A Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for the Removal of Carbamazepine
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Conductivity and pH Measurement
2.3. Quantification of CBZ
2.4. 2D Electrochemical Process
2.5. CBZ Adsorption Experiments
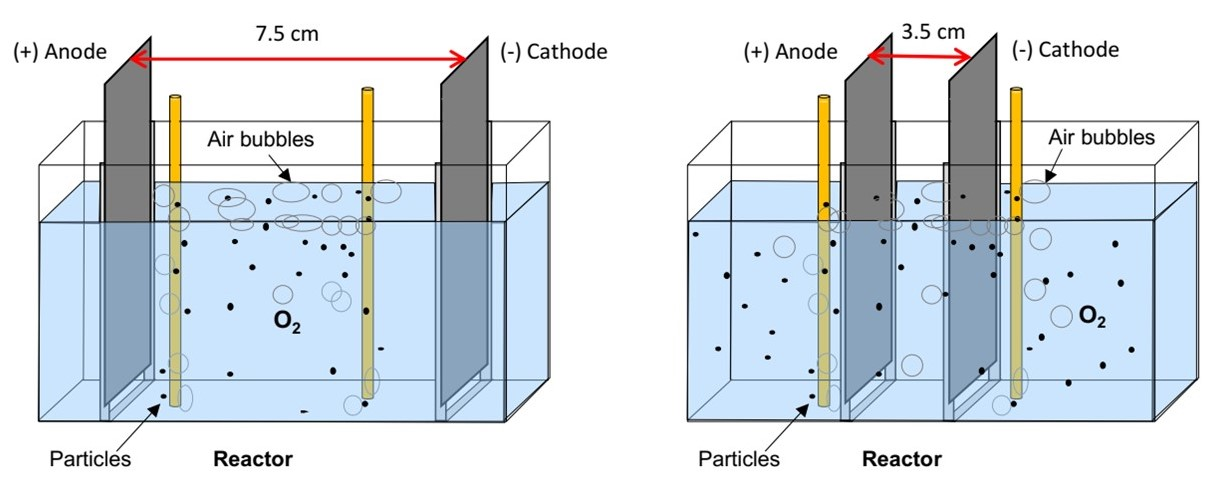
2.6. 3D Electrochemical Process
2.7. Data Analysis
2.7.1. Modeling of Kinetic and Equilibrium Adsorption Studies
2.7.2. Electrochemical Treatment Processes
Statistical Analysis
Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. 2D Electrochemical Process Operational Conditions
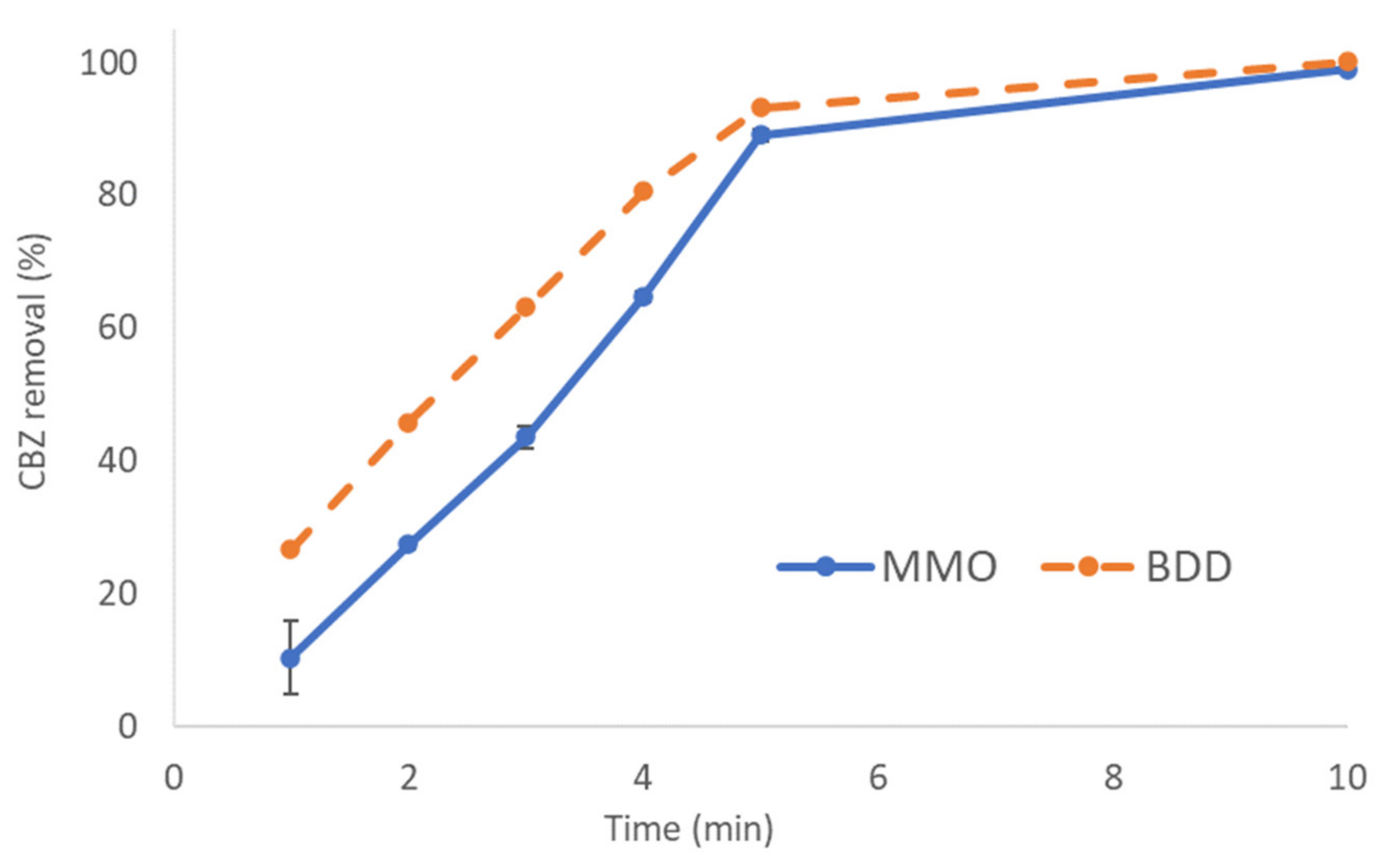
3.1.1. Effect of Anode Material on CBZ Removal
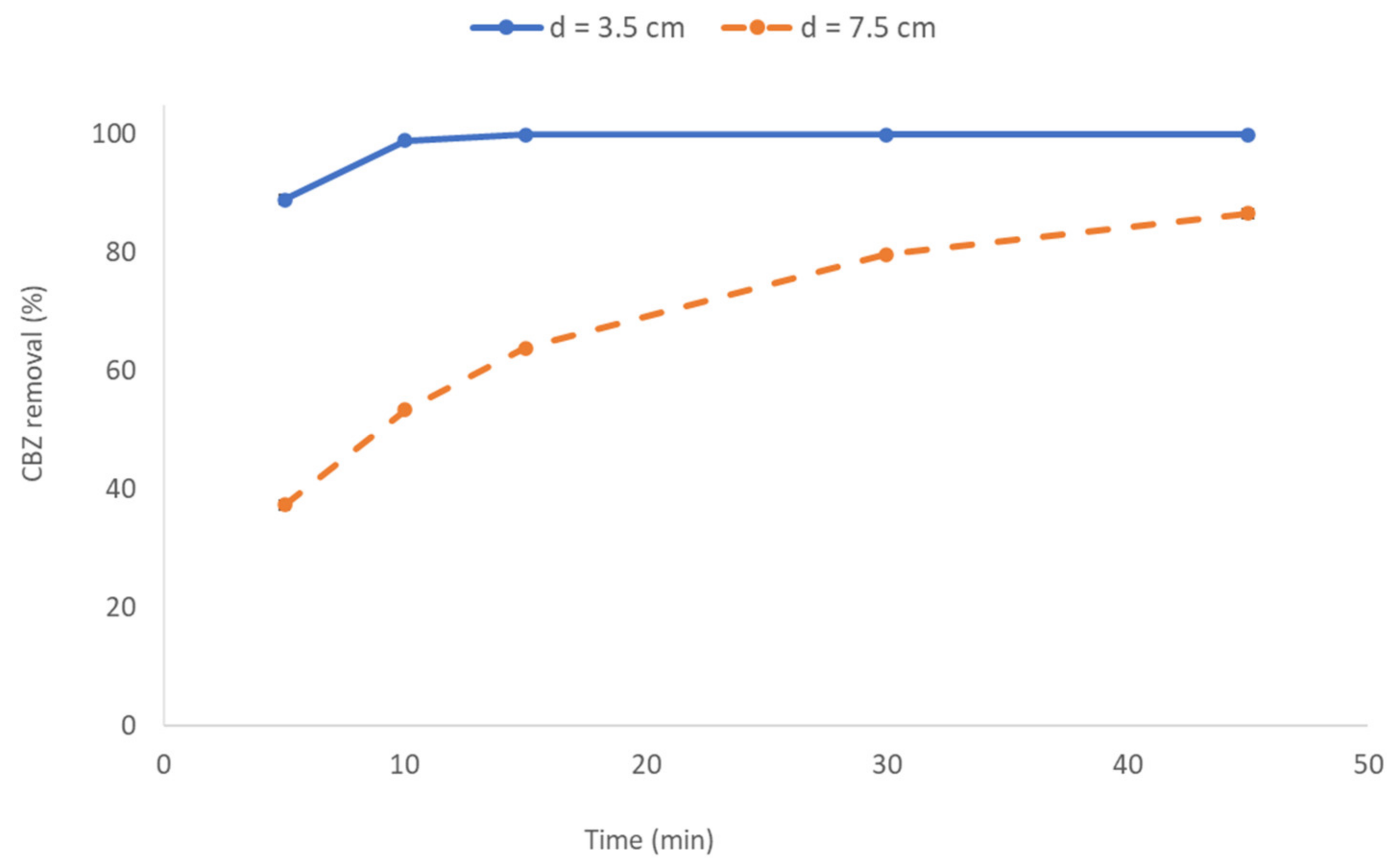
3.1.2. Effect of Interelectrode Distance, Reaction Time, and Current Density on CBZ Removal
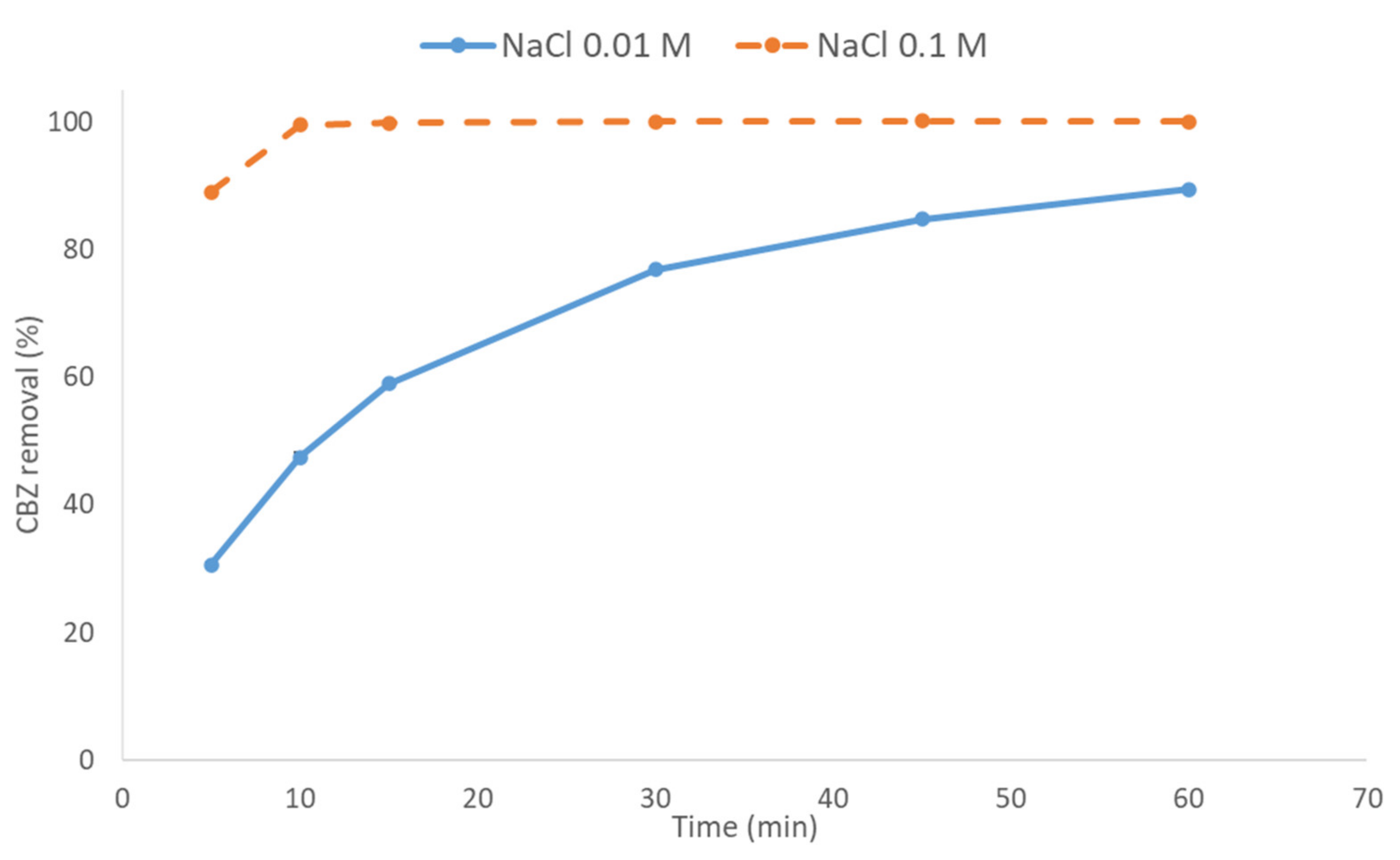
3.1.3. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration on CBZ Removal
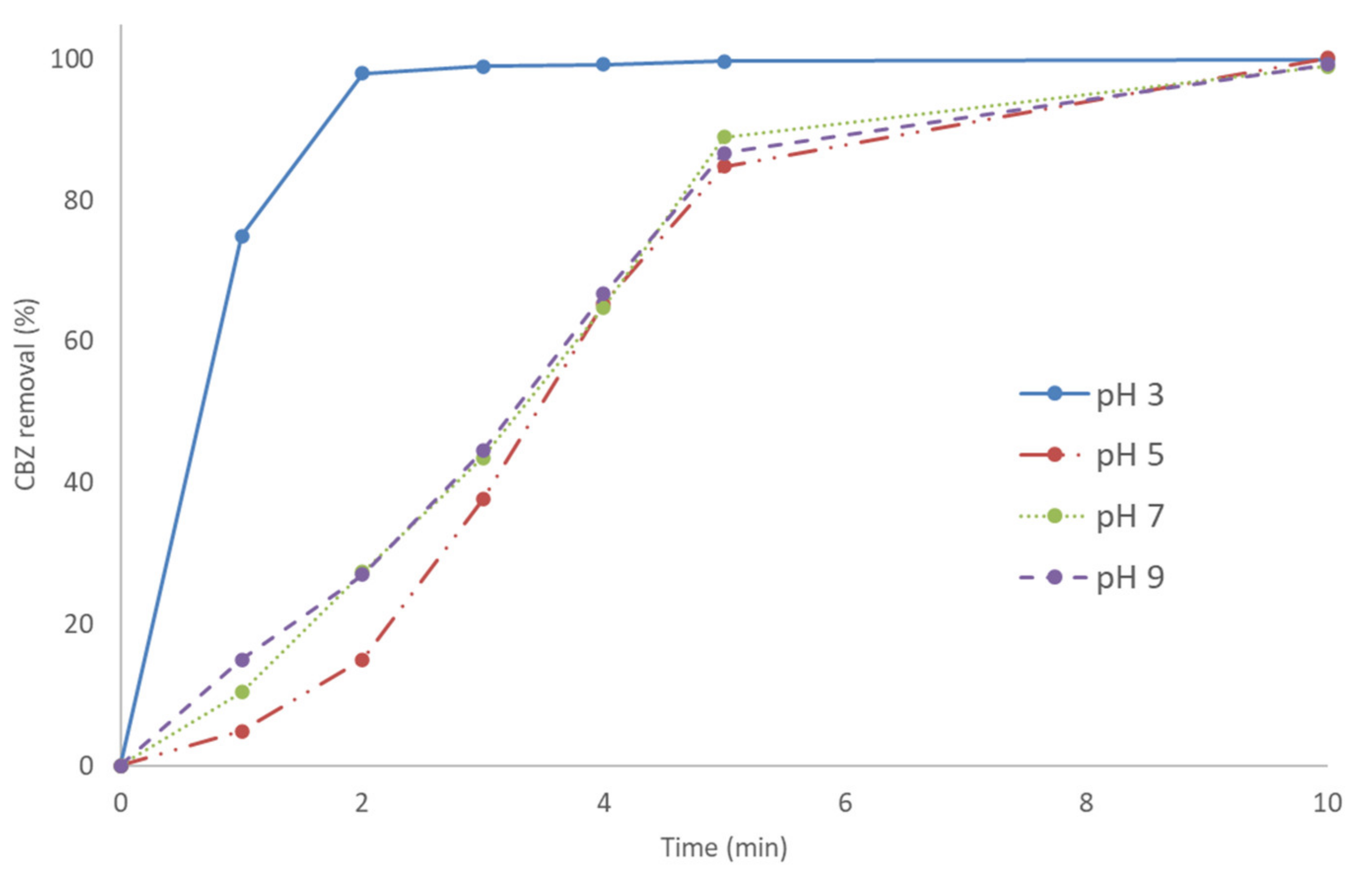
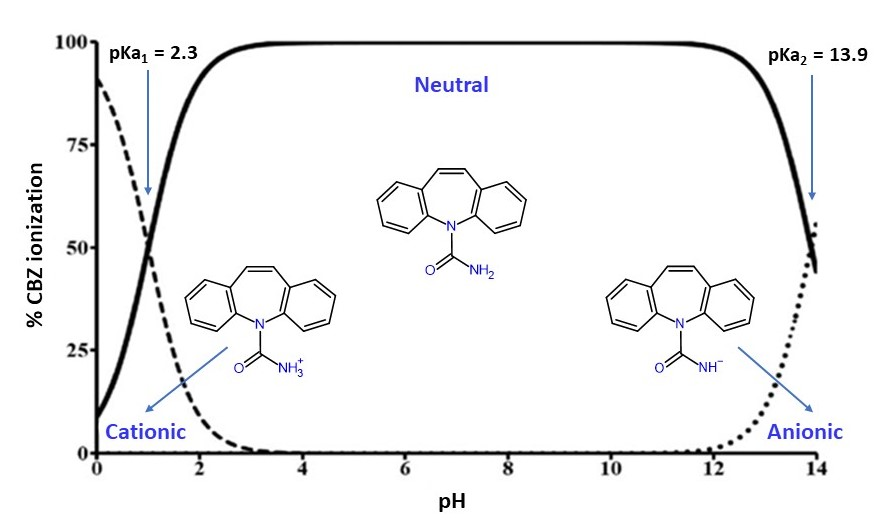
3.1.4. Effect of pH on CBZ Removal
3.1.5. Effect of Initial CBZ Concentration on CBZ Removal
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Characterization of the Adsorbents
3.2.2. Kinetic Studies and Isotherms
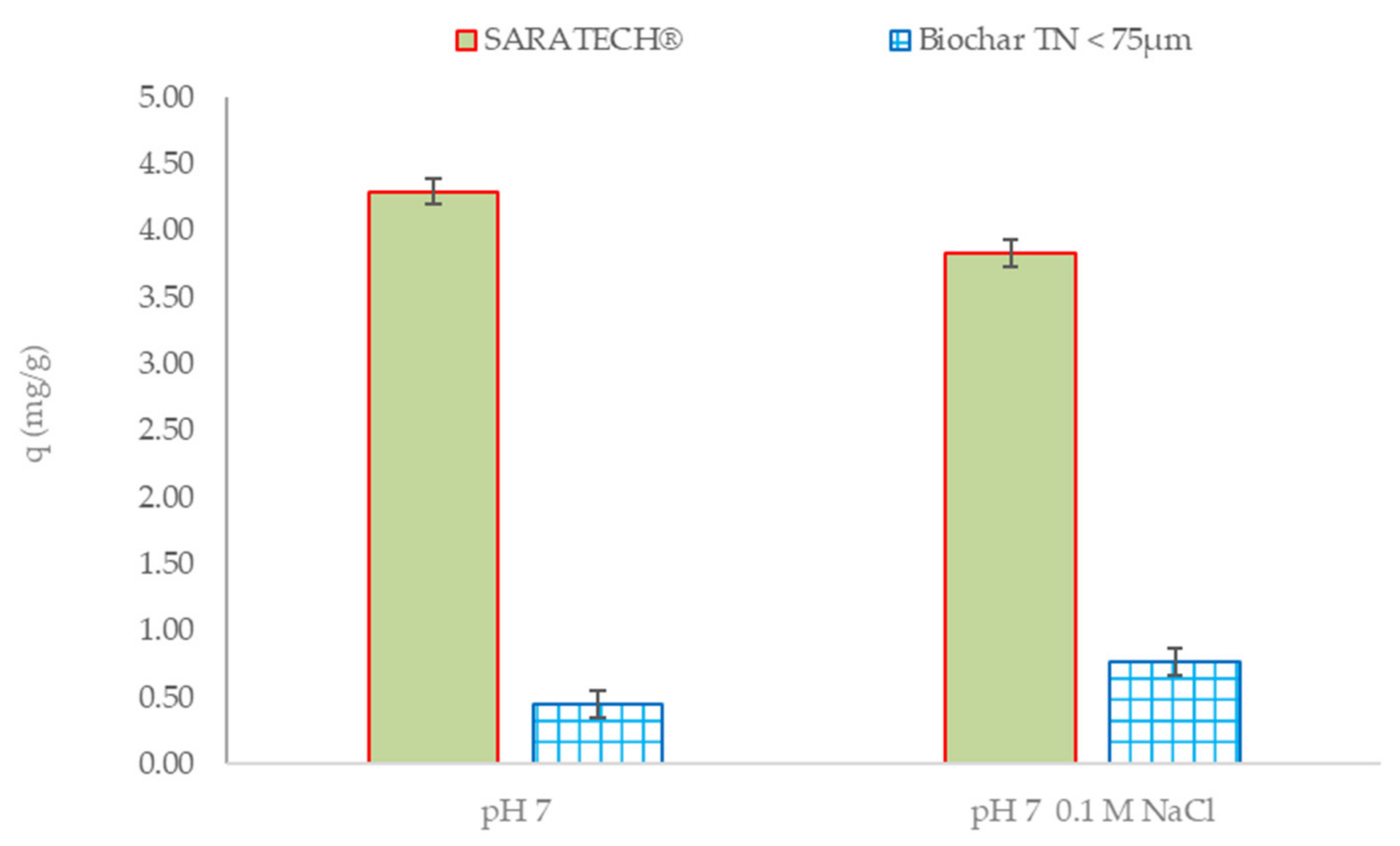
3.2.3. Effects of Different Parameters on CBZ Adsorption
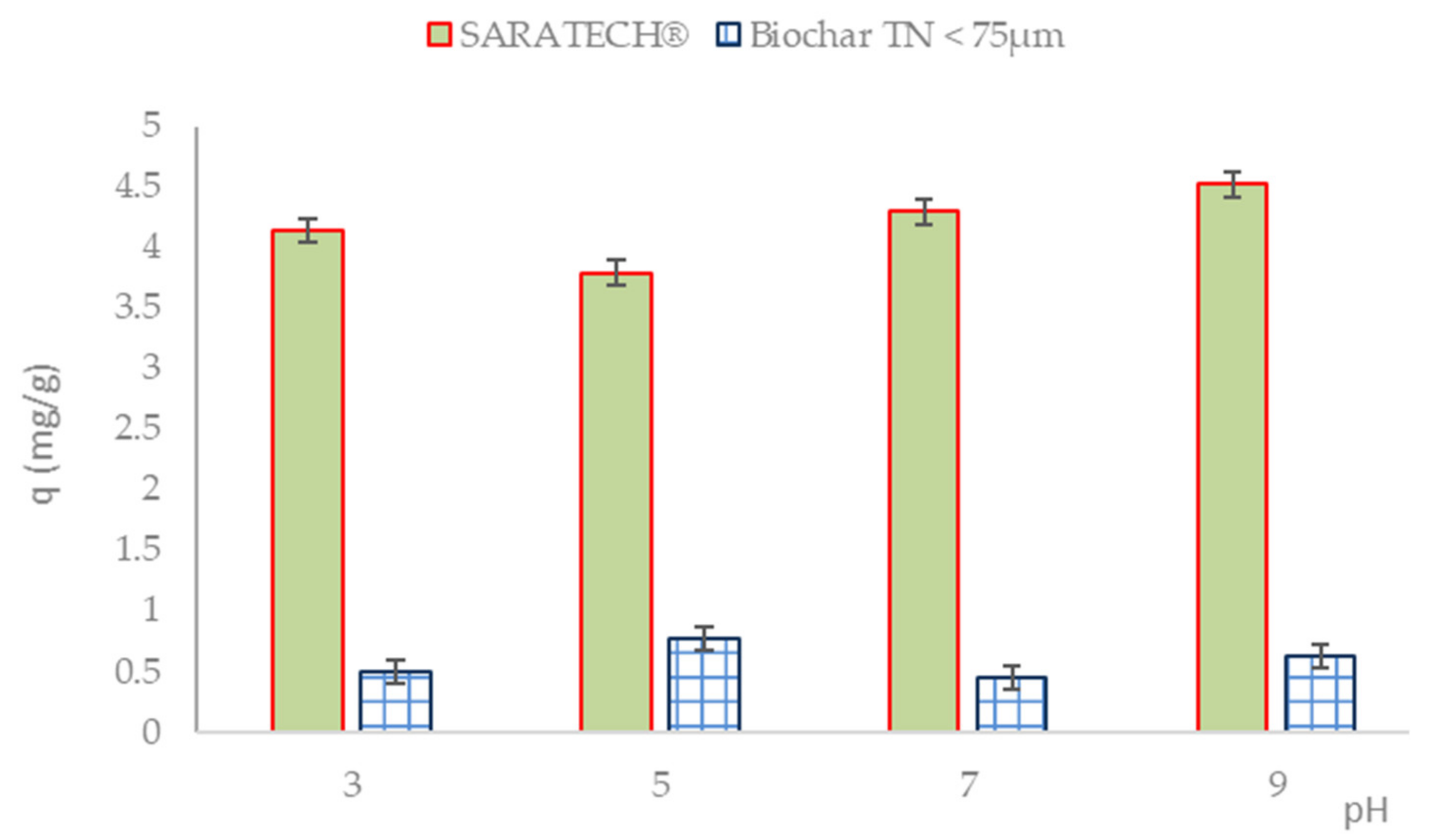
Influence of pH
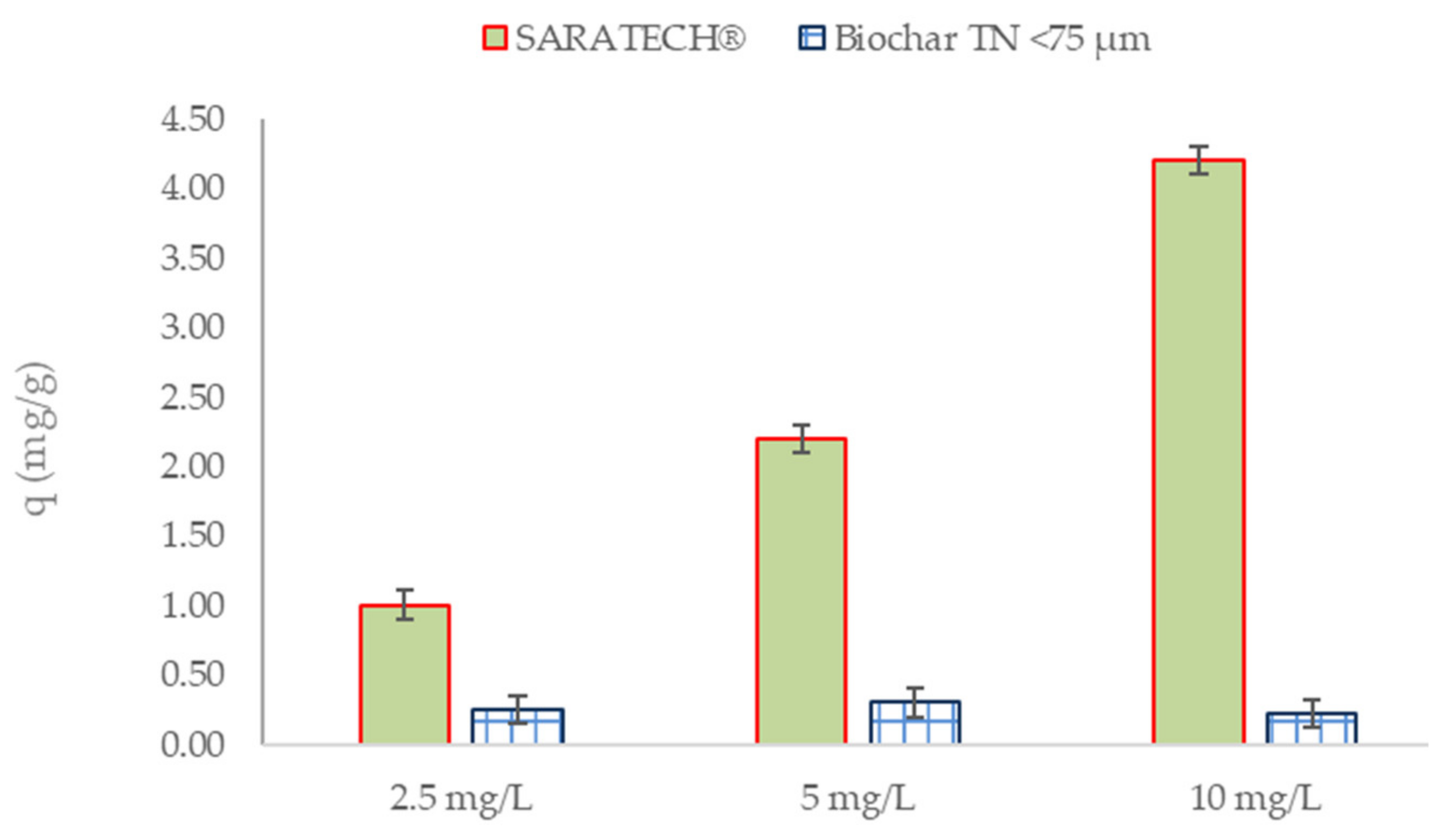
Influence of Initial CBZ Concentration
Influence of Electrolyte
3.3. 3D Experiments
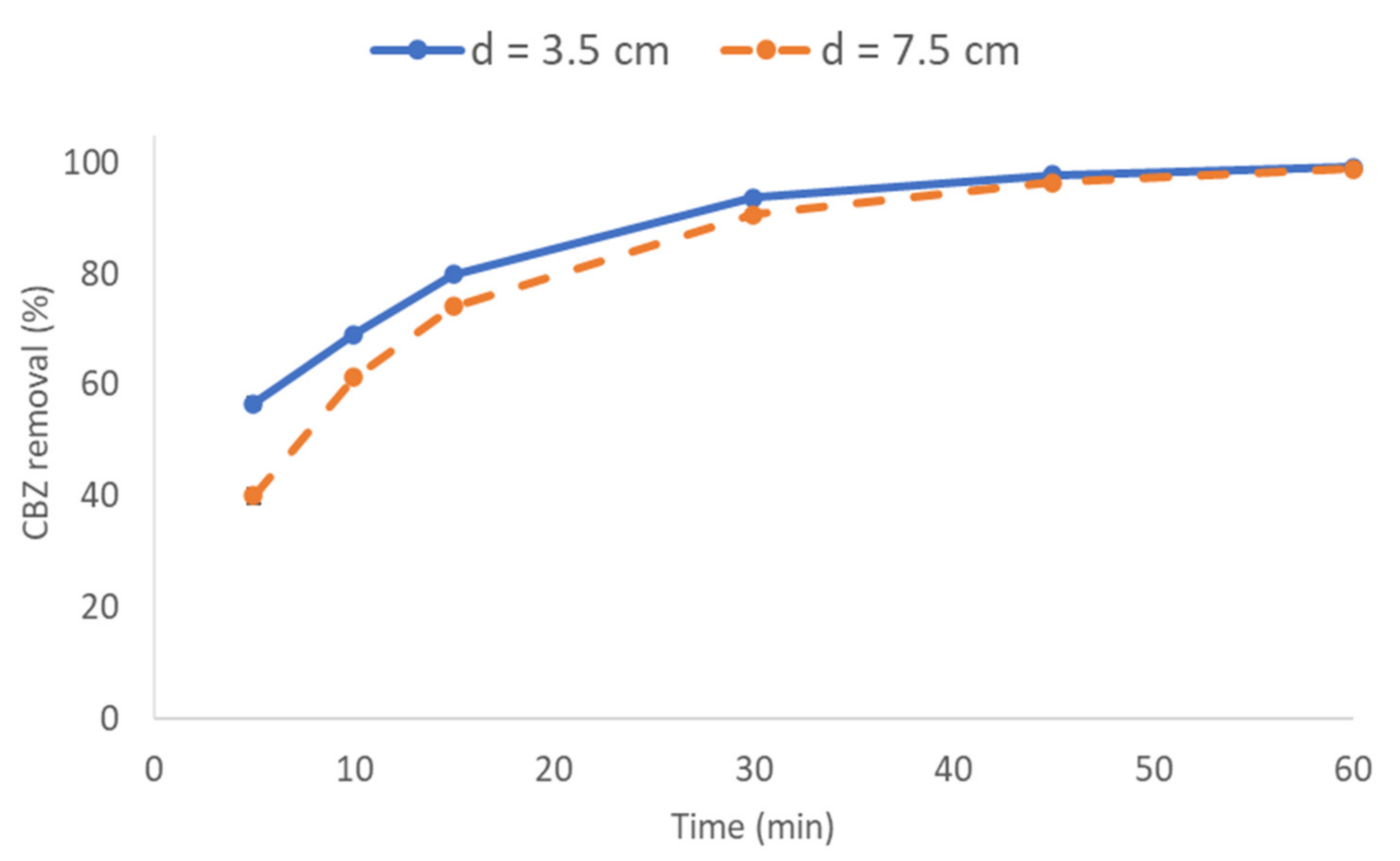
3.3.1. Effect of Interelectrode Distance on CBZ Removal
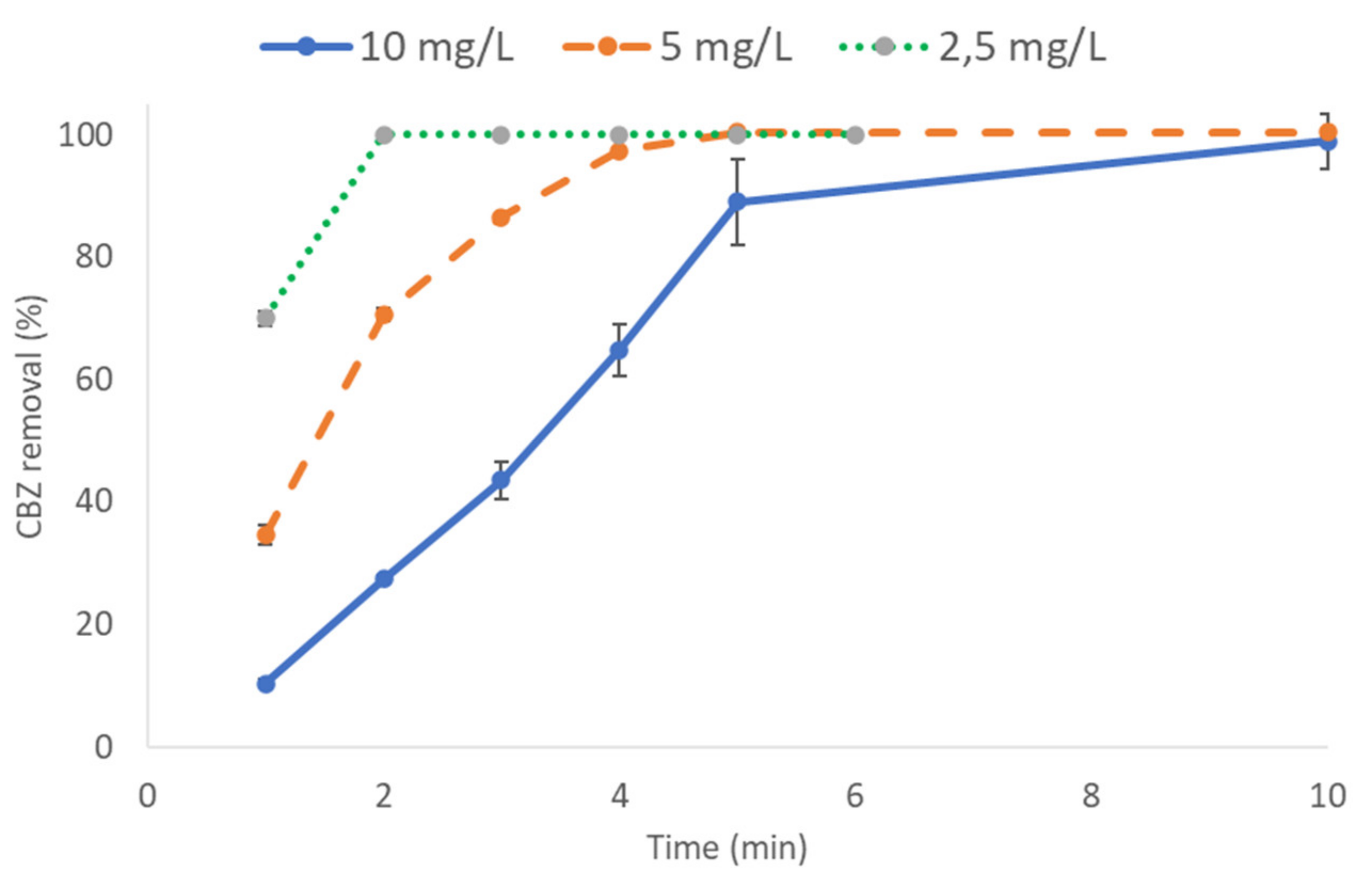
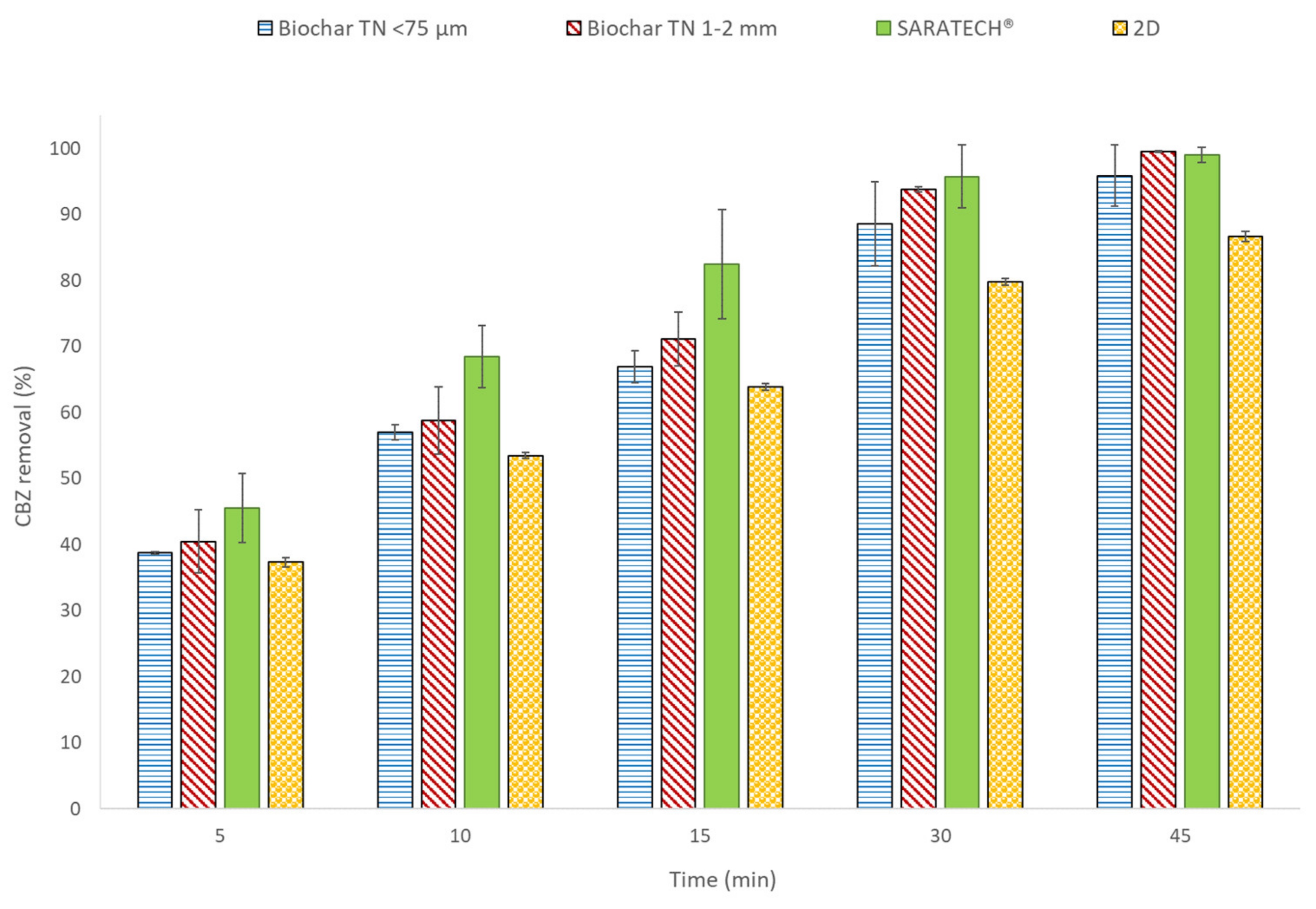
3.3.2. Effect of the Particulate Electrode on CBZ Removal
3.3.3. Effect of the Reaction Time on CBZ Removal
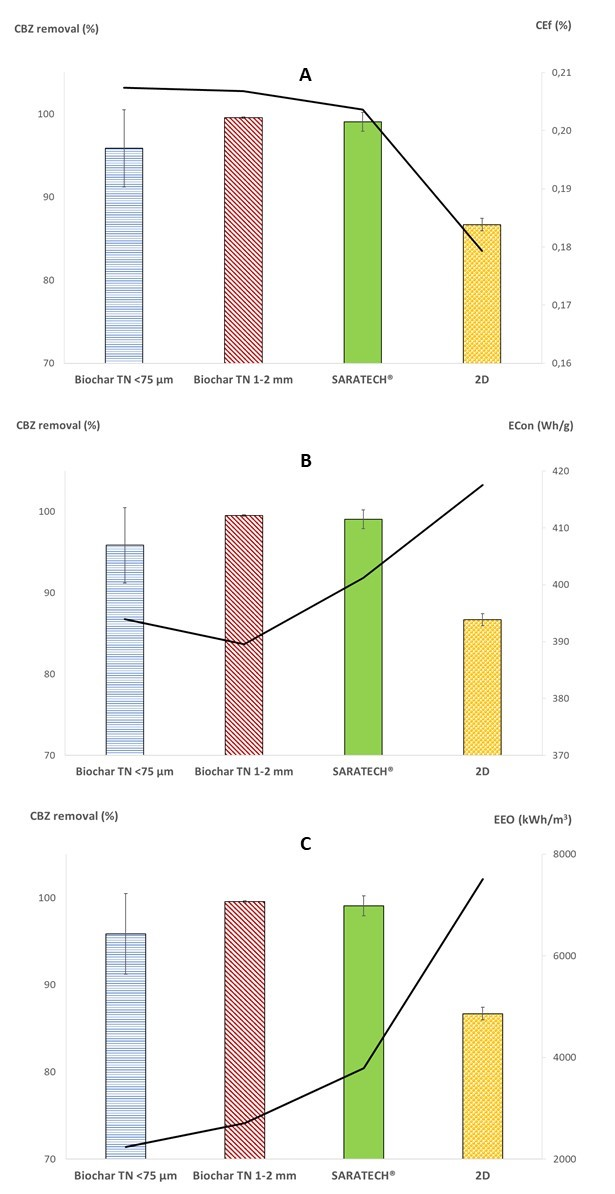
3.3.4. Effect on Energy Consumption, Current, and Electric Efficiencies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paíga, P.; Santos, L.; Delerue-Matos, C. Development of a multi-residue method for the determination of human and veterinary pharmaceuticals and some of their metabolites in aqueous environmental matrices by SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 135, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klatte, S.; Schaefer, H.-C.; Hempel, M. Pharmaceuticals in the environment—A short review on options to minimize the exposure of humans, animals and ecosystems. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2017, 5, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2010, 35, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caban, M.; Stepnowski, P. How to decrease pharmaceuticals in the environment? A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, A.; Adler, N. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Scientific evidence of risks and its regulation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Courtier, A.; Cadiere, A.; Roig, B. Human pharmaceuticals: Why and how to reduce their presence in the environment. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 15, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xi, H.; Xu, L.; Jin, M.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H. Ecotoxicological effects, environmental fate and risks of pharmaceutical and personal care products in the water environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.C. Occurrence, sources, and fate of pharmaceuticals in aquatic environment and soil. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 187, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, B.R.; Venkatesan, P.; Kanimozhi, R.; Basha, C.A. Removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewater by electrochemical oxidation using cylindrical flow reactor and optimization of treatment conditions. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2009, 44, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Cao, X.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, G. Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2015, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurado, A.; Vàzquez-Suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; López de Alda, M.; Pujades, E.; Barceló, D. Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater in Spain: A review of sources, recent occurrence and fate in a European context. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 440, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCance, W.; Jones, O.A.H.; Edwards, M.; Surapaneni, A.; Chadalavada, S.; Currell, M. Contaminants of Emerging Concern as novel groundwater tracers for delineating wastewater impacts in urban and peri-urban areas. Water Res. 2018, 146, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Mordechay, E.; Tarchitzky, J.; Chen, Y.; Shenker, M.; Chefetz, B. Composted biosolids and treated wastewater as sources of pharmaceuticals and personal care products for plant uptake: A case study with carbamazepine. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Y. Ecotoxicological Effect of Single and Combined Exposure of Carbamazepine and Cadmium on Female Danio rerio: A Multibiomarker Study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wick, A.; Fink, G.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H.; Ternes, T.A. Fate of beta blockers and psycho-active drugs in conventional wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahlmann, A.; Brack, W.; Schneider, R.J.; Krauss, M. Carbamazepine and its metabolites in wastewater: Analytical pitfalls and occurrence in Germany and Portugal. Water Res. 2014, 57, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Geißen, S.-U.; Gal, C. Carbamazepine and diclofenac: Removal in wastewater treatment plants and occurrence in water bodies. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yang, S.; Asif, M.B.; Sencadas, V.; Shawkat, S.; Sanderson-Smith, M.; Gorman, J.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Yamamoto, K. Carbamazepine as a Possible Anthropogenic Marker in Water: Occurrences, Toxicological Effects, Regulations and Removal by Wastewater Treatment Technologies. Water 2018, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shenker, M.; Harush, D.; Ben-Ari, J.; Chefetz, B. Uptake of carbamazepine by cucumber plants—A case study related to irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasca-Pérez, E.; Galar-Martínez, M.; García-Medina, S.; Pérez-Coyotl, I.A.; Ruiz-Lara, K.; Cano-Viveros, S.; Pérez-Pastén Borja, R.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M. Short-term exposure to carbamazepine causes oxidative stress on common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 66, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, R.; Marques, R.; Noronha, J.P.; Carvalho, G.; Oehmen, A.; Reis, M.A.M. Assessing the removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a full-scale activated sludge plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1818–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjenovic, J.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Analysis of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and removal using a membrane bioreactor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1365–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellona, C.; Drewes, J.E.; Oelker, G.; Luna, J.; Filteau, G.; Amy, G. Comparing nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for drinking water augmentation. J. AWWA 2008, 100, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerton, A.M.; Andrews, R.C.; Bagley, D.M. The influence of natural organic matter and cations on the rejection of endocrine disrupting and pharmaceutically active compounds by nanofiltration. Water Res. 2009, 43, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wert, E.C.; Rosario-Ortiz, F.L.; Snyder, S.A. Effect of ozone exposure on the oxidation of trace organic contaminants in wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, S.K.; Kang, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; van de Merwe, J.P.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Price, W.E. Photolysis and UV/H2O2 of diclofenac, sulfamethoxazole, carbamazepine, and trimethoprim: Identification of their major degradation products by ESI–LC–MS and assessment of the toxicity of reaction mixtures. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 112, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirazi, E.; Torabian, A.; Nabi-Bidhendi, G. Carbamazepine Removal from Groundwater: Effectiveness of the TiO2/UV, Nanoparticulate Zero-Valent Iron, and Fenton (NZVI/H2O2) Processes. Clean 2013, 41, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, A.; Palacios, S.; Vicente, R.; Vercher, R.F.; Malato, S.; Arques, A.; Amat, A.M. Solar photo-Fenton at mild conditions to treat a mixture of six emerging pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Fu, J.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Matis, K.A. New approaches on the removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewaters with adsorbent materials. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kårelid, V.; Larsson, G.; Björlenius, B. Pilot-scale removal of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater: Comparison of granular and powdered activated carbon treatment at three wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouteris, G.; Saroj, D.; Melidis, P.; Hai, F.I.; Ouki, S. The effect of activated carbon addition on membrane bioreactor processes for wastewater treatment and reclamation—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grover, D.P.; Zhou, J.L.; Frickers, P.E.; Readman, J.W. Improved removal of estrogenic and pharmaceutical compounds in sewage effluent by full scale granular activated carbon: Impact on receiving river water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghdi, M.; Taheran, M.; Pulicharla, R.; Rouissi, T.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Pine-wood derived nanobiochar for removal of carbamazepine from aqueous media: Adsorption behavior and influential parameters. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 5292–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alighardashi, A.; Aghta, R.S.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Improvement of Carbamazepine Degradation by a Three-Dimensional Electrochemical (3-EC) Process. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GracePavithra, K.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Jaikumar, V.; SundarRajan, P. A review on three-dimensional eletrochemical systems: Analysis of influencing parameters and cleaner approach mechanism for wastewater. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 873–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshwar, K.; Ibanez, J.G.; Swain, G.M. Electrochemistry and the environment. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1994, 24, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, H.; Shi, S.; Zhang, G.; Ni, J. Electrolytic treatment of C.I. Acid Orange 7 in aqueous solution using a three-dimensional electrode reactor. Dyes Pigment. 2008, 77, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.J.; Moreira, M.M.; Paíga, P.; Dias, D.; Bernardo, M.; Carvalho, M.; Lapa, N.; Fonseca, I.; Morais, S.; Figueiredo, S.; et al. Evaluation of the adsorption potential of biochars prepared from forest and agri-food wastes for the removal of fluoxetine. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. Kongl. Vetensk. Acad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.R.; Bircher, K.G.; Tumas, W.; Tolman, C.A. Figures-of-merit for the technical development and application of advanced oxidation technologies for both electric- and solar-driven systems (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Z. Preparation and characterization of cerium-doped multiwalled carbon nanotubes electrode for the electrochemical degradation of low-concentration ceftazidime in aqueous solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 199, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Suo, N.; Long, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y. Preparation of particle electrodes from manganese slag and its degradation performance for salicylic acid in the three-dimensional electrode reactor (TDE). Chemosphere 2019, 216, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Niu, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y. Electrochemical mineralization of sulfamethoxazole by Ti/SnO2-Sb/Ce-PbO2 anode: Kinetics, reaction pathways, and energy cost evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 97, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Gao, S.; Xia, X. Accelerated photocatalytic oxidation of carbamazepine by a novel 3D hierarchical protonated g-C3N4/BiOBr heterojunction: Performance and mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIZI, M. Activated Carbon and the Principal Mineral Constituents of a Natural Soil in the Presence of Carbamazepine. Water 2019, 11, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil, A.; Taoufik, N.; Garcia, A.M.; Korili, S.A. Comparative removal of emerging contaminants from aqueous solution by adsorption on an activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3017–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixidó, M.; Pignatello, J.J.; Beltrán, J.L.; Granados, M.; Peccia, J. Speciation of the Ionizable Antibiotic Sulfamethazine on Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 45, 10020–10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, K.C.; Yang, C.-C.; Chen, K.-F.; Tsai, Y.-P. Recent Trends in Removal Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products by Electrochemical Oxidation and Combined Systems. Water 2020, 12, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. Three-dimensional electrochemical process for wastewater treatment: A general review. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarlou, H.; Pedersen, N.L.; Fini, M.N.; Muff, J. Synergy optimization for the removal of dye and pesticides from drinking water using granular activated carbon particles in a 3D electrochemical reactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22206–22213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.L.; Fini, M.N.; Molnar, P.K.; Muff, J. Synergy of combined adsorption and electrochemical degradation of aqueous organics by granular activated carbon particulate electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 208, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, K.; Ncibi, M.C.; Shestakova, M.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of carbamazepine from MBR effluent by electrochemical oxidation (EO) using a Ti/Ta2O5-SnO2 electrode. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 221, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Time (min) | % Acetonitrile (B) | Oven Temperature (°C) | Injection Volume (µL) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 35 | 20 | 1.0 | 285 |
| 7 | 80 | ||||
| 10 | 10 | ||||
| 14 | 10 |
| j (mA/cm2) | Interelectrode Distance (cm) | CBZ Removal (%) | Potential (V) | ECon (Wh/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.67 | 3.5 | 96.4 | 5.40 | 68.7 |
| 7.5 | 80.2 | 8.20 | 118 | |
| 13.30 | 3.5 | 99.3 | 7.70 | 91.2 |
| 7.5 | 99.1 | 16.5 | 193 | |
| 26.70 | 3.5 | 99.9 | 13.6 | 158 |
| 7.5 | 99.2 | 25.8 | 301 |
 |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | SARATECH®-102282 | Biochar TN | Biochar TN |
| Ash content (%) | 0.2 | 5.90 | 5.90 |
| Moisture content (%) | 0.1 | 4.32 | 4.32 |
| Particle size (mm) | 0.457 | <0.075 | 1.0–2.0 |
| Surface area (m2/g) BET | 1736 | 62 | 62 |
| Kinetic Models | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adsorbents | Pseudo first order | Pseudo second order |
| SARATECH® | -- | -- |
| Biochar < 75 µm | R2 = 0.998 | -- |
| qe = 0.769 mg/g | ||
| k1 = 1388 min−1 | ||
| Biochar 1–2 mm | R2 = 0.916 | R2 = 0.908 |
| qe = 0.137 mg/g | qe = 0.153 mg/g | |
| k1 =0.119 min−1 | k2 = 1.00 g/mg·min | |
| Equilibrium Models | ||
| Adsorbents | Langmuir | Freundlich |
| SARATECH® | R2 = 0.849 | R2 =0.976 |
| qm = 7.95 mg/g | KF = 4.97 (mg/g)·(L/mg)1/n | |
| KL = 2.66 L/mg | nF = 3.66 | |
| Biochar < 75 µm | R2 = 0.945 | R2 = 0.988 |
| qm = 1.12 mg/g | KF = 0.495 (mg/g)·(L/mg)1/n | |
| KL = 0.643 L/mg | nF = 3.03 | |
| Biochar 1–2 mm | R2 = 0.981 | R2 = 0.992 |
| qm = 0.754 mg/g | KF = 0.503 (mg/g)·(L/mg)1/n | |
| KL = 1.06 L/mg | nF =3.19 | |
| Processes | 3D | 2D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Biochar TN < 75 µm | Biochar TN 1–2 mm | SARATECH® | None | |
| % CBZ removal | 95.9 | 99.5 | 99.1 | 86.7 | |
| First-order model | R2 | 0.9994 | 0.9731 | 0.9991 | 0.9835 |
| k1, s−1 | 0.00112 | 0.00199 | 0.00167 | 0.000635 | |
| Half-life, min | 10.5 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 19.3 | |
| Second-order model | R2 | 0.9009 | 0.7298 | 0.8387 | 0.9952 |
| k2, L/(mol.s) | 237 | 2050 | 1045 | 59.5 | |
| Half-life, min | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 6.7 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correia-Sá, L.; Soares, C.; Freitas, O.M.; Moreira, M.M.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Correia, M.; Paíga, P.; Rodrigues, A.J.; Oliveira, C.M.; Figueiredo, S.A.; et al. A Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for the Removal of Carbamazepine. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146432
Correia-Sá L, Soares C, Freitas OM, Moreira MM, Nouws HPA, Correia M, Paíga P, Rodrigues AJ, Oliveira CM, Figueiredo SA, et al. A Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for the Removal of Carbamazepine. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(14):6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146432
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorreia-Sá, Luísa, Cristina Soares, Olga Matos Freitas, Manuela Maria Moreira, Henri Petrus Antonius Nouws, Manuela Correia, Paula Paíga, António José Rodrigues, Carlos Miguel Oliveira, Sónia Adriana Figueiredo, and et al. 2021. "A Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for the Removal of Carbamazepine" Applied Sciences 11, no. 14: 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146432
APA StyleCorreia-Sá, L., Soares, C., Freitas, O. M., Moreira, M. M., Nouws, H. P. A., Correia, M., Paíga, P., Rodrigues, A. J., Oliveira, C. M., Figueiredo, S. A., & Delerue-Matos, C. (2021). A Three-Dimensional Electrochemical Process for the Removal of Carbamazepine. Applied Sciences, 11(14), 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146432











