Abstract
Proper irrigation management, especially for tomatoes that are sensitive to water, is the key to ensuring sustainable tomato production. Using a low-cost sensor coupled with IoT technology could help to achieve precise control of the moisture content in the plant root-zone soil and apply water on demand with minimum human intervention. An IoT-based precision irrigation system was developed for growing Momotaro tomato seedlings inside a dark chamber. Four irrigation thresholds, 5%, 8%, 12%, and 15%, and two irrigation systems, surface and subsurface drip irrigation, were compared to assess which threshold and irrigation system referred the ideal tomato seedling growth. As a result, the 12% soil moisture threshold applied through the subsurface drip irrigation system significantly (p < 0.05) increased tomato seedling growth in soil composed of a main blend of peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite. Furthermore, in two repeated experiments, a subsurface drip irrigation system with 0.86 distribution uniformity used 10% less water than the surface drip irrigation system. The produced tomato seedlings were transplanted to open fields for further assessment. A low-power wide area networking Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) protocol was developed with remote monitoring and controlling capability for irrigation management. Two irrigation systems, including surface and subsurface drip irrigations, were used to compare which system resulted in higher tomato yields. The results showed that the subsurface drip irrigation system with 0.74 distribution uniformity produced 1243 g/plant, while each plant produced 1061 g in the surface drip irrigation system treatment. The results also indicated that the LoRaWAN-based subsurface drip irrigation system was suitable under outdoor conditions with easy operation and robust controlling capability for tomato production.
1. Introduction
Climate change, the overgrowing human population, and increasing water scarcity challenge irrigated agriculture and bring a critical time for agricultural production management in many parts of the world. Among the challenges, the impacts of climate change may further enhance drought severity, particularly in arid and semiarid regions. Ragab et al. [1] have highlighted that arid and semiarid regions, including North Africa and some parts of the middle east, may experience 20–25% rainfall reduction, especially during the dry season (April-September), by 2050. This decrease in rainfall is associated with a temperature rise of 2–2.75 °C in those areas [1]. Additionally, in the Thar Desert (India-Pakistan-Afghanistan), estimations suggest that the annual average temperature may increase from 1.75 to 2.5 °C [1]. The increase in temperature results in a higher evapotranspiration rate and plant water requirements. Higher evapotranspiration has a severe impact on vegetable production, such as tomato, which is a water-sensitive plant. Tomato is one of the most popular and water-demanding vegetables [2,3] grown across the world and has the greatest area under cultivation [4]. Water is the key factor governing tomato plant growth and yield [5,6].
Water deficit is the main factor affecting tomato crop production throughout the growing season in arid regions. The frequent watering needs for tomato crop, irrigation is the main source for meeting plant water requirements in arid regions where limited amounts of rainfall are prominent. This condition calls for adopting effective irrigation systems for tomato production by which water use efficiency is maximized while water loss is minimized. Different irrigation technologies have been practiced for growing tomatoes, including overhead irrigation systems [7,8], which are highly associated with waste of water and nutrients [9], and sub-surface irrigation technologies, which have the potential to limit runoff of water and fertilizers, but there is a chance of water loss through evaporation [10]. Furthermore, microirrigation systems, which have been shown to be a promising technology since they reduce nitrate leaching and runoff by 40–50% compared to overhead irrigation technologies [11].
Microirrigation systems, including drip irrigation, are effective irrigation technologies for growing vegetables [12]. In this type of irrigation system, water losses are usually minimized due to the high-water application efficiency and effective water delivery [2,13]. Jiang et al. [14] found that tomato yield increased by 10% using a drip irrigation system under the conditions of 50% and 55% lower water and nitrogen fertilizer applications, respectively, compared to common farming practices. Additionally, drip irrigation systems have the benefit of reducing water and N supplies while increasing water and N use efficiency as opposed to furrow irrigation systems [15]. Due to the mentioned benefits, microirrigation technology has been widely used for different crops, including broccoli [16], sugar beet [3], cucumber [17], eggplant [15], potato [18], and tomato [19]. However, the task of irrigation remains a challenge for producers. This problem can be addressed using IoT-based technology in monitoring and controlling irrigation systems. Employing IoT technologies in irrigation operations not only reduces labor requirements but also saves water by up to 90% compared with traditional irrigation practices [20]. Moreover, IoT technologies incorporating soil moisture sensors have significant potential using Arduino microcontrollers. Soil moisture reading systems with capacitive sensors connected to microcontrollers have been used in monitoring networks with LoRa (Long Range) transmission from real-time evaluation of soil permeability [21,22].
IoT-based technologies make the challenging task of irrigation easier and more precise by employing low-cost sensors and controlling modules. The system can help to obtain a precise measurement of soil moisture in the plant root zone and apply the required proportion of water at the right time. Water stress may damage metabolic processes and photosynthetic apparatuses, leading to a decrease in crop growth [23]. Ors et al. [24] found that water stress conditions can permanently damage plant growth by disrupting root and stem development and by reducing the width and number of leaves. With the presence of limited water in the root zone, plants undergo a chemical environmental change in their roots, which impacts the rate of photosynthesis [25]. On the other hand, applying an excess of water adversely affects the active oxygen metabolism of plants, which affects the photosynthetic proportion, developmental stages of plants, and crop production [26]. Liu et al. [27] studied drip irrigation scheduling for tomatoes in a greenhouse and found that pan crop coefficients of 0.9 and 1.1 had no significant impact on yield. Thus, applying the correct threshold at the right time is vital for reasonable tomato production. The amount and timing of irrigation is determined through a process called irrigation scheduling. Weighing [28,29] and modified Penman–Monteith approaches are the common irrigation scheduling methods for indoor tomato production. These methods are quite challenging due to labor, the large amount of data requirements, and being time-consuming, which make them impractical most of the time.
Additionally, most studies focused on other stages of tomato, such as vegetative, flowering, and total yield [30,31,32], and usually overlooked the seedling and germination stage, which is the most crucial stage of tomato growth since this stage will impact other stages of tomato, including total yields. Thus, under the scenario of growing water scarcity, climate change, and labor shortage, developing and employing efficient irrigation technology that runs based on cost-effective and user-friendly soil moisture sensor feedback are the key to quality and higher tomato production.
Therefore, the objective of this study was to develop a precise irrigation system to minimize water losses and determine the correct threshold for soil moisture content in an irrigation system for growing and transplanting seedlings from indoor to outdoor conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Indoor Experiments for Seedling Germination
The research was conducted at the Laboratory of Bioproduction and Machinery, Tsukuba Plant Innovation Research Center (T-PIRC), Japan. Momotaro tomato seeds, which are very famous in Japan due to their high yield and quality, were collected and used in this study. Tomato seeds were germinated inside a dark chamber in the laboratory. The dark chamber consisted of three main layers and three trays were placed in each layer (Figure 1). Soil for germination was the main blend of peat moss, vermiculite, and perlite with a pH of 6 and had a high-water holding capacity. Seeds were placed at a depth of 1 cm in the soil, and later irrigation was carried out. Throughout the germination time, environmental parameters such as air temperature, humidity, light intensity, and soil moisture conditions were monitored. Irrigation was performed using four soil moisture thresholds, 5%, 8%, 12%, and 15%, three times over the whole growing season. The moisture level was kept at 5%, 8%, 12%, and 15% or over throughout the experiment period. The experiment consisted of two main treatments comprising the irrigation system and irrigation threshold with three replications (Figure 2). Randomization of treatments was not considered since the experimental plots were adjacent to each other and water application was difficult to maintain in the small tray side by side with a different moisture content of 5%, 8%, 12%, and 15%. Additionally, the soil used for this experiment was not outdoor field soil with significant heterogeneity.
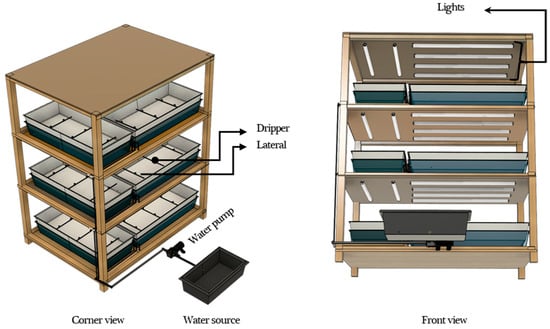
Figure 1.
3-D design and overall setup for the indoor seed germination system.
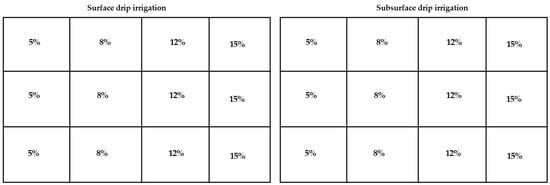
Figure 2.
Experimental arrangements of plots for indoor seedlings germination system.
Regular watering was carried out to overcome water stress. During seedling growth, no fertilizer was applied since the soil had enough nutrients for the seedlings to grow.
Light, which is another key factor governing plant growth, was evenly distributed over the seedlings, and a timer was scheduled for 15 h per day to provide them with a sufficient amount of illumination needed for ideal growth. All treatments were provided with the same growth conditions except for the moisture level, which was different for each.
2.2. Sensor Calibration
Capacitive soil moisture sensors were evaluated and calibrated using another soil moisture sensor with high accuracy. Soil samples were collected and placed inside several small cups with different moisture percentages varying from dry to saturated conditions. The readings of each sensor were recorded separately, and finally, a comparison was made between the capacitive soil moisture sensors and other soil moisture content sensors. Using the regression, the correlation and coefficient were found for each capacitive soil moisture sensor. Consequently, these coefficients were used in programming to read the sensor data and adjust them accordingly.
2.3. Sensor and Irrigation System Installation
In three layers, three trays were used in each, and in the first layer, a surface drip irrigation system was installed, while in the second layer, a subsurface drip irrigation system was installed and in the third layer both irrigation systems were installed. Individual trays were considered as a single treatment and block with three replications since each tray was partitioned into three equal size parts. Trays had small holes at the bottom to let extra water drain away and avoid water logging. Furthermore, each tray was covered by another tray to collect drainage water and consequently deduct the drained water from the total water applied during each watering time. A small water container was placed in the first layer of the chamber where irrigation lines were connected to supply water. A mainline hose crossed the first and second layers and connected to a three-way valve where various sub-mainline hoses originated from and supplied water to each tray lateral hose. Watering was carried out based on capacitive soil moisture sensor readings, and the three-way valve was manually controlled.
Six capacitive soil moisture sensors were employed in all trays, where each tray had a single sensor. Sensors were installed in the tray at 6 cm deep and 0.6 cm from the dripper and plant. All the sensors were interfaced with a low-cost data logger or microcontroller using an Arduino Uno® (ATmega328, Auduino LLC, New York, NY, USA) that was placed inside a small plastic box. In addition to the capacitive soil moisture sensors, other sensors, including a temperature and humidity sensor (DHT11), light intensity sensor (BH1750), and WiFi module (ESP8266), were connected to the microcontroller (Arduino Uno) (Figure 3). A 12 V power adopter was also connected to the relay to provide the required power for controlling the water pump. Data were uploaded onto the cloud server (ThingSpeak) in one-minute time intervals. The cloud system was used to display and store data for accessing and retrieving later. Two LED lights were allocated to every tray or in the row of tomato seeds that was illuminated by a single light.
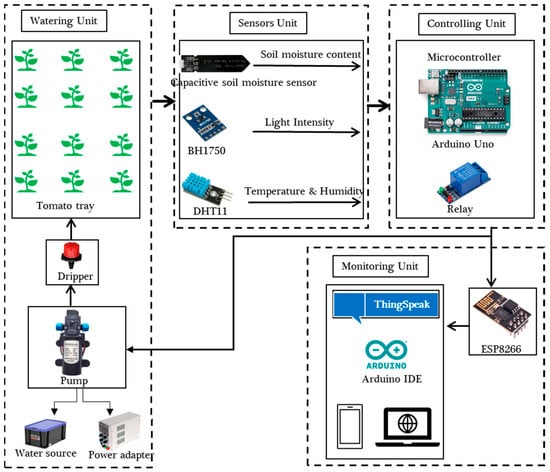
Figure 3.
Components of the IoT-based precision irrigation system for indoor seedling germination system.
2.4. IoT-Based Precision Irrigation Control System
To control the developed irrigation systems, simple codes were used to make the system user-friendly and robust. The user can log into the ThingSpeak platform by entering the username and password and can remotely know the field condition. The IoT-based precision irrigation system for indoor seedling germination was operated through relay and solenoid valves (Figure 4).
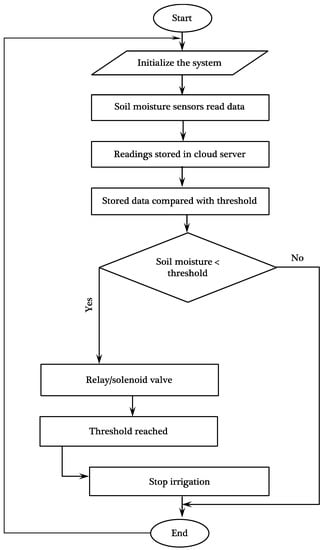
Figure 4.
Block diagram and flow chart of the IoT-based precision irrigation system for indoor seedlings germination system.
2.5. Data Analysis
After 45 days, for each tray, 9 seeds were sown, and the overall germination percentage was calculated considering the total seeds compared to how many seeds emerged in the soil. Using a ruler and digital balance, other agronomical parameters were measured. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 28® and Ms. Excel® Microsoft Office Excel 2022. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05) were carried out.
To assess the overall performance of the developed irrigation systems, distribution uniformity was calculated using the following Equation (1) [33]:
where DUiq is the irrigation distribution uniformity, Qlq is the average of the lowest quarter of the observed discharge values and Qmean is the mean of the discharge values.
Employing Equation (2) [31] helped to calculate the overall seed germination percentage and distinguish between the two irrigation systems and the soil moisture thresholds.
where GP is the overall seed germination percentage, N is the number of germinated seeds and N1 is the total number of seeds used in the germination experiment.
2.6. Data Storage and Data Sharing
The collected data using the low-cost capacitive soil moisture sensors were uploaded to the cloud server (ThingSpeak®) on a timely basis. In ThingSpeak, the data could be shared with other people by making them public or using them only for oneself. The cloud also helped to store the data and utilize them later. To build a connection between the sensors and the cloud server, information including the channel ID and write API key was used. Using the cloud platform helped to monitor the soil moisture conditions remotely and provided water whenever the seedlings needed it, which did not allow seedlings to experience water stress.
2.7. Outdoor Field Experiments for Transplanting Germinated Seedlings
In the outdoor experiments to transplant the tomato seedlings, a similar experiment was used; however, IoT-based LoRaWAN technology was employed outdoors for watering and environmental information at the experimental farm of the Tsukuba Plant Innovation Research Center (T-PIRC) (Figure 5). The experiments were conducted in an open field at T-PIRC from July to August 2022. The experimental field is located at 36° latitude and 140° longitude with an average altitude of 67 m above sea level. The soil texture of the field was clay loam. Seedlings that were grown using a subsurface drip irrigation system with a 12% threshold inside the laboratory were transplanted outside for further assessment. In the field, seedlings were transplanted in rows with a 50 cm distance between each plant and 60 cm between each row. The components of the outdoor materials and methods are described in the following sections.

Figure 5.
Experiment with an outdoor field location and LoRaWAN at the Tsukuba Plant Innovation Research Centre (T-PIRC).
2.7.1. Experimental Field Design and Layout
The experiment had two treatments: surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems with three replications each. The field was divided into two equal parts and then irrigation treatments were arranged (Figure 6). However, the treatments were not randomized due to the easy operation of the irrigation systems. Distributing irrigation systems side by side was a convenient way to perform consecutive replications in the field experiments. Further experiments with more replications are required for randomization.
Figure 6.
Experimental arrangements for the outdoor tomato seedling transplantation and germination.
The ThingSpeak® Arduino IDE system was installed to collect the data and operate the solenoid valve using a relay that was installed at the field level with drippers arranged in the surface and subsurface drip systems (Figure 7).
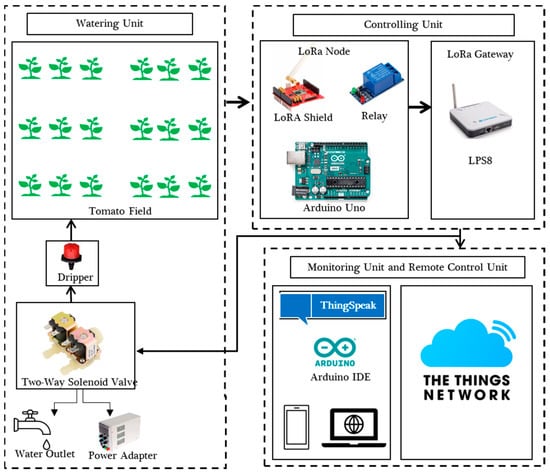
Figure 7.
Outdoor field irrigation system for tomato seedlings transplantation and production system.
2.7.2. Irrigation System Installation
In the open field, two irrigation systems comprising surface drip irrigation and subsurface drip irrigation systems were installed. Water was directed from a water outlet through a mainline hose that in turn was interfaced with a two-way solenoid valve (Figure 8). The solenoid valve was connected to the LoRa End Node that was placed inside a small waterproof box. Irrigation was carried out by sending commands from the cloud server to the end node where the irrigation system was directed to start irrigation. Each of the irrigation systems had three laterals that distributed water to drippers. In the case of the subsurface drip irrigation system, laterals were buried in the soil to a depth of 15 cm, which was the same depth as the initial depth of tomato plants. For surface drip irrigation, laterals were placed to a depth of 5 cm to protect the hose from sunlight and make them suitable for long-term use.
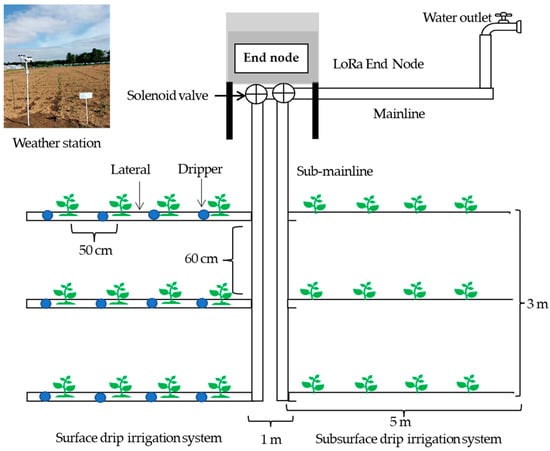
Figure 8.
Field layout and arrangement of tomato seedlings transplanted at the outdoor conditions for surface drip irrigation and subsurface drip irrigation systems.
2.7.3. Irrigation Scheduling
Irrigation was performed based on a soil water balance model where environmental parameters, including temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, solar radiation, and rainfall, were used as input data. Before calculating the irrigation requirements, the collected environmental data were used in the FAO CROPWAT to calculate the reference evapotranspiration. Later, the reference evapotranspiration was multiplied by crop coefficients to achieve crop evapotranspiration. The general equation of soil water balance is presented as follows [34]:
where Dc is the soil moisture deficit (net irrigation requirement) in the root-zone of plant for the current day, Dp is the soil moisture deficit on the previous day, ETc is the crop evapotranspiration rate for the current day, P is the gross precipitation for the current day, Irr is the irrigation amount infiltrated into the soil for the current day, U is the upflux of shallow groundwater into the root zone, SRO is the surface runoff, and DP is the deep percolation or drainage. However, in our study, we used Equation (3) [34], which is the modified version of the soil water balance equation. In our experimental field, the groundwater level was not shallow enough to contribute to the root zone water, and there was no deep percolation or surface runoff due to the use of drip irrigation systems.
2.7.4. Hardware Components
The hardware consisted of the LoRa gateway (LPS8), which had the capability of bridging 8 channels or nodes to the server simultaneously, and the LoRa node (Arduino Uno + LoRa shield), which had two-way relay channels and a 12 V solenoid valve were used in the experiment.
LoRa Gateway
The gateway used in this study was the Dragino model LPS8, which was purchased from Amazon. The gateway was placed inside the laboratory and connected to the power outlet and the internet via Wi-Fi. It has been configured with the Things Network (TTN) server.
LoRa Node
The LoRa node was built, and a LoRa shield with an antenna was stacked onto an Arduino UNO microcontroller unit. Two solenoid valves were connected to digital pins D8 and D11 of the Arduino UNO toward the LoRa node. The LoRa node firmware was set up by importing LoRaWAN-MAC-in-C (LMIC) sketch Arduino IDE software® Arduino IDE 2.1.0.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Indoor Experimental Results
In the indoor experiment, the following parameters were selected and compared to assess what irrigation soil moisture threshold and microirrigation system resulted in higher and healthier tomato seedling growth.
3.1.1. Calibration of Capacitive Soil Moisture Sensor
The capacitive soil moisture sensors were compared to soil moisture content sensors using soil samples ranging from 0% to 55%, dry and saturated conditions, respectively. It was found that capacitive soil moisture sensors with higher moisture content had better measurement accuracy compared with the moisture content sensor. The low-cost sensors used in this study were capable of detecting the general trend of the soil–water changes. As can be seen from the calibration illustrations (Figure 9), strong correlations (R2 ≥ 0.92) have been achieved. However, their measurements among the sensors varied, and this influence might be due to the texture of the soil [35,36]. It is also found that the sensors with the same physical appearance had different reading values. This problem could be overcome by conducting detailed in-situ calibrations. It was found that employing the low-cost capacitive soil moisture sensor minimized the cost and made the irrigation scheduling process efficient. Similarly, the same recommendation was made by other studies due to ease of implementation and importance [13,36].
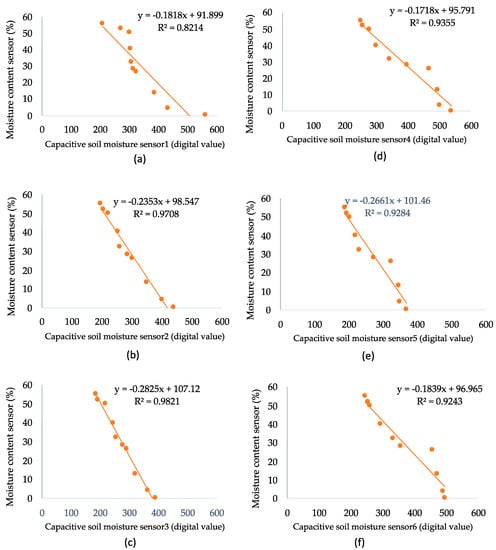
Figure 9.
(a) Relationships between moisture content sensor and capacitive soil moisture sensor 1, (b) capacitive soil moisture sensor 2, (c) capacitive soil moisture sensor 3, (d) capacitive soil moisture sensor 4, (e) capacitive soil moisture sensor 5, and (f) capacitive soil moisture sensor 6.
Additionally, the developed seed germination system provided consistent light of 15 h/day, to prepare the seedlings to adapt without any challenge whenever transplanted to outdoor conditions where the temperature might be different compared to the indoor environment. The light system helped to prevent transplanting shock, which tomato seedlings usually face when taken to outdoor environments without preparing them for outdoor conditions. This is one of the first steps that has been taken toward cutting the period that is required for tomato seedlings to be prepared and be able to adapt well to the new environment or colder temperature. Another key attempt that we made was to assess which irrigation systems and soil moisture thresholds were ideal for growing healthy tomato seedlings. By repeating the experiment twice, the results indicated that applying a 12% soil moisture threshold through a subsurface drip irrigation system increased overall tomato seedling growth. The selected agronomical parameters had a positive trend with increasing soil moisture regardless of what type of irrigation systems were used. This was mainly due to the high-water holding capacity of the soil; in the presence of greater soil moisture, plants were able to absorb the required proportion of water.
3.1.2. Environmental Conditions
Environmental parameters, including temperature, humidity, and light intensity, were monitored (Figure 10). The temperature during the experiment was quite consistent since it was in an indoor environment. Similarly, the humidity level had a slight variation in both growing seasons.
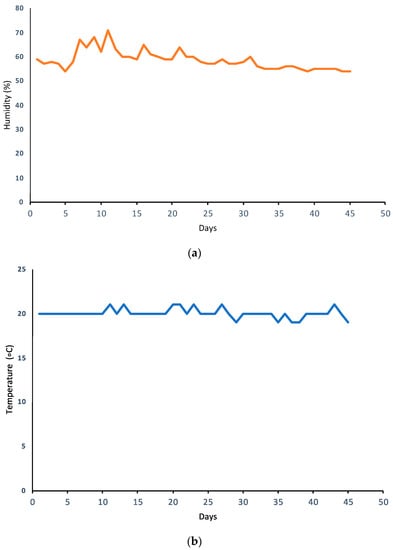
Figure 10.
Environmental conditions: (a) humidity and (b) temperature for indoor environmental conditions.
3.1.3. Agronomic Results
Agronomical parameters, including the germination percentage, root length, fresh root weight, shoot length, fresh shoot weight, and fresh seedling weight, were carried out. The reactions of the selected parameters toward the irrigation amount increased regardless of whether a surface drip irrigation system or subsurface drip irrigation system was used. The amount of water applied had a significant (p < 0.05) impact on overall germination (%), where seeds had a lower germination rate in the 5% soil moisture threshold as opposed to 8% and had a significantly lower number of seeds germinated compared to 12% and 15%. Tomato seed germination followed a positive trend with increasing soil moisture threshold in both of the experiments, particularly with the surface drip irrigation system (Table 1). In the case of the subsurface drip irrigation system, the applied amount of water also significantly (p < 0.05) impacted the seed germination rate. In the experiment, the 5% soil moisture threshold had the lowest seed germination rate, while the 12% and 15% soil moisture thresholds had the highest seed germination rate. The results of the study indicated that plant growth increased until the 12% threshold was reached because, before this percentage, the seedlings were not able to absorb enough water due to the cohesion forces of the soil particles. It also can be concluded that the 15% soil moisture threshold did not result in ideal tomato seedling production due to the presence of an excessive proportion of water where seedlings were not able to absorb the required water.

Table 1.
Effect of surface and sub-surface drip irrigation systems and four soil moisture thresholds on germination percentage, root length, fresh root weight, shoot length, fresh shoot weight, and fresh seedling weight in the first experiment.
Root length showed no significant reaction toward the amount of water applied in both the irrigation systems and experiments. On the other hand, root weight significantly increased with a greater amount of water application, especially in the surface irrigation system in the experiment.
Shoot length significantly (p < 0.05) increased with a greater rate of moisture application in the surface drip irrigation system, especially with the 12% moisture threshold, and achieved the greatest length compared to 8% and 5%. In contrast, in the experiment with the subsurface drip irrigation system, there was no significant increase observed with the four soil moisture thresholds, but in the second experiment, the seeds that were grown with the 12% soil moisture threshold developed the largest shoots, while the 5% tomato seedlings grew the shortest shoots. Moreover, 8% and 15% of the seedlings were between those two treatments.
Seedling shoots with the subsurface drip irrigation system were not considerably (p < 0.05) increased with the four soil moisture thresholds. The shot weight significantly (p < 0.05) increased with the surface drip irrigation system with 12% moisture application, followed by 5%, 8%, and 15%. Similarly, with the subsurface drip irrigation system, seedlings achieved significantly (p < 0.05) higher shoot weights, highest to lowest at 12%, 8%, 15%, and 5%, respectively. Seedling weight was not considerably (p < 0.05) affected by either the irrigation system or soil moisture thresholds.
3.1.4. Irrigation System Performance
In both experiments, surface drip irrigation showed better performance than the subsurface drip irrigation system. The low performance results of nearly 71% on average in terms of distribution uniformity in the subsurface drip irrigation system were due to the clogging problem (Table 2). The reaction of tomato seedlings varied slightly with the two microirrigation systems. Although it is commonly perceived that surface irrigation systems such as sprinklers usually result in better tomato seedling production since the seeds are placed almost close to the surface of the soil, this common assertion cannot be taken as a general assertion. The comparison results showed that using a subsurface drip irrigation system considerably (p < 0.05) impacted seedling growth. Given the concept of precision irrigation, where the input, including water, should be minimized, subsurface irrigation systems used 10% (Figure 11) less water than surface drip irrigation systems. The results of this study agreed with the work of another researcher [37]. Additionally, making the irrigation system fully automatic was also possible, but the problem could be associated with the controlling system, the time lag of sensors, unreliability in measurement [38], and the challenge of interpreting sensor data, particularly in micro irrigation systems such as drip irrigation, where the soil water distribution is heterogeneous [39]. However, there were limitations in this research to randomized small plots as the water distribution was easier to move to the adjacent plot. Additionally, the soil which was used in the experiment was not field soil with significant heterogeneity and suitable for germination. That’s why 5%, 8%, 12%, and 15% moisture level was chosen to continue the experiment.

Table 2.
Irrigation system performance in indoor and outdoor experiments.
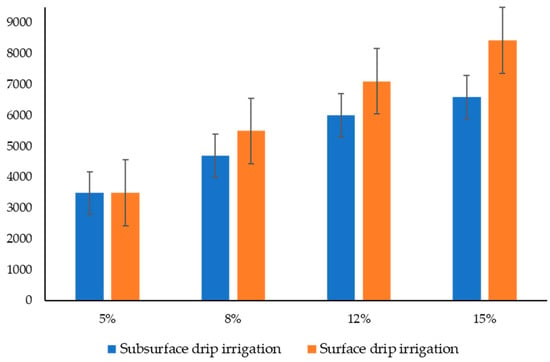
Figure 11.
The total amount of water used in the indoor seed germination system.
3.2. Outdoor Experimental Results
In the outdoor environment, the system was also assessed to determine whether the irrigation system performance had an acceptable range of efficiency. The following sections describe the experimental results under outdoor conditions when the seedlings were transplanted into the field.
3.2.1. Environmental Conditions
Environmental parameters were monitored throughout the whole season to calculate net crop water requirements. The atmospheric temperature ranged from 15 °C to 32 °C. The relative humidity varied from 62% to 96% during the experimental season (Figure 12). Due to frequent rainfall, irrigation was carried out only four times, while at other times, sufficient rainfall was occurring to fulfill tomato plant water requirements.
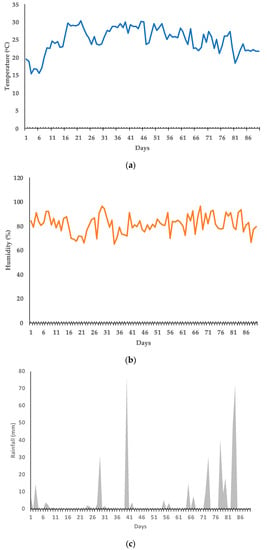
Figure 12.
Environmental parameters: (a) temperature, (b) humidity, and (c) rainfall during the tomato growing season.
3.2.2. Irrigation System Performance
Under field conditions, irrigation scheduling is commonly conducted based on three main groups: the soil–water balance method, which incorporates environmental parameters, soil water content or potential, and the method that monitors plant water status [8,24]. In this study, we carried out irrigation based on the soil–water balance equation. With this soil–water balance, an IoT system was enabled for the management of irrigation systems for monitoring throughout the growing period. In particular, the long-range controlling technology LoRaWAN was used to monitor and control precision irrigation systems. Throughout the tomato crop growing season, irrigation was carried out using The Things Network (TTN) platform without any problems. Additionally, this system needed a lower power requirement because a sleep period was set just after the completion of irrigation to minimize power consumption. Further benefits can be achieved by adding a soil moisture sensor in the outdoor environment and a water level sensor that can help the grower to know the amount of water they apply remotely. Overall, the surface drip irrigation system had better performance in terms of distribution uniformity, which was close to 0.88 (Table 2). The subsurface drip irrigation system had poor results due to clogging of the drippers or emitter. However, further field trials is required to confirm the variability of water distribution in the large plots for evaluating irrigation performances.
3.2.3. Tomato Fresh Yield
As shown in Table 2, the subsurface drip irrigation system resulted in higher tomato production. The seedling transplanting experiments under outdoor conditions had problems under local weather conditions, and rain occurred several times, which could not be adjusted for the soil–water balance method. However, in arid weather conditions, the developed system can be implemented with a long-range controlling system by adjusting weather parameters. The yield obtained by implementing this system was lower than the production level of growers producing tomatoes in Japan [40]. The low yield was mainly because the cutter pillar once attacked the tomato plants in the field. As shown in Table 3, the subsurface drip irrigation system resulted in higher tomato production. Each plant produced approximately 1243 g and 1061 g in the subsurface and surface drip irrigation systems, respectively. However, for agronomical cases, in the outdoors, further research on transplanting in different years can be conducted.

Table 3.
Total tomato fresh weight (g plant−1).
4. Conclusions
In arid conditions, tomato seedling transplantation is challenging due to the shock of transplantation by light and water stress in outdoor environments. To overcome tomato seedling transplantation shock under arid land conditions, research has been conducted to develop tomato seedling germination at a significant threshold, which can be adjusted under outdoor field conditions for higher tomato production per plant. In this research, an IoT-based sensing system was employed to develop an indoor seedling germination system where a 12% threshold of the subsurface drip irrigation system resulted in the highest seedling levels of growth based on agronomical parameters. Transplanted seedlings were grown under outdoor conditions with a comparison of two irrigation systems using soil–water balance methods with a long-range IoT control platform using the LoRaWAN system. The results showed that the subsurface drip irrigation system with 0.74 distribution uniformity produced 1243 g/plant, while each plant produced 1061 g in the surface drip irrigation system treatment. The study results suggest that a 12% soil moisture threshold was the ideal moisture content for running irrigation for tomato seedling germination and transplanting to outdoor conditions. The low-cost sensors were able to monitor the soil moisture content consistently, and the sensor measurements can be used as guidance for irrigation scheduling. In the outdoor environment, LoRa technology was capable of performing irrigation operations based on soil–water balance methods. Further research will be carried out to evaluate agronomical parameters for plant biomass development, flowering, and fruit counting systems through IoT and advanced image processing sensors during the growing periods of tomatoes under arid field conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.S. and T.A.; methodology, M.H.S.; software, M.H.S. and investigation, M.H.S. and resources T.A.; data curation, M.H.S. writing—original draft preparation, M.H.S.; writing—review and editing, T.A.; supervision, T.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that was generated and analyzed during this study can be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request, however, restrictions apply to the data reproductivity and commercially confident details.
Acknowledgments
The authors like to acknowledge Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), Project for the Promotion and Enhancement of the Afghan Capacity for Effective Development (PEACE), Batch-10 to support graduate program sponsor at the University of Tsukuba. The authors would like to thank the Tsukuba Plant Innovation Research Center (T-PIRC), University of Tsukuba, for providing facilities for conducting this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ragab, R.; Prudhomme, C. Climate change and water resources management in arid and semi-arid regions: Prospective and challenges for the 21st century. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 81, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmasarkar, E.C.; Sharmasarkar, S.; Miller, S.D.; Vance, G.F.; Zhang, R. Assessment of drip and flood irrigation on water and fertilizer use efficiencies for sugarbeets. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 46, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiymaz, S.; Ertek, A. Yield and quality of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) at different water and nitrogen levels under the climatic conditions of Kirsehir, Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangare, D.D.; Singh, Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Minhas, P.S. Growth, fruit yield and quality of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) as affected by deficit irrigation regulated on phenological basis. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.P.; Salter, P.J. Effects of different water-regimes on the growth of tomatoes under glass. Nature 1953, 171, 480–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, D. Effects of soil moisture on water transport, photosynthetic carbon gain and water use efficiency in tomato are influenced by evaporative demand. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 226, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huett, D.O. Fertiliser use effciency by containerised nursery plants 1. Plant growth and nutrient uptake. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1997, 48, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovar, D.I. Root and shoot modification by irrigation. HortTechnology 1998, 8, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, C.J.; Currey, A.; Atkinson, I.; Horticultural Research; NSW Agriculture; Nursery Industry Association of Australia. Managing Water in Plant Nurseries: A Guide to Irrigation, Drainage and Water Recycling in Containerised Plant Nurseries; NSW Agriculture: Wollongbar, NSW, Australia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Argo, W.R.; Biernbaum, J.A. The effect of irrigation method, water-soluble fertilization, replant nutrient charge, and surface evaporation on early vegetative and root growth of poinsettia. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1994, 120, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicklenton, P.R.; Cairns, K.G. Plant water relations and mineral nutrition of containerized nursery plants in relation to irrigation method. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1996, 76, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.D.; Cao, H.X.; Liu, S.Q.; Gu, X.B.; Cao, Y.X. Response of yield, quality, water and nitrogen use efficiency of tomato to different levels of water and nitrogen under drip irrigation in Northwestern China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, K.L.; Fan, Z.B.; Wei, Y.P.; Lin, S.; Wang, J.G. Simulating the fate of nitrogen and optimizing water and nitrogen management of greenhouse tomato in North China using the EU-Rotate_N model. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Song, X.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; Jiang, L.H.; Yang, J.C. Responses of agronomic benefit and soil quality to better management of nitrogen fertilizer application in greenhouse vegetable land. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aujla, M.S.; Thind, H.S.; Buttar, G.S. Fruit yield and water use efficiency of eggplant (Solanum melongema L.) as influenced by different quantities of nitrogen and water applied through drip and furrow irrigation. Sci. Hortic. 2007, 112, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, T.; Arin, L.; Erdem, Y.; Polat, S.; Deveci, M.; Okursoy, H.; Gultas, H.T. Yield and quality response of drip irrigated broccoli (Brassica oleracea L.) under different irrigation regimes, nitrogen applications and cultivation periods. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Chi, D.C.; Wang, Q.; Fang, J.; Fang, X.Y. Yield and quality response of cucumber to irrigation and nitrogen fertilization under subsurface drip irrigation in solar greenhouse. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.X.; Wu, X.X.; Shock, C.C.; Chu, L.Y.; Gu, X.X.; Xue, X. Effects of drip irrigation regimes on potato tuber yield and quality under plastic mulch in arid Northwestern China. Field Crops Res. 2011, 122, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuscu, H.; Turhan, A.; Ozmen, N.; Aydinol, P.; Demir, A.O. Optimizing levels of water and nitrogen applied through drip irrigation for yield, quality, and water productivity of processing tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 55, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Villa-Medina, J.F.; Nieto-Garibay, A.; Porta-Gándara, M.Á. Automated irrigation system using a wireless sensor network and GPRS module. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 63, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Bergonzoli, S.; Abu El Khair, D.; Comolli, R.; Ferré, C.; Bisaglia, C. Monitoring the uniformity of soil permeability for orchard precision irrigation. Acta Hortic. 2021, 1314, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Bergonzoli, S.; Bisaglia, C.; Picchio, R.; Scarfone, A. The Correlation between Proximal and Remote Sensing Methods for Monitoring Soil Water Content in Agricultural Applications. Electronics 2023, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; Long, X.; Deng, Y.; Wu, H.; Hu, J. Irrigation decision model for tomato seedlings based on optimal photosynthetic rate. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ors, S.; Ekinci, M.; Yildirim, E.; Sahin, U.; Turan, M.; Dursun, A. Interactive effects of salinity and drought stress on photosynthetic characteristics and physiology of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) seedlings. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 137, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.H.; Li, M.N.; Cai, Z.L.; Zhao, R.S.; Hong, T.T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Optimal irrigation and fertilizer amounts based on multi-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of yield, growth and fruit quality on cherry tomato. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkelish, A.A.; Alhaithloul, H.A.S.; Qari, S.H.; Soliman, M.H.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Pretreatment with Trichoderma harzianum alleviates waterlogging-induced growth alterations in tomato seedlings by modulating physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 171, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Duan, A.-W.; Li, F.-S.; Sun, J.-S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Sun, C.-T. Drip irrigation scheduling for tomato grown in solar greenhouse based on pan evaporation in North China plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.D.; Sinclair1, T. The effect of pot size on growth and transpiration of maize and soybean during water deficit stress. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, I.J.; De Datta, S.K.; Steponkus, P.L. Effect of water deficit stress on diffusive resistance, transpiration, and spikelet desiccation of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ann. Bot. 1993, 72, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibomana, I.C.; Aguyoh, J.N.; Opiyo, A.M. Water stress affects growth and yield of container grown tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) plants. GJBB 2013, 2, 461–466. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Omran, A.M.; Al-Harbi, A.R.; Wahb-Allah, M.A.; Mahmoud, N.; Al-Eter, A. Impact of irrigation water quality, irrigation systems, irrigation rates and soil amendments on tomato production in sandy calcareous soil. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2010, 34, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yoshida, H.; Goto, E.; Hikosaka, S. Development of an Irrigation Method with a Cycle of Wilting–Partial Recovery Using an Image-Based Irrigation System for High-Quality Tomato Production. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ella, V.B.; Reyes, M.R.; Yoder, R. Effect of Hydraulic Head and Slope on Water Distribution Uniformity of a Low-Cost Drip Irrigation System. 2008. Available online: www.oired.vt.edu (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Andales, A.A.; Chávez, J.L.; Bauder, T.A. Irrigation Scheduling: The Water Balance Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, R.; Pringle, H.C.; Barnes, E.M. Evaluation of soil moisture sensors. In Proceedings of Irrigation Show and Education Conference; Irrigation Association: Falls Church, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Qi, Z.; Burghate, R.; Yuan, S.; Jiao, X.; Xu, J. Irrigation scheduling approaches and applications: A review. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, A.A.; Abdel-Fattah, G.M.; Elhindi, K.M. Improving growth, flower yield, and water relations of snapdragon (Antirhinum majus L.) plants grown under well-watered and water-stress conditions using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Photosynthetica 2012, 50, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolz, R.; Kammerer, G. Evaluating a sensor setup with respect to near-surface soil water monitoring and determination of in-situ water retention functions. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaloglou, S.; Soulis, K.X.; Dercas, N. Simulation of soil water dynamics under surface drip irrigation from equidistant line sources. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4131–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashide, T.; Heuvelink, E. Physiological and morphological changes over the past 50 years in yield components in tomato. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2009, 134, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).