Abstract
Phosphorus (P) excess in the aquatic environment is a source of eutrophication leading to the deterioration of water quality and biodiversity loss. Methods of in situ controlling P in lakes and reservoirs mostly require the addition of chemical substances to a water body without the possibility of controlling their future interactions with the environment. This study compared the performance of two solutions, laminates and modules, developed for non-invasive P removal from aquatic ecosystems with the use of calcite mineral as a P-reactive material. Both techniques enable reductions in the orthophosphate (OP) availability in lake water, and its removal from the ecosystem, without the permanent deposition of the P binding agent in the environment. In a laboratory mesocosm experiment, both, laminates and modules, lowered the OP concentration in lake water for at least 6 weeks compared to no treatment; the efficiency of modules was, however, much higher. They effectively eliminated the OP initially available in the system and further captured the OP newly supplied by the decomposition processes, showing continuous OP uptake, while laminates appeared to exhaust their capacity after about 1 week. This was mostly because of technical design—the calcite dose per m2 of the surface area was 168 times higher in modules compared to laminates. Treatment using both techniques caused a slight pH decrease compared to no treatment with a minor change of up to 0.2 point. Modules have the most potential for the implementation in practice as they are able to decrease the OP concentration for relatively long time periods of weeks to months without the need to be exchanged. They offer a refillable and reusable system for P control, removal, and recovery. Field tests should be performed to verify the performance of modules and laminates under in-lake conditions and complex interactions with the aquatic organisms to check for possible limitations and/or synergies between the non-invasive P removal techniques and native processes.
Keywords:
eutrophication; phosphorus removal; lake restoration; calcite; limestone; laminate; module 1. Introduction
Phosphorus (P) is one of the nutrients necessary for aquatic organisms to develop and grow. However, its excess in the aquatic environment causes eutrophication with a number of negative effects on ecosystems, such as oxygen depletion, alkaline pH, and massive blooms of phytoplankton, including toxic cyanobacteria [1]. The results are changes in biodiversity, water quality deterioration, and limitations in the use of water bodies [1,2,3]. Therefore, external solutions to combat P transport to water bodies are employed and developed [4], such as inflow treatment [5], buffer zones [6], and permeable reactive barriers [7]. In lakes, however, a large pool of phosphorus is usually stored in the sediment, part of which being released to the water column, leading to an internal phosphorus loading [8,9]. Thus, strategies to in situ manage P excess in water bodies are applied [4], frequently aiming at immobilizing the dissolved P (orthophosphates, OP) by the addition of P binding agents into the water column (or sediments) and reducing the P flux from the sediment [10]. Substances used for this purpose are usually aluminum (or iron) salts or lanthanum-enriched clay [11,12,13,14].
The application of P binding agents may lead to some non-target effects on the lake ecosystem. Although they are typically dosed and distributed evenly to the lake water column, the accumulation of binding agents in specific lake areas has been reported, e.g., due to wind effects [15,16,17]. Increased concentrations of ammonia [18] and metals [17,19] have also been observed. What is more, the stability of the P fixation on the binding materials can be reduced under variations of physio-chemical conditions [20,21,22] and/or under the effect of physical and biological processes, especially in shallow lakes, where wind resuspension strongly affects the agent interactions with sediments [23,24,25]. Aging processes can further lead to reduced P sorption on the materials applied [26,27]. Adverse effects on the aquatic organisms caused by the reactive agents have also been reported [28,29,30].
At the same time, the need for P recovery and closing the P cycle has been increasingly noticed [31,32,33] also in the area of lake restoration [34,35]. P management strategies enabling P removal from the aquatic ecosystem and its recovery for further reuse are regarded to have priority among lake restoration options [36]. Technologies for not only inactivating but permanently removing P from the catchment have been suggested and developed for flowing waters, e.g., small streams [37,38].
Taking this into consideration, we developed a novel approach for P removal from water bodies enabling the application of a binding agent into the water column for a given time, using packaging or a carrier, to allow P sorption and the subsequent removal of the carrier together with the P-loaded binding agent (Figure 1). Such a measure ensures P inactivation and P removal from the ecosystem and eliminates risks related to the disposal of the binding agent in the aquatic environment. We thus called this approach a non-invasive phosphorus removal [39]. The P binding agent can be applied to a water body in a given site at target depth and, for a given period, without the risk of being allocated. At the same time, the removal of the agent together with the inactivated orthophosphate (OP) opens the chances for P recovery and reuse.
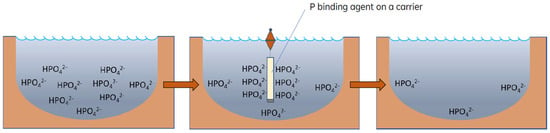
Figure 1.
Principle of the non-invasive phosphorus removal approach.
Our first attempts to develop solutions for non-invasive P removal were based on a simple technical concept of placing the P binding material in packaging made of a porous elastic fabric [40] (similar to the idea developed shortly afterwards by Zamparas et al. [35], called “tea-bags”). An important limitation of this approach comprised losses of the P binding agent from the packaging due to the porous structure of the packaging material (which was necessary for ensuring the contact of the solution with the P sorbing medium) or a reduction in the OP uptake (compared to freely added agents) caused by less permeable packaging materials [35,40]. To increase the exposure of the binding material (its area effectively interacting with the OP ions in the surrounding water), we developed another solution—the so-called laminates, which are strip-shaped, flat surfaces covered with a thin layer of the sorbing medium [39]. In a short-term experiment, the laminates showed good stability in the lake water and OP removal reduced by 21% (on average) compared to the lose P-reactive material [41]. However, laminates only allow for the application of a relatively small amount of the reactive agent if applied in a reasonable number [39]. Thus, we further developed another solution, with the so-called modules being tray-shaped structures filled with the P binding material and arranged in tiers. This approach makes it possible to apply larger doses of the agent per unit area of the carrier, still maintaining a relatively large surface of the agent exposed in water. The design of the modules employs the use of refillable trays and thus enables the exchange and recharge of the reactive material (which is not possible in the case of laminates). In this study, we performed a long-term experiment to compare the longevity of both developed solutions (laminates and modules) in terms of their sorption properties and effects on lake water chemistry. The study built upon short-term batch experiments on laminates and testing the prototype of modules in a long-term flow-through experiments, both performed in synthetic lake waters [39,41].
As the P binding agent, we used mineral calcite in the form of a limestone rock. Calcite, consisting of calcium carbonate, is a natural component of aquatic ecosystems contributing to P cycling in the environment [42]. In lakes, it plays an important role in their self-purification, generally sequestering P from the water column during the process of co-precipitation and/or contributing to P retention in sediments [42,43,44,45]. The source of calcite-based materials for different applications comprises carbonate rocks, such as limestones, or synthetic calcites [46,47,48,49]. Bio-waste materials containing calcite (or its polymorph, aragonite), e.g., eggshell or oystershell, have received attention as well [50,51,52]. Calcite is generally considered a non-toxic and low-cost adsorbent [53,54]. Depending on the physio-chemical conditions, the P uptake onto calcite can employ different mechanism: adsorption, co-precipitation, and/or phosphate precipitation with newly formed calcium salts [55,56,57,58,59], the latter process being generally more stable compared to reversible adsorption [56]. Calcite materials have been investigated as potential reactive agents with respect to phosphate, and other polluting substances, to be used in different settings, including lakes [46,47], rivers [60], or wastewater [54,61].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Calcite Material
Calcite material used in this study was produced using limestone rock as a starting material. Limestone came from Jurassic deposits in Bukowa mine (Bukowa, Poland) operated by the company Lhoist Bukowa Poland. The mineral calcite constituted 95% of the material by mass [62]. The grain size of the initial material was ≤4 cm, with a particle diameter d90 of 3120 µm and specific surface area (SSA) of 7.2 m2 g−1 (determined with the BET method; see Section 2.4 for details). To increase its SSA and affinity for the OP, the limestone material was further ground in a laboratory ball mill (Pulverisette 6; Fritsch, Idar-Oberstein, Germany) for 30 min at a grinding speed of 350 rpm using 37 balls of the total mass of 500 g (corresponding to the sample mass/ball mass ratio of 10:1). Resulting material parameters were grain size of d90 = 55 µm and SSA = 15 m2 g−1. In a simple batch test, this material removed 7–20 times more OP compared to the initial limestone sample, depending on the reaction time employed (Figure 2).
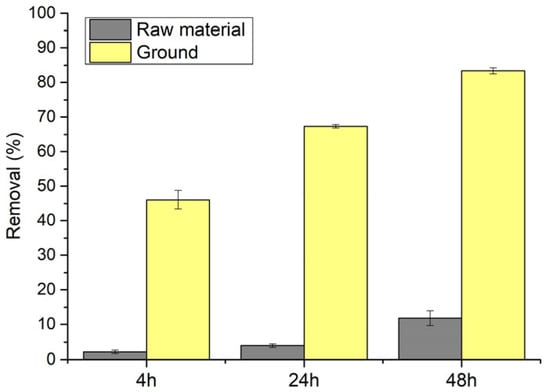
Figure 2.
Orthophosphate (OP) removal by the raw material (limestone) and ground limestone (grinding time 30 min, grinding speed of 350 rpm, ball to sample mass ratio 10:1; planetary ball mill) in a batch test. Initial orthophosphate concentration = 3 mg PO43− L−1 (~1.3 mg P-PO4 L−1); the limestone dosage = 1 g L−1. The results were means from duplicate experiments.
2.2. Carriers Tested
Laminates were strip-shaped sheets covered with calcite (Figure 3a). They consisted of a carrier material coated with an adhesive layer made of biodegradable glue, the main components of which were water and carbohydrates [41]. A calcite layer of about 2 mm thickness was attached to the glue. This was achieved by spreading finely grained calcite material over the laminate surface. The glue layer was capable of keeping the calcite particles fixed in the laminate structure, still enabling the contact between the active surface and surrounding water. However, compared to the freely added calcite material (as powder), the laminates fixed 9–33% less OP depending on the properties of the calcite used (different grain size and surface area) and experimental conditions [41]. This was probably because the calcite particles were partially covered with a glue layer, which limited the active mineral surface contributing to the OP sorption [39,41].
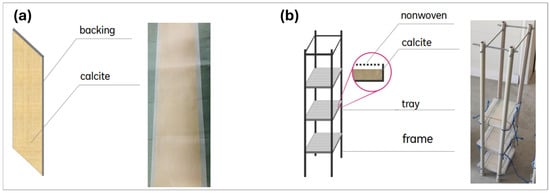
Figure 3.
Laminates (a) and modules (b).
Modules (Figure 3b) consisted of tray-shaped surfaces fixed on a vertically oriented frame. The trays were arranged one above the other and filled with the reactive material and covered with a polyamide mesh. This type of mesh had been previously proven to prevent the calcite grains from being flushed out from the trays while enabling water penetration into the interiors of the trays [39]. Technically, the modules were similar to the solution proposed by Carleton et al. [38] for an instream water treatment system consisting of cartridges filled with a reactive material placed in mesh bags.
2.3. Experimental Design and Experimental Conditions
For a comparative test of the two carrier types, laminates and modules, an incubation experiment in mesocosms was performed (Figure 4). Lake water was sampled from the eutrophic Lake Skarlińskie (NE Poland) in April and transported to the laboratory. The lake water was further poured into plastic chambers (diameter of 57 cm, height of 81 cm) (Figure 4). Each chamber was filled with 180 L of the lake water and left without any intervention for about 6 days to stabilize. After 6 days, modules and laminates were immersed or suspended in chambers and further incubated for 42 days. Two laminate strips were used, with a total surface area of 1500 cm2 (15 × 50 cm each) and a total mass of calcite of about 3.6 g (Figure 4). Modules consisted of three trays with the total surface area of 740 cm2 (13 × 19 cm each), filled with calcite with the total mass of 300 g and covered with mesh to prevent material loss. Chambers without any additions served as control. The whole volume of water in each chamber was mixed twice a day. Incubation took place without light access. During the experiment, the temperature in the laboratory hall was 8.0–13.5 °C. The experiment was conducted in duplicates.
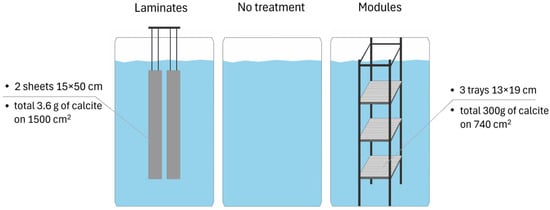
Figure 4.
Experimental design.
At the beginning of the experiment, the concentration of total phosphorus in the lake water was 0.63 mg L−1, of which 0.16 mg L−1 was OP (as P-PO4). The concentration of total nitrogen was 0.4 mg/L, of which only a small portion (0.024 mg L−1) was inorganic nitrogen. The water was characterized with alkaline pH (7.9), high oxygen concentration (10.5 mg O2 L−1, saturation of 95%) and relatively high content of chlorophyll “a” (17 µg/L), showing primary production already taking place during sampling for the experiment.
During the experiment, the lake water properties were monitored in each mesocosm every 3 days in the first week of the incubation and once a week during the remaining experiment duration. Temperature, conductivity, and pH were measured in situ at the depth of 30 cm. For the other parameters, including concentration of the OP, calcium, and alkalinity, the water samples were taken from the depth of 30 cm. Determination methods for all the parameters monitored are described in detail in Section 2.4. The change in total water volume at the end of the experiment due to sampling was about 3%.
2.4. Measurements
Particle size diameter of the calcite material was measured using laser diffraction method (Mastersizer 3000, Malvern, Worcestershire, UK) for three subsamples after dilution in water without any additional treatment (surface active agent or ultrasounds). The suspensions were highly stirred to disperse the fine particles in water. For the initial material, as its particle size was too high for the laser measurements, the particle size was determined by volumetric sieve analysis for three subsamples. The specific surface area (SSA) was measured with the BET method (Autoflow BET+; Quantachrome Instruments, Boynton Beach, FL, USA) in three replicates as well.
Temperature, pH, and conductivity (25 °C) of the lake water prior and during the incubation experiment were measured with a portable multi-meter (Hach HQ30d, Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA). Concentration of phosphate was determined spectrophotometrically using the blue method with the addition of the ascorbic and molybdenum acid at the wavelength of 880 nm after sample filtration through mixed cellulose ester filters (0.45 µm). The concentrations of calcium and alkalinity were determined in the filtered samples (same filtration method) by ion chromatography and titration method using hydrochloric acid against phenolphthalein (Merck test no 11109, Darmstadt, Germany), respectively.
3. Results
The concentrations of the OP in the lake water showed different dynamics depending on the treatment applied. In the control mesocosm the OP concentration showed a rising tendency throughout the experiment duration and increased from 0.52 to 0.61 mg PO43− L−1 (Figure 5a). Consequently, the OP mass balance for this mesocosm was positive (Figure 5b). This indicates release processes due to the decomposition of the organic material without the reuse of the free phosphate (limited light access). Compared to control, in the chambers with laminates and modules, a different pattern in the OP dynamics was clearly visible. The OP concentration decreased starting from the very initial stage of the experiment. This effect was seen already after 3 days—the OP concentration continued to decrease while an opposite change took place in the control mesocosm (Figure 5a). Initially, both, laminates and modules, showed similar levels of OP elimination, lowering the OP availability by about 17–18% within 7 days compared to the initial level and 24–26% compared to the control chamber (Figure 5a). At this point, the OP mass balance was thus clearly negative in both treatments (Figure 5b). At longer exposure, the laminates were not able to force a further decline, and the OP concentration started to rise, almost reaching the initial OP level (Figure 5a). However, the OP concentration remained at least 15% lower compared to the control mesocosm for the next 35 days (Figure 5a).
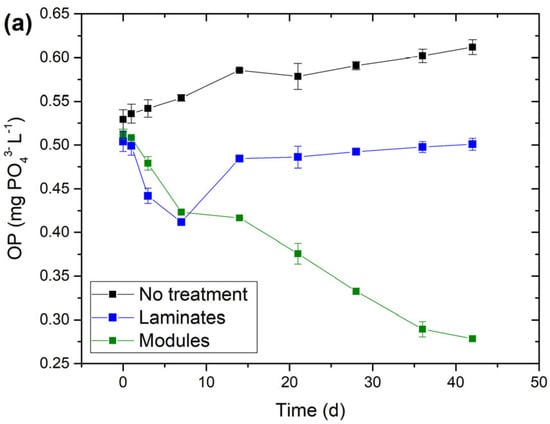
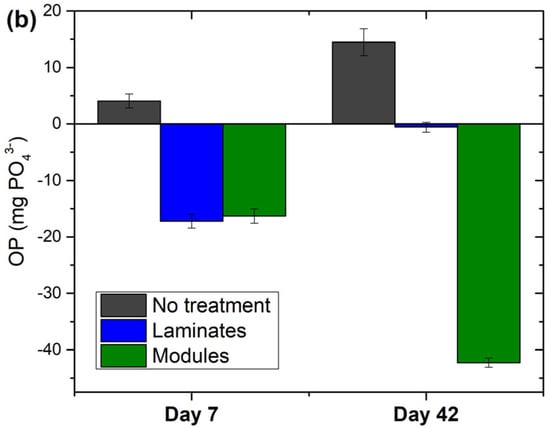
Figure 5.
OP availability in the lake water during incubation experiment: (a) OP concentration (mg PO43− L−1); (b) OP balance (mg PO43−) calculated as a change in the total OP mass present in the lake water at the beginning of the experiment; lake water volume was corrected for the reduction due to sampling. Day 0 in chart (a) indicates initial conditions. The laminates and modules were placed into experimental chambers at the end of day 0. ‘No treatment’ refers to lake water without any additions. Results were means ± SDs from duplicate experiments.
Modules, in contrast, showed continuous OP elimination lasting throughout the experiment duration (~40 days) and did not show any signs of approaching their sorption capacity (Figure 5a). Compared to the initial conditions, at the end of the experiment, the modules reduced the OP concentration by 45% (from 0.51 to 0.28 mg PO43− L−1) while an increase of ca. 18% took place in the control mesocosm (0.52 to 0.61 mg PO43− L−1). Thus, the OP balance in the treatment with modules was negative and accounted for −42.3 mg PO43− L−1 (which was 16 times more compared to laminates (−2.6 mg PO43− L−1) (Figure 5b)). With respect to the control, in the lake water treated with modules, the OP concentration was 54% lower at the end of the experiment (0.28 vs. 0.61 mg PO43− L−1) (Figure 5a). We left the incubation chamber with modules for the next two weeks and observed slight but continuous OP sorption onto modules (with the OP concentration reaching ca 0.24 mg PO43− L−1 after 2 months).
To further compare the performance of laminates and modules, we calculated the total mass of the OP removed by laminates and modules (Table 1). The modules removed 2.7 times more OP compared to laminates. At the total areas of calcite layer of 740 cm2 and 1500 cm2 for modules and laminates, respectively, this produced a ca. 6-fold difference in the P removed per unit of surface area with a clear advantage for the modules. However, at the total mass of calcite applied (300 vs. 3.6 g, accordingly), this yielded almost 30 times more P removed by laminates when expressing the OP uptake per gram of the calcite material (Table 1).

Table 1.
The OP removal during incubation calculated based on the OP concentration difference between the control mesocosm (no treatment) and treatment using laminates and modules. OP mass was corrected for the water volume reduction due to sampling. mg PO43− stands for the total mass of the OP removed from the lake water; mg PO43− cm−2 indicates OP mass removed per unit of surface area of the calcite layer exposed in the mesocosm while mg PO43− g−1 indicates the OP mass removed by unit mass of calcite.
The pH of the lake water tended to increase during the experiment and changed from 7.8–7.9 to 8.1–8.3 (Figure 6a). The treatment applied had a clear effect on the lake water pH. In the presence of laminates and modules, depending on the treatment duration, the pH was 0.05–0.22 lower compared to the control chamber, and this difference could be seen throughout the experiment duration, with the pH being slightly lower under the use of laminates compared to modules (Figure 6a). The concentration of calcium in the control mesocosm was rather stable and fluctuated in a small range between 58 and 62 mg Ca2+ L−1 (Figure 6b). Similar values were observed in treated chambers (laminates and modules). The exception was a slightly higher concentration of 65 mg Ca2+ L−1 recorded after 3 weeks in the treatment with laminates (Figure 6b). In none of the mesocosms, the calcium concentration showed a trend in time.
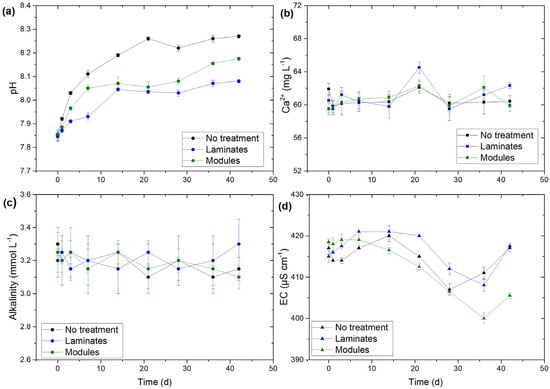
Figure 6.
pH (a), concentration of calcium (b), alkalinity (c) and conductivity (d) in the lake during incubation. ‘No treatment’ refers to lake water without any additions. Results were means ± SDs from duplicate experiments. Day 0 indicates initial conditions. The laminates and modules were placed into experimental chambers at the end of day 0.
Alkalinity fluctuated in a small range of 3.1–3.3 mmol L−1 (at the measurement accuracy of 0.2 mmol L−1 (Figure 6c)). Although no trend could be seen, in the control mesocosm, the alkalinity was lower during the incubation, compared to the initial conditions; the same pattern could be noticed in the treatment using modules. Meanwhile, in the mesocosms with laminates, the alkalinity increased at some points in time compared to the initial level, especially at the end of the experiment (Figure 6c). Electrolytic conductivity changed in a small range between 400 and 420 µS cm−1. The dynamics in time were generally the same in all chambers, with a slight increase at the beginning of the experiment and further decline after 2 weeks (Figure 6d).
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect on Phosphorus
The availability of OP in the experiment generally increased as indicated by the rise in OP concentration in the treatment chamber by 18% within ~40 days (Figure 5a). The source of this increase was probably the OP supply from the decomposition of dead organic matter initially present in the lake water and its new pool coming from dying phytoplankton when the light access ceased. The OP dynamics observed in the treatment chambers were different and revealed large differences in the efficiency and longevity of laminates and modules (Figure 5a). Although both solutions lowered the OP concentration in the lake water for at least 6 weeks (42 days) compared to no treatment, the laminates were able to force continuous OP decline for a relatively short period of about 1 week. This showed that their sorption capacity had still not been exhausted and/or the sorption removed more OP than the native processes delivered. After a longer time, the treatment using laminates was not capable of keeping the declining trend and the OP concentration started to rise, generally corresponding to the dynamics observed in the control mesocosm (Figure 5a). This suggests that the calcite material in laminates reached saturation (the sorption ceased) and/or the OP supply (the source of which was the decomposition of organic material) was higher compared to OP removal via sorption processes. Another possible factor contributing to the reverse in the declining trend in OP availability was the desorption of phosphate ions from the calcite material. OP can be completely desorbed from calcite under phosphate-free conditions [56]. In our experiment, however, in the mesocosm with laminates, the phosphate was still present after 7–14 days (when the OP started to increase) at the concentration of about 0.41–0.49 mg PO43− L−1 (Figure 5a), so we did not expect a complete or substantial desorption under these conditions. However, even though the OP concentration started to increase after 1 week of incubation, the laminates kept it on a still lower level compared to the control mesocosm (16% lower after 42 days), mitigating the OP supply effect (Figure 5a,b). Modules, in contrast, showed continuous OP elimination throughout the experiment duration. After 42 days, the treatment using modules reduced the OP concentration by 45% compared to the starting conditions and kept it on a 54% lower level compared to the control chamber (where the OP availability in the lake water continuously increased) (Figure 5a). Thus, the modules first effectively eliminated the OP available in the system (initially present in the lake water) and further captured the OP newly supplied by the decomposition processes.
The distinctly higher efficiency and longevity of modules compared to laminates in removing OP in our experiment obviously resulted from the much larger calcite content applied using modules. At the surface area of modules being more than two times smaller compared to laminates (741 vs. 1500 cm2), they contained 83 times more active agent (300 vs. 3.6 g). Thus, the number of active sites available for OP adsorption was accordingly higher. Consequently, the calcite dose per m2 of the surface area was 168 times higher in modules compared to laminates (4050 vs. 24 g). This reflected the contrasting technical design—a thicker calcite layer of ca. 2 cm could be applied in modules (which was determined by the depth of trays) while the calcite layer formed onto laminates was only ˜2 mm thick (which was determined by the adhesive force of glue). That was why the modules were able to ensure OP uptake for a longer time compared to laminates. Thus, as revealed by the mesocosm study, the laminates can be regarded as a constituting short-term measure (to be applied for short periods, such as days). This generally verified the results of our previous short-term experiment using laminates [41]. If a prolonged effect is necessary, repeated applications of laminates for short periods should be considered rather than longer exposure in the aquatic environment. To achieve a longer lasting effect (weeks, months) without the need to exchange carriers, modules represent a more advisable solution.
As a consequence of technical design, the modules and laminates also showed contrasting OP removal features when comparing unit area or unit mass of the calcite applied using the two solutions (Table 1). In terms of OP uptake per surface area of the carrier, modules were clearly more efficient as they fixed about six times more OP compared to laminates (Table 1). This was because they contained 168 times more calcite per m2 of the carrier, as previously mentioned. What was more, the performance of laminates was also affected by the calcite fixation by the glue layer reducing the OP removal onto laminates by up to 33% compared to loose (powdered) calcite [41], making part of the calcite layer not accessible for the water.
At the same time, when comparing laminates and modules based on the OP mass removed per unit mass of calcite applied, the modules were able to remove about 0.2 mg PO43− g−1 while the performance of the laminates was almost 30 times higher (6.0 mg PO43− g−1) (Table 1). This was the result of a much larger solid-to-solution ratio in the case of the treatment with modules. At the same time, it showed that a large part of the calcite material applied in modules did not contribute to the OP uptake and was still available, at least in theory, for the adsorbing ions. This was in accordance with the observation that at the end of the experiment, the OP concentration was still declining in the mesocosms with modules (Figure 5a), so the OP removal could be expected to last for a longer time compared to the experiment duration. This was highly likely as continuous OP uptake lasting as long as 7 months could be achieved when testing the modules prototype in a flow-through laboratory experiment [39].
The differences in OP uptake between laminates and modules impact their potential in developing a P recovery strategy following use in lake treatment. Taking into account the large solid-to-solution ratio when using modules, and the resulting low OP mass removed per unit mass of the calcite material (0.2 vs. 6.0 mg PO43− g−1 in the case of laminates, Table 1), modules appear to be a less favorable solution in terms of phosphorus recovery (less phosphorus per mass of calcite to be possibly recycled). Nevertheless, in technical terms, the recovery of calcite and phosphorus from a module is technically simpler. This is because it only requires the removal of the mesh and calcite from trays. Meanwhile, in the case of laminates, the P binding material needs to be separated from the backing, which will not be possible selectively, i.e., without the glue layer. The inevitable side effect will be the production of waste as the laminate’s backing material (food foil) after such a separation will likely not be reusable. At the same time, modules present a more sustainable solution compared to laminates as their construction enables the reuse and refilling of the frame and trays with the new portion of the P binding agent after the saturation of modules with the OP will be achieved.
The above discussion shows clear advantages of modules in terms of their OP removal potential, simplicity of application and reuse, and possible P recycling. However, to gain a substantial elimination of the OP available in the lake water in this study, the modules needed at least a few weeks (Figure 5a). This means their effect on the OP availability would be achieved gradually. Zamparas et al. [35], when testing their tea-bag design (the sorbent placed in bags), observed altered sorption kinetics compared to the sorbent applied as powder and explained it with a physical influence of the bag material, limiting the water exchange between the bag interior and the surrounding solution. Such an effect was rather not possible in the case of our study as we did not observe any kinetic difference between the OP removal when using loose calcite and calcite layer in modules (both with and without mesh coverage) in the prototype tests [39]. Still, in field applications, the kinetics of OP uptake by modules can be strongly affected by specific in-lake conditions. In particular, OP delivery to the calcite layer can be limited under field conditions compared to laboratory tests. Mixing was applied in our experiment to assure a contact between the lake water and calcite layer in both carriers (laminates and modules), while in a water body, the transport will be determined by diffusion and advection, possibly representing a less dynamic exchange compared to our experimental conditions.
Assuming a sort of a delay in the substantial OP uptake by the calcite layer in modules (Figure 5a), the phytoplankton will be able to assimilate OP for some time following the modules’ installation in a water body if the modules are applied in the euphotic zone (light access). In this context, to more effectively prevent intense phytoplankton growth by reducing the OP availability, the modules should be applied in advance before the start of the vegetation season (if they are to be used in the surficial layers of a water body). Another solution is their application at higher depths, below the euphotic zone, as simulated in our experiment. The possibility of adjusting the depth of application is an important advantage of the non-invasive P removal approach [41]. In such a case (treatment of deeper layers below the euphotic zone), the P inactivation will mainly address the P released by the decomposition of detritus settling from the euphotic zone and/or liberated from the sediments iby internal loading. By this, the P binding onto the modules can limit the OP transport between deeper layers and the productive zone and consequently contribute to lower OP concentrations in the upper water layers. A similar approach is sometimes used in traditional P immobilization in lakes by applying the P biding agent into hypolimnion [63].
Regarding the kinetics and efficiency of the OP uptake by modules and laminates, few modifications to the technical design are possible. The problem of relatively low mass of calcite present in laminates could be, in theory, overcome by adjusting the size of the laminates’ area and their number. However, if one would like to add the same amount of calcite as applied in modules, 12.5 m2 of the laminates’ area would be needed for 180 L of the lake water (the lake volume used in the experiment in each chamber), which is unrealistic in field applications. Another option to increase the laminate’s performance in OP removal is the two-side coverage of the carrier material with the calcite material. Although this will double the calcite mass possible to be applied per unit surface area of the laminate, it is still in an order of magnitude less compared to modules. Finally, in the case of modules, a further adjustment option is a change in their design by enlarging the number of trays and reducing the thickness of the P binding agent layer added to a single tray. This will enhance the surface area of the agent interacting with the solution, most likely causing a faster sorption (compared to using few trays with thicker layers of the reactive material, as in the design we employed in this study).
Another improvement option, applicable for both laminates and modules, is enhancing the sorption ability of the P binding agent applied. The efficiency of the calcite material can be modified in a number of ways. One of them is using synthetic calcites showing typically higher surface areas and OP capacity compared to ground limestones, at, however, a higher material cost [46,48,64]. The mechanical processing of limestones is a further option as it can boost the sorption properties of powders by modifying their granularity and surface area [61,65]. The material used in our design was mechanically activated by grinding, which increased its affinity for the OP by at least seven times (see Section 2.1). A short grinding time of 0.5 h was applied as it was practically convenient. Prolonging the grinding time or increasing the force of grinding (e.g., by modifying the grinding speed) can further boost the sorption potential [66]. Using calcite with another natural P binding agent is also possible. Amare et al. [67] enhanced the P adsorption of calcite by up to two times by combining it with dolomite. A common method for improving the CaCO3 reactivity is its calcination to produce more reactive CaO. Using this approach, Bus et al. [54] enhanced the OP uptake of eggshell waste by 80%. However, the higher reactivity of CaO means its rapid dissolution and a resulting pH increase, reaching a very high level of around 12 [54]. Although calcination offers an excellent possibility to gain efficient P removal, the strongly alkaline properties of CaO exclude this as an option in our target field of applications (lakes and other aquatic ecosystems).
At the same time, it has to be noted that in real world applications, the efficiency and kinetics of OP sorption onto modules (and laminates) will strongly depend on the actual in-lake conditions and may vary from those observed under our experimental design. Surfaces submerged in water (such as the laminates and modules tested in this study) should be expected to undergo a rapid colonization by periphyton, even within few days, as reported for example by Szłauer-Łukaszewska [68] and Joebgen et al. [69], who applied artificial structures for enhancing self-purification in water bodies. Thus, laminates or modules can be easily overgrown by aquatic organisms, including algae (assuming sufficient light access). If primary producers develop onto the modules/laminates, an additional biologically mediated OP removal can decrease the OP availability and, by this, support the performance of laminates/modules in limiting phytoplankton growth. Such a process has been reported by Joebgen et al. [69] for artificial substrates applied in lakes. Assuming the generally higher underwater area of modules, compared to laminates, this effect is to be expected to be more important in the case of modules. What is more, biological processes taking place in the ecosystem during module/laminate exposure can also affect the behavior of calcite, e.g., by promoting [70] or inhibiting mineral dissolution [71] with possible consequences for material reactivity and OP sorption. We discussed these potential interactions in Bańkowska-Sobczak et al. [41]. Furthermore, lake water properties during treatment will also influence the performance of non-invasive P removal in lakes when using calcite as a P binding agent. These are mainly temperature, pH, saturation with respect to calcite, and OP concentration, as they affect the occurrence and efficiency of OP uptake by adsorption, co-precipitation, and precipitation (see the review provided in Bańkowska-Sobczak [62]). As these parameters change in lakes with season and depth, the performance of calcite-based solutions for P inactivation and removal will depend on the timing and depth of application [41,62].
4.2. Other Effects
pH in experimental chambers generally increased during the incubation (Figure 6a). Photosynthesis could not be a reason for that in our experimental design due to a lack of light access. Therefore, we conclude the pH increased as a result of the water–air CO2 exchange due to the mixing employed (twice a day.) In the later stage of the experiment, the pH seemed to stabilize, showing either equilibrium conditions and/or increasing effects of the detritus decay as this process generally lowered the pH [70,72], in our experiment possibly preventing the pH from rising more. Importantly, throughout the incubation duration, the pH was lower in the mesocosms with modules and laminates compared to no treatment, with the lowest pH when using laminates (Figure 6a). In a natural setting, we would expect such an effect to take place due to reduced OP availability and thus limited primary production. In our experimental design, where the lake water had access to light only during short periods of the lake water mixing, this factor had to be excluded. Under our experimental conditions, the lower pH in the presence of laminates and modules could have resulted from the precipitation of calcium carbonate. The calcite layer, present on/in laminates/modules, could have worked as a surface promoting (heterogenous) precipitation of native calcium as CaCO3. Importantly, the total area of the calcium carbonate layer exposed during the experiment as laminates was about two times higher compared to that exposed as modules (1500 vs. 740 cm2). This explains the lower pH in the water treated with laminates (compared to control and modules). However, we did not detect clear signs of CaCO3 formation such as a loss of calcium or alkalinity (Figure 6b,c). The concentration of calcium was generally stable and changed in a small range between 59 and 62 mg Ca2+ L−1 (laminates and modules). Only in the treatment using laminates, a short-time increase in calcium concentration could be observed after about 3 weeks, together with a slight increase in the alkalinity (Figure 6b,c), suggesting, rather, the dissolution of calcite and not precipitation (without, however, any detectable effect on pH; Figure 6a). The saturation index with respect to calcite for the lake water was 0.4 at the beginning of the incubation but it slightly increased due to the pH rise to ca. 0.6 at the end of the incubation. Although theoretical equilibrium exists at the saturation index value of 0, the range between –0.5 and +0.5 is frequently treated as constituting equilibrium conditions, i.e., considering uncertainties resulting from measurement methods [73]. Therefore, the saturation index in our experiment (0.4–0.6) should be interpreted as equilibrium (where precipitation and dissolution balance each other) or slight oversaturation (where the precipitation theoretically prevails). Thus, the CaCO3 precipitation in mesocosms treated with laminates/modules is possible, although no other signs of this process, apart from lowering pH (compared to the control mesocosm), could be detected.
Another reason for the lower pH observed in the chambers with laminates and modules was that a physical effect occurred. Both solutions could retain the organic matter (settling from the water column). Szlauer-Łukaszewska [68], who tested underwater polypropylene sheets for enhanced self-purification in a wastewater reservoir, reported a substantial deposition of detritus on these structures. In our case, the source of the organic material could have comprised both the detritus initially present in the lake water as well as a new pool coming from the dying phytoplankton after the start of the experiment (when the light access ceased). In such a case, the decrease in pH (as affected by the decomposition of the organic material) could be more pronounced in the water column of the treatment mesocosms compared to the control, where the material could easily settle to the bottom. The water in every chamber was, however, mixed twice a day, so we expected homogeneous conditions to be provided in the water column.
At the same time, it has to be noted that the lake water properties were most likely influenced by the water–air gas exchange and processing of the organic material, so their dynamics might not have clearly reflected the possible transformations of the limestone present on laminates and modules (i.e., its dissolution), especially due to the fact that the calcium carbonate doses in the two treatments were different. What is more, the decay of organic matter and calcium carbonate behavior can be coupled. This is because the decomposition of detritus produces carbonate alkalinity by releasing inorganic carbon species. At the same time, it is supposed to promote calcium carbonate dissolution by the production of H+ ions [70]. Meanwhile, dissolved organic compounds, adsorbing on the surface of calcite, show inhibiting effects on its dissolution [74,75] similarly to biofilm developing on the mineral surface [71]. Therefore, it should be expected that the pH, concentration of calcium, and alkalinity dynamics were modified by complex processes and interactions taking place in the lake water. In large-scale applications in the field, the effect of the treatment on the lake water properties discussed here will be affected by a number of factors, similarly to the performance in OP uptake (see Section 4.1.). The possible dissolution and/or precipitation of CaCO3 (and resulting change in lake water properties) will depend on the initial and subsequent physio-chemical conditions in the lake (pH; temperature) as they affect calcite solubility, with generally higher dissolution rates if applied in deep layers (hypolimnion) [62] due to low temperature, typically lower pH, and undersaturation with respect to calcite (see the review provided in Bańkowska-Sobczak [62]). Specific substances (e.g., iron [76] or magnesium [77]) can also influence the CaCO3 transformations, thus the variability observed in field applications can be also determined by the geochemical features of lakes.
To summarize, the effects of both solutions tested, laminates and modules, on the lake water physico-chemistry were similar and mainly seen in the lake water pH, which was slightly lower (by up to 0.2 point) under both treatments compared to the control chamber. Laminates tended to decrease the lake water pH a bit more compared to modules. However, in both cases, the pH was only slightly modified and remained in a range typical for natural waters. This was in agreement with our previous studies on laminates [41], conducted under a range of environmental conditions, although in a short-term experiment only.
4.3. Possible Application and Management
The treatment of a water body using the approach proposed in this study requires the structures (laminates/modules) to be safely exposed in the water column and removed after the finished treatment. We generally imagine that these structures can be installed in water by suspending them on buoys, as schematically shown in Figure 1 in Section 1, or onto a floating platform. After the end of the operation, the modules can be cleaned of the used reactive material, refilled, and applied in the same or another location. In the case of laminates, the reuse of the carrier (laminate backing) will not be possible, which presents a challenge in terms of waste management [41].
It is also worth taking a closer look at the quantitative aspects of the application of both solutions in the aquatic environment. When expressing the experimental design for 1 m3 of lake water, we gain 0.41 m2 of the total tray surface in five modules and 0.83 m2 of laminates (11 strips with the size of 15 × 50 cm). The corresponding calcite mass values are 1.65 and 0.020 kg, respectively. To compare this with conventional methods for P immobilization in lakes, we assessed the dosages needed for treating 1 ha of a lake area. And so, assuming the lake depth of 5 m, we obtained the mass of calcite of 1 t in the case of laminates and 82 t in the case of modules. The material dosage in the case of laminates was thus comparable to that applied when using the common P binging agent, Phoslock, in a single addition, which was 1.4–6.7 t ha−1 [78]. The material consumption in the case of modules was substantially larger. Still, it was comparable to the amount of calcite needed when restoring the lake by sediment treatment. This required the formation of an active barrier on the sediment surface to prevent internal loading. The typical thickness of a calcite barrier is ca. 1 cm [46,47,79], corresponding to about 100 t per ha of the lake’s bottom, which was close to 82 t ha−1 in the case of our modules. If we need to scale the dimensions of the modules and laminates from our mesocosm experiment to field conditions, the estimated total surface area would be 40,000 m2 in the case of laminates and 20,000 m2 in the case of modules when treating the total volume of 1 ha of a lake with a depth of 5 m. Such dimensions are basically unrealistic. It is more reasonable to assume that one module should be installed, for example, for a treatment area of ca. 10 m2 of a lake surface with an adjusted mass of the P binding agent. Then we obtain 1000 modules per ha of lake, which is still a very high number, especially when considering the application and removal of these structures. Limiting the number of modules would require their loading with a higher mass for the P binding agent, which would be possible by enlarging the number of trays and/or adjusting their depth. In this light, the method proposed can be difficult to implement in large-scale applications. It may be suitable for rather small water bodies instead, or specific areas, such as the vicinities of recreational zones or inflows, polluted bays, or deep lake regions (where the OP accumulates above the sediment due to internal loading).
Although technical issues are an important challenge here, we believe that the numerous advantages of the proposed approach compensate for these difficulties. The most important benefits from implementing solutions for non-invasive P removal are the possibility of adjusting the depth and duration of the treatment and the removal of the P-loaded agent from the aquatic environment, enhancing the P export and reducing the risks of side effects of the treatment. We believe non-invasive P removal is a good direction for the development of P immobilization and removal methods to be used in aquatic environments, for minimizing potential adverse impacts and enabling the P binding agent and P reuse.
5. Summary and Conclusions
The study employed an incubation experiment in natural lake water to compare the performance of two solutions, laminates and modules, developed for non-invasive P removal from aquatic ecosystems. Both techniques enable reductions in the OP availability in the lake water and its removal from the ecosystem without the permanent deposition of the P binding agent in water bodies. Both treatments, using laminates and modules, lowered the OP concentration in the lake water for at least 6 weeks (42 days) compared to no treatment, but the performance of modules was much higher. They effectively eliminated the OP initially available in the system (present in the lake water) and further captured the OP newly supplied by the decomposition processes, showing continuous OP uptake, while laminates appeared to exhaust their fixation capacity after about 1 week. Both solutions caused only a slight pH decrease compared to the control treatment, with a minor change of up to 0.2 points. The distinctly higher efficiency and longevity of modules compared to laminates results mostly from technical design as much larger calcite mass can be applied on a carrier when using modules (the calcite dose per m2 of the surface area is 168 times higher in modules compared to laminates (4050 vs. 24 g)). To achieve a long-lasting effect (weeks, months) without the need to exchange the carriers, modules represent a more advisable solution compared to laminates. Therefore, modules have the most potential for the implementation in practice as they are able to decrease the OP concentration for relatively long time periods of weeks to months without the need to be exchanged. What is more, they offer a refillable and reusable system for P control, removal, and recovery. As modules need at least few weeks to substantially reduce the OP concentration, their application is mostly advisable before start of the vegetation season (or expected intense primary production of phytoplankton) and/or below the euphotic zone.
In the future, field tests at a semi-technical scale should be performed to verify the performance of modules and laminates under actual in-lake conditions and complex interactions with the aquatic organisms to check for possible limitations and/or synergies between non-invasive P removal techniques and native processes. Long-term (months) treatment should be employed to check for the maximum longevity of OP removal that can be gained. Further research is needed on the reuse of the binding agent and P recycling, particularly regarding the separation of reactive materials from laminates and modules, as well as the potential for P recovery or direct reuse of the P-loaded binding agent, for instance as a soil amendment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.-S., D.B., D.P.-F. and G.B.; data curation, A.B.-S., D.B. and D.P.-F.; formal analysis, A.B.-S., D.B. and D.P.-F.; funding acquisition, A.B.-S., D.B., D.P.-F. and G.B.; investigation, A.B.-S., D.P.-F., J.I., Ł.K. and W.L.; methodology, A.B.-S., D.B. and D.P.-F.; project administration, D.B. and G.B.; resources, A.B.-S., D.B., D.P.-F. and G.B.; supervision, D.B. and G.B.; validation, A.B.-S., D.B. and D.P.-F.; visualization, A.B.-S., D.B. and D.P.-F.; writing—original draft, A.B.-S. and D.B.; writing—review and editing, A.B.-S., D.B., D.P.-F., J.I., Ł.K., W.L. and G.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was funded by the European Union and Republic of Poland within the Smart Growth Operational Program 2014–2020, Priority axis I: Support for R&D activity of enterprises, R&D projects of enterprises, industrial research and development works (grant number POIR.01.01.01–00-0981/17–00).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
Krzysztof Machujski (APRS) is greatly acknowledged for his technical engagement in constructing the prototype of modules.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jakub Idźkowski and Łukasz Kozłowicz were employed by the company APRS. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health risk assessment of cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in drinking water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; García Molinos, J.; Heino, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Xu, J. Eutrophication causes invertebrate biodiversity loss and decreases cross-taxon congruence across anthropogenically-disturbed lakes. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poikane, S.; Kelly, M.G.; Free, G.; Carvalho, L.; Hamilton David, P.H.; Katsanou, K.; Lürling, M.; Warner, S.; Spears, B.M.; Irvine, K. A global assessment of lake restoration in practice: New insights and future perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Köhler, A.; Beulker, C.; Fastner, J.; van de Weyer, K.; Hegewald, T.; Hupfer, M. Decades needed for ecosystem components to respond to a sharp and drastic phosphorus load reduction. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 4621–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frątczak, W.; Michalska-Hejduk, D.; Zalewski, M.; Izydorczyk, K. Effective phosphorous reduction by a riparian plant buffer zone enhanced with a limestone-based barrier. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 130, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, A.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Baryła, A. Phosphorus reactive materials for permeable reactive barrier filling—Lifespan estimations. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 245, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowska, A.A.; Izydorczyk, K. Phosphorus Fractions Transformation in Sediments Before and After Cyanobacterial Bloom: Implications for Reduction of Eutrophication Symptoms in Dam Reservoir. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 211, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hermans, M.; Niemistö, J.; Jilbert, T. Elevated internal phosphorus loading from shallow areas of eutrophic boreal lakes: Insights from porewater geochemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamarna, M.Z.; Tandyrak, R. Lakes Restoration Approaches. Limnol. Rev. 2021, 21, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowska, J.; Augustyniak, R.; Łopata, M.; Parszuto, K.; Tandyrak, R.; Płachta, A. From Saprotrophic to Clear Water Status: The Restoration Path of a Degraded Urban Lake. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R.; Kozak, A.; Messyasz, B. Internal Phosphorus Loading from the Bottom Sediments of a Dimictic Lake During Its Sustainable Restoration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, W.M.; Richardson, R.J. Influence of Phoslock® on legacy phosphorus, nutrient ratios, and algal assemblage composition in hypereutrophic water resources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4544–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akther, F.; Cutright, T.J. Control of Cyanobacterial Algal Blooms and Soluble Reactive Phosphorus Using PAK-27 and Phoslock®. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2024, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dithmer, L.; Nielsen, U.G.; Lürling, M.; Spears, B.M.; Yasseri, S.; Lundberg, D.; Moore, A.; Jensen, N.D.; Reitzel, K. Responses in sediment phosphorus and lanthanum concentrations and composition across 10 lakes following applications of lanthanum modified bentonite. Water Res. 2016, 97, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.B.; Gibbons, H.L.; Brattebo, S.K.; Corson-Rikert, H.A. Distribution of aluminium and phosphorus fractions following alum treatments in a large shallow lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2017, 33, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterhout, F.; Waajen, G.; Yasseri, S.; Manzi Marinho, M.; Pessoa Noyma, N.; Mucci, M.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Lanthanum in Water, Sediment, Macrophytes and chironomid larvae following application of Lanthanum modified bentonite to lake Rauwbraken (The Netherlands). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, M.A.; Alperin, M.J. The efficacy of Phoslock® in reducing internal phosphate loading varies with bottom water oxygenation. Water Res. X 2021, 11, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauer, G.; Teien, H.-C. Risk of acute toxicity for fish during aluminium application to hardwater lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4020–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupfer, M.; Hilt, S. Lake Restoration. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Jørgensen, S.E., Fath, B.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 2080–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzel, K.; Andersen, F.T.; Egemose, S.; Jensen, H.S. Phosphate adsorption by lanthanum modified bentonite clay in fresh and brackish water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Mucci, M.; Lürling, M. Influence of temperature and pH on phosphate removal efficiency of different sorbents used in lake restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huser, B.J.; Egemose, S.; Harper, H.; Hupfer, M.; Jensen, H.; Pilgrim, K.M.; Reitzel, K.; Rydin, E.; Futter, M. Longevity and effectiveness of aluminum addition to reduce sediment phosphorus release and restore lake water quality. Water Res. 2016, 97, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hullebusch, E.; Deluchat, V.; Chazal, P.M.; Baudu, M. Environmental impact of two successive chemical treatments in a small shallow eutrophied lake: Part I. Case of aluminium sulphate. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, R.; Ślusarczyk, J.; Kaliszewski, T.; Szulczewski, A.; Nowacki, P. “Proteus”, a new device for application of coagulants directly to sediment during its controlled resuspension. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 2010, 30, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, J.; Anderson, M.A.; Amrhein, C. Influence of aging on phosphorus sorption to alum floc in lake water. Water Res. 2006, 40, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Qiu, B.; Lin, J. Effect of common ions aging treatment on adsorption of phosphate onto and control of phosphorus release from sediment by lanthanum-modified bentonite. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewek, A.; Rybak, M.; Drzewiecka, K.; Niedzielski, P.; Polak, J.; Klimaszyk, P. The impact of iron coagulant on the behavior and biochemistry of freshwater mussels Anodonta cygnea and Unio tumidus during lake restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.; Joniak, T. Changes in Chara hispida L. morphology in response to phosphate aluminium coagulant application. Limnol. Rev. 2018, 18, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, M.; Drzewiecka, K.; Woźniak, M.; Öksüz, S.; Krueger, M.; Sobczyński, T.; Ratajczak, I.; Joniak, T. Iron overload consequences for submerged plants stoichiometry, homeostasis and performance. Biogeochemistry 2023, 163, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, D.L.; Corman, J.; Edwards, M.; Elser, J.J. Sustainability Challenges of Phosphorus and Food: Solutions from Closing the Human Phosphorus Cycle. BioScience 2011, 61, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, A.R.; Beijer, S.; Narain, G.C.; Schipper, W.; Slootweg, J.C. Phosphorus recovery and recycling—Closing the loop. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 5, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, V.; Castillo, R.; Magrí, A.; Holzapfel, E.; Vidal, G. Phosphorus recovery from domestic wastewater: A review of the institutional framework. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łożyńska, J.; Dunalska, J.A.; Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Zhang, L.; Mitsch, W.J. Treatment of Hypolimnion Water on Mineral Aggregates as the Second Step of the Hypolimnetic Withdrawal Method Used for Lake Restoration. Minerals 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Drosos, M.; Kapsalis, V.C.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Chorus, I.; Spears, B.; Nõges, P.; Nürnberg, G.K.; Tammeorg, P.; Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Paerl, H.; Huser, B.; et al. Sustainable lake restoration: From challenges to solutions. WIREs Water 2024, 11, e1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Bus, A. Removal of phosphorus using suspended reactive filters (SRFs)—Efficiency and potential applications. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, G.; Glowczewski, J.; Cutright, T.J. Design and Preliminary Testing of an In-Field Passive Treatment System for Removing Phosphorus from Surface Water. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryputniewicz-Flis, D.; Bańkowska Sobczak, A.; Burska, D.; Idźkowski, J.; Kozłowicz, Ł.; Brenk, G. Non-invasive Removal of Phosphorus from Lakes Using Processed Calcite-Based Materials. In Chemical Lake Restoration; Zamparas, M.G., Kyriakopoulos, G.L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 145–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burska, D.; Pryputniewicz-Flis, D.; Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Brenk, G.; Woszczyk, T. The efficiency of P-removal from natural waters with sorbents placed in water permeable nonwovens. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 362, 012099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Pryputniewicz Flis, D.; Burska, D.; Idźkowski, J.; Kozłowicz, Ł.; Brenk, G. Non-invasive immobilisation and removal of phosphate from lakes using submerged laminates with calcite—Preliminary results. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, J.R. Calcium carbonate and phosphorus interactions in inland waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2025, 10, 158–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vicente, I.; Amores, V.; Cruz-Pizarro, L. Instability of shallow lakes: A matter of the complexity of factors involved in sediment and water interaction? The ecology of the Iberian inland waters: Homage to Ramon Margalef. Limnetica 2006, 25, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gunten, K.; Trew, D.; Smerdon, B.; Alessi, D.S. Natural controls on phosphorus concentrations in small Lakes in Central Alberta, Canada. Can. Water Resour. J. Rev. Can. Des Ressour. Hydr. 2022, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, H.; Wu, X.; An, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Q.; Dong, B. Relationship between the coprecipitation of phosphorus-on-calcite by submerged macrophytes the phosphorus cycle in water. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.; Roberts, S.; James, R.; Taylor, J.; Donnert, D.; Furrer, R. Use of active barriers to reduce eutrophication problems in urban lakes. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berg, U.; Nuemann, T.; Donnert, D.; Nuesch, R.; Stüben, D. Sediment capping in eutrophic lakes—Efficiency of undisturbed calcite barriers to immobilize phosphorus. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 9, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Błażejczyk, A.; Popek, Z.; Eiche, E.; Fischer, U. Phosphorus inactivation in lake sediments using calcite materials and controlled resuspension—Mechanism and efficiency. Minerals 2020, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trach, Y.; Melnychuk, V.; Trach, R. The removal of cationic and anionic pollutions from water solutions using Ukrainian limestones: Comparative analysis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 275, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, A.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Baryła, A. Calcined eggshell as a P reactive media filter-batch tests and column sorption experiment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T. Microstructural Characterization of Calcite-Based Powder Materials Prepared by Planetary Ball Milling. Materials 2013, 6, 3361–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.; Liu, X.; Rahaman, M.S.; Maruo, M. Eggshell waste as a promising adsorbent for phosphorus recovery from wastewater: A review. Water Biol. Secur. 2025, 4, 100319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, W. Boosting the phosphate adsorption of calcite by low Mg2+-Doping. Environ. Res. 2025, 267, 120692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, A.; Budzanowska, K.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Baryła, A. Raw and Calcined Eggshells as P-Reactive Materials in a Circular Economy Approach. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, L.J.; House, W.A. Precipitation of calcite in the presence of inorganic phosphate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 203, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sø, H.U.; Postma, D.; Jakobsen, R.; Larsen, F. Sorption of phosphate onto calcite; results from batch experiments and surface complexation modelling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 2911–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Putnis, C.V.; Menneken, M.; Putnis, A. Kinetics of calcium phosphate nucleation and growth on calcite: Implications for predicting the fate of dissolved phosphate species in alkaline soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, W. Phosphate uptake by calcite: Constraints of concentration and pH on the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates. Chem. Geol. 2021, 579, 120365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, H.; Rains, M.; Taşcı, Y.; Zhang, J.; Trout, K.; Lewis, D.; Das, A.; Dalton, R. Why is calcite a strong phosphorus sink in freshwater? Investigating the adsorption mechanism using batch experiments and surface complexation modelling. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trach, Y.; Trach, R. Possibility of using a mixture of calcium salts to decrease sulphate concentration and total mineralisation of surface and mine waters. Acta Sci. Pol. Archit. 2022, 21, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Hu, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, O. Activating CaCO3 to enhance lead removal from lead-zinc solution to serve as green technology for the purification of mine tailings. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bańkowska-Sobczak, A. Calcite as a candidate for non-invasive phosphorus removal from lakes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 683–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, M.; Gabriel, O.; Rutzen, C.; Koschel, R. Lake restoration by hypolimnetic Ca(OH)2 treatment: Impact on phosphorus sedimentation and release from sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1504–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnert, D.; Berg, U.; Weidler, P.G.; Nüesch, R.; Song, Y.; Salecker, M.; Kusche, I.; Bumiller, W.; Friedrich, F. Phosphorus removal and recovery from waste water by crystallization. Wasser Geotechnol. 2002, 3, 115–132. [Google Scholar]
- Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Pryputniewicz-Flis, D.; Idźkowski, J.; Kozłowicz, Ł.; Brenk, G.; Diduszko, R.; Ostrowska, A.; Burska, D. Mechanical activation of a natural calcite for enhanced orthophosphate sorption. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xiong, B.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Song, S. Effect of anions species on copper removal from wastewater by using mechanically activated calcium carbonate. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, A.; Kassa, Y.; Lemma, B.; Bhaskarwar, A.N.; Mullu, T.; Tibebe, D. Optimised phosphate adsorption using a synergistic calcite-dolomite mix: A novel approach for water treatment. Chem. Ecol. 2025, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlauer-Łukaszewska, A. Succession of periphyton developing on artificial substrate immersed in polysaprobic wastewater reservoir. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Jöbgen, A.; Palm, A.; Melkonian, M. Phosphorus removal from eutrophic lakes using periphyton on submerged artificial substrata. Hydrobiologia 2004, 528, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Wang, Y.; Wehrli, B. Cycling of calcite in hard-water lakes of different trophic states. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1678–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüttge, A.; Conrad, P.G. Direct observation of microbial inhibition of calcite dissolution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, W.E. The carbon cycle and biogeochemical dynamics in lake sediments. J. Paleolimnol. 1999, 21, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upchurch, S.; Scott, T.M.; Alfieri, M.; Fratesi, B.; Dobecki, T.L. The Karst Systems of Florida: Understanding Karst in a Geologically Young Terrain; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 93–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.M.; Clouse, J.A.; Longo, J.M. Adsorption of organic compounds on carbonate minerals: 3. Influence on dissolution rates. Chem. Geol. 1993, 109, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebron, I.; Suarez, D.L. Calcite nucleation and precipitation kinetics as affected by dissolved organic matter at 25 °C and pH > 7.5. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, W.A.; Donaldson, L. Adsorption and coprecipitation of phosphate on calcite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 112, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wu, X.; Xian, H.; Zhu, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, H.; He, H. Heterogeneous Nucleation and Growth of CaCO3 on Calcite (104) and Aragonite (110) Surfaces: Implications for the Formation of Abiogenic Carbonate Cements in the Ocean. Minerals 2020, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Meis, S.; Anderson, A.; Kellou, M. Comparison of phosphorus (P) removal properties of materials proposed for the control of sediment P release in UK lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Grace, M.R.; Sun, G.; Zou, Y. Application of ferrihydrite and calcite as composite sediment capping materials in a eutrophic lake. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).