Abstract
Digital game-based learning (DGBL) and Gamification are emerging methodological strategies in education. This research aims to analyze the effects on academic performance and motivation after an experience combining DGBL and Gamification in university students. The sample comprises 126 students, of whom 38 were in the experimental group. Three measurement instruments have been used: an evaluative test to measure academic performance, the Questionnaire on Motivation for Cooperative Playful Learning Strategies (CMELAC) and a questionnaire with three open-ended questions, which complement the measurement of motivation. This analysis is conducted using independent sample t-tests. We undertook a Bonferroni adjustment to the alpha level (new p = 0.017). The results show significant differences in academic performance between the control and experimental groups. Motivation shows high values among all participants. No significant differences were found between the two experimental subgroups when the competition was added to the dynamics. In conclusion, the results of the present study support the gamified DGBL method as an exciting teaching tool that corresponds to students’ active learning and provide valuable immediate feedback on students’ attempts, improvements in academic performance and a high level of motivation.
1. Introduction
We are currently at a critical educational moment. Teachers in the 21st century have many pedagogical resources at their disposal, aiming to respond to current academic demands. In the last decades, Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) have gained significant importance in society and possibly in the future of education, following a clear objective: to improve the quality of the teaching-learning process [1]. Several studies show the validity of ICT tools, such as the use of the internet [2] or tools that promote digital socialization [3] in the educational world, even in a situation as critical as a global pandemic [4,5]. These ICT tools were incorporated into the pedagogical field, providing teachers with tools with a more formative use for the student, such as the LKT (Learning and Knowledge Technologies). This interesting connection [6] corroborates the recommendations of the 2030 agenda, especially the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) which refer to quality education and innovation [7]. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) [8] adopted the new global framework on education for sustainable development (ESD). It focuses on integrating ESD into policies, learning environments and capacity development of educators, among others. Therefore, to adapt and achieve the objectives pursued by both the United Nations and UNESCO, it is necessary to research and discover the most appropriate methodologies and educational strategies for each educational context and field.
The educational community needs to achieve more sustainable and meaningful learning [9], which requires a change in traditional approaches, transforming the memorization of the traditional method into more active learner participation [10]. Traditional teaching methods and techniques are no longer sufficient to meet current educational demands. Therefore, institutions and teachers must develop their practices and use new strategies [11]. In recent decades, much research has been conducted on playful pedagogical strategy [12].
Traditional learning theory focuses on the cognitive dimension and does not include the emotional and social dimensions of learning [13]. The use of games in education has been driven by researchers [14] who argued that games are essential to learning. Rapid advances in ICT and digital games have led to these technologies being seen as ideal solutions to address the education system’s shortcomings and increase student motivation and teacher acceptance [15].
In physical education, the enjoyment of any game is a fundamental right of every human being and providing excellent opportunities for developing creativity and imagination [16,17,18]. The game as a pedagogical resource allows us to work on the fundamental knowledge that will help the development of any person as a future active member of our society.
Game-Based Learning (GBL) uses games and their relationship to reality, content and the educational process, with a clear objective, the resolution or completion of tasks and the associated competencies [19]. GBL is a methodology that focuses on designing and implementing games [20] to ensure that students enjoy the playful experience [21] and guides students toward an ultimate educational goal. However, we should distinguish GBL from ‘Gamification’ [22,23]. We have already seen that GBL is based on using games as content to achieve an educational goal [24]. For example, using the trivia game, a world-famous quiz game that is also adapted to an educational context [25], changing the categories and questions to reinforce the subject content would already be a clear example of GBL.
Gamification, on the other hand, is defined as using certain game elements in a nongame context [26]. In this case, only one element of the trivial game is selected. An example of Gamification would be to provide learners with rewards in the form of objects as in the original game, for completing a task. The Game Design Element (MDA) has three crucial acronyms to consider. The first letter stands for mechanics, closely related to the game system and how it works; the second stands for dynamics, which describes the player’s behavior; and the third letter stands for aesthetics, which represents the emotional reactions it elicited from the player [27].
We note, then, that GBL and Gamification are two different terms but are compatible. The combination of both strategies, using games as an activity or content enhanced by a gamified dynamic, makes students enjoy all the elements and benefits of the game. [28].
Several studies show that Gamification on tasks, readings and classroom activities positively affects student learning and motivation [28,29]. At the same time, other research [30,31] has shown that creating and implementing games in the classroom improves academic performance and motivation. However, what would happen if, in addition to proposing a gamified dynamic, the pedagogical resources used were digital games?
In recent years, GBL has been digitized due to its adaptation to the characteristics of this generation of learners, for whom technology acceptance [32] and coherent use is an essential motivating element [33,34]. These digital games connect with a constructivist vision of learning, as they offer digital exploratory environments for learners and are ideal for experimenting and building cognitive and emotional learning [35,36,37]. Gamified DGBL is an educational strategy that creates a playful dynamic with game elements, focusing on digital games as educational activities.
1.1. Gamified Game-Based Learning and Academic Performance
GBL deepens students’ understanding of educational content so that they can solve complex problems and develop creative and critical thinking [38]. The study carried out on an information and communication technology by [39], shows that the combination of Gamification dynamics, such as leaderboards, rewards, points and challenges improves the effects of engagement on academic performance. In the same way, [40], in the context of physical education, showed that the academic performance of the gamified group increased. The use of the DGBL methodology also reported positive effects on academic performance in the study conducted by [41], with a significant increase in the scores of students who used videogames.
On the other hand, the results of studies on improving academic performance due to the use of game elements vary depending on the context of implementation [42]. A longitudinal study by [43] shows that students in the gamified course perform worse on final exams than those in the nongamified class. The author’s reason is that giving rewards that encourage competition through a digital leaderboard is detrimental to motivation. The use of the game in the specific case of [44], could not affirm that this methodology improved academic performance through digital games.
1.2. Gamified Game-Based Learning and Motivation
In the educational context, motivation is considered one of the critical factors leading to academic success [45,46]. Regarding types of motivation, the most traditional distinction, the self-determination theory [47], distinguishes intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation and demotivation. Intrinsic motivation drives activities for genuine individual interest and satisfaction, while extrinsic motivation refers to doing an activity for some separable outcome rather than for inherent enjoyment [47]. Conversely, demotivation is the lack of a volitional impulse to engage in any activity [48]. That does not originate from a self-determined motivation [49]. One element related to motivation is Flow, described as intense concentration or absolute absorption in an activity [14]. In educational contexts, high flow levels in exercises have been shown to promote optimal learning experiences [50,51].
Different studies show the positive impact of GBL on student motivation [52,53,54]. According to [55] and the author’s self-determination theory, intrinsic motivation increases engagement and performance more effectively than extrinsic motivation. When learners enjoy the internal logic [18] or the dynamics of the game, learning is experienced as an enjoyable situation, so intrinsic motivation increases [56]. Using the mechanics of how games work, such as levels, points, leaderboards and a competitive environment, can increase students’ external and internal motivation to participate in these learning situations. Intrinsic motivation is associated with Flow, motivation for learning and engagement with an activity so that the game would be a successful motivational enhancer [57]. Another critical concept is academic motivation, which drives, leads, sustains effort, activates cognitive resources for learning and has intrinsic and extrinsic reinforcers [58,59].
The study of [60] reported that most articles describe positive motivational outcomes, with significantly higher participation in activities and forums, increased attendance and downloading of material. From a similar perspective, [61] implemented an experiment using the DGBL, obtaining significantly positive results in the motivation variable, specifically in the confidence level. On the other hand, it was also experimented [62] with video-based games, which positively affected learners’ intrinsic motivation.
In contrast to previous studies it was found that there were no significant variations in intrinsic motivation after applying Gamification in the classroom [40]. One aspect to consider is the degree of specificity when assessing motivation for the subject studied, as they did [63] obtained nonsignificant motivational results when applying a GBL methodology on the mobile phone.
According to [64], there is currently a gap between learning models and the expectations of our education systems. So there is a need to adapt to new trends. Therefore, some studies recommend focusing on learning and emotional materials that promote active roles and interactions to make learning more motivating [65]. Furthermore [66] believes that active participation of students in their learning process is more critical for developing motivational skills [67], experiences and academic performance [68]. The systematic literature review in [42] identified several benefits of game-based learning, such as improved motivation, attitude, perceived learning and student performance. As some authors have shown in their studies, GBL or Gamification provides higher motivation and academic performance than a traditional educational approach [69,70,71].
Considering the wide range of effects of DGBL and Gamification and the theoretical framework of reference, this paper posed three research questions (RQ) related to the object of study:
RQ1: Are there significant differences between gamified DGBL and a traditional educational methodology on students’ academic performance?
RQ2: What level of motivation toward Flow, motivation for learning and motivation for the task does a gamified DGBL experience bring about in students?
RQ3: Are there significant differences between competitive and individual Gamified DGBL dynamics on students’ academic performance and motivation?
Regarding these questions, this study expects to study the effect of a pedagogical experience based on gamified DGBL methodology (through games and gamified dynamics) on academic performance and motivation toward Flow, motivation for learning and motivation for the task of university students studying Physical Activity and Sport Sciences.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This research corresponds to a mixed methods design [72,73] with quantitative and qualitative data by assessing spatially and temporally delimited events [74]. The research distinguished between a control group (CG) and an experimental group (EG). The decision to belong to one group or the other was entirely voluntary, as the voluntary consent of the human subject is essential in research [75]. The students could decide, without any conditions or incentives, to follow the selected contents of the assignment using a traditional methodology (lectures and classroom exercises) or to participate in a gamified DGBL method. In both groups, the distribution of the sessions, the contents, the evaluation and the grading criteria were the same (except for the interactive activities incorporated in the DGBL methodology). Therefore, the difference between the experimental and control groups was mainly due to the implementation of 10 interactive activities compared to the use of the traditional methodology in the control group.
2.2. Participants
A total of 126 university students (M = 18; SD = 0.92; age range = 17–22) enrolled in the subject Theory and Practice of Motor Game participated in this study; 77 were men (61%) and 49 were women (39%). In total, 30% of the students (n = 38) voluntarily chose to participate in the experimental group, while 70% (n = 88) elected to be part of the control group. For the study, the experimental group was randomly divided into two subgroups: the competitive experimental group, EGc (n = 17) and the individual experimental group EGi (n = 21). The methodological proposal was presented as a solution to the complexity of the theoretical content, roles, subroles and motor communication of the subject Theory and Practice of Motor Game to address the low academic and motivational performance of previous courses.
The research project was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Catalan Sports Administration (reference: 008/CEICEGC/2022).
2.3. Instruments
Three instruments were used to analyze the effect of gamified DGBL on academic performance and motivation.
Academic performance: to assess the level of learning acquired by the students, a specific test was designed for the contents selected for this experience, created and validated by the subject teacher. The test consisted of 10 random questions from a bank of 30 that were conceptual and procedural.
Motivation: the validated Motivation for Cooperative Learning Strategies questionnaire (CMELAC) [76] was used to measure perceived motivational orientation after the completion of the intervention toward task, learning and Flow. The questionnaire contains a total of 14 items assessing task motivation (5 items), learning motivation (6 items) and flow (3 items). A 5-point Likert scale (1: strongly disagree and 5: strongly agree) was applied (Table 1). The data-gathering adaptation is based on eliminating two items that refer exclusively to teamwork. This instrument was very well-adapted to the proposed experience, as it analyses the motivation aroused in game-related situations.
Using a qualitative approach, students answered three open-ended questions to support the information collected in the CMELAC questionnaire. The aim of combining the two methods was to identify the real reasons for the scores obtained in the CMELAC and to deepen the analysis from a common perspective.
Question 1—After completing gamified digital games, do you think it is motivating that the teacher applies this methodology on the virtual platform? Why?
Question 2—To make the activities more motivating, what do you think could be added?
Question 3—Did the gamified digital games motivate you to log into the course platform more frequently?
2.4. Procedure
In order to carry out the research, the head teacher of the subject was contacted to establish the curricular contents that needed a methodological transformation. Once the two contents (roles, subroles and motor communication in sports games) had been selected, ten digital games were developed and validated to incorporate these contents.
So, after reviewing and adding the digital games to the virtual platform, the experimental phase of the research began. In both groups, the distribution of the sessions, the contents, the evaluation and the grading criteria, except for the interactive activities attached to the DGBL methodology, was the same. So, the difference between the experimental and control groups was mainly due to the availability of digital games, compared to the traditional methodology in the control group. The division of the experimental groups is as follows: competitive experimental group (EGc, n = 21) and individual experimental group (EGi, n = 17) were ultimately randomized. The students in the experimental group were able to play ten games (Table A1 in Appendix A). Two digital games of each type were created for the research: crossword, interactive picture, memory game, word search and role videogame. The experiment was conducted over two months (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
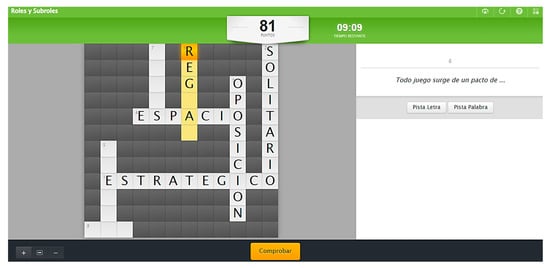
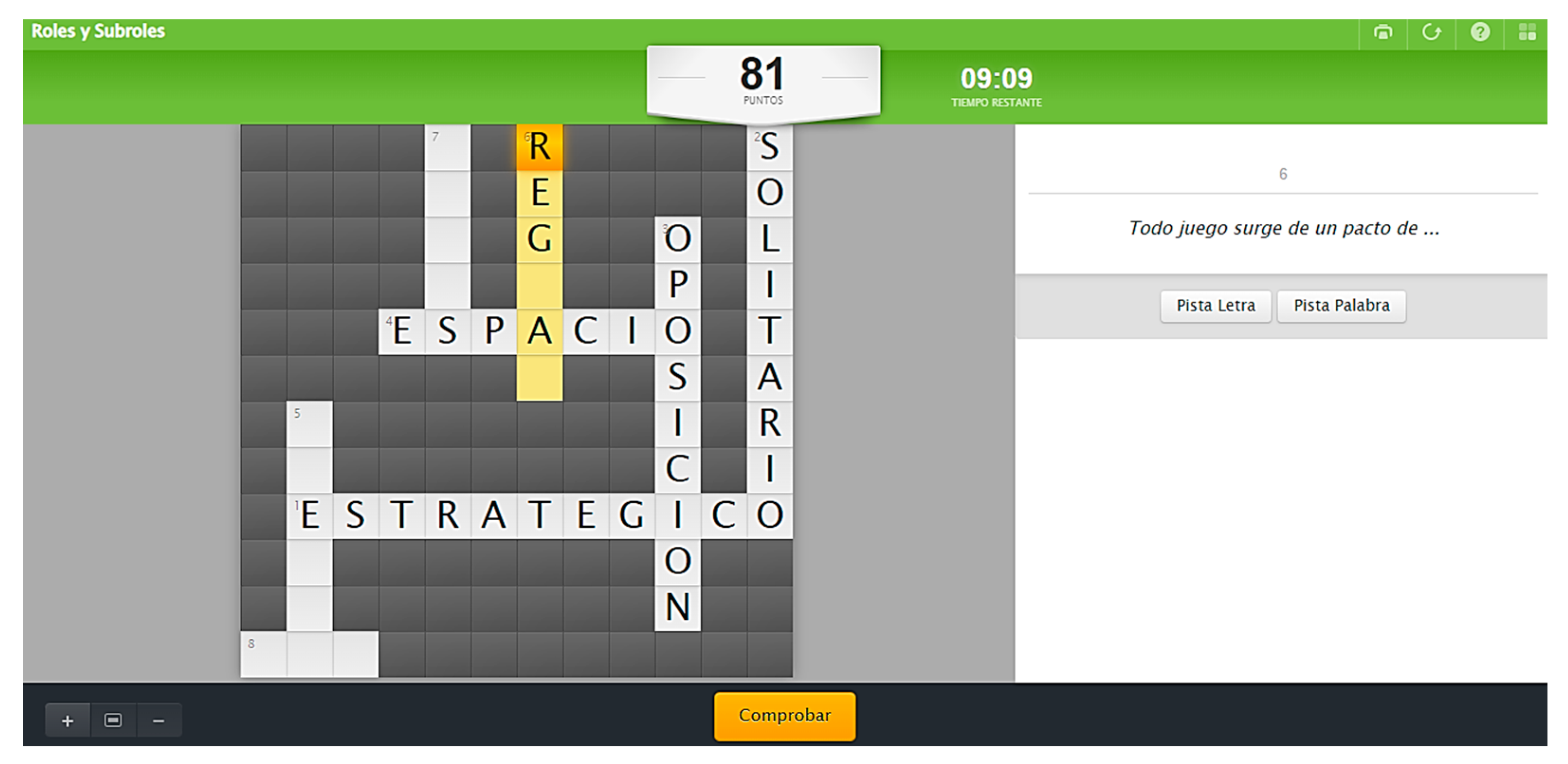
Figure 1.
Activity crossword puzzle of the content ‘Roles and Sub-roles’.
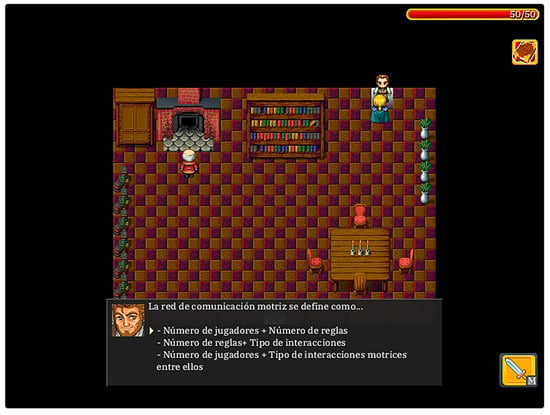
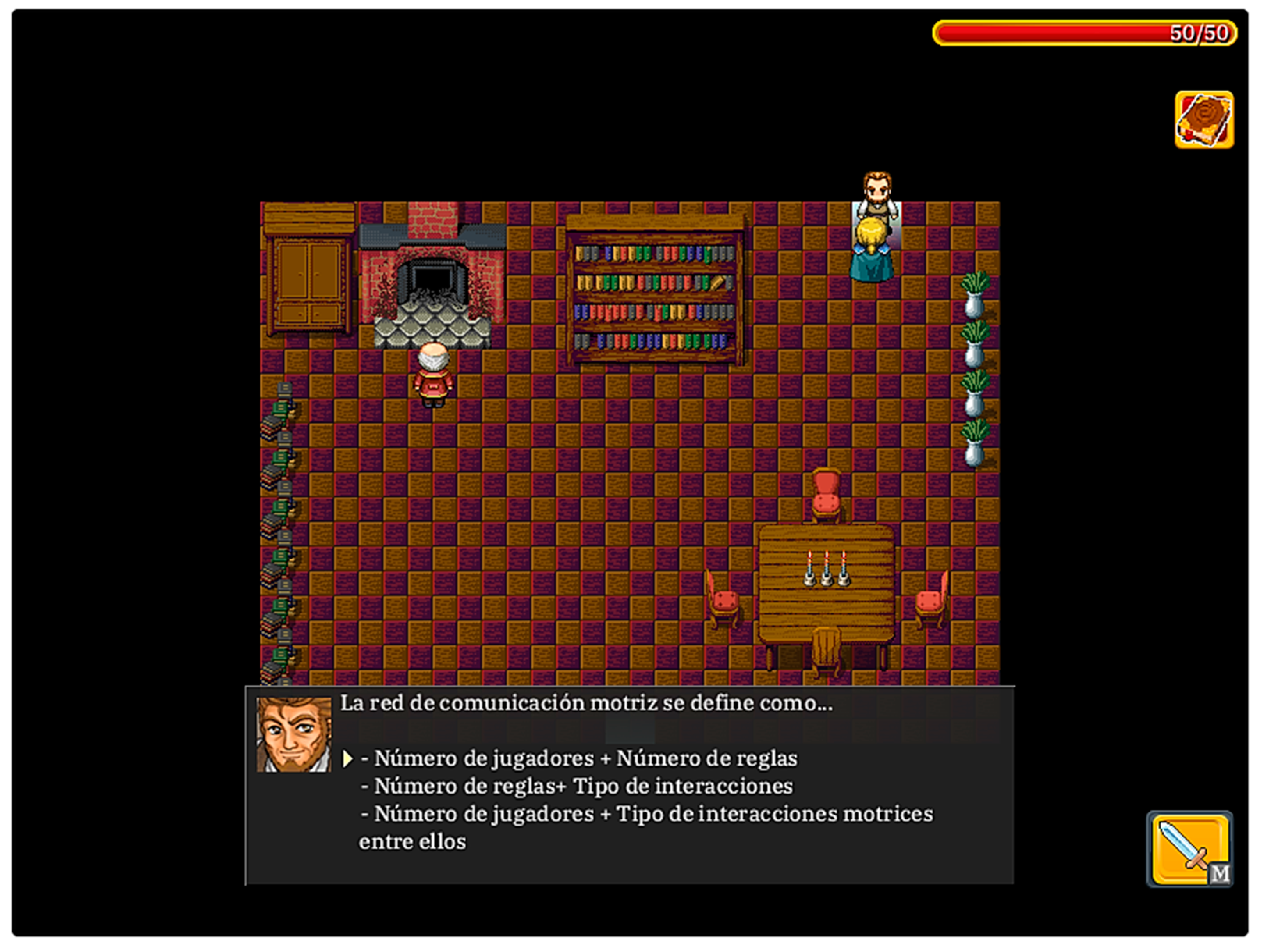
Figure 2.
Activity role-playing videogame of the content ‘Motor Communication’.
The games were the same for both experimental groups; the only difference was the gamification game elements. Students in the noncompetitive experimental group (EGi) had to complete individual challenges (Figure 3) and received a badge for each game completed. On the other hand, the students in the competitive experimental group (EGc) added the points they achieved in the activities according to the time and mistakes they made to achieve the best possible position on the leaderboard (Figure 4).

Figure 3.
Dynamics of individual gamification by challenges. EGi group.
Figure 4.
Competitive gamification dynamics with classification. EGc group.
At the end of the experience, both groups were tested on their knowledge, and the students in the experimental group were given the CMELAC questionnaire. Finally, they were asked the three open-ended questions specified before.
2.5. Data Analysis
Data were initially evaluated through preliminary analyses that included the study of data distribution and missing values. In this regard, no missing data were observed in our study. Then, the data analysis addressed two different, complementary approaches.
Firstly, we tested the effect of the intervention on students’ academic performance, comparing the experimental and the control groups. In such analysis, dependent variables were students’ roles and sub-roles academic performance, motor communication academic performance and total performance. This analysis was conducted with a t-test for independent samples, which compares the means of the groups analyzed [77]. As a result of the multiple t-tests performed during our analyses, we undertook a Bonferroni adjustment to the alpha level (new p = 0.017).
Secondly, we tested for possible differences depending on the type of Gamification experienced. Independent sample t-tests were used again, with the dependent variables being students’ academic performance (i.e., roles, motor communication and total), gamification scores (i.e., roles score, motor communication score and total score) and motivation (i.e., task motivation, Motivation to learn and Flow). We also considered a Bonferroni adjustment to the alpha level (new p = 0.006) in those comparisons. All analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics, v. 23.
A deductive procedure was used in the analysis of the qualitative data [78] based on the consideration of the questions asked and the subsequent development of the coding [79] (Table 1). However, during the data analysis, the inductive method was also used to expand the list of subcategories. The software ATLAS.ti version 7 was used.

Table 1.
Categories and subcategories.
Table 1.
Categories and subcategories.
| Categories | Subcategories |
|---|---|
| Task motivation | Innovation Visual design Interactivity |
| Motivation to learn | Intrinsic motivation Extrinsic motivation |
| Flow | Fun Adequacy of the level |
3. Results
3.1. Comparing Experimental and Control Group
Table 2 presents the comparison between the experimental and control groups. As data were considered to follow a normal distribution, we conducted a series of t-tests to analyze possible differences between experimental and control groups. However, all three differences were p < 0.05, after the Bonferroni correction (i.e., p set at < 0.017), experimental and control groups were assumed to present differences in communication performance (Mdifference = 0.66) and total performance (Mdifference = 1.13).

Table 2.
Comparison between experimental and control groups.
3.2. Comparing Two Types of Gamification
This study used two types of gamification strategies: competitive and individual. In Table 3, we present the results of the comparison of those two groups regarding students’ academic performance, gamification scores and motivation. As can be observed, no differences were found in any of these variables. In this regard, however, we would like to highlight that a significant number of students that participated in the intervention presented moderate or high levels of motivation (i.e., mean score equal or above 4): task motivation (% competitive = 58.8%; % individual = 61.9%), motivation to learn (% competitive = 47.1%; % individual = 57.1%) and flow (% competitive = 58.8%; % individual = 47.6%).

Table 3.
Comparison between competitive and individual Gamification.
3.3. Qualitative Results
The content analysis of the qualitative data shows the following results for each of the questions:
- Question 1—After completing gamified digital games, do you think it is motivating that the teacher applies this methodology on the virtual platform? Why?
Out of the 38 students of the experimental group, 36 stated positively that the gamified digital games had an impact on their motivation, e.g., “Yes, in this way, the more theoretical content is worked on in a fun way and not in the traditional way as it is taught in the classroom. On the other hand, the fact of being able to play the games gives the student the possibility to self-manage the time” (student 12); “Yes, because it can motivate students to learn more about the subject, consult contents or other aspects related to it” (student 2).
In contrast, we found a response that rejects the use of technology for this type of dynamics: “ No. I suppose that the significance lies in the activity, not in the platform ( as it could also have been done face-to-face without the use of technology).” (student 23). Table 4 shows the number and percentage of coded responses obtained by group and in total.

Table 4.
Question 1. Comparison between competitive, individual gamifications and comment examples.
- Question 2—To make the activities more motivating, what do you think could be added?
The comments obtained in this question have been coded into responses referring to the improvement of the dynamics/mechanics of the game, e.g., “Possibly direct interactivity between participants” (student 4) or “Less chance of attempts and doing it in class in teams” (student 29). Additionally, there were responses that refer to improvements in the games, e.g., “Seeking to associate this activity with the current tastes of the group, such as the use of video games” (student 9). Table 5 shows the number and percentage of responses coded by categories and subcategories of the second question.

Table 5.
Question 2. Comparison between competitive, individual gamifications and comment examples.
- Question 3—Did the gamified digital games motivate you to log into the course platform more frequently?
The coding of the responses shows that 8% of the students did not perceive a direct relationship between the use of the strategy and motivation with the virtual platform. Comments such as the following confirm this: “I didn’t log on to the platform more times. I just tried to complete the games with the knowledge obtained in class” (student 17). On the other hand, 92% of the students say that the gamified digital games have motivated them to access the platform. For example, “Positively. Increasing my motivation to keep trying to get the first place, and for that reason, I reviewed the contents we had on the virtual platform” (student 28). Table 6 shows the responses coded and compared by groups.

Table 6.
Question 3. Comparison between competitive, individual gamifications and comment examples.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to examine the effect of the gamified DGBL strategy on students’ academic performance motivation toward flow, motivation for learning and motivation for the task.
According to the variables presented in the first research question, the application of gamified DGBL led to significant differences in the academic performance of the students in the experimental group compared to those in the control group. The results of the content tests show that the mean score of the experimental group is 1.12 points higher than that of the control group, which is, statistically, significant. On the other hand, there are no differences between the two experimental groups, so the competitive component of Gamification did not affect academic performance. The use of a virtual leaderboard, badges and points did not show a different result, so we can conclude that the gamification proposal contributed to a high level of academic performance in both cases, with or without the competitive element.
Some authors have already justified the positive effects of gamified DGBL on academic performance [30,31] and Gamification [39,40,41]. The present study covers the unknown of the use of the two combined strategies, DGBL and Gamification, thus obtaining significant values on the academic performance of the students in the experimental group. The activities based on videogames, and the dynamics enhanced with game elements, have caused the students to achieve better grades.
The second research question addressed a key factor contributing to student learning, motivation. The educational intervention using digital games showed that 90% of the students who played the games showed medium and high motivation levels. In particular, motivation to learn received the highest scores (4.03), which could be influenced by the elements and dynamics of the games. Followed by motivation for the task (4.02), where the games proposed during the experience were rated very positively, and flow (4.01), reflecting that the design and content of the gamified activities were appropriate and fun for the students. There were no significant differences within the experimental subgroups. However, it is interesting to note that they scored better on the three motivational factors when the dynamic did not include a competitive element.
In the literature, and specifically in physical education, motivation and improvements related to physical performance have been investigated [80,81,82], but equally important are those that demonstrate effects on learning or task motivation [52,53,54]. In addition, the qualitative data show that more than half of the participants attribute their high scores to motivation for learning, more specifically, to intrinsic motivation [83,84]. The flow factor has been a determining factor in the positive or negative evaluation of the experience. In all the questions posed to the students, very positive comments were obtained, and many suggestions for improvement were made. The students see the enjoyment during practice and the appropriateness of the difficulty of the video games as relevant. Regarding motivation for the task, even though it received many positive evaluations, it did not prove to be decisive in increasing or decreasing the participant’s motivation. It was the category that received the most recommendations for constructive improvement, including aspects related to visualization and game interactivity.
In this research, the differentiation between the two gamification dynamics used in the experimental group, competitive and noncompetitive, was not a significant differential factor. Giving an answer to the third research question posed since both groups showed positive effects on academic performance and motivation [85]. Competition in physical education is a highly motivating dynamic [86]. This affirmation is demonstrated by comments from the group of students with a noncompetitive dynamic: “I would have liked to be able to compete against my classmates on the internet” or “Seeing the leaderboard would have motivated me more than getting a badge.” So, before proposing Gamification or designing a game, it is necessary to know the concerns and preferences of the participants.
Consequently, the integration of DGBL and Gamification in physical education can be used to achieve positive academic and motivational results in university learning and not only focus on pursuing aspects such as physical performance [87] or health improvement [88]. This way, the proposed methodology can be consolidated as a teaching resource, applicable in various contexts and pursuing different educational purposes.
Finally, this research has limitations, such as the small number of participants in the experimental group, so a study with a broader representation of both groups is needed. Following the research design, it is also necessary to measure before and after to know the natural effect of the suggested methodology. Applying these gamified video games to other subjects of the degree or educational stages would help to see whether age or educational content is a differential factor. In addition, it would be appropriate to apply different types of gamification dynamics and other more interactive videogames not used in this study to determine if there are any differences in the results.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the results obtained in the study justify the use of DGBL and Gamification in university studies of physical education, which significantly improves academic performance and fosters a high level of intrinsic motivation in students. Therefore, gamified DGBL could be considered a promising pedagogical strategy for physical education teachers when students show low motivation toward the content. Making the games available on the virtual platform also provides the teacher with interesting data, such as the time spent playing and the number of times the group or a particular student has completed the activity. In this way, teachers can evaluate or interpret the relationships between the DGBL and Gamification and their students.
The present study aims to investigate the motivational and academic effects that result from combining different gamification strategies. In doing so, a door is opened to the teachers’ methodological imagination to find the tools that best fit their particular context. The data obtained in the study suggest that using gamified digital games in situations that are not very motivating or very theoretical is a good choice in physical education. To evaluate this strategy’s impact, further studies and different educational contexts are needed to confirm the results obtained in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; methodology, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; validation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; formal analysis, A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; investigation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; validation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; data curation, A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; writing— original draft preparation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; validation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; writing—review and editing, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; validation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; visualization, A.R.-A.; supervision, A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; validation, R.C.-S., A.R.-A. and P.L.-B.; project administration, A.R.-A. and P.L.-B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Institut Nacional d’Educació Física de Catalunya (INEFC), Universitat de Lleida (UdL).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Sports Administration of Catalonia (code: 008/CEICEGC/2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Institut Nacional d’Educació Física de Catalunya (INEFC) of the Generalitat de Catalunya (Catalonia, Spain).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Digital games descriptions.
Table A1.
Digital games descriptions.
| Games Description | |
|---|---|
| Crossword puzzle. The game consists of guessing the word corresponding to each number with the support of a definition, image or audio. | 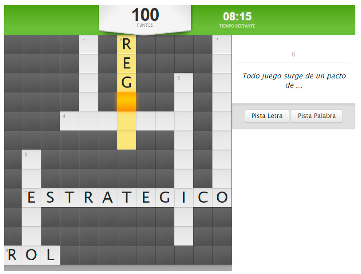 |
| Interactive picture. The game relates the concepts appearing on the screen with the corresponding graphic representation. | 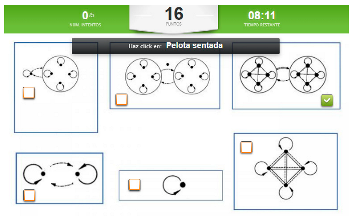 |
| Memory game. A game evaluates the player’s memory. You must be able to match the concept with the graphic representation. If you fail, the cards are turned over. | 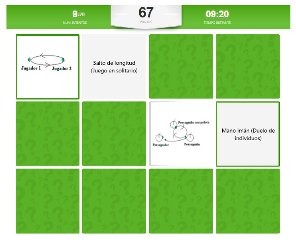 |
| Word search game. Search game in a vastness of letters. Find all the concepts related to the topic specified in the exercise. | 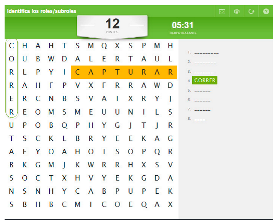 |
| Role videogame. A video game based on a story, where you have to collect objects, discover places and answer well to the challenges proposed by the characters of the video game. If you succeed, you will reach the final level of the game. | 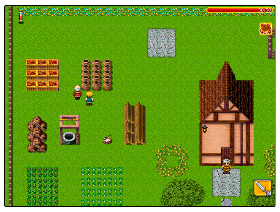 |
References
- Bingimlas, K.A. Barriers to the Successful Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning Environments: A Review of the Literature. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2009, 5, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, C.; Lee, M.J.W. Social Software and Participatory Learning: Pedagogical Choices with Technology Affordances in the Web 2.0 Era. In ICT: Providing choices for learners and learning. Proceedings ascilite Singapore 2007; Centre for Educational Development, Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2007; pp. 664–675. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, T.E. Using Online Social Networking for Teaching and Learning: Facebook Use at the University of Cape Town. Communicatio 2009, 35, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.; Maksum, H. Utilization of E-Learning-Based ICT Learning Using the Google Classroom Application During the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Educ. Res. Eval. 2020, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukri, A.; Nordin, L.; Salleh, F.I.M.; Raidzwan, S.N.M.; Ahmad, R. UniKL Students’ Perception on Synchronous Learning Using ICT as Learning Tools to Learn English. J. Crit. Rev. 2020, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cespón, M.T. ICT/LKT and COVID-19: Use and Needs of Galician Secondary Teachers. Digit. Educ. Rev. 2021, 39, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development United Nations United Nations Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. United Nations. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/publications/transforming-our-world-2030-agenda-sustainable-development-17981 (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- UNESCO. Libro de Consulta Sobre La Educación Para El Desarrollo Sostenible. Instrum. De Aprendiz. Y Form. 2012, 4, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- MODELL, H.I.; MICHAEL, J.A. Promoting Active Learning in the Life Science Classroom: Defining the Issues. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 701, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J. Where’s the Evidence That Active Learning Works? Am. J. Physiol. -Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2006, 30, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensky, M. Digital Natives, Digital Immigrants Part 1. Horiz. 2001, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R.H.; Lin, H.T.; Sun, J.C.Y.; Wu, J.J. Improving Learning Achievement in Science Education for Elementary School Students via Blended Learning. Int. J. Online Pedagog. Course Des. 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illeris, K. Towards a Contemporary and Comprehensive Theory of Learning. Int. J. Lifelong Educ. 2003, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvis, P.H.; Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1991, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabos, B. Media in the Classroom: An Alternative History. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association, Seattle, WA, USA, 10-14 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lavega, P.; Aráujo, P.; Jaqueira, A.R. Teaching Motor and Emotional Competencies in University Students. Cult. Cienc. Y Deporte 2013, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milteer, R.M.; Ginsburg, K.R.; Mulligan, D.A.; Ameenuddin, N.; Brown, A.; Christakis, D.A.; Cross, C.; Falik, H.L.; Hill, D.L.; Hogan, M.J.; et al. The Importance of Play in Promoting Healthy Child Development and Maintaining Strong Parent-Child Bond: Focus on Children in Poverty. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlebas, P. Juegos, Deporte y Sociedad. Léxico de Praxiología Motriz; Paidotribo: Barcelona, Spain, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Ifenthaler, D. Designing Engaging Educational Games and Assessing Engagement in Game-Based Learning. In Handbook of Research on Serious Games for Educational Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.J.; Hung, C.M.; Chen, N.S. Improving Learning Achievements, Motivations and Problem-Solving Skills through a Peer Assessment-Based Game Development Approach. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2014, 62, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, M. Creative and Playful Learning: Learning through Game Co-Creation and Games in a Playful Learning Environment. Think Ski. Creat 2010, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azawi, R.; Al-Faliti, F.; Al-Blushi, M. Educational Gamification Vs. Game Based Learning: Comparative Study. Int. J. Innov. Manag. Technol. 2016, 1, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fatta, H.; Maksom, Z.; Zakaria, M.H. Game-Based Learning and Gamification: Searching for Definitions. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2018, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Hanneghan, M.; el Rhalibi, A. Introduction to Games-Based Learning. In Games-Based Learning Advancements for Multi-Sensory Human Computer Interfaces: Techniques and Effective Practices; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2009; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasella, R. Pemanfaatan Modifikasi Permainan Trivial Pursuit Sebagai Media Pembelajaran Guna Meningkatkan Kosakata Bahasa Inggris Anak. EduBasic J. J. Pendidik. Dasar 2019, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deterding, S.; Dixon, D.; Khaled, R.; Nacke, L. From Game Design Elements to Gamefulness: Defining “Gamification”. In Proceedings of the 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments, MindTrek 2011, Tampere, Finland, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Lee, W.H. Dynamical Model for Gamification of Learning (DMGL). Multimed Tools Appl. 2015, 74, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesare, E.; Roselli, T.; Corriero, N.; Rossano, V. Game-Based Learning and Gamification to Promote Engagement and Motivation in Medical Learning Contexts. Smart Learn Environ. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.T. Gamifying the Flipped Classroom Using Game-Based Learning Materials. ELT J. 2018, 72, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dela Cruz, C.S.; Arenas, M.R.; Palaoag, T.D.; Berba, E.M. Game-based learning system: An exceptional learners motivation for better performance. Int. J. Organ. Bus. Excell. 2021, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lipowski, M. Sports Gamification: Evaluation of Its Impact on Learning Motivation and Performance in Higher Education. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X. Technology Acceptance, Technological Self-Efficacy, and Attitude Toward Technology-Based Self-Directed Learning: Learning Motivation as a Mediator. Front Psychol 2020, 11, 564294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares Triquet, J.C. Generation Z and Gamification: The Pedagogical Drawing of a New Educational Society. Tejuelo 2020, 32, 263–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Zamorano, L.R.; López Sánchez, J.Á.; Godoy-Caballero, A.L.; Bueno Muñoz, C. Gamification and Active Learning in Higher Education: Is It Possible to Match Digital Society, Academia and Students’ Interests? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, E.; Connolly, T.M.; Hainey, T. The Role of Psychology in Understanding the Impact of Computer Games. Entertain Comput. 2011, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kark, R. Games Managers Play: Play as a Form of Leadership Development. Acad. Manag. Learn. Educ. 2011, 10, 257–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, P. A Theoretical Framework for Serious Game Design. Int. J. Game-Based Learn. 2012, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, S.; Luglietti, R.; Margoudi, M.; Oliveira, M.; Taisch, M. Learning and Motivational Effects of Digital Game-Based Learning (DGBL) for Manufacturing Education –The Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Game. Comput. Ind. 2018, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakıroğlu, Ü.; Başıbüyük, B.; Güler, M.; Atabay, M.; Yılmaz Memiş, B. Gamifying an ICT Course: Influences on Engagement and Academic Performance. Comput Hum. Behav. 2017, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriz-Valero, A.; Østerlie, O.; Martínez, S.G.; García-Jaén, M. Gamification in Physical Education: Evaluation of Impact on Motivation and Academic Performance within Higher Education. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthan, R.; Senger, J.L. The Impact of Specially Designed Digital Games-Based Learning in Undergraduate Pathology and Medical Education. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhash, S.; Cudney, E.A. Gamified Learning in Higher Education: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Comput Hum. Behav. 2018, 87, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanus, M.D.; Fox, J. Assessing the Effects of Gamification in the Classroom: A Longitudinal Study on Intrinsic Motivation, Social Comparison, Satisfaction, Effort, and Academic Performance. Comput Educ 2015, 80, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneli, V.; Giannakos, M.; Chorianopoulos, K. Serious Games as a Malleable Learning Medium: The Effects of Narrative, Gameplay, and Making on Students’ Performance and Attitudes. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2017, 48, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovich, S.; Schunn, C.; Higashi, R.M. Are Badges Useful in Education?: It Depends upon the Type of Badge and Expertise of Learner. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2013, 61, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, E.; Buckley, P. Research Ethics in Teaching and Learning. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2014, 51, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. La Teoría de La Autodeterminación y La Facilitación de La Motivación Intrínseca, El Desarrollo Social, y El Bienestar Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.A.; Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior. Contemp. Sociol 1988, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, D.; Tobin, V. A Modification to the Behavioural Regulation in Exercise Questionnaire to Include an Assessment of Amotivation. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2004, 26, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admiraal, W.; Huizenga, J.; Akkerman, S.; Dam, G. ten. The Concept of Flow in Collaborative Game-Based Learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Trevino, L.K.; Ryan, L. The Dimensionality and Correlates of Flow in Human-Computer Interactions. Comput. Hum. Behav. 1993, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldemir, T.; Celik, B.; Kaplan, G. A Qualitative Investigation of Student Perceptions of Game Elements in a Gamified Course. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 78, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, M.E.; Alsalhi, N.R.; Al-Qatawneh, S.; AlQudah, H.A.; Jaradat, M. The Impact of Game-Based Learning (GBL) on Students’ Motivation, Engagement and Academic Performance on an Arabic Language Grammar Course in Higher Education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 3251–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppmann, R.; Bekk, M.; Klein, K. Gameful Experience in Gamification: Construction and Validation of a Gameful Experience Scale [GAMEX]. J. Interact. Mark. 2018, 43, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Self-Determination Theory in Health Care and Its Relations to Motivational Interviewing: A Few Comments. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanarajah, S. Increasing Intrinsic Motivation of Programming Students: Towards Fix and Play Educational Games. Issues Inf. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2018, 15, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Chen, M.P. The Effects of Game Strategy and Preference-Matching on Flow Experience and Programming Performance in Game-Based Learning. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2010, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawiyah, T. The Influence of Students Motivation Toward Students Achievement. Int. J. Lang. Teach. Educ. 2018, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otis, N.; Grouzet, F.M.E.; Pelletier, L.G. Latent Motivational Change in an Academic Setting: A 3-Year Longitudinal Study. J. Educ. Psychol. 2005, 97, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicheva, D.; Dichev, C.; Agre, G.; Angelova, G. Gamification in Education: A Systematic Mapping Study. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2015, 18, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.H. Evaluating Learners’ Motivational and Cognitive Processing in an Online Game-Based Learning Environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.W.; Chen, C.H.; Shih, S.J. The Interactivity of Video and Collaboration for Learning Achievement, Intrinsic Motivation, Cognitive Load, and Behavior Patterns in a Digital Game-Based Learning Environment. Comput. Educ. 2019, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizenga, J.; Admiraal, W.; Akkerman, S.; ten Dam, G. Mobile Game-Based Learning in Secondary Education: Engagement, Motivation and Learning in a Mobile City Game: Original Article. J. Comput. Assist. Learn 2009, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, B.K.; Zin, Z.B.M. Traditional and Inquiry-Based Learning Pedagogy: A Systematic Critical Review. Int. J. Instr. 2018, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Shelley, A.; Heo, D. The Regulation of Learning and Co-Creation of New Knowledge in Mobile Learning. Knowl. Manag. E-Learn. 2019, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusegun, S. Constructivism Learning Theory: A Paradigm for Teaching and Learning. IOSR J. Res. Method Educ. Ver. I 2015, 5, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Corbacho, A.M.; Minini, L.; Pereyra, M.; González-Fernández, A.E.; Echániz, R.; Repetto, L.; Cruz, P.; Fernández-Damonte, V.; Lorieto, A.; Basile, M. Interdisciplinary Higher Education with a Focus on Academic Motivation and Teamwork Diversity. Int. J. Educ. Res. Open 2021, 2, 100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwan, N.; Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alfarraj, O.; Alzahrani, A.; Yahaya, N.; Al-Rahmi, A.M. Integrated Three Theories to Develop a Model of Factors Affecting Students’ Academic Performance in Higher Education. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 98725–98742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubenfeld, T.; Zenker, D. A Game-Based Approach to an Entire Physical Chemistry Course. J. Chem. Educ. 2015, 92, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.J.; Beedle, J.; Rouse, S.E. Gamification: A Study of Business Teacher Educators’ Knowledge of, Attitudes Toward, and Experiences With the Gamification of Activities in the Classroom. J. Res. Bus. Educ. 2014, 56, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Stansbury, J.A.; Earnest, D.R. Meaningful Gamification in an Industrial/Organizational Psychology Course. Teach. Psychol. 2017, 44, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, M.T.; Camerino, O.; Castañer, M.; Sánchez-Algarra, P. Mixed Methods En La Investigación de La Actividad Física y El Deporte. Rev. De Psicol. Del Deporte 2014, 23, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Camerino, O.; Castañer, M.; Anguera, M.T. Mixed Methods Research in the Movement Sciences: Case Studies in Sport, Physical Education and Dance; Routledge: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.S. Case Studies: Types, Designs, and Logics of Inference. Confl. Manag. Peace Sci. 2008, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.V.; Boyd, K.M.; Webb, D.J. The Revision of the Declaration of Helsinki: Past, Present and Future. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 57, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-León, A.; Camacho-Lazarraga, P.; Guerrero-Puerta, M.A.; Guerrero-Puerta, L.; Alias, A.; Aguilar-Parra, J.M.; Trigueros, R. Development and Validation of a Questionnaire on Motivation for Cooperative Playful Learning Strategies. Int J Env. Res Public Health 2021, 18, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K. T Test as a Parametric Statistic. Korean J. Anesth. 2015, 68, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyatzis, R. Thematic Analysis and Code Development: Transforming Qualitative Information; SAGE: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fereday, J.; Muir-Cochrane, E. Demonstrating Rigor Using Thematic Analysis: A Hybrid Approach of Inductive and Deductive Coding and Theme Development. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2006, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel Cenizo-Benjumea, J.; Javier Vázquez-Ramos, F.; Ferreras-Mencía, S. Effect of a Gamified Program on Physical Fitness and Motor Coordination. Cultura 2022, 17, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Pérez-López, I.J.; Delgado-Fernández, M. The “$in TIME” Gamification Project: Using a Mobile App to Improve Cardiorespiratory Fitness Levels of College Students. Games Health J. 2020, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Durá, J.; Cabrera González, A.; Rodríguez-Negro, J.; Monleón García, C. Results of a Postural Education Program, with a Gamified Intervention vs Traditional Intervention. Sportis. Sci. J. Sch. Sport Phys. Educ. Psychomot. 2021, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfield, J.; Wilkerson, B. Increasing Student Intrinsic Motivation And Self-Efficacy Through Gamification Pedagogy. Contemp. Issues Educ. Res. (CIER) 2014, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekler, E.D.; Brühlmann, F.; Tuch, A.N.; Opwis, K. Towards Understanding the Effects of Individual Gamification Elements on Intrinsic Motivation and Performance. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 71, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.S.; Hung, Y.S.; Kwan, L.Y.Y. The Impact of Peer Competition and Collaboration on Gamified Learning Performance in Educational Settings: A Meta-Analytical Study. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, S.G.; Blanco, P.S.; Valero, A.F. Cooperative versus Competitive Methodologies: Effects on Motivation in PE Students. Retos 2021, 39, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Christensen, E.M.; Eather, N.; Sproule, J.; Annis-Brown, L.; Lubans, D.R. The PLUNGE Randomized Controlled Trial: Evaluation of a Games-Based Physical Activity Professional Learning Program in Primary School Physical Education. Prev. Med. 2015, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, C.S.; del Río, N.G.; Toledo-Delgado, P.A.; García-Peñalvo, F.J. Active Game-Based Solutions for the Treatment of Childhood Obesity. Sensors 2021, 21, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).