A Multi-Scale Cross-Fusion Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Attention Mechanism Transformer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose the DAT module, which can focus on both internal attention and external attention and helps to enhance the correlation between different samples.
- Through a multi-scale feature fusion method, the feature information of different scales is effectively combined, and the effective information is fully preserved.
- A pure Transformer structure, DAT-Unet, for medical image segmentation is designed, and the effectiveness of our method is proved on two different public datasets. Compared to other methods, our method has many advantages.
2. Relate Work
2.1. CNN-Based Methods
2.2. Transformer-Based Methods
2.3. Skip Connection
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Architecture
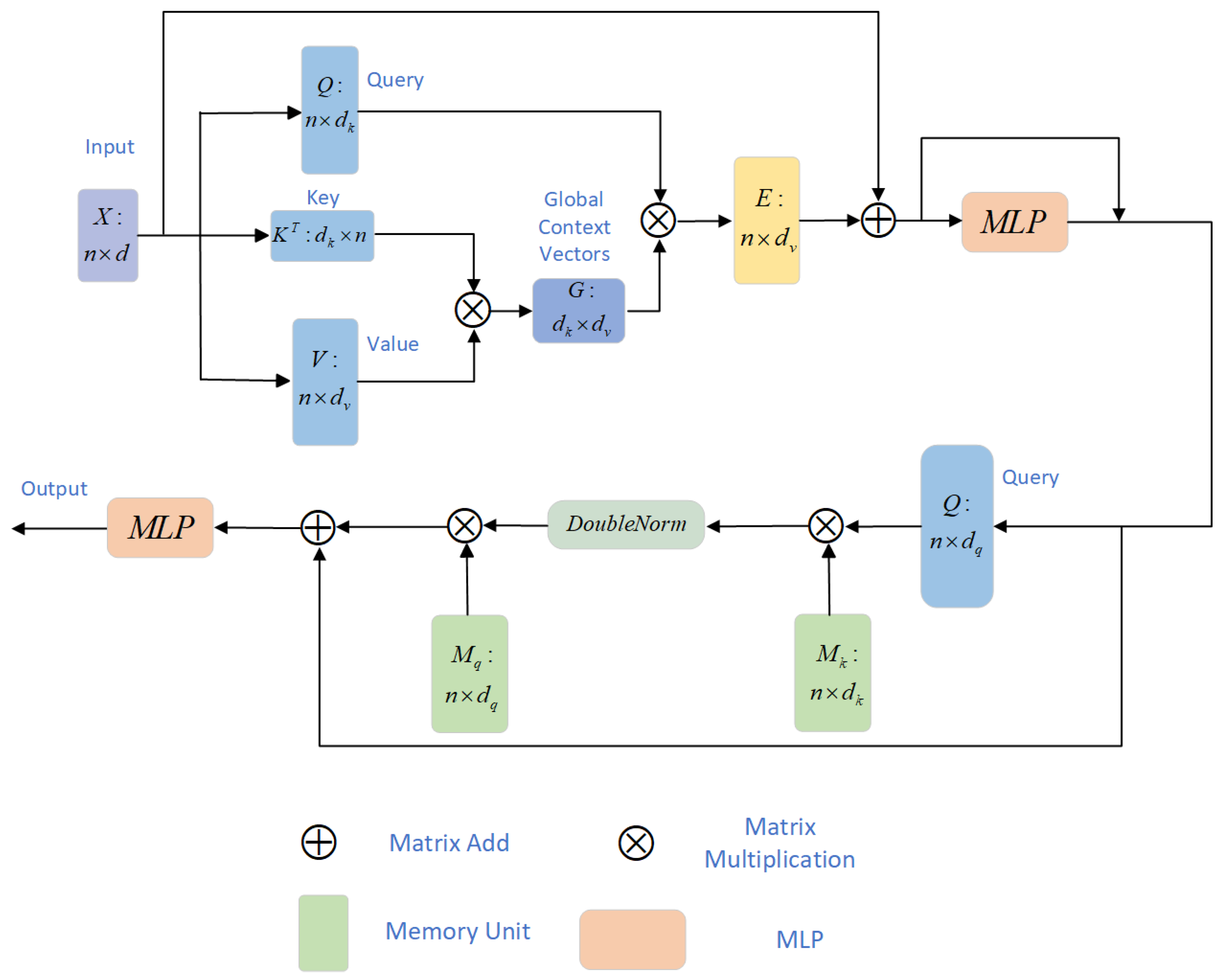
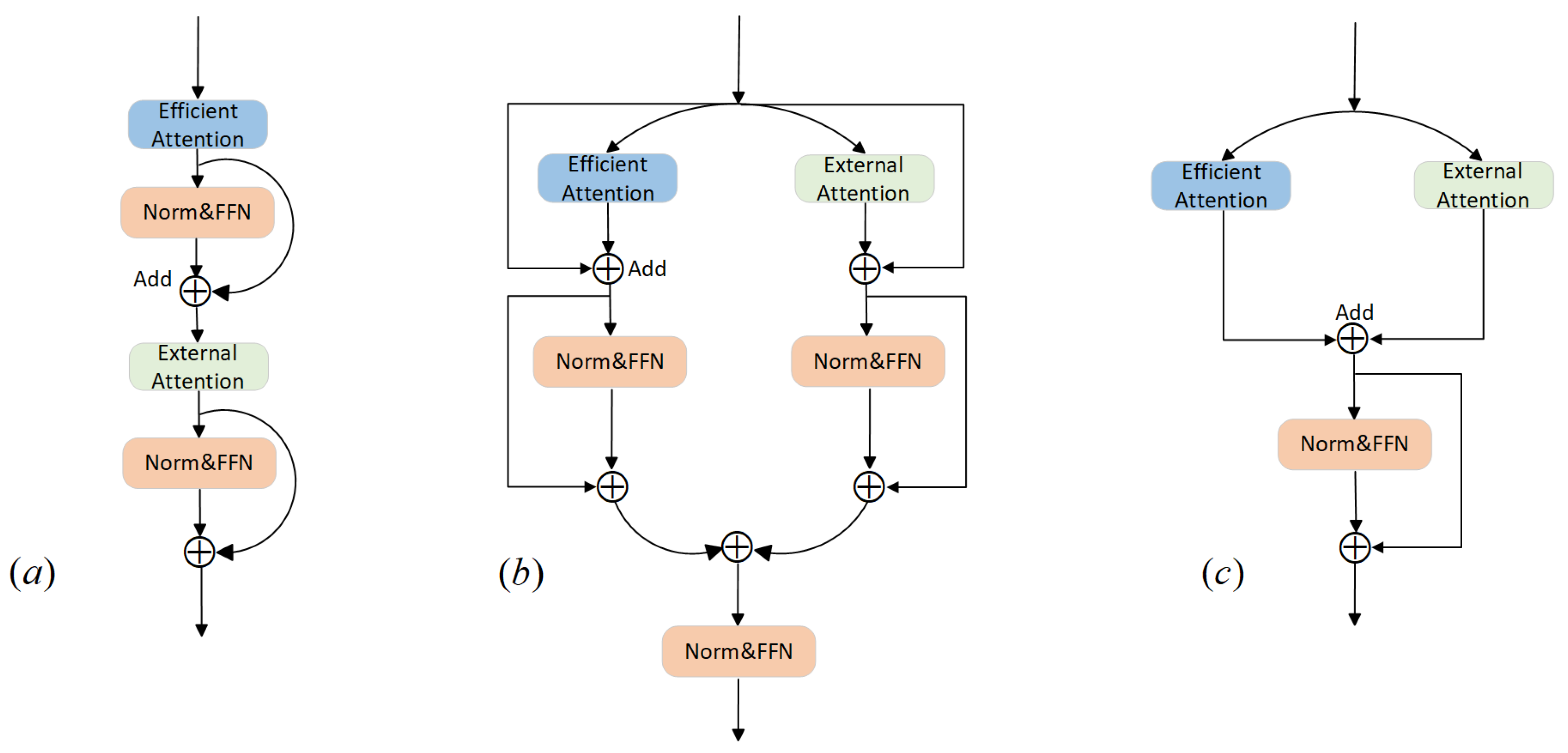
3.2. Dual-Attention Transformer (DAT)
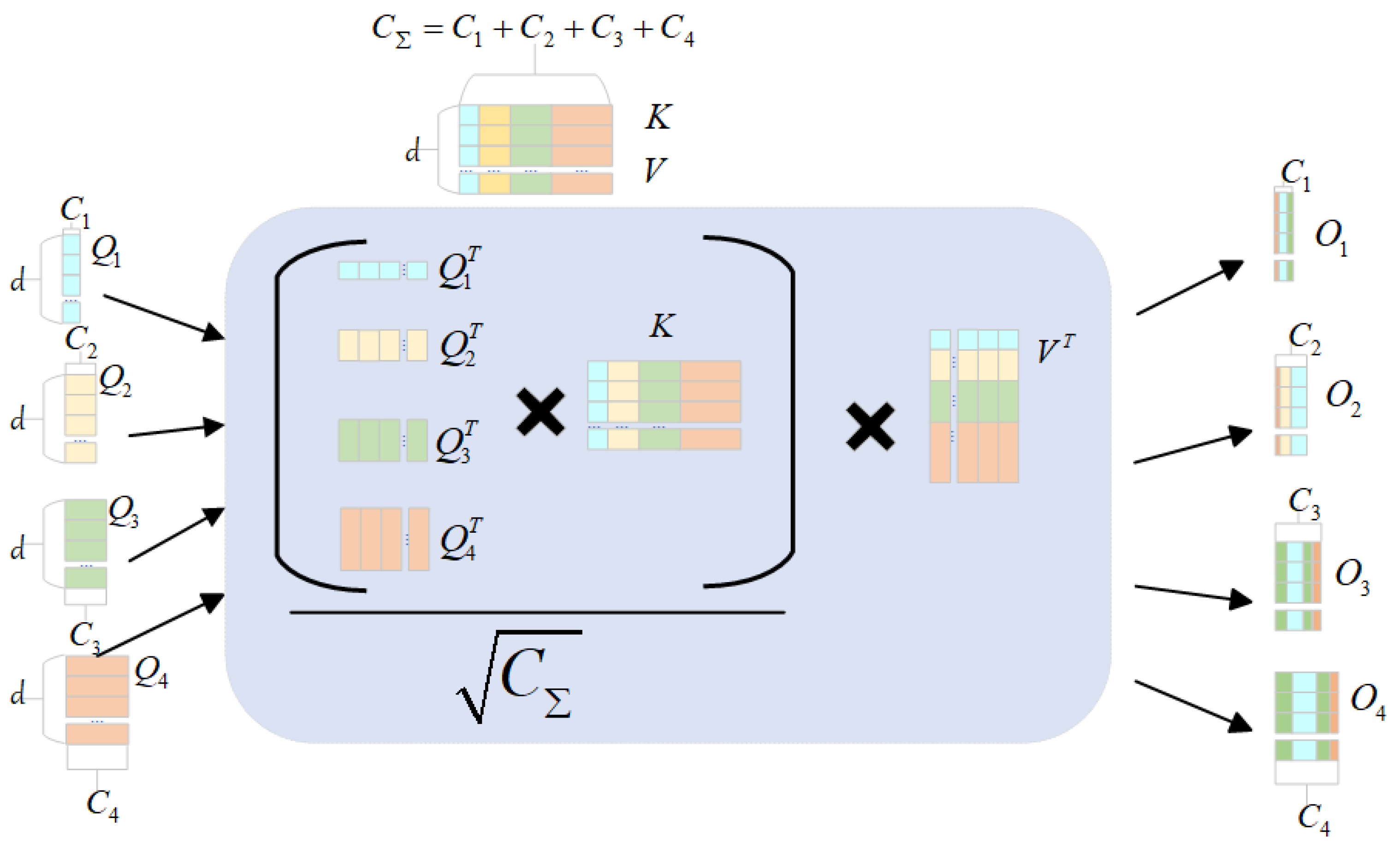
3.3. Efficient Attention
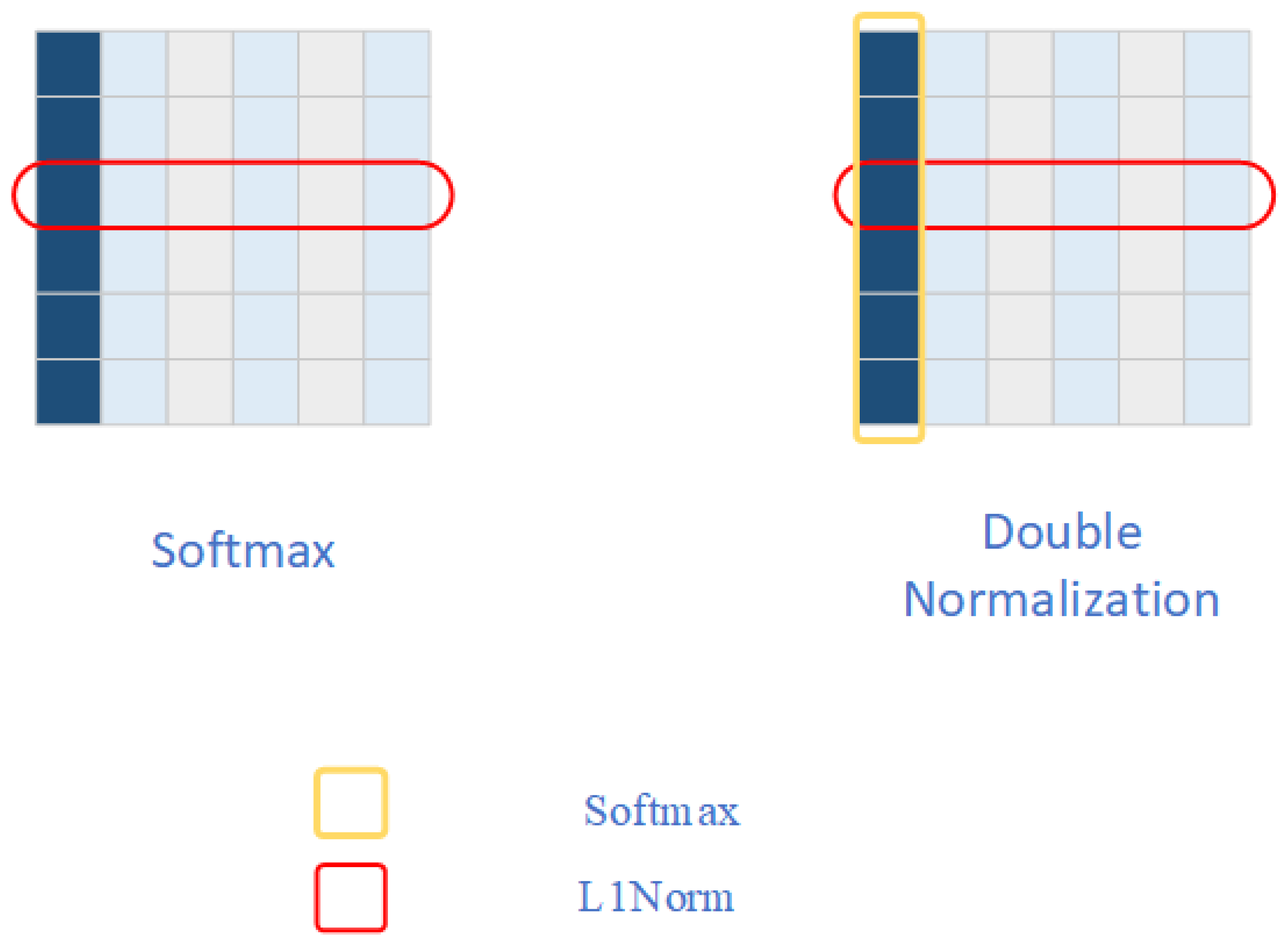
3.4. External Attention
Double Normalization
3.5. Multi-Scale Channel Cross-Fusion Module
3.5.1. Channel-Wise Cross-Fusion Transformer
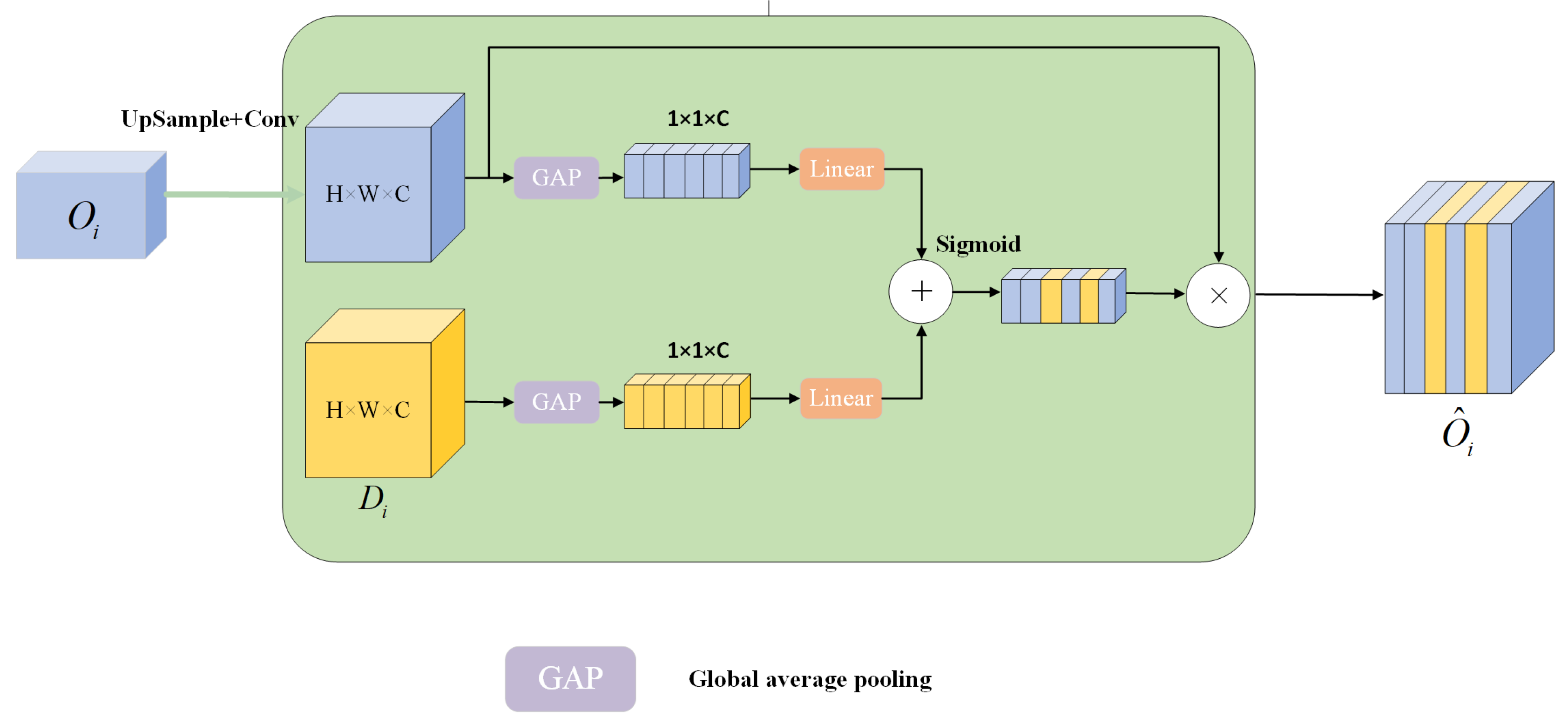
3.5.2. Channel-Wise Cross-Attention (CCA)
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Loss Function
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Experimental Details
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Comparative Experiment
5.2. Evaluation of Dataset
5.3. Ablation Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Yang, G.; Lio, P. A residual dense vision transformer for medical image super-resolution with segmentation-based perceptual loss fine-tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11184. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Kickingereder, P.; Wick, W.; Bendszus, M.; Maier-Hein, K.H. Brain tumor segmentation and radiomics survival prediction: Contribution to the brats 2017 challenge. In Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries: Proceedings of the Third International Workshop, BrainLes 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 14 September 2017; Revised Selected Papers; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. Transfuse: Fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2021: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021, Proceedings, Part I; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zeng, Z.; Veeravalli, B.; Guan, C. Act-net: Asymmetric co-teacher network for semi-supervised memory-efficient medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; pp. 1426–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Tragakis, A.; Kaul, C.; Murray-Smith, R.; Husmeier, D. The fully convolutional transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 3660–3669. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, D.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.; Yuan, H.; Huang, M.; Zhuang, J.; Hu, J.; Shi, Y. Positional contrastive learning for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2021: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021, Proceedings, Part II; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Qi, L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y. Revisiting weak-to-strong consistency in semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 7236–7246. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Shih, H.A.; Xing, F.; Santarnecchi, E.; Fakhri, G.E.; Woo, J. Incremental Learning for Heterogeneous Structure Segmentation in Brain Tumor MRI. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.19404. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Hasan, M.; Yakopcic, C.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06955. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Fang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y. Robust retinal vessel segmentation from a data augmentation perspective. In Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis: Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop, OMIA 2021, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2021, Strasbourg, France, 27 September 2021; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Koehler, G.; Ulrich, C.; Baumgartner, M.; Petersen, J.; Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Maier-Hein, K. MedNeXt: Transformer-driven Scaling of ConvNets for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.09975. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Marculescu, R. Multi-scale Hierarchical Vision Transformer with Cascaded Attention Decoding for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.16892. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Du, A. Big Model and Small Model: Remote modeling and local information extraction module for medical image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 136, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2022 Workshops: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022, Proceedings, Part III; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, M.; Vo-Ho, V.K.; Le, N.T. 3DConvCaps: 3DUnet with Convolutional Capsule Encoder for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 4392–4398. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Tang, Y.; Nath, V.; Yang, D.; Myronenko, A.; Landman, B.; Roth, H.R.; Xu, D. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 574–584. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.F.R.; Fan, Q.; Panda, R. Crossvit: Cross-attention multi-scale vision transformer for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; Kim, S. How do vision transformers work? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.06709. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, A.; Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Zhang, D. Ds-transunet: Dual swin transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 4005615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, S.; Luo, P. Multi-compound transformer for accurate biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2021: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021, Proceedings, Part I; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Tan, S.; Lin, J.; Bu, W. PCAT-UNet: UNet-like network fused convolution and transformer for retinal vessel segmentation. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, R.; Arimond, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Kazerouni, A.; Merhof, D. Dae-former: Dual attention-guided efficient transformer for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.13504. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yi, S.; Li, H. Efficient attention: Attention with linear complexities. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3531–3539. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Liu, Z.N.; Mu, T.J.; Hu, S.M. Beyond self-attention: External attention using two linear layers for visual tasks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 5436–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cao, P.; Wang, J.; Zaiane, O.R. Uctransnet: Rethinking the skip connections in u-net from a channel-wise perspective with transformer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2022; Volume 36, pp. 2441–2449. [Google Scholar]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W.; Fishman, E.; Yuille, A. Domain adaptive relational reasoning for 3d multi-organ segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Proceedings, Part I; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.W.; Wu, J. UNet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Lin, L.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Tong, R. Mixed transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 2390–2394. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, M.; Kazerouni, A.; Soltany, M.; Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Merhof, D. Hiformer: Hierarchical multi-scale representations using transformers for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 6202–6212. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Marculescu, R. Medical image segmentation via cascaded attention decoding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 6222–6231. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X. Missformer: An effective medical image segmentation transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.07162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. Ce-net: Context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; He, X. Levit-unet: Make faster encoders with transformer for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

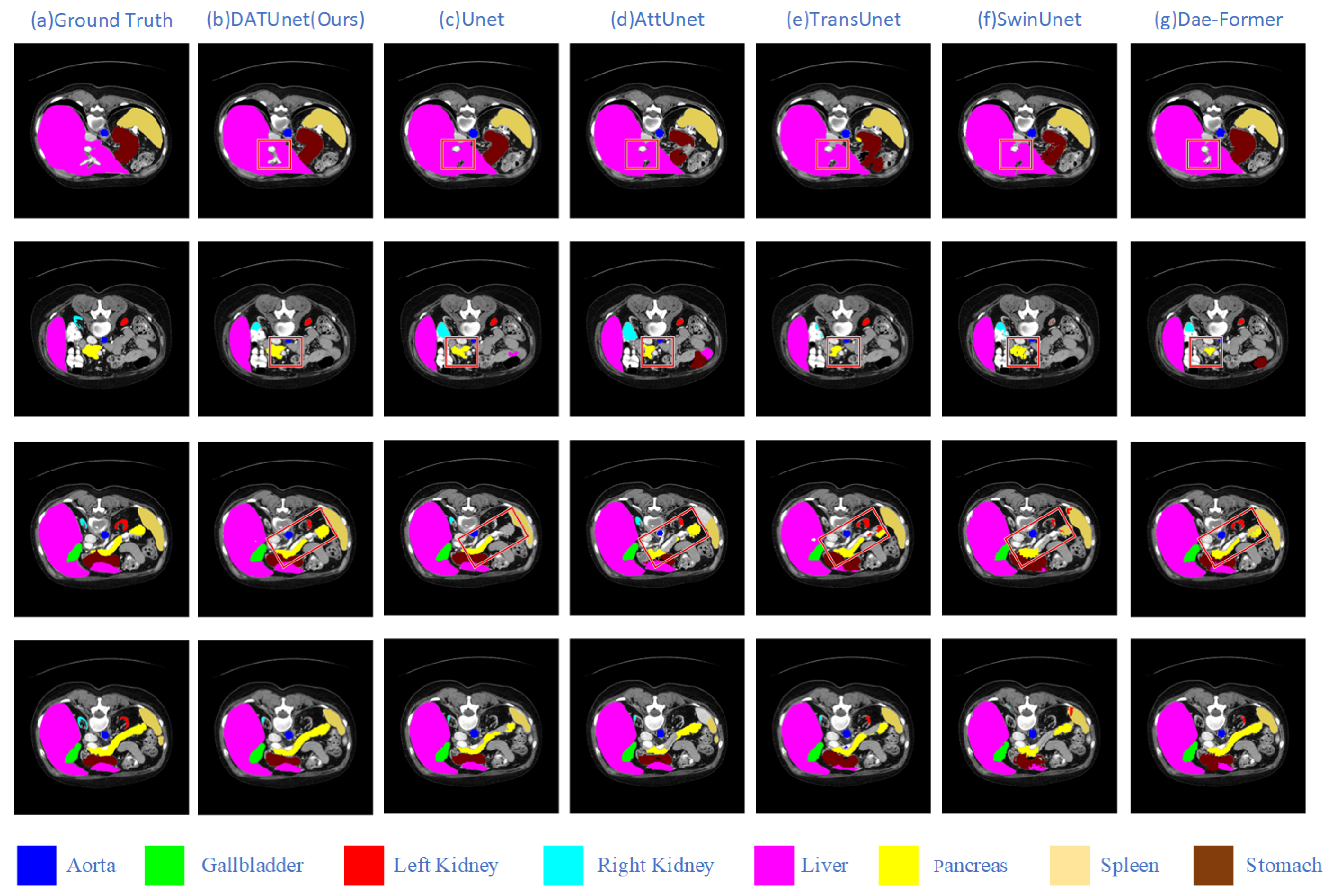
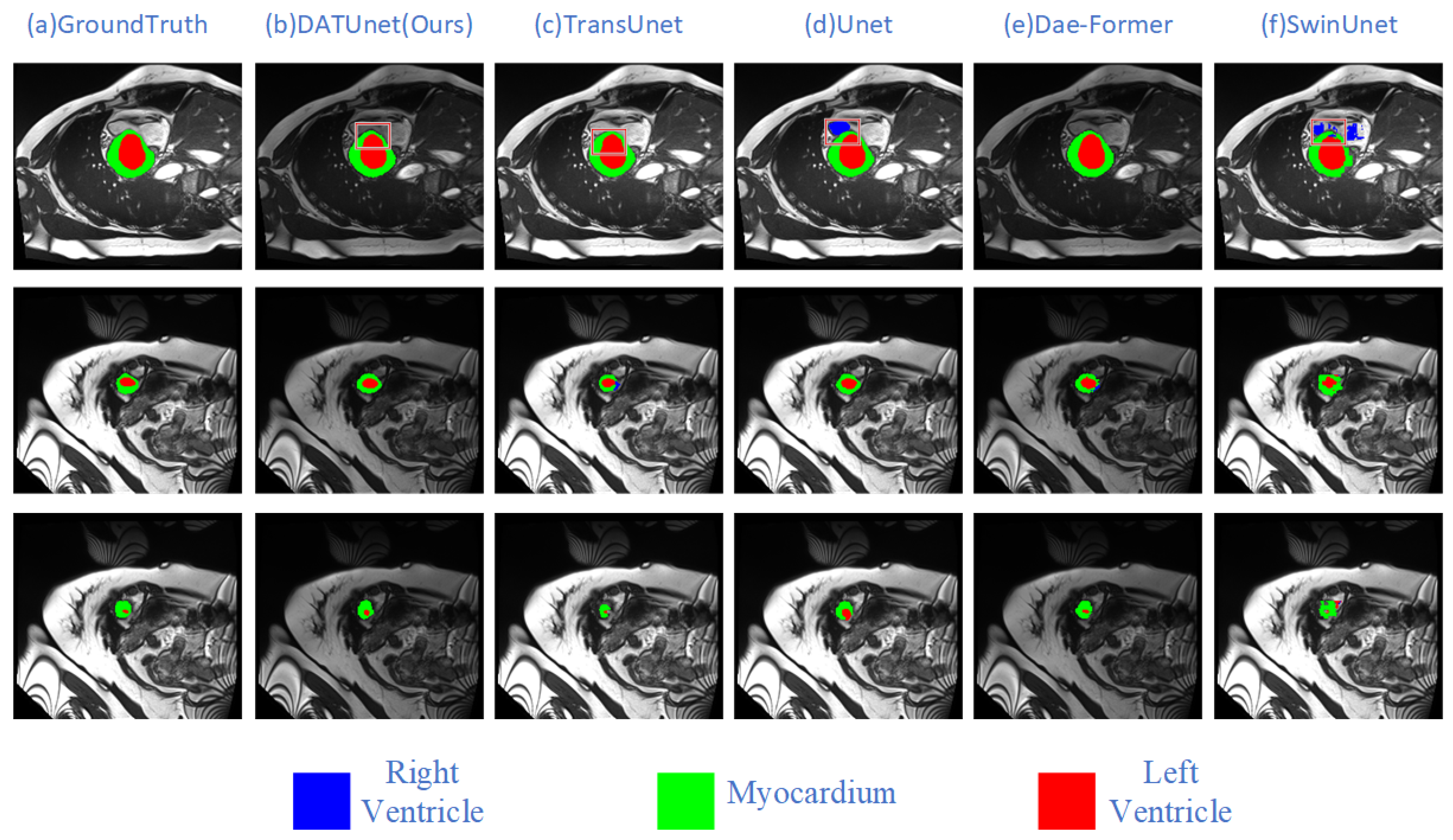
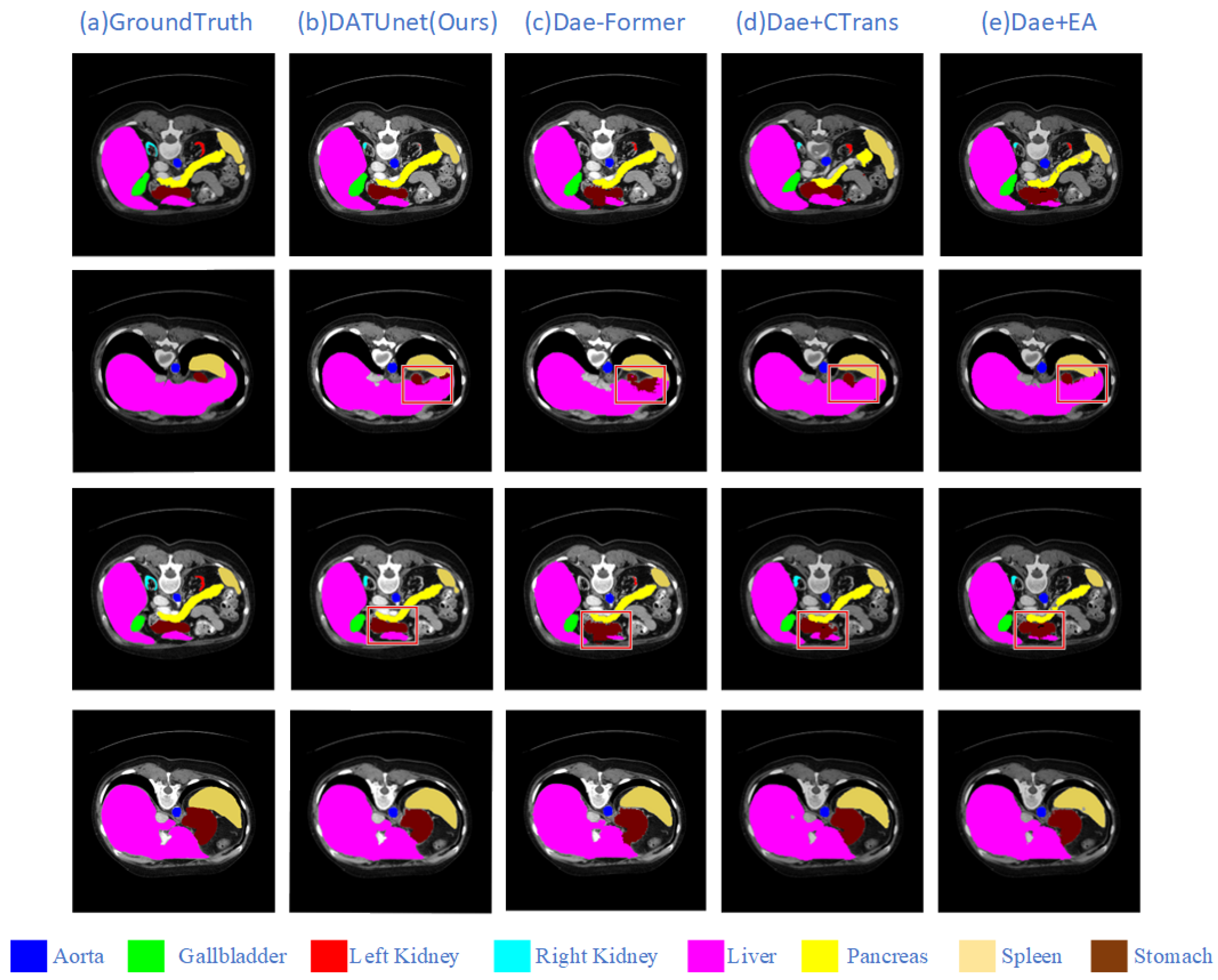
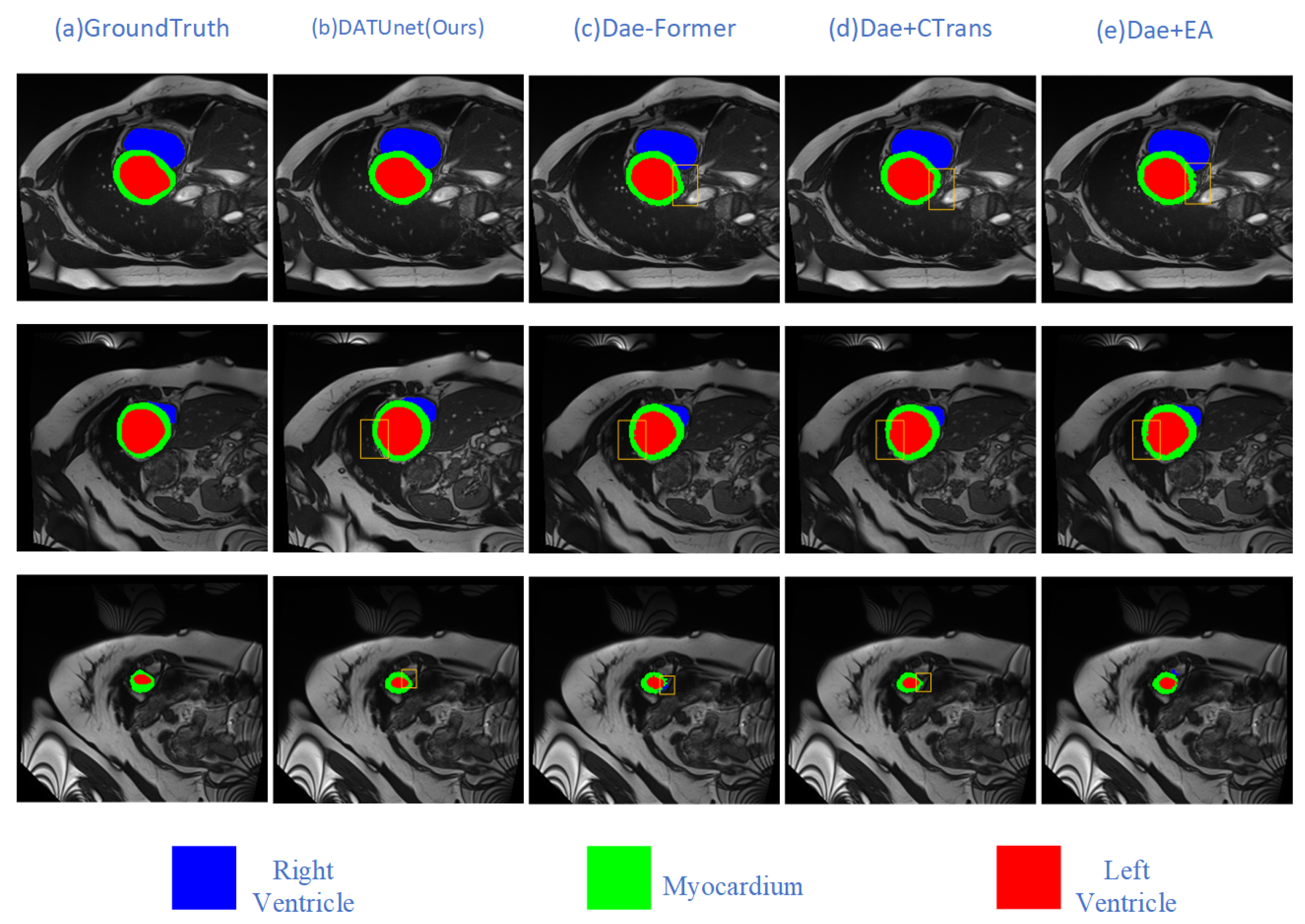
| Method | Model | DSC↑ | HD95↓ | Aorta | Gallbladder | Kidney (L) | Kidney (R) | Liver | Pancreas | Spleen | Stomach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | V-Net [36] | 68.81 | - | 75.34 | 51.87 | 77.10 | 80.75 | 87.84 | 40.05 | 80.56 | 56.98 |
| DARR [37] | 69.77 | - | 74.74 | 53.77 | 72.31 | 73.24 | 94.08 | 54.18 | 89.90 | 45.96 | |
| R50 UNet [13] | 74.68 | 36.87 | 84.18 | 62.84 | 79.19 | 71.29 | 93.35 | 48.23 | 84.41 | 73.92 | |
| R50 AttnUNet [38] | 75.57 | 36.97 | 55.92 | 63.91 | 79.20 | 72.71 | 93.56 | 49.37 | 87.19 | 74.95 | |
| UNet [13] | 76.85 | 39.70 | 89.07 | 69.72 | 77.77 | 68.60 | 93.43 | 53.98 | 86.67 | 75.58 | |
| UNet++ [33] | 78.13 | 25.65 | 89.27 | 62.35 | 83.00 | 78.98 | 94.53 | 56.70 | 85.99 | 74.20 | |
| UNet3+ [39] | 73.81 | 30.82 | 86.32 | 59.06 | 79.16 | 71.26 | 93.13 | 46.56 | 84.94 | 70.08 | |
| DeepLabv3+ [40] | 77.63 | 39.95 | 88.04 | 66.51 | 82.76 | 74.21 | 91.23 | 58.32 | 87.43 | 73.53 | |
| Att-UNet [34] | 77.77 | 36.02 | 89.55 | 68.88 | 77.98 | 71.11 | 93.57 | 58.04 | 87.30 | 75.75 | |
| Transformer | R50 ViT [15] | 71.29 | 32.87 | 73.73 | 55.13 | 75.80 | 72.20 | 91.51 | 45.99 | 81.99 | 73.95 |
| ViT [15] | 61.50 | 39.61 | 44.38 | 39.59 | 67.46 | 62.94 | 89.21 | 43.14 | 75.45 | 69.78 | |
| TransUNet [15] | 77.48 | 31.69 | 87.23 | 63.13 | 81.87 | 77.02 | 94.08 | 55.86 | 85.08 | 75.62 | |
| Swin-UNet [17] | 79.13 | 21.55 | 85.47 | 66.53 | 83.28 | 79.61 | 94.29 | 56.58 | 90.66 | 76.60 | |
| MT-UNet [41] | 78.59 | 26.59 | 87.92 | 64.99 | 81.47 | 77.29 | 93.06 | 59.46 | 87.75 | 76.81 | |
| HiFormer [42] | 80.39 | 14.70 | 86.21 | 65.69 | 85.23 | 79.77 | 94.61 | 59.52 | 90.99 | 81.08 | |
| TransCASCADE [43] | 82.68 | 17.34 | 86.63 | 68.48 | 87.66 | 84.56 | 94.43 | 65.33 | 90.79 | 83.52 1 | |
| MISSFormer [44] | 81.96 | 18.20 | 86.99 | 68.65 | 85.21 | 82.00 | 94.41 | 65.67 | 91.92 | 80.81 | |
| DAE-Former [27] | 82.43 | 17.46 | 88.96 | 72.30 1 | 86.08 | 80.88 | 94.98 | 65.12 | 91.94 1 | 79.19 | |
| DATUnet(Ours) | 83.64 1 | 13.99 1 | 89.78 1 | 70.52 | 89.06 1 | 84.93 1 | 95.65 1 | 68.01 1 | 91.61 | 79.53 |
| Method | Model | DSC↑ | RV | Myo | LV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | R50 U-Net [13] | 87.55 | 87.10 | 80.63 | 94.92 |
| R50 Att-UNet [38] | 86.75 | 87.58 | 79.20 | 93.47 | |
| CE-Net [45] | 87.21 | 85.68 | 83.97 | 91.98 | |
| UNet [13] | 88.28 | 86.08 | 86.04 | 92.72 | |
| UNet++ [33] | 89.06 | 87.66 | 86.47 | 93.06 | |
| UNet3+ [39] | 88.28 | 86.08 | 86.04 | 92.72 | |
| Transformer | R50 ViT [15] | 87.57 | 86.07 | 81.88 | 94.75 |
| TransUNet [15] | 89.71 | 88.86 | 84.53 | 95.73 | |
| Swin-UNet [17] | 90.00 | 88.55 | 85.62 | 95.83 1 | |
| UNETR [19] | 88.61 | 85.29 | 86.52 | 94.02 | |
| DAE-Former [27] | 89.00 | 87.78 | 86.99 | 92.22 | |
| DATUnet(Ours) | 90.35 1 | 88.89 1 | 88.79 1 | 93.42 |
| Method | DSC↑ | HD95↓ |
|---|---|---|
| DAE-Former [27] | 82.43 | 17.46 |
| DAE-Former + CTrans | 82.64 | 13.18 1 |
| DAE-Former + EA | 83.12 | 16.49 |
| DATUnet(Ours) | 83.64 1 | 13.99 |
| Method | DSC↑ | RV | Myo | LV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAE-Former [27] | 89.00 | 87.78 | 86.99 | 92.22 |
| DAE-Former + CTrans | 90.08 | 88.51 | 88.58 | 93.16 |
| DAE-Former + EA | 89.68 | 87.12 | 90.23 1 | 91.69 |
| DATUnet(Ours) | 90.35 1 | 88.89 1 | 88.79 | 93.42 1 |
| Dual-Attention Strategy | DSC↑ | HD95↓ |
|---|---|---|
| Sequential | 83.64 | 13.99 |
| Simple Additive | 80.13 | 26.22 |
| Complex Additive | 82.58 | 17.31 |
| Methods | Params(M) | DSC↓ | HD95↓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLapv3 + (CNN) [40] | 59.50 | 77.63 | 39.95 |
| Swin-Unet [17] | 27.17 | 79.13 | 21.55 |
| TransUNet [15] | 105.28 | 77.48 | 31.69 |
| LeVit-Unet [46] | 52.17 | 78.53 | 16.84 |
| MISSFormer [44] | 42.5 | 81.96 | 18.20 |
| HiFormer [42] | 25.51 | 80.39 | 14.70 |
| DAE-Former [27] | 48.1 | 82.43 | 17.46 |
| DATUnet | 59.44 | 83.64 | 13.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, S. A Multi-Scale Cross-Fusion Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Attention Mechanism Transformer. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910881
Cui J, Wang L, Jiang S. A Multi-Scale Cross-Fusion Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Attention Mechanism Transformer. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(19):10881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910881
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Jianguo, Liejun Wang, and Shaochen Jiang. 2023. "A Multi-Scale Cross-Fusion Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Attention Mechanism Transformer" Applied Sciences 13, no. 19: 10881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910881
APA StyleCui, J., Wang, L., & Jiang, S. (2023). A Multi-Scale Cross-Fusion Medical Image Segmentation Network Based on Dual-Attention Mechanism Transformer. Applied Sciences, 13(19), 10881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131910881






