Bisphosphonates and Their Influence on the Implant Failure: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Focused Question
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
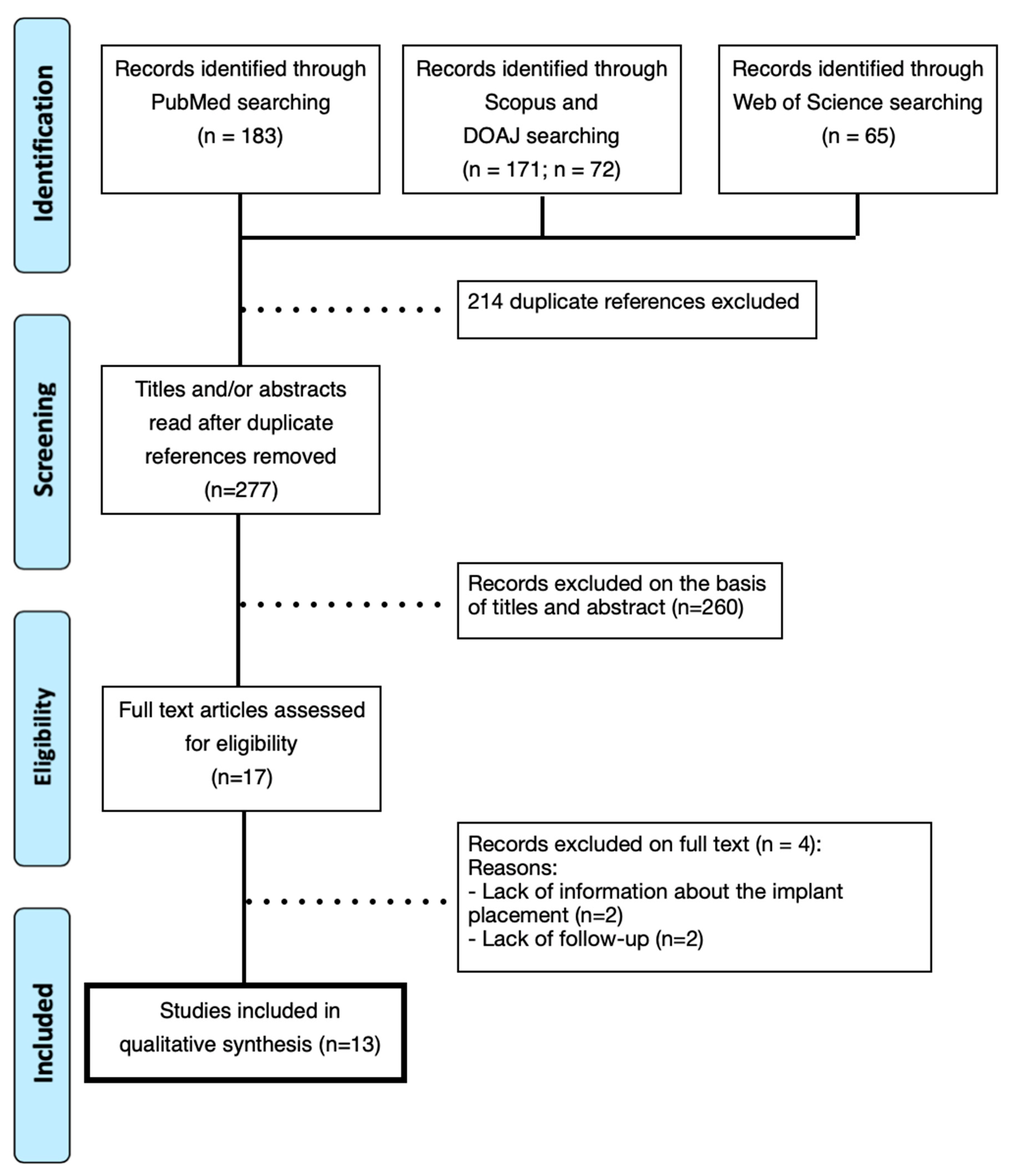
2.3. Literature Search and Screening
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Quality Assessment
3. Results
| Authors (Year) | Country | Research Question | Patient Information | Design (n) | Pacient Status/Implant | N. of Implants Assessed (Site) | Risk Factors | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flieger (2019) [15] | Poland | Placement of two missing teeth with insertion of immediate implants in a patient medicated with BPs | F, 56 yo | n = 1; case report | Absence of bone loss in both implants; normal peri-implant soft tissue condition (no signs of inflammation) | 2 (15, 24) | Hypertension | implant survival |
| 2 | Bayani et al. (2019) [21] | Iran | Report of implant placement in a patient with MRONJ | M, 54 yo | n = 1; case report | Minimal bone loss | 1 (14) | Non-smoking, good oral hygiene | implant survival |
| 3 | Holzinger et al. (2014) [14] | Austria | Development of MRONJ in patients treated with BPs who received implants. | F; average of 65.7 ± 8.5 yo | n = 13; retrospective study | NR | 1 (47) | 7 former smokers; and 5 smokers | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 4 | Tripodakis et al. (2012) [16] | Greece | Care in the placement of implants and prevention of MRONJ in patients with BP therapy | F, 70 and 65 yo | n = 2; case report | No observed complications | 3 (14, 15, 17) 14 (13, 14, 16, 17, 25, 26, 27, 28, 36, 37, 38, 46, 47, 48) | 1 with hypertension and hyperlipidemia | implant survival |
| 5 | Caicedo-Rubio et al. (2017) [23] | Spain | Insertion of implants in a patient treated with IV bisphosphonates | M, 61 yo | n = 1; case report | Generalized gingival inflammation; peri-implant tissues without inflammation; loss of 1.25 mm of crestal bone in the implant area 36 | 3 (36, 37, 46) | Smoker (20 cigarettes/day); Stroke prior to 2007; poor oral hygiene | implant survival |
| 6 | Favia et al. (2015) [22] | Italy | Patient with breast cancer affected by MRONJ | F, 66 yo | n = 1; case report | Pain; purulent secretion; right-sided inferior alveolar nerve paresthesia | 7 (16, 31, 35, 36, 41, 44, 46) | Poor oral hygiene | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 7 | Junquera et al. (2011) [24] | Spain | Mandibular dental implant placement in a patient with MRONJ | M, 59 yo | n = 1; case report | Left lower lip paresthesia; purulent discharge; necrotic bone | 2 | NR | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 8 | Kwon et al. (2014) [17] | Korea | Analysis of MRONJ characteristics around dental implants | 2 M, 17 F; 42 to 85 yo | n = 19; prospective study | Necrotic bone exposure, purulent discharge; fistula; swelling for more than 8 weeks | 23 | Hypertension; and Diabetes | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 9 | Shirota et al. (2009) [25] | Japan | MRONJ around implants in maxillary molars | F, 54 yo | n = 1; case report | Pain; bone exposure; redness; swelling | 3 (15, 25, 27) | NR | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 10 | Yajima et al. (2017) [18] | Japan | BMD and influence of the use of BPs on early implant failure | F, >60 yo | n = 11; retrospective study | NR | 25 | Diabetes, smoking, steroid, poor oral hygiene were excluded | Implant survival and failure cases |
| 11 | Favia et al. (2011) [26] | Italy | Occurrence of MRONJ after implant insertion | F, 65 yo | n = 1; case report | non-loading | 2 (35, 36) | No pre-existing bone lesions | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 12 | Jacobsen et al. (2013) [19] | Switzerland | Report of 14 patients with mandibular osteopathology associated with BP therapy and dental implant insertion | 11 F and 3 M | n = 14; case series | purulent; periapical radiolucency surrounding the implants | 23 | NR | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| 13 | Storelli et al. (2019) [20] | Italy | MRONJ after implant placement in a patient undergoing oral BF therapy | F, 77 years old | n = 1; case report | Necrotic bone; pain; abscess; nerve paresthesia; fistula; exposed bone; lack of healing | 8 | Non-smoking, hypothyroidism, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, arterial fibrillation | Implant failure (MRONJ) |
| Authors (Year) | BP Type | BP Generation | Route of Administration | Antibiotic Treatment | Duration | Patient/Implant Status | Type of the Dental Implant | Risk Factors | Implant Failure Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Flieger (2019) [15] | Alendronate | 2nd | Oral 70 mg/week for 24 months | Before surgery amoxicillin + clavulanic acid. 1000 mg day/7 days | No discontinuation | Absence of bone loss; normal condition of peri-implant soft tissue (no signs of inflammation) | ICX-plus (3.45 × 10 mm) at bone level | Hypertension | 0% |
| 2 | Bayani et al. (2019) [21] | Zoledronate | 3rd | IV 3.5 mg/month for 22 months | Before surgery 2g amoxicillin/clavulanic acid. After: 1000 mg 2×/day/7 days | Discontinued 6 months before surgery and resumed 8 months after | Minimal bone loss | Superline; Dentium (3.6 × 10 mm) | Non-smoking, good oral hygiene | 0% |
| 3 | Holzinger et al. (2014) [14] | Zolendronate (n = 7) Alendronate (n = 3) Pamidronate (n = 2) Ibandronate (n = 1) | 3rd (n = 8) 2nd (n = 5) | 7—IV 4 mg/month 3—Oral 70 mg/week 2—Oral 90 mg/month 1—IV 3 mg each 3 months | NR | 3—BPs after implant placement 3—BPs before implant placement 7—BPs before and after implant placement | NR | NR | 7 former smokers; and 5 smokers | 63.8% |
| 4 | Tripodakis et al. (2012) [16] | Risedronate Alendronate | 2nd 3rd | 1—Oral for 2 months 1—Oral for 4 years | 24h before surgery 500 mg of amoxicillin up to 10 days after surgery | Discontinued 3 months before surgery and resumed 3 months after surgery | No complications observed | Branemark System Mk III Groovy a 13 mm; SPI, Alpha Bio 16 mm | 1 with hypertension and hyperlipidemia | 0% |
| 5 | Caicedo-Rubio et al. (2017) [23] | Zoledronate | 3rd | IV 5 mg each 6 months for 4 years | Before surgery, amoxicillin 500 mg every 8 h until 6 days after surgery | Discontinued 2 months before surgery and resumed 1 month after | Generalized gingival inflamation; peri-implants good health; 1.25 mm loss of of crestal bone in the implant area 36 | MIS Implants Technologies LTD 7.5 × 10 mm and 75 × 11.5 mm subcrestal | Smoker (20 cigarettes/day); Stroke prior to 2007; poor oral hygiene | 0% |
| 6 | Favia et al. (2015) [22] | Zoledronate | 3rd | IV 4 mg monthly for 33 months | NR | 6 months after implant placement | Pain; pus secretion; right inferior alveolar nerve paresthesia | NR | Poor oral hygiene | 57.1% |
| 7 | Junquera et al. (2011) [24] | Zoledronate | 3rd | IV 4 mg monthly | NR | 9 months after implant placement | Lower left labial paraesthesia; purulent secretion; necrotic bone | Endosseous dental implants | NR | 50% |
| 8 | Kwon et al. (2014) [17] | Zolendronate Alendronate Ibandronate Risedronate | 3rd 2nd | Oral ou IV | NR | Started before surgery (n = 16) and after (n = 3) | Necrotic bone exposure, pus secretion; fistula; swelling for more than 8 weeks | NR | Hypertension; and Diabetes | 15.8% |
| 9 | Shirota et al. (2009) [25] | Pamidronate Zolendronate | 2nd 3rd | IV (P 17 times and Zolendronate 9 times) in 16 months | NR | 4 years after implant placement | Pain; bone exposure; redness; swelling | NR | NR | 66.7% |
| 10 | Yajima et al. (2017) [18] | Alendronate | 2nd | Oral | NR | No discontinuation. Using BF: 3.8 + 2.1 years | NR | NR | Diabetes, smoking, steroid, poor oral hygiene were excluded | 12% |
| 11 | Favia et al. (2011) [26] | Clodronate | 1st | IV 300 mg twice a month | NR | Discontinuation 3 months before surgery | Purulent secretion; periapical radioluscency surrounding the implants | NR | No pre-existing bone lesions | 100% |
| 12 | Jacobsen et al. (2013) [19] | 9—Zoledronate 2—Alendronate 1—Ibandronate 2—Pamidronate | 2nd 3rd | IV e Oral in 3 months | NR | NR | Necrotic bone; ache; abscess; nerve paraesthesia; fistula; exposed bone; no healing | NR | NR | 100% |
| 13 | Storelli et al. (2019) [20] | Alendronate | 2nd | Oral 70 mg once a week | NR | No discontinuation. Use started 3 years before surgery | Inflamed peri-implant tissues; bleeding on probing; bone resorption < 2 mm around implants; purulent secretions; exposure of necrotic bone; mobility | NR | Non-smoking, hypothyroidism, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, arterial fibrillation | 100% |
4. Discussion
4.1. BP Use and Dental Implants
4.2. Dental Implants Characteristics
4.3. Implants Associated with Risk Factors
4.4. MRONJ and Route of Administration
4.5. MRONJ and Implant Failure
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayesh, R.S.; Dhinakarsamy, V. Osseointegration. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, H.; Correia, A.R.M.; Castilho, R.M.; Fernandes, G.V.O. Zirconia Implants and Marginal Bone Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2020, 35, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.V.O.; Costa, B.M.G.N.; Trindade, H.F.; Castilho, R.M.; Fernandes, J.C.H. Comparative analysis between extra-short implants (≤6 mm) and 6 mm-longer implants: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Aust. Dent. J. 2022, 67, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.R.E.; Otero, A.I.P.; Fernandes, J.C.H.; Nassani, L.M.; Castilho, R.M.; Fernandes, G.V.O. Clinical Performance Comparing Titanium and Titanium-Zirconium or Zirconia Dental Implants: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Zirconia versus titanium in dentistry: A review. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, K.; Chopra, A.; Narayan, A.I.; Balakrishnan, D. Is zirconia a viable alternative to titanium for oral implant? A critical review. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2018, 62, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, S.; Drake, M.T.; Ebetino, F.H.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Russell, R.G.G. Pharmacology of bisphosphonates. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S. Application of bisphosphonates in dentistry: A review of literature. Indian J. Public Health Res. Dev. 2019, 10, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelazius, R.; Poskevicius, L.; Sakavicius, D.; Grimuta, V.; Juodzbalys, G. Dental Implant Placement in Patients on Bisphosphonate Therapy: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2018, 9, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, N.R.; Lima, L.B.; Moura, M.B.; Veloso-Guedes, C.C.F.; Simamoto-Júnior, P.C.; Magalhães, D. Bisphosphonate treatment and dental implants: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2016, 21, e644–e651. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Xie, D. Zoledronic acid enhances bone-implant osseointegration more than alendronate and strontium ranelate in ovariectomized rats. Osteoporos Int. 2013, 24, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, F.G.; Pansani, T.N.; Soares, D.G.; Cardoso, L.M.; Hebling, J.; de Souza Costa, C.A. Influence of bisphosphonates on the adherence and metabolism of epithelial cells and gingival fibroblasts to titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, D.; Seemann, R.; Matoni, N.; Ewers, R.; Millesi, W.; Wutzl, A. Effect of dental implants on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, R. Bilateral bone ridge splitting in maxilla with immediate implant placement in a patient with osteoporosis: A clinical report with 2-year follow-up. Case Rep. Dent. 2019, 6, 1458571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodakis, A.P.; Kamperos, G.; Nikitakis, N.; Sklavounou-Andrikopoulou, A. Implant therapy on patients treated with oral bisphosphonates. J. Osseointegration 2012, 4, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, T.G.; Lee, C.O.; Park, J.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Rijal, G.; Shin, H.I. Osteonecrosis associated with dental implants in patients undergoing bisphosphonate treatment. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, N.; Munakata, M.; Fuchigami, K.; Sanda, M.; Kasugai, S. Influence of bisphosphonates on implant failure rates and characteristics of postmenopausal woman mandibular jawbone. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 43, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.; Metzler, P.; Rössle, M.; Obwegeser, J.; Zemann, W.; Grätz, K.W. Osteopathology induced by bisphosphonates and dental implants: Clinical observations. Clin. Oral Investig. 2013, 17, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, S.; Storelli, S.; Palandrani, G.; Dondi, C.; Tagliatesta, L.; Rossi, A. Severe case of Osteonecrosis following implant placement in a patient in therapy with bisphosphonates: A case report. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 45, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayani, M.; Anooshirvani, A.A.; Keivan, M.; Mohammad-Rabei, E. Dental implant in a multiple myeloma patient undergoing bisphosphonate therapy: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favia, G.; Tempesta, A.; Limongelli, L.; Crincoli, V.; Piattelli, A.; Maiorano, E. Metastatic breast cancer in medication-related osteonecrosis around mandibular implants. Am. J. Case Rep. 2015, 16, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo-Rubio, M.; Ferrés-Amat, E.; Ferrés-Padró, E. Implant-supported fixed prostheses in a Patient with Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A 4-year follow-up. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e1482–e1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junquera, L.; Gallego, L.; Pelaz, A. Multiple Myeloma and Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Mandible Associated with Dental Implants. Case Rep. Dent. 2011, 2011, 568246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirota, T.; Nakamura, A.; Matsui, Y.; Hatori, M.; Nakamura, M.; Shintani, S. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw around dental implants in the maxilla: Report of a case: Case Report. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favia, G.; Piattelli, A.; Sportelli, P.; Capodiferro, S.; Iezzi, G. Osteonecrosis of the Posterior Mandible after Implant Insertion: A Clinical and Histological Case Report. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2011, 13, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, J.A.; Cooper, C.; Rizzoli, R.; Reginster, J.Y. Correction to: European guidance for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2020, 31, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, N.E. Epidemiology, etiology, and diagnosis of osteoporosis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 194, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.J.; Begoña, L.; Anitua, E.; Cobos, R.; Orive, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of alendronate and zoledronate for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2013, 29, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaloo, T.; Pi-Anfruns, J.; Moshaverinia, A.; Sim, D.; Grogan, T.; Hadaya, D. The Effects of Systemic Diseases and Medications on Implant Osseointegration: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2019, 34, s35–s49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämmerle, C.H.; Brägger, U.; Bürgin, W.; Lang, N.P. The effect of subcrestal placement of the polished surface of ITI implants on marginal soft and hard tissues. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1996, 7, 11–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Chover, H.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Gomar-Vercher, S.; Agustín-Panadero, R.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M. Impact of crestal and subcrestal implant placement in peri-implant bone: A prospective comparative study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2016, 21, e103–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Wang, H.L. Medical contraindications to implant therapy: Part I: Absolute contraindications. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Participants (P) | Patients using bisphosphonates |
| Intervention (I) | Placement of one or more dental implants |
| Control (C) | Different generations and administration routes of BFs |
| Outcomes (O) | Dental implant failure rate |
| Database | Equation Implemented | Filters |
|---|---|---|
| Pubmed/ MEDLINE | ((((((((((((diphosphonates [MeSH Terms]) OR bisphosphonates [MeSH Terms]) OR clodronate [MeSH Terms]) OR etidronate [MeSH Terms]) OR alendronate [MeSH Terms]) OR pamidronate [MeSH Terms]) OR risedronate [MeSH Terms]) OR ibandronate [MeSH Terms]) OR “bisphosphonate- associated osteonecrosis of the jaw” [MeSH Terms]) OR tiludronate) OR neridronate) OR minodronate) OR zoledronate AND (osseointegration OR dental implants [MeSH Terms]) | In English, from January 2000 to December 2021, humans |
| Scopus | ALL ((diphosphonates OR bisphosphonates OR clodronate alendronate OR risedronate OR bisphosphonate-associated AND osteonecrosis AND jaw) OR tiludronate OR neridronate OR etidronate OR pamidronate OR ibandronate OR (minodronate OR zoledronate) AND (osseointegration OR dental AND implants) AND (failure AND rate)) AND PUBYEAR > 1999 AND PUBYEAR < 2022 AND (LIMIT-TO (PUBSTAGE, “final”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Humans”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, “English”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (SRCTYPE, “j”)) | In English, from January 2000 to December 2021, humans, final stage |
| Web of Science | (diphosphonates OR bisphosphonates OR clodronate OR etidronate OR alendronate OR pamidronate OR risedronate OR ibandronate OR (bisphosphonate-associated AND osteonecrosis AND of AND the AND jaw) OR tiludronate OR neridronate OR minodronate OR zoledronate) AND (osseointegration OR dental implants) AND failure (All Fields) | In English, from January 2000 to December 2021 |
| DOAJ | (diphosphonates OR bisphosphonates OR clodronate OR etidronate OR alendronate OR pamidronate OR risedronate OR ibandronate OR (bisphosphonate-associated AND osteonecrosis AND of AND the AND jaw) OR tiludronate OR neridronate OR minodronate OR zoledronate) AND (osseointegration OR dental implants) AND failure (All Fields) | In English, from January 2000 to December 2021, humans |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebelo, C.G.; Fernandes, J.C.H.; Bernardo, N.; Couto, P.; Fernandes, G.V.O. Bisphosphonates and Their Influence on the Implant Failure: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063496
Rebelo CG, Fernandes JCH, Bernardo N, Couto P, Fernandes GVO. Bisphosphonates and Their Influence on the Implant Failure: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(6):3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063496
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebelo, Cristiana Gomes, Juliana Campos Hasse Fernandes, Nuno Bernardo, Patrícia Couto, and Gustavo Vicentis Oliveira Fernandes. 2023. "Bisphosphonates and Their Influence on the Implant Failure: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 13, no. 6: 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063496
APA StyleRebelo, C. G., Fernandes, J. C. H., Bernardo, N., Couto, P., & Fernandes, G. V. O. (2023). Bisphosphonates and Their Influence on the Implant Failure: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063496










