Physical Interpretation of Nanofluid (Copper Oxide and Silver) with Slip and Mixed Convection Effects: Applications of Fractional Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
3. Basics of Fractional Simulations
4. Solution by Atangana–Baleanu (AB) Operator
4.1. AB Operator for Temperature Profile
4.2. Velocity Field via AB-Fractional Derivative
5. Modeling via CF Time-Fractional Derivative
5.1. Energy Field via CF-Fractional Derivative
5.2. Velocity Field via CF-Fractional Derivative
6. Special Cases
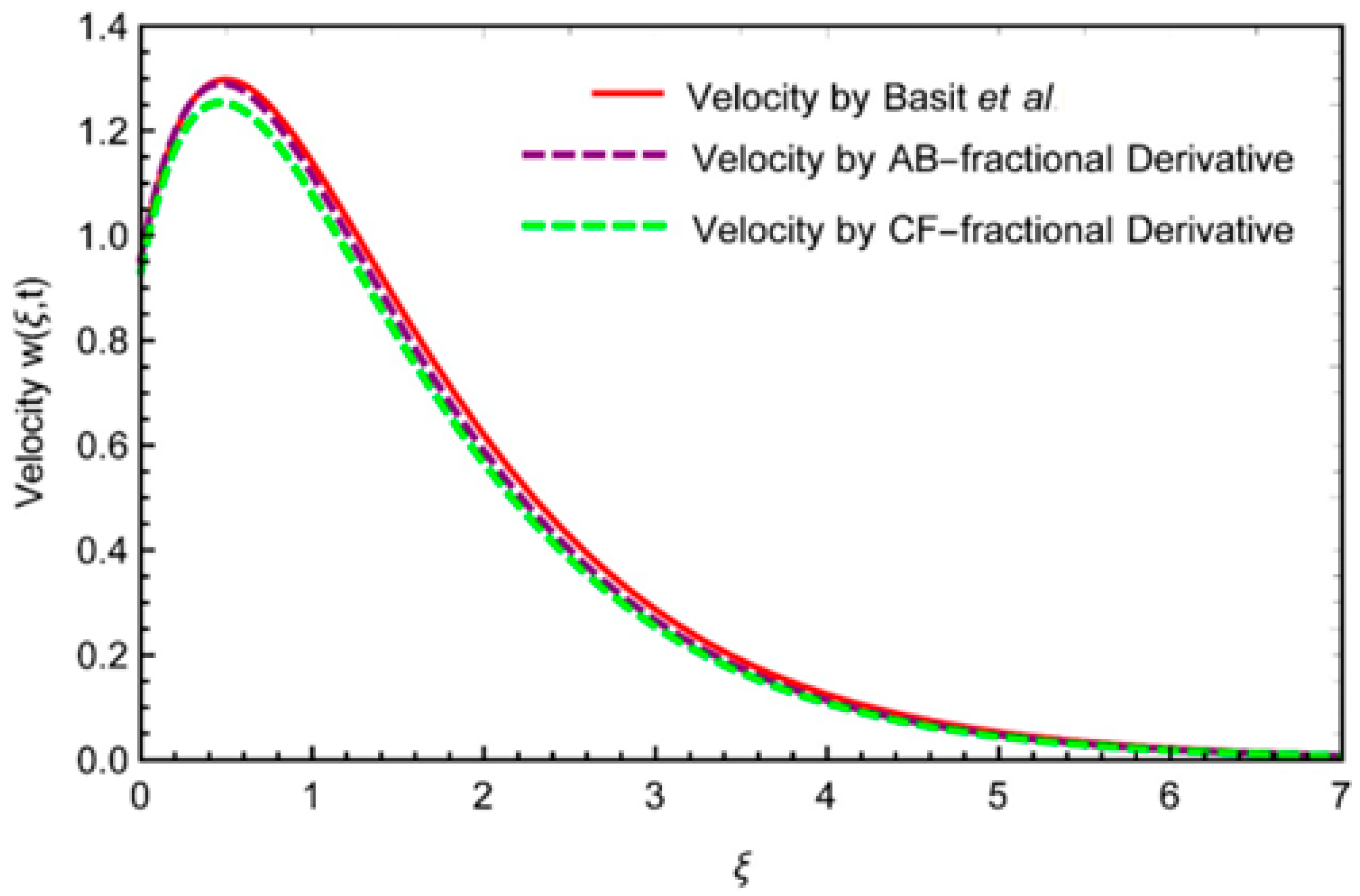
7. Validation of Results
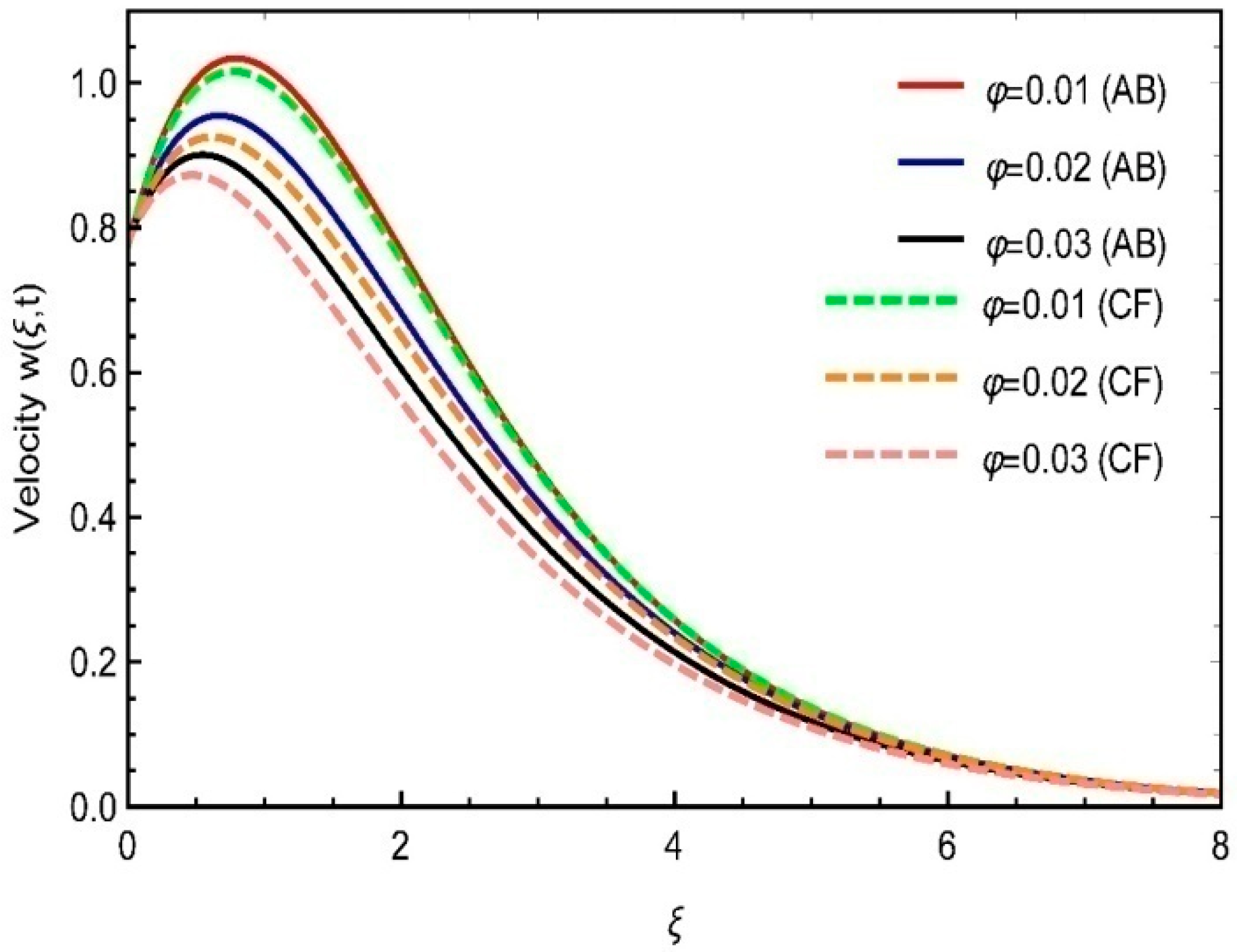
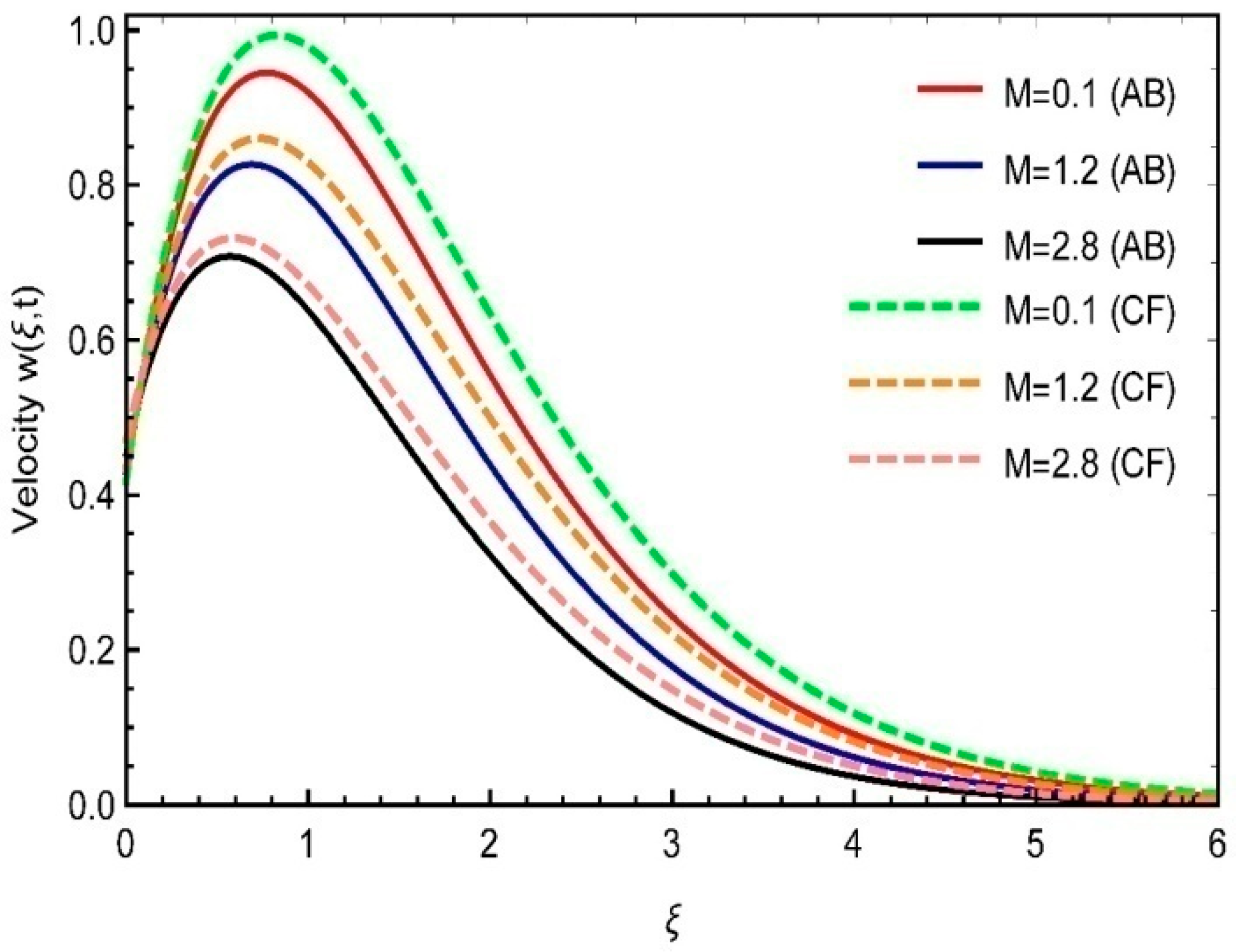
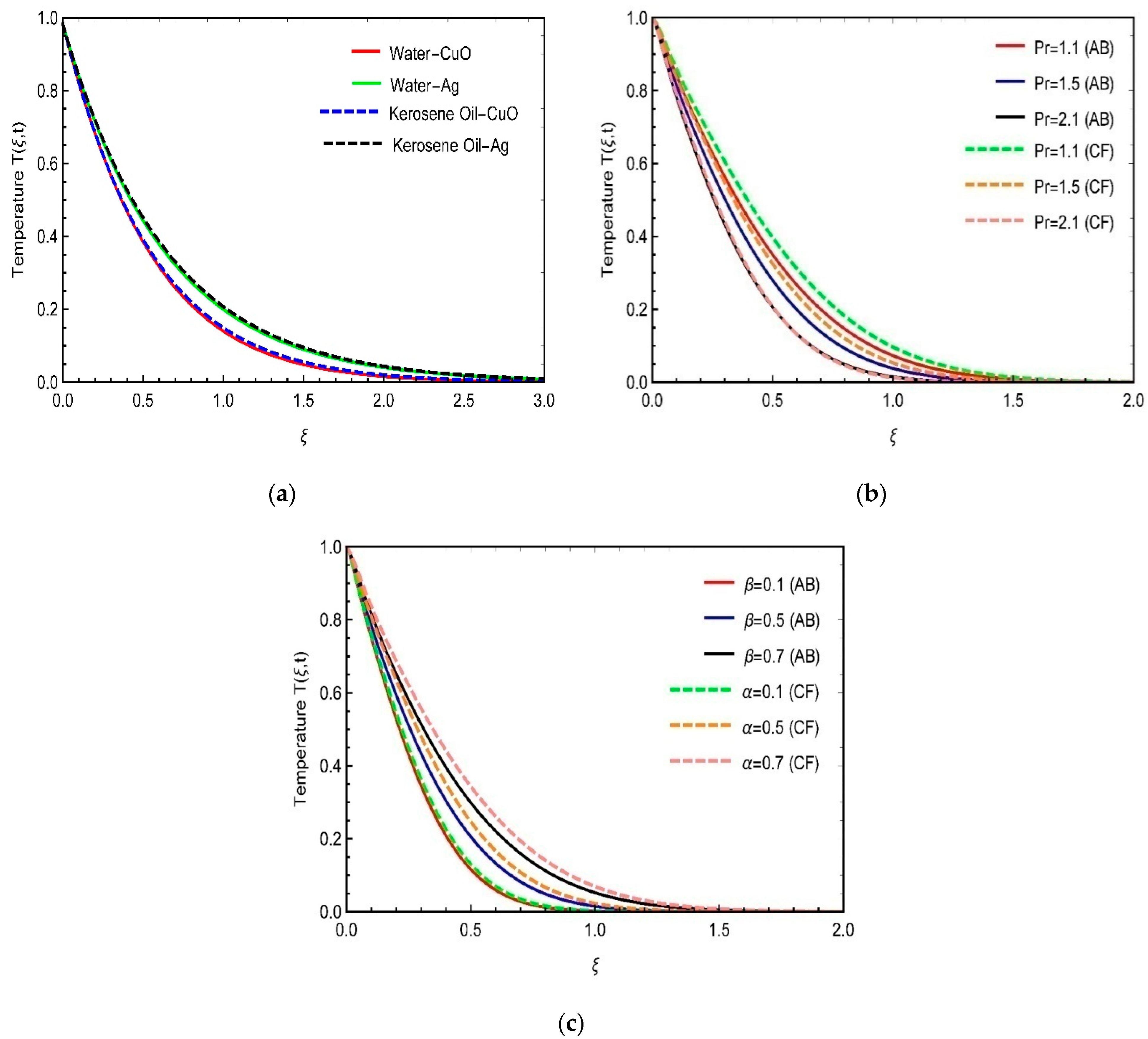
8. Physical Analysis of Results
9. Concluding Remarks
- ❖
- The thermal characteristics of heat transfer could be magnificently improved in the presence of copper oxide and silver nanoparticles.
- ❖
- A relatively improved profile of velocity was observed for the copper–water-based suspension compared to the kerosene-oil suspension.
- ❖
- A lower velocity rate was observed for the volume fraction and increasing values of fractional parameters.
- ❖
- The increasing thermal outcomes were predicted for the suspension of kerosene oil and silver nanoparticles compared to copper oxide and water-based material.
- ❖
- Decaying thermal outcomes were observed when the fractional parameters and Prandtl number were varied.
- ❖
- ❖
- These results can be further extended by incorporating various thermal features such as entropy generation, exponential heat sources, activation energy, joule heating, and bioconvection and by using different non-Newtonian models.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Velocity | |
| Time | |
| Constant Velocity | |
| Density | |
| Temperature | |
| Thermal conductivity | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Grashof number | |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| Density of nanoparticles | |
| Magnetic parameter | |
| Nanofluid | |
| slip parameter | |
| AB-fractional derivative operator | |
| CF-fractional derivative operator | |
| Nusselt number | |
| Skin Friction | |
| CF | Caputo–Fabrizio fractional derivative |
| Laplace variable by AB | |
| Laplace variable by CF | |
| Acceleration due to gravity | |
| AB | Atangana–Baleanu fractional derivative |
| Density of base fluid |
References
- Choi SUS 1995 Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles Proc Int Mech Eng Congress San Francisco USA ASME FED 231/MD66 99–105.
- Mahdavi, M.; Sharifpur, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Meyer, J.P. Nanofluid flow and shear layers between two parallel plates: A simulation approach. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2020, 14, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, A.; Wakif, A.; Thumma, T.; Shah, N.A. Towards a new MHD non-homogeneous convective nanofluid flow model for simulating a rotating inclined thin layer of sodium alginate-based Iron oxide exposed to incident solar energy. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 130, 105800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Rasel, S.K.; Adewole, J.K.; al Kalbani, K.S. Finite element simulation on the convective double diffusive water-based copper oxide nanofluid flow in a square cavity having vertical wavy surfaces in presence of hydro-magnetic field. Results Eng. 2022, 13, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.E.; Mohsenian, S.; Gouran, S.; Zolfagharian, A. A novel spectral relaxation approach for nanofluid flow past a stretching surface in presence of magnetic field and nonlinear radiation. Results Phys. 2022, 32, 105141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Al-Khaled, K.; Gouadria, S.; El-Zahar, E.R.; Usman Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.I.; Malik, M.Y. Numerical simulations for three-dimensional rotating porous disk flow of viscoelastic nanomaterial with activation energy, heat generation and Nield boundary conditions. Waves Random Complex Media 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman; Bhatti, M.M.; Ghaffari, A.; Doranehgard, M.H. The role of radiation and bioconvection as an external agent to control the temperature and motion of fluid over the radially spinning circular surface: A theoretical analysis via Chebyshev spectral approach. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenian, S.; Gouran, S.; Ghasemi, S.E. Evaluation of weighted residual methods for thermal radiation on nanofluid flow between two tubes in presence of magnetic field. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 32, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klazly, M.; Bognar, G. Heat transfer enhancement for nanofluid flows over a microscale backward-facing step. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 8161–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N.; Mabood, F.; Shahzad, S.A.; Badruddin, I.A. Hydrothermal variations of radiative nanofluid flow by the influence of nanoparticles diameter and nanolayer. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 130, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthtamilselvan, M.; Suganya, S.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M. Stagnation-Point Flow of the Williamson Nanofluid Containing Gyrotactic Micro-organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A Phys. Sci. 2021, 91, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mdallal, Q.M.; Renuka, A.; Muthtamilselvan, M.; Abdalla, B. Ree-Eyring fluid flow of Cu-water nanofluid between infinite spinning disks with an effect of thermal radiation. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2947–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milici, C.; Draganescu, G.; Machado, J.T. Introduction to Fractional Differential Equations; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, M.; Fabrizio, M. A new definition of fractional derivative without singular kernel. Prog. Fract. Differ. Appl. 2015, 1, 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Atangana, A.; Baleanu, D. New fractional derivatives with non-local and non-singular kernel: Theory and application to heat transfer model. Therm. Sci. 2016, 20, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, H.; Oreijah, M.; Guedri, K.; Khan, S.U.; Yang, S.; Yasmin, S.; Khan, M.I.; Bafakeeh, O.T.; Tag-ElDin, E.S.M.; Galal, A.M. Gyrotactic motile microorganisms impact on pseudoplastic nanofluid flow over a moving Riga surface with exponential heat flux. Crystals 2022, 12, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Javed, H.M.A.; Ahmad, M.I.; Qureshi, A.A.; Khan, M.I.; Alnuwaiser, M.A.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, M.A.; Tag-Eldin, E.; Shahid, A.; et al. A brief assessment on recent developments in efficient electrocatalytic Nitrogen reduction with 2D non-metallic nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, N.; Qasim, I.; Khan, M.I.; Ahmed, M.W.; Guedri, K.; Bafakeeh, O.T.; Tag-Eldin, E.S.M.; Galal, A.M. Antibacterial applications of low pressure plasma on degradation of multidrug resistant V. cholera. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamatha, S.U.; Devi, R.L.V.R.; Ahammad, N.A.; Shah, N.A.; Rao, B.M.; Raju, C.S.K.; Khan, M.I.; Guedri, K. Multi-linear regression of triple diffusive convectively heated boundary layer flow with suction and injection: Lie group transformations. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Kiranakumar, H.V.; Thejas, R.; Naveen, C.S.; Khan, M.I.; Prasanna, G.D.; Reddy, S.; Oreijah, M.; Guedri, K.; Bafakeeh, O.T.; Jameel, M. A review on electrical and gas-sensing properties of reduced graphene oxide-metal oxide nanocomposites. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Farooq, W.; Tag-ElDin, E.S.M.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.I.; Guedri, K.; Elattar, S.; Waqas, M.; Galal, A.M. Heat transport exploration for hybrid nanoparticle (Cu, Fe3O4)-based blood flow via tapered complex wavy curved channel with slip features. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, N.S.; Arifina, N.M.; Khashi’ie, N.S.; Pop, I.; Bachok, N.; Hafidzuddin, M.E.H. MHD mixed convection flow of a hybrid nanofluid past a permeable vertical flat plate with thermal radiation effect. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 3323–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashorynejad, H.R.; Shahriari, A. MHD natural convection of hybrid nanofluid in an open wavy cavity. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puneetha, V.; Khan, M.I.; Jameel, M.; Geudri, K.; Galal, A.M. The convective heat transfer analysis of the casson nanofluid jet flow under the influence of the movement of gyrotactic microorganisms. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 9, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Khan, S.U.; Haq, A.U.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, M.R. Non-singular fractional computations for the radiative heat and mass transfer phenomenon subject to mixed convection and slip boundary effects. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 155, 111708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Khan, S.U.; Al-Khaled, K.; Khan, M.I.; Haq, A.U.; Alotaibi, F.; Mousa, A.A.A.; Qayyum, S. A fractional model for the kerosene oil and water-based Casson nanofluid with inclined magnetic force. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 787, 139277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.I.; Farid, S.; Muhammad, T.; Khan, M.I.; Galal, A.M. Fractional order simulations for the thermal determination of graphene oxide (GO) and molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) nanoparticles with slip effects. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Raza, A.; Al-Khaled, K.; Khan, S.U.; Farid, S.; Wang, Y.; IjazKhan, M.; Malik, M.Y.; Saleem, S. Fractional-order simulations for heat and mass transfer analysis confined by elliptic inclined plate with slip effects: A comparative fractional analysis. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Asjad, M.I.; Akgül, A. Convective flow of a fractional second grade fluid containing different nanoparticles with Prabhakar fractional derivative subject to non-uniform velocity at the boundary. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehfest, H. Algorithm 368: Numerical inversion of Laplace transforms [D5]. Commun. ACM 1970, 13, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, D.Y. Macro-to Microscale Heat Transfer: The Lagging Behavior; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]


| Materials | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 997.1 | 4179 | 0.613 | 21 | |
| kerosene oil | 884 | 1910 | 0.114 | 70 |
| 6320 | 531.8 | 76.5 | 1.80 | |
| 10,500 | 235 | 429 | 1.89 |
| Temperature Change by Stehfest [31] | Temperature Change by Tzou [32] | Velocity Change by Stehfest [31] | Velocity Change by Tzou [32] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.9314 | 0.9313 | 0.5159 | 0.5130 |
| 0.3 | 0.6380 | 0.6379 | 0.5733 | 0.5703 |
| 0.5 | 0.4368 | 0.4367 | 0.5759 | 0.5730 |
| 0.7 | 0.2989 | 0.2988 | 0.5471 | 0.5443 |
| 0.9 | 0.2044 | 0.2043 | 0.5019 | 0.4993 |
| 1.1 | 0.1397 | 0.1397 | 0.4496 | 0.4473 |
| 1.3 | 0.0954 | 0.0954 | 0.3962 | 0.3940 |
| 1.5 | 0.0651 | 0.0651 | 0.3448 | 0.3429 |
| 1.7 | 0.0445 | 0.0444 | 0.2943 | 0.2957 |
| 1.9 | 0.0303 | 0.0303 | 0.2546 | 0.2532 |
| Nusselt Number by Stehfest [31] | Nusselt Number by Tzou [32] | Skin Friction by Stehfest [31] | Skin Friction by Tzou [32] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.768353 | 0.762176 | 0.964697 | 0.9650723 |
| 0.3 | 0.706666 | 0.701632 | 0.985097 | 0.9855834 |
| 0.5 | 0.658185 | 0.654153 | 1.2411443 | 1.247146 |
| 0.7 | 0.614201 | 0.611155 | 1.410835 | 1.417757 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bafakeeh, O.T.; Raza, A.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.I.; Nasr, A.; Khedher, N.B.; Tag-Eldin, E.S.M. Physical Interpretation of Nanofluid (Copper Oxide and Silver) with Slip and Mixed Convection Effects: Applications of Fractional Derivatives. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110860
Bafakeeh OT, Raza A, Khan SU, Khan MI, Nasr A, Khedher NB, Tag-Eldin ESM. Physical Interpretation of Nanofluid (Copper Oxide and Silver) with Slip and Mixed Convection Effects: Applications of Fractional Derivatives. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(21):10860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110860
Chicago/Turabian StyleBafakeeh, Omar T., Ali Raza, Sami Ullah Khan, Muhammad Ijaz Khan, Abdelaziz Nasr, Nidhal Ben Khedher, and El Sayed Mohamed Tag-Eldin. 2022. "Physical Interpretation of Nanofluid (Copper Oxide and Silver) with Slip and Mixed Convection Effects: Applications of Fractional Derivatives" Applied Sciences 12, no. 21: 10860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110860
APA StyleBafakeeh, O. T., Raza, A., Khan, S. U., Khan, M. I., Nasr, A., Khedher, N. B., & Tag-Eldin, E. S. M. (2022). Physical Interpretation of Nanofluid (Copper Oxide and Silver) with Slip and Mixed Convection Effects: Applications of Fractional Derivatives. Applied Sciences, 12(21), 10860. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122110860








