An Investigation of Wood Baseball Bat Durability as a Function of Bat Profile and Slope of Grain Using Finite Element Modeling and Statistical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
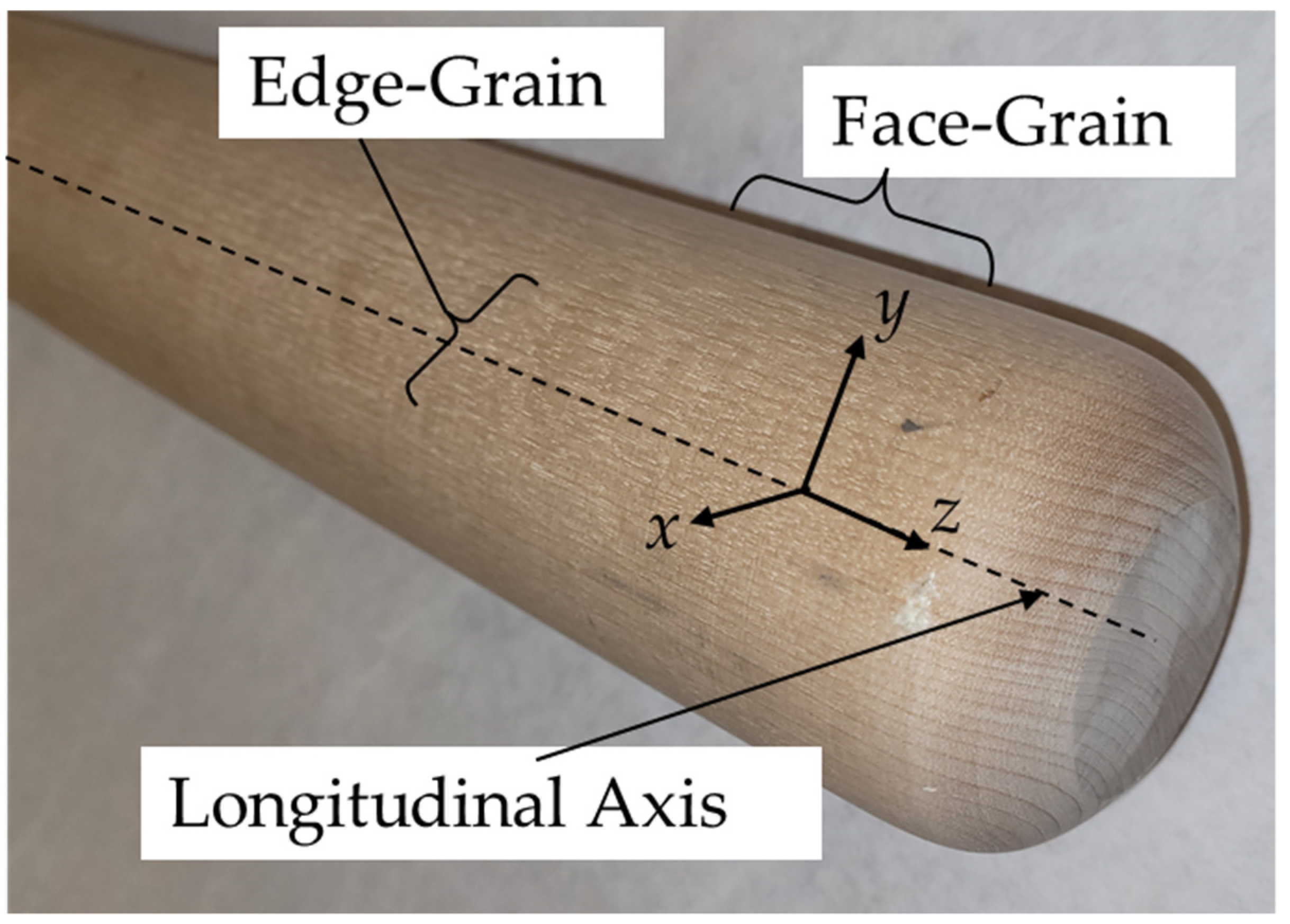
2.1. Wood
2.2. Baseball Bat Profiles
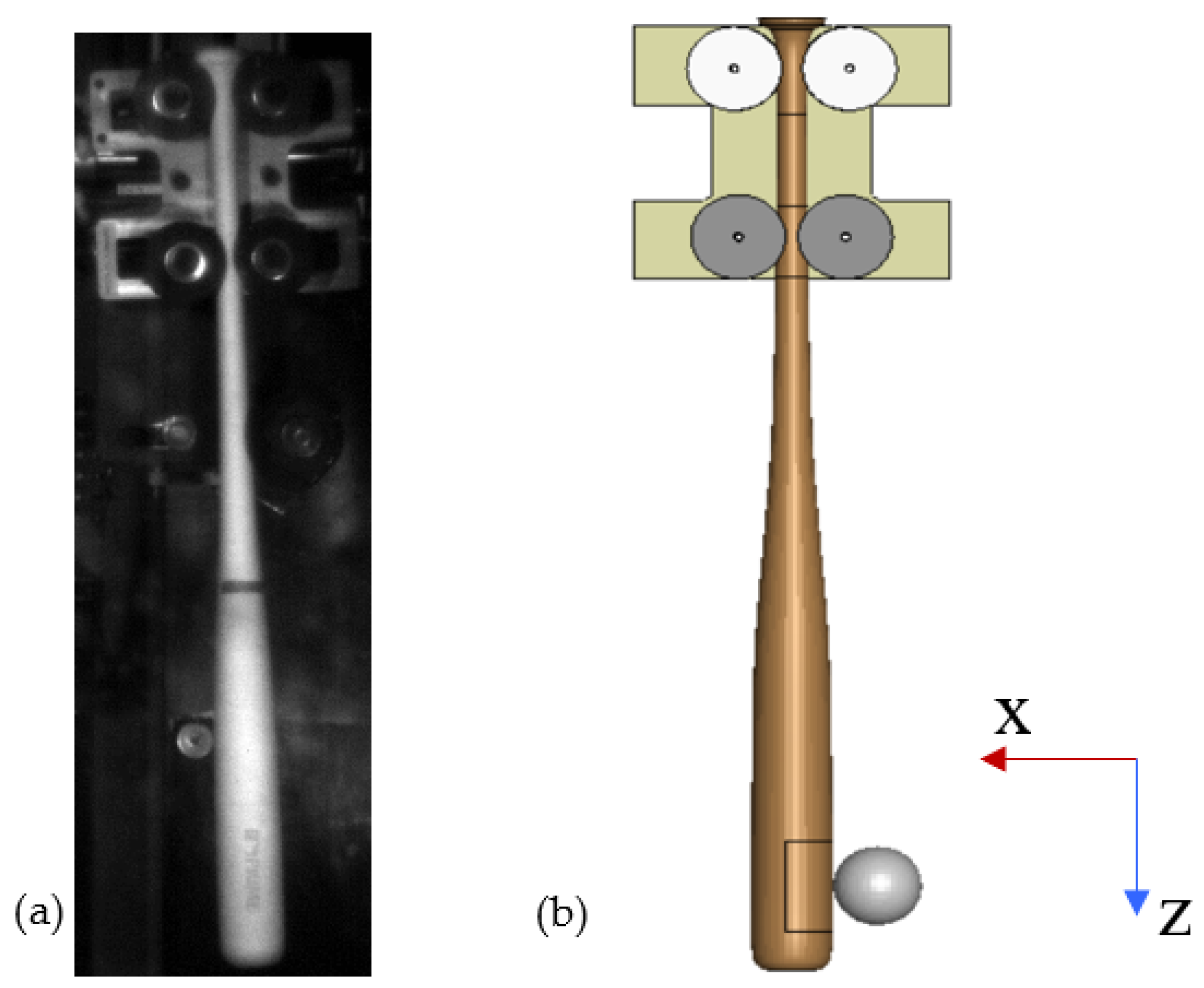
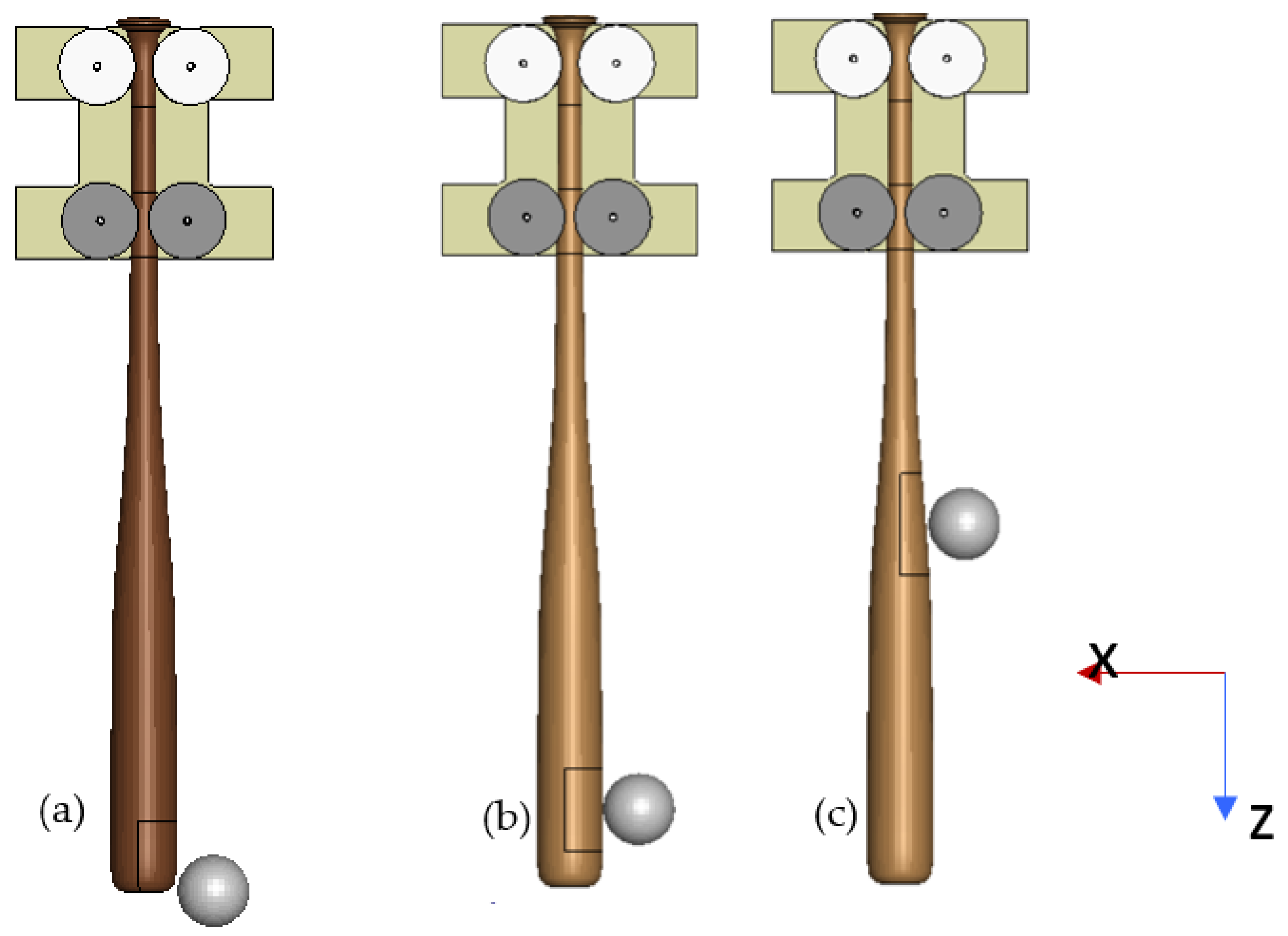
2.3. Finite Element Analysis
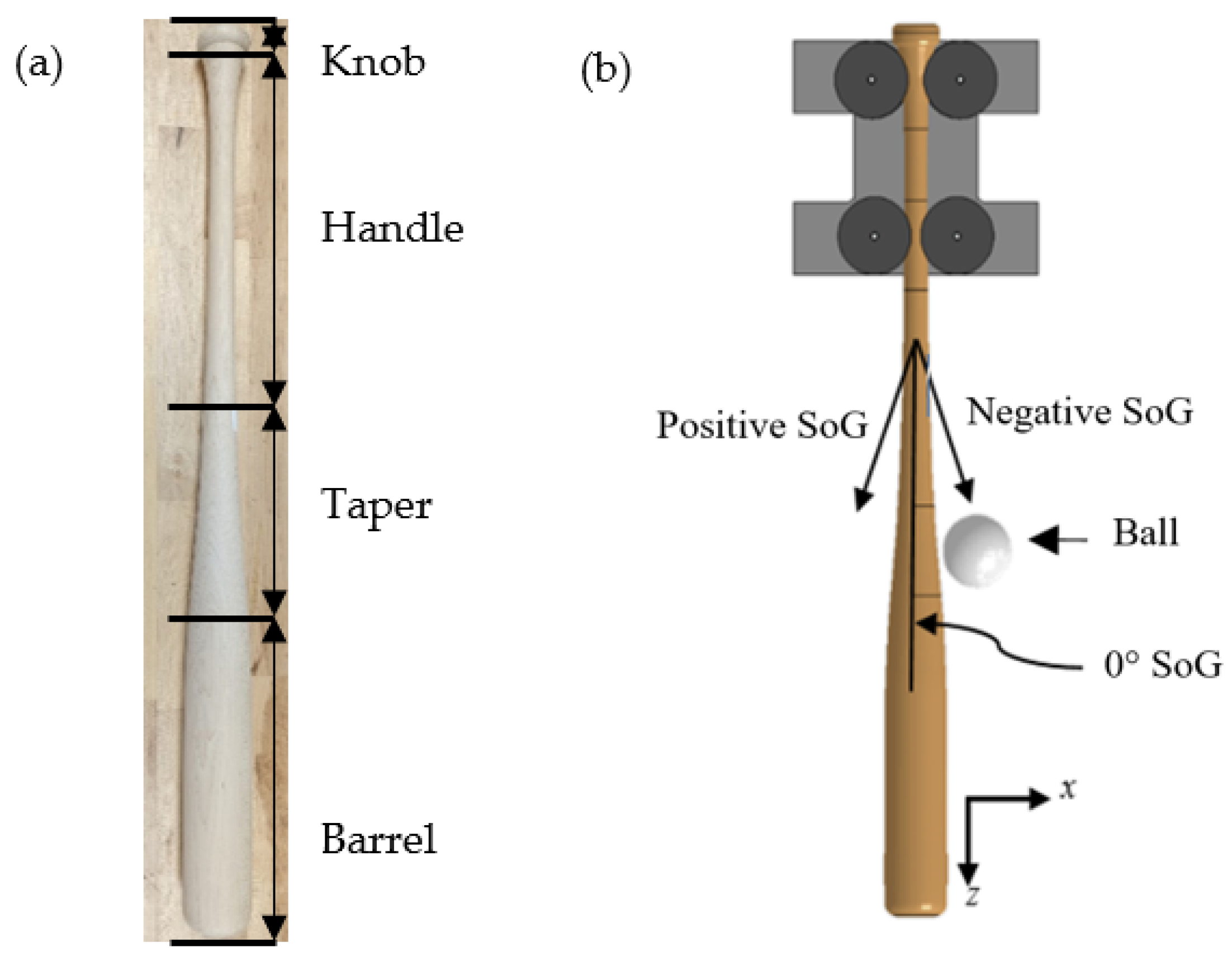
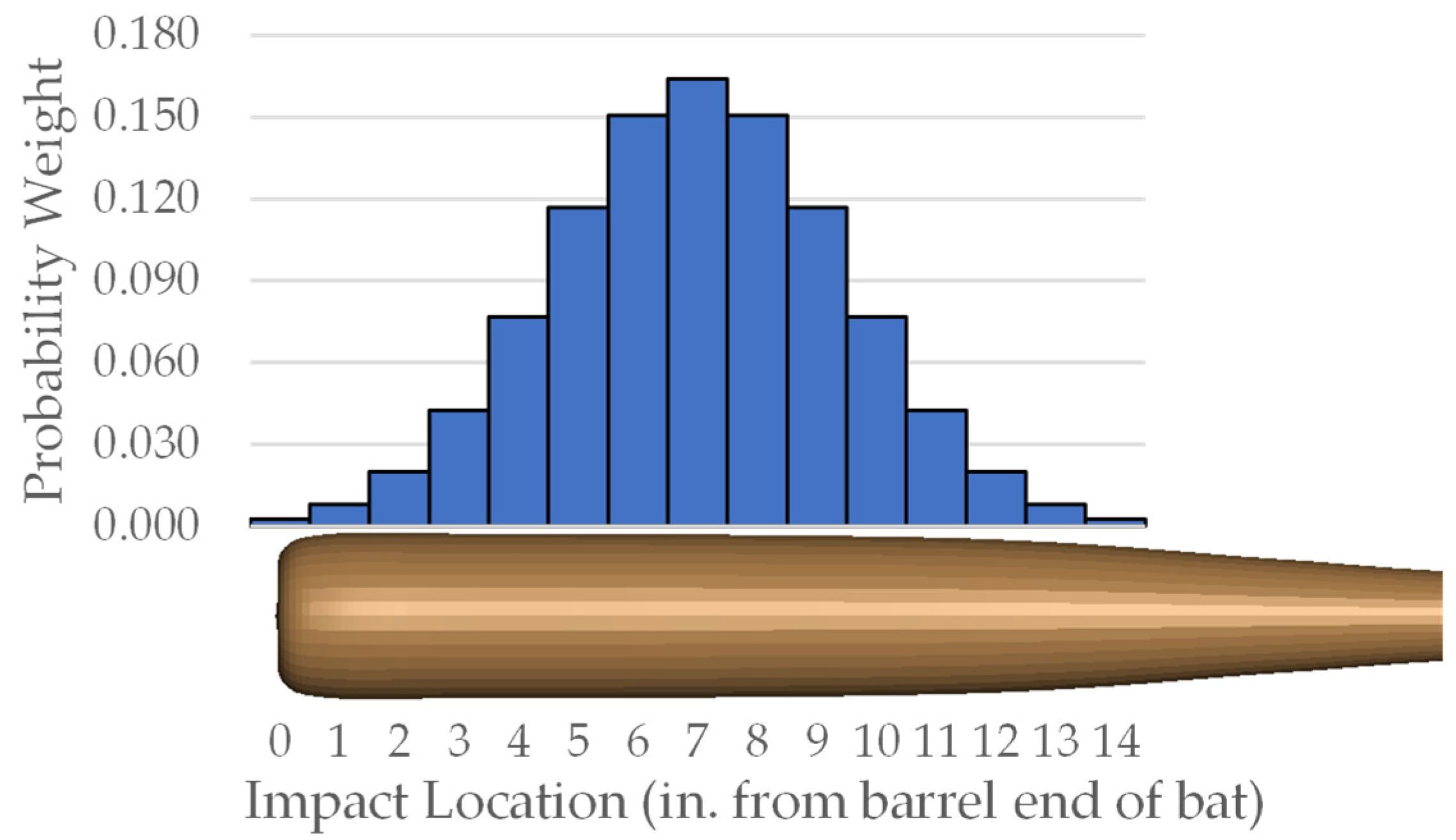
2.4. Impact Locations
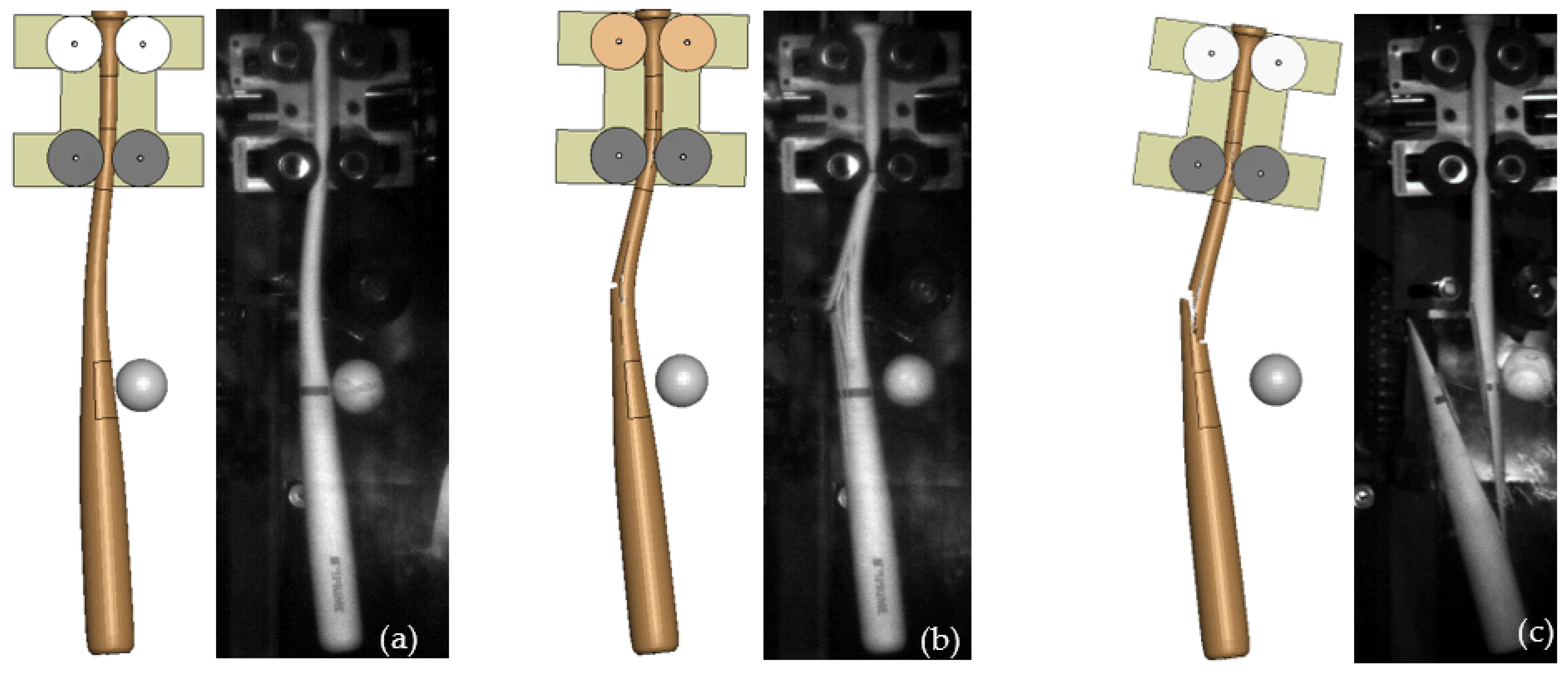
2.5. Wood Failure
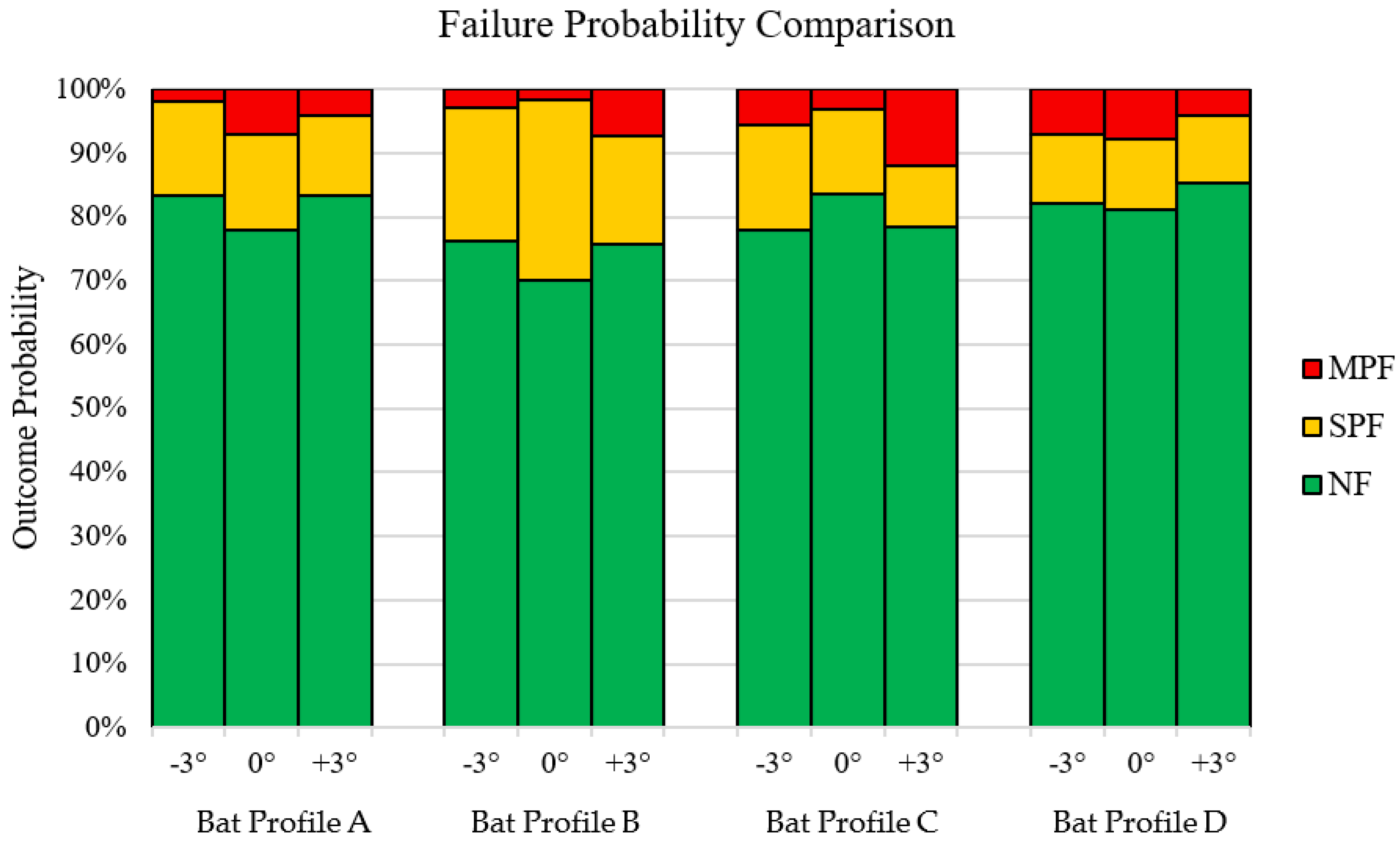
2.6. Failure Probability Analysis
2.7. Probability Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. LS-DYNA Material Properties Used in Finite Element Modeling
| Material Property | LS-DYNA Material Variable | Unit | Profile A | Profile B | Profile C | Profile D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume | - | in3 | 79.7 | 84.2 | 82.2 | 90.4 |
| Density | RO | lb/in3 | 0.0243 | 0.0230 | 0.0236 | 0.0214 |
| Strain-To-Failure | MAXEPS | - | 0.0234 | 0.0223 | 0.0227 | 0.0208 |
| Parallel Normal Modulus | EL | psi | 2,250,424 | 2,198,507 | 2,220,880 | 2,135,444 |
| Perpendicular Normal Modulus | ET | psi | 146,278 | 142,903 | 144,357 | 138,804 |
| Parallel Shear Modulus | GLT | psi | 249,797 | 244,034 | 246,518 | 237,034 |
| Perpendicular Shear Modulus | GTR | psi | 79,666 | 77,828 | 78,620 | 75,596 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | PR | - | 0.476 | 0.476 | 0.476 | 0.476 |
| Parallel Tensile Strength | XT | psi | 21,821 | 20,518 | 21,079 | 18,936 |
| Parallel Compressive Strength | XC | psi | 10,882 | 10,232 | 10,512 | 9443 |
| Perpendicular Tensile Strength | YT | psi | 2097 | 1972 | 2026 | 1820 |
| Perpendicular Compressive Strength | YC | psi | 2043 | 1921 | 1974 | 1773 |
| Parallel Shear Strength | SXY | psi | 3238 | 3045 | 3128 | 2810 |
| Perpendicular Shear Strength | SYZ | psi | 4534 | 4263 | 4380 | 3937 |
| Material Property | LS-DYNA Material Variable | Unit | Profile A | Profile B | Profile C | Profile D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume | - | cm3 | 1306.0 | 1379.8 | 1347.0 | 1481.4 |
| Density | RO | g/cm3 | 0.673 | 0.637 | 0.653 | 0.592 |
| Strain-To-Failure | MAXEPS | - | 0.0234 | 0.0223 | 0.0227 | 0.0208 |
| Parallel Normal Modulus | EL | MPa | 15,516.1 | 15,158.2 | 15,312.4 | 14,723.4 |
| Perpendicular Normal Modulus | ET | MPa | 1008.6 | 985.3 | 995.3 | 957.0 |
| Parallel Shear Modulus | GLT | MPa | 1722.3 | 1682.6 | 1699.7 | 1634.3 |
| Perpendicular Shear Modulus | GTR | MPa | 549.3 | 536.6 | 542.1 | 521.2 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | PR | - | 0.476 | 0.476 | 0.476 | 0.476 |
| Parallel Tensile Strength | XT | MPa | 150.5 | 141.5 | 145.3 | 130.6 |
| Parallel Compressive Strength | XC | MPa | 75.0 | 70.5 | 72.5 | 65.1 |
| Perpendicular Tensile Strength | YT | MPa | 14.5 | 13.6 | 14.0 | 12.5 |
| Perpendicular Compressive Strength | YC | MPa | 14.1 | 13.2 | 13.6 | 12.2 |
| Parallel Shear Strength | SXY | MPa | 22.3 | 21.0 | 25.6 | 19.4 |
| Perpendicular Shear Strength | SYZ | MPa | 31.3 | 29.4 | 30.2 | 27.1 |
References
- Tinkler-Davies, B.; Ramage, M.H.; Shah, D.U. Replacing willow with bamboo in cricket bats. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part P J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2021, 17543371211016592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, G.J.; Hassett, L.P.; Brádaigh, C.M. Mechanical analysis of equipment for the game of hurling. Sports Eng. 1998, 1, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, S.; Mather, J.; Brooks, R. Cricket Bat design and analysis through impact vibration modelling. In The Engineering of Sport; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, D. The Timeline History of Baseball; Thunder Bay Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrieri, V. How Maple Bats Kicked Ash and Conquered Baseball. Deadspin. 28 August 2018. Available online: https://deadspin.com/how-maple-bats-kicked-ash-and-conquered-baseball-1828559282 (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Thompson, A. The Science Behind Breaking Baseball Bats Live Science, Future US, Inc. 15 July 2008. Available online: https://www.livescience.com/2699-science-breaking-baseball-bats.html (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Major League Baseball. Safety and Health Advisory Committee Conducts First Meeting; Major League Baseball: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Major League Baseball. MLB, MLBPA Adopt Recommendations of Safety and Health Advisory Committee; Major League Baseball: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Saraceno, J. Taking a Swing as Safer Bats. USA Today, 15 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Drane, P.; Sherwood, J.; Colosimo, R.; Kretchmann, D. A study of wood baseball bat breakage. Procedia Eng. 2012, 34, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ruggiero, E.; Sherwood, J.; Drane, P.; Kretschmann, D. An investigation of bat durability by wood species. Procedia Eng. 2012, 34, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, E.; Sherwood, J.; Drane, P.; Duffy, M.; Kretschmann, D. Finite Element Modeling of Wood Bat Profiles for Durability. Procedia Eng. 2014, 72, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drane, P.; Fortin-Smith, J.; Sherwood, J.; Kretschmann, D. Predict the Relationship Between Wood Baseball Bat Profile and Durability. Procedia Eng. 2016, 147, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin-Smith, J.; Sherwood, J.; Drane, P.; Kretschmann, D. A Finite Element Investigation of the Relationship Between Bat Taper Geometry and Bat Durability. Procedia Eng. 2016, 147, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin-Smith, J.; Sherwood, J.; Drane, P.; Ruggiero, E.; Campshure, B.; Kretschmann, D. A Finite Element Investigation into the Effect of Slope of Grain on Wood Baseball Bat Durability. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/9/18/3733 (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Fortin-Smith, J.; Sherwood, J.; Drane, P.; Kretschmann, D. Characterization of Maple and Ash Material Properties as a Function of Wood Density for Bat/Ball Impact Modeling in LS-DYNA. Procedia Eng. 2016, 147, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drane, P.J.; Sherwood, J.A.; Shaw, R.H. An Experimental Investigation of Baseball Bat Durability. In The Engineering of Sport 6; Moritz, E.F., Haake, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Campshure, B.; Drane, P.; Sherwood, J. An Investigation of Maple Wood Baseball Bat Durability as a Function of Bat Profile Using LS-DYNA. In Proceedings of the 16th International LS-DYNA Users Conference, 10–11 June 2020; Available online: https://www.dynalook.com/conferences/16th-international-ls-dyna-conference/modeling-t11-1/t11-1-c-modeling-062.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Trentacoste, M.F. Manual for LS-DYNA Wood Material Model 143; p. 166. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/35895/dot_35895_DS1.pdf?download-document-submit=Download (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Marray, Y.D.; Reid, J.D.; Faller, R.K.; Bielenberg, B.W.; Paulsen, T.J. Evaluation of LS-DYNA Wood Material Model 143; Federal Highway Adminstration: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- LivermoreSoftware Technology (LST). LS-DYNA Keyword User’s Manual. 2020. Available online: https://www.dynasupport.com/manuals/ls-dyna-manuals/ls-dyna_manual_volume_ii_r12.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2021).
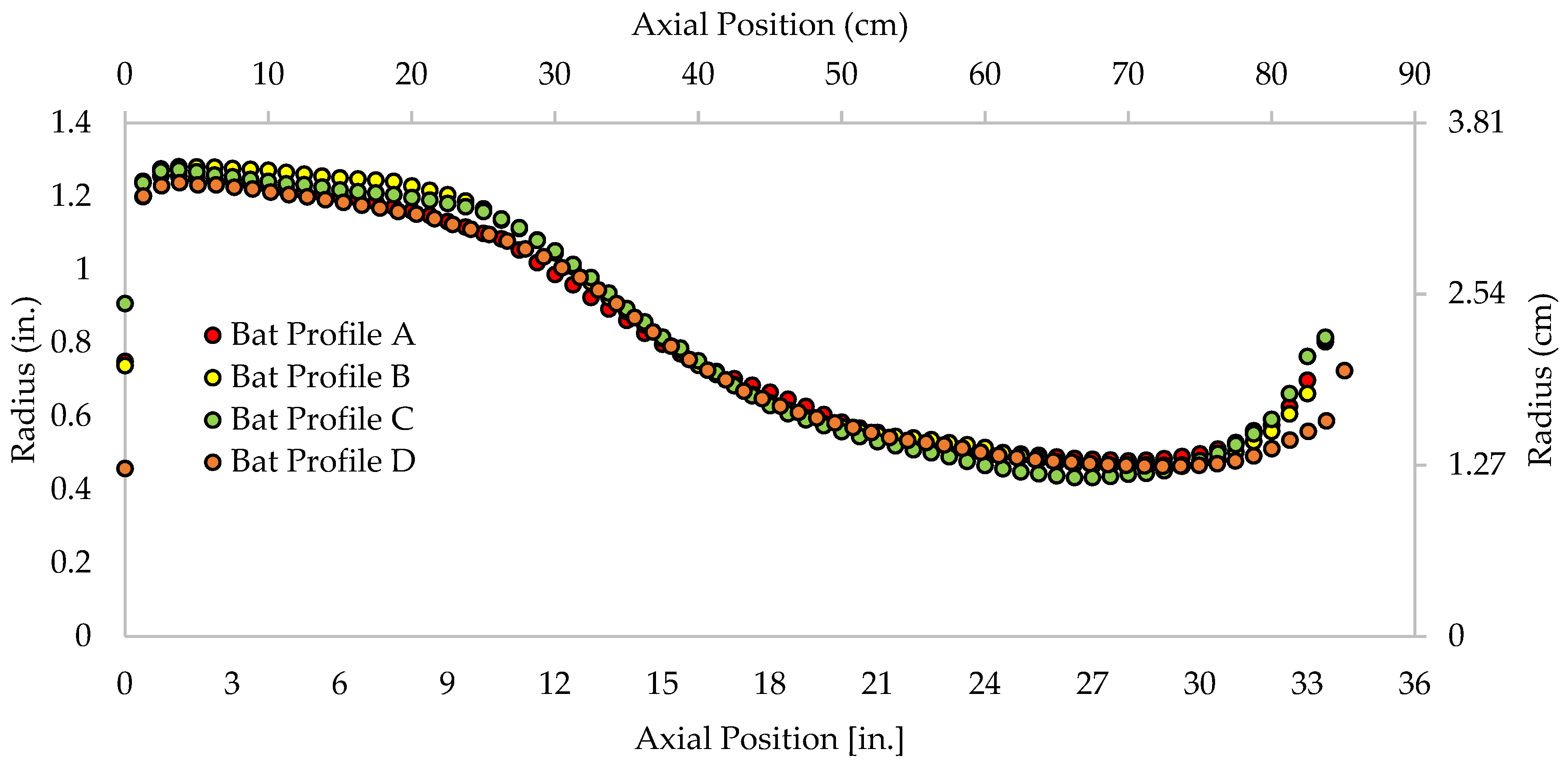
| Profile | Volume | Density | Min Handle Diameter | Max Barrel Diameter | 6-Inch Sweet Spot Diameter | 11-Inch Transition Diameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in3 (cm3) | lb/in3 (g/cm3) | in. (cm) | in. (cm) | in. (cm) | in. (cm) | |||||||
| A | 79.7 | (1306) | 0.0243 | (0.673) | 0.479 | (1.217) | 1.257 | (3.193) | 1.201 | (3.051) | 1.054 | (2.677) |
| B | 84.2 | (1380) | 0.0230 | (0.637) | 0.465 | (1.181) | 1.281 | (3.254) | 1.251 | (3.178) | 1.112 | (2.824) |
| C | 82.2 | (1347) | 0.0236 | (0.672) | 0.434 | (1.102) | 1.273 | (3.233) | 1.218 | (3.093) | 1.115 | (2.832) |
| D | 90.4 | (1481) | 0.0214 | (0.592) | 0.497 | (1.262) | 1.326 | (3.368) | 1.269 | (3.223) | 1.133 | (2.878) |
| Bat Profile | Mean Values | Standard Deviation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF% | SPF% | MPF% | NF% | SPF% | MPF% | |
| A | 81.5 | 14.2 | 4.3 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 2.5 |
| B | 74.1 | 21.9 | 4.0 | 3.4 | 5.7 | 2.9 |
| C | 80.0 | 13.1 | 6.9 | 3.1 | 3.5 | 4.5 |
| D | 82.9 | 10.7 | 6.4 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campshure, B.; Drane, P.; Sherwood, J.A. An Investigation of Wood Baseball Bat Durability as a Function of Bat Profile and Slope of Grain Using Finite Element Modeling and Statistical Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073494
Campshure B, Drane P, Sherwood JA. An Investigation of Wood Baseball Bat Durability as a Function of Bat Profile and Slope of Grain Using Finite Element Modeling and Statistical Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(7):3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073494
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampshure, Blake, Patrick Drane, and James A. Sherwood. 2022. "An Investigation of Wood Baseball Bat Durability as a Function of Bat Profile and Slope of Grain Using Finite Element Modeling and Statistical Analysis" Applied Sciences 12, no. 7: 3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073494
APA StyleCampshure, B., Drane, P., & Sherwood, J. A. (2022). An Investigation of Wood Baseball Bat Durability as a Function of Bat Profile and Slope of Grain Using Finite Element Modeling and Statistical Analysis. Applied Sciences, 12(7), 3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12073494







