Edible Films Based on Ovine Second Cheese Whey with Oregano Essential Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Films Preparation
- WPI: films only with whey protein isolate.
- WS 2:1: films of WPI–SCW mixture in a protein proportion of 2:1.
- WS 1:1: films of WPI–SCW mixture in a protein proportion of 1:1.
- WS 1:2: films of WPI–SCW mixture in a protein proportion 1:2.
- SCW: films only with ovine second cheese whey.
- WS 2:1O1: films of WPI–SCW mixture in protein proportion 2:1 with 1% EO.
- WS 1:1O1: films of WPI–SCW mixture in protein proportion 1:1 with 1% EO.
- WS 1:2O1: films of WPI–SCW mixture in protein proportion 1:2 with 1% EO.
- WS 2:1O2: films of WPI–SCW mixture in protein proportion 2:1 with 2% EO.
- WS 1:1O2: films of WPI–SCW mixture in protein proportion 1:1 with 2% EO.
- WS 1:2O2: films of WPI–SCW mixture in protein proportion 1:2 with 2% EO.
2.3. Film Thickness
2.4. Water Vapor Permeability
2.5. Dry Matter Content, Water Solubility and Density
2.6. Color and Opacity
2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.8. Antioxidant Activity
2.9. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
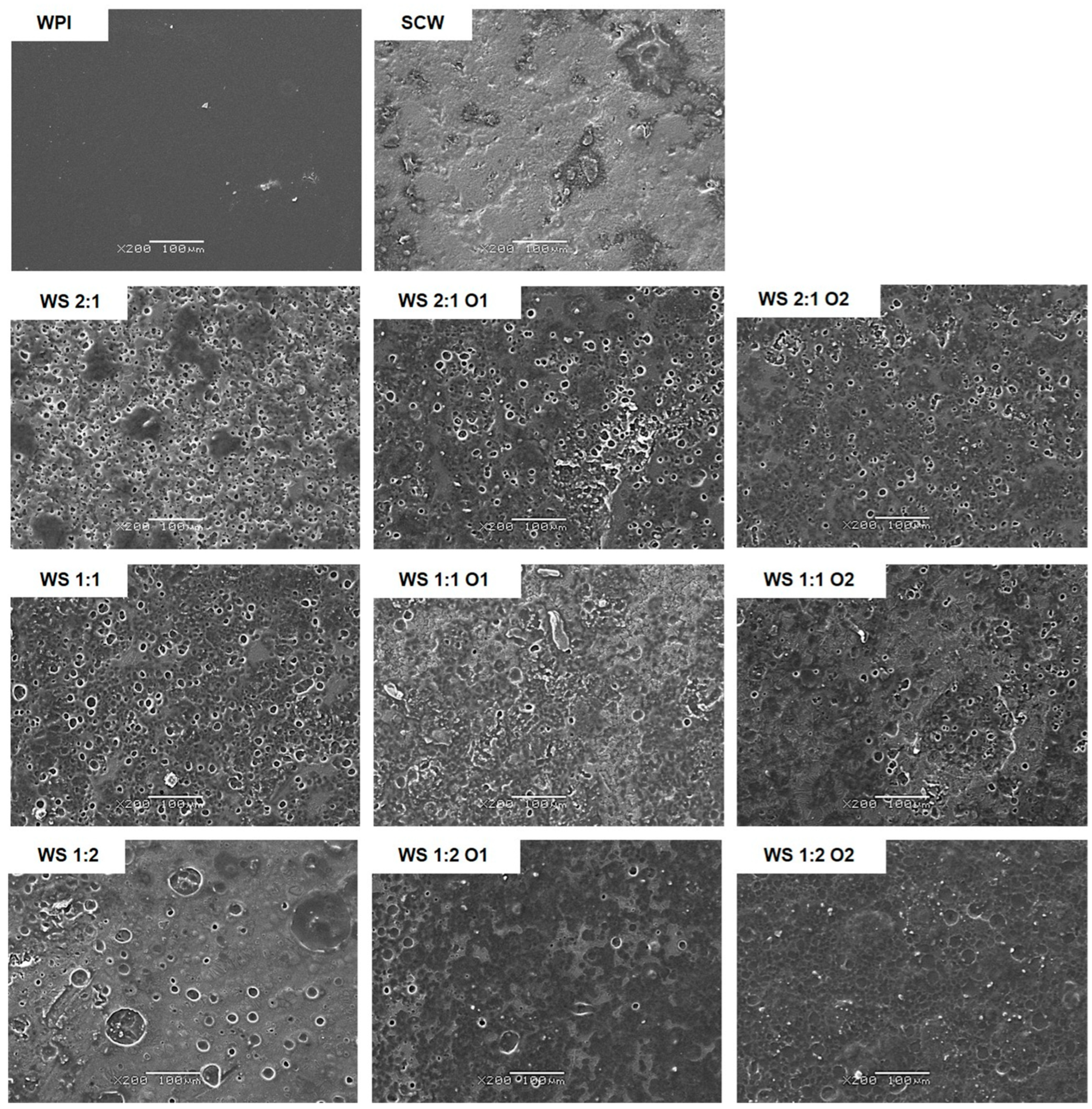
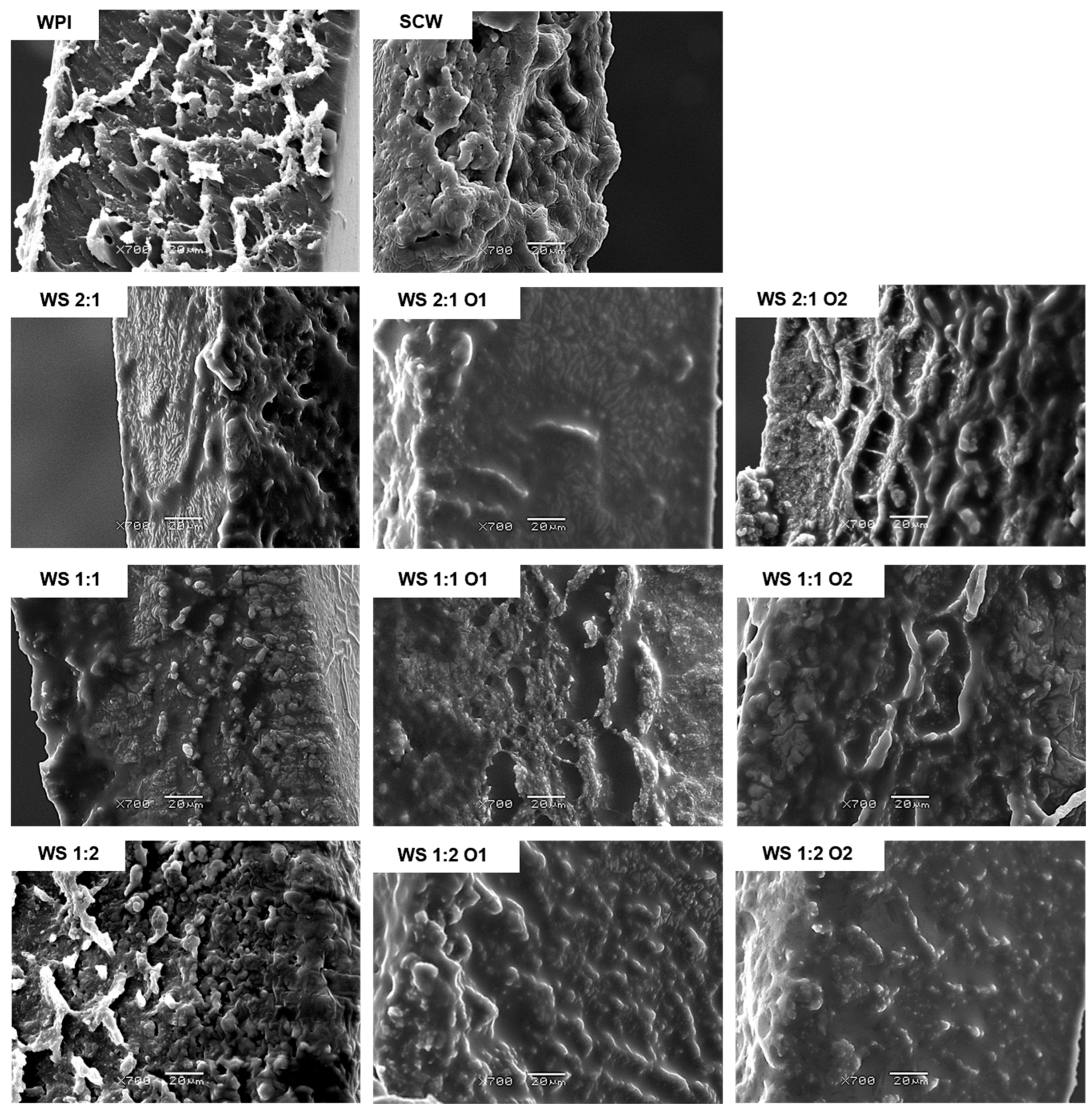
2.11. Microstructure Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
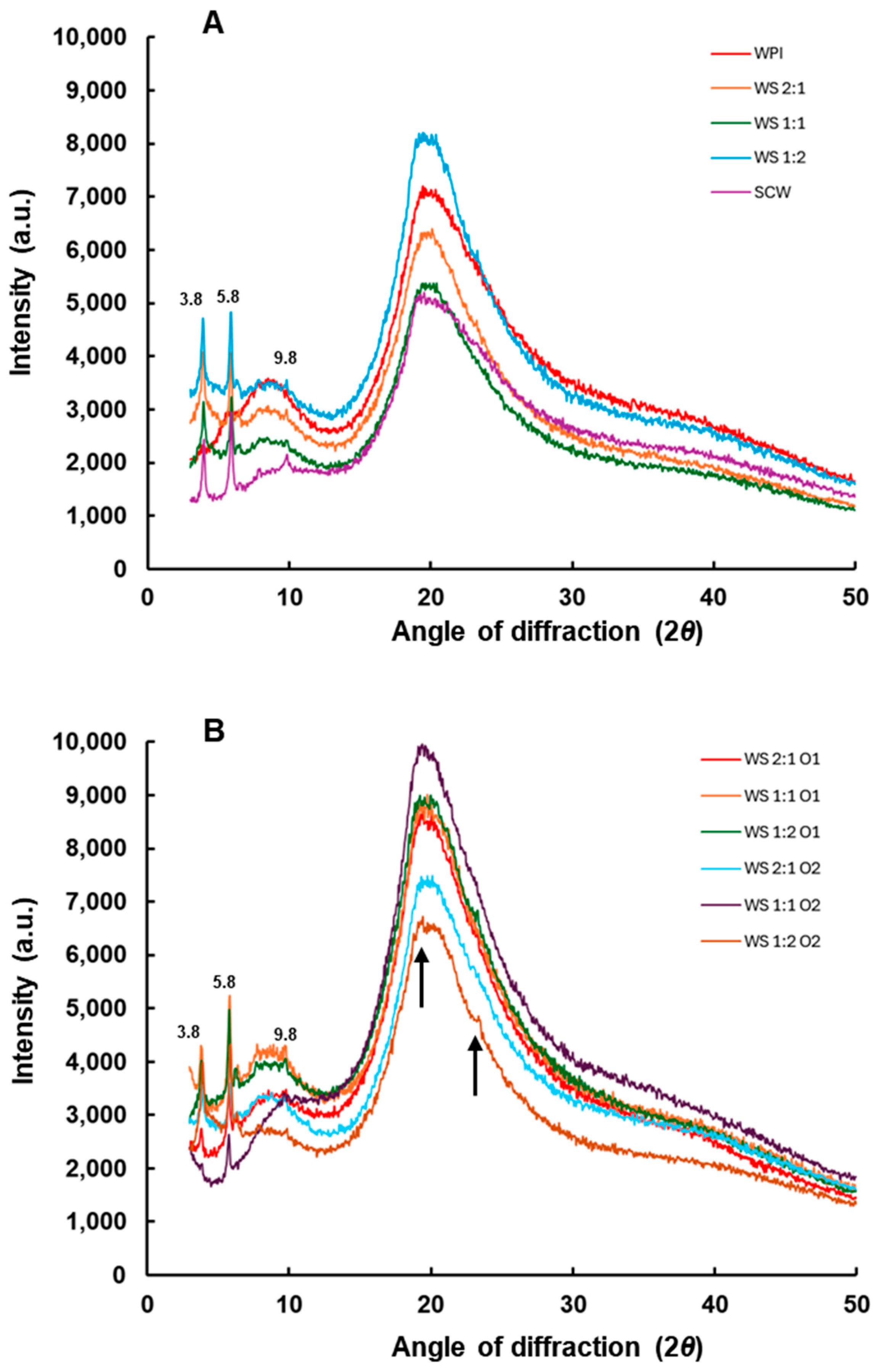
2.12. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Visual Appearance
3.2. Water Vapor Permeability, Thickness, Dry Matter Content, Solubility and Density
3.3. Color
3.4. Mechanical Properties
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
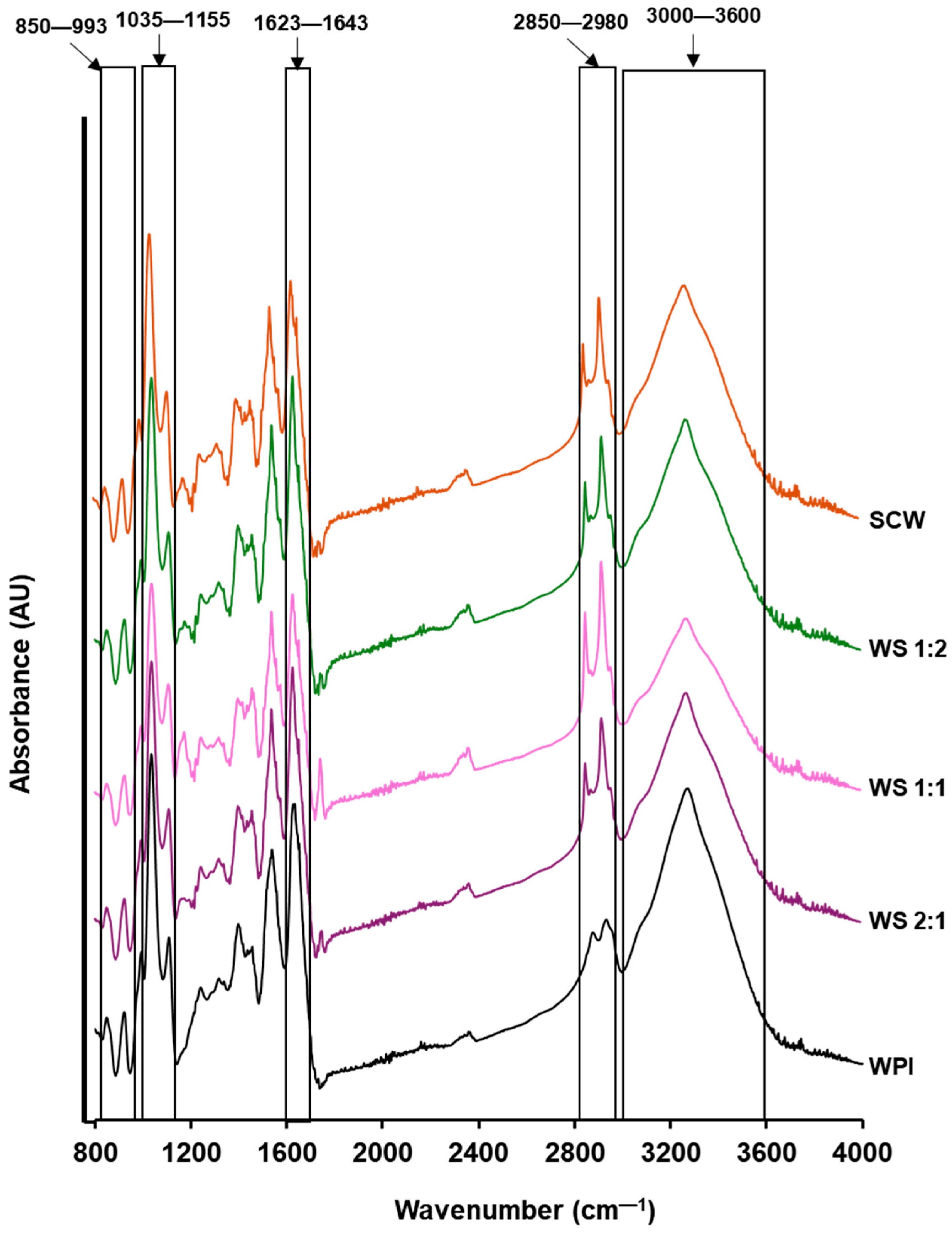
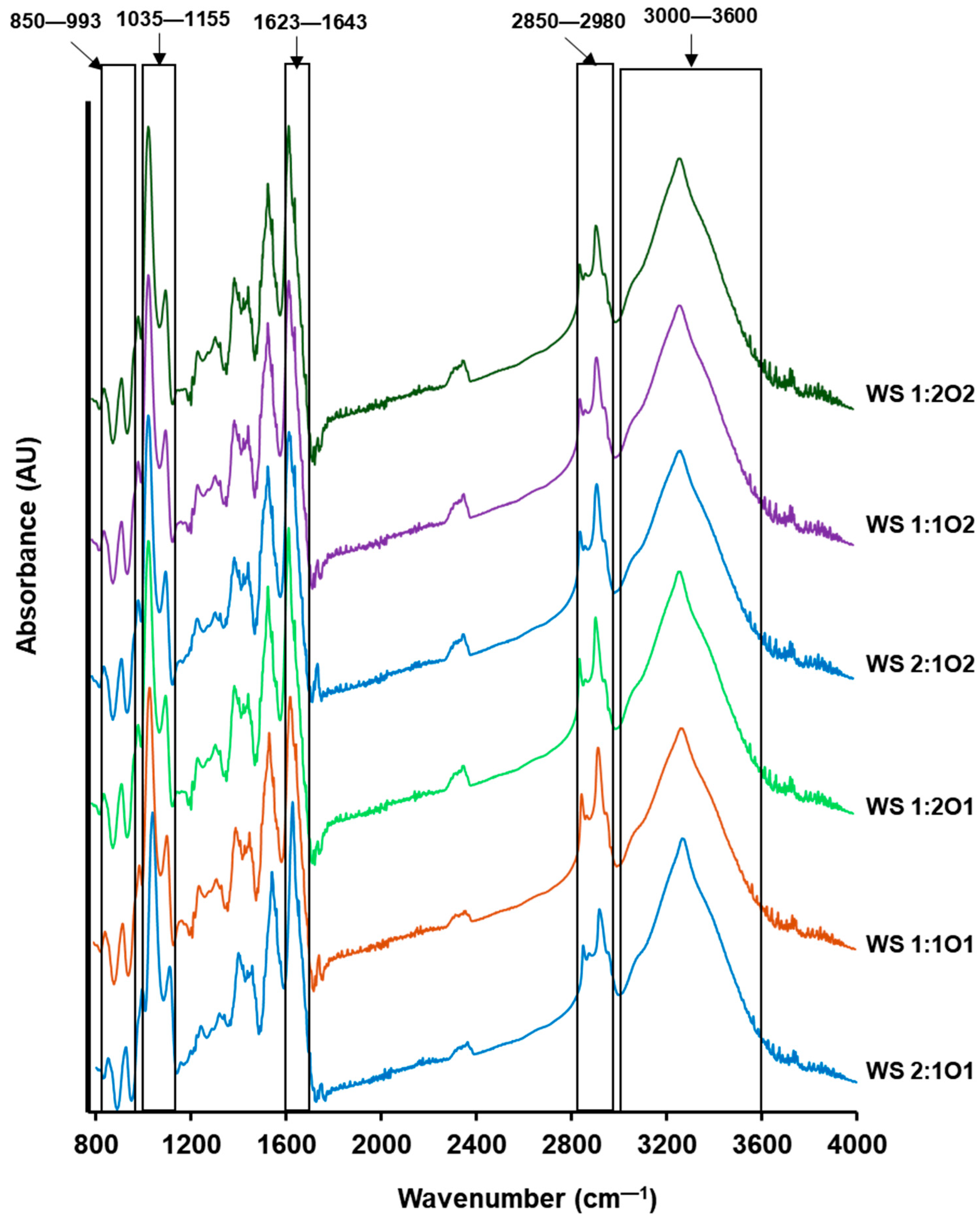
3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
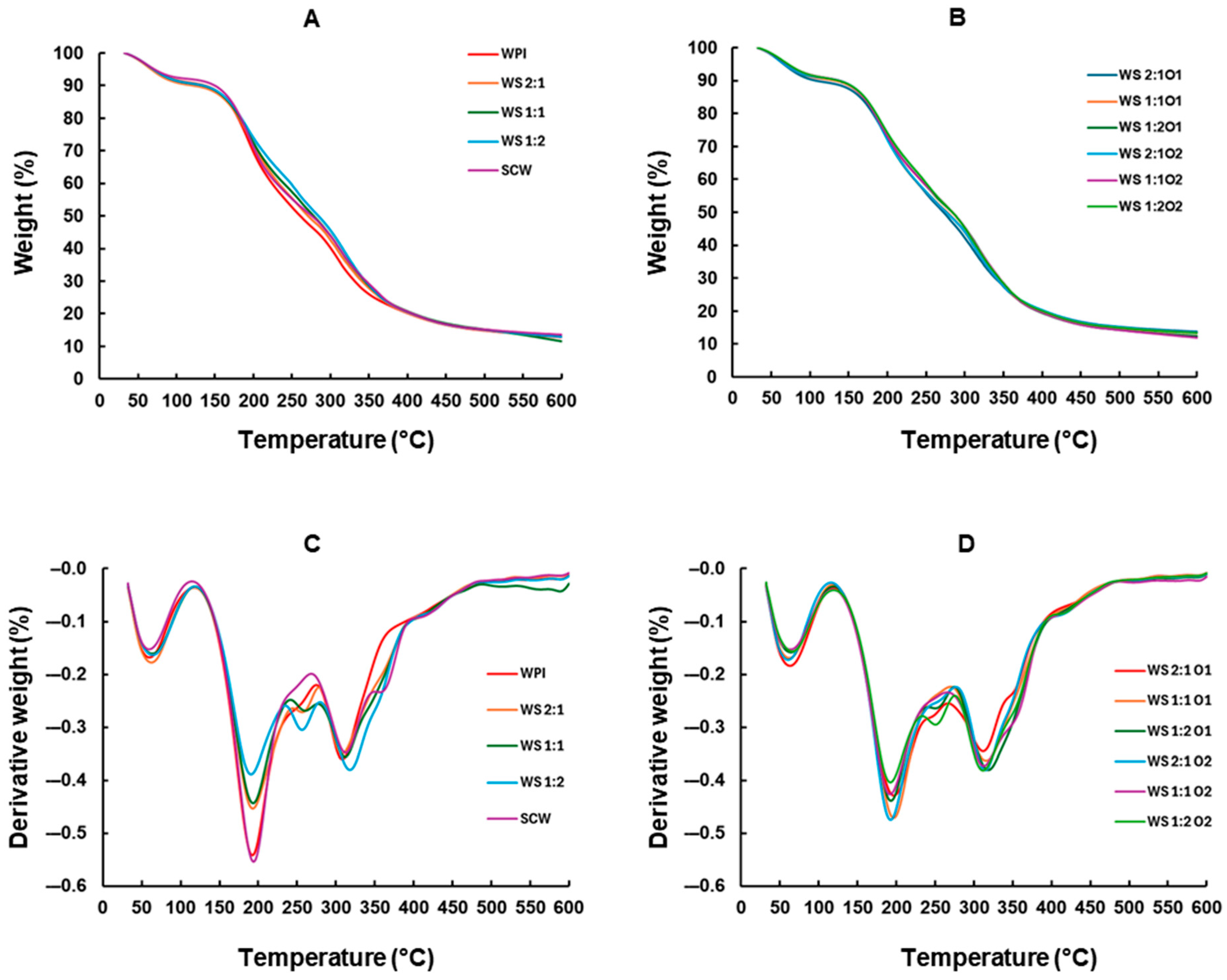
3.7. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.8. Microstructure
3.9. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCW | Second cheese whey |
| EO | Essential oil |
| WPI | Whey protein isolate |
| WVP | Water vapor permeability |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Nilsson, F.; Silva, N.; Schelin, J. Single-use versus reusable packaging for perishable liquid foods-Exploring evidence from research on climate impact and food safety. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 207, 107655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.F.; Díaz, O.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C.D. A review of recent developments in edible films and coatings-focus on whey-based materials. Foods 2024, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2025/40 of 19 December 2024 on Packaging and Packaging Waste, Amending Regulation (EU) 2019/1020 and Directive (EU) 2019/904, and Repealing Directive 94/62/EC. Official Journal of the European Union, 22nd January 2025. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2025/40/oj (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Gaspar, M.C.; Braga, M.E. Edible films and coatings based on agrifood residues: A new trend in the food packaging research. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 50, 101006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Bian, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, W. Application of protein-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Yoo, J.; Yun, J.; Kang, H.-B.; Seol, K.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Ham, J.-S. Application of whey protein-based edible films and coatings in food industries: An updated overview. Coatings 2021, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.; Furuta, M. Influence of γ-irradiation on mechanical and water barrier properties of corn protein-based films. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y. Wheat gluten–based coatings and films: Preparation, properties, and applications. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.F.; Marnotes, N.G.; Rubio, O.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Pereira, C.D. Dairy by-products: A review on the valorization of whey and second cheese whey. Foods 2021, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Arregi, M.; Cabezudo, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Whey protein films for sustainable food packaging: Effect of incorporated ascorbic acid and environmental assessment. Polymers 2023, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Whey protein edible films modified with almond and walnut oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, A.; D’ambrosio, S.; Cimini, D.; Falco, L.; D’Agostino, M.; Finamore, R.; Schiraldi, C. No waste from waste: Membrane-based fractionation of second cheese whey for potential nutraceutical and cosmeceutical applications, and as renewable substrate for fermentation processes development. Fermentation 2022, 8, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.; Pietruszka, H.; Bożek, A.; Szkolnicka, K.; Gomes, D.; Díaz, O.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C. Sheep’s Second Cheese Whey Edible Coatings with Oregano and Clary Sage Essential Oils Used as Sustainable Packaging Material in Cheese. Foods 2024, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seydim, A.C.; Sarikus-Tutal, G.; Sogut, E. Effect of whey protein edible films containing plant essential oils on microbial inactivation of sliced Kasar cheese. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydim, A.C.; Sarikus, G. Antimicrobial activity of whey protein based edible films incorporated with oregano, rosemary and garlic essential oils. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajimon, A.; Edakkadan, A.S.; Subhash, A.J.; Ramya, M. Incorporating oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) Essential oil onto whey protein concentrate based edible film towards sustainable active packaging. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 2408–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.P.L.F.; Bertan, L.C.; De Rensis, C.M.V.B.; Bilck, A.P.; Vianna, P.C.B. Whey protein-based films incorporated with oregano essential oil. Polímeros 2017, 27, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, H.; Özselek, Y.; Turan, O.Y.; Fıratlıgil, E.; Karbancioğlu-Güler, F. Whey protein isolate edible films incorporated with essential oils: Antimicrobial activity and barrier properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, Á.; Díaz, O. Impact of nanoclays addition on chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) flour film properties. Foods 2024, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. E 96-93—Standard test method for water vapor transmission of materials. In Annual Book of ASTM Standard; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993; pp. 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, E.; Emir, A.A.; Sumnu, G.; Kahyaoglu, L.N. Citric acid cross-linked curcumin/chitosan/chickpea flour film: An active packaging for chicken breast storage. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, L.; Niu, P.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y. Preparation and characterization of chitosan film incorporated with thinned young apple polyphenols as an active packaging material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, O.; Candia, D.; Cobos, A. Effects of ultraviolet radiation on properties of films from whey protein concentrate treated before or after film formation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, B.; Thakur, R.; Voung, Q.V.; Chockchaisawasdee, S.; Golding, J.B.; Scarlett, C.J.; Stathopoulos, C.E. Optimization of physical and optical properties of biodegradable edible films based on pea starch and guar gum. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 86, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Reyes, J.M.; Rodríguez-Quiroz, R.E.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J.P.; Rodríguez-Romero, B.A.; Flores-Breceda, H.; Napoles-Armenta, J.; Romero-Soto, I.C.; Galindo-Rodríguez, S.A.; Báez-González, J.G.; Treviño-Garza, M.Z. Production and characterization of biocomposite films of bacterial cellulose from kombucha and coated with chitosan. Polymers 2022, 14, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. D882—Standard test method for tensile properties of thin plastic sheeting. In Annual Book of ASTM Standard; American Society for Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, C.V.; Costa, T.M.H.; Rios, A.O.; Flores, S.H. Comparative study on the properties of films based on red rice (Oryza glaberrima) flour and starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocakulak, S.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Chickpea flour-based biofilms containing gallic acid to be used as active edible films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, O.; Ferreiro, T.; Rodríguez-Otero, J.L.; Cobos, A. Characterization of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) flour films: Effects of pH and plasticizer concentration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Bin Song, K. Development of a chicken feet protein film containing essential oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christaki, S.; Moschakis, T.; Kyriakoudi, A.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Mourtzinos, I. Recent advances in plant essential oils and extracts: Delivery systems and potential uses as preservatives and antioxidants in cheese. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, S.; Pereira, L.; Domingues, F.; Ramos, A.; Luís, Â. Optimization of whey protein-based films incorporating Foeniculum vulgare Mill. essential oil. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, V.; Hosseini, S.E.; Sharifan, A. Effect of edible chitosan film enriched with anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) essential oil on shelf life and quality of the chicken burger. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki, W.S.; Tatol, M. Colour difference ΔE—A survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, G.; Shivani. Thyme essential oil nano-emulsion/Tamarind starch/Whey protein concentrate novel edible films for tomato packaging. Food Control 2022, 138, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, O.L.; Reinas, I.; Silva, S.I.; Fernandes, J.C.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A.; Pocas, M.F.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X. Effect of whey protein purity and glycerol content upon physical properties of edible films manufactured therefrom. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2004; pp. 137–165. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.M.; Souza, B.W.S.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Effects of electric fields on protein unfolding and aggregation: Influence on edible films formation. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2912–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniloski, D.; McCarthy, N.A.; Auldist, M.J.; Vailjevic, T. Properties of sodium caseinate as affected by the β-casein phenotypes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 626, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinache, A.; Tozar, T.; Smarandache, A.; Andrei, I.R.; Nistorescu, S.; Nastasa, V.; Staicu, A.; Pascu, M.L.; Romanitan, M.O. Spectroscopic characterization of emulsions generated with a new laser-assisted device. Molecules 2020, 25, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakidou, A.; Tsimidou, M.Z.; Kiosseoglou, V. Storage behavior of caseinate-based films incorporating maize germ oil bodies. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.P.; Peltzer, M.A.; Garrigós, M.C.; Jiménez, A. Structure and mechanical properties of sodium and calcium caseinate edible active films with carvacrol. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.; Pereira, C.G.; Junior, J.C.A.; Viana, C.C.R.; Neves, L.N.O.; da Silva, P.H.F.; Bell, M.J.V.; dos Anjos, V.C. FTIR-ATR determination of protein content to evaluate whey protein concentrate adulteration. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 99, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Xi, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and characterization of active films based on oregano essential oil microcapsules/soybean protein isolate/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Yan, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Preparation and characterization of an active packaging film loaded with tea tree oil-hydroxyapatite porous microspheres. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 199, 116783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.G.-G.; Almasi, H. Physical characteristics, release properties, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of whey protein isolate films incorporated with thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) extract-loaded nanoliposomes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomide, R.A.C.; de Oliveira, A.C.S.; Luvizaro, L.B.; Yoshida, M.I.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Borges, S.V. Biopolymeric films based on whey protein isolate/lignin microparticles for waste recovery. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.A.; Almasi, H.; Ghadertaj, A.; Mehryar, L. Whey protein isolate-based films incorporated with nanoemulsions of orange peel (Citrus sinensis) essential oil: Preparation and characterization. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
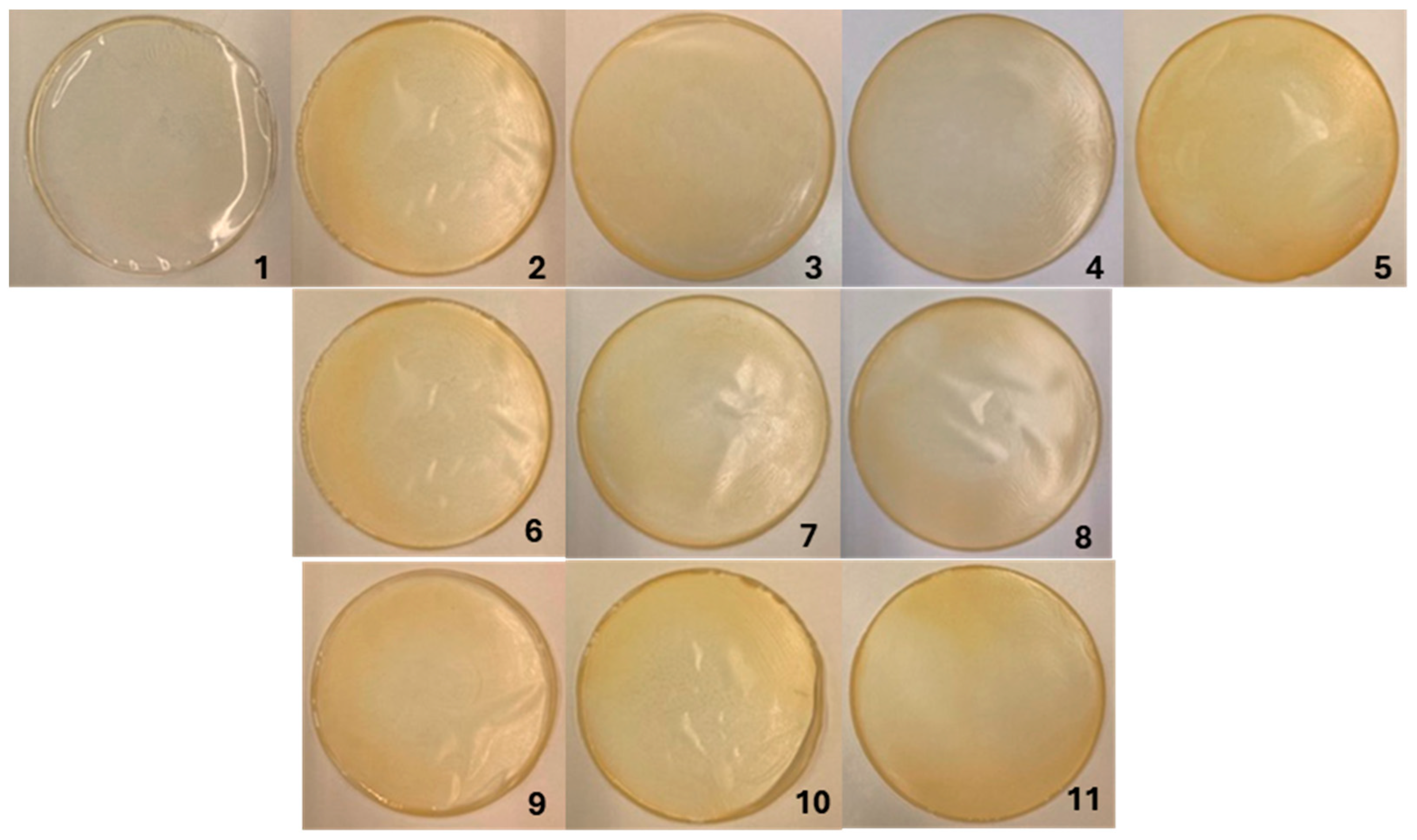
| Film | WVP (ng s−1 m−1 Pa−1) | Thickness μm | Dry Matter (g/100 g) | Solubility (% D.M.) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 0.156 ± 0.04 | 150.67 ± 58.66 | 57.77 ± 0.9 a | 81.44 ± 0.94 d | 1.43 ± 0.15 a |
| WS 2:1 | 0.135 ± 0.05 | 166.33 ± 40.27 | 63.34 ± 1.7 ab | 79.04± 3.22 cd | 1.73 ± 0.27 ab |
| WS 1:1 | 0.089 ± 0.01 | 131.83 ± 33.45 | 65.59 ± 2.04 b | 78.86 ± 2.85 cd | 2.07 ± 0.06 ab |
| WS 1:2 | 0.104 ± 0.03 | 172.33 ± 40.55 | 66.69 ± 2.24 b | 77.68 ± 2.44 bcd | 1.49 ± 0.23 a |
| SCW | 0.141 ± 0.03 | 160.17 ± 16.37 | 66.79 ± 1.20 b | 66.49 ± 3.64 a | 1.98 ± 0.16 ab |
| WS 2:1O1 | 0.137 ± 0.05 | 124.17 ± 11.51 | 67.93 ± 0.55 b | 71.54 ± 0.99 ab | 3.27 ± 0.06 b |
| WS 1:1O1 | 0.141 ± 0.009 | 173.83 ± 5.30 | 66.34 ± 0.53 b | 74.59 ± 0.27 abcd | 1.76 ± 0.22 ab |
| WS 1:2O1 | 0.147 ± 0.03 | 184.00 ± 38.94 | 63.86 ± 1.00 b | 74.05 ±1.95 abcd | 1.69 ± 0.58 ab |
| WS 2:1O2 | 0.120 ± 0.03 | 139.67 ± 25.15 | 63.33 ± 1.68 ab | 80.16 ± 4.43 cd | 2.27 ± 0.73 ab |
| WS 1:1O2 | 0.102 ± 0.003 | 123.00 ± 17.32 | 66.56 ± 2.97 b | 74.12 ± 6.64 abcd | 2.53 ± 1.11 ab |
| WS 1:2O2 | 0.117 ± 0.007 | 142.33 ± 6.25 | 64.83 ± 4.25 b | 68.48 ± 2.98 ab | 2.11 ± 0.96 ab |
| Two-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| F | p Value | ||
| WVP | Proportion WPI/SCW | 0.98 | 0.393 |
| Addition of OE | 3.40 | 0.056 | |
| Interaction | 0.69 | 0.609 | |
| Thickness | WPI/SCW | 2.05 | 0.158 |
| OE | 2.21 | 0.139 | |
| Interaction | 2.07 | 0.127 | |
| Dry matter | WPI/SCW | 0.88 | 0.432 |
| OE | 0.65 | 0.534 | |
| Interaction | 2.60 | 0.071 | |
| Solubility | WPI/SCW | 2.57 | 0.104 |
| OE | 6.01 | 0.010 | |
| Interaction | 3.65 | 0.024 | |
| Density | WPI/SCW | 2.78 | 0.089 |
| OE | 2.18 | 0.141 | |
| Interaction | 2.54 | 0.076 | |
| Film | L* | a* | b* | ΔE | Opacity | Whiteness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 92.96 ± 0.49 c | −3.04 ± 0.09 ab | 3.15 ± 2.04 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 14.91 ± 0.25 a | 91.59 ± 1.19 d |
| WS 2:1 | 90.08 ± 1.35 b | −3.11 ± 0.10 a | 7.04 ± 1.59 ab | 4.92 ± 2.18 ab | 18.55 ± 0.22 b | 87.43 ± 1.92 cd |
| WS 1:1 | 88.16 ± 1.25 ab | −2.89 ± 0.13 abc | 9.86 ± 2.16 bcd | 8.33 ± 4.13 bc | 22.00 ± 1.18 de | 84.30 ± 2.26 bc |
| WS 1:2 | 88.51 ± 0.97 ab | −2.46 ± 0.32 bc | 13.00 ± 2.27 cd | 10.83 ± 2.93 bcd | 26.82 ± 0.59 g | 82.46 ± 2.22 b |
| SCW | 86.16 ± 1.32 a | −1.10 ± 0.52 d | 18.11 ± 2.21 e | 16.58 ± 2.22 d | 23.81 ± 1.79 ef | 77.17 ± 2.48 a |
| WS 2:1O1 | 88.60 ± 1.00 ab | −3.06 ± 0.09 ab | 8.86 ± 1.45 bc | 7.21 ± 1.21 bc | 19.55 ± 0.66 bcd | 85.17 ± 0.40 bc |
| WS 1:1O1 | 88.52 ± 0.62 ab | −2.92 ± 0.17 ab | 11.60 ± 1.33 bcd | 9.54 ± 2.37 bc | 21.28 ± 0.65 cde | 83.41 ± 1.24 bc |
| WS 1:2O1 | 88.09 ± 0.60 ab | −2.25 ± 0.21 c | 14.67 ± 1.68 de | 12.53 ±1.65 cd | 27.61 ± 1.16 g | 80.96 ± 1.59 ab |
| WS 2:1O2 | 88.82 ± 0.74 b | −3.03 ± 0.07 ab | 9.63 ± 0.71 bc | 7.74 ± 0.90 bc | 18.83 ± 0.73 bc | 84.94 ± 1.00 bc |
| WS 1:1O2 | 88.91 ± 0.27 b | −2.85 ± 0.15 abc | 11.52 ± 1.07 bcd | 9.33 ± 2.99 bc | 21.86 ± 0.59 de | 83.75 ± 0.84 bc |
| WS 1:2O2 | 88.44 ± 0.12 ab | −2.58 ± 0.16 abc | 13.15 ± 1.54 cde | 11.01 ± 1.70 bcd | 24.83 ± 0.82 fg | 82.28 ± 1.16 b |
| Two-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Parameters | F | p Value | |
| L* | WPI/SCW | 2.24 | 0.135 |
| OE | 0.82 | 0.455 | |
| Interaction | 1.27 | 0.317 | |
| a* | WPI/SCW | 34.18 | 0.000 |
| OE | 0.55 | 0.586 | |
| Interaction | 1.30 | 0.307 | |
| b* | WPI/SCW | 22.78 | 0.000 |
| OE | 3.08 | 0.071 | |
| Interaction | 0.56 | 0.698 | |
| ΔE | WPI/SCW | 8.961 | 0.002 |
| OE | 1.267 | 0.306 | |
| Interaction | 0.273 | 0.892 | |
| Opacity | WPI/SCW | 207.33 | 0.000 |
| OE | 3.54 | 0.050 | |
| Interaction | 4.24 | 0.014 | |
| Whiteness | WPI–SCW | 15.03 | 0.000 |
| OE | 2.43 | 0.117 | |
| Interaction | 0.56 | 0.693 | |
| Film | Tensile Strength at Maximum (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Puncture Strength (MPa) | Puncture Deformation (%) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 1.57 ± 0.73 ef | 52.17 ± 17.32 ef | 2.40 ± 0.66 e | 18.92 ± 5.74 h | 7.41 ± 2.08 a |
| WS 2:1 | 1.17 ± 0.18 de | 57.26 ± 14.77 ef | 1.74 ± 0.14 d | 15.71 ± 3.89 gh | 15.00 ± 8.45 bc |
| WS 1:1 | 1.19 ± 0.22 de | 45.20 ± 9.83 de | 1.87 ± 0.36 de | 9.57 ± 2.40 def | 11.24 ± 2.60 abc |
| WS 1:2 | 0.46 ± 0.14 ab | 19.56 ± 7.79 abc | 0.51 ± 0.16 abc | 3.55 ± 1.33 abc | 16.75 ± 4.22 c |
| SCW | 0.17 ± 0.05 a | 3.57 ± 1.18 a | 0.20 ± 0.03 a | 0.93 ± 0.28 a | 9.25 ± 4.13 ab |
| WS 2:1O1 | 1.02± 0.25 cd | 30.32 ± 9.27 bcd | 2.07 ± 0.59 de | 12.34 ± 2.42 fg | 12.29 ± 3.04 abc |
| WS 1:1O1 | 0.61 ± 0.12 abc | 34.32 ± 10.99 cd | 0.94 ± 0.11 bc | 7.62 ± 1.11 cde | 8.07 ± 2.99 a |
| WS 1:2O1 | 0.41 ± 0.08 a | 15.01 ± 4.65 ab | 0.47 ± 0.11 ab | 2.56 ± 0.95 ab | 7.09 ± 1.54 a |
| WS 2:1O2 | 1.90 ± 0.36 f | 68.22 ± 14.30 f | 1.77 ± 0.48 d | 11.14 ± 3.47 ef | 14.66 ± 3.27 bc |
| WS 1:1O2 | 0.95 ± 0.16 bcd | 27.59 ± 8.70 bc | 1.05 ± 0.17 c | 5.52 ± 0.94 bcd | 9.91 ± 2.08 ab |
| WS 1:2O2 | 0.55 ± 0.09 abc | 17.98 ± 3.34 abc | 0.66 ± 0.13 abc | 3.57 ± 1.00 abc | 7.54 ± 2.37 a |
| Two-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Properties | F | p Value | |
| TS | WPI/SCW | 104.22 | 0.000 |
| OE | 28.09 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | 14.07 | 0.000 | |
| EB | WPI/SCW | 70.25 | 0.000 |
| OE | 13.53 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | 11.73 | 0.000 | |
| PS | WPI/SCW | 112.63 | 0.000 |
| OE | 3.88 | 0.026 | |
| Interaction | 11.03 | 0.000 | |
| PD | WPI/SCW | 117.44 | 0.000 |
| OE | 10.66 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | 2.76 | 0.035 | |
| EM | WPI/SCW | 8.12 | 0.000 |
| OE | 11.12 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | 3.47 | 0.013 | |
| Film | Antioxidant Activity (mg DPPH/g Film) |
|---|---|
| WPI | 1.06 ± 0.27 a |
| WS 2:1 | 1.19 ± 0.31 a |
| WS 1:1 | 1.04 ± 0.16 a |
| WS 1:2 | 0.97 ± 0.16 a |
| SCW | 1.09 ± 0.13 a |
| WS 2:1O1 | 1.52 ± 0.18 abc |
| WS 1:1O1 | 1.35 ± 0.08 a |
| WS 1:2O1 | 1.48 ± 0.15 ab |
| WS 2:1O2 | 2.08 ± 0.21 cd |
| WS 1:1O2 | 2.00 ± 0.30 bcd |
| WS 1:2O2 | 2.19 ± 0.40 d |
| Two-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant Activity | F | p Value | |
| DPPH | WPI/SCW | 1.02 | 0.376 |
| EO | 57.79 | 0.000 | |
| Interaction | 0.60 | 0.667 | |
| Film | Stage I 32–120 °C | Stage II 120–235 °C | Stage III 235–370 °C | Stage IV 370–600 °C | Total Weight Loss | Residual Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 9.21 | 34.76 | 33.38 | 10.55 | 87.28 | 12.72 |
| WS 2:1 | 9.94 | 31.24 | 35.41 | 10.58 | 86.70 | 13.30 |
| WS 1:1 | 9.39 | 28.64 | 36.57 | 13.05 | 88.64 | 11.36 |
| WS 1:2 | 9.42 | 26.70 | 39.22 | 11.39 | 87.19 | 12.81 |
| SCW | 8.09 | 32.55 | 34.09 | 11.02 | 86.44 | 13.56 |
| WS 2:1O1 | 10.49 | 28.70 | 36.49 | 9.76 | 86.34 | 13.66 |
| WS 1:1O1 | 9.57 | 30.79 | 36.57 | 10.10 | 86.79 | 13.21 |
| WS 1:2O1 | 9.21 | 28.01 | 38.65 | 10.91 | 87.68 | 12.32 |
| WS 2:1O2 | 9.22 | 30.31 | 36.35 | 10.30 | 86.65 | 13.35 |
| WS 1:1O2 | 9.13 | 28.64 | 38.44 | 11.55 | 88.20 | 11.80 |
| WS 1:2O2 | 9.20 | 27.32 | 39.38 | 10.40 | 86.72 | 13.28 |
| Film | Stage I 32–120 °C | Stage II 120–235 °C | Stage IIIa 235–370 °C | Stage IIIb 235–370 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI | 62.7 | 193.0 | nd | 308.1 |
| WS 2:1 | 62.3 | 192.8 | 257.3 | 307.8 |
| WS 1:1 | 63.5 | 193.2 | 257.4 | 311.3 |
| WS 1:2 | 63.8 | 190.6 | 257.3 | 318.3 |
| SCW | 61.1 | 194.0 | nd | 312.5 |
| WS 2:1O1 | 63.6 | 195.9 | 246.2 | 311.9 |
| WS 1:1O1 | 62.2 | 197.0 | 247.2 | 315.8 |
| WS 1:2O1 | 65.4 | 193.1 | 249.9 | 316.8 |
| WS 2:1O2 | 61.2 | 192.6 | 251.3 | 314.4 |
| WS 1:1O2 | 64.4 | 193.4 | 251.7 | 314.4 |
| WS 1:2O2 | 66.1 | 192.3 | 250.3 | 312.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pires, A.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C.; Díaz, O. Edible Films Based on Ovine Second Cheese Whey with Oregano Essential Oil. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105325
Pires A, Cobos A, Pereira C, Díaz O. Edible Films Based on Ovine Second Cheese Whey with Oregano Essential Oil. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105325
Chicago/Turabian StylePires, Arona, Angel Cobos, Carlos Pereira, and Olga Díaz. 2025. "Edible Films Based on Ovine Second Cheese Whey with Oregano Essential Oil" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105325
APA StylePires, A., Cobos, A., Pereira, C., & Díaz, O. (2025). Edible Films Based on Ovine Second Cheese Whey with Oregano Essential Oil. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5325. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105325








