4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Class I Histone Deacetylases in Human Umbilical Cord Endothelial Cells
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HUVEC Culture
2.2. Western Blot and HDAC Inhibitory Assay
3. Results
3.1. HR Decreased HDAC Expression and Increased Ac-Lys
3.2. HR Inhibited Class I HDAC Activity in HUVECs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The Many Roles of Histone Deacetylases in Development and Physiology: Implications for Disease and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aka, J.A.; Kim, G.W.; Yang, X.J. Histone Deactylases: The Biology and Clinical Implication; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–12. ISBN 978-3-642-21630-5. [Google Scholar]
- Reichert, N.; Choukrallah, M.A.; Matthias, P. Multiple Roles of Class I HDACs in Proliferation, Differentiation, and Development. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 2173–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, R.; Richard, C.S.; Santos, M.M. The Role of Butyrate in Surgical and Oncological Outcomes in Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartl, S.; Taplick, J.; Lagger, G.; Khier, H.; Kuchler, K.; Seiser, C. Identification of Mouse Histone Deacetylase 1 as a Growth Factor-Inducible Gene. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 5033–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, P.; Seidler, B.; Schuler, S.; Schnieke, A.; Gottlicher, M.; Schmid, R.M.; Saur, D.; Schneider, G. HDAC2 Mediates Therapeutic Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the BH3-Only Protein NOXA. Gut 2009, 58, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, C.M.; Luo, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, T.; Floss, T.; Goettlicher, M.; Noppinger, P.R.; Wurst, W.; et al. Hdac2 Regulates the Cardiac Hypertrophic Response by Modulating Gsk3 Beta Activity. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kook, H.; Lepore, J.J.; Gitler, A.D.; Lu, M.M.; Wing-Man, Y.W.; Mackay, J.; Zhou, R.; Ferrari, V.; Gruber, P.; Epstein, J.A. Cardiac Hypertrophy and Histone Deacetylase-Dependent Transcriptional Repression Mediated by the Atypical Homeodomain Protein Hop. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, H.J.; Sohn, I.S.; Nam, K.I.; Park, J.E.; Qian, Y.R.; Yin, Z.; Ahn, Y.; Jeong, M.H.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, N.; et al. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylation Blocks Cardiac Hypertrophy Induced by Angiotensin II Infusion and Aortic Banding. Circulation 2006, 113, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, S.; Padova, M.D.; Serra, C.; Caretti, G.; Simone, C.; Maklan, E.; Minetti, G.; Zhao, P.; Hoffman, E.P.; Puri, P.L.; et al. Deacetylase Inhibitors Increase Muscle Cell Size by Promoting Myoblast Recruitment and Fusion through Induction of Follistatin. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.S.; Yang, C.P.; Bowen, R.C.; Bai, O.; Li, X.M.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X. Valproic Acid Enhances Axonal Regeneration and Recovery of Motor Function after Sciatic Nerve Axotomy in Adult Rats. Brain Res. 2003, 975, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabiec, A.M.; Krausz, S.; de Jager, W.; Burakowski, T.; Groot, D.; Sanders, M.E.; Prakken, B.J.; Maslinski, W.; Eldering, E.; Tak, P.P.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Suppress Inflammatory Activation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient Synovial Macrophages and Tissue. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2718–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caro, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Branca, J.J.V.; Micheli, L.; Citraro, R.; Russo, E.; De Sarro, G.; Ghelardini, C.; Calignano, A.; Russo, R. Pain Modulation in WAG/Rij Epileptic Rats (A Genetic Model of Absence Epilepsy): Effects of Biological and Pharmacological Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozubek, A.; Tyman, J.H.P. Resorcinolic Lipids, the Natural Non-Isoprenoid Phenolic Amphiphiles and Their Biological Activity. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushneruk, M.A.; Tugarova, A.V.; Il’chukova, A.V.; Slavkina, E.A.; Starichkova, N.I.; Bogatyrev, V.A.; Antoniuk, L.P. Factors Inducing Transition from Growth to Dormancy in Rhizobacteria Azospirillum Brasilense. Mikrobiologiia 2013, 82, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, E.; González, J.; Peiró, J.M.; Oria, R.; Lopez-Buesa, P. Browning Prevention by Ascorbic Acid and 4-Hexylresorcinol: Different Mechanisms of Action on Polyphenol Oxidase in the Presence and in the Absence of Substrates. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, C464–G470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.S.; Huff, J.E.; Haseman, J.; Hall, A.; Baskin, G.; Cowan, M. Inhibition of Some Spontaneous Tumors by 4-Hexylresorcinol in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1988, 11, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program. NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of 4-Hexylresorcinol (CAS No. 136-77-6) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies). Natl. Toxicol. Program. Tech. Rep. Ser. 1988, 330, 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.W.; Park, Y.W.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, J.Y. 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits NF-κB Phosphorylation and has a Synergistic Effect with Cisplatin in KB Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Kim, A.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kweon, H. 4-Hexylresorcinol Stimulates the Differentiation of SCC-9 Cells through the Suppression of E2F2, E2F3 and Sp3 Expression and the Promotion of Sp1 Expression. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, Y.W.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, A.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Chae, W.S. 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Transglutaminase-2 Activity and has Synergistic Effects Along with Cisplatin in KB Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, H.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, J.Y. Inhibition of Foreign Body Giant Cell Formation by 4-Hexylresorcinol through Suppression of Diacylglycerol Kinase Delta Gene Expression. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Seok, H.; Choi, J.Y. Topical Delivery of 4-Hexylresorcinol Promotes Wound Healing via Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Suppression. Burns 2016, 42, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G. Immunomodulation for Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg 2020, 42, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Yoon, C.S.; Kim, S.G.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, S.K. Effects of 4-Hexylresorcinol on Protein Expressions in RAW 264.7 Cells as Determined by Immunoprecipitation High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Jo, Y.Y.; Garagiola, U.; Choi, J.Y.; Kang, Y.J.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, S.G. Increased Level of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors by 4-Hexylresorcinol is Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor-β1 and Accelerates Capillary Regeneration in the Burns in Diabetic Animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumai, R.; Komatsu, Y.; Nishino, N.; Khochbin, S.; Yoshida, M.; Horinouchi, S. Potent Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Built from Trichostatin A and Cyclic Tetrapeptide Antibiotics Including Trapoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.K. 4-Hexylresorcinol-Induced Angiogenesis Potential in Human Endothelial Cells. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg 2020, 42, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, S.K. 4-Hexylresorcinol-Induced Protein Expression Changes in Human Umbilical Cord Vein Endothelial Cells as Determined by Immunoprecipitation High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.S.; Parmigiani, R.B.; Marks, P.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5541–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhao, S.; Ammanamanchi, S.; Brattain, M.; Venkatasubbarao, K.; Freeman, J.W. Trichostatin A Induces Transforming Growth Factor Beta Type II Receptor Promoter Activity and Acetylation of Sp1 by Recruitment of PCAF/p300 to a Sp1.NF-Y Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10047–10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Béguet-Crespel, F.; Marinelli, L.; Jamet, A.; Ledue, F.; Blottière, H.M.; Lapaque, N. Butyrate Produced by Gut Commensal Bacteria Activates TGF-Beta1 Expression Through the Transcription Factor SP1 in Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Baek, J.H.; Jang, J.E.; Lee, S.W.; Moon, E.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.K.; Chung, H.Y.; et al. Histone Deacetylases Induce Angiogenesis by Negative Regulation of Tumor Suppressor Genes. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.G. 4-Hexylresorcinol and Silk Sericin Increase the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor via Different Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagger, G.; O’Carroll, D.; Rembold, M.; Khier, H.; Tischler, J.; Weitzer, G.; Schuettengruber, B.; Hauser, C.; Brunmeir, R.; Jenuwein, T.; et al. Essential Function of Histone Deacetylase 1 in Proliferation Control and CDK Inhibitor Repression. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskara, S.; Chyla, B.J.; Amann, J.M.; Knutson, S.K.; Cortez, D.; Sun, Z.W.; Hiebert, S.W. Deletion of Histone Deacetylase 3 Reveals Critical Roles in S Phase Progression and DNA Damage Control. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Liu, T.; Gao, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, M. 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis by Suppressing the NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Reverses Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

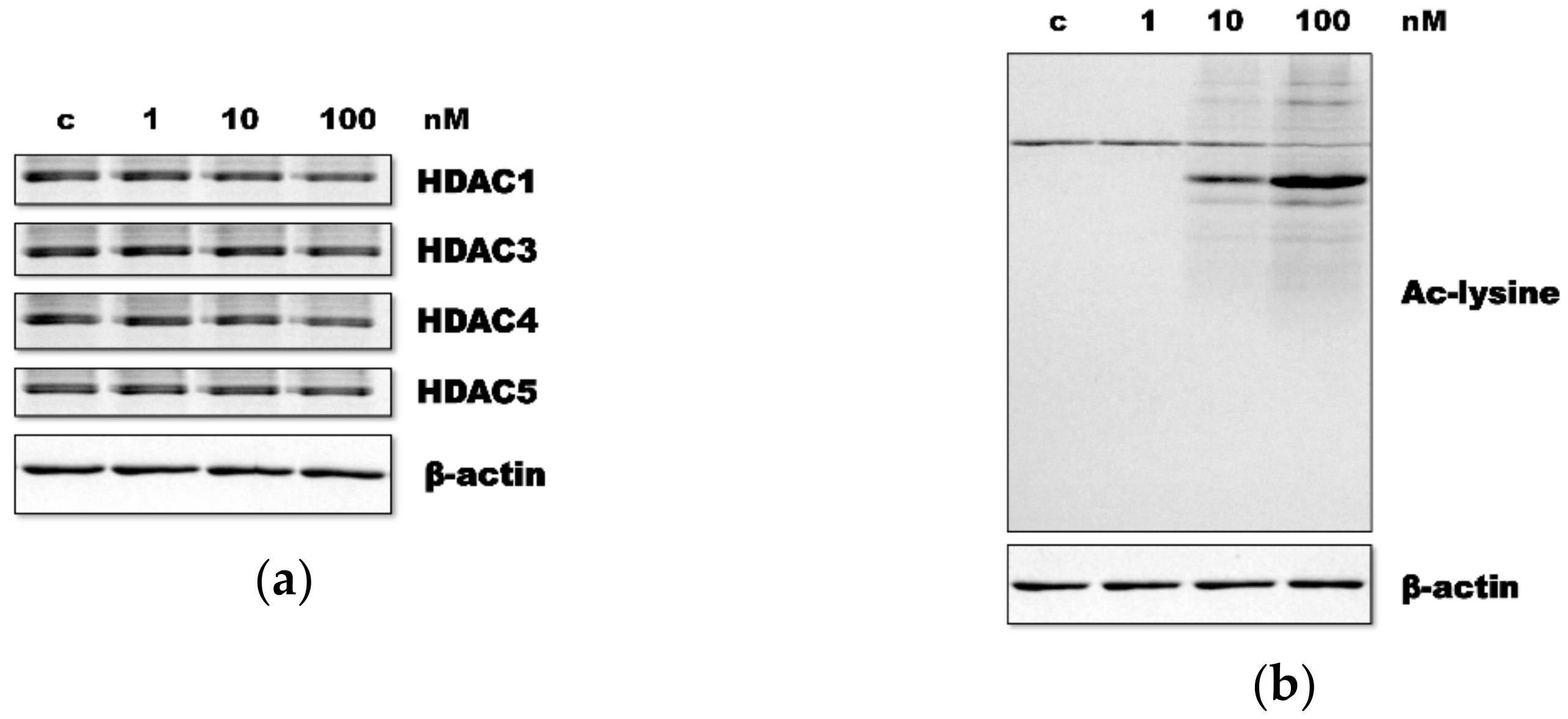

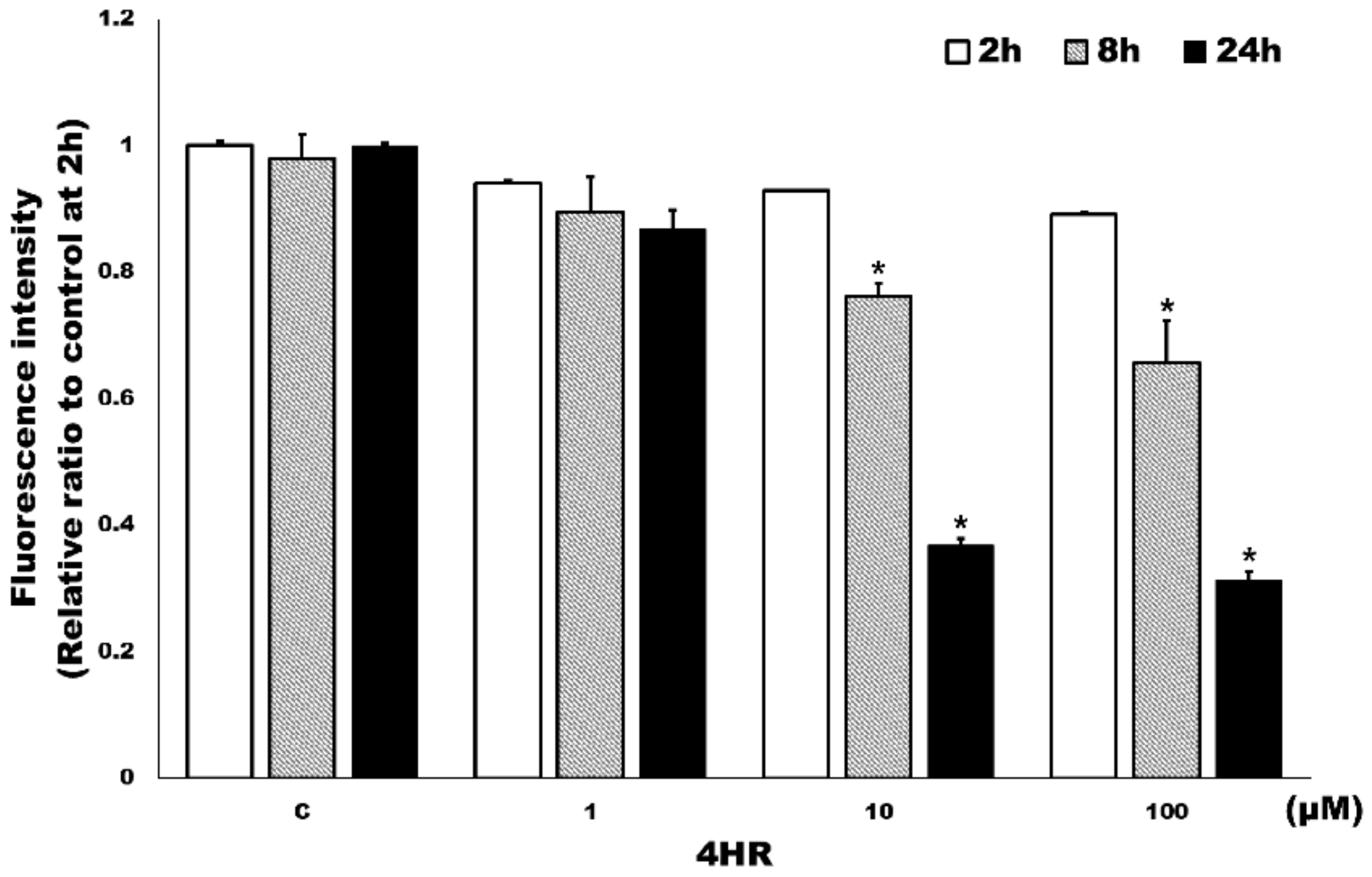
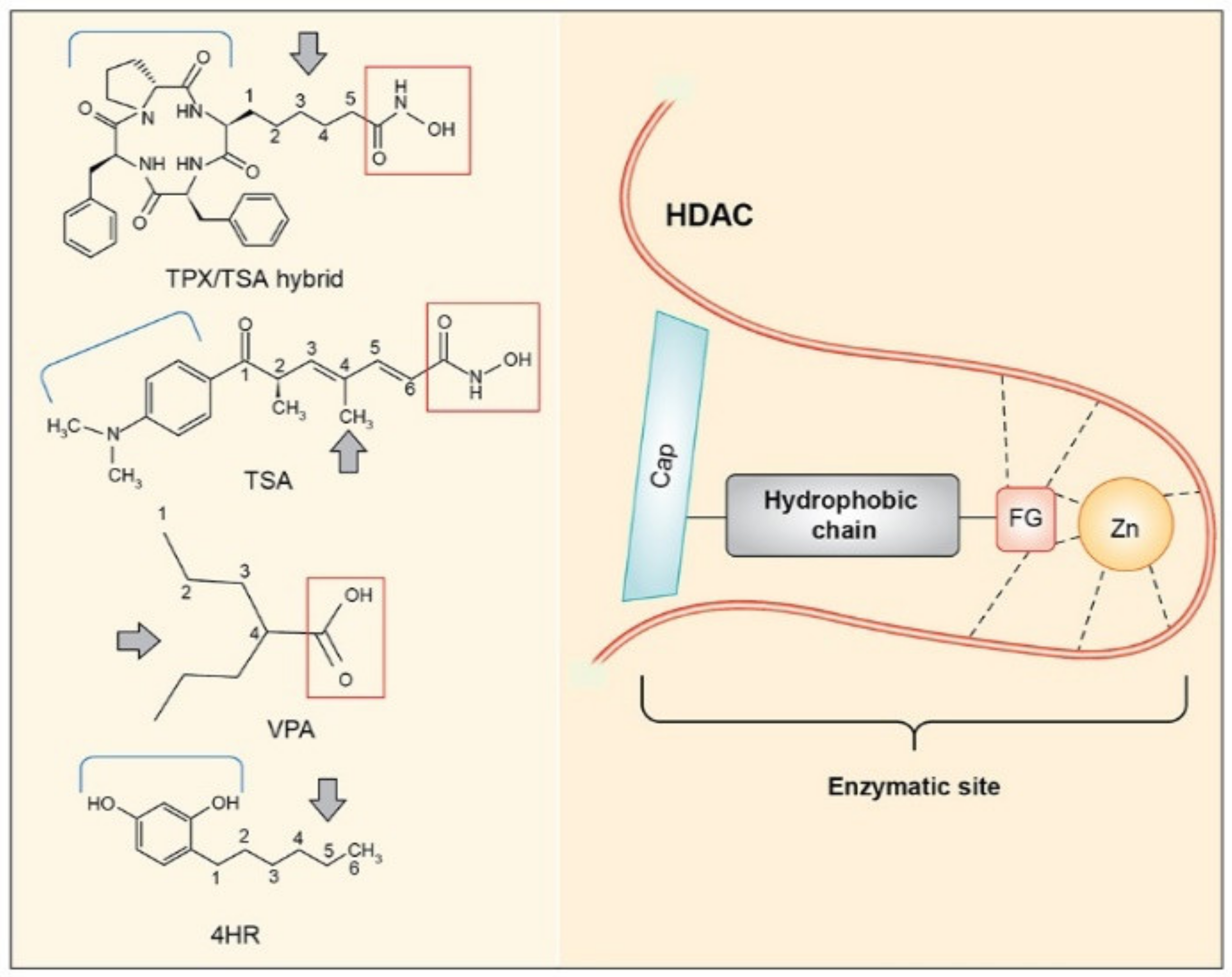
| Class | Members |
|---|---|
| I | HDAC1, 2, 3, 8 |
| IIA | HDAC4, 5, 7, 9 |
| IIB | HDAC6, 10 |
| III | SIRT1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
| IV | HDAC11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-Y.; Kweon, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-G. 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Class I Histone Deacetylases in Human Umbilical Cord Endothelial Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083486
Kim J-Y, Kweon H-Y, Kim D-W, Choi J-Y, Kim S-G. 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Class I Histone Deacetylases in Human Umbilical Cord Endothelial Cells. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(8):3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083486
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jwa-Young, Hae-Yong Kweon, Dae-Won Kim, Je-Yong Choi, and Seong-Gon Kim. 2021. "4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Class I Histone Deacetylases in Human Umbilical Cord Endothelial Cells" Applied Sciences 11, no. 8: 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083486
APA StyleKim, J.-Y., Kweon, H.-Y., Kim, D.-W., Choi, J.-Y., & Kim, S.-G. (2021). 4-Hexylresorcinol Inhibits Class I Histone Deacetylases in Human Umbilical Cord Endothelial Cells. Applied Sciences, 11(8), 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083486








