Biomechanical Impact of Vertebral Augmentation Techniques: Clinical and Radiological Results in the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology and Literature Search Strategy
3. Specific Devices
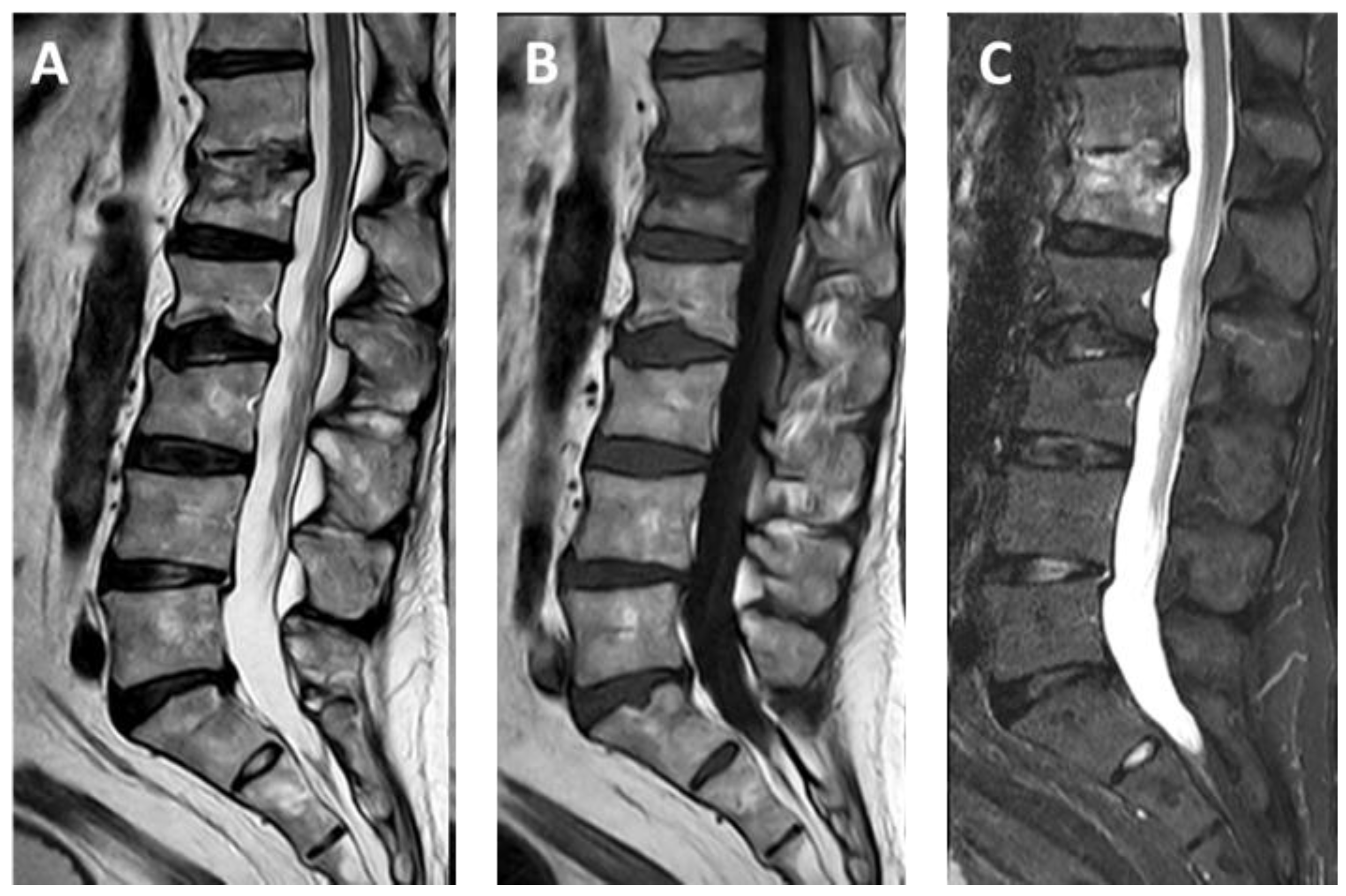
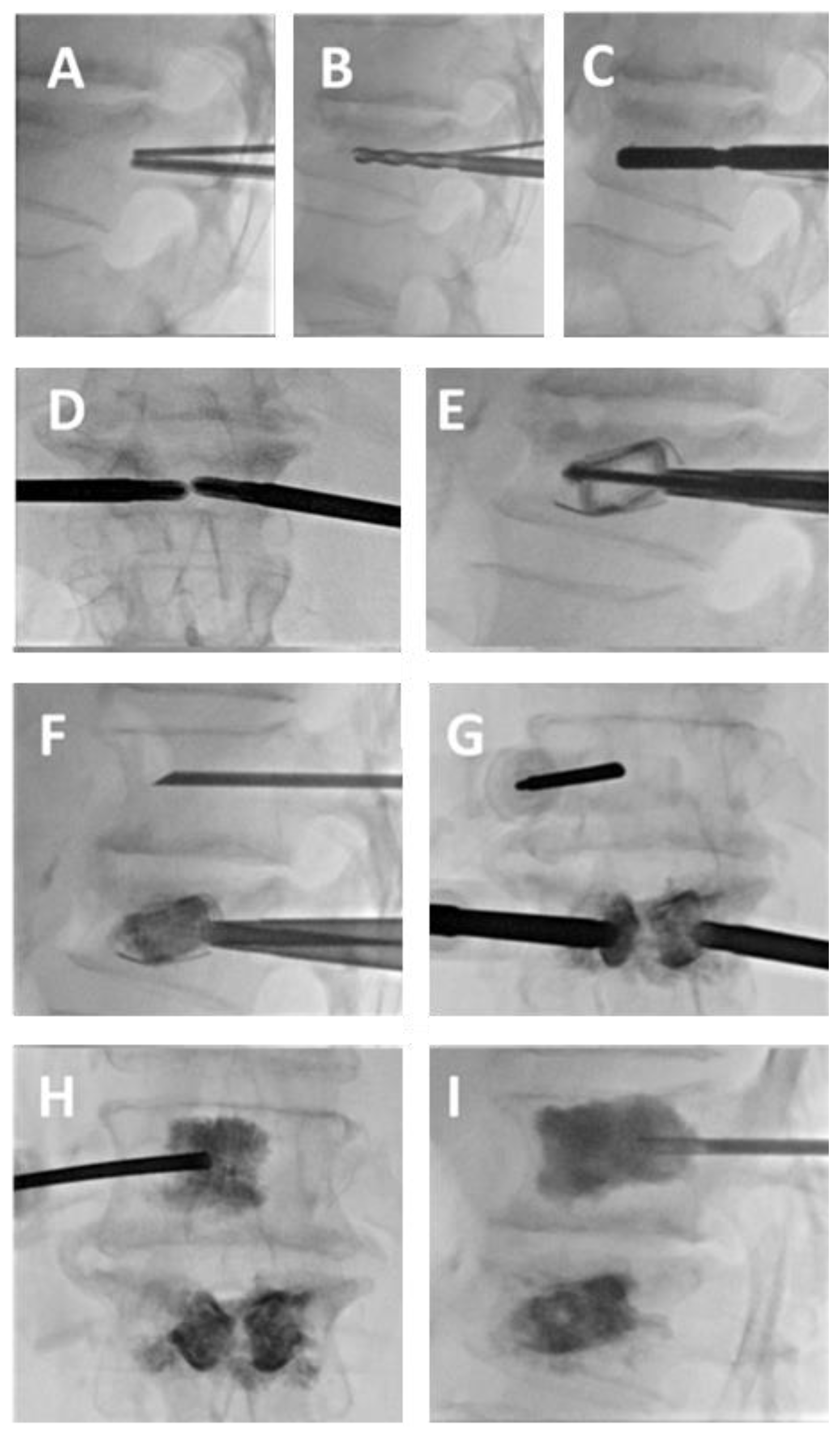
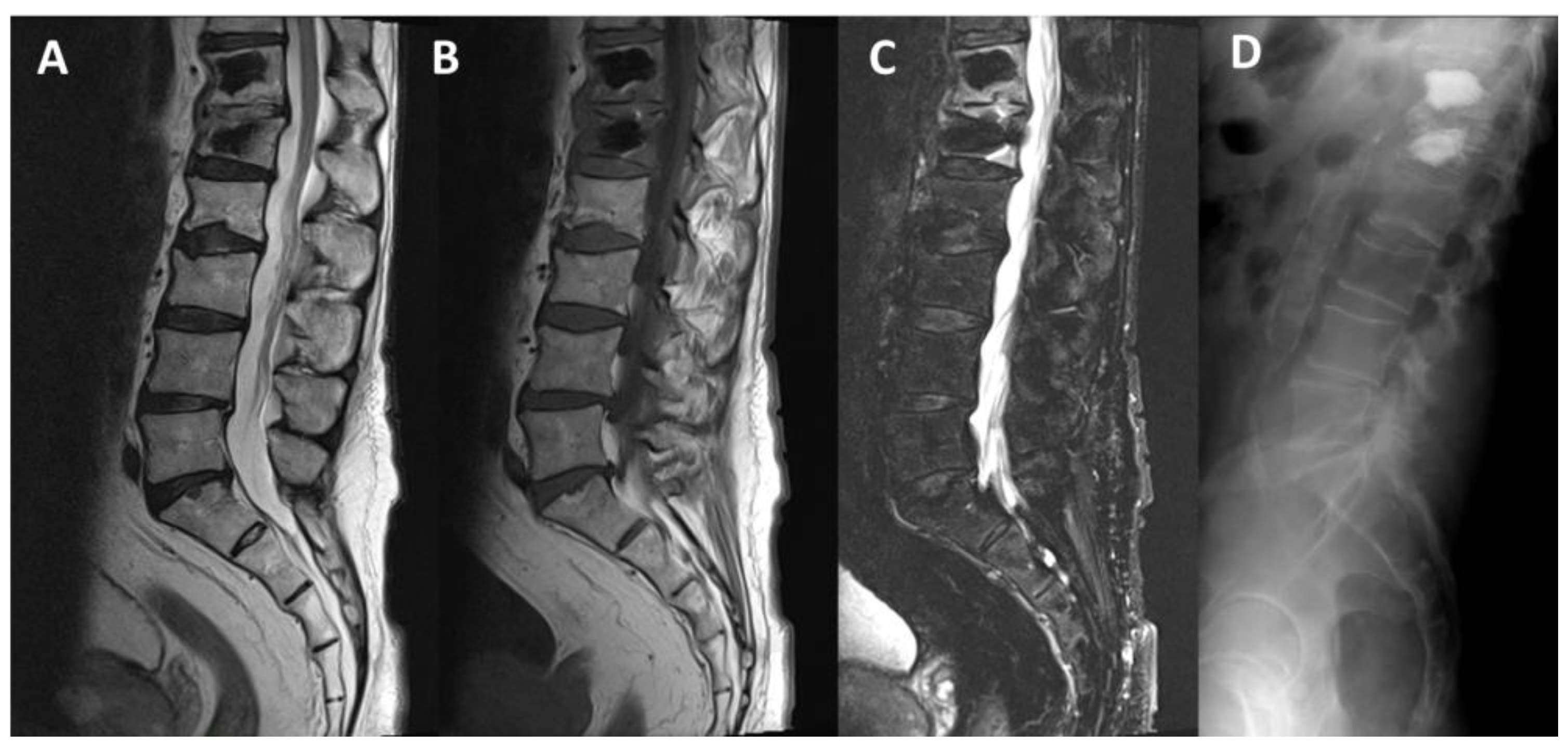
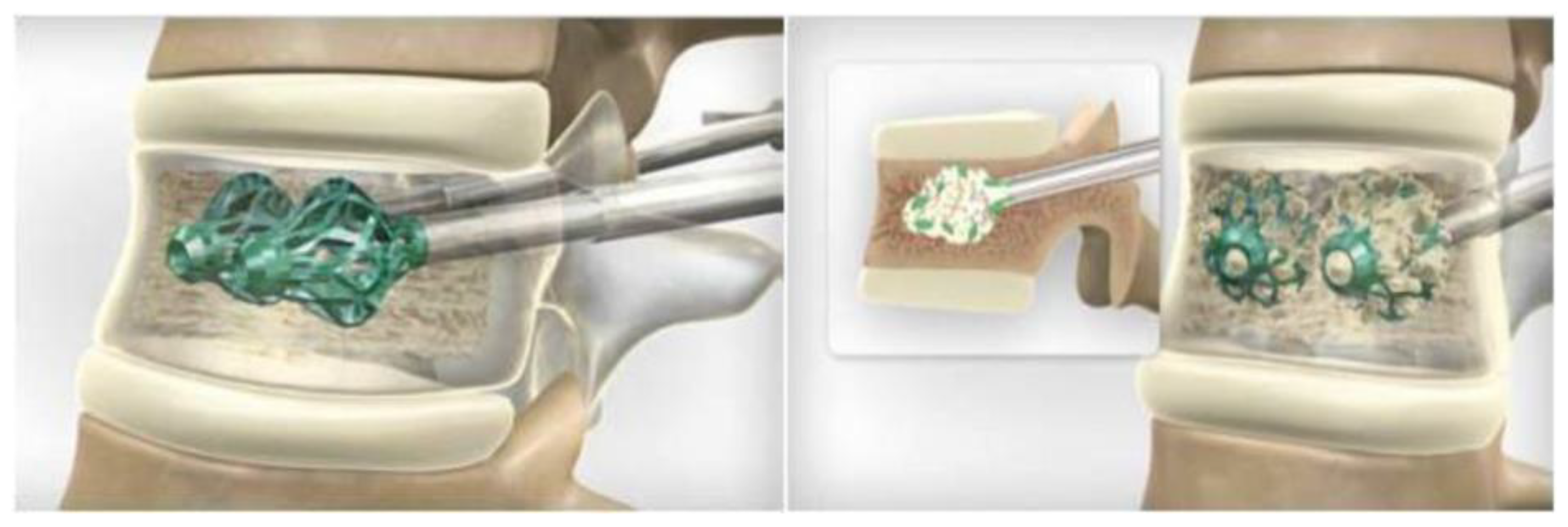
3.1. SpineJack®
3.2. Vertebral Body Stenting System®
3.3. OsseoFix®
4. Discussion
4.1. Biomechanical Impact
4.2. PVAS Devices in Tumoral Vertebral Compression Fractures
4.3. Pain Relief and Complication Rate
4.4. Combined Treatments
4.5. Cost and Justification, Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VP | Vertebroplasty |
| PVAS | Percutaneous vertebral augmentation system |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| PMMA | polymethyl methacrylate |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
References
- Galibert, P.; Deramond, H.; Rosat, P.; Le Gars, D. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie 1987, 33, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saracen, A.; Kotwica, Z. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty: An analysis of 1100 procedures performed in 616 patients. Medicine 2016, 95, e3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGirt, M.J.; Parker, S.L.; Wolinsky, J.-P.; Witham, T.F.; Bydon, A.; Gokaslan, Z.L. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures: An evidenced-based review of the literature. Spine J. 2009, 9, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Adams, M.A.; Dolan, P. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty Can Restore Normal Spine Mechanics Following Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture. J. Osteoporos. 2010, 2010, 729257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltes, C.; Fountas, K.N.; Machinis, T.; Nikolakakos, L.G.; Dimopoulos, V.; Davydov, R.; Kassam, M.; Johnston, K.W.; Robinson, J.S. Immediate and early postoperative pain relief after kyphoplasty without significant restoration of vertebral body height in acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Neurosurg. Focus 2005, 18, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, A.J.; Lee, G.L.; Keaveny, T.M. Mechanisms of initial endplate failure in the human vertebral body. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 3126–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schützenberger, S.; Schwarz, S.M.; Greiner, L.; Holub, O.; Grabner, S.; Huf, W.; Sailler, A.; Fialka, C. Is vertebral body stenting in combination with CaP cement superior to kyphoplasty? Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 2602–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, D.; Galzio, R.; Kazakova, A.; Pantalone, A.; Grillea, G.; Bartolo, M.; Salini, V.; Magliani, V. Third-generation percutaneous vertebral augmentation systems. J. Spine Surg. 2016, 2, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, D.; Krüger, A.; Ardura, F.; Hansen-Algenstaedt, N.; Hassel, F.; Barreau, X.; Beyerlein, J. Clinical Outcome After the Use of a New Craniocaudal Expandable Implant for Vertebral Compression Fracture Treatment: One Year Results from a Prospective Multicentric Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 927813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, D.; Pantalone, A.; Bigossi, F.; Pineto, F.; Lucantoni, D.; Salini, V. New perspective for third generation percutaneous vertebral augmentation procedures: Preliminary results at 12 months. J. Craniovertebral Junction Spine 2012, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Oberkircher, L.; Figiel, J.; Floßdorf, F.; Bolzinger, F.; Noriega, D.C.; Ruchholtz, S. Height restoration of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures using different intravertebral reduction devices: A cadaveric study. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disch, A.C.; Schmoelz, W. Cement augmentation in a thoracolumbar fracture model: Reduction and stability after balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebral body stenting. Spine 2014, 39, E1147–E1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fürderer, S.; Anders, M.; Schwindling, B.; Salick, M.; Düber, C.; Wenda, K.; Urban, R.; Glück, M.; Eysel, P. Vertebral body stenting. A method for repositioning and augmenting vertebral compression fractures. Orthopade 2002, 31, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.N.; Swift, A.J.; Maliakal, P.J. Single centre prospective study of the efficacy of percutaneous cement augmentation in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 27, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.M.L.; Osterhoff, G.; Schlickeiser, J.; Jenni, R.; Wanner, G.A.; Ossendorf, C.; Simmen, H.-P. Vertebral body stenting versus kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A randomized trial. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, S.A.; Wetterau, E.; Ender, M.; Kühn, J.-P.; Merk, H.R.; Kayser, R. Percutaneous Stabilization System Osseofix® for Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures—Clinical and Radiological Results after 12 Months. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschler, A.; Ender, S.A.; Ulmar, B.; Herlyn, P.; Mittlmeier, T.; Gradl, G. Cementless fixation of osteoporotic VCFs using titanium mesh implants (OsseoFix): Preliminary results. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 853897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, S.A.; Gradl, G.; Ender, M.; Langner, S.; Merk, H.R.; Kayser, R. Osseofix® system for percutaneous stabilization of osteoporotic and tumorous vertebral compression fractures—Clinical and radiological results after 12 months. Rofo 2014, 186, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandham, S.; Islim, A.; Alhamad, S.; Thambiraj, S. The outcome of expandable titanium mesh implants for the treatment of multi-level vertebral compression fractures caused by multiple myeloma. SICOT J. 2021, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upasani, V.V.; Robertson, C.; Lee, D.; Tomlinson, T.; Mahar, A.T. Biomechanical comparison of kyphoplasty versus a titanium mesh implant with cement for stabilization of vertebral compression fractures. Spine 2010, 35, 1783–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, S.A.; Eschler, A.; Ender, M.; Merk, H.R.; Kayser, R. Fracture care using percutaneously applied titanium mesh cages (OsseoFix®) for unstable osteoporotic thoracolumbar burst fractures is able to reduce cement-associated complications—Results after 12 months. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, E. Radiographic measuring methods in vertebral fractures. Hefte Unfallheilkunde 1971, 108, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Outline for the Study of Scoliosis—ScienceOpen. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/book?vid=76a12f1e-c7ef-4cc2-8aec-0904b520cd98 (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Ghofrani, H.; Nunn, T.; Robertson, C.; Mahar, A.; Lee, Y.; Garfin, S. An evaluation of fracture stabilization comparing kyphoplasty and titanium mesh repair techniques for vertebral compression fractures: Is bone cement necessary? Spine 2010, 35, E768–E773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eschler, A.; Ender, S.A.; Schiml, K.; Mittlmeier, T.; Gradl, G. Bony healing of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures in the elderly using percutaneously applied titanium mesh cages and a transpedicular fixation system with expandable screws. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzinger, F.; Oglaza, J.F.; Krüger, A.; Swider, P. Measurement of implant deployment and related forces in kyphoplasty by percutaneous approach. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krüger, A.; Baroud, G.; Noriega, D.; Figiel, J.; Dorschel, C.; Ruchholtz, S.; Oberkircher, L. Height restoration and maintenance after treating unstable osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures by cement augmentation is dependent on the cement volume used. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega, D.C.; Ramajo, R.H.; Lite, I.S.; Toribio, B.; Corredera, R.; Ardura, F.; Krüger, A. Safety and clinical performance of kyphoplasty and SpineJack® procedures in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A pilot, monocentric, investigator-initiated study. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippiadis, D.K.; Marcia, S.; Ryan, A.; Beall, D.P.; Masala, S.; Deschamps, F.; Kelekis, A. New Implant-Based Technologies in the Spine. CardioVascular Interv. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, A.; Schmuck, M.; Noriega, D.C.; Ruchholtz, S.; Baroud, G.; Oberkircher, L. Percutaneous Dorsal Instrumentation of Vertebral Burst Fractures: Value of Additional Percutaneous Intravertebral Reposition-Cadaver Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 434873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, R.; Schmitt, L.; Gierer, P.; Schmitz, K.-P.; Noriega, D.; Mittlmeier, T.; Meeder, P.-J.; Martin, H. Minimum cement volume required in vertebral body augmentation—A biomechanical study comparing the permanent SpineJack device and balloon kyphoplasty in traumatic fracture. Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, P. Diagnosis and treatment of bone disease in multiple myeloma: Spotlight on spinal involvement. Scientifica 2013, 2013, 104546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoes, J.N.; Jacobs, J.W.G.; Hulsmans, H.M.J.; De Nijs, R.N.J.; Lems, W.F.; Bruyn, G.A.W.; Geusens, P.P.M.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J. High incidence rate of vertebral fractures during chronic prednisone treatment, in spite of bisphosphonate or alfacalcidol use. Extension of the alendronate or alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis-trial. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.G.; Patel, A. Denosumab: A potential new treatment option for recurrent Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the spine. SICOT J. 2019, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoumakidou, G.; Too, C.W.; Koch, G.; Caudrelier, J.; Cazzato, R.L.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. CIRSE Guidelines on Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation. CardioVascular Interv. Radiol. 2017, 40, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikos, K.; Greggi, T.; Faldini, C.; Vommaro, F.; Scarale, A. Osteoporotic thoracolumbar compression fractures: Long-term retrospective comparison between vertebroplasty and conservative treatment. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, C.; Faiella, E.; Derudas, D.; Ballicu, N.; Melis, L.; Zedda, S.; Marsico, S. Re-expansion of vertebral compression fractures in patients with multiple myeloma with percutaneous vertebroplasty using spinejack implants: A preliminary and retrospective study. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1121981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, C.; Marsico, S.; Derudas, D.; Ballicu, N.; Melis, L.; Zedda, S.; de Felice, C.; Calabrese, A.; De Francesco, D.; Venturini, M.; et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Reconstruction (PVR) Technique of Pathological Compression Fractures: An Innovative Combined Treatment of Microwave Ablation, Bilateral Expandable Titanium SpineJack Implants Followed by Vertebroplasty. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Main Use | Material | Operating Principle | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kyphon | Treatment of recent fractures, osteoporosis, and metastasis | Elastomer | Balloon-based |
| SpineJack® | Manages both recent and older fractures, osteoporosis, metastasis | Titanium | Deformable metallic structure |
| Vertebral Body Stenting® (VBS) | Recent fractures, osteoporosis, metastasis | Titanium | Balloon combined with a deformable metallic component |
| OsseoFix® | Osteoporotic vertebral collapse | Titanium | Deformable metallic structure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faiella, E.; Vaccarino, F.; Santucci, D.; Vergantino, E.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Grasso, R.F. Biomechanical Impact of Vertebral Augmentation Techniques: Clinical and Radiological Results in the Literature. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010426
Faiella E, Vaccarino F, Santucci D, Vergantino E, Beomonte Zobel B, Grasso RF. Biomechanical Impact of Vertebral Augmentation Techniques: Clinical and Radiological Results in the Literature. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(1):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010426
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaiella, Eliodoro, Federica Vaccarino, Domiziana Santucci, Elva Vergantino, Bruno Beomonte Zobel, and Rosario Francesco Grasso. 2025. "Biomechanical Impact of Vertebral Augmentation Techniques: Clinical and Radiological Results in the Literature" Applied Sciences 15, no. 1: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010426
APA StyleFaiella, E., Vaccarino, F., Santucci, D., Vergantino, E., Beomonte Zobel, B., & Grasso, R. F. (2025). Biomechanical Impact of Vertebral Augmentation Techniques: Clinical and Radiological Results in the Literature. Applied Sciences, 15(1), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010426








