Abstract
Peri-implant infections are the most common complications related to the placement of dental implants. There are many microbial similarities between peri-implantitis and periodontitis but due to current laboratory techniques there are just as many differences. This review was performed to assess changes in the oral microbiota at sites with peri-implant disease, according to the state of the art. The peri-implant microbiota presents a lower microbial quality than the periodontal microbiota, becoming increasingly complex as it progresses from peri-implant mucositis to peri-implantitis. The microbial difference detected between the peri-implant and periodontal microbiota is primarily related to whole bacterial populations, rather than specific bacterial taxa. The use of probiotics could support the reduction of peri-implant pockets, in association with mechanical debridement, due to their mechanism of action of competitive inhibition for adhesion sites. The peri-implant microbiota represents a qualitatively inferior but quantitatively superior bacterial ecosystem for some bacterial genera compared to the periodontal microbiota, showing that a progression from healthy state to peri-implantitis causes changes in microbiota composition in the absence of specific disease-causing bacteria. Transcriptomics could provide useful information for the prevention, diagnosis, and therapy of peri-implant pathology through knowledge of bacterial virulence factors.
1. Introduction
Dental implants are medical–surgical devices placed in the jaw bones in order to replace one or more missing teeth by prosthetics [1]. The process that leads to integration of dental implants into the bone was described by Branemark in the 1960s and is called osseointegration, which is a direct connection, both structural and functional, between the vital bone and the surface of a loaded (i.e., prosthetic) implant [2].
Peri-implant infections are the most common complications related to the placement of dental implants: they are classified into peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis [3]. According to the most recent guidelines, the diagnosis of peri-implant mucositis can be made if bleeding on probing (BOP) or suppuration is present in the absence of radiographic crestal bone loss (beyond initial remodeling); peri-implantitis also involves bone resorption (beyond initial remodeling) and, consequently, an increase in probing pocket depth (PPD) [4].
The prevalence of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis can be as high as 80% and 56%, respectively [5].
Risk factors related to the development of peri-implant disease reported in the literature are: smoking [6], genetic factors such as a combined IL-1 genotype positivity [7], history of periodontitis [8], poor oral hygiene [9], systemic diseases (uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular and immunodepressive diseases) [10], iatrogenic causes (such as extra cement) [11], poor peri-implant soft tissue quality (keratinized gingiva thickness < 2 mm) [12], history of one or more implant losses [13], excessive occlusal loading [14], and titanium particles [15].
The primary etiological factor in the development of peri-implant diseases is the biofilm, which is a complex microbial community consisting of numerous micro-organisms that can communicate with each other through fine molecular processes (known as “quorum sensing”) [16]. The oral microbiota consists of more than 700 different species, which rarely live in planktonic form but aggregate in communities to form the biofilm; it can grow both on mineralized tooth surfaces, leading to periodontitis, and on titanium implant surfaces, leading to peri-implant mucositis and, in the long term, peri-implantitis [17].
Salivary film, termed “acquired pellicle”, is a bacteria-free biofilm that covers dental and implant surfaces exposed to the oral cavity due to the presence of saliva; different surface receptors are expressed in order to set up molecular links with late bacterial colonizers [18].
Salivary film on titanium surfaces does not include low molecular weight cystatins and mucins, in contrast to biofilms adherent to enamel surfaces [19]. However, the underlying differences in the composition of films formed on titanium does not appear to represent a risk factor that can increase initial bacterial adhesion to implant surfaces [20].
It has been shown that only 30 min after implant insertion, there is a conspicuous bacterial colonization able to develop a well-organized biofilm in the peri-implant space after 2 weeks [17]. In the following months, the peri-implant biofilm that has formed appears to be qualitatively less diversified in micro-organisms than that present on neighboring teeth, if present [21].
There are many similarities in the microbial composition and immunological processes underlying the pathogenesis of periodontitis and peri-implantitis, but there are some significant differences that have to be considered [22].
From a histological and immunophysiological point of view, there are some important differences that make dental implants more susceptible to oral infections [23]. Whereas natural teeth are placed in the alveoli by the periodontal ligament (PDL), osseointegrated implants have a direct connection to the bone: the absence of the PDL reduces the blood flow to the supraperiosteal vessels and, consequently, limits the amount of nutrients and immunity cells that can come out of the vessels to deal with the ongoing bacterial infection [24]. In addition, the arrangement of the supracrestal connective fibers is circumferential around the implants, rather than perpendicular as in natural teeth: this anatomical feature represents a less effective physical barrier against submucosal bacterial invasion [25].
Therefore, the aim of this narrative review is to present the most recent data regarding differences in the oral microbiota in healthy peri-implant sites and peri-implantitis sites, comparing bacterial species to sites with periodontitis, showing species in common.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Focused Questions
Does the peri-implant oral microbiota, with or without peri-implant disease, change from the periodontal oral microbiota? Are some specific bacterial strains present in healthy peri-implant sites, or with peri-implant mucositis or peri-implantitis?
2.2. Elegibility Criteria
The following inclusion criteria guided the analysis of the studies:
Type of studies. Clinical trials, case-control studies, cross-sectional studies, cohort studies, narrative reviews, and systematic reviews.
Type of participants. Patients with healthy peri-implant and/or periodontal sites, patients with peri-implant mucositis and/or gingivitis, patients with peri-implantitis and/or periodontitis.
Type of interventions. Changes in the peri-implant microbiota compared to the periodontal microbiota, both in health and disease, assessed through case-control, cross-sectional, cohort, clinical, and review studies.
Outcome type. Quantitative and qualitative changes in the peri-implant microbiome compared with the periodontal microbiota with possible identification of specific bacterial genera.
Only studies that met all inclusion criteria were included. However, the following exclusion criteria were included: (I) studies where only the periodontal microbiota was analyzed, (II) presence of concomitant systemic diseases/treatments that could influence the results, (III) in vitro or animal clinical studies, (IV) non-titanium implant materials, and (V) absence of Ethics Committee approval.
2.3. Search Strategy
The PICO model (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) was used to perform this narrative review, through a literature search of the Pubmed (MEDLINE) and Scopus electronic databases. Abstracts of studies that evaluated changes in the peri-implant oral microbiota in comparison to the periodontal microbiota in health or disease were reviewed.
2.4. Research
The search was performed using the following keywords: “microbiota” AND “dental implants”, “microbiota” AND “peri-implant mucositis”, microbiota” AND “peri-implantitis”, “microbiota” AND “periodontology”, “microbiota” AND “periodontitis”, “microbiota” AND “dysbiosis”.
3. Synthesis of Results
The peri-implant microbiota shows less bacterial differentiation than the periodontal microbiota, becoming more complex when switching from peri-implant mucositis to peri-implantitis. The microbial differences found between the peri-implant and periodontal microbiota are mainly related to bacterial populations belonging to the classes Bacteroidia, Spirochaetes, Synergistia, Clostridia and Deltaproteobacteria [24]. However, some bacterial strains were detected only at sites with peri-implantitis, such as Porphyromonas spp. HOT-395, Porphyromonas nigrescens, Porphyromonas oris, Treponema maltophilum, Dialister invisus, Eubacterium saphenum, Filifactor alocis, Freitbacterium fastidiosum, Mitsuokella spp. HOT 131, Chloroflexi spp., Tenericutes spp. and Fretibacterium HMT 360 [26].
Detecting the bacterial populations that compose the oral peri-implant dysbiotic microbiota is important in the prevention, diagnosis, and therapy of peri-implant pathologies, regarding the introduction of probiotics as an additional therapy to the gold standard mechanical debridement [27].
Risk of Bias
The risk of bias of the main articles reviewed is shown in Table 1. This review has a moderate risk of bias.

Table 1.
Risk of bias of studies is represented by the green symbol, low risk of bias; and the yellow symbol, moderate risk of bias.
The result of the search reveals that, with the MeSH terms “microbiology” AND “dentistry” there are 30,353 articles; with “microbiology” AND “periodontology” there are 6772 publications; with “microbiology” AND “dental” AND “implants”, 1580 articles; with “microbiota” AND “dentistry”, 2609 publications; with “microbiota” AND “periodontology”, 994 articles; and with “microbiota” AND “dental” AND “implants”, 268 publications.
Regarding the MeSH terms “microbiology” AND “dental implants”, production mainly consists of original articles (>85%) and reviews (>11%). The other studies are conference paper (1.4%) and letter, book chapter, editorial, note, conference review, short survey and retracted (<1%). For the MeSH terms “microbiota” AND “dental implants”, the main publications are original articles (>80%), reviews (>14%), and book chapter (>3%). Less cited are conferences and books (<1%).
Figure 1 shows the trend of publications over the years regarding peri-implant bacterial population studies. Using the MeSH terms “microbiology” AND “dental” AND “implants”, the first study present on Scopus dates to 1970 [39], however on PubMed (MEDLINE) until 1977 [40] there are no studies; with the MeSH terms “microbiota” AND “dental” AND “implants”, the first study present on both Scopus and PubMed (MEDLINE) is from 1986 [41].
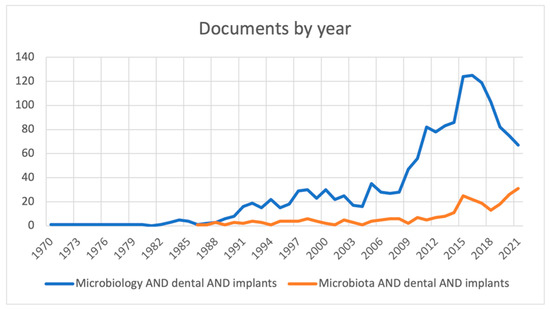
Figure 1.
Number of research papers published until 2021.
There is a high increase in the number of publications with the MeSH term “microbiology”, in contrast with “microbiota”, since this term had not yet been introduced. From 2014 to 2015, an increase is seen with the MeSH terms “microbiology” and “microbiota”, from 86 articles to 124 and from 11 to 25, respectively; from 2015 to 2021, the trend for “microbiology” is decreasing, from 124 to 67 articles, while for “microbiota” it is increasing, from 25 to 31 publications, since in the literature this term has been used recently to define resident microorganisms in the oral cavity.
4. Discussion
Implant health will be achieved if a symbiosis is established between the host and the peri-implant biofilm; however, in the presence of peri-implantitis risk factors, dysbiotic changes can occur to the microbiota constituting the peri-implant biofilm, setting off peri-implant soft tissue inflammatory processes, leading to peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis [23]. The implant material has gained interest in recent years because it may participate in peri-implant biofilm dysbiosis [42]. As a result of the process of corrosion and attrition of the implant, caused by both the exposure of titanium for long periods to oral environment and the frictional forces developing physiologically at the implant-abutment interface, ions and nano- or microparticles of this metal may be released at the peri-implant soft tissue level [43]. To date, it is unclear whether such release of metallic material can establish a tissue inflammatory response and, in association with the presence of the microbial component, play an important role in the progression of peri-implant disease [44].
Regarding the implant material, the addition of niobium and zirconium to the titanium implant alloy has been shown to have a similar bacterial adhesion pattern compared to implants composed of titanium and vanadium, with a slight increase in adhesion of A. naeslundii and S. sanguinis [28].
In the presence of poor oral hygiene for a period longer than three weeks, it has been found that dysbiosis of the peri-implant biofilm occurs, with bacterial proliferation of Tannerella forsythia, Prevotella intermedia, Fretibacterium Fastidiosum and Treponema denticola [29].
Few systematic reviews have shown that the peri-implant microbiota is similar to the periodontal microbiota in health or disease [30,45]. However, with the use of more recent molecular techniques, capable of analyzing and detecting with more precision a considerably higher number of microorganisms, the first microbial differences between submucosal biofilms, in implants, and subgingival biofilms, in teeth, have been highlighted [31]. Although logic might suggest that implants and adjacent teeth have a similar microbiota because they share a similar ecological niche, i.e., the interdental space, more recent studies suggest the presence of important differences in diagnosis and therapy, probably due to different anatomy, histology, and peri-implant immunological characteristics [46].
The first studies aimed to identify bacteria around healthy implants and, in the presence of peri-implant pathologies, used anaerobic cultures and phase-contrast microscopy, detecting Gram-positive cocci and non-motile bacilli at the level of healthy implants; in the presence of peri-implant mucositis, a greater presence of cocci, motile bacilli and spirochetes was observed, while other Gram-negative, motile and anaerobic species emerged in peri-implantitis [17].
Subsequently, with the advent of newer techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), or checkerboard DNA-DNA hybridization (CKB), a more precise inventory of micro-organisms involved in peri-implant infections has been provided, often assessing the presence of periodontopathogenic bacteria: this includes members of the “red complex” bacterial cluster, including Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, Treponema denticola, but also Treponema I-III and Synergistetes cluster A [24].
From these early studies, the main differences in the peri-implant oral microbiota compared to the periodontal microbiota indicated the presence of pathogens such as Peptostreptococcus spp. or Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus [32].
Through the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS), which is a sequencing technology used to rapidly determine the order of nucleotides in whole genomes or targeted regions of DNA or RNA, it has been possible to provide quantitatively and qualitatively enhanced classification of the oral microbiota [47].
The first study which used NGS to compare the peri-implant and periodontal microbiota was by Kumar [33]; it was concluded that 85% of the individuals analyzed shared <8% bacteria between peri-implant and periodontal sites. It was shown that the peri-implant microbiota appears to be, both in health and disease, quantitatively and qualitatively lower than the periodontal microbiota. In addition, the authors highlighted the presence, at the peri-implant site, of bacterial genera that are not present at the periodontal site: for example, the genera Burkholderia, Anaerovorax, Anaerococcus, Aerofilium and Exiguobacterium. The predominant genera in the peri-implant microbiota were Butyrivibrio, Campylobacter, Eubacterium, Prevotella, Selenomonas, Streptococcus, Actinomyces, Leptotrichia, Propionibacterium, Peptococcus, Lactococcus, and Treponema. Implant sites with peri-implantitis had lower concentrations of Prevotella and Leptotrichia and higher concentrations of Actinomyces, Peptococcus, Campylobacter, Streptococcus nonmutans, Butyrivibrio, Pseudoramibacter alactolyticus, and Streptococcus mutans than healthy peri-implant sites [31]. Finally, this study found the presence of a higher amount of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi and Staphylococcus hominis in sites with peri-implantitis compared to sites with periodontitis [33].
In a later study, also based on the use of NGS, an increased concentration of Prevotella nigrescens was shown in sites with peri-implantitis, while bacteria such as Peptostreptococcaceae spp. and Desulfomicrobium orale were significantly higher in periodontitis. In addition, the greater the severity of peri-implantitis, the higher the concentration of Treponema sp. HMT-257, which is correlated with radiographic bone resorption, subsequent increase in peri-implant pocket, and suppuration [34].
Another study showed a gradual differentiation of the microbial community from peri-implant health to peri-implant mucositis and finally to peri-implantitis. An increased concentration of periodontal bacteria such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, and Prevotella intermedia was detected at sites with peri-implant mucositis, whereas in the presence of peri-implantitis, the study observed the presence of quantitatively rich microbial communities, with an increased concentration of bacteria from the genus Eubacterium spp. [35]. Moreover, if the subject is a smoker, in healthy peri-implant sites the peri-implant microbiota is qualitatively less diversified, but there are more bacteria typical of peri-implant disease; instead, in sites with peri-implant mucositis, there is a quantitative reduction of bacterial species typically present in a healthy peri-implant site, also reducing its bacterial diversification; finally, it has been demonstrated that there are no qualitatively and quantitatively significant changes in the progression from peri-implant mucositis to peri-implantitis [36].
Bacteria from the classes Gammaproteobacteria (genus Vibrio), Epsilonproteobacteria (genus Campylobacter), and Bacilli (genus Granulicatella) were identified in greater amounts in the peri-implant crevicular fluid of healthy sites, whereas the classes Gammaproteobacteria (genus Acinetobacter and Moraxella) and Actinobacteria (genus Micrococcus) mainly in sites with peri-implantitis [37].
Bacteria belonging to the genus Filifactor, typically found at sites with chronic periodontitis, Dialister, Mogibacterium, Propionibacterium, Acinetobacter, Staphylococcus, Paludibacter, and Bradyrhizobium were identified only at healthy peri-implant sites [38].
The introduction of a new sequencing system, called MiSeq Illumina, has the advantage of reducing the procedural error and increasing the ability to detect more bacterial species. It has been shown that, at healthy peri-implant sites, there is a predominance of bacteria belonging to the class Actinomycetia and bacterial species such as Veillonella dispar, Rothia dentocariosa and Streptococcus sanguinis, while in the presence of peri-implantitis, the microbiota is characterized by the quantitative increase of bacteria belonging to the classes Bacteroidia, Spirochaetes, Synergistia (species Synergistetes spp. HOT-360), Clostridia (species Clostridiales spp. HOT-093 and Catonella morbi), Deltaproteobacteria, of periodontopathogenic bacteria belonging to the “red complex” and finally of bacterial species such as Porphyromonas spp. HOT-395, Porphyromonas nigrescens, Porphyromonas oris, Treponema maltophilum, Dialister invisus, Eubacterium saphenum, Filifactor alocis, Freitbacterium fastidiosum, Mitsuokella spp. HOT 131, Chloroflexi spp., Tenericutes spp. and Fretibacterium HMT 360 [26].
Based on the studies in the literature, through the introduction of NGS and the MiSeq Illumina system, the authors agreed that the peri-implant and periodontal microbiota presents quantitative and qualitative differences: in particular, the peri-implant microbiota presents less bacterial diversification than the periodontal microbiota, regardless of health or disease status, becoming more complex as it moves from peri-implant mucositis to peri-implantitis [35]. The microbial diversity detected between the peri-implant and periodontal microbiota should not be related to quantitative and qualitative changes in individual bacterial species, but rather to bacterial populations [36].
Results of the single study performed to date, based on the assessment of bacterial messenger RNAs (mRNAs), suggest that the intrinsic characteristics of the microorganisms composing the microbiota in sites with peri-implantitis and periodontitis, which favor the expression of bacterial pathogenicity, are similar to each other [27]. However, the capacity for inter-bacterial interaction appears to be more sophisticated at sites with peri-implantitis, with the presence of some significantly associated bacterial species [27].
Summary table of the main clinical trial and systematic review included in this work is shown in Table S1 (Supplementary Materials) and a complete list of bacteria typically presents in healthy peri-implant sites, with peri-implantitis, and with periodontitis are shown in Figure 2, also highlighting bacterial species in common.
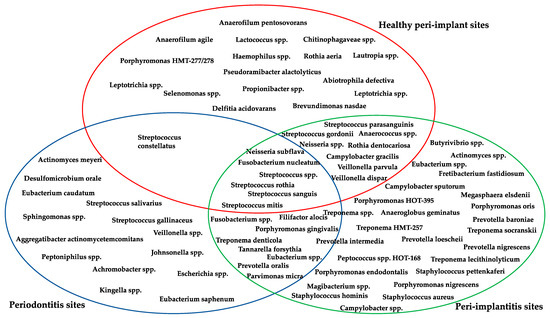
Figure 2.
Bacterial species in healthy peri-implant sites and with peri-implantitis, in sites with periodontitis, and in common between the two sites [26,27,29,31,32,33,34,35,37].
5. Conclusions
Peri-implant microbiota presents a different bacterial ecosystem compared to the periodontal microbiota, as it is qualitatively lower, in terms of microbial diversity, but quantitatively higher for some bacterial genera.
In addition, the progression from the healthy state to peri-implantitis shows changes in the composition of the microbiota in the absence of specific disease-causing bacteria.
Further studies are needed to evaluate the functional changes and virulence factors of the bacterial strains that belongs to peri-implant microbiota, which are directly proportional to the pathogenic capacity of the microbiota itself in disease evolution. Knowing these factors could help in improving prevention, diagnosis and treatment of peri-implant disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app12073250/s1, Table S1: Summary table of the main studies included in this narrative review.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and A.S.; methodology, A.S. and A.B.; software, A.S.; validation, S.G. and M.P. (Maurizio Pascadopoli); formal analysis, A.S.; investigation, A.B.; resources, A.B.; data curation, P.Z. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.P. (Maurizio Pascadopoli) and M.P. (Matteo Pellegrini); writing—review and editing, A.S., S.G. and M.P. (Maurizio Pascadopoli); visualization, A.S. and A.B.; supervision, A.S.; and project administration, A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Upon request to the corresponding author, the data are available for use.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siadat, H.; Alikhasi, M.; Beyabanaki, E. Interim Prosthesis Options for Dental Implants. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 4, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Dimitriou, R.; Parvizi, J.; Babis, G.C. Biology of implant osseointegration. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2009, 9, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Wisitrasameewon, W.; Humain, M.; Thunyakitpisal, P. Peri-implantitis Update: Risk Indicators, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant disease and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant disease and conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S286–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romanos, G.E.; Weitz, D. Therapy of peri-implant diseases. Where is the evidence? J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, P.L.; Aguiar, T.; Pinheiro, M.P.F.; Machado, A.; Pinheiro, A.R. Smoking as a Risk Factor for the Development of Periimplant Diseases. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreiotelli, M.; Koutayas, S.O.; Madianos, P.N.; Strub, J.R. Relationship between interleukin-1 genotype and peri-implantitis: A literature review. Quintessence Int. 2008, 39, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chen, Z.; Pan, W.L.; Wang, H.L. Is History of Periodontal Disease Still a Negative Risk Indicator for Peri-implant Health under Supportive Post-implant Treatment Coverage? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhe, J.; Meyle, J.; Group D of European Workshop on Periodontology. Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smeets, R.; Henningsen, A.; Jung, O.; Heiland, M.; Hammächer, C.; Stein, J.M. Definition, etiology, prevention and treatment of peri-implantitis—A review. Head Face Med. 2014, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapoff, C.A.; Lahey, B.J. Crestal bone loss and the consequences of retained excess cement around dental implants. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2012, 33, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thoma, D.S.; Naenni, N.; Figuero, E.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Schwarz, F.; Jung, R.E.; Sanz-Sánchez, I. Effects of soft tissue augmentation procedures on peri-implant health or disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervaeke, S.; Collaert, B.; Cosyn, J.; Deschepper, E.; De Bruyn, H. A multifactorial analysis to identify predictors of implant failure and peri-implant bone loss. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e298–e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, C.D.; Almas, K. The implant surface characteristics and peri-implantitis. An evidence-based update. Odontostomatol. Trop. 2016, 39, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mombelli, A.; Hashim, D.; Cionca, N. What is the impact of titanium particles and biocorrosion on implant survival and complications? A critical review. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2018, 29, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Li, M.; Gregory, R.L. Bacterial interactions in dental biofilm. Virulence 2014, 2, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Charalampakis, G.; Bostanci, N.; Stadlinger, B. Peri-implant infections of oral biofilm etiology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 830, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Thurnheer, T.; Paqué, P.N. Biofilm Models to Study the Etiology and Pathogenesis of Oral Diseases. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2021, 29, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, N.G.; Aparicio, C. The salivary pellicle on dental biomaterials. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.C.; Nagay, B.E.; Bertolini, M.; Costa-Oliveira, B.E.; Sampaio, A.A.; Ratamal-Valdes, B.; Shibli, J.A.; Feres, M.; Barão, V.A.; Souza, J.G.S. Fitting pieces into the puzzle: The impact of titanium-based dental implant surface modifications on bacterial accumulation and polymicrobial infections. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 298, 102551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. Inflammatory cytokine profiles in the crevicular fluid around clinically healthy dental implants compared to the healthy contralateral side during the early stages of implant function. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 108, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrowiecki, R.; Mielczarek, A.; Zaręba, T.; Tyski, S. Oral microbiome and peri-implant diseases: Where are we now? Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2017, 13, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belibasakis, G.N. Microbiological and immuno-pathological aspects of peri-implant diseases. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Manoil, D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovski, S.; Lee, R. Comparison of peri-implant and periodontal marginal soft tissues in health and disease. Periodontol. 2000 2018, 76, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiba, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kachi, H.; Koyanagi, T.; Maruyama, N.; Murase, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Maruyama, F.; Izumi, Y.; Nakagawa, I. Distinct interacting core taxa in co-occurrence networks enable discrimination of polymicrobial oral diseases with similar symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pantaroto, H.N.; Amorim, K.P.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Souza, J.G.S.; Ricomini-Filho, A.P.; Rangel, E.C.; Ribeiro, A.L.R.; Vaz, L.G.; Barão, V.A.R. Proteome analysis of the salivary pellicle formed on titanium alloys containing niobium and zirconium. Biofouling 2019, 35, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Chaparro, P.J.; Duarte, P.M.; Shibli, J.A.; Montenegro, S.; Heluy, S.L.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Faveri, M.; Feres, M. The Current Weight of Evidence of the Microbiologic Profile Associated With Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal-Valdes, B.; Formiga, D.C.; Almeida, M.L.; Fritoli, A.; Figueiredo, K.A.; Westphal, M.; Gomes, P.; Feres, M. Does subgingival bacterial colonization differ between implants and teeth? A systematic review. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabdoub, S.M.; Tsigarida, A.A.; Kumar, P.S. Patient-specific analysis of periodontal and peri-implant microbiomes. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 168S–175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kensara, A.; Hefni, E.; Williams, M.A.; Saito, H.; Mongodin, E.; Masri, R. Microbiological Profile and Human Immune Response Associated with Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 210–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Mason, M.R.; Brooker, M.R.; O’Brien, K. Pyrosequencing reveals unique microbial signatures associated with healthy and failing dental implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, N.; Maruyama, F.; Takeuchi, Y.; Aikawa, C.; Izumi, Y.; Nakagawa, I. Intraindividual variation in core microbiota in peri-implantitis and periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, T.; Lin, J.; Chen, F. Subgingival microbiome in patients with healthy and ailing dental implants. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, S.P.; Fontes, M.; Ribeiro, F.V.; Corrêa, M.G.; Nishii, D.; Cirano, F.R.; Casati, M.Z.; Casarin, R.C.V. Smoking habit modulates peri-implant microbiome: A case-control study. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Diversity analysis of subgingival microbial bacteria in peri-implantitis in Uygur population. Medicine 2018, 97, e9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakis, G.A.; Olmedo, D.G. Peri-implantitis is not periodontitis: Scientific discoveries shed light on microbiome-biomaterial interactions that may determine disease phenotype. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 86, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizatugu, R.; Dinamarco, P.R. Possibility of periapical contamination of teeth prepared for pin implant prosthesis following root canal obturation. Rev. Assoc. Paul. Cir. Dent. 1970, 24, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Klawitter, J.J.; Weinstein, A.M.; Cooke, F.W.; Peterson, L.J.; Pennel, B.M.; McKinney, R.V., Jr. An evaluation of porous alumina ceramic dental implants. J. Dent. Res. 1977, 56, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, J.; Natiella, J. Biomaterials, biocompatibility, and peri-implant considerations. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 30, 2–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kniha, K.; Heussen, N.; Modabber, A.; Hölzle, F.; Möhlhenrich, S.C. The effect of zirconia and titanium surfaces on biofilm formation and on host-derived immunological parameters. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 50, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagay, B.E.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Barao, V.A.R. Insight into Corrosion of Dental Implants: From Biochemical Mechanisms to Designing Corrosion-Resistant Materials. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messous, R.; Henriques, B.; Bousbaa, H.; Silva, F.S.; Teughels, W.; Souza, J.C.M. Cytotoxic effects of submicron- and nano-scale titanium debris released from dental implants: An integrative review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Sabogal, M.A.; Castillo, D.M.; Rincón, M.V.; Gómez, L.A.; Lesmes, Y.A.; Chambrone, L. Microbiome and Microbial Biofilm Profiles of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1066–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Jin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.C.; Zhou, Q. Periodontal and Peri-Implant Microbiome Dysbiosis Is Associated with Alterations in the Microbial Community Structure and Local Stability. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 785191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Yu, W.H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The human oral microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

