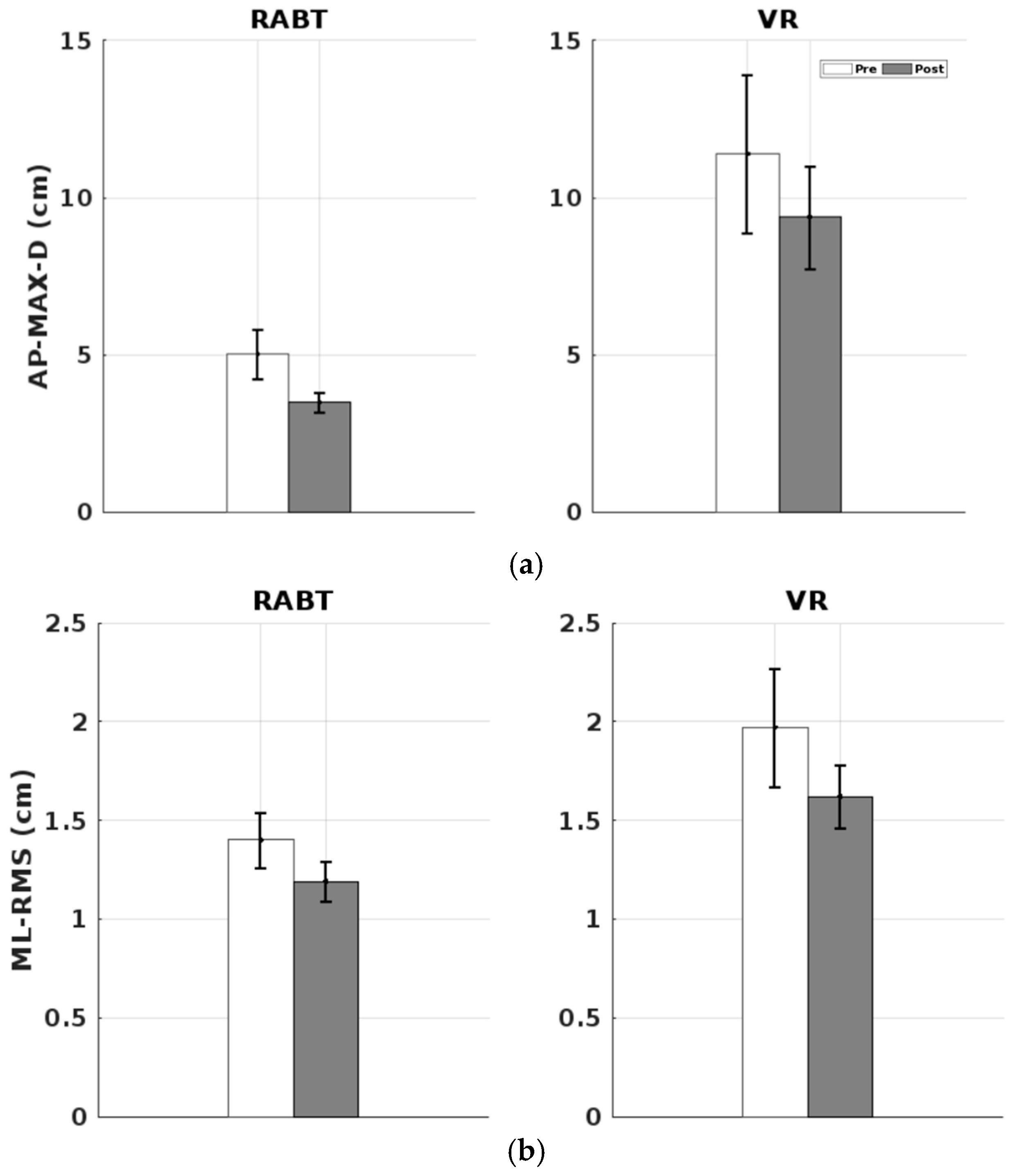
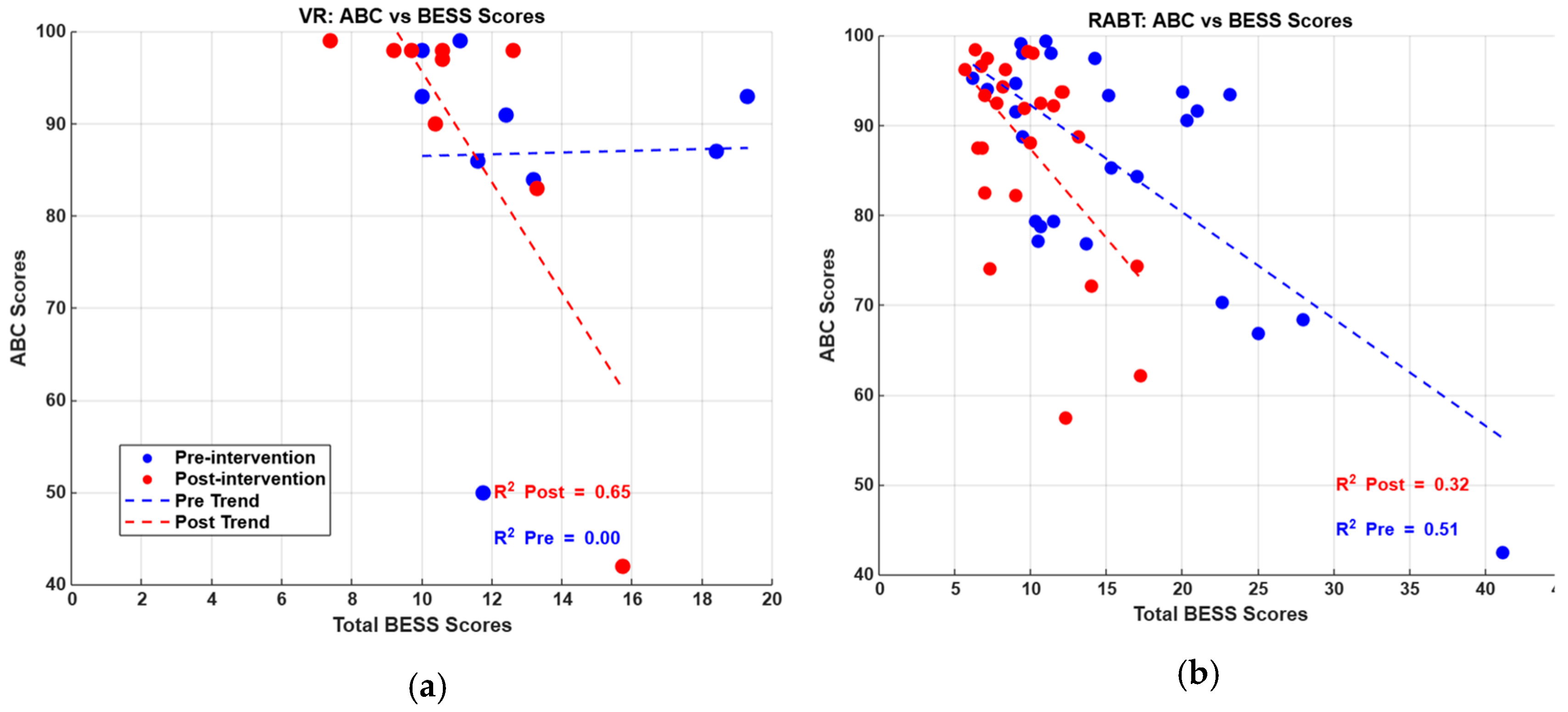
3.1. VR and RABT Balance Performance in Healthy Older Participants Based on Equivalent Baseline Ability
3.2. VR and RABT Balance Performance in Healthy Older Participants
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stefanacci, R.G.; Wilkinson, J.R. Falls in Older Adults. 2023. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/geriatrics/falls-in-older-adults/falls-in-older-adults (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Older Adult Falls Data. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: www.cdc.gov/falls/data-research/index.html (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Facts about Falls. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: www.cdc.gov/falls/data-research/facts-stats/index.html (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Wilson, O.; Arnold, N.; Thompson, L.A. Investigating the effects of virtual reality-based training on balance ability and balance confidence in older individuals. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.A.; Badache, M.; Brusamolin, J.A.R.; Savadkoohi, M.; Guise, J.; De Paiva, G.V.; Suh, P.; Guerrero, P.S.; Shetty, D. Multidirectional Overground Robotic Training Leads to Improvements in Balance in Older Adults. Robotics 2021, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.; Zheng, W.; Shi, M.; Yang, F. Scientometric Research and Critical Analysis of Gait and Balance in Older Adults. Sensors 2024, 24, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WISQARS Explore Fatal and Nonfatal Data. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://wisqars.cdc.gov/explore/?o=MORT&y1=2023&y2=2023&g=00&t=0&i=0&m=20810&s=0&r=0&me=0&ry=2&yp=65&e=0&a=ALL&a1=0&a2=199&g1=0&g2=199 (accessed on 17 February 2025).
- Shirota, C.; Van Asseldonk, E.H.; Matjačić, Z.; Vallery, H.; Barralon, P.; Maggioni, S.; Buurke, J.H.; Veneman, J.F. Robot-supported assessment of balance in standing and walking. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidler, J.; Brennan, D.; Black, I.; Nichols, D.; Brady, K.; Nef, T. ZeroG: Overground gait and balance training system. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, A.K.; Al-Manaseer, F.; Knowlton, L.M.; Tuma, F. Virtual reality (VR) as a simulation modality for technical skills acquisition. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 71, 102945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubin, O.; Alnajjar, F.; Jishtu, N.; Alsinglawi, B.; Mahmud, A.A. Exoskeletons With Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Gamification for Stroke Patients’ Rehabilitation: Systematic Review. JMIR Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2019, 6, e12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Kondo, I.; Hirano, S.; Kagaya, H.; Saitoh, E.; Osawa, A.; Fujinori, Y. Training with a balance exercise assist robot is more effective than conventional training for frail older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Eunhee, C. Effects of a gait training program using a walking-assist wearable robot on community-dwelling older adults. Innov. Aging 2024, 8 (Suppl. 1), 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Calderon, A.; Maggioni, S. Challenges in Adaptive Robot-Assisted Gait Training: The Balancing Act of Minimizing Assistance While Preserving Safety; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kim, Y.W.; Lee, S.J.; Shin, J.C. Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Individuals With Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2024, 48, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K. Virtual reality gait training to promote balance and gait among older people: A randomized clinical trial. Geriatrics 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebêlo, F.L.; de Souza Silva, L.F.; Doná, F.; Barreto, A.S.; Quintans, J.D.S.S. Immersive virtual reality is effective in the rehabilitation of older adults with balance disorders: A randomized clinical trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 149, 111308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedian-Nasab, N.; Jaberi, A.; Shirazi, F.; Kavousipor, S. Effect of virtual reality exercises on balance and fall in elderly people with fall risk: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.A.; Badache, M.; Brusamolin, J.A.R.; Savadkoohi, M.; Guise, J.; de Paiva, G.V.; Suh, P.; Sanchez Guerrero, P.; Shetty, D. Investigating Relationships between Balance Confidence and Balance Ability in Older Adults. J. Aging Res. 2021, 2021, 3214366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okhuoya, O.; Thompson, L.A. Comparing Virtual Reality and Robotic Training Effects on Balance Ability and Confidence in Older Adults. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5909. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115909
Okhuoya O, Thompson LA. Comparing Virtual Reality and Robotic Training Effects on Balance Ability and Confidence in Older Adults. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5909. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115909
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkhuoya, Oluwasola, and Lara A. Thompson. 2025. "Comparing Virtual Reality and Robotic Training Effects on Balance Ability and Confidence in Older Adults" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5909. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115909
APA StyleOkhuoya, O., & Thompson, L. A. (2025). Comparing Virtual Reality and Robotic Training Effects on Balance Ability and Confidence in Older Adults. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5909. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115909




