Older Adults’ Experience of an Exergaming Intervention to Improve Balance and Prevent Falls: A Nested Explanatory Qualitative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Framework for the Focus Group Design
2.1.1. Sampling Strategy and Size
2.1.2. Study Participants and Setting
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. Permissions and Consent
2.2.2. Focus Group Discussions
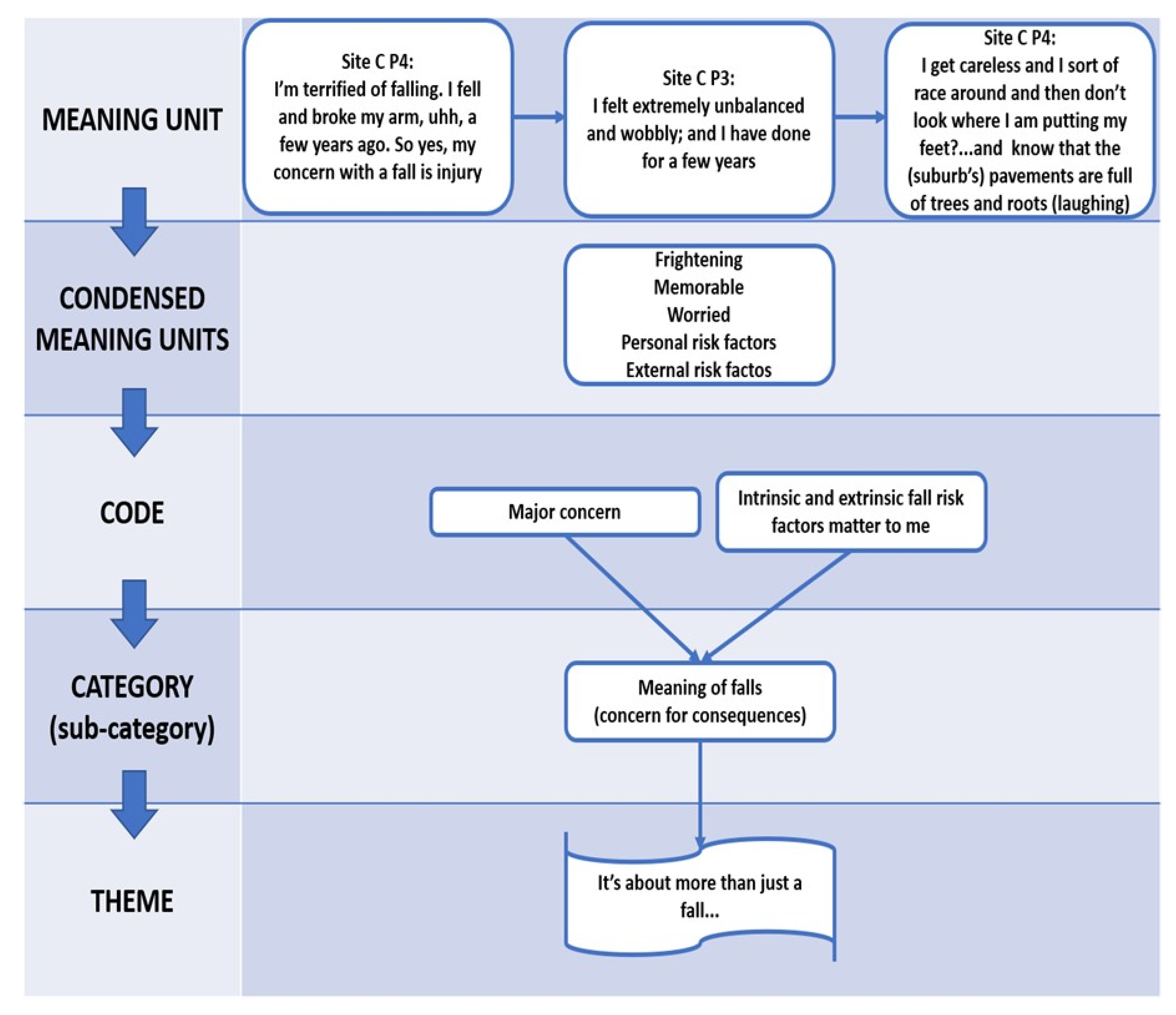
3. Data Analysis
3.1. Phases in the Analysis Process
3.1.1. Preparatory Phase
3.1.2. Organizing Phase
3.1.3. Reporting Phase
4. Trustworthiness
5. Results
5.1. Participants’ (OEP and WBB) Attitudes towards Falls and Fall Prevention
5.2. WBB Participants’ Experience of the Intervention
- Site C P1: “So you’re not hanging onto any support?”
- Site C P4: “I’m not hanging onto stuff.”
- Group: “Oh, wow.”
5.3. Barriers and Facilitators to Participation in the WBB Intervention
5.4. Barriers
5.5. Facilitators
5.6. Results of Systems Usability Scale
6. Discussion
6.1. Participants’ Constructs of Falls
6.2. Participants’ Experiences with the WBB Intervention
6.3. Motivation Challenges and Possible Solutions
6.3.1. Shift to Group Activity
6.3.2. A Wii Bit More Fun
6.3.3. Use of Methods to Enhance Self-Efficacy: Motivational Interviewing
7. Conclusions: Lessons Learned and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Topic Guide
References
- Da Silva Francisco, A.A. ‘Gerontogrowth’ and population ageing in Africa and the Global AgeWatch Index. J. Econ. Ageing 2017, 9, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornby-Turner, Y.C.; Peel, N.M.; Hubbard, R.E. Health assets in older age: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2017, 7, 013226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apt, N.A. Preface. In Ageing in Africa: Sociolinguistic and Anthropological Approaches; Makoni, S., Stroeken, K., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; Available online: https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=QTg7DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT7&dq=Africa+%2B+ageing&ots=PYIQMTMWgv&sig=6Vkri6kIZrjJkU2tkJOWEN8na_Y#v=onepage&q=Africa%20%2B%20ageing&f=false (accessed on 2 May 2018).
- Ajaero, C.K.; De Wet, N.; Odimegwu, C.O. Integrating rural–urban differentials in the appraisal of prevalence and risk factors of non-communicable diseases in South Africa. GeoJournal 2020, 85, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, R.; Christian, C. Access to health care in post-apartheid South Africa: Availability, affordability, acceptability. Health Econ. Policy Law 2020, 15, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewitte, K.; Singh, A. Aging in South Africa. In Functional Performance in Older Adults, 4th ed.; Bonder, B.R., Dal Bello-Haas, V., Eds.; FA Davis: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, G.; Mrengqwa, L.; Geffen, L. “They don’t care about us”: Older people’s experiences of primary healthcare in Cape Town, South Africa. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, L.D.; Grimmer, K.A.; Twizeyemariya, A.; Coetzee, M.; Leibbrandt, D.C.; Louw, Q.A. Health system challenges affecting rehabilitation services in South Africa. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 43, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoateng, A.Y.; Biney, E.; Ewemooje, O.S. Social determinants of chronic ill-health in contemporary South Africa: A social disadvantage approach. Soc. Sci. J. 2021, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, B. The Challenge of Geriatric Medicine; Oxford Medical Publications: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gazibara, T.; Kurtagic, I.; Kisic-Tepavcevic, D.; Nurkovic, S.; Kovacevic, N.; Gazibara, T.; Pekmezovic, T. Falls, risk factors and fear of falling among persons older than 65 years of age. Psychogeriatrics 2017, 17, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Eckstrom, E.; Harmer, P.; Fitzgerald, K.; Voit, J.; Cameron, K.A. Exercise and fall prevention: Narrowing the research-to-practice gap and enhancing integration of clinical and community practice. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2016, 64, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S. Falls: Prevention and Management. In Geriatric Medicine. A Problem-Based Approach; Nair, B.K.R., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Ganz, D.A.; Latham, N.K. Prevention of falls in community-dwelling older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, C. Measures of falls, static and dynamic balance in independent older adults in Cape Town, South Africa. J. Vestib. Res. 2016, 26, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.J.; Wallbank, G.K.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Howard, K.; Clemson, L.; Hopewell, S.; Lamb, S.E. Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornos-Muñoz, L.; Moreno-Casbas, T.; Sánchez-Pablo, C.; Bays-Moneo, A.; Fernández-Domínguez, J.C.; Rich-Ruiz, M.; Gea-Sánchez, M. Efficacy of the Otago Exercise Programme to reduce falls in community-dwelling adults aged 65–80 years old when delivered as group or individual training. J. Adv. Nurs. 2018, 74, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.N.; Pachpute, S. The effects of Otago Exercise Programme for fall prevention in elderly people. Int. J. Physiother. 2015, 2, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Mackintosh, S.; Halbert, J. Does the ‘Otago exercise programme’ reduce mortality and falls in older adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deverall, E.; Kvizhinadze, G.; Pega, F.; Blakely, T.; Wilson, N. Exercise programmes to prevent falls among older adults: Modelling health gain, cost-utility and equity impacts. Inj. Prev. 2019, 25, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rispel, L.C.; Blaauw, D.; Ditlopo, P.; White, J. Human resources for health and universal health coverage: Progress, complexities and contestations. South Afr. Health Rev. 2018, 2018, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Benavent-Caballer, V.; Rosado-Calatayud, P.; Segura-Ortí, E.; Amer-Cuenca, J.J.; Lisón, J.F. The effectiveness of a video-supported group-based Otago exercise programme on physical performance in community-dwelling older adults: A preliminary study. Physiotherapy 2015, 102, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amorim, J.S.C.; Leite, R.C.; Brizola, R.; Yonamine, C.Y. Virtual reality therapy for rehabilitation of balance in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Rheumatol. 2018, 58, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirelman, A.; Maidan, I.; Shiratzky, S.S.; Hausdorff, J.M. Virtual reality training as an intervention to reduce falls. In Falls and Cognition in Older Persons; Montero-Odasso, M., Camicioli, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira, J.A.; Guaratto, T.F.; Bacha, J.M.R.; Evangelista, R.A.; Bocalini, D.S.; Greve, J.M.D.A.; Alonso, A.C. Virtual reality in the rehabilitation of the balance in the elderly. Man. Ther. Posturology Rehabil. J. 2018, 15, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, Y.-Y.; Scherer, Y.K.; Montgomery, C.A. Effects of using Nintendo Wii (TM) exergames in older adults: A review of the literature. J. Aging Health 2015, 27, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saka, S.; Oosthuizen, F.; Nlooto, M. National Policies and older people’s healthcare in Sub-Saharan Africa: A scoping review. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, J.H. The distinction between randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and preliminary feasibility and pilot studies: What they are and are not. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2014, 44, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cresswell, J.W.; Plano Clark, V.L. Choosing a mixed methods design. In Designing and conducting mixed methods research, 2nd ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 53–106. [Google Scholar]
- Schreier, M. Qualitative content analysis. In The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis; Flick, U., Ed.; Sage: London, UK, 2014; pp. 170–183. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, K.E.; Gandha, T.; Culbertson, M.J.; Carlson, C. Focus group evidence: Implications for design and analysis. Am. J. Eval. 2014, 35, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagle, B.; Williams, N. Methodology Brief: Introduction to Focus Groups. Available online: http://www.mmgconnect.com/projects/userfiles/File/FocusGroupBrief.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Suzuki, L.A.; Ahluwalia, M.K.; Arora, A.K.; Mattis, J.S. The pond you fish in determines the fish you catch: Exploring strategies for qualitative data collection. Couns. Psychol. 2007, 35, 295–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusch, P.I.; Ness, L.R. Are we there yet? Data saturation in qualitative research. Qual. Rep. 2015, 20, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.C.; Valencia, W.M. Exercise and older adults. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 34, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnik, D.B.; Shamoo, A.E. The Singapore statement on research integrity. Account. Res. 2011, 18, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaismoradi, M.; Jones, J.; Turunen, H.; Snelgrove, S. Theme development in qualitative content analysis and thematic analysis. J. Nurs. Educ. Pract. 2016, 6, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onwuegbuzie, A.J.; Dickinson, W.B.; Leech, N.L.; Zoran, A.G. A qualitative framework for collecting and analyzing data in focus group research. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2009, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaismoradi, M.; Turunen, H.; Bondas, T. Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nurs. Health Sci. 2013, 15, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, M. How to plan and perform a qualitative study using content analysis. Nurs. Open 2016, 2, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, C.; Joffe, H. Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2020, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnick, B.; Jenkins, L.S. Testing the reliability and validity of the self-efficacy for exercise scale. Nurs. Res. 2000, 49, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, J. SUS—A quick and dirty usability scale. In Usability Evaluation in Industry; Jordan, P.W., McClelland, B.T.I.L., Weerdmeester, B.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1996; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.R. The system usability scale: Past, present, and future. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2018, 34, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, W.R. Physical activity and rehabilitation in elderly. In Rehabilitation Medicine for Elderly Patients; Masiero, S., Carraro, U., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Stringhini, S.; Carmeli, C.; Jokela, M.; Avendaño, M.; McCrory, C.; d’Errico, A.; Bochud, M.; Barros, H.; Costa, G.; Chadeau-Hyam, M. Socioeconomic status, non-communicable disease risk factors, and walking speed in older adults: Multi-cohort population based study. BMJ 2018, 360, k1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloyd-Sherlock, P.; Amoakoh-Coleman, M. A critical review of intervention and policy effects on the health of older people in sub-Saharan Africa. Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 250, 112887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Sherlock, P. Long-term care for older people in South Africa: The enduring legacies of apartheid and HIV/AIDS. J. Soc. Policy 2019, 48, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardiner, S.; Glogowska, M.; Stoddart, C.; Pendlebury, S.; Lasserson, D.; Jackson, D. Older people’s experiences of falling and perceived risk of falls in the community: A narrative synthesis of qualitative research. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2017, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuvemo Johnson, S.; Martin, C.; Anens, E.; Johansson, A.-C.; Hellström, K. Older adults’ opinions on fall prevention in relation to physical activity level. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2018, 37, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Shawis, T.; Haines, R.; Merza, R.; Barawy, O. Falls in older people: A perspective from Kurdistan of Iraq. Middle East J. Age Ageing 2014, 11, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worapanwisit, T.; Prabpai, S.; Rosenberg, E. Correlates of falls among community-dwelling elderly in Thailand. J. Aging Res. 2018, 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payette, M.-C.; Belanger, C.; Léveillé, V.; Grenier, S. Fall-related psychological concerns and anxiety among community-dwelling older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavedán, A.; Viladrosa, M.; Jürschik, P.; Botigué, T.; Nuín, C.; Masot, O.; Lavedán, R. Fear of falling in community-dwelling older adults: A cause of falls, a consequence, or both? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppala, L.J.; Wermelink, A.M.; de Vries, M.; Ploegmakers, K.J.; van de Glind, E.M.; Daams, J.G.; van der Velde, N.; Blain, H.; Bousquet, J.; Bucht, G. Fall-risk-increasing drugs: A systematic review and meta-analysis: II. Psychotropics. J. Am. Med Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 371.e11–371.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Carmen Panini, A.; Teves, M.R.; Giraudo, E.; Garraza, M.H.; Calderón, C.P. Psychotropic medication use in the elderly. In Psychiatry and Neuroscience Update-Vol. II; Gargiulo, P., Mesones-Arroyo, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 293–306. [Google Scholar]
- Catalan-Matamoros, D.; Gomez-Conesa, A.; Stubbs, B.; Vancampfort, D. Exercise improves depressive symptoms in older adults: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 244, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonerock, G.L.; Hoffman, B.M.; Smith, P.J.; Blumenthal, J.A. Exercise as treatment for anxiety: Systematic review and analysis. Ann. Behav. Med. 2015, 49, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Torres, S.; Fahey, T.D.; Rivera, M.A. Adherence to exercise programs in older adults: Informative report. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Room, J.; Hannink, E.; Dawes, H.; Barker, K. What interventions are used to improve exercise adherence in older people and what behavioural techniques are they based on? A systematic review. BMJ Open 2017, 7, 019221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereles, L.; Jackson, R.; Rosenal, T.; Nixon, L. Listening with a narrative ear: Insights from a study of fall stories in older adults. Can. Fam. Physician 2017, 63, e50. [Google Scholar]
- Osho, O.; Owoeye, O.; Armijo-Olivo, S. Adherence and attrition in fall prevention exercise programs for community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2018, 26, 304–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merom, D.; Pye, V.; Macniven, R.; van de Ploeg, H.; Milat, A.; Sherrington, C.; Lord, S.; Bauman, A. Prevalence and correlates of participation in fall prevention exercise/physical activity by older adults. Prev. Med. 2012, 55, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.A.; Wilhelm, J.; Chen, Y.; Blehm, R.; Nutt, J.; Chen, Z.; Serdar, A.; Horak, F.B. Effects of group, individual, and home exercise in persons with Parkinson Disease: A randomized clinical trial. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2015, 39, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherrington, C.; Tiedemann, A.; Fairhall, N.; Close, J.C.T.; Lord, S.R. Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: An updated meta-analysis and best practice recommendations. NSW Public Health Bull. 2011, 22, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, V.L.S.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Fernandes, L.C.; Menezes, R.L.d. Postural changes versus balance control and falls in community-living older adults: A systematic review. Fisioter. Em. Mov. 2018, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burton, E.; Farrier, K.; Hill, K.D.; Codde, J.; Airey, P.; Hill, A.-M. Effectiveness of peers in delivering programs or motivating older people to increase their participation in physical activity: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beauchamp, M.R.; Ruissen, G.R.; Dunlop, W.L.; Estabrooks, P.A.; Harden, S.M.; Wolf, S.A.; Liu, Y.; Schmader, T.; Puterman, E.; Sheel, A.W. Group-based physical activity for older adults (GOAL) randomized controlled trial: Exercise adherence outcomes. Health Psychol. 2018, 37, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Wang, L.; Siever, J.; Medico, T.D.; Jones, C.A. Loneliness and social isolation among older adults in a community exercise program: A qualitative study. Aging Ment. Health 2019, 23, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hausknecht, S.; Schell, R.; Kaufman, D. Can a Wii bowling tournament improve older adults’ attitudes towards digital games? In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference of Computer Supported Education CSEDU (2016), Rome, Italy, 21–23 August 2016; SCITEPRESS Science and Technology Publications Ltd.: Setúbal, Portugal, 2016; pp. 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Theng, Y.-L. Examining the influencing factors of exercise intention among older adults: A controlled study between exergame and traditional exercise. Cyberpsychology Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, T.B.F.; de Medeiros, C.S.P.; de Oliveira, V.H.B.; Vieira, E.R.; de Cavalcanti, F.A.C. Effectiveness of exergames for improving mobility and balance in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, K.D.; Hunter, S.W.; Batchelor, F.A.; Cavalheri, V.; Burton, E. Individualized home-based exercise programs for older people to reduce falls and improve physical performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2015, 82, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.H.; Schou, L.; Lund, H.H.; Langberg, H. The physical effect of exergames in healthy elderly—A systematic review. Games Health 2013, 2, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montero-Alía, P.; Miralles-Basseda, R.; López-Jiménez, T.; Muñoz-Ortiz, L.; Jiménez-González, M.; Prat-Rovira, J.; Albarrán-Sánchez, J.L.; Manresa-Domínguez, J.M.; Andreu-Concha, C.M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.C.; et al. Controlled trial of balance training using a video game console in community-dwelling older adults. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkkukangas, M.; Sundler, A.J.; Söderlund, A.; Eriksson, S.; Johansson, A.-C. Older persons’ experiences of a home-based exercise program with behavioral change support. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2017, 33, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkkukangas, M.; Söderlund, A.; Eriksson, S.; Johansson, A.-C. Fall preventive exercise with or without behavior change support for community-dwelling older adults: A randomized controlled trial with short-term follow-up. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 42, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazh, H. Feasibility of conducting a randomized controlled trial to evaluate the effect of motivational interviewing on hearing-aid use. Int. J. Audiol. 2016, 55, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkkukangas, M.; Hultgren, S. Implementation of motivational interviewing in a fall prevention exercise program: Experiences from a randomized controlled trial. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyi, P.L.; Pelser, A. The missing link: Finding space for gerontology content into university curricula in South Africa. Gerontol. Geriatr. Educ. 2019, 40, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedford, O.; Yeh, K.-H. The history and the future of the psychology of filial piety: Chinese norms to contextualized personality construct. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, P. SA Smartphone Penetration Now at Over 80%, Says ICASA. Available online: https://www.itweb.co.za/content/GxwQDM1AYy8MlPVo (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- McGaughey, R.E.; Zeltmann, S.M.; McMurtrey, M.E. Motivations and obstacles to smartphone use by the elderly: Developing a research framework. Int. J. Electron. Financ. 2013, 7, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, S.J. Usability of technology for older adults: Where are we and where do we need to be. J. Usability Stud. 2019, 14, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wollersheim, D.; Merkes, M.; Shields, N.; Liamputtong, P.; Wallis, L.; Reynolds, F.; Koh, L. Physical and psychosocial effects of Wii video game use among older women. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Soc. 2010, 8, 85–98. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rogers, C.; Shamley, D.; Amosun, S. Older Adults’ Experience of an Exergaming Intervention to Improve Balance and Prevent Falls: A Nested Explanatory Qualitative Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411678
Rogers C, Shamley D, Amosun S. Older Adults’ Experience of an Exergaming Intervention to Improve Balance and Prevent Falls: A Nested Explanatory Qualitative Study. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(24):11678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411678
Chicago/Turabian StyleRogers, Christine, Delva Shamley, and Seyi Amosun. 2021. "Older Adults’ Experience of an Exergaming Intervention to Improve Balance and Prevent Falls: A Nested Explanatory Qualitative Study" Applied Sciences 11, no. 24: 11678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411678
APA StyleRogers, C., Shamley, D., & Amosun, S. (2021). Older Adults’ Experience of an Exergaming Intervention to Improve Balance and Prevent Falls: A Nested Explanatory Qualitative Study. Applied Sciences, 11(24), 11678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411678





