Infrastructure BIM Platform for Lifecycle Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
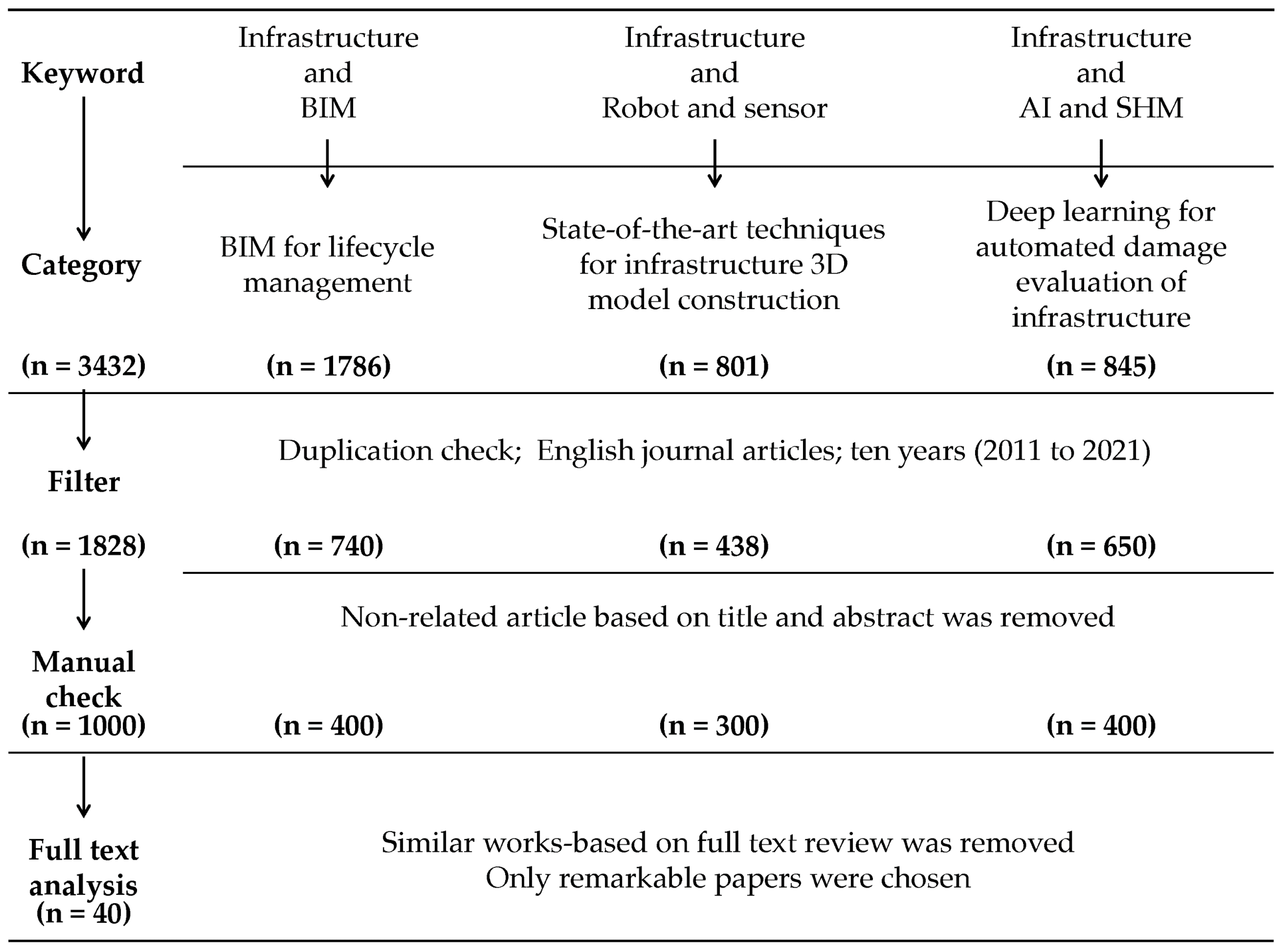
2.1. Categorizing Keywords and Topics
2.2. Collection of Relevant Articles from Web of Science
2.3. Filter Applying
2.4. Full Text Analysis and Detail Categorization of Articles Based on Main Purpose
3. Literature Reviews of Infrastructure Lifecycle Management
3.1. BIM for Infrastructure Lifecycle Management
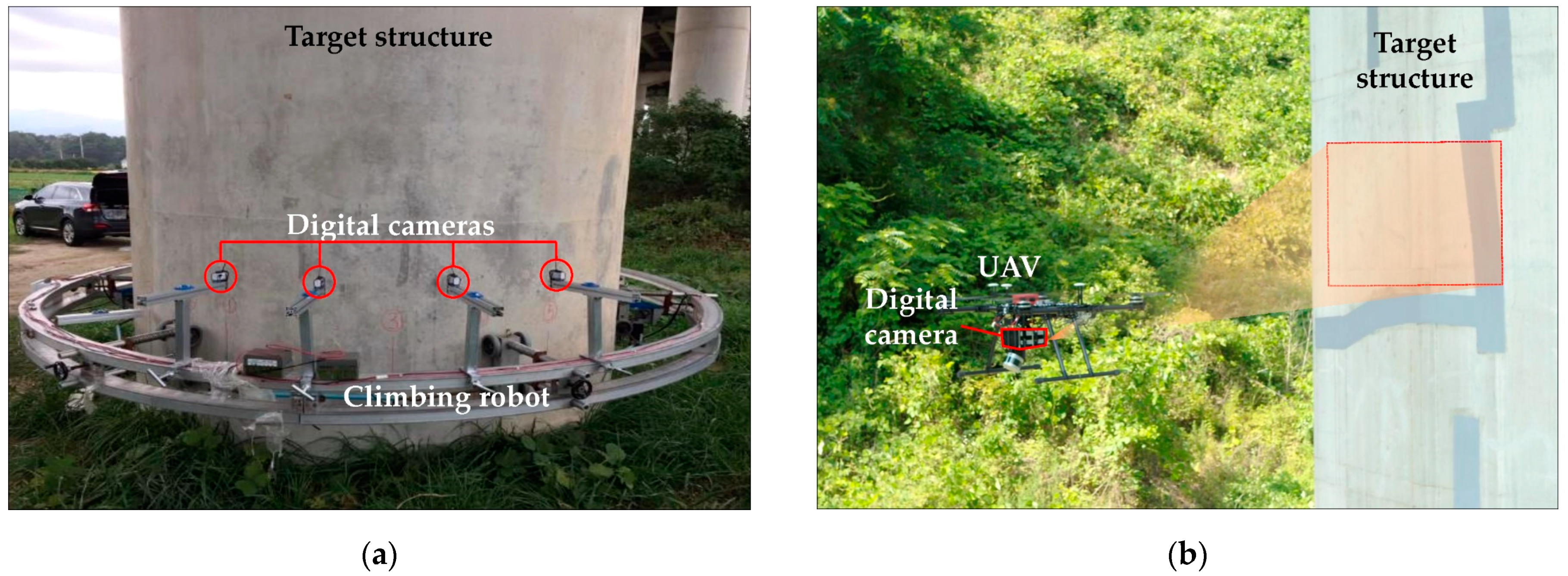
3.2. State-of-the-Art Techniques for 3D Model Construction of Infrastructure
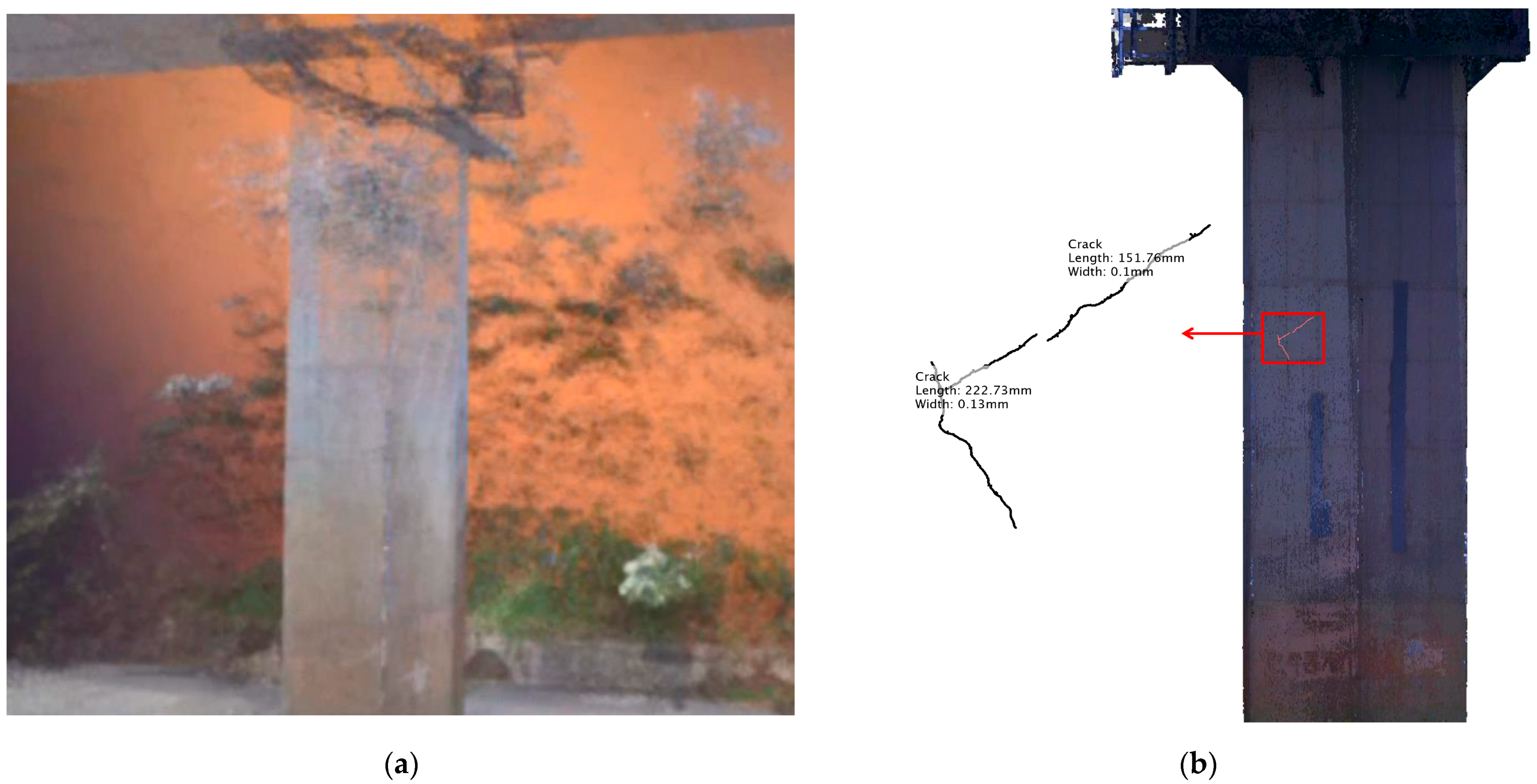
3.3. Deep Learning for Automated Damage Evaluation of Infrastructure
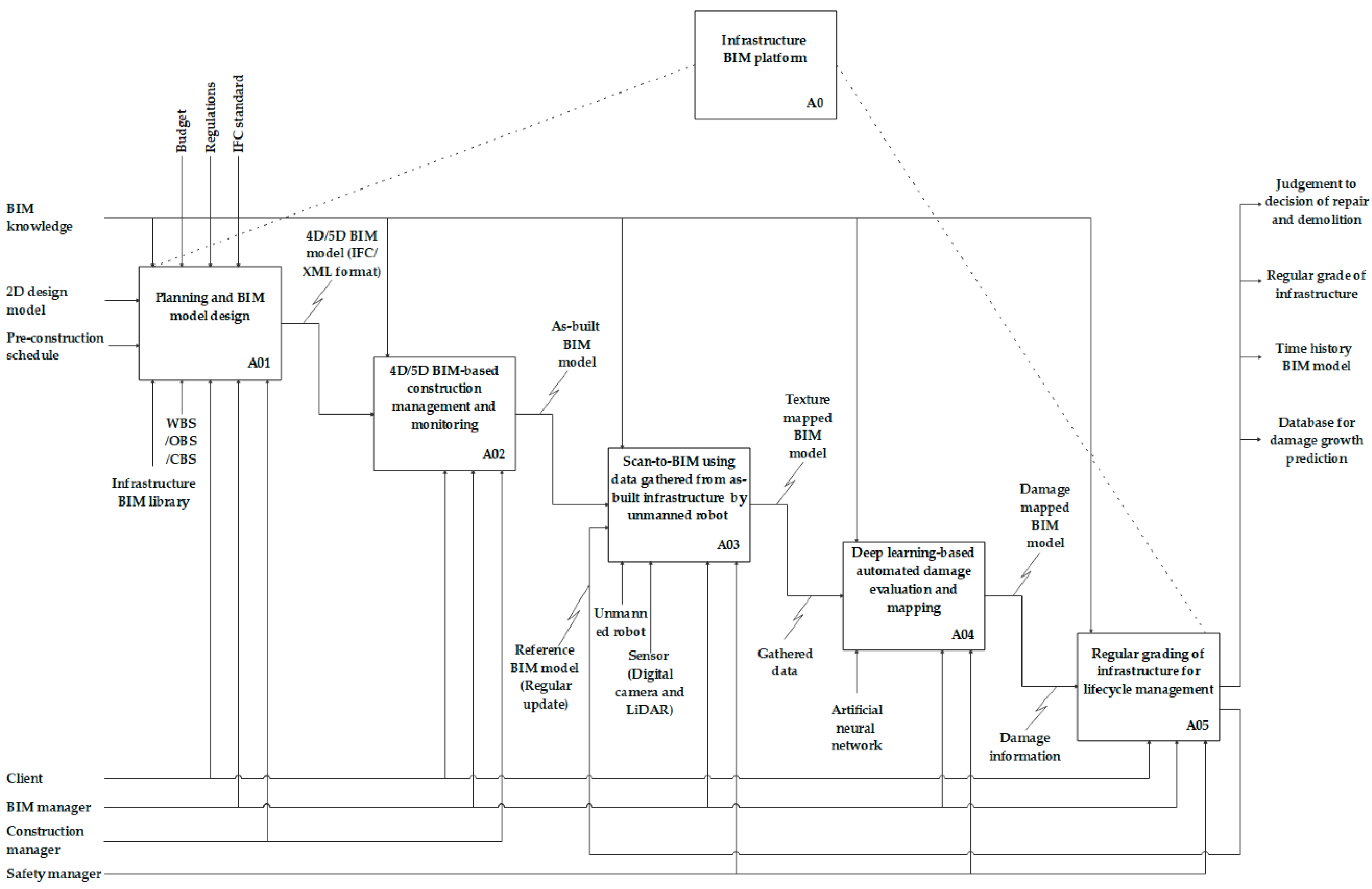
4. Infrastructure BIM Platform
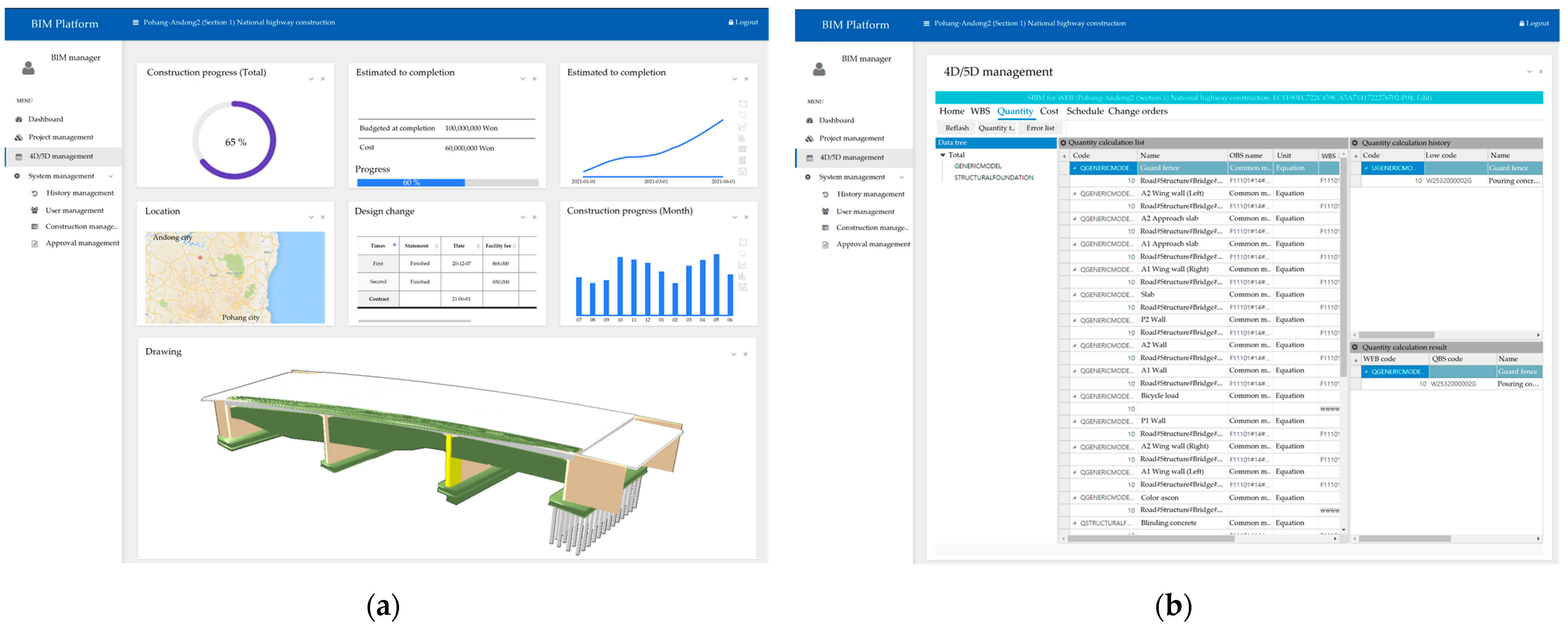
4.1. Web-Based Infrastructure BIM Platform
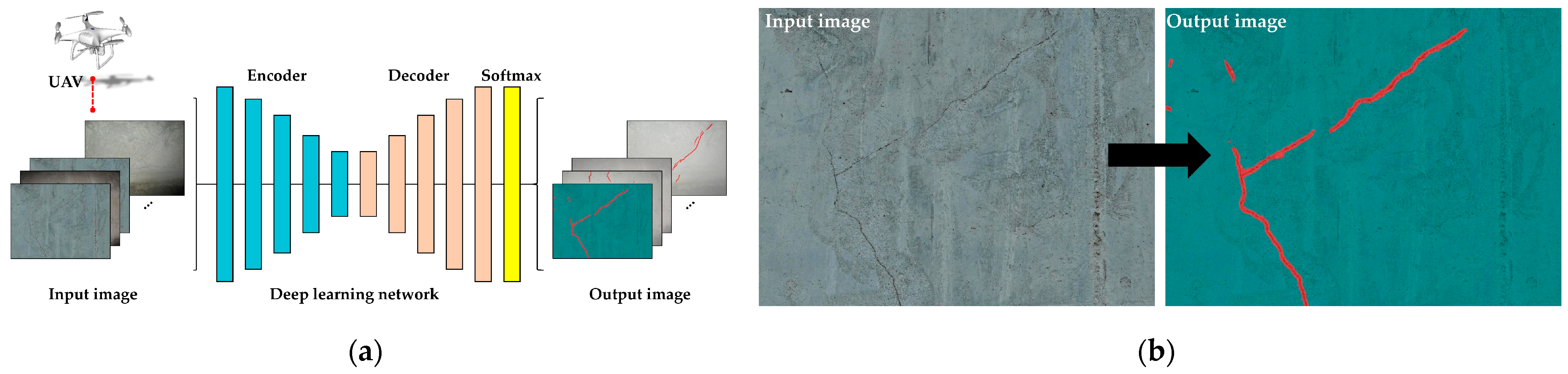
4.2. Management of Infrastructure Using State-of-the-Art Techniques
4.3. Future Work for Digital Twin
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costin, A.; Adibfar, A.; Hu, H.J.; Chen, S.S. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for transportation Infrastructure—Literature review, applications, challenges, and recommendations. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, A.; Li, H.J.; Lark, R.; Dunn, S. BIM for infrastructure: An overall review and constructor perspective. Autom. Constr. 2016, 71, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Lu, Q.Q.; Deng, Y.C. Analytical review and evaluation of civil information modeling. Autom. Constr. 2016, 67, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, S.; Chen, A.M.S. Integration of Information and Automation Technologies in Bridge Engineering and Management: Extending the State of the Art. J. Transp. Res. Board 2006, 1976, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, A.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Y.X.; Mozaffari, E. Mobile model-based bridge lifecycle management system. Comput. Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2006, 21, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, M.; Borrmann, A.; Rank, E.; Hinz, S.; Kolbe, T.H.; Schilcher, M.; Mundani, R.P.; Jubierre, J.R.; Flurl, M.; Thomsen, A.; et al. Collaborative multi-scale 3D city and infrastructure modeling and simulation. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLII-4/W4, Tehran, Iran, 7–10 October 2017; pp. 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgertshofer, S.; Borrmann, A. Using graph rewriting methods for the semi-automatic generation of parametric infrastructure models. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2017, 33, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chan, N.K.Y.; Huang, T.; Skitmore, M.; Yang, J. Virtual prototyping for planning bridge construction. Autom. Constr. 2012, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.; An, Y.K.; Kim, B.; Cho, S. Automated crack evaluation of a high-rise bridge pier using a ring-type climbing robot. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 36, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Jang, K.; An, Y.K. Deep super resolution crack network (SrcNet) for improving computer vision-based automated crack detectability in in situ bridges. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Paal, S.G.; Rashidi, A.; Zhu, Z.; Konig, M.; Brilakis, I. Achievements and Challenges in Machine Vision-Based Inspection of Large Concrete Structures. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2014, 17, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Building Information Modeling Market by Component Deployment Mode, Project Life Cycle, Building Type, Application, and End User: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2020–2027; Allied Analytics LLP: Pune, India, 2020.
- Ministry of Land Infrastructure and Transport. Full-Scale Introduction of BIM in the Construction Industry, Full-Scale Promotion! Available online: http://www.molit.go.kr/USR/NEWS/m_71/dtl.jsp?id=95084979 (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Shin, J.-Y.; Ju, K.-B.; Son, A.-Y.; Moon, H. A Study on the BIM Platform Required Functions and Application for Road and River Construction Project Management. J. Korean Inst. Commun. Inf. Sci. 2020, 45, 1893–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autodesk. Construction Management Software|Autodesk BIM 360. Available online: https://www.autodesk.com/bim-360/ (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Trimble. Trimble Connect. Available online: https://connect.trimble.com/ (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Bentley. Bently. Available online: https://www.bentley.com (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Chihib, M.; Salmeron-Manzano, E.; Novas, N.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Bibliometric Maps of BIM and BIM in Universities: A Comparative Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, H.; La, H.M.; Gucunski, N. Review of Non-Destructive Civil Infrastructure Evaluation for Bridges: State-of-the-Art Robotic Platforms, Sensors and Algorithms. Sensors 2020, 20, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.; Eslamlou, A.D.; Pekcan, G. Data-Driven Structural Health Monitoring and Damage Detection through Deep Learning: State-of-the-Art Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, M.; Borrmann, A. Model-based quality assurance in railway infrastructure planning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 109, 2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Park, J.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, S.H. Improving Applicability for Information Model of an IFC-Based Steel Bridge in the Design Phase Using Functional Meanings of Bridge Components. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrmann, A.; Kolbe, T.H.; Donaubauer, A.; Steuer, H.; Jubierre, J.R.; Flurl, M. Multi-Scale Geometric-Semantic Modeling of Shield Tunnels for GIS and BIM Applications. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 30, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, T.; Attarzadeh, M.; Tiong, R.L.K.; Chidambaram, C.; Yu, Z. Productivity improvement of precast shop drawings generation through BIM-based process re-engineering. Autom. Constr. 2015, 54, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardet, A.; Boton, C. A parametric BIM approach to foster bridge project design and analysis. Autom. Constr. 2021, 126, 103679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.H.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, H.Y. Benefit-Cost Analysis of Building Information Modeling (BIM) in a Railway Site. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.M.; Lee, Y.B.; Shim, C.S.; Park, K.L. Bridge information models for construction of a concrete box-girder bridge. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2012, 8, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.H.; Ellul, C.; Swiderska, M. Decision Making in the 4th Dimension-Exploring Use Cases and Technical Options for the Integration of 4D BIM and GIS during Construction. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Vonthron, A.; Konig, M. A tunnel information modelling framework to support management, simulations and visualisations in mechanised tunnelling projects. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Hisham, M. Implementing earned value management using bridge information modeling. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawlana, M.; Vandatikhaki, F.; Doriani, A.; Hammad, A. Integrating 4D modeling and discrete event simulation for phasing evaluation of elevated urban highway reconstruction projects. Autom. Constr. 2015, 60, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, H.B.; Wu, X.G. Using nD technology to develop an integrated construction management system for city rail transit construction. Autom. Constr. 2012, 21, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdepenas, P.; Perez, M.D.E.; Henche, C.; Rodriguez-Escribano, R.; Fernandez, G.; Lopez-Gutierrez, J.S. Application of the BIM Method in the Management of the Maintenance in Port Infrastructures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Lo, T.P.; Long, D.B. An integrated system framework of building information modelling and geographical information system for utility tunnel maintenance management. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 79, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafat, A.; Khan, M.S.; Latif, K.; Tanoli, W.A.; Park, W.; Seo, J. BIM-GIS-Based Integrated Framework for Underground Utility Management System for Earthwork Operations. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddupalli, C.; Sadhu, A.; Azar, E.R.; Pattyson, S. Improved visualization of infrastructure monitoring data using building information modeling. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 15, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Sresakoolchai, J.; Zhou, Z.H. Sustainability-Based Lifecycle Management for Bridge Infrastructure Using 6D BIM. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, I.H.; Jeon, H.; Baek, S.C.; Hong, W.H.; Jung, H.J. Application of Crack Identification Techniques for an Aging Concrete Bridge Inspection Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Sensors 2018, 18, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, J. Real-time crack assessment using deep neural networks with wall-climbing unmanned aerial system. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.; Santos, R.; Shibasaki, A.; Montenegro, P.; Carvalho, H.; Calcada, R. Remote inspection of RC structures using unmanned aerial vehicles and heuristic image processing. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A.; Borrmann, A. Combining inverse photogrammetry and BIM for automated labeling of construction site images for machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2019, 106, 102879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.B.; Song, M.; Kim, S.; Won, J.H. Change Monitoring at Expressway Infrastructure Construction Sites Using Drone. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilan, M.; Justo, A.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, A.; Riveiro, B. 3D Point Cloud to BIM: Semi-Automated Framework to Define IFC Alignment Entities from MLS-Acquired LiDAR Data of Highway Roads. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lu, W.S.; Xue, F.; Tang, P.B.; Li, L.H. Automatic building building information model reconstruction in high-density urban areas: Augmenting multi-source data with architectural knowledge. Autom. Constr. 2018, 93, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Choi, W.; Buyukozturk, O. Deep Learning-Based Crack Damage Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Cho, S. Automated Vision-Based Detection of Cracks on Concrete Surfaces Using a Deep Learning Technique. Sensors 2018, 18, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, K.; Kim, N.; An, Y.K. Deep learning-based autonomous concrete crack evaluation through hybrid image scanning. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 1722–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorafshan, S.; Thomas, R.J.; Maguire, M. Comparison of deep convolutional neural networks and edge detectors for image-based crack detection in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.D.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Tran, V.D. Automatic recognition of asphalt pavement cracks using metaheuristic optimized edge detection algorithms and convolution neural network. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Chu, H.H.; Shi, P.; Wang, W.; Kong, X. Region-Based CNN Method with Deformable Modules for Visually Classifying Concrete Cracks. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Lee, V.C.S. Imaging-based crack detection on concrete surfaces using You Only Look Once network. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 20, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Li, L.Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Lim, J.H. A novel hybrid approach for crack detection. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Choi, W.; Suh, G.; Mahmoudkhani, S.; Buyukozturk, O. Autonomous Structural Visual Inspection Using Region-Based Deep Learning for Detecting Multiple Damage Types. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 731–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.B.; Chang, C.C.; Jamshidi, M. Concrete bridge surface damage detection using a single-stage detector. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, C.V.; Anh, L.D. Autonomous concrete crack detection using deep fully convolutional neural network. Autom. Constr. 2019, 99, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.M.; Kim, J.M. Vision-Based Autonomous Crack Detection of Concrete Structures Using a Fully Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, C.C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.R.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.L. Automatic Pixel-Level Crack Detection on Dam Surface Using Deep Convolutional Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.Y.; Zhao, X.F.; Zhou, G.Y. Automatic pixel-level multiple damage detection of concrete structure using fully convolutional network. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 34, 616–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Cha, Y.J. SDDNet: Real-Time Crack Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 8016–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.H.; Cha, Y.J. Autonomous UAVs for Structural Health Monitoring Using Deep Learning and an Ultrasonic Beacon System with Geo-Tagging. Comput.-Aided Civil. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, A.; König, M.; Koch, C.; Beetz, J. Building Information Modeling: Technology Foundations and Industry Practice; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 63–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kaewunruen, S.; Sresakoolchai, J.; Ma, W.T.; Phil-Ebosie, O. Digital Twin Aided Vulnerability Assessment and Risk-Based Maintenance Planning of Bridge Infrastructures Exposed to Extreme Conditions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Topic | Keyword |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Infrastructure; Bridge; Tunnel; Road; Railway |
| BIM | Building Information Modelling (BIM); Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM); Civil Information Modeling (CIM); Planning; Design; Construction; Management; Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) |
| Robot and sensor | Vision camera; Digital camera; 3D LiDAR; Point cloud; Unmanned robot; Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV); Photogrammetry; Structure-from-Motion (SfM); Scan-to-BIM |
| AI and SHM | Deep learning; Convolutional neural network (CNN); Structural Health Monitoring (SHM); Damage detection; Anomaly detection; Damage evaluation; Crack; Efflorescence; Rust; Leakage; Spalling |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, K.; Kim, J.-W.; Ju, K.-B.; An, Y.-K. Infrastructure BIM Platform for Lifecycle Management. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110310
Jang K, Kim J-W, Ju K-B, An Y-K. Infrastructure BIM Platform for Lifecycle Management. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(21):10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110310
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Keunyoung, Jong-Woo Kim, Ki-Beom Ju, and Yun-Kyu An. 2021. "Infrastructure BIM Platform for Lifecycle Management" Applied Sciences 11, no. 21: 10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110310
APA StyleJang, K., Kim, J.-W., Ju, K.-B., & An, Y.-K. (2021). Infrastructure BIM Platform for Lifecycle Management. Applied Sciences, 11(21), 10310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110310







