1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to motor impairments such as tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability [
1]. Additionally, non-motor symptoms, including cognitive decline, depression, and autonomic dysfunction, significantly impact patients’ quality of life [
2,
3]. While pharmacological treatments, such as levodopa, provide symptomatic relief, they do not halt disease progression, necessitating complementary therapeutic approaches [
4]. Recent advances in rehabilitation strategies emphasize the role of exercise therapy in mitigating PD symptoms by promoting neuroplasticity, improving motor function, and enhancing overall well-being [
5,
6]. Among these interventions, high-intensity exercise protocols have garnered attention due to their potential to slow disease progression and improve motor performance [
7,
8].
Technology offers new applications in training methods. Home-based training solutions (i.e., telerehabilitation, sensory stimuli training, etc.) are nowadays easily accessible, providing flexible scheduling, individual tailoring, larger training volume, real-time feedback, and increased motivation [
9]. In particular, state-of-the-art technologies, such as virtual reality and brain–computer interfaces, enhance neuroplasticity [
10]. During this process, the brain reorganizes itself by building new neural connections based on experience and learning. Different forms of virtual reality, including simple screen-based and fully immersive headset applications, offer new possibilities in rehabilitation, often along with real-time monitoring.
In parallel, immersive virtual reality (VR) technologies are revolutionizing neurological rehabilitation by providing engaging, multisensory environments that enhance motor learning and motivation [
11,
12]. VR-based interventions leverage interactive feedback, gamified exercises, and task-specific training to address motor deficits in patients with PD [
13]. The integration of high-intensity VR-based agility training has demonstrated significant improvements in postural control, mobility, and cognitive–motor integration, making it a promising adjunct to traditional rehabilitation [
14]. The IntegraPark Study and other recent trials have highlighted the feasibility and efficacy of VR-enhanced high-intensity exercise programs for patients with PD. These interventions, often employing rowing, cycling, and agility-based movements, provide task-specific training within immersive settings, promoting sustained engagement and neuroplastic adaptations [
13]. By incorporating real-time feedback, adaptive difficulty levels, and cognitive challenges, VR-based rehabilitation fosters motor skill acquisition, balance retraining, and executive function improvement [
15]. Despite promising findings, further research is warranted to establish optimal training protocols, long-term efficacy, and the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying high-intensity VR therapy in PD [
16,
17]. The present study aims to evaluate the impact of a structured high-intensity VR training program on motor function, balance, aerobic capacity, and quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. By leveraging state-of-the-art VR exergames, motion tracking, and adaptive training paradigms, we seek to advance rehabilitation strategies for individuals affected by PD [
18]. Exergames or exergaming refers to the activity of playing video games that involve physical exertion. It is an entertaining and motivating form of exercise, mostly targeting professional athletes, patients in rehabilitation after injuries or with neurology problems (i.e., stroke, Parkinson’s, MS, etc.), and the older adult population [
19,
20,
21,
22]. The term is related to the terms gamification and serious gaming. Exergames are a special form of serious games, where intensive physical exercise is involved. Exergaming can also be performed in virtual reality environments [
23,
24,
25]. In addition, exergames have already been used for and tailored to patients with Parkinson’s [
9,
12,
26,
27,
28,
29]. High-intensity training (HIIT) in the form of VR-exergaming has been demonstrated as an effective tool to increase enjoyment and maintain motivation [
30]. However, proper setting of the intensity level is a critical issue [
31]. VR-based HIIT can significantly enhance physiological parameters by maintaining motivation compared to traditional high-intensity methods [
32]. Studies indicate that HIIT can enhance dopamine release, synaptic plasticity, and motor learning, ultimately leading to improved mobility and stability in patients with PD [
33,
34].
This randomized clinical trial compared the effects of four high-intensity interventions—Exergame, Cycling, Agility, and Robot-assisted (C-Mill) therapy—without a non-exercising control group. The objective of this study was to compare the effectiveness of four high-intensity rehabilitation strategies—Exergame, Cycling, Agility Training, and Robot-Assisted C-Mill Therapy—on motor function, balance, gait performance, cardiovascular response, and quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
The novelty of this study is twofold: (1) it is among the first randomized clinical trials to compare four distinct high-intensity rehabilitation modalities (Exergame, Cycling, Agility, and Robot-assisted training) in patients with Parkinson’s disease; and (2) it uniquely integrates cardiovascular monitoring (heart rate and Borg RPE) during immersive VR-based high-intensity training. This dual focus enables a more comprehensive evaluation of both the safety and effectiveness of high-intensity rehabilitation protocols for PD.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study is a quantitative, randomized, blinded, pre–post, prospective clinical trial. Patient allocation was conducted using a computer-generated randomization process to minimize selection bias. The groups were structured as follows. Exergame group (n = 25): Participants engaged in interactive, gamified VR-based exercises specifically designed to enhance agility, balance, and motor coordination. Cycling group (n = 25): Patients performed high-intensity cycling exercises, continuously monitored with real-time motion tracking to ensure safety and optimal performance. Agility Training group (n = 25): Participants underwent structured agility-based exercises conducted in a clinical setting, focusing on dynamic balance and motor control. Robot-Assisted Training group (n = 25): This group utilized robotic-assisted treadmills (e.g., Cmill) to improve gait, stability, and functional mobility. Before the intervention, all participants had been receiving standard physiotherapy, which was temporarily suspended for the duration of the study to ensure exclusive participation in the assigned intervention programs. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrollment, in accordance with ethical guidelines. Baseline characteristics, including sex distribution, were recorded, with 37 males and 37 females participating in the study, contributing to a total of 74 evaluable participants. The intervention groups were assessed using standardized clinical measures, including the Berg Balance Scale, Dynamic Gait Index, BESTest, and Tinetti Assessment Tool (TAT), to evaluate motor function, balance, and fall risk. The inclusion criteria were as follows: diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (Hoehn & Yahr stage 2–4), stable pharmacological treatment, Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score of ≥24, and the ability to walk independently for at least 6 m with or without assistive devices.
The exclusion criteria included severe cognitive impairment (MMSE < 24), presence of comorbid neurological or orthopedic disorders affecting mobility, unstable cardiovascular disease, recent orthopedic surgery (within 6 months), ongoing participation in other clinical trials, or any contraindications to high-intensity physical activity, as determined by the treating physician.
2.2. Outcomes
The randomization process was conducted using a computer-generated stratified allocation method to ensure an even distribution of disease severity, age, and medication regimen across groups. To minimize bias, the study followed a single-blind design, meaning that the assessors conducting baseline and post-intervention evaluations were unaware of participants’ group assignments. All participants were randomized into one of four intervention groups. No non-intervention control group was included. To reduce variability in motor function assessments, all evaluations were conducted while participants were in their “ON” medication state. Before starting the intervention, participants received standardized pre-training instructions to familiarize them with the testing equipment and the specifics of their assigned intervention. Strict safety protocols were maintained throughout the study, and a physical therapist was always present during training sessions to provide assistance in cases of fatigue or discomfort. To ensure accurate monitoring, all training sessions were recorded for adherence tracking and progress evaluation.
2.2.1. Functional Performance Outcomes
Functional mobility assessments included the Timed Up and Go (TUG) test, the 10-Meter Walk Test (10 MWT), and the Six-Minute Walk Test (6 MWT), which helped quantify agility and endurance improvements. Furthermore, the Schwab and England Functional Independence Measure (FIM) was included to assess the degree of autonomy in daily life.
2.2.2. Balance and Posturography Outcomes
Improvements in balance and gait performance were measured using standardized tools such as the Berg Balance Scale (BBS), Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), Balance Evaluation Systems Test (BESTest), and the Tinetti Assessment Tool (TAT). Posturography metrics were analyzed to evaluate center of pressure (COP) displacement, sway area, and velocity changes, providing insights into the participants’ balance stability.
2.2.3. Cardiovascular and Physiological Monitoring
Cardiovascular and physiological responses were also monitored, with heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP) measured before and after training sessions. The Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) was used to gauge exercise intensity levels, ensuring that participants maintained high-intensity engagement safely.
2.2.4. Quality of Life Outcomes
Quality of life measures were assessed using the Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire (PDQ-39) and the EQ-5D Health Questionnaire, which provided subjective evaluations of mobility, self-care, daily activities, and emotional well-being. Lastly, potential neuroplastic effects were explored to understand long-term motor learning adaptations and neurorehabilitative potential.
No participant dropout occurred during the intervention. Attendance exceeded 95%, and there were no missing data points in post-intervention assessments. Therefore, no imputation methods or special statistical handling for missing data were required.
2.3. Cardiovascular, Physiological Monitoring, and Follow-Up Assessments
Heart rate, blood pressure, and Borg RPE were recorded at every training session. Posturography and quality of life outcomes were assessed within one week before and after the 14-week training period. Physiological responses to training were monitored through heart rate (HR), measured before and after each session, recording both average and maximal values. Blood pressure (BP), including systolic and diastolic values, was assessed pre- and post-training to evaluate cardiovascular responses. Posturography metrics analyzed center of pressure (COP) sway, comparing eyes open vs. closed and firm vs. unstable surfaces to assess balance control and postural stability. Sway velocity, displacement, and sway area (cm2) provided objective measures of stability and fall risk. Participants were closely observed for dizziness, fatigue, or cardiovascular distress, with safety protocols ensuring hydration breaks and supervised rest periods to minimize exercise-induced discomfort. Post-intervention assessments were conducted within one week of the 14-week training period, using the same baseline evaluation tests. The EQ-5D Health Questionnaire assessed mobility, self-care, daily activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression, while the EQ-5D Visual Analog Scale (VAS) measured self-reported health status. These follow-ups provided quantitative data on motor function improvements, agility, and fall risk reduction, enabling statistical analysis of treatment efficacy across intervention groups.
3. Intervention
The intervention aimed to evaluate the effects of high-intensity training on motor function, balance, and mobility in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Participants were divided into four groups: Exergame, Cycling, Agility Training, and Robot-Assisted Training (Cmill). Each group participated in two supervised training sessions per week over a 14-week period, with each session lasting 30 to 45 min. Each training session consisted of a 5 min warm-up, a 20–35 min main training phase, and a 5 min cool-down, including stretching and breathing exercises. The Exergame group engaged in interactive, gamified virtual reality (VR) exercises designed to improve agility, balance, and motor coordination. The Cycling group performed high-intensity cycling exercises monitored through real-time motion tracking to ensure optimal performance and safety. The Agility Training group participated in structured agility-based exercises in a clinical setting, focusing on dynamic balance and motor control. The Robot-Assisted Training group used robotic-assisted treadmills (e.g., Cmill) to enhance gait, stability, and functional mobility. Training intensity was regulated using the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) scale and heart rate monitoring. At the end of each session, participants rated their perceived exertion, which was categorized as low (RPE 9–11), moderate (RPE 12–13), high (RPE 14–17), and maximal (RPE ≥ 18). All training sessions were supervised by certified physical therapists to ensure safety and correct execution. The sessions took place in a controlled clinical environment, and attendance was digitally recorded to monitor adherence and progression throughout the intervention.
3.1. Exergaming
The measurement setup was based on the Microsoft Xbox 360 core system. As the successor of the first console, it offers online gaming and updates, media streaming, and connection to several peripheral devices, such as the Kinect motion-sensing camera [
35]. The Kinect sensor is a widely known and used external device for the Xbox. It contains RGB cameras and infrared detectors for depth mapping, which allows real-time recognition of gestures/body movements. Although there exist various updates and newer versions of the Xbox family, this system is also capable of providing an exergaming environment for scientific experiments [
36,
37,
38,
39]. Kinect Adventures! is a sports video game collection for the Xbox 360. It uses the Kinect camera and is one of the most popular games for this system. Five mini-games are included, all of them using full-body motion. In these short games, players aim to collect as many points (called adventure pins) as possible. This gaming environment has been available for scientific purposes since the introduction of the platform [
10,
12,
40,
41]. For our experiment, two of the games were selected: Reflex Ridge and Space Pop. Reflex Ridge is a competitive game where players are placed on a virtual moving platform. During the game, players race on this platform, jumping over and leaning away from obstacles and limboing to avoid hitting the head. They also gain points by touching collectibles. Space Pop is very similar. Here, players move and float in a zero-gravity environment. The goal is to pop transparent virtual soap balls. This environment utilizes depth information; thus, players have to move back and forth in front of the sensor. Additionally, they can fly upward by flapping their arms. Both games are time-limited (about 3 min). Third-party developers also offer applications for the console. Just Dance is a motion-based rhythm game (Ubisoft) that features various songs, along with pre-designed choreography and dance moves on the screen. Players have to mimic the routines and are scored on their accuracy. The game can be played with the Kinect system [
42]. This was the third game selected as an exergaming solution for our experiment.
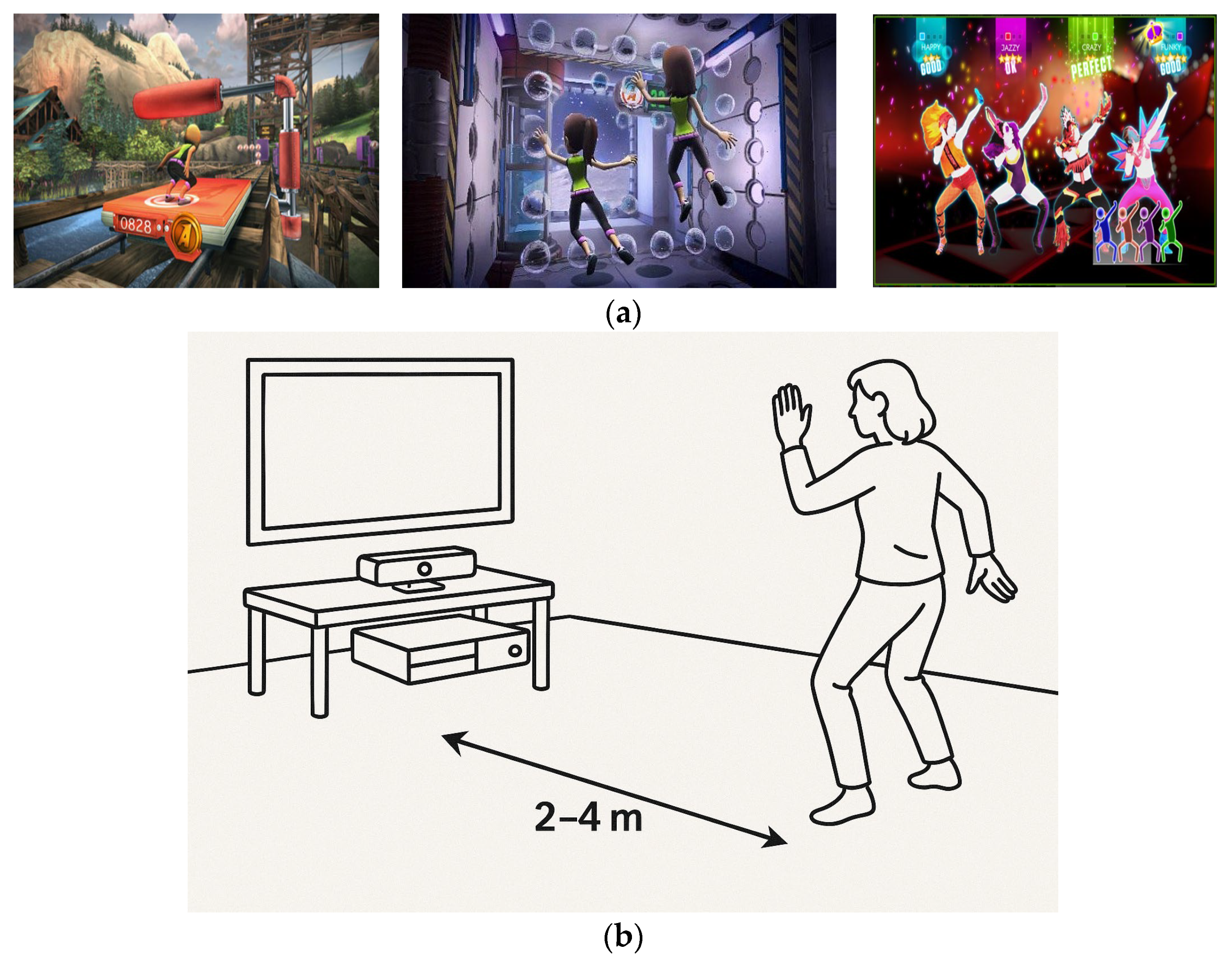
Figure 1a shows screenshots of the games. To provide a clear understanding of the intervention structure, the sequence, duration, and break periods for the exergaming sessions are detailed here. Each training session included three exergames:
Reflex Ridge,
Space Pop, and
Just Dance. These games were played in a fixed sequence during each session, beginning with
Reflex Ridge, followed by
Space Pop, and concluding with
Just Dance. Each game lasted approximately 3 min, resulting in a total active gameplay time of 9 min per session. Between games, participants were allowed a 1 to 2 min rest period to recover and rehydrate, ensuring both safety and consistent performance. This structure was repeated in each of the twice-weekly sessions across the 14-week intervention period. The inclusion of short breaks between games was crucial for maintaining the intended high-intensity level while minimizing fatigue and cardiovascular strain in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. All sessions followed a standardized warm-up (5 min), main training (20–35 min, including the games), and cool-down protocol (5 min), ensuring uniformity across the intervention.
Figure 1b illustrates the Kinect-based motion tracking setup used during the exergaming sessions. This configuration enabled full-body motion capture in a VR-free setting, allowing participants to engage interactively with the exergames while maintaining safety and ease of use. The setup’s real-time feedback capability played a critical role in enhancing engagement and monitoring performance.
3.2. Cycling
Experimental Setup
All cycling sessions were conducted using electromagnetically braked stationary ergometers (e.g., Monark Ergomedic 828E or equivalent), which provided real-time monitoring of cadence, torque output, and heart rate. Participants were seated in an upright position with adjustable saddle height and handlebar positioning to ensure ergonomic alignment and comfort. Pedals were equipped with foot straps to maintain proper foot placement and bilateral engagement. Each ergometer was connected to a display that showed the target cadence (80–100 RPM), heart rate zone (70–80% of HRmax), and real-time feedback to guide effort. Heart rate was continuously recorded using a chest strap monitor (Polar H10), while the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) was noted at the end of each session. Sessions were performed in a controlled clinical environment under the supervision of a certified physiotherapist to ensure safety, appropriate intensity, and adherence to the HIIT protocol.
The high-intensity cycling intervention aimed to improve lower limb strength, neuromuscular coordination, and cardiovascular endurance in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Using stationary cycling with real-time motion tracking and resistance modulation, sessions followed a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) framework, alternating between maximal effort and active recovery to optimize aerobic capacity and neuromuscular control. Participants cycled at 70–80% of HRmax, ensuring a sustained cardiovascular challenge while promoting dopaminergic activation and neuroplasticity. Training intensity was regulated using heart rate monitoring and the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE). Ergometrically controlled bikes adjusted resistance based on cadence (80–100 RPM), torque output, and real-time feedback, addressing gait disturbances like bradykinesia and freezing of gait. Sessions emphasized bilateral motor engagement to enhance muscle coordination and limb symmetry. Dual-tasking consisted of performing cognitive tasks (e.g., simple arithmetic or word recall) while cycling. Physiological and biomechanical parameters, including heart rate variability, cadence stability, and torque fluctuations, were continuously monitored to ensure progressive overload while preventing excessive strain. This high-intensity cycling protocol acted as a neuromodulatory intervention, stimulating dopamine release, promoting neuroplasticity, and mitigating motor decline. By combining intensity modulation, cognitive–motor integration, and real-time performance feedback, it aimed to enhance locomotor stability, gait control, and functional independence, improving overall quality of life in individuals with Parkinson’s disease [
43].
3.3. Robotic Therapy
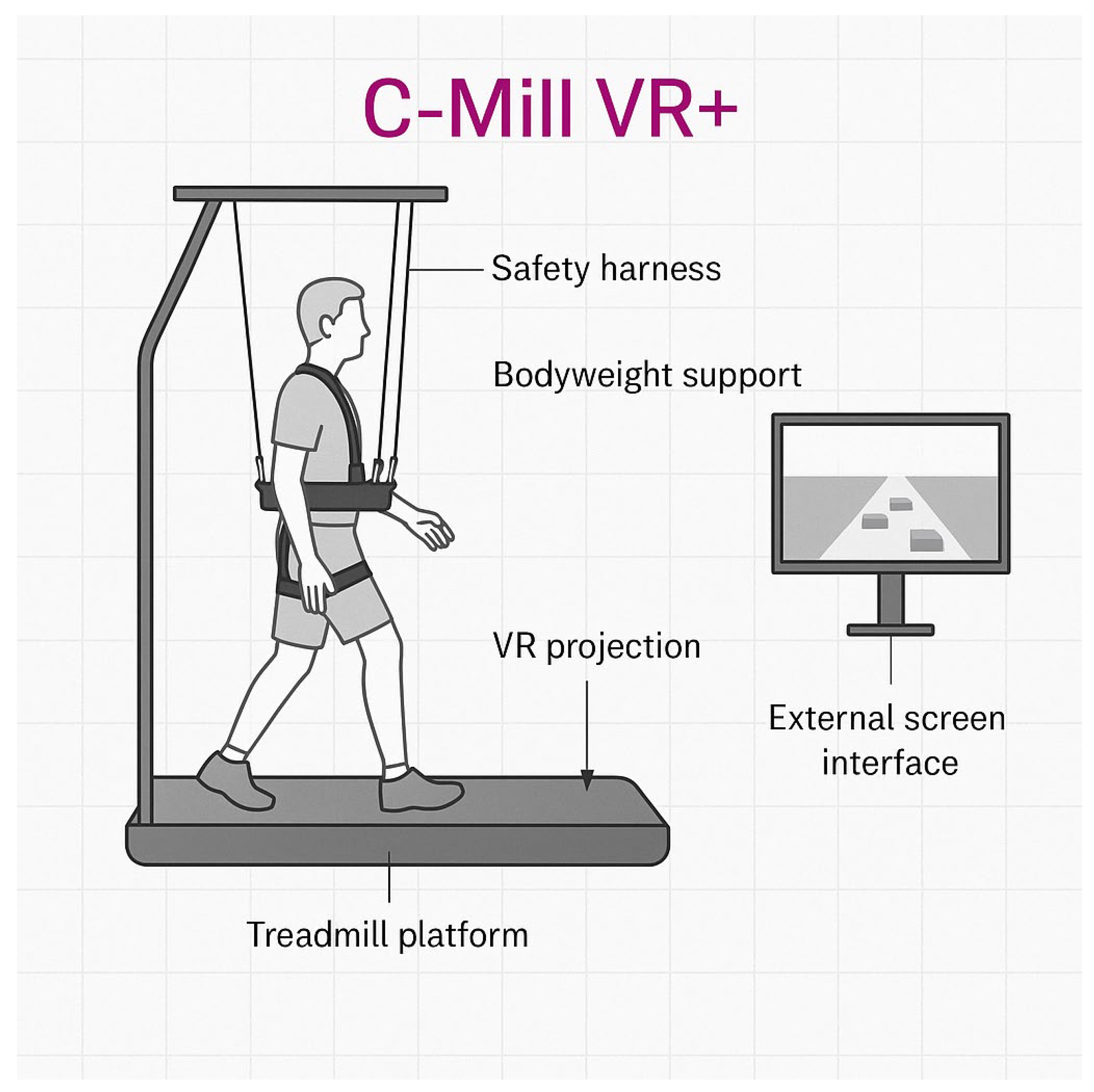
The robotic therapy intervention utilized the C-Mill VR+ system, a treadmill-based rehabilitation platform developed by Motek (a division of Hocoma AG, Volketswil, Switzerland). It combines gait training with augmented and virtual reality (VR) to improve mobility, postural control, and gait adaptability in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. The system simulates real-life walking conditions through VR projections and provides real-time feedback, adjustable task complexity, and a bodyweight support structure with a fall safety harness. The main components of the setup are illustrated in
Figure 2, including the treadmill with an embedded VR projection interface, safety harness, bodyweight support, and an external screen for therapist feedback.
Visual cues projected onto the treadmill challenge participants to adapt their gait, step length, and weight distribution in response to dynamic stimuli. This setup is particularly beneficial for addressing freezing of gait (FOG), postural instability, and step asymmetry. Spatial–temporal gait parameters, such as step length, step width, and stance phase durations, were assessed during treadmill walking. These are visualized in
Figure 3, which illustrates stance phases and step characteristics for both the left and right limbs, including dual- and single-stance durations.
Training modules included step adjustments, targeted foot placement, and dual-tasking exercises to enhance cognitive–motor integration.
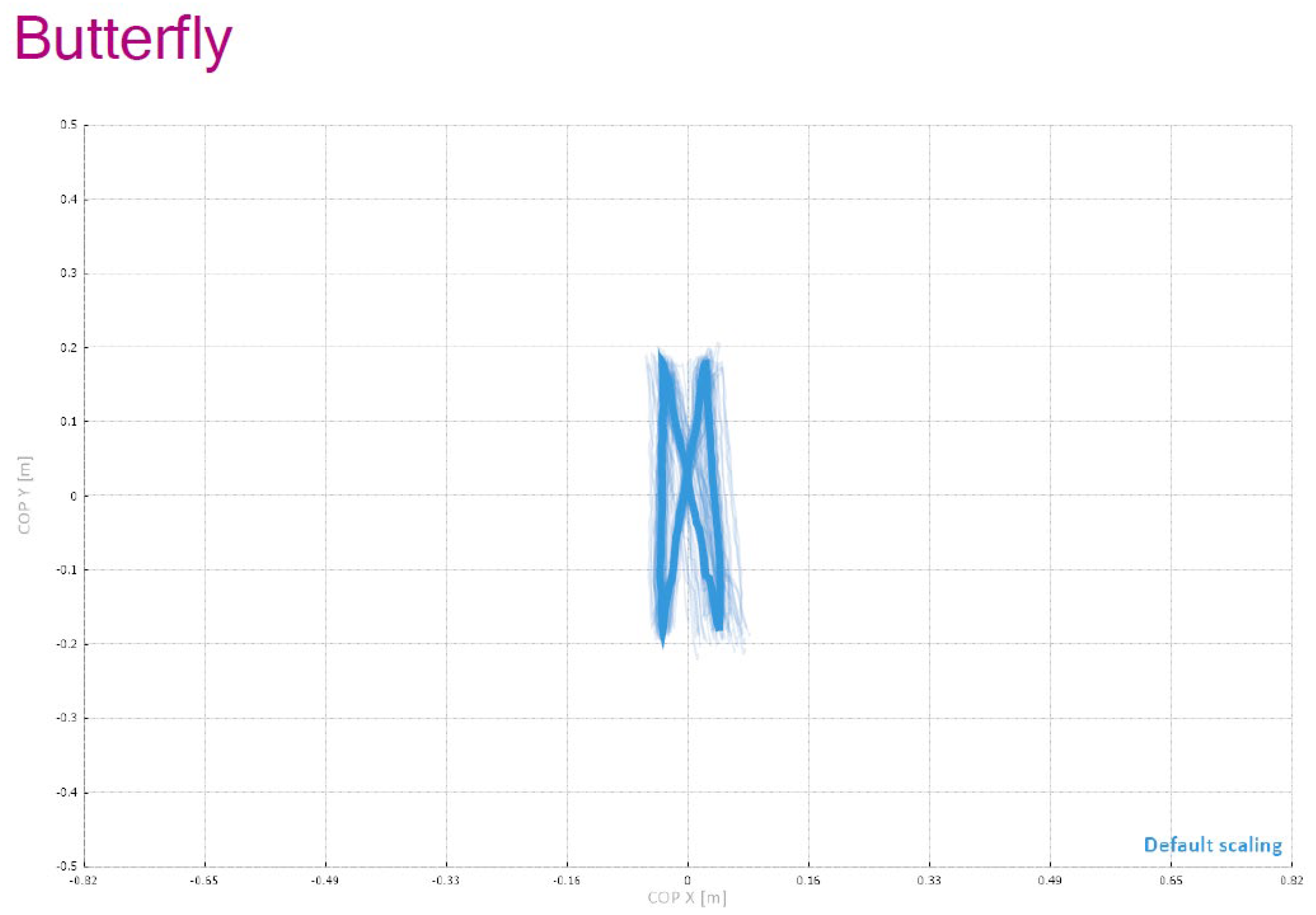
Figure 4 provides a schematic overview of the entire C-Mill VR+ system setup used in this study, including the “Butterfly” visual element, which functions as a symmetrical stepping guide designed to improve balance and spatial coordination by encouraging patients to perform controlled weight shifting and precise foot placement during gait training.
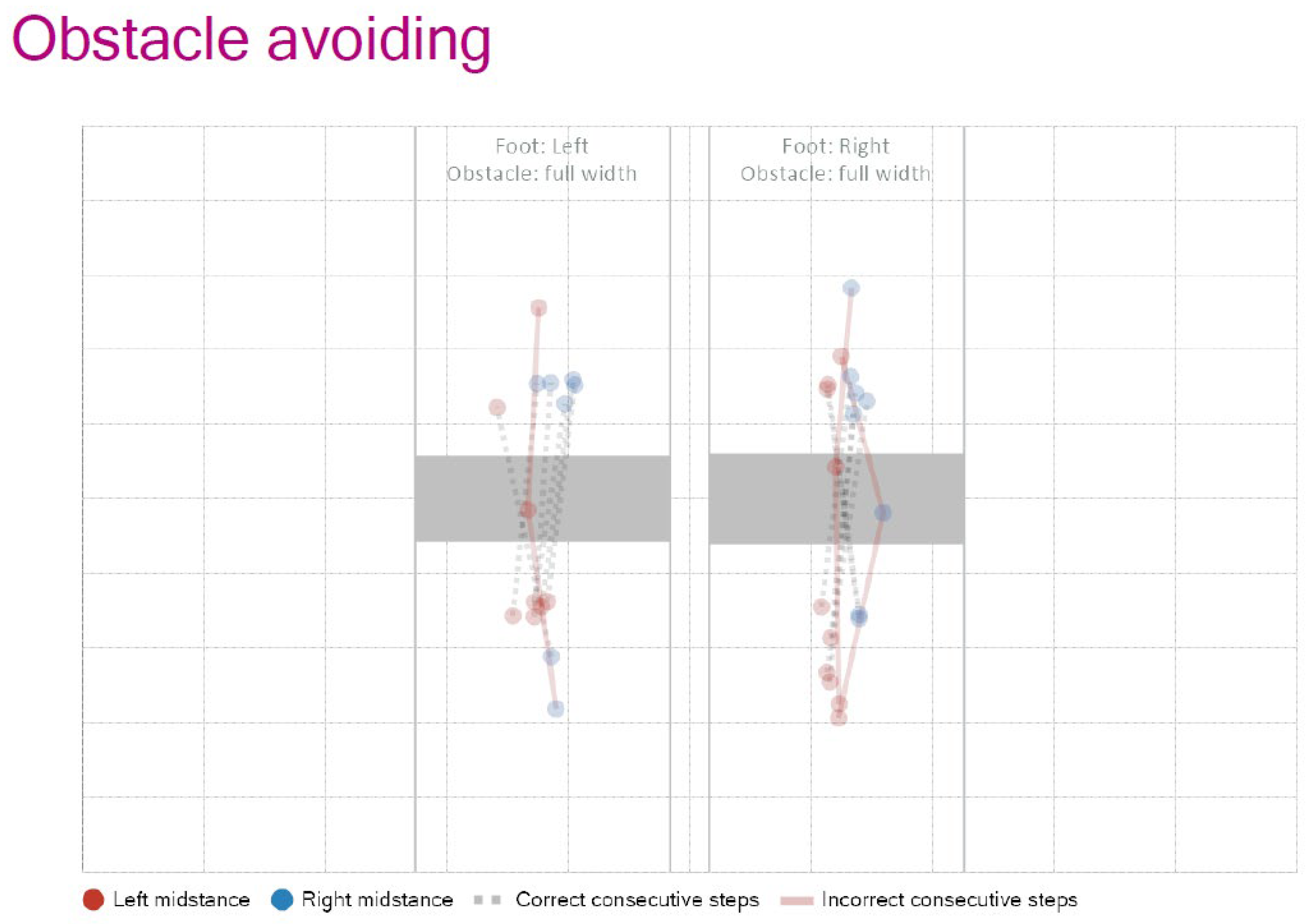
To evaluate more complex motor adaptation, obstacle avoidance tasks were also integrated.
Figure 5 shows representative trajectories of foot placement in response to full-width obstacles, indicating correct and incorrect step patterns for both limbs. To further challenge participants, the “Random Stepping Stones” task was used, in which the stepping targets appeared unpredictably. Performance metrics from this task—such as step frequency, hit/miss ratio, and obstacle avoidance success rate—are summarized in
Figure 6, alongside subjective feedback on task difficulty and the use of handrails.
Throughout all sessions, physiological and biomechanical parameters—such as step variability, stride length, cadence, and center of pressure (COP) displacement—were continuously recorded. Task complexity was progressively increased by modifying obstacle frequency, step targets, and walking speed, ensuring adaptation to individual capabilities. The built-in safety system allowed for high-intensity training in a secure environment. This multimodal approach was designed to stimulate motor learning, improve postural control, and reduce FOG events in people with Parkinson’s disease.
3.4. Agility Training
The agility training protocol was designed to enhance gait mechanics, coordination, balance, postural control, and muscular strength through a structured series of progressive exercises. These exercises were performed both with and without specialized equipment, including Dynair cushions, Bosu balls, fitballs, Pilates balls, weighted balls, end-weighted sticks, TRX systems, coordination ladders, and barriers. To promote adaptability and neuromuscular control, the training regimen incorporated systematic variations in surface stability, movement direction, execution speed, and task complexity, including height-based challenges [
44,
45]. The level of difficulty was continuously adjusted based on individual progress, ensuring a progressively tailored training experience. The intervention required participants to engage in high-level attentional control, executive functioning, and rapid cognitive processing in response to multimodal sensory inputs, including visual and auditory stimuli. The agility training was performed under the supervision of a certified physical therapist to ensure safety and correct execution. Exercises demanded dynamic balance shifts, rapid changes in movement direction, and complex coordination under varying stability conditions. Participants trained with a diverse set of specialized equipment, such as Dynair air cushions, BOSU balls, fitballs and Pilates balls, weighted balls ranging from 1 to 3 kg, end-weighted sticks, TRX suspension systems, coordination ladders, and small hurdles measuring 20 to 30 cm in height. A schematic diagram of a typical agility training station is included to provide visual context regarding the setup and exercise variety used in the program. The training introduced unpredictable sensory conditions to enhance neuromuscular adaptability, requiring participants to perform movements on surfaces of varying firmness, manipulate objects of different weights, adjust movement velocity, and respond to external cues either reflexively or deliberately [
46]. The intensity of the training was modulated through systematic adjustments in movement speed, accuracy, task complexity, and physical exertion, optimizing motor learning while maintaining safety. By integrating these dynamic components, the agility training aimed to improve functional mobility, enhance postural stability, and facilitate motor adaptability, thereby contributing to overall neuromuscular rehabilitation in individuals with Parkinson’s disease [
47,
48,
49]. Dual-tasking elements were incorporated to improve executive function, attentional control, and sensorimotor integration, crucial for balance and gait adaptability.
4. Results
To evaluate the effects of high-intensity training on patients with Parkinson’s disease, all statistical analyses were conducted using R software (R 4.5.0) and SPSS software (30.0.0). The study population was divided into four intervention groups, each receiving a specific type of training: Exergame, Cycling, Agility, and Robot (Cmill). These interventions aimed to assess improvements in motor function, balance, postural stability, and overall quality of life. A comprehensive statistical approach was applied, utilizing various analytical methods. T-tests were used to compare pre- and post-intervention outcomes within each group. Cohen’s effect size was used to determine the magnitude of observed differences. One-way ANOVA was used to evaluate differences between intervention groups. Tukey-HSD post-hoc tests were used for pairwise group comparisons. The Shapiro–Wilk normality test was used to assess data distribution. The Wilcoxon test for non-parametric comparisons where normality assumptions were violated. Correlation analysis was used to explore associations between disease severity, functional scores, and quality of life indicators. Borg Scale Analysis was used to measure perceived exertion during training interventions. This structured data analysis approach provided robust insights into the therapeutic efficacy of each intervention, allowing for a detailed evaluation of their impact on functional performance and quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease. To enhance the interpretability of results, 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated and reported for all key outcomes, including gait speed, balance (Berg), functional independence (FIM), posturography sway metrics, and perceived exertion (Borg RPE scores).
4.1. Baseline Characteristics
A total of 100 individuals diagnosed with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (PD) were selected for this study based on predefined inclusion criteria. Participants were randomly allocated in a 1:1:1:1 ratio into four intervention groups: Exergame (female, n = 12; male, n = 13), Cycling (female, n = 11; male, n = 14), Agility (female, n = 12; male, n = 13), and Robot (Cmill) (female, n = 11; male, n = 14). The mean disease duration was comparable across all groups, averaging 7.2 years (±1.5). The physical characteristics of participants, including age, height, weight, Hoehn and Yahr stage, and MMSE scores, are summarized in
Table 1, where detailed group distributions are also provided. Statistical analysis revealed no significant differences between the four groups regarding these variables (all
p > 0.05), ensuring a balanced allocation. During the intervention period, Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) values were recorded across all therapy sessions. The mean RPE scores for each group were as follows: Exergame (14.9 ± 0.5), Cycling (14.6 ± 0.4), Agility (14.7 ± 0.6), and Robot (Cmill) (14.2 ± 0.5). There were no statistically significant differences in perceived exertion levels between the four groups (
p > 0.05), indicating a consistent training intensity across intervention types. When evaluating functional assessments, significant baseline differences were detected between groups in the 10-Meter Walk Test (F = 3.42,
p = 0.047) and COP WEC Sway (F = 9.87,
p < 0.001). No other initial outcome measures, including the Berg Balance Scale, Dynamic Gait Index, or Functional Independence Measure, demonstrated statistically significant between-group differences before the intervention.
4.2. Functional and Motor Performance Assessments
The evaluation of functional and motor performance revealed significant improvements across different therapy groups (
p < 0.001). The 10 m walk test results demonstrated notable differences in maximal walking speed (
p < 0.001). The greatest improvements were observed in the Exergame and Cycling groups. In the first trial, the mean speed ranged from 0.67 m/s to 0.93 m/s, while in the second trial, it increased significantly, reaching a range of 1.12 m/s to 1.32 m/s (
p < 0.001), indicating improved gait efficiency post-intervention. Functional independence, measured using the Functional Independence Measure (FIM), also showed significant improvement (
p < 0.001). The total FIM score increased across all therapy groups, with motor-related FIM scores rising from 39–49 (baseline) to 67–78 (post-intervention), demonstrating improved motor function. The Falls Efficacy Scale revealed a significant decline in fall-related fear post-intervention (
p < 0.001), with scores improving from 74–89 (baseline) to 48–56 (post-intervention), reflecting increased confidence in balance and mobility. The Berg Balance Scale (BBS) exhibited substantial progress, particularly in the Exergame and Cycling groups (
p < 0.0001), with scores increasing from 23–26 to 36–38 post-intervention. A comprehensive summary of all pre- and post-intervention results, including functional and motor outcome measures across the four groups, is provided in
Table 2.
4.3. Posturography and Balance Assessments
The posturography results provided further insights into postural stability across different therapy groups. Statistical analysis revealed significant group differences in COP sway parameters (
p < 0.05). The mean sway area measured in a single step was 14.94 cm
2 (SD = 4.20), while in four steps, this value significantly increased to 33.31 cm
2 (SD = 12.51), highlighting the progressive complexity of weight transfer. The center of pressure (COP) deviation was notably lower in the Exergame and Cycling groups, suggesting enhanced postural control, whereas the Robot (Cmill) group exhibited the highest instability. Statistical analysis revealed significant group differences in COP sway parameters. The Sway (mm) COP-WEO 1 parameter indicated that the Robot (Cmill) group (M = 13.44 mm, SD = 4.86) had significantly greater balance fluctuations than the Exergame (M = 10.88 mm, SD = 4.18) and Agility (M = 10.52 mm, SD = 5.91) groups (
p < 0.05). Similarly, the Sway (mm) COP-WEC 1 parameter demonstrated significantly worse balance in the Robot (Cmill) group (M = 12.05 mm, SD = 3.53) compared to the Cycling group (M = 9.98 mm, SD = 3.12) (
p < 0.05). The Sway (mm) COP-NEC 1 parameter showed that the Robot (Cmill) group (M = 15.86 mm, SD = 8.07) performed significantly worse than the Exergame and Cycling groups (
p < 0.01). A Shapiro–Wilk test was conducted to assess the normality of various variables, revealing significant deviations from normality (
p < 0.05) in the Sway (mm) COP-WEO 2 group (
p < 0.01), Sway (mm) COP-WEC 2 and NEC 2 groups (
p < 0.05), as well as Velocity (cm/s) 1 steps1 and 2 steps1 variables (
p < 0.05). The detailed numerical values for group-level sway parameters (WEO, WEC, NEC) and perceived exertion (Borg RPE scores) are summarized in
Table 3. The posturography outcomes presented in
Table 3 include only COP Sway (mm) measures. COP Velocity and COP Area metrics were not analyzed in this study.
4.4. Heart Rate and Borg Scale Analysis
The assessment of perceived exertion using the Borg Scale revealed moderate to high exertion levels across therapy groups. The mean Borg RPE scores ranged from 14 to 18, indicating moderate- to high-intensity physical demand. ANOVA results demonstrated significant differences between groups, particularly in Borg1 (F = 8.66, p < 0.0001) and Borg20 (F = 4.01, p = 0.0098). The Tukey-HSD test further confirmed that Group 4 experienced significantly higher exertion compared to Groups 2 and 3 (p < 0.0001). Heart rate monitoring showed notable variations across therapy groups. The average heart rate (HR) during exercise ranged between 85.32 bpm and 88.32 bpm, with peak HR values exceeding 100 bpm in some cases. These findings suggest that therapy intensity effectively engaged participants in cardiovascular exertion.
4.5. Group Comparisons and Statistical Significance
A one-way ANOVA analysis revealed significant differences in balance control, velocity, and sway area across therapy groups (p < 0.05). Specifically, the Sway (mm) COP-WEO 2 parameter demonstrated notable variations among the groups (F = 3.585, p = 0.0166), indicating substantial differences in balance stability. Similarly, the Sway (mm) COP-NEO 2 parameter showed significant disparities in therapy effects, with F = 12.484, p < 0.001, confirming that different interventions had varying impacts on postural control. The Sway (mm) COP-NEC 2 parameter also exhibited significant differences (F = 5.219, p = 0.0022), highlighting that postural instability was more pronounced in certain therapy groups. Further analysis revealed significant velocity variations across groups, particularly in the 2 steps1, 2 steps2, and 2 steps3 conditions (p < 0.05), suggesting differential therapy effects on movement speed. Additionally, area measurements for 2 steps1 and 2 steps3 showed significant differences (F = 3.767, p = 0.0132 and F = 5.905, p = 0.00097, respectively), indicating distinct patterns of postural adjustments across therapies. A Tukey-HSD post-hoc test was performed to identify pairwise differences among therapy groups. Results demonstrated a significant difference in Sway (mm) COP-WEO 2 between Agility and Exergame therapies (p = 0.0156). Additionally, Sway (mm) COP-NEO 2 showed a substantial disparity, with Cycling therapy exhibiting considerably different outcomes compared to the other groups (p < 0.0001). In terms of movement velocity, the Agility group differed significantly from the Cycling group in 2 steps1 velocity (p = 0.0153). Postural sway area analysis in 2 steps3 revealed that Cycling therapy led to significantly distinct results compared to the other groups (p = 0.0023–0.0148). A paired t-test further confirmed substantial within-group improvements following therapy interventions. Specifically, Sway (mm) COP-WEO 1 vs. WEO 2 revealed a strong improvement in balance control (p < 0.001). Velocity measures also improved significantly, with 1 steps1 vs. 2 steps1 showing a highly significant increase in movement speed (p < 0.001). Additionally, Area (cm2) 1 steps4 vs. 2 steps4 demonstrated a marked reduction in sway area (p < 0.001), suggesting enhanced postural stability following the interventions.
4.6. Functional Outcomes and Quality of Life Measures
The impact of different therapy modalities on functional outcomes and quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease was assessed using standardized evaluation measures. Significant improvements were observed across all therapy groups in the UPDRS (Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale), with
p < 0.0001, indicating that the interventions effectively enhanced motor function and daily life activities. The Berg Balance Scale analysis demonstrated notable improvements in balance control, particularly in the Agility and Robot therapy groups, which exhibited the largest effect sizes (
p < 0.0001). Furthermore, the Schwab and England Independence Scale results showed significant differences in functional independence levels across therapy groups (
p = 0.0045), highlighting the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs in maintaining autonomy in daily activities. In addition to motor function and independence, the psychological and emotional well-being of participants improved significantly post-intervention. The Beck Depression Inventory revealed substantial reductions in depression scores (
p < 0.001), indicating that engaging in high-intensity exercise programs had a positive impact on mental health. Similarly, the PDQ-39 Emotional Well-Being domain analysis confirmed significant improvements in mood and emotional stability (
p = 0.0005), further supporting the benefits of therapy in enhancing the overall quality of life. To determine the clinical relevance of observed improvements, we compared the average pre–post changes with established Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) and Minimum Detectable Change (MDC) values for key outcomes: A gait speed improvement of ≥0.10 m/s is considered clinically meaningful in patients with PD; our study found gains of 0.40–0.54 m/s across all groups, exceeding this threshold. The Functional Independence Measure (FIM) showed an average increase of 25–30 points, well above the 22-point MCID commonly cited for PD populations. Improvements on the Berg Balance Scale (BBS) exceeded the 5-point MDC threshold in all groups, indicating real functional gains. The Tinetti Assessment Tool scores improved beyond the 3–4 point MDC range, supporting the clinical validity of balance changes. On the Falls Efficacy Scale, a change of ≥11 points is considered clinically meaningful; our data showed changes of 16–23 points. These findings confirm that the statistical significance observed throughout the analysis is supported by meaningful, clinically relevant improvements in functional performance and patient safety indicators. See
Table 4 for a detailed summary of the MCID/MDC thresholds and the observed clinical improvements across groups.
4.7. Correlations and Borg Scale Analysis
Correlation tests were conducted to examine the relationships between key clinical variables. Pearson and Spearman correlation analyses revealed that age and Hoehn–Yahr disease stage were not significantly correlated, suggesting that disease severity progression was not directly linked to age-related factors. However, a notable correlation was identified between UPDRS-MEDL2 scores and disease duration in Group 3 (r = 0.3880, p = 0.055), indicating a potential trend in symptom progression over time. Additionally, heart rate regulation was significantly correlated with Parkinson’s symptoms (r = 0.323, p = 0.001), suggesting a connection between autonomic function and disease manifestations. The Borg Scale was used to assess perceived exertion across therapy groups. The mean Borg RPE scores ranged between 14.99 and 15.09, reflecting moderate exertion levels during therapy sessions. ANOVA results for the Borg Scale revealed significant differences between groups, particularly in Borg1 (F = 8.66, p < 0.0001) and Borg20 (F = 4.01, p = 0.0098), suggesting that different therapy modalities induced varying degrees of exertion. A Tukey-HSD test further confirmed that Group 4 exhibited significantly higher exertion levels compared to Groups 2 and 3 (p < 0.0001), indicating that certain interventions required greater physical effort.
4.8. Sociodemographic and Clinical Characteristics
A total of 100 patients with PD were enrolled and randomly assigned to one of four intervention groups: Exergame (n = 25), Cycling (n = 25), Agility Training (n = 25), and Robot-Assisted Training (Cmill) (n = 25). The gender distribution was balanced, with 37 males and 37 females. Participants’ disease severity ranged from Hoehn and Yahr stages 2–4, ensuring representation of individuals with moderate PD progression. Baseline assessments confirmed homogeneity across clinical and functional characteristics among groups.
5. Discussion
This study provides compelling evidence for the effectiveness of high-intensity exercise therapies in improving multiple clinical domains in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). These findings address both primary outcomes—motor function, postural stability, and quality of life—as well as secondary outcomes, such as balance metrics, gait parameters, cardiovascular response, and perceived exertion. In this revised discussion, we aim to interpret our findings with greater emphasis on the clinical implications and internal consistency of our dataset, rather than reiterating previous studies. We specifically focus on why certain interventions—particularly Exergame and Cycling—demonstrated superior improvements compared to Robot-assisted therapy. Potential mechanisms include greater task specificity, higher engagement levels, and real-time feedback provided by immersive VR. These factors may have contributed to enhanced motor learning, motivation, and adherence. Our findings suggest that personalized rehabilitation strategies tailored to patient responsiveness and motivation may yield better functional outcomes in Parkinson’s disease.
5.1. Motor Function and Functional Independence (Primary Outcome)
A key finding of this study was the significant enhancement in motor performance across all high-intensity therapy groups. This supports the primary outcome related to motor function, as defined in
Section 2.2. Exergame and Cycling therapies, in particular, yielded substantial improvements in walking speed (10 MWT), endurance (6 MWT), and Functional Independence Measure (FIM) scores. These improvements reflect more efficient neuromuscular coordination, higher gait adaptability, and greater independence in daily activities. These results confirm prior findings that high-intensity, movement-based interventions can facilitate motor learning and plasticity in patients with PD, thereby enhancing overall functional mobility [
16]. Agility therapy also demonstrated notable gains in movement control and coordination, affirming its relevance as a viable high-intensity strategy. Conversely, Robot-assisted (Cmill) training showed limited improvements in motor function, likely due to the constrained movement environment and reduced active engagement. These improvements were not only statistically significant but also exceeded established thresholds for clinical relevance. Specifically, gait speed improvements of ≥0.10 m/s are generally considered clinically meaningful in patients with PD, and our data showed average increases of ~0.30–0.50 m/s. Furthermore, improvements in FIM scores of ≥22 points are indicative of clinically significant functional gains, with our intervention groups improving by ~25–30 points on average. In addition, the changes observed in balance-related outcomes (e.g., Berg Balance Scale, Tinetti) exceeded the Minimum Detectable Change (MDC) values for individuals with PD. By distinguishing between statistical and clinical significance, our findings support the real-world impact of high-intensity rehabilitation on mobility and independence in Parkinson’s disease.
5.2. Postural Control and Balance (Primary and Secondary Outcomes)
Posturography assessments and clinical balance scales revealed significant changes, particularly in the Exergame and Cycling groups. These changes validate the primary outcome of postural stability, as well as secondary balance-related endpoints. Improvements in the Berg Balance Scale (BBS), Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), and BESTest scores confirmed enhanced dynamic equilibrium and reduced sway during tasks. COP sway parameters further supported these clinical findings by revealing improved balance control and decreased postural deviation in the Exergame and Cycling groups compared to Robot therapy. These results underscore the importance of dynamic, externally responsive movement environments in promoting neuromuscular adaptability in PD.
5.3. Gait Efficiency and Dual-Task Performance (Secondary Outcome)
The study also addressed secondary gait-related outcomes, such as step variability, targeted foot placement, and dual-task execution. These parameters improved markedly in the Exergame and Agility groups, suggesting that cognitive-motor integration tasks—particularly those involving rapid visual feedback—are effective in mitigating gait instability and freezing episodes. The Exergame group, which combined audiovisual cues with obstacle negotiation, outperformed others in both gait precision and adaptability, indicating a strong link between cognitive load and motor correction in PD rehabilitation.
5.4. Cardiovascular Responses and Perceived Exertion (Secondary Outcome)
A major secondary outcome of this study involved cardiovascular exertion and physiological response. Borg RPE scores between 14 and 18 across all groups confirmed moderate-to-high intensity levels. Heart rate monitoring revealed significant inter-group variability, with the Cycling and Robot groups reaching the highest exertion levels. These cardiovascular adaptations are important not only for physical endurance but also for autonomic regulation—a domain often affected in Parkinson’s disease. The observed heart rate regulation patterns suggest a potential link between therapy intensity and autonomic improvement, warranting further investigation. These findings align with previous reports indicating that structured aerobic exertion can improve cardiorespiratory capacity and possibly modulate neurovegetative symptoms in PD [
44,
50].
5.5. Quality of Life and Emotional Well-Being (Primary Outcome)
Consistent with the third primary outcome, significant improvements were observed in quality of life indicators. The PDQ-39 Emotional Well-being subscale and Beck Depression Inventory revealed reductions in depressive symptoms and improved emotional regulation, particularly in the Exergame and Cycling groups. These changes likely reflect increased autonomy and confidence, as also indicated by the decline in fall-related fear (Falls Efficacy Scale) [
51]. EQ-5D scores further supported gains in self-reported health status. These findings emphasize that high-intensity rehabilitation has not only motor but also psychological and emotional benefits, which are critical for long-term adherence and quality of life [
44].
5.6. Statistical Validation and Individualized Responses
The robustness of these findings is supported by comprehensive statistical analyses. ANOVA and Tukey-HSD tests revealed significant between-group differences, while paired t-tests and Wilcoxon analyses confirmed consistent within-group improvements across primary and secondary outcomes. Shapiro-Wilk tests highlighted inter-individual variability, suggesting the need for personalized rehabilitation protocols. Correlation analyses also revealed that therapy responsiveness was more closely related to individual adaptability than to age or disease duration, reinforcing the value of tailored approaches.
5.7. Implications and Future Directions
This study strongly supports integrating high-intensity, task-oriented therapies into rehabilitation protocols for PD. The observed outcomes across motor, balance, cardiovascular, and psychosocial domains confirm the multi-dimensional efficacy of such interventions. However, further research is needed to address the following aspects. Durability of effects: The long-term sustainability of these improvements remains to be established through follow-up studies. Tailored protocols: Individual response variability calls for flexible therapy models based on patient characteristics. Combined strategies: Multimodal approaches (e.g., combining Exergame with Cycling) may amplify the benefits seen in isolated therapies. Mechanistic studies: Understanding the neurophysiological underpinnings of motor and psychological improvements will deepen clinical relevance.
6. Conclusions
This randomized controlled trial demonstrated that high-intensity exercise therapies significantly improve both primary (motor function, postural stability, and quality of life) and secondary outcomes (balance, gait parameters, cardiovascular response, and subjective exertion) in Parkinson’s disease rehabilitation. Among the modalities tested, Exergame and Cycling therapies showed the most comprehensive benefits, making them strong candidates for standard integration into clinical programs. The combination of dynamic balance challenges, cognitive–motor demands, and aerobic exertion led to substantial improvements in gait efficiency, postural control, and emotional resilience. The results also suggest that response to therapy is influenced more by individual adaptability and lifestyle than by demographic or disease duration factors. Given the demonstrated safety and efficacy, incorporating high-intensity, personalized training strategies into rehabilitation protocols for Parkinson’s disease is not only feasible but highly advisable. Future research should prioritize long-term outcomes, individualized treatment planning, and exploration of neuroplastic mechanisms to further enhance clinical practice. Beyond statistical significance, our findings demonstrated clinically meaningful improvements in key functional outcomes. Gait speed increased by 0.30–0.50 m/s on average, exceeding the 0.10 m/s threshold commonly accepted as clinically relevant in Parkinson’s disease. Similarly, Functional Independence Measure (FIM) scores improved by 25–30 points, surpassing the 22-point threshold for clinical impact. Balance outcomes such as the Berg Balance Scale and Tinetti Assessment Tool also exceeded established Minimum Detectable Change values. These findings support not only the statistical robustness but also the practical effectiveness of high-intensity, technology-enhanced rehabilitation for patients with PD.