A Fast Acquisition Algorithm for Hybrid Signals of 5G and BeiDou B1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We analyze the BeiDou and 5G system signals, summarize the 5G frequency bands close to the BeiDou signals, and discuss the NR spectrum characteristics and radiation characteristics of 5G. Finally, the current ITU protection standard for navigation signals is analyzed.
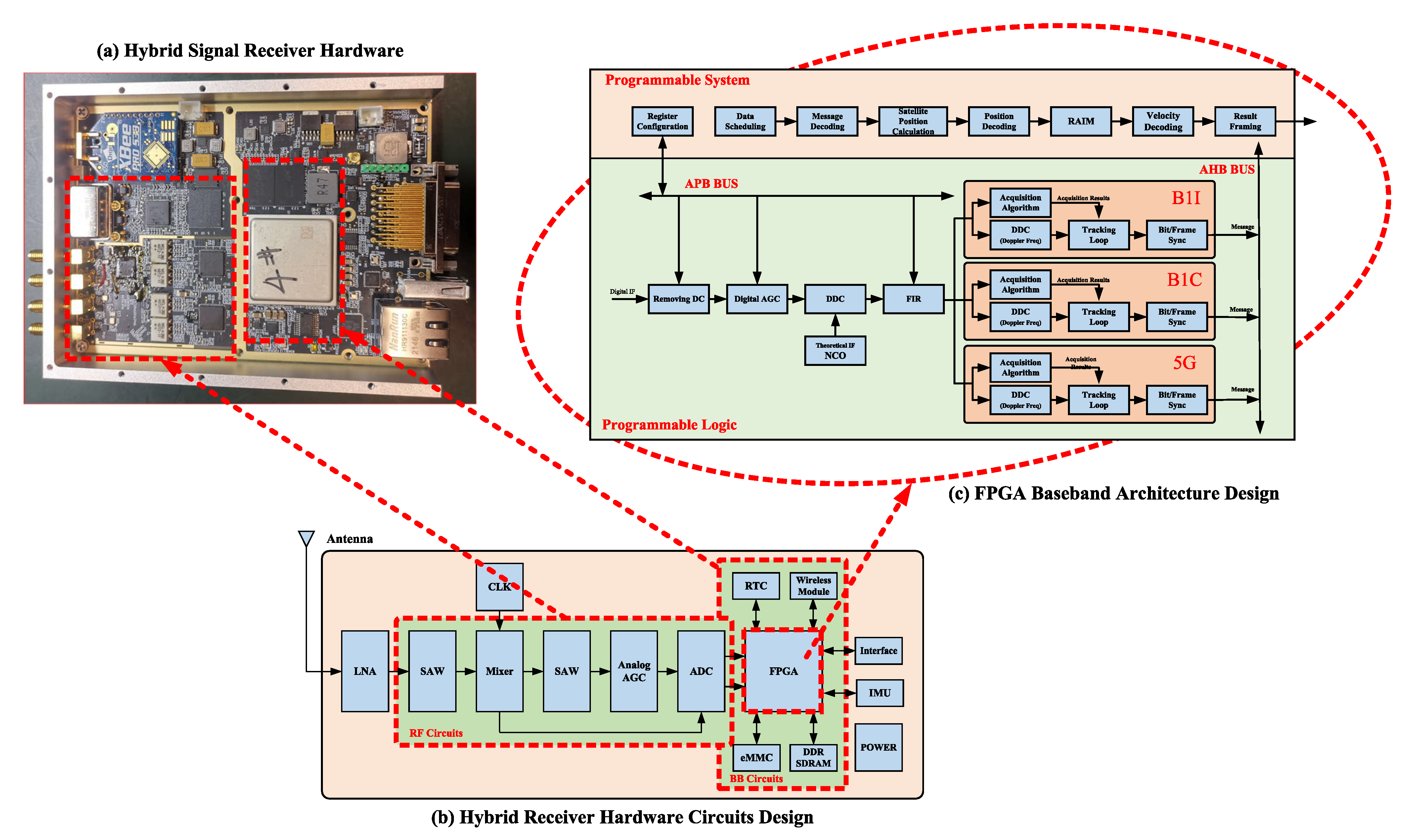
- We provide a detailed analysis of the mixed-signal regime and frequency planning and design a hybrid receiver architecture compatible with both signals, and hardware design for the RF front-end circuit, clock circuit, baseband circuit, and interface circuit.
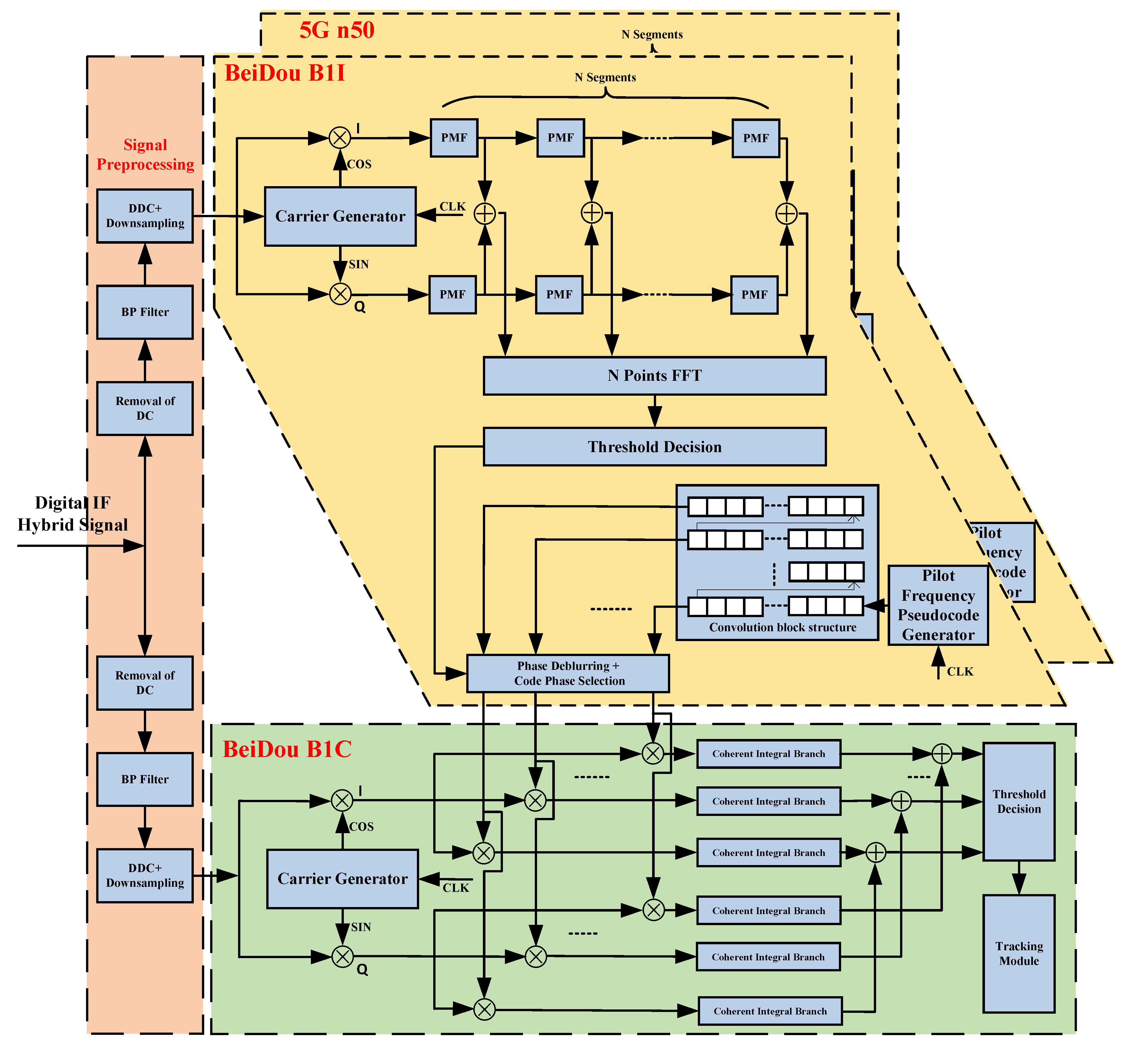
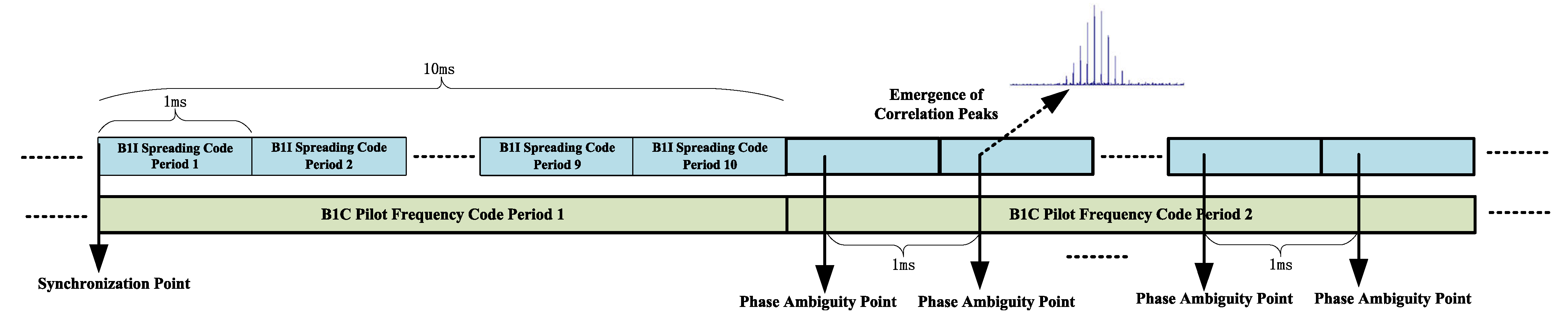
- We propose a strong-correlation-based SC-PMF-FFT fast capture algorithm, which utilizes the strong correlation of signal broadcast on the B1 frequency point of BeiDou, performs fast decoding phase ambiguity processing for the strongly correlated signals from B1I to B1C, and reuses the structure of the CDMA system signal capture algorithm to complete the fast capture of 5G signals using an OFDM system.
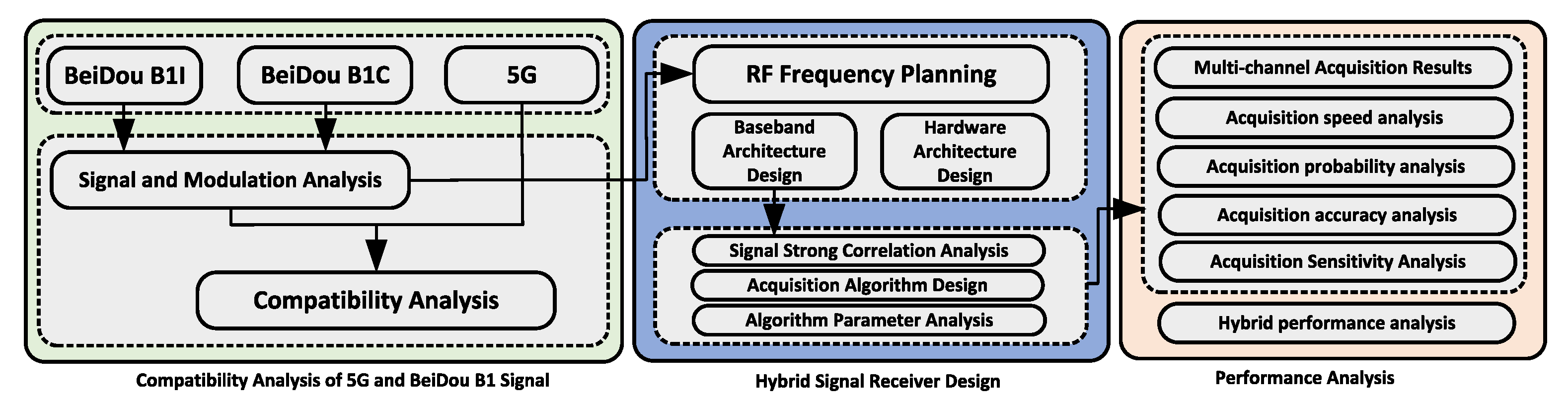
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Compatibility Analysis of 5G and BeiDou B1 Signal
2.1.1. BeiDou B1 Signal System
2.1.2. 5G Signal System
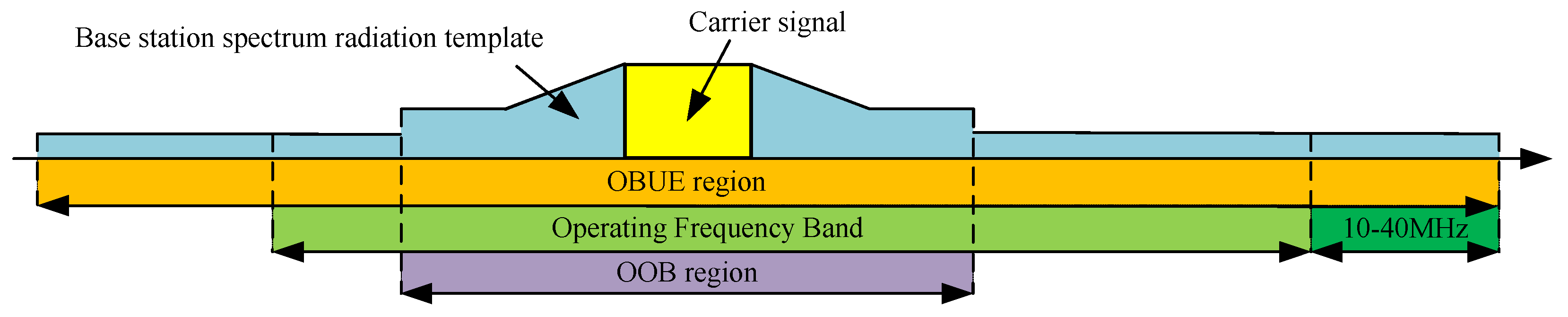
2.1.3. 5G and BeiDou B1 Band Compatibility Analysis
- The type of 5G signal.
- The power of the 5G signal arriving at the BeiDou receiver.
- The frequency interval between the BeiDou signal and the 5G signal.
2.2. Receiver Acquisition Algorithm Design
2.2.1. Receiver Hardware Architecture Design
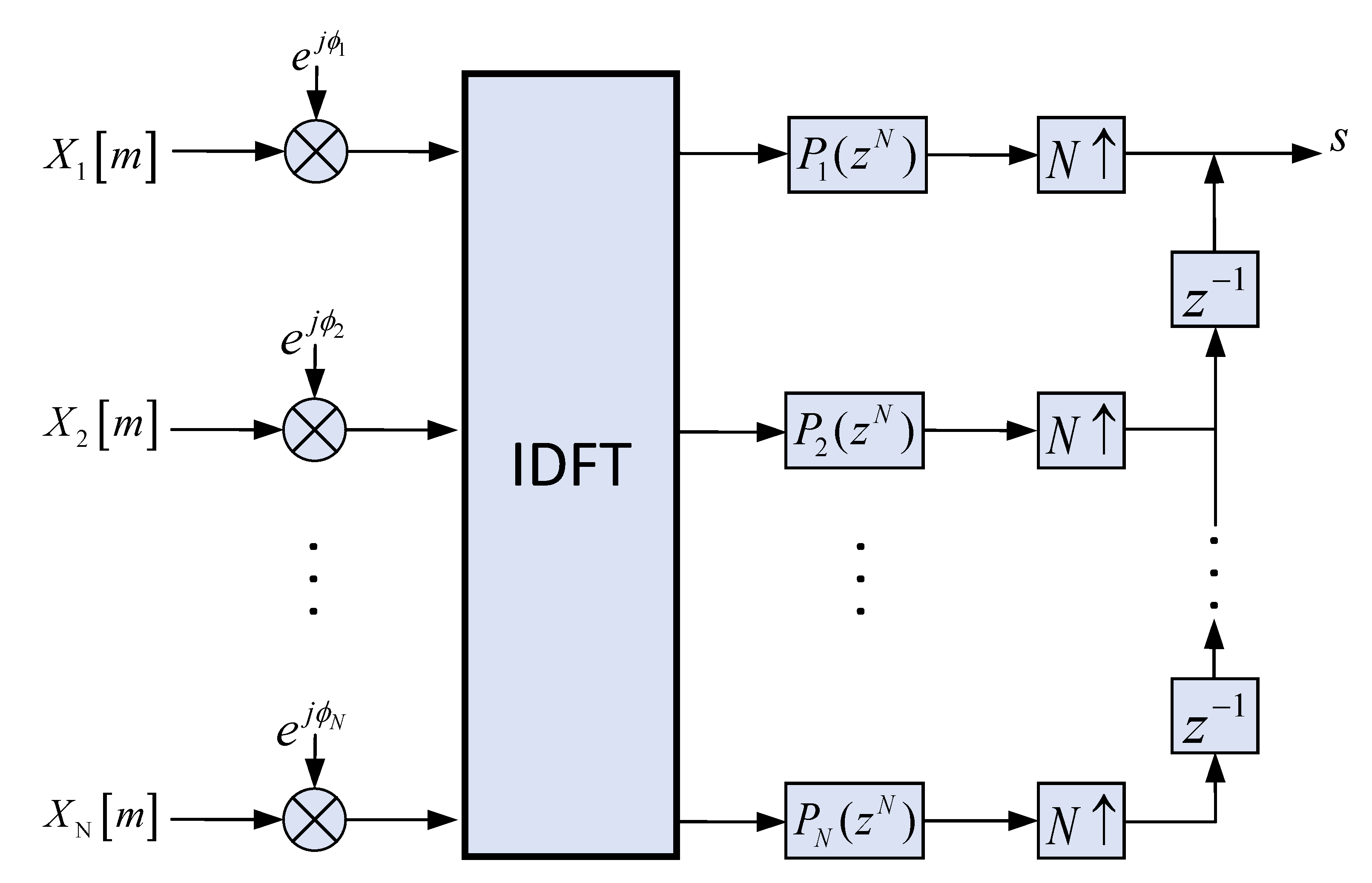
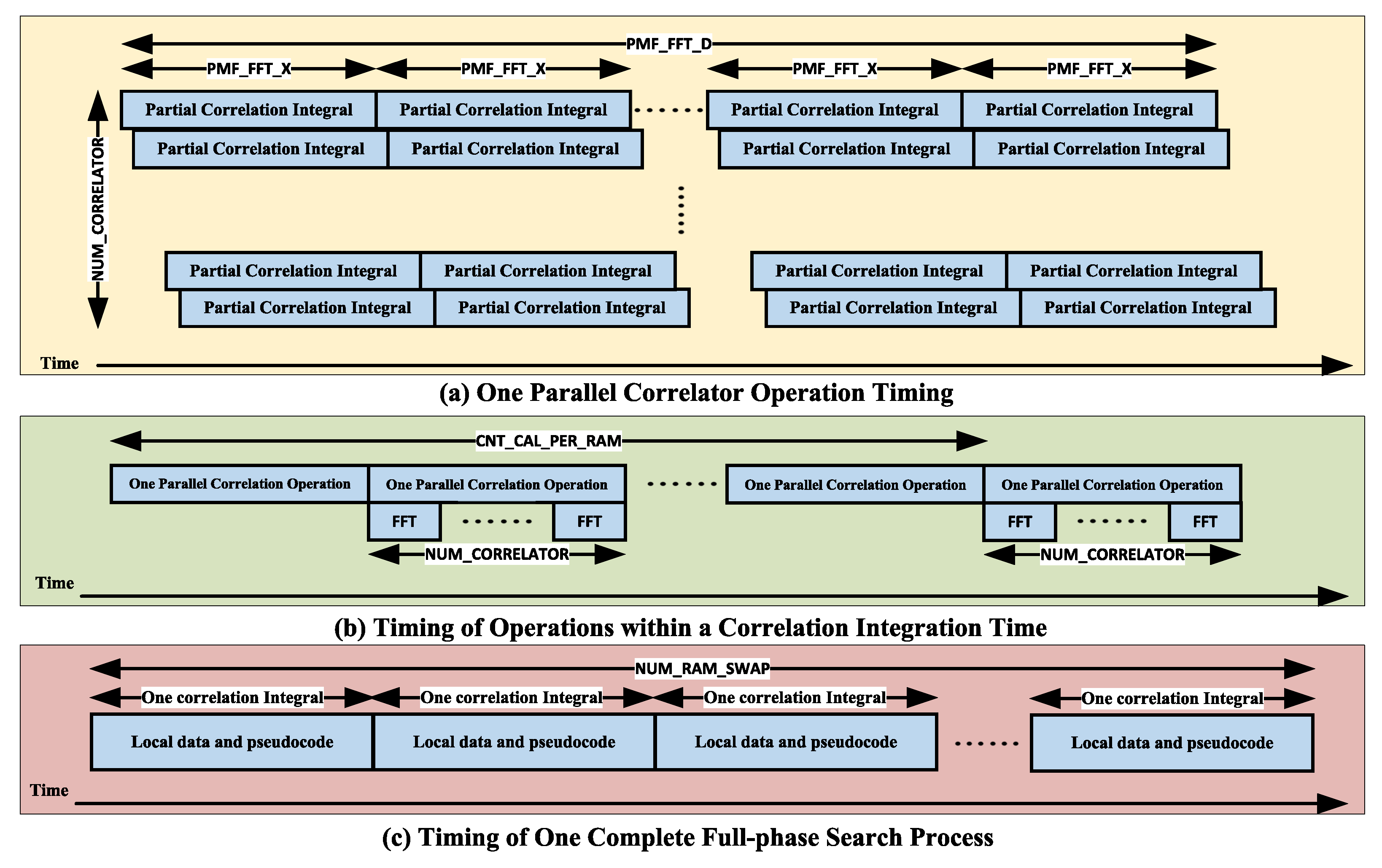
2.2.2. Receiver Hybrid Coherent Acquisition Algorithm Design
- determines the FFT calculation resolution = downsampling rate ÷ ÷ .
- = (downsampling rate × coherent integration time) ÷, but with ≤ .
- = operating clock ÷ (downsampling rate × coherent integration time), with the result rounded down.
- = downsampling rate × coherent integration length ÷(), the result is rounded upwards, the reasonable choice of and , there will be no phase secondary alignment problems. Otherwise, there may be two related peaks. Otherwise, two correlation peaks may occur.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hybrid Signal Receiver Hardware Design
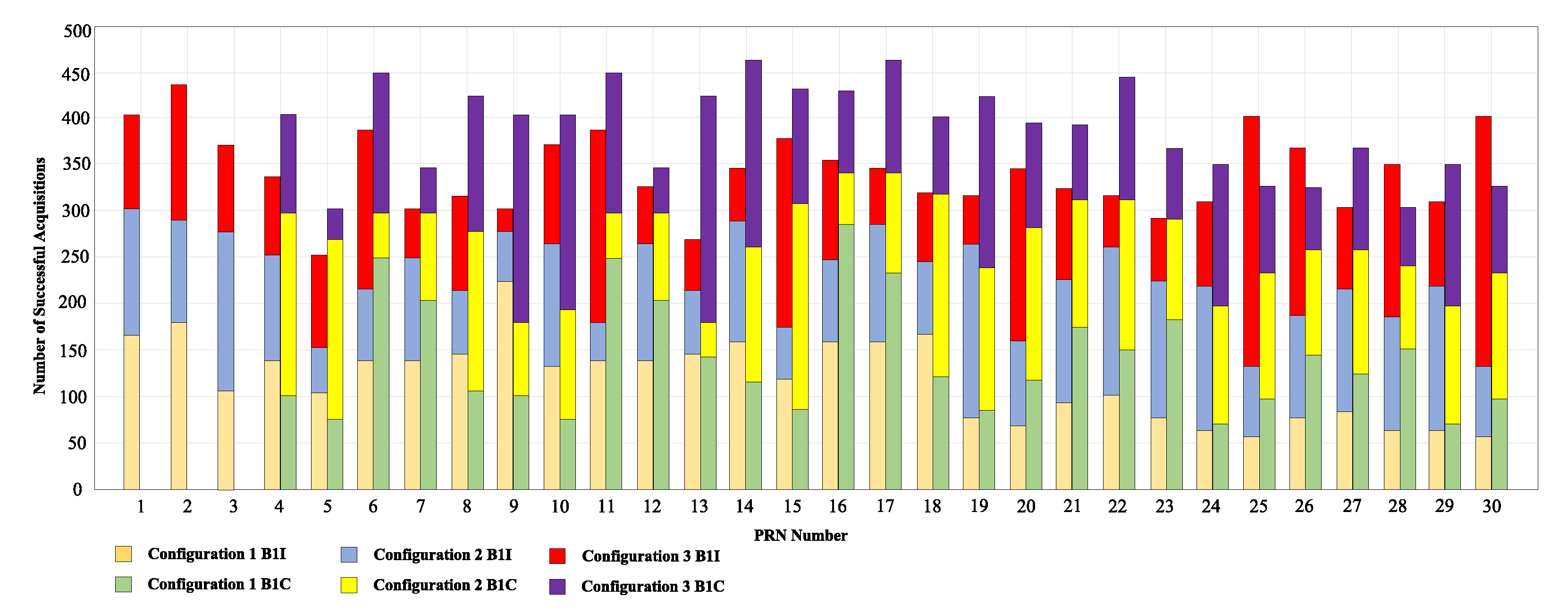
3.2. Receiver Hybrid Coherent Acquisition Performance Analysis
3.3. 5G Out-of-Band and B1 Signal Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FPGA | Field programmable gate array |
| DSP | Digital signal processing |
| GPU | Graphics processing unit |
| DSPs | Digital signal processors |
| DRAM | Dynamic random access memory |
| MCMM | Mixed mode clock manager |
| PLL | Phase lock loop |
| FIFO | First input first output |
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter |
| BDS | BeiDou navigation satellite system |
| BPSK | Binary phase shift keying |
| CNR | Carrier to noise ratio |
| CDMA | Code division multiple access |
| DLL | Delay lock loop |
| DSSS-CDMA | Direct-sequence spread-spectrum code division multiple access |
| ELS | Early late slope |
| EKF | Extend Kalman filter |
| FDD | Frequency division duplexing |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transformation |
| FIR | Finite impulse response |
| FLL | Frequency-locked loop |
| Galileo | Galileo satellite navigation system |
| GLONASS | Global navigation satellite system |
| GNSS | Global navigation satellite system |
| GPS | Global positioning system |
| HRC | High-resolution correlator |
| IFFT | Inverse fast Fourier transformation |
| LNA | Low-noise amplifier |
| LPF | Low pass filter |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| MIMO | Multiple input multiple outputs |
| NCO | Numerically controlled oscillator |
| OFDM | Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing |
| PMF | Partial matched filters |
| PNT | Positioning navigation and timing |
| PPS | Pulse per second |
| PRN | Pseudorandom noise |
| QAM | Quadrature amplitude modulation |
| SA | Selective availability |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| TDD | Time division duplexing |
| TD-SCDMA | Time division synchronous code division multiple access |
| UWB | Ultra wideband |
| WGN | White Gaussian noise |
References
- del Peral-Rosado, J.A.; Nolle, P.; Rothmaier, F.; Razavi, S.M.; Lindmark, G.; Jiang, X.; Shrestha, D.; Gunnarsson, F.; Parsawar, S.; Mundlamuri, R.; et al. Proof-of-Concept of Dedicated Aerial 5G and GNSS Testbed for Enhanced Hybrid Positioning. In Proceedings of the 35th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2022), Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 September 2022; pp. 2362–2376. [Google Scholar]
- Fabius, M.; Lapeyre, D.; Messager, F.; Kiely, I.; Arzel, L.; Pomies, A. GEONAV IoT-Study of Hybrid 5G/GNSS Positioning. In Proceedings of the 34th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2021), St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 September 2021; pp. 725–752. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.; Zou, D.; Han, T.; Zhang, X.; Shen, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, P.; Yin, T. A New Type of 5G-Oriented Integrated BDS/SON High-Precision Positioning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, T.; Ding, R.; Seco-Granados, G.; You, L.; Gao, X. Location-based timing advance estimation for 5G integrated LEO satellite communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 6002–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famili, A.; Foruhandeh, M.; Atalay, T.; Stavrou, A.; Wang, H. GPS Spoofing Detection by Leveraging 5G Positioning Capabilities. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Latin-American Conference on Communications (LATINCOM), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 30 November–2 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, A.; Xu, Y. A GNSS/5G integrated three-dimensional positioning scheme based on D2D communication. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klus, R.; Talvitie, J.; Valkama, M. Neural network fingerprinting and GNSS data fusion for improved localization in 5G. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Localization and GNSS (ICL-GNSS), Tampere, Finland, 1–3 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti, A.; Vanelli-Coralli, A.; Conti, M.; Andrenacci, S.; Chatzinotas, S.; Maturo, N.; Evans, B.; Awoseyila, A.; Ugolini, A.; Foggi, T.; et al. Architectures and key technical challenges for 5G systems incorporating satellites. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 2624–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, S.; Guo, C.; Guo, W.; Deng, C.; Liu, J. Structure and performance analysis of fusion positioning system with a single 5G station and a single GNSS satellite. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2023, 26, 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chaloupka, Z.; Ries, L.; Samperi, A.; Waller, P.; Crisci, M. Phase synchronization for 5G using mass market GNSS receivers. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Frequency and Time Forum (EFTF), Torino, Italy, 10–12 April 2018; pp. 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.; Tay, W.P.; Zhao, K.; Ling, K.V.; Sin, K.K. A 5G/GNSS Integrated Positioning Method. In Proceedings of the 35th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2022), Denver, CO, USA, 19–23 September 2022; pp. 2429–2443. [Google Scholar]
- Shamaei, K.; Kassas, Z.M. Receiver design and time of arrival estimation for opportunistic localization with 5G signals. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 4716–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tu, R.; Hong, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Lu, X. Performance Analysis of BDS–5G Combined Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Sun, C.; Dempster, A.G.; Zhao, H.; Cheong, J.W.; Feng, W. GNSS-5G hybrid positioning based on multi-rate measurements fusion and proactive measurement uncertainty prediction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Liu, W.; Yuan, H.; Ge, J. High-precision time synchronization networking algorithm for 5G base station based on GNSS. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2020, 42, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Destino, G.; Saloranta, J.; Seco-Granados, G.; Wymeersch, H. Performance analysis of hybrid 5G-GNSS localization. In Proceedings of the 2018 52nd Asilomar Conference on Signals,Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lukcin, I.; Duong, P.; Dietmayer, K.; Ali, S.U.; Kram, S.; Seitz, J.; Felber, W. A combined ray tracing simulation environment for hybrid 5G and GNSS positioning. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Localization and GNSS (ICL-GNSS), Tampere, Finland, 1–3 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Del Peral-Rosado, J.A.; Nolle, P.; Razavi, S.M.; Lindmark, G.; Shrestha, D.; Gunnarsson, F.; Kaltenberger, F.; Sirola, N.; Särkkä, O.; Roström, J.; et al. Design considerations of dedicated and aerial 5G networks for enhanced positioning services. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th Workshop on Satellite Navigation Technology (NAVITEC), Virtual, 5–7 April 2022; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Tu, R.; Hong, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Lu, X. Combined positioning algorithm based on BeiDou navigation satellite system and raw 5G observations. Measurement 2022, 190, 110763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tu, R.; Han, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Lu, X. Performance research of real-time kinematic/5G combined positioning model. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 035115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Fu, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, F. Radar-assisted UAV detection and identification based on 5G in the Internet of Things. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2019, 2019, 2850263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alghisi, M.; Biagi, L. Positioning with GNSS and 5G: Analysis of Geometric Accuracy in Urban Scenarios. Sensors 2023, 23, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, P.; Wang, X.; Zou, D.; Chu, Z.; Guo, Y. Acquisition performance of B1I abounding with 5G signals. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2022, 33, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Kassas, Z.M. Kalman Filter-Based Integrity Monitoring for GNSS and 5G Signals of Opportunity Integrated Navigation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Peral-Rosado, J.A.; Saloranta, J.; Destino, G.; López-Salcedo, J.A.; Seco-Granados, G. Methodology for simulating 5G and GNSS high-accuracy positioning. Sensors 2018, 18, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mata, F.; Grec, F.; Azaola, M.; Blázquez, F.; Fernández, A.; Dominguez, E.; Cueto-Felgueroso, G.; Seco-Granados, G.; del Peral-Rosado, J.; Staudinger, E.; et al. Preliminary field trials and simulations results on performance of hybrid positioning based on GNSS and 5G signals. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2020), Online, 22–25 September 2020; pp. 387–401. [Google Scholar]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Open Service Signal B1C (Version 1.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Open Service Signal B1I (Version 3.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Open Service Signal B2a (Version 1.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Open Service Signal B3I (Version 1.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Henri, Y.; Matas, A. RNSS and the ITU radio regulations. In Proceedings of the InsideGNSS, Red Bank, NJ, USA, 1 January 2018; pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Series, M. Recommendation ITU-R M.1903-1, 2019. Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/m/R-REC-M.1903-1-201909-I!!PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Series, M. Recommendation ITU-R M.1318-1, 2007. Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/m/R-REC-M.1318-1-200710-I!!PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Tamazin, M.; Noureldin, A.; Korenberg, M.J.; Massoud, A.; Navigation and Instrumentation Research Group. Robust fine acquisition algorithm for GPS receiver with limited resources. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.S.; Lin, Y.C. A new multi-C/A code acquisition method for GPS. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Signal | Modulation | PN Code Length (Chips) | PN Code Rate (Mcps) | Message Rate (bps) | Spread Spectrum Gain (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1I | BPSK | 2046 | 2.046 | D1:50 D2:500 | 33.1 |
| B1C | BOC(1,1) QMBOC(6,1,4/33) | 10,230 | 1.023 | 100 | 40.1 |
| B2a | BPSK(10) BPSK(10) | 10,230 | 10.23 | 200 | 47.1 |
| B2b | BPSK(10) | 10,230 | 10.23 | 200 | 47.1 |
| B3I | BPSK | 10,230 | 10.23 | D1:50 D2:500 | 40.1 |
| Signal Name | B1I | B1C | B2a | B2b | B3I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Message Type | D1/D2 | B-CNAV1 | B-CNAV2 | B-CNAV3 | D1/D2 |
| Broadcast Method | D1:MEO/IGSO D2:GEO | MEO/IGSO | MEO/IGSO | MEO/IGSO | D1:MEO/IGSO D2:GEO |
| Component | Modulation | Phase Relationship | Power Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1/4 | |||
| 90 | 29/44 | |||
| 0 | 1/11 | |||
| NR Frequency Band | Uplink Frequency Band (MHz) | Downlink Frequency Band (MHz) | Duplex Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| n1 | 1920–1980 | 2110–2170 | FDD |
| n2 | 1850–1910 | 1930–1990 | FDD |
| ...... | ..... | ...... | ...... |
| n50 | 1432–1517 | 1432–1517 | TDD |
| n51 | 1427–1432 | 1427–1432 | TDD |
| ...... | ...... | ...... | ..... |
| n74 | 1427–1470 | 1475–1518 | FDD |
| n75 | N/A | 1432–1517 | SDL |
| n76 | N/A | 1427–1432 | SDL |
| ...... | ...... | ...... | ...... |
| n95 | 2010–2025 | N/A | SUL |
| SCS (KHz) | 5 MHz | 10 MHz | 15 MHz | 20 MHz | … | 70 MHz | 80 MHz | 90 MHz | 100 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRB | NRB | NRB | NRB | … | NRB | NRB | NRB | NRB | |
| 15 | 25 | 52 | 79 | 106 | … | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| 30 | 11 | 24 | 38 | 51 | … | 189 | 217 | 245 | 273 |
| 60 | N/A | 11 | 18 | 24 | … | 93 | 107 | 121 | 135 |
| NR Frequency Band | Uplink Frequency Band (MHz) | Downlink Frequency Band (MHz) | Duplex Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| n50 | 1432–1517 | 1432–1517 | TDD |
| n51 | 1427–1432 | 1427–1432 | TDD |
| n74 | 1427–1470 | 1475–1518 | FDD |
| n75 | N/A | 1432–1517 | SDL |
| n76 | N/A | 1427–1432 | SDL |
| n92 | 832–862 | 1432–1517 | FDD |
| n93 | 880–915 | 1427–1432 | FDD |
| n94 | 880–915 | 1432–1517 | FDD |
| Key Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Duplex mode | FDD/TDD |
| Basic waveform | Downlink: CP-OFDM/Uplink: CP-OFDM, DFT-S-OFDM |
| Carrier bandwidth | Below 6 GHz: 100 MHz max/Above 6 GHz: 400 MHz max |
| Modulation mode | QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM |
| Subcarrier interval | Below 6 GHz: 15 KHz, 30 KHz, 60 KHz/Above 6 GHz: 60 KHz, 120 KHz, 240 KHz |
| BeiDou B1 (MHz) | 5G n50 (MHz) | |
|---|---|---|
| RF | 1561.098∼1575.42 | 1427∼1517 |
| Baseband IF | 20.46 | 120 |
| Local Oscillator Frequency | 1540.638 | 1592 |
| Baseband BandWidth | 4.092 | 90 |
| Baseband BandWidth/2 | 2.046 | 45 |
| RF Range | 1559.052∼1577.466 | 1427∼1517 |
| Baseband IF Range | 18.414∼22.506 | 75∼165 |
| ADC Sampling Rate | 20.46 | 200 |
| Parameter | BeiDou B1 | 5G n50 |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Clock | 120 MHz | 120 MHz |
| Downsampling Rate | 30 MHz | 90 MHz |
| Coherent Integration Time | 1 ms | 5 ms |
| Number of Partial Coherent Integration () | 600 | 3000 |
| Number of Chunks () | 20 | 100 |
| Number of Points of FFT () | 128 | 128 |
| Number of Parallel Correlators () | 60 | 300 |
| Number of Parallel Correlators within Each Correlation Integration () | 5 | 1 |
| Number of RAM Switches of the Data within the Correlation Integration () | 40 | 1000 |
| Calculation Steps | Multiplier Computation Cost | Adder Computation Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Downsampling | ||
| Coherent Integration | ||
| FFT | ||
| Total |
| Coherent Integration Time (ms) | Search Data Phase Point | X | D | N | Doppler Range (KHz) | Effective Doppler Range (KHz) | Doppler Calculation Resolution (Hz) | Code Phase Resolution (Chip) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1I | 1 | 12,000 | 600 | 20 | 128 | −10∼+10 | −2.5∼+2.5 | 156.25 | 0.1705 |
| B1C | 1 | 60,000 | 600 | 100 | 128 | −50∼+50 | −12.5∼+12.5 | 781.25 | 0.1705 |
| 5G n50 | 1 | 12,000 | 600 | 20 | 128 | −10∼+10 | −2.5∼+2.5 | 156.25 | 0.1705 |
| Coherent Integration Time (ms) | Search Data Phase Point | SC_PMF_FFT_X | SC_PMF_FFT_D | SC_PMF_FFT_N | Doppler Calculation Resolution (Hz) | Code Phase Resolution (Chip) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration 1 | 1 | 12,000 | 600 | 20 | 128 | 78.125 | 0.1705 |
| Configuration 2 | 2 | 24,000 | 600 | 100 | 128 | 156.25 | 0.3410 |
| Configuration 3 | 5 | 60,000 | 600 | 500 | 128 | 312.50 | 0.8525 |
| C/No (dB·Hz) | Number of Acquisitions | Success Rate | Phase Search Time (ms) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 Hz | 600 Hz | 900 Hz | |||
| 38.9 | 500 | 100.0% | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| 35.9 | 500 | 100.0% | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| 32.9 | 498 | 99.6% | 4 | 10 | 15 |
| 29.9 | 483 | 96.6% | 5 | 11 | 16 |
| 26.9 | 432 | 86.4% | 10 | 20 | 40 |
| 23.9 | 359 | 71.8% | 15 | 29 | 60 |
| 20.9 | 261 | 52.2% | 47 | 93 | 121 |
| 17.9 | 146 | 29.2% | 289 | 465 | 567 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Zhuang, C.; Feng, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Hu, S.; Yang, X. A Fast Acquisition Algorithm for Hybrid Signals of 5G and BeiDou B1. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7818. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137818
Yang X, Zhuang C, Feng W, Wang Q, Yang Z, Hu S, Yang X. A Fast Acquisition Algorithm for Hybrid Signals of 5G and BeiDou B1. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7818. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137818
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xu, Chen Zhuang, Wenquan Feng, Qiang Wang, Zhe Yang, Shan Hu, and Xu Yang. 2023. "A Fast Acquisition Algorithm for Hybrid Signals of 5G and BeiDou B1" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7818. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137818
APA StyleYang, X., Zhuang, C., Feng, W., Wang, Q., Yang, Z., Hu, S., & Yang, X. (2023). A Fast Acquisition Algorithm for Hybrid Signals of 5G and BeiDou B1. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7818. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137818







