Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Bladder Cancer Detection: Where Do We Stand?
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
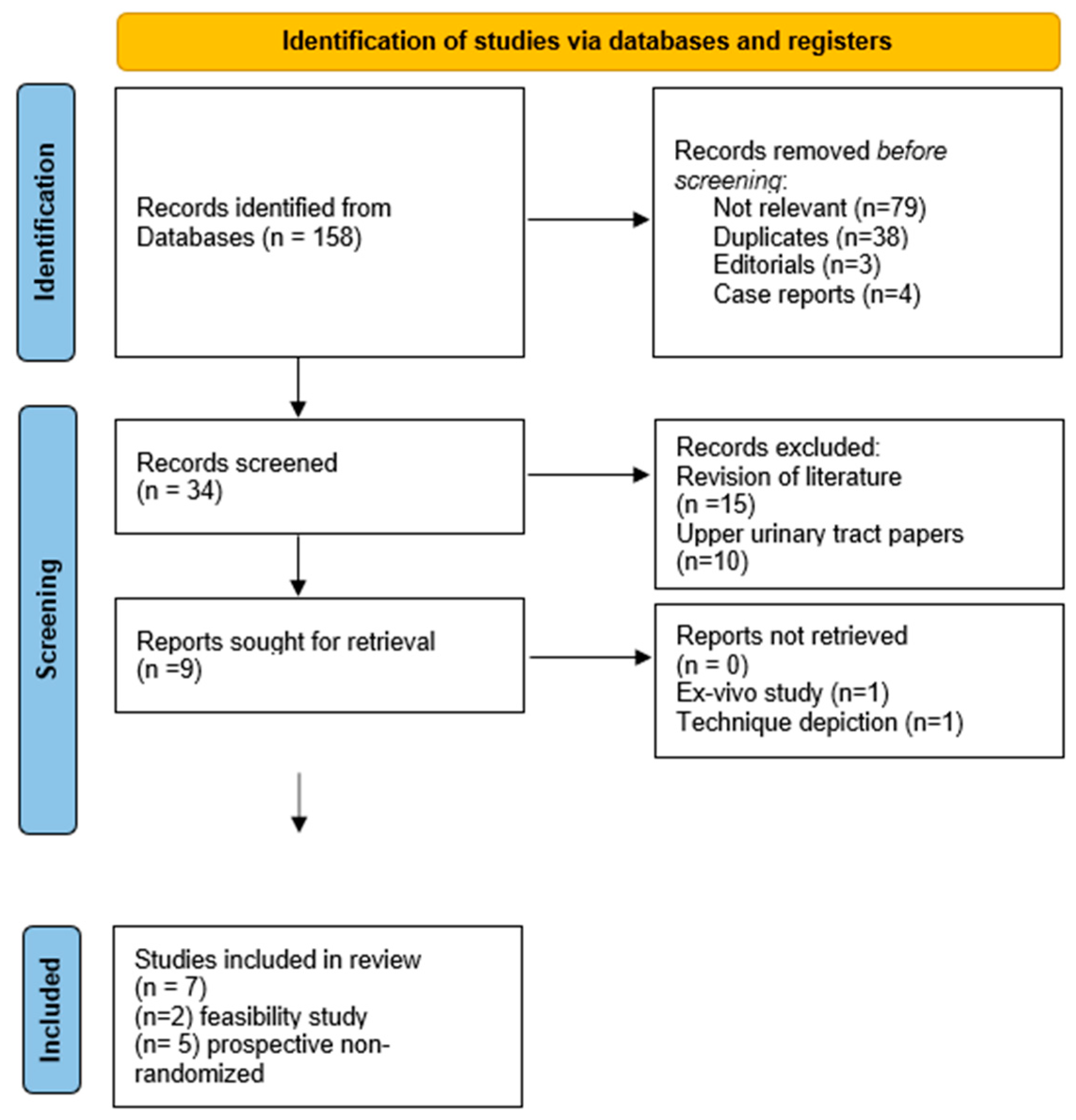
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Quality Assessment and Data Extraction
2.3. Confocal Microscopy Instrumentation, Technique, and Image Interpretation
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. CLE Feasibility
4.2. CLE Advantages for BCa Management
4.3. CLE Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCa | bladder cancer |
| CIS | carcinoma in situ |
| CLE | confocal laser endomicroscopy |
| HAL | hexylaminolevulinate |
| HG | high-grade |
| LG | low-grade |
| NBI | narrow-banding imaging |
| NMIBC | non-muscle invasive bladder cancer |
| OCT | optical coherence tomography |
| PDD | photodynamic diagnosis |
| PRISMA | preferring reporting items for systematic reviews and metanalysis |
| QUADAS | quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies |
| SPIES | Storz professional image enhancement system |
| UTUC | upper tract urothelial carcinoma |
| WLC | white-light cystoscopy |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K. Bladder cancer: A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaak, D.; Ohlmann, C.; Stenzl, A. Aktuelle und etablierte Diagnoseverfahren beim Harnblasenkarzinom. Der Urol. 2018, 57, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumberbatch, M.G.; Foerster, B.; Catto, J.W.; Kamat, A.M.; Kassouf, W.; Jubber, I.; Shariat, S.F.; Sylvester, R.J.; Gontero, P. Repeat Transurethral Resection in Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapini, A.; Minervini, A.; Masala, A.; Schips, L.; Pycha, A.; Cindolo, L.; Giannella, R.; Martini, T.; Vittori, G.; Zani, D.; et al. A comparison of hexaminolevulinate (Hexvix®) fluorescence cystoscopy and white-light cystoscopy for detection of bladder cancer: Results of the HeRo observational study. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 3634–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiung, P.-L.; Hardy, J.; Friedland, S.; Soetikno, R.; Du, C.B.; Wu, A.; Sahbaie, P.; Crawford, J.M.; Lowe, A.W.; Contag, C.; et al. Detection of colonic dysplasia in vivo using a targeted heptapeptide and confocal microendoscopy. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeji, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yoshida, D.; Tanoue, K.; Ueda, M.; Masunari, A.; Utsunomiya, T.; Imamura, M.; Honda, H.; Maehara, Y.; et al. Development and assessment of morphologic criteria for diagnosing gastric cancer using confocal endomicroscopy: An ex vivo and in vivo study. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie 2006, 38, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawley, J.B. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Teich, W.; Frenzel, F.; Hoffmann, K.; Radke, J.; Rösler, J.; Faust, K.; Blank, A.; Brandenburg, S.; Misch, M.; et al. Optical Characterization of Sodium Fluorescein In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liu, J.-J.; Adams, W.; Sonn, G.A.; Mach, K.E.; Pan, Y.; Beck, A.H.; Jensen, K.C.; Liao, J.C. Dynamic Real-time Microscopy of the Urinary Tract Using Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. Urology 2011, 78, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonn, G.A.; Mach, K.E.; Jensen, K.; Hsiung, P.-L.; Jones, S.-N.; Contag, C.H.; Wang, T.D.; Liao, J.C. Fibered Confocal Microscopy of Bladder Tumors: An ex Vivo Study. J. Endourol. 2009, 23, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonn, G.A.; Jones, S.-N.E.; Tarin, T.V.; Du, C.B.; Mach, K.E.; Jensen, K.C.; Liao, J.C. Optical Biopsy of Human Bladder Neoplasia With In Vivo Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Liu, J.-J.; Hsiao, S.T.; Pan, Y.; Mach, K.E.; Leppert, J.; McKenney, J.K.; Rouse, R.V.; Liao, J.C. Interobserver Agreement of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Bladder Cancer. J. Endourol. 2013, 27, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, M.; Liem, E.I.; Savci-Heijink, C.D.; Freund, J.E.; Marquering, H.A.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; de Bruin, D.M. Toward Automated In Vivo Bladder Tumor Stratification Using Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Dai, B.; Ye, D.-W.; Zhu, Y.-P. Optical biopsy of bladder cancer using confocal laser endomicroscopy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeh, S.U.; Koh, D.H.; Chung, D.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Goh, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.D. Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy During Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumors Improves the Diagnostic Accuracy and Therapeutic Efficacy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, E.I.; Freund, J.E.; Heijink, D.S.; de la Rosette, J.J.; Kamphuis, G.M.; Baard, J.; Liao, J.C.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; de Reijke, T.M.; de Bruin, D.M. Validation of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Features of Bladder Cancer: The Next Step Towards Real-time Histologic Grading. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 6, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beji, S.; Lam, G.W.; Østergren, P.B.; Toxvaerd, A.; Sønksen, J.; Fode, M. Diagnostic value of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy versus conventional endoscopic biopsies of non-muscle invasive bladder tumors: A pilot study. Scand. J. Urol. 2020, 55, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Compérat, E.M.; Escrig, J.L.D.; Gontero, P.; Liedberg, F.; Masson-Lecomte, A.; Mostafid, A.H.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur. Urol. 2021, 81, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gakis, G.; Ngamsri, T.; Rausch, S.; Mischinger, J.; Todenhöfer, T.; Schwentner, C.; Schmid, M.A.; Hassan, F.A.-S.; Renninger, M.; Stenzl, A. Fluorescence-guided bladder tumour resection: Impact on survival after radical cystectomy. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, M.; Babjuk, M.; Catto, J.; Jichlinski, P.; Shariat, S.F.; Stenzl, A.; Stepp, H.; Zaak, D.; Witjes, J.A. Hexyl Aminolevulinate–Guided Fluorescence Cystoscopy in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Patients with Non–Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Critical Review of the Current Literature. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, T.; Rausch, S.; Fahmy, O.; Gakis, G.; Stenzl, A. Optical improvements in the diagnosis of bladder cancer: Implications for clinical practice. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2017, 9, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, D.V.; Altobelli, E.; Liao, J.C. Advances in Imaging Technologies in the Evaluation of High-Grade Bladder Cancer. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2015, 42, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Yu, Y.-B.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Luan, X.-R. Meta-analysis of confocal laser endomicroscopy for the detection of colorectal neoplasia. Color. Dis. 2013, 15, e488–e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-K.; Liu, D.; Sun, L.-M. Diagnostic performance of confocal laser endomicroscopy for optical diagnosis of gastric intestinal metaplasia: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breda, A.; Territo, A.; Guttilla, A.; Sanguedolce, F.; Manfredi, M.; Quaresima, L.; Gaya, J.M.; Algaba, F.; Palou, J.; Villavicencio, H. Correlation Between Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (Cellvizio®) and Histological Grading of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: A Step Forward for a Better Selection of Patients Suitable for Conservative Management. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavora, F.; Fajardo, D.A.; Lee, T.K.; Lotan, T.; Miller, J.S.; Miyamoto, H.; Epstein, J.I. Small Endoscopic Biopsies of the Ureter and Renal Pelvis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, K.; Party, O.B.O.T.E.Y.A.U.C.W.; Palisaar, R.-J.; Brock, M.; Bach, P.; von Landenberg, N.; Löppenberg, B.; von Bodman, C.; Noldus, J.; Roghmann, F. Transurethral resection of bladder tumours: Established and new methods of tumour visualisation. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegmair, M.C.; Rother, J.; Grychtol, B.; Theuring, M.; Ritter, M.; Günes, C.; Michel, M.S.; Deliolanis, N.C.; Bolenz, C. Multiparametric Cystoscopy for Detection of Bladder Cancer Using Real-time Multispectral Imaging. Eur. Urol. 2019, 77, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marien, A.; Rock, A.; El Maadarani, K.; Francois, C.; Gosset, P.; Mauroy, B.; Bonnal, J.-L. Urothelial Tumors and Dual-Band Imaging: A New Concept in Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Luo, W.-J.; Dai, B.; Ye, D.-W.; Zhu, Y.-P. Diagnostic Performance of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for the Detection of Bladder Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Urol. Int. 2020, 104, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pen, C.; Palazzo, L.; Napoléon, B. A health economic evaluation of needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy for the diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Endosc. Int. Open 2017, 5, E987–E995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Publication | Patients’ Selection | Index Test | Reference Standard | Flow and Timing | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk of bias | Applicability | Risk of bias | Applicability | Risk of bias | Applicability | Risk of bias | |
| Lucas 2019 [17] | Low | Low | High | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Wu 2019 [18] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Lee 2019 [19] | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Liem 2020 [20] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Beji 2021 [21] | High | Low | Unclear | Low | High | Low | Unclear |
| Author, Year of Publication [Ref] | Type of Study | Cellvizio Probe and Penetration Depth | Contrast Delivery Method (n) | Enrolled Patients (n) | Median Age (Range) | Overall Lesions (n) | Inter-Observer Agreement CLE Images | Histology-CLE Correspondence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sonn, 2009 [15] | Feasibility | 2.6 mm–60 µm | EV (10) BI (5) Both (12) | 27 | 73 (range 47–90) | NR | NR | NR |
| Chang, 2013 [16] | Feasibility | NR | NR | NR | NR | 31 | -Experienced CLE urologists 90% -Novice CLE urologists 77% -Pathologists 81% | NR |
| Lucas, 2019 [17] | Prospective | 2.6 | BI | 53 | NR | 72 | Software-based interpretation | PPV: 74% NPV: 88% |
| Wu, 2019 [18] | Prospective | 2.6 mm | BI | 21 | 61 (32–81) | 21 | NR | 81% |
| Lee, 2019 [19] | Prospective | 2.5 mm | BI | 75 | 68.32 (±9.45 SD) | 119 | NR | PPV: 93.6% NPV: 68% |
| Liem, 2020 [20] | Prospective | 2.6 mm–65 µm | BI | 53 | 70 (62–79) | 66 | 76% | 70% |
| Beji, 2020 [21] | Prospective- pilot study | 2.6 mm | EV | 12 | 74 (52–94) | 34 | 73,5% | PPV: 54.6% NPV: 82.3% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naselli, A.; Guarneri, A.; Pirola, G.M. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Bladder Cancer Detection: Where Do We Stand? Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199990
Naselli A, Guarneri A, Pirola GM. Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Bladder Cancer Detection: Where Do We Stand? Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(19):9990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199990
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaselli, Angelo, Andrea Guarneri, and Giacomo Maria Pirola. 2022. "Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Bladder Cancer Detection: Where Do We Stand?" Applied Sciences 12, no. 19: 9990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199990
APA StyleNaselli, A., Guarneri, A., & Pirola, G. M. (2022). Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Bladder Cancer Detection: Where Do We Stand? Applied Sciences, 12(19), 9990. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12199990






