Transcriptome Analysis of Egg Yolk Sialoglycoprotein on Osteogenic Activity in MC3T3-E1 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Regents
2.2. Preparation of EYG
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Determination of Proliferative Activity
2.5. ALP Activity Assay
2.6. Determination of COL-I and OCN Content
2.7. Alizarin Red Staining Assay
2.8. RNA-seq
2.9. qRT-PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
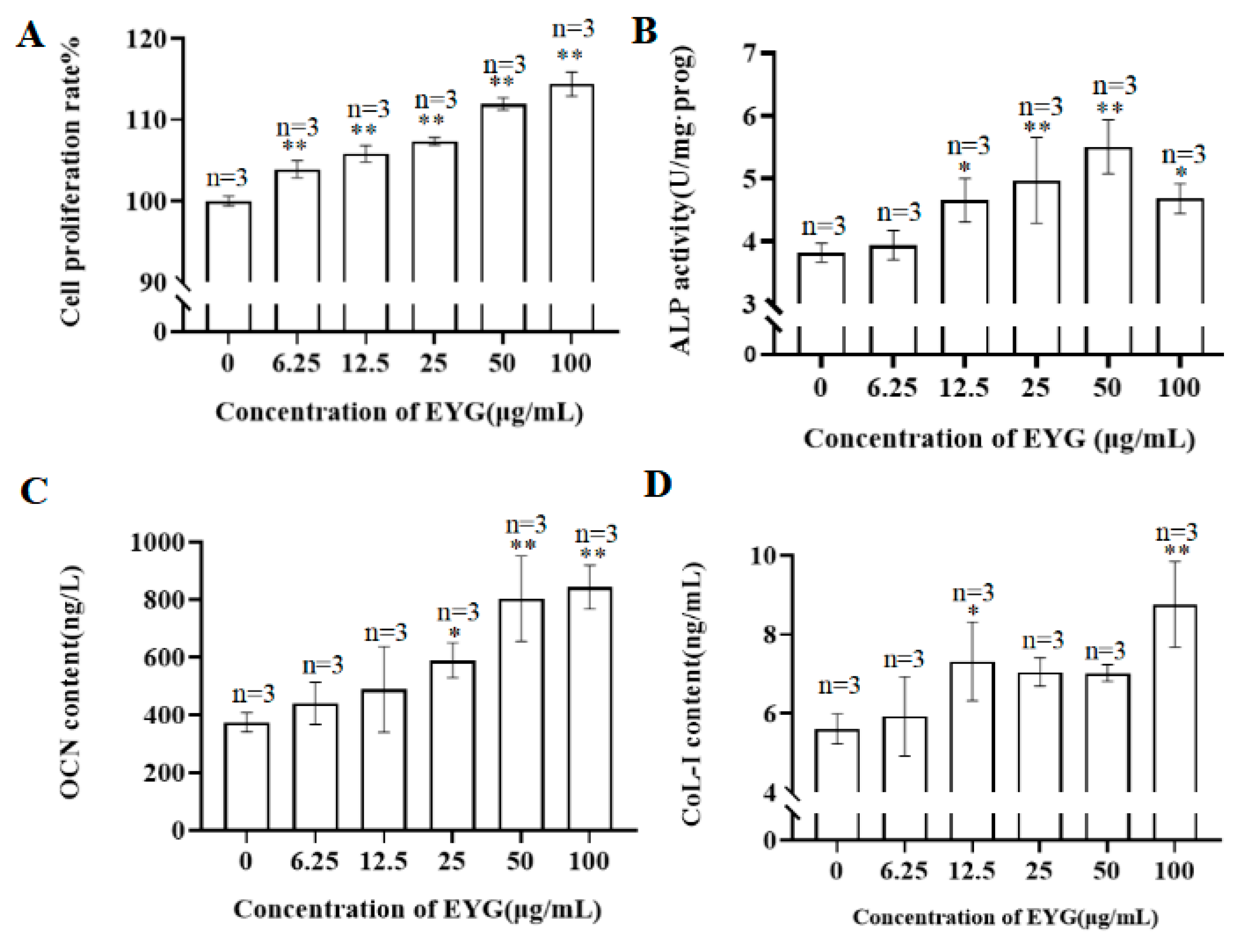
3.1. Effect of EYG on Proliferation of MC3T3-E1 Cells
3.2. Effect of EYG on ALP Activity
3.3. Effect of EYG on COL-I and OCN Content
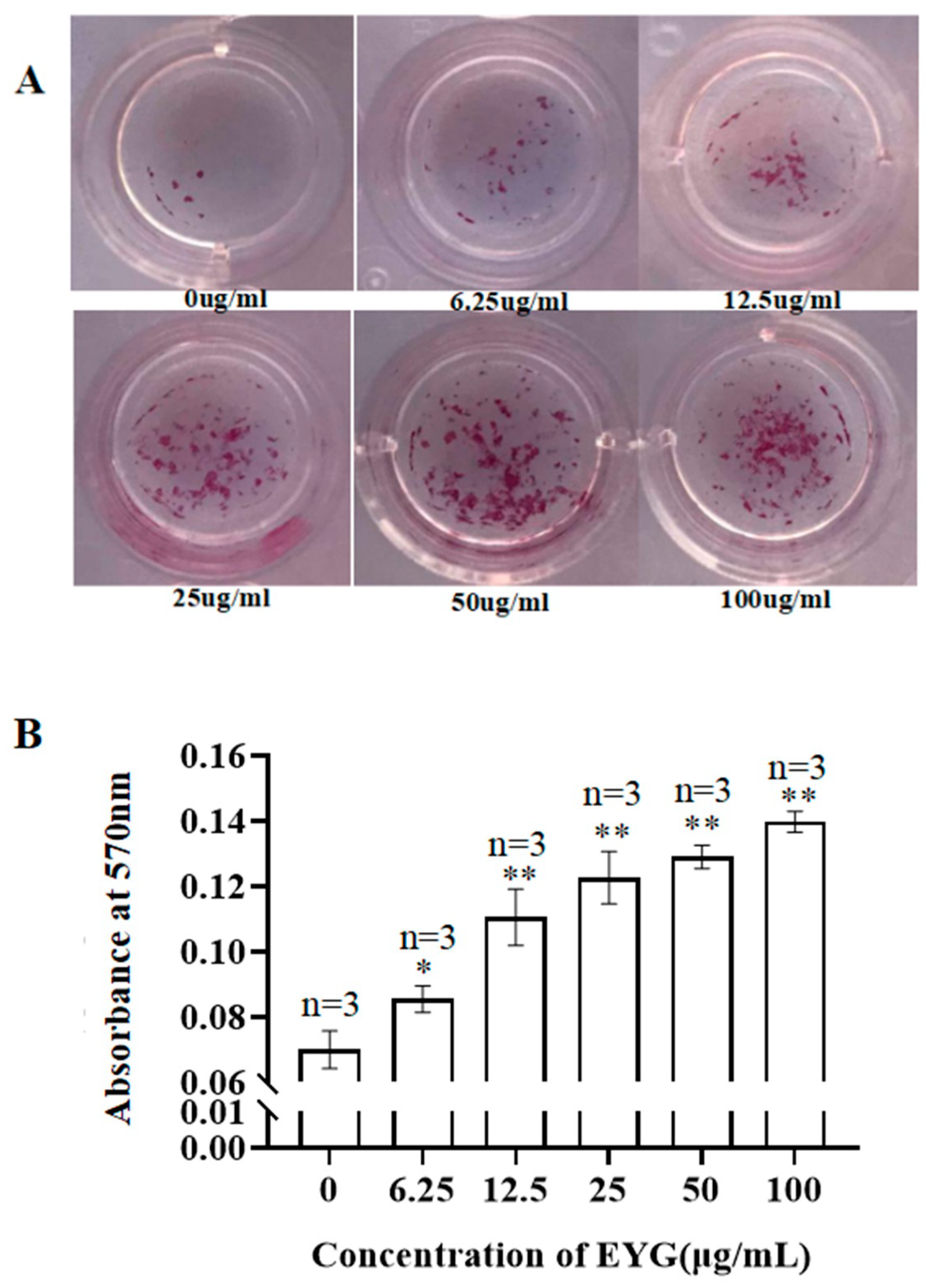
3.4. Effect of EYG on Mineralization of MC3T3-E1 Cells
3.5. Screening of DEGs
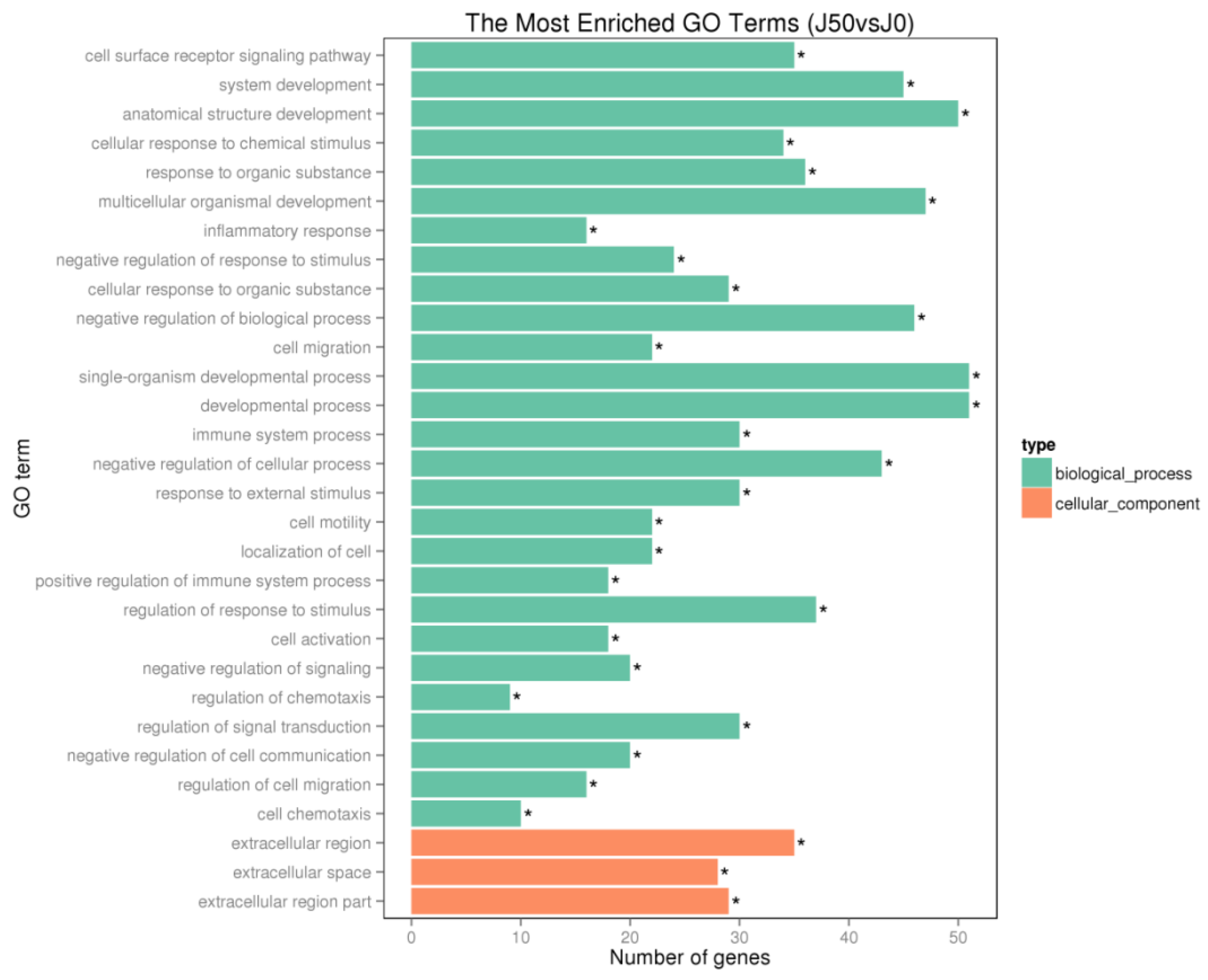
3.6. GO Analysis
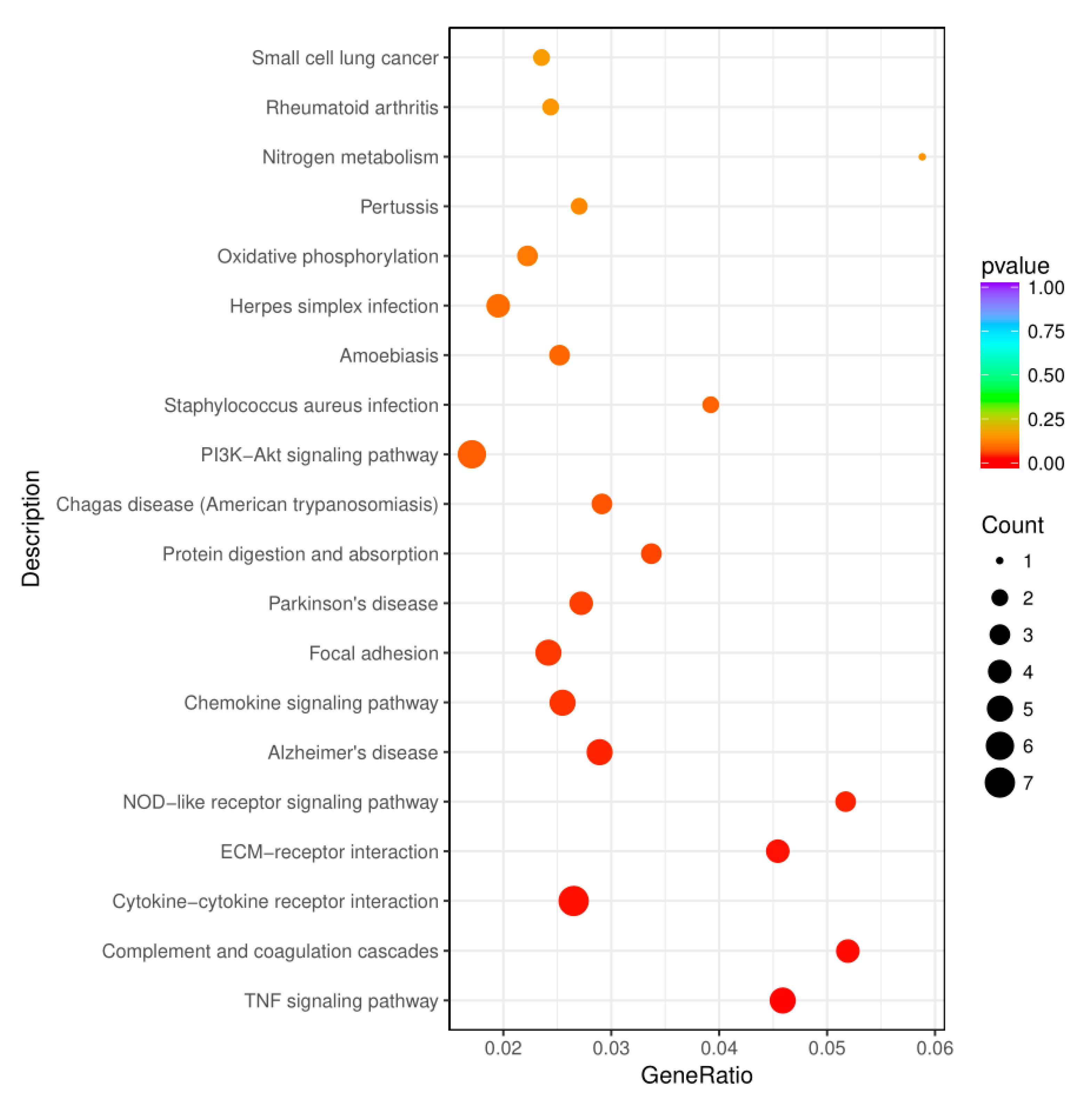
3.7. KEGG Analysis
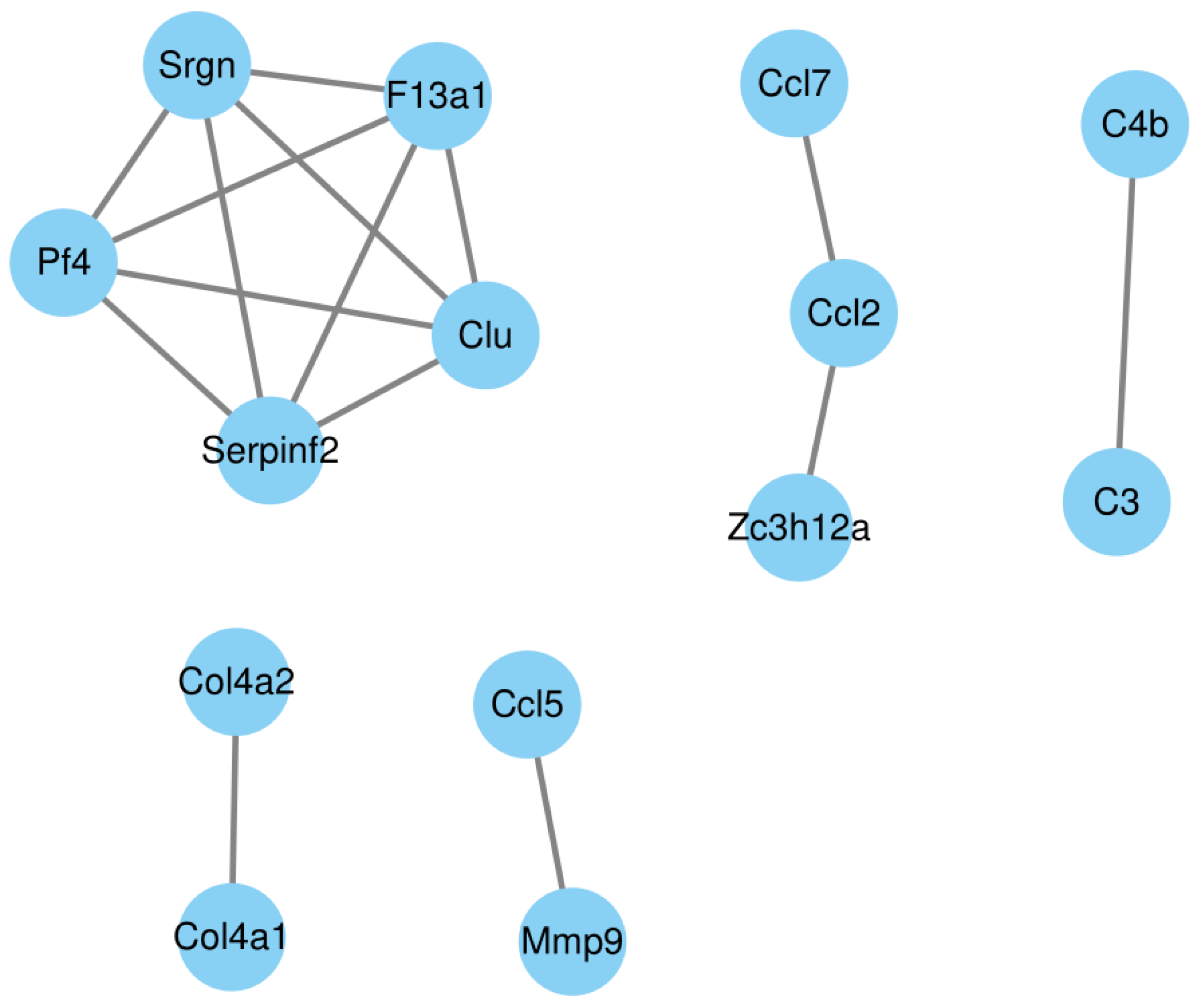
3.8. PPI (Protein–Protein Interaction) Network
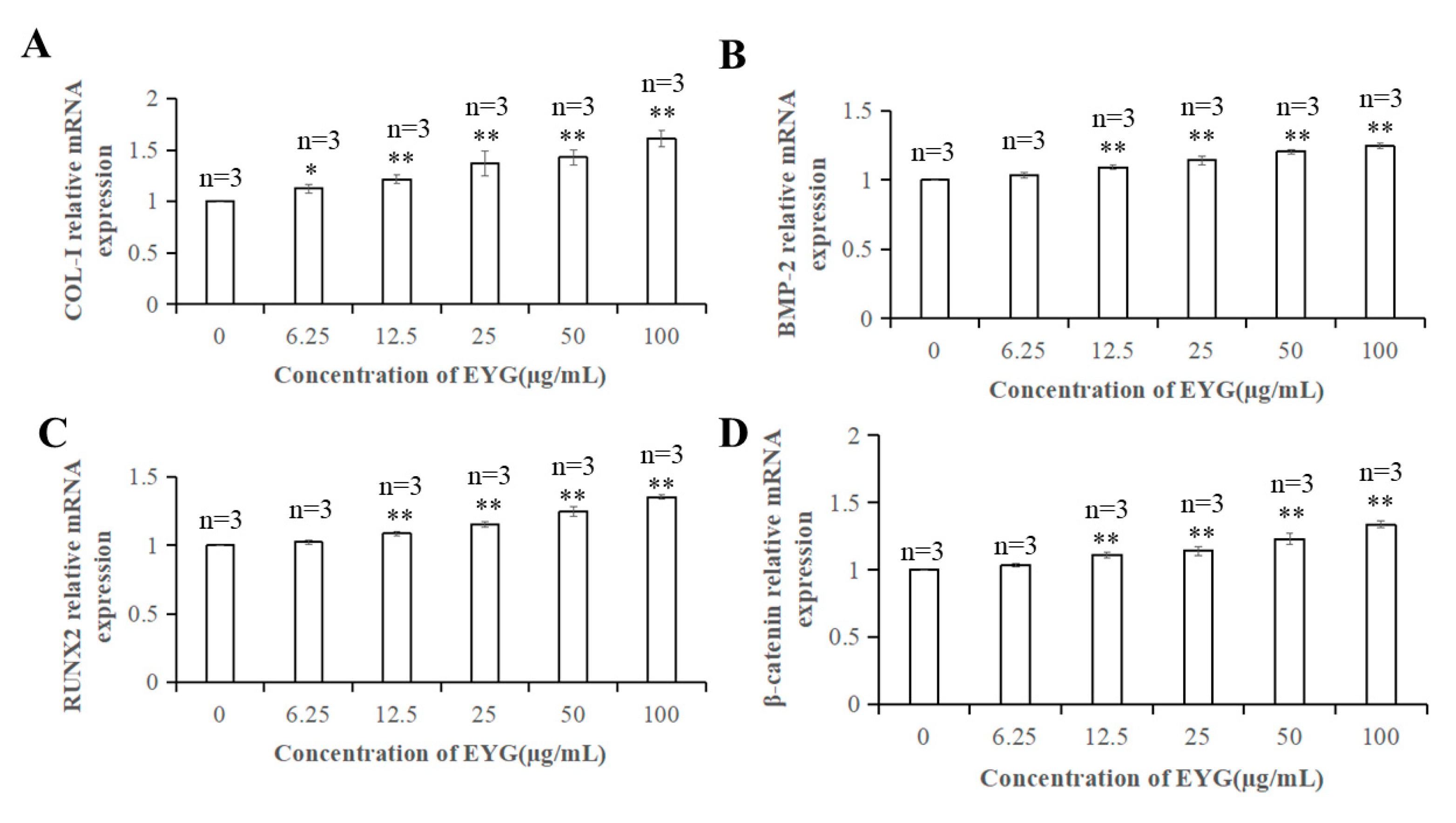
3.9. qRT-PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummings, S.R.; Black, D. Bone mass measurements and risk of fracturein caucasian women: A review of findings from prospective studies. Am. J. Med. 1995, 98, 24S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirries, A.; Schubert, A.K.; Zimmermann, R.; Jabari, S.; Ruchholtz, S.; El-Najjar, N. Thymoquinone accelerates osteoblast differentiation and activates bone morphogenetic protein-2 and ERK pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.B. Effects of 0.4 T rotating magnetic field exposure on density, strength, calcium and metabolism of rat thigh bones. Bioelectromagnetics 2010, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, T.; Takahashi, N. Regulatory mechanisms of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Oral Dis. 2010, 8, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, K.; Takahashi, A.; Watanabe, M.; Nomura, Y. Shark protein improves bone mineral density in ovariectomized rats and inhibits osteoclast differentiation. Nutrition 2014, 30, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.-L.; Park, K.H.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, D.H. Isoflavone-enriched soybean leaves attenuate ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats by anti-inflammatory activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Comparative study of DHA-enriched phosphatidylcholine and EPA-enriched phosphatidylcholine on ameliorating high bone turnover via regulation of the osteogenesis-related Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovariectomized mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10094–10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Meng, K.; Gu, Z.; Yun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, Q.; Pan, F.; Shen, X.; Xia, G.; et al. Arecanut (Areca catechu L.) Seed Polyphenol-Ameliorated Osteoporosis by Altering Gut Microbiome via LYZ and the Immune System in Estrogen-Deficient Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, S.; Xue, C. Sialoglycoproteins prepared from the eggs of Carassius auratus prevent bone loss by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway in ovariectomized rats. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Sialoglycoproteins isolated from the eggs of Carassius auratus prevents osteoporosis by suppressing the activation of osteoclastogenesis related NF-κB and MAPK pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Phosphorylated Peptides from Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Prevent Estrogen Deficiency Induced Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Bone Resorption in Ovariectomized Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9550–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalis, E.; Economides, A.N.; Gazzerro, E. Bone morphogenetic proteins, their antagonists, and the skeleton. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B. Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Proliferation/Differentiation Interrelationships During Progressive Development of the Osteoblast Phenotype. Endocr. Rev. 1993, 14, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.C.; Larrouture, Q.C.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Beer-Stoltz, D.; Liu, L.; Tuan, R.S.; Robinson, L.J.; Schlesinger, P.H.; Nelson, D.J. Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Matrix Formation In Vivo and In Vitro. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2017, 23, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.S.; Poundarik, A.A.; Cabral, J.M.S.; da Silva, C.L.; Vashishth, D. Biomimetic matrices for rapidly forming mineralized bone tissue based on stem cell-mediated osteogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, T. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by transcription factors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 99, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkkonen, K.; Hieta, R.; Kytölä, V.; Nykter, M.; Kiviranta, R. Comparative analysis of osteoblast gene expression profiles and Runx2 genomic occupancy of mouse and human osteoblasts in vitro. Gene 2017, 626, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, B.A.; García, A.J. Exogenous Runx2 Expression Enhances in Vitro Osteoblastic Differentiation and Mineralization in Primary Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, R.; Bodnarova, K.; Arrabal, P.M.; Cifuentes, M.; Becerra, J. Combining bone morphogenetic proteins-2 and -6 has additive effects on osteoblastic differentiationin vitroand accelerates bone formationin vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 104, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijke, P.T. Bone morphogenetic protein signal transduction in bone. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2006, 22, S7–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazono, K.; Maeda, S.; Imamura, T. BMP receptor signaling: Transcriptional targets, regulation of signals, and signaling cross-talk. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Millán, M.; Gónzalez-Martín, M.C.; Ruíz, P.; Almeida, M.; Ros, M.A.; González-Macías, J. La vía Wnt/β-catenina disminuye la cantidad de osteoclastos en el hueso y favorece su apoptosis. Rev. Osteoporos. Metab. Miner. 2019, 11, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, C.; Piemontese, M.; Lumetti, S.; Manfredi, E.; Passeri, G. GSK3b-inhibitor lithium chloride enhances activation of Wnt canonical signaling and osteoblast differentiation on hydrophilic titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.A., 2nd; Bialek, P.; Ahn, J.D.; Starbuck, M.; Patel, M.S.; Clevers, H.; Taketo, M.M.; Long, F.; McMahon, A.P.; Lang, R.A.; et al. Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Tan, B. The PI3K/AKT pathway promotes fracture healing through its crosstalk with Wnt/β-catenin. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, S.; Leem, K.H. Protective effect of egg yolk peptide on bone metabolism. Menopause N. Y. 2011, 18, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Wang, S.; He, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Anti-osteoporotic activity of sialoglycoproteins isolated from the eggs of Carassius auratus by promoting osteogenesis and increasing OPG/RANKL ratio. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 15, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Dai, Y.; Wang, F.; Mai, X.; Wang, J. Metabonomic analysis in investigating the anti-osteoporotic effect of sialoglycoprotein isolated from eggs of carassius auratus on ovariectomized mice. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seko, A.; Koketsu, M.; Nishizono, M.; Enoki, Y.; Ibrahim, H.R.; Juneja, L.R.; Kim, M.; Yamamoto, T. Occurrence of a sialylglycopeptide and free sialylglycans in hen’s egg yolk. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1997, 1335, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Gu, G.; Xue, M.; Wang, P.G.; Chen, M. An Efficient Approach for Large-Scale Production of Sialyglycopeptides from Egg Yolks. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 31, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Koie, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ino, A.; Watabe, K.; Kim, M.; Kanayama, K.; Otsuji, K. Effects of food enriched with egg yolk hydrolysate (bone peptide) on bone metabolism in orchidectomized dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, K.H.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.K. Effects of Egg Yolk Proteins on the Longitudinal Bone Growth of Adolescent Male Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 2388–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Leem, K.-H.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.K. Egg yolk soluble protein stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Bao, W.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Dong, J.; Huang, W. A simplified procedure for gram-scale production of sialylglycopeptide (SGP) from egg yolks and subsequent semi-synthesis of Man3GlcNAc oxazoline. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 396, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Prudden, A.R.; Bosman, G.P.; Boons, G.J. Improved isolation and characterization procedure of sialylglycopeptide from egg yolk powder. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 452, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Duan, Z.; Chen, M.; Meng, K.; Chen, S.; Shen, X.; Xia, G.; Zhao, M. Collagen Peptides Isolated from Salmo salar and Tilapia nilotica Skin Accelerate Wound Healing by Altering Cutaneous Microbiome Colonization via Upregulated NOD2 and BD14. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1621–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y. Thermal processed Crassostrea gigas impact the mouse gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Olson, D.; Cheng, B.; Guo, X.; Wang, K. Sanguis Draconis resin stimulates osteoblast alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization in MC3T3-E1 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Chen, W.; Qi, D.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, P. Echinacoside promotes bone regeneration by increasing OPG/RANKL ratio in MC3T3-E1 cells. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Ju, W.C.; Yeo, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Seo, H.S.; Uchida, Y.; Cho, Y. Increased OPG/RANKL ratio in the conditioned medium of soybean-treated osteoblasts suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, T.; Tan, L.; Cheng, J. Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile in callus tissues of osteoporotic phenotype mice induced by osteoblast-specific Krm2 overexpression. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 19, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Duan, R.; Wu, B.; Huang, W.; Zhang, X.; Qu, M.; Liu, T.; Yu, X. Gene expression profiles and bioinformatics analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 promotion of osteogenic differentiation. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e00921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.-Z.; Li, N.; Guo, Y.-C.; Chen, T.-P. Pentraxin 3 promotes the osteoblastic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber-Lang, M.; Ignatius, A.; Brenner, R.E. Role of Complement on Broken Surfaces After Trauma. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 865, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.P.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, L.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yang, Y.J.; Yu, B. Quantitative proteomics reveals ELP2 as a regulator to the inhibitory effect of TNF-alpha on osteoblast differentiation. J. Proteom. 2015, 114, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.-C. ATF3 mediates the inhibitory action of TNF-α on osteoblast differentiation through the JNK signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.; Sul, O.; Chung, S.; Suh, J.; Choi, H.S. Lack of NOD2 attenuates ovariectomy-induced bone loss via inhibition of osteoclasts. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 235, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, W.; Luo, R.; Song, Y.; Tu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C. BCL3 regulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by interacting with TRAF6 in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Bone 2018, 114, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Sharp, T.; Khorsand, B.; Fischer, C.; Amendt, B.A. MicroRNA-200c Represses IL-6, IL-8, and CCL-5 Expression and Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160915. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.K.; Chang, H.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, C.C.; Galson, D.L.; Hong, C.Y.; Kok, S.H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate diminishes CCL2 expression in human osteoblastic cells via up-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt/Raf-1 interaction: A potential therapeutic benefit for arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 58, 3145–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, S.; Bhonde, R.; Gupta, P.K.; Totey, S. Extracellular matrix protein mediated regulation of the osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Differentiation 2012, 84, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R.D.; Padalhin, A.R.; Kim, B.; Park, M.K.; Lee, B.T. Evaluation of bone regeneration potential of injectable extracellular matrix (ECM) from porcine dermis loaded with biphasic calcium phosphate (BCP) powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshiba, T.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. The balance of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells by matrices that mimic stepwise tissue development. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klees, R.F.; Salasznyk, R.M.; Vandenberg, S.; Bennett, K.; Plopper, G.E. Laminin-5 activates extracellular matrix production and osteogenic gene focusing in human mesenchymal stem cells. Matrix Biol. 2007, 26, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, A.B. Focal Adhesion Kinase Plays a Role in Osteoblast Mechanotransduction In Vitro but Does Not Affect Load- Induced Bone Formation In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licini, C.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Mattioli-Belmonte, M. Collagen and non-collagenous proteins molecular crosstalk in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 49, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.S.; Cabral, J.M.S.; da Silva, C.L.; Vashishth, D. Bone Matrix Non-Collagenous Proteins in Tissue Engineering: Creating New Bone by Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix. Polymer 2021, 13, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, F.-H.; Hales, B.F. The Effects of Class-Specific Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors on the Development of Limbs During Organogenesis. Toxicol. Ences Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2015, 148, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jeanne, M.; Gould, D.B. Genotype-phenotype correlations in pathology caused by collagen type IV alpha 1 and 2 mutations. Matrix Biol. 2016, 57, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, B. Gene expression profile of the bone microenvironment in human fragility fracture bone. Bone 2009, 44, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, H. Morphological and proteomic analysis of early stage of osteoblast differentiation in osteoblastic progenitor cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 2291–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, A.; Jin, Z. COL4A2 in the tissue-specific extracellular matrix plays important role on osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4265–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| COL-I | F- GACAGGCGAACAAGGTGACAGAG |
| R- CAGGAGAACCAGGAGAACCAGGAG | |
| BMP2 | F- AAGCGTCAAGCCAAACACAAACAG |
| R- GAGGTGCCACGATCCAGTCATTC | |
| RUNX2 | F- CGGCAAGATGAGCGACGTGAG |
| R- TGCTGCTGCTGCTGCTGTTG | |
| β-CATENIN | F- TGCCGTTCGCCTTCATTATGGAC |
| β-ACTIN | R- TGGGCAAAGGGCAAGGTTTCG F- GTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA R- GTAACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC |
| Pathway | ID | Gene Name | Corrected p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UP | ||||||
| ECM–receptor interaction | mmu04512 | COL2A1 | 0.016550785 | |||
| COL4A2 | ||||||
| COL4A1 | ||||||
| Protein digestion and absorption | mmu04974 | COL2A1 | 0.016550785 | |||
| COL4A2 | ||||||
| COL4A1 | ||||||
| Focal adhesion | mmu04510 | COL2A1 | 0.016550785 | |||
| COL4A2 | ||||||
| COL4A1 | ||||||
| PDGFB | ||||||
| Amoebiasis | mmu05146 | COL2A1 | 0.024727215 | |||
| COL4A2 | ||||||
| COL4A1 | ||||||
| DOWN | ||||||
| TNF signaling pathway | mmu04668 | CCL5 | 0.028943572 | |||
| CCL2 | ||||||
| NOD2 | ||||||
| MMP9 | ||||||
| BCL3 | ||||||
| Complement and coagulation cascades | mmu04610 | F13a1 | 0.036868851 | |||
| C4b | ||||||
| Serpinf2 | ||||||
| C3 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, S.; Meng, K.; Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Xiang, Q.; Quan, Z.; Xia, G.; Shen, X. Transcriptome Analysis of Egg Yolk Sialoglycoprotein on Osteogenic Activity in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146428
He S, Meng K, Chen M, Zhu L, Xiang Q, Quan Z, Xia G, Shen X. Transcriptome Analysis of Egg Yolk Sialoglycoprotein on Osteogenic Activity in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(14):6428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146428
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Sizhe, Keke Meng, Muxue Chen, Lehui Zhu, Qingying Xiang, Zhangyan Quan, Guanghua Xia, and Xuanri Shen. 2021. "Transcriptome Analysis of Egg Yolk Sialoglycoprotein on Osteogenic Activity in MC3T3-E1 Cells" Applied Sciences 11, no. 14: 6428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146428
APA StyleHe, S., Meng, K., Chen, M., Zhu, L., Xiang, Q., Quan, Z., Xia, G., & Shen, X. (2021). Transcriptome Analysis of Egg Yolk Sialoglycoprotein on Osteogenic Activity in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Applied Sciences, 11(14), 6428. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146428






