Design of Bipolar Optical Code-Division Multiple-Access Techniques Using Phase Modulator for Polarization Coding in Wireless Optical Communication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Modified quadratic congruence (MQC) code: With fixed in-phase cross-correlation, the MQC code resolves the interference, which is the main factor limiting the performance of the OCDMA system [26].
- Maximum length sequence (M-sequence) code: M-sequence code is a type of pseudorandom binary sequence with length 2m−1. The bit sequences can be generated using maximal linear feedback shift registers and periodically reproduce every sequence of bits that can be represented by the shift registers [29].
- A simple, cost-effective, and moderate security scheme for a bipolar OCDMA system with a phase modulator was proposed for FSO communication. The proposed system maintains the SAC-OCDMA principles, which eliminate the MAI problem. The proposed system improves the transmission rate compared to the previous scheme with an optical switch [21]. Moreover, because all signature codes were utilized to transmit data, the proposed Bi-OCDMA improved power efficiency compared to our previous scheme with dual EOM [22].
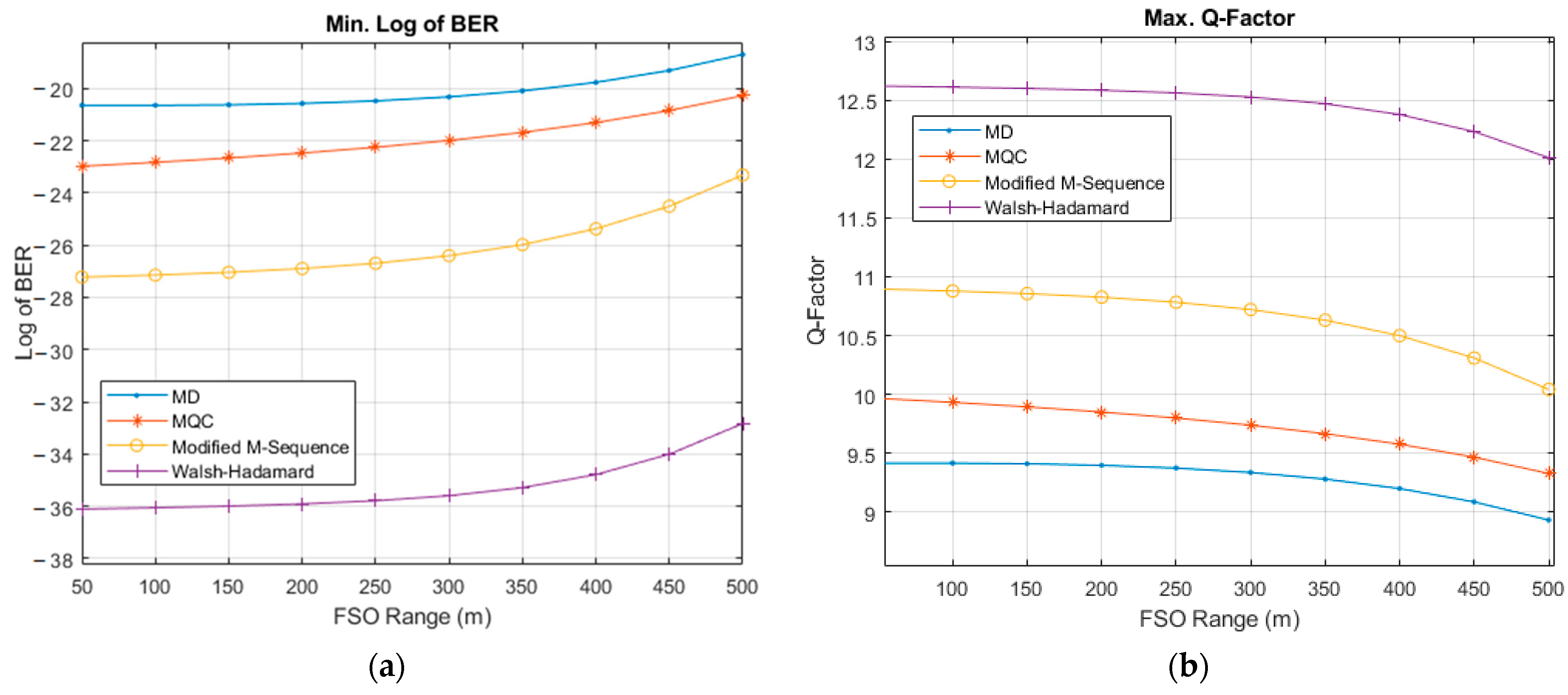
- The proposed system was investigated under extreme weather conditions using different SAC-OCDMA codes. The performance measurements were observed in terms of BER and quality factor (Q-factor), both for additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) and AWGN with a fading channel.
- The proposed Bi-OCDMA architecture was further tested under different turbulence-induced fading conditions, and a performance comparison was performed between different SAC-OCDMA. The fading model implemented the gamma–gamma fading channel model.
2. The Proposed Bi-OCDMA System
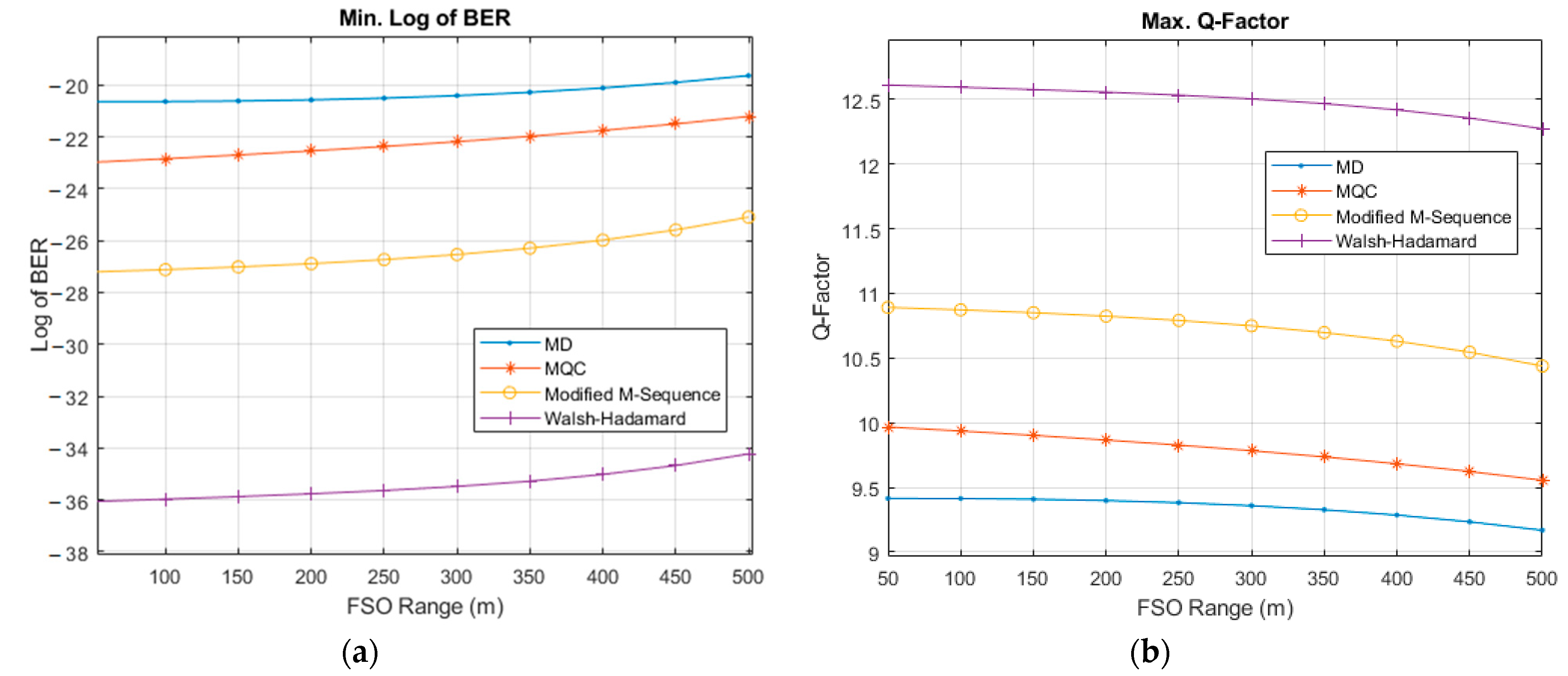
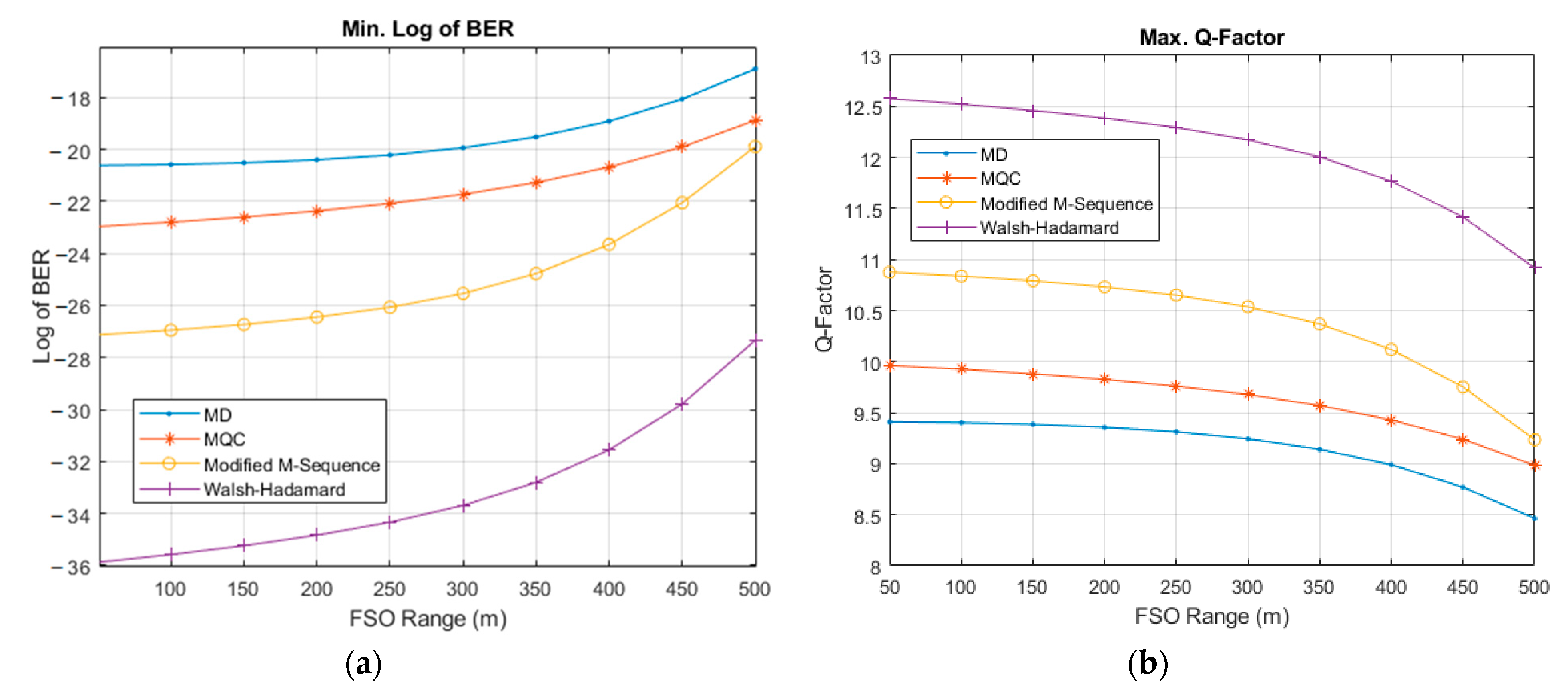
3. Simulation Setup and Results
3.1. Feasibility of the Proposed Bi-OCDMA
3.2. Performance of The Proposed Bi-OCDMA
- Thermal noise:
- Shot-Signal Noise:
- Shot-ASE Noise:
- Signal-ASE Noise:
- ASE-ASE Beat Noise:
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.Y.; Jiang, D.J. 5G: Vision and Requirements for Mobile Communication System towards Year 2020. Chin. J. Eng. 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadiku, M.N.O.; Musa, S.M.; Nelatury, S.R. Free Space Optical Communications: An Overview. Eur. Sci. J. 2016, 12, 1857–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dat, P.T.; Kanno, A.; Inagaki, K.; Umezawa, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Kawanishi, T. Hybrid Optical Wireless-mmWave: Ultra High-Speed Indoor Communications for Beyond 5G. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Paris, France, 29 April–2 May 2019; pp. 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.-N.; Bohata, J.; Spacil, J.; Dousek, D.; Komanec, M.; Zvanovec, S.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Ortega, B. M-QAM Transmission over Hybrid Microwave Photonic Links at the K-band. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 33745–33756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakkour, M.; Aghzout, O.; Chaoui, F. Theoretical Analysis of a Novel WDM Optical Long-Haul Network Using the Split-Step Fourier Method. Int. J. Opt. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Malhotra, J. A high-speed long-haul wavelength division multiplexing–based inter-satellite optical wireless communication link using spectral-efficient 2-D orthogonal modulation scheme. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2019, 33, e4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sharma, A.B. High-Speed Optical Time-Division Multiple-Access (OTDMA) Networks Using Optical Signal Processing. Photonic Netw. Commun. 1999, 1, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Upadhyay, R.; Bhatt, U.; Kumar, A. DEC TDMA: A Delay Controlled and Energy Efficient Clustered TDMA Mechanism for FiWi Access Network. Optik 2020, 164921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, C.B.M.; Aljunid, S.A.; Ghani, F.; Fadhil, H.A.; Anuar, M.S. Phase Induced Intensity Noise Evasion in SAC-OCDMA Systems Using Flexible Cross Correlation (FCC) Code Algorithm. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci 2013, 7, 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaleb, S.A.A.; Fayed, H.; Aziz, A.; Aly, M. Enhanced Spectral Amplitude Coding OCDMA System Utilizing a Single Photodiode Detection. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldhaibani, A.; Aljunid, S.A.; Anuar, M.S.; Abdullah, A.R.A.J. Increasing performance of SAC-OCDMA by combine OFDM technique. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2014, 66, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zefreh, M.R.; Salehi, J.A. Theoretical Studies of Ultrashort Light Pulse Spectrally-Phase-Encoded OCDMA System Using Power-Cubic Optical Nonlinear Preprocessor. IEEE J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 5062–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khafaji, H.M.R.; Aljunid, S.A.; Fadhil, H.A. Spectral efficiency analysis of bipolar spectral amplitude coding optical code-division multiple access systems using different one-dimensional codes. IET Optoelectron. 2012, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, B. An OCDMA Scheme to Reduce Multiple Access Interference and Enhance Performance for Optical Subscriber Access Networks. ETRI J. 2004, 26, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.; Yen, R.; Dimyati, K.; Abdullah, M. Using Bipolar Codes in Non-coherent Optical CDMA Systems to Stabilize Decision Threshold for BER Performance Improvement. J. Opt. Commun. 2006, 27, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khafaji, H.; Ngah, R.; Aljunid, S.; Rahman, T. A new two-code keying scheme for SAC-OCDMA systems enabling bipolar encoding. J. Mod. Opt. 2015, 62, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Gupta, S. Novel Bipolar Reconfigurable Code for OCDMA Network. IJAERD 2018, 5, 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Goel, A. New bipolar spectral amplitude code for cardinality enhancement in OCDMA network. J. Opt. 2020, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Su, Y.W.; Sato, T. Performance Analysis of Polarization Modulated Direct Detection Optical CDMA Systems over Turbulent FSO Links Modeled by the Gamma-Gamma Distribution. Photonics 2015, 2, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Yan, L.-S.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yi, A.-L.; Pan, W.; Luo, B. Use of Polarization Freedom Beyond Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Kataoka, N.; Wada, N. Rapid Reconfigurable OCDMA System Using Single-Phase Modulator for TimePolarization-Division Multiplexing to Support High-Speed and Spectral-Efficient Data Transmission. Light Sci. Appl. 2016, 6, e16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.C.; Wijanto, E.; Lien, T.-C.; Lai, P.-H.; Tseng, S.-P. Multiple Access Techniques for Bipolar Optical Code Division in Wireless Optical Communications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83511–83523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.P.; Wijanto, E.; Lai, P.H.; Cheng, H.C. Bipolar Optical Code Division Multiple Access Techniques Using a Dual Electro-Optical Modulator Implemented in Free-Space Optics Communications. Sensors 2020, 20, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Kataoka, N.; Wada, N. Rapid Reconfigurable OCDMA System Using Single-Phase Modulator for Time-Domain Spectral Phase Encoding/Decoding and DPSK Data Modulation. J. Lightwave Technol. 2011, 29, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissaoui, A.; Hacini, L. Performance Comparison of Different SAC-OCDMA-FSO Detection Techniques in Presence of Atmospheric Losses. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Image and Signal Processing and their Applications (ISPA), Mostaganem, Algeria, 24–25 November 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, U.; Panda, C. Performance Analysis of Hybrid SAC-OCDMA-OFDM Model over Free Space Optical Communication. CCF Trans. Netw. 2020, 3, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Yang, C.C.; Chiu, I.M. Hybrid MQC/M-Matrices Coding over Non-Coherent Spectral/Spatial Optical CDMA Networks. IJMOT 2006, 1, 592–595. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.T.; Chen, W. A Study of Bipolar Walsh-Hadamard Coding Method in Optical CDMA Networks. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 284–287, 2667–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Yang, C.C.; Tseng, S.P. Complementary Walsh–Hadamard coded optical CDMA coder/decoders structured over arrayed-waveguide grating routers. Opt. Commun. 2004, 229, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Huang, J.F.; Tseng, S.P. Optical CDMA Network Codecs Structured with M-Sequence Codes over Waveguide-Grating Routers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2004, 16, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Gupta, A. Performance of Different OCDMA Codes with FWM and XPM Nonlinear Effects. J. Opt. Commun. 2016, 38, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, T.; Aljunid, S.A.; Fadhil, H.A.; Ahmad, R.B.; Saad, M.N.M. Design and simulation a new code with zero cross-correlation for SAC-OCDMA networks. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 6, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fayadh, R.; Wali, M.; Bonneya, M. Establishment Network by Using FSO Link Based on MD Code for Hybrid SCM-SAC-OCDMA Wireless System. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2018, 8, 5107–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motealleh, M.; Mohsen, M. Simulation of a SAC-OCDMA 10 User ×15 Gb/s System Using MD Code. Int. J. Opt. Appl. 2014, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-T.; Cheng, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, W.-B. Performance Analysis of Dual Unipolar/Bipolar Spectral Code in Optical CDMA Systems. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2013, 11, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mrabet, H.; Mhatli, S.; Dayoub, I.; Giacoumidis, E. Performance Analysis of AO-OFDM-CDMA with Advanced 2D-Hybrid Coding for Amplifier-Free LR-PONs. IET Optoelectron. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-Nhat, N.; Elsherif, M.A.; Malekmohammadi, A. Investigations of High-Speed Optical Transmission Systems Employing Absolute Added Correlative Coding (AACC). Opt. Fiber Technol. 2016, 30, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avlonitis, N.; Yeatman, E.; Jones, M.; Hadjifotiou, A. Multilevel Amplitude Shift Keying in Dispersion Uncompensated Optical Systems. IET Optoelectron. 2006, 153, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Telecommunication Union. Propagation Data Required for the Design of Terrestrial Free-Space Optical Links; P Series Radiowave propagation; International Telecommunication Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; p. 1817-1. [Google Scholar]
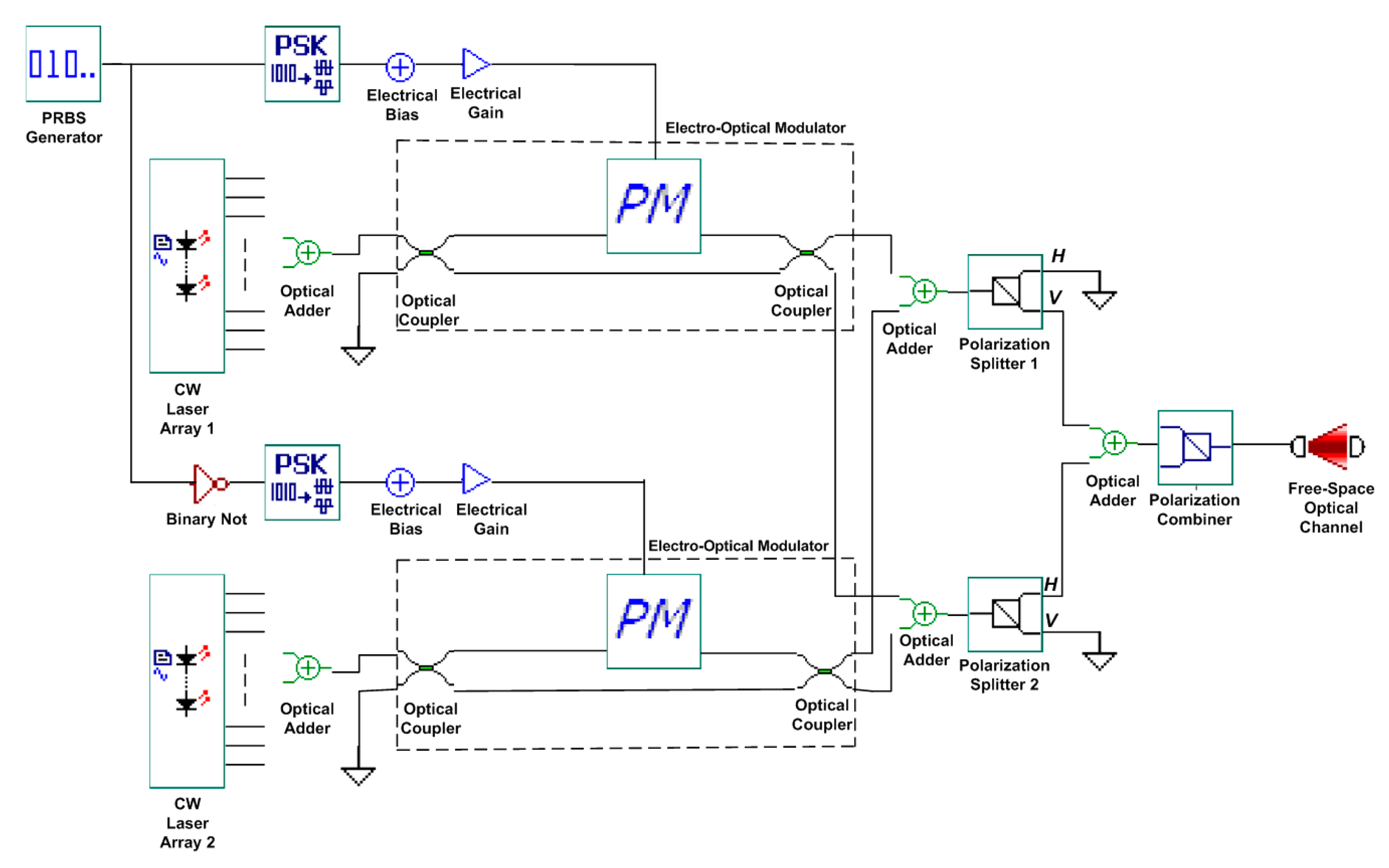
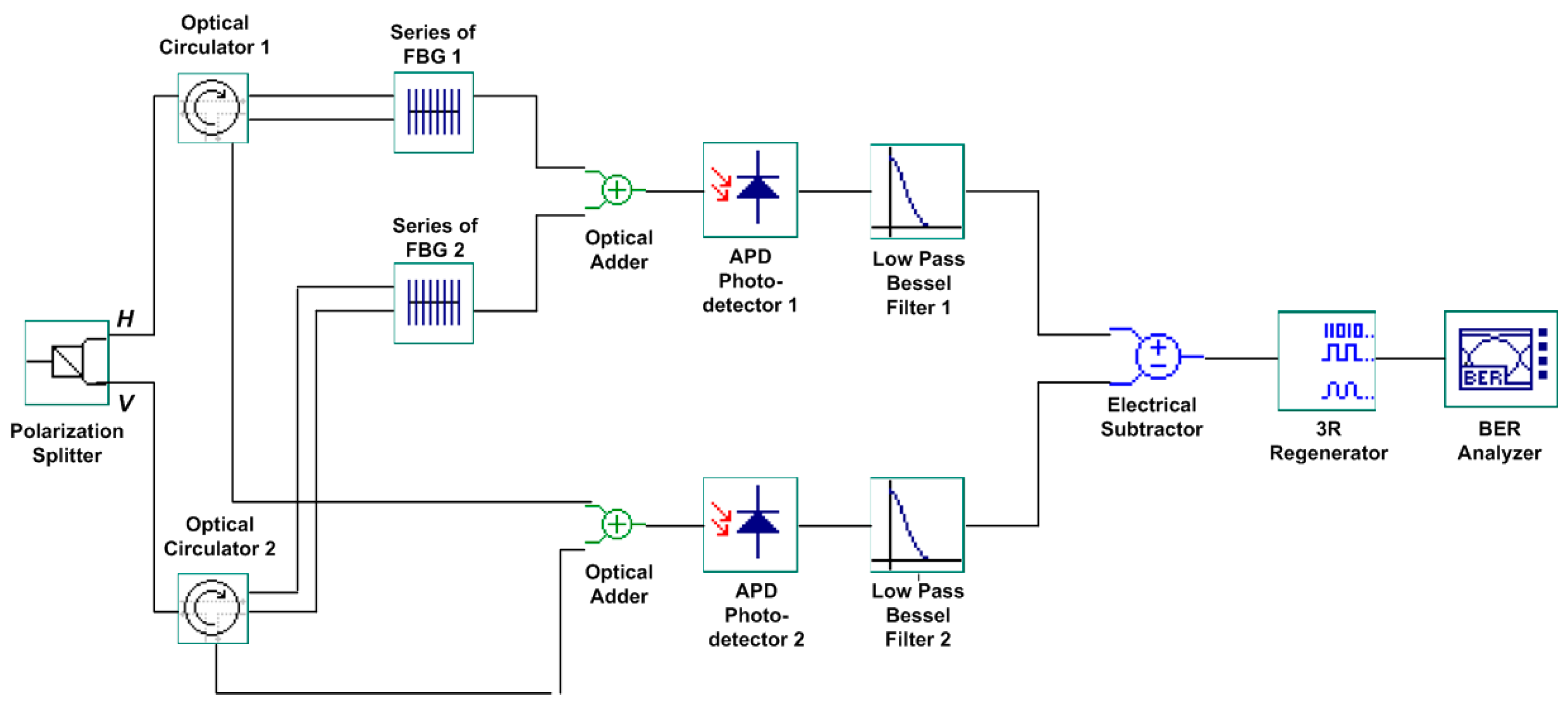
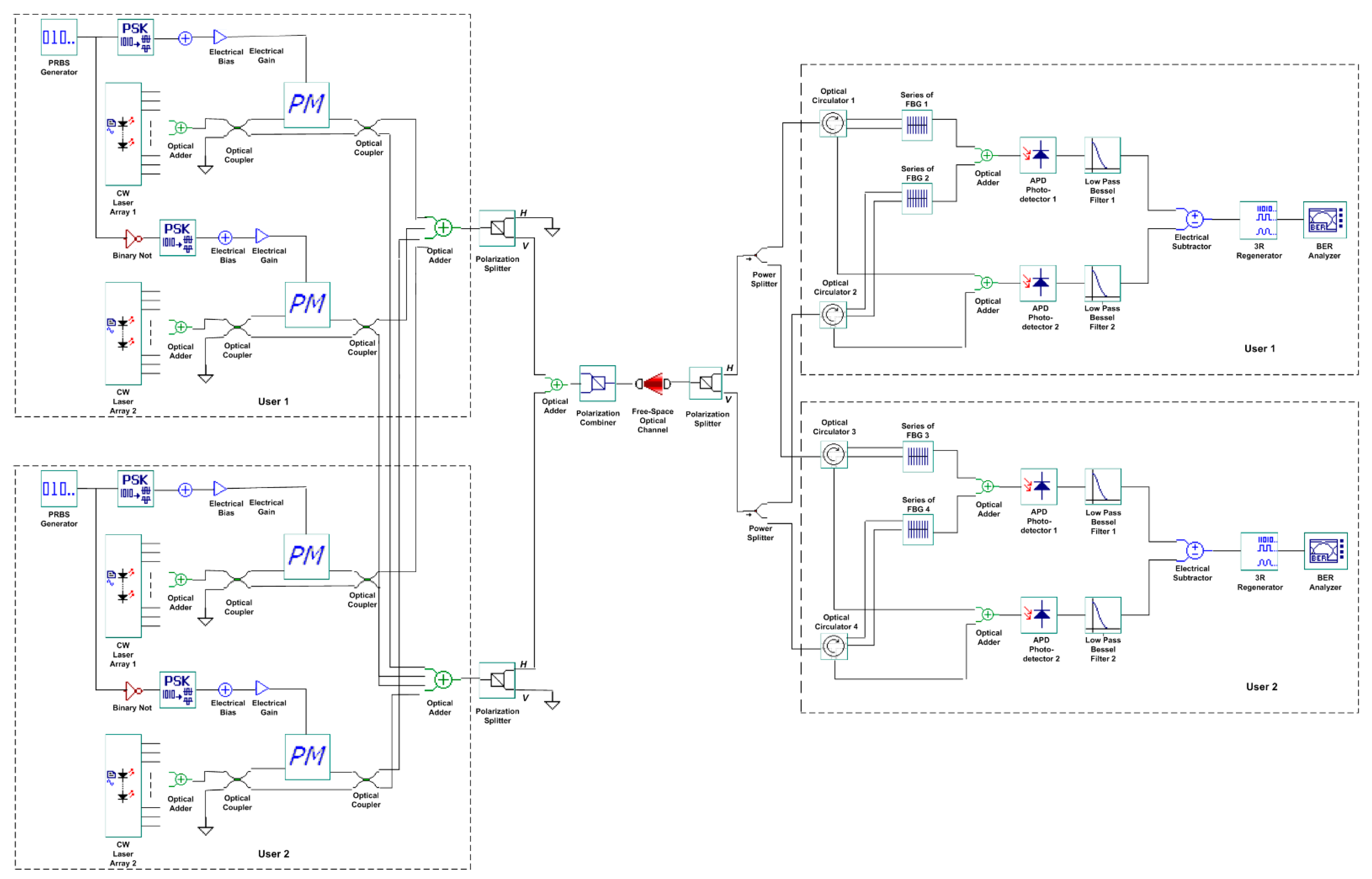

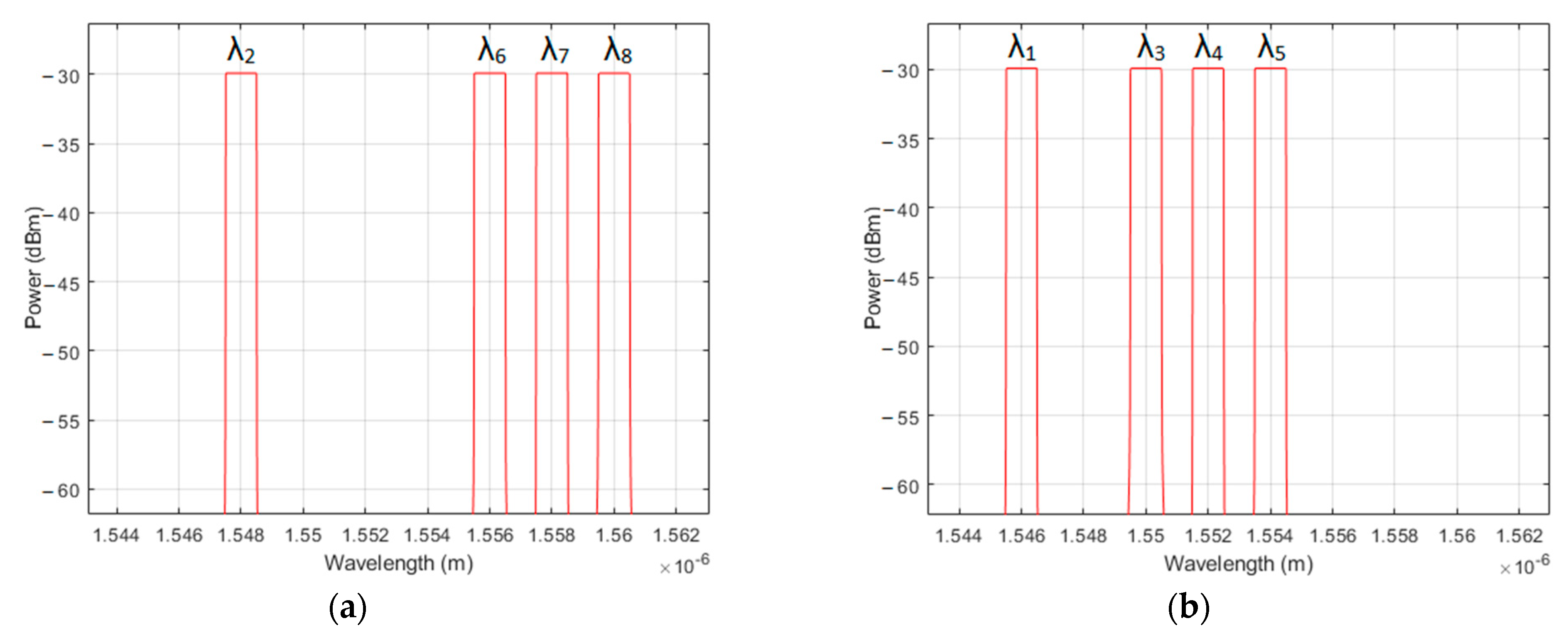
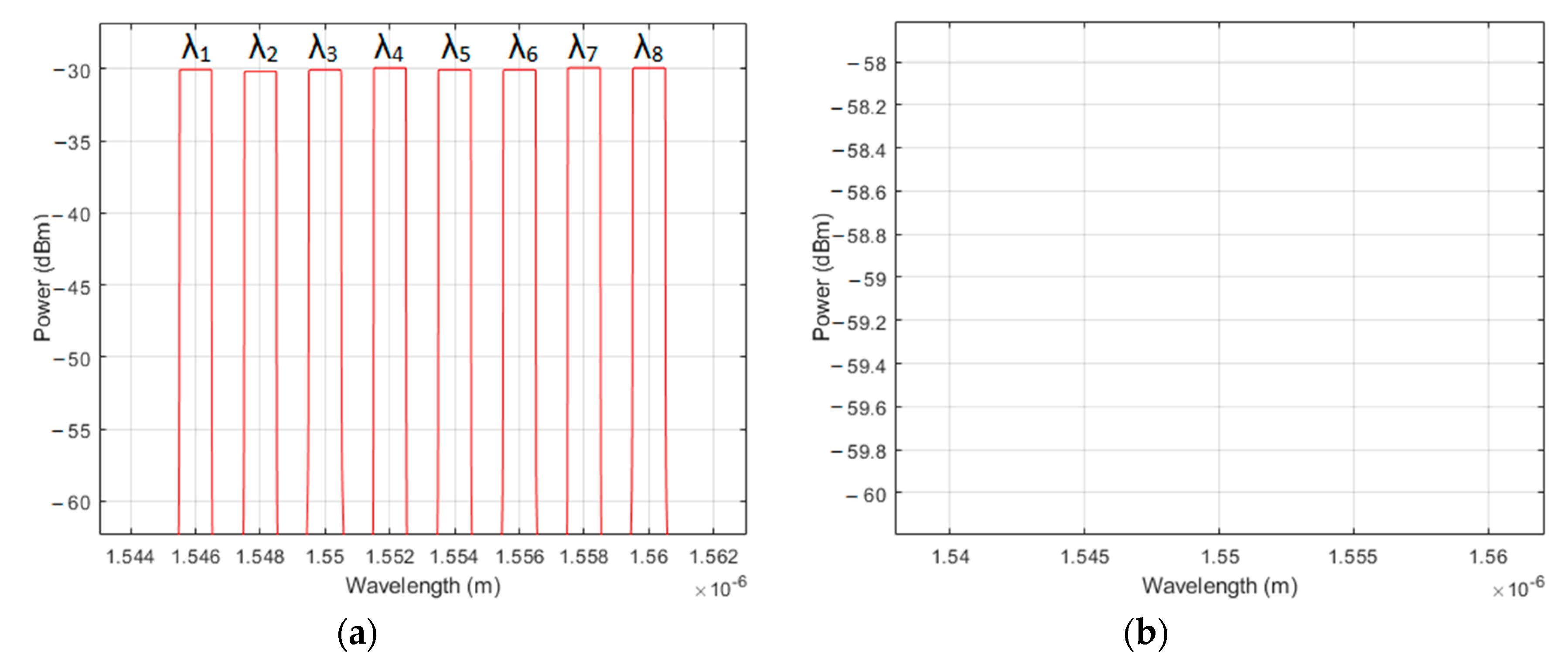

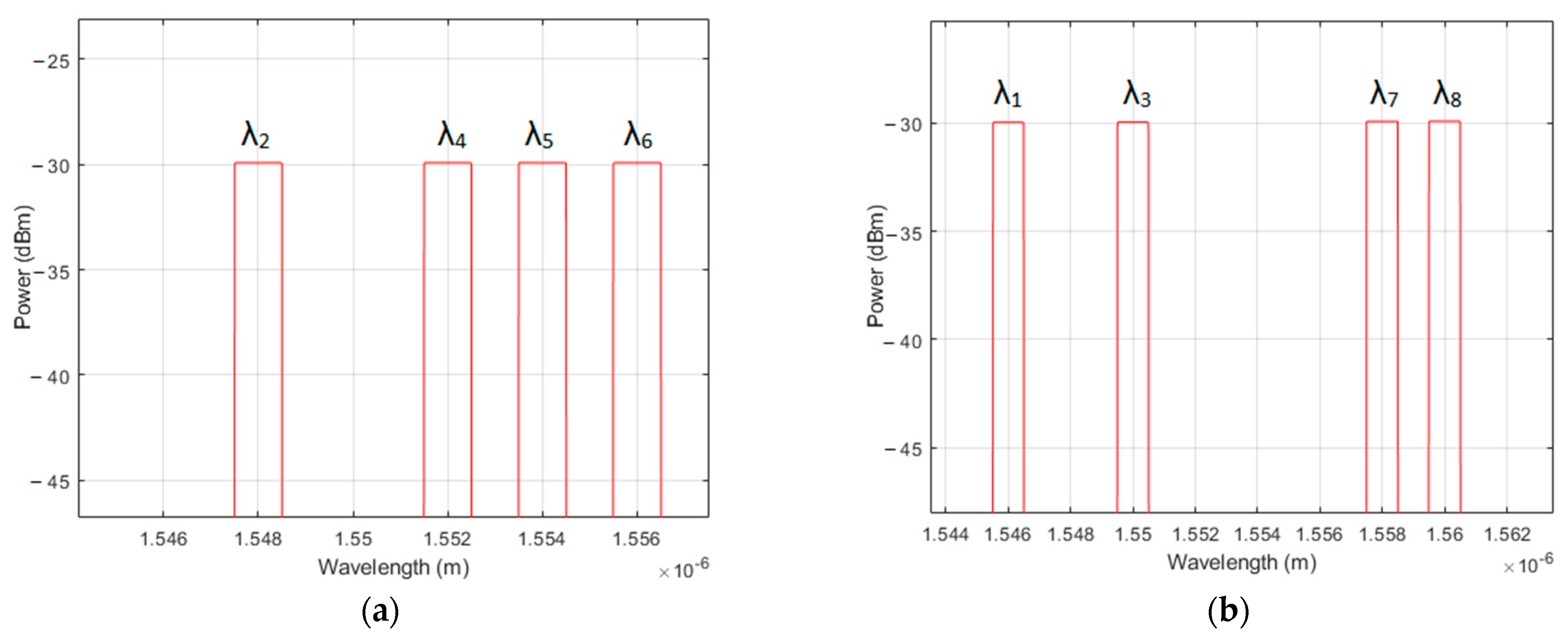
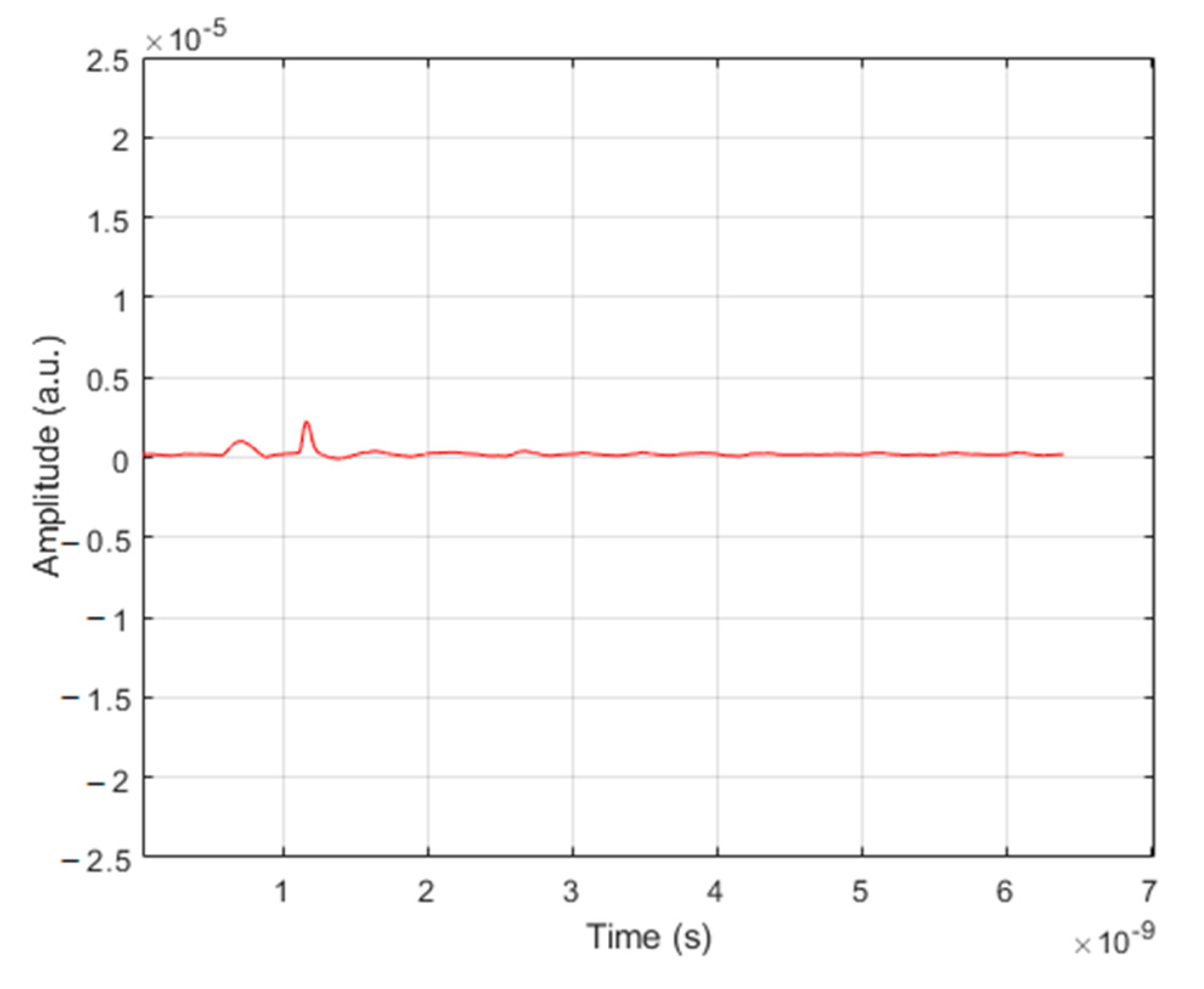
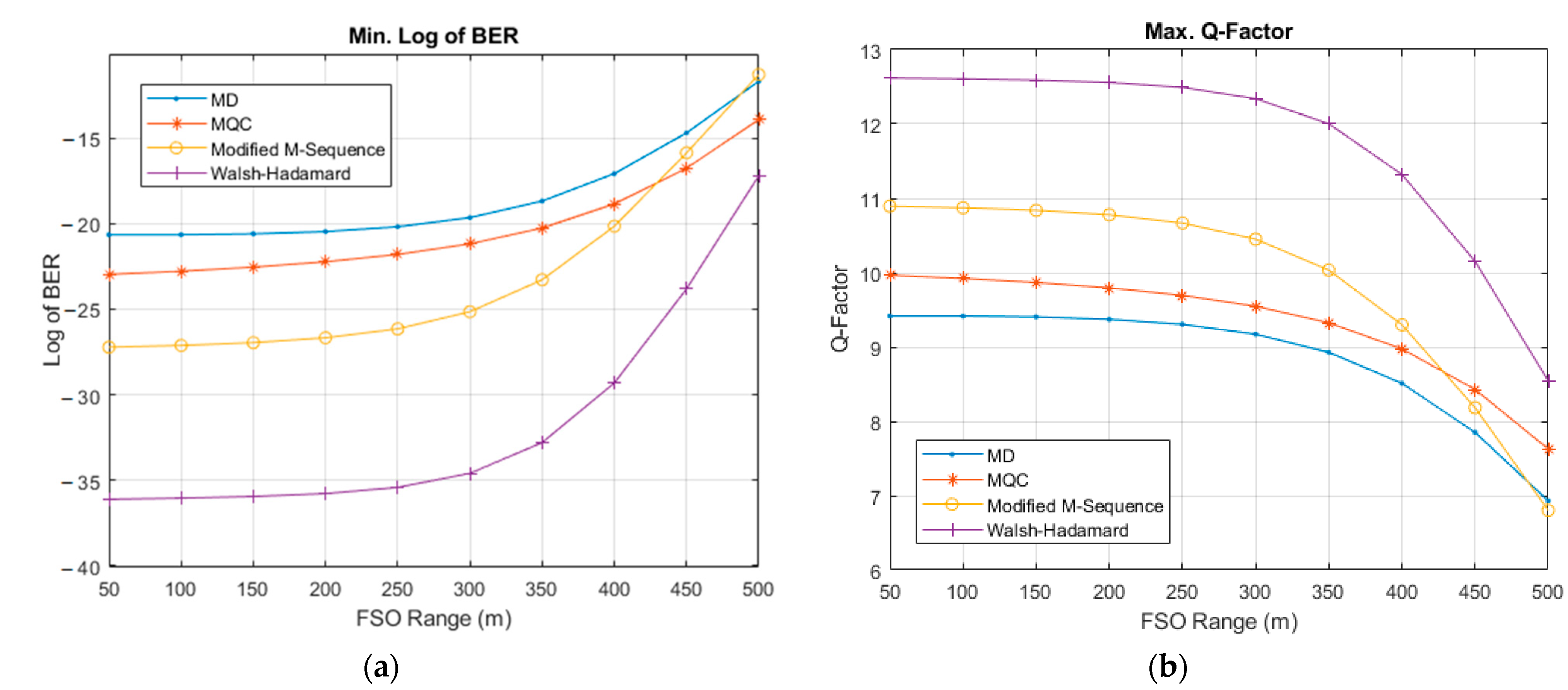
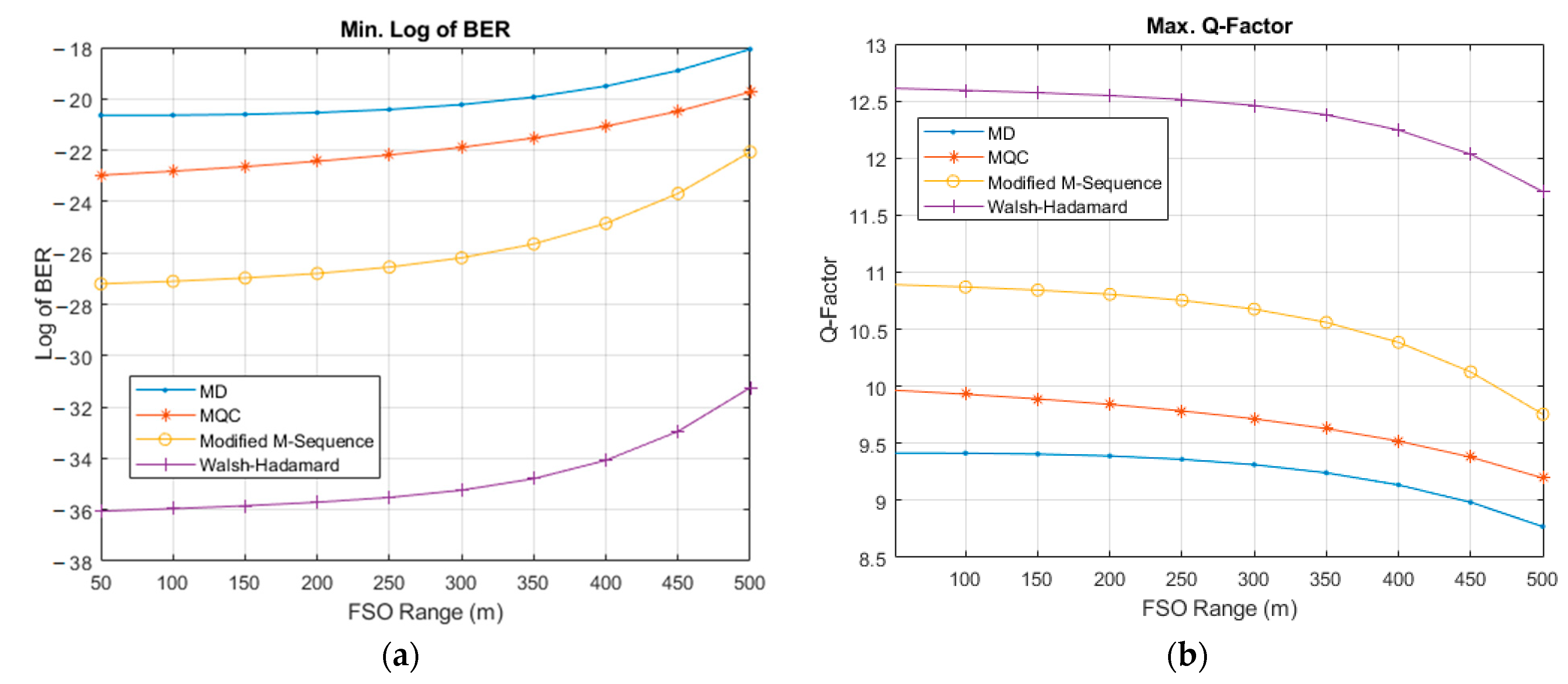
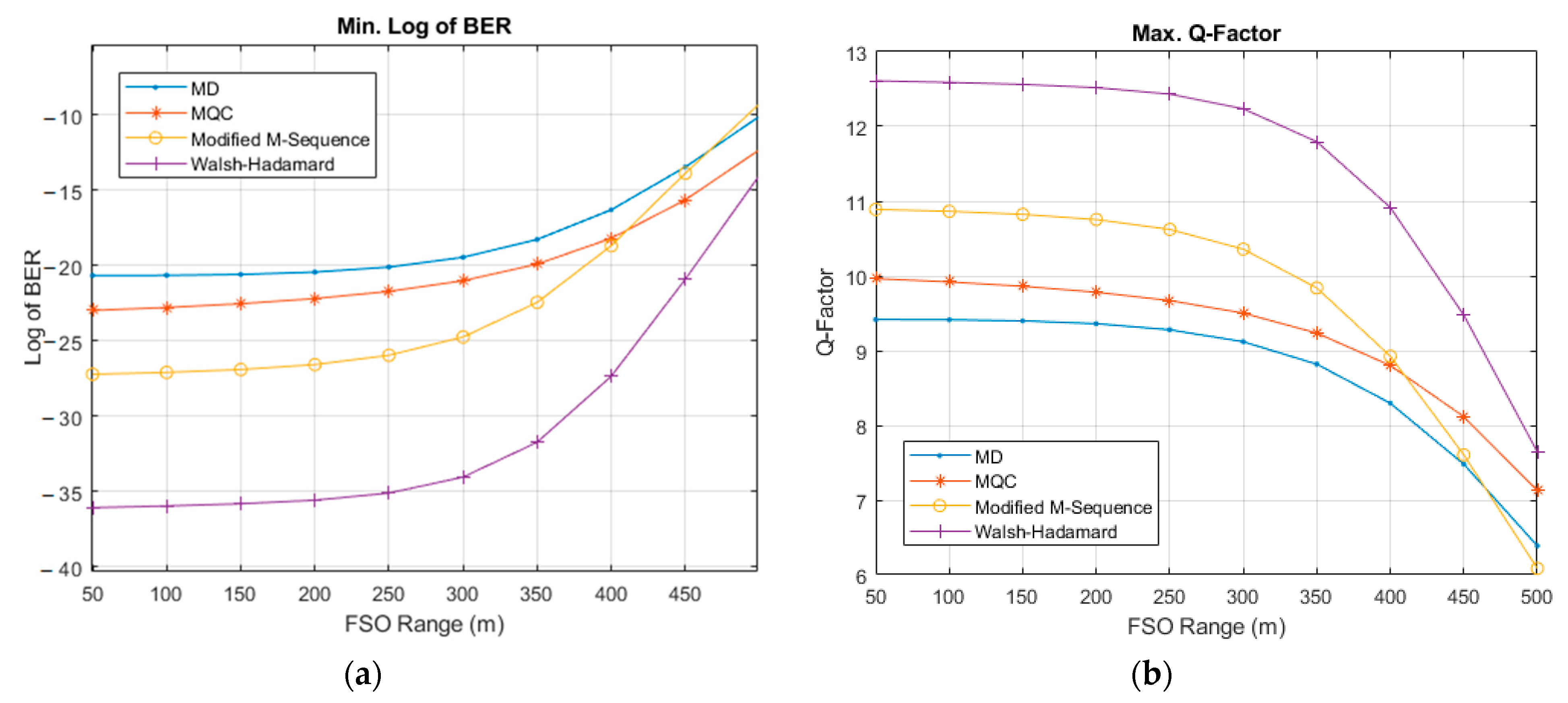
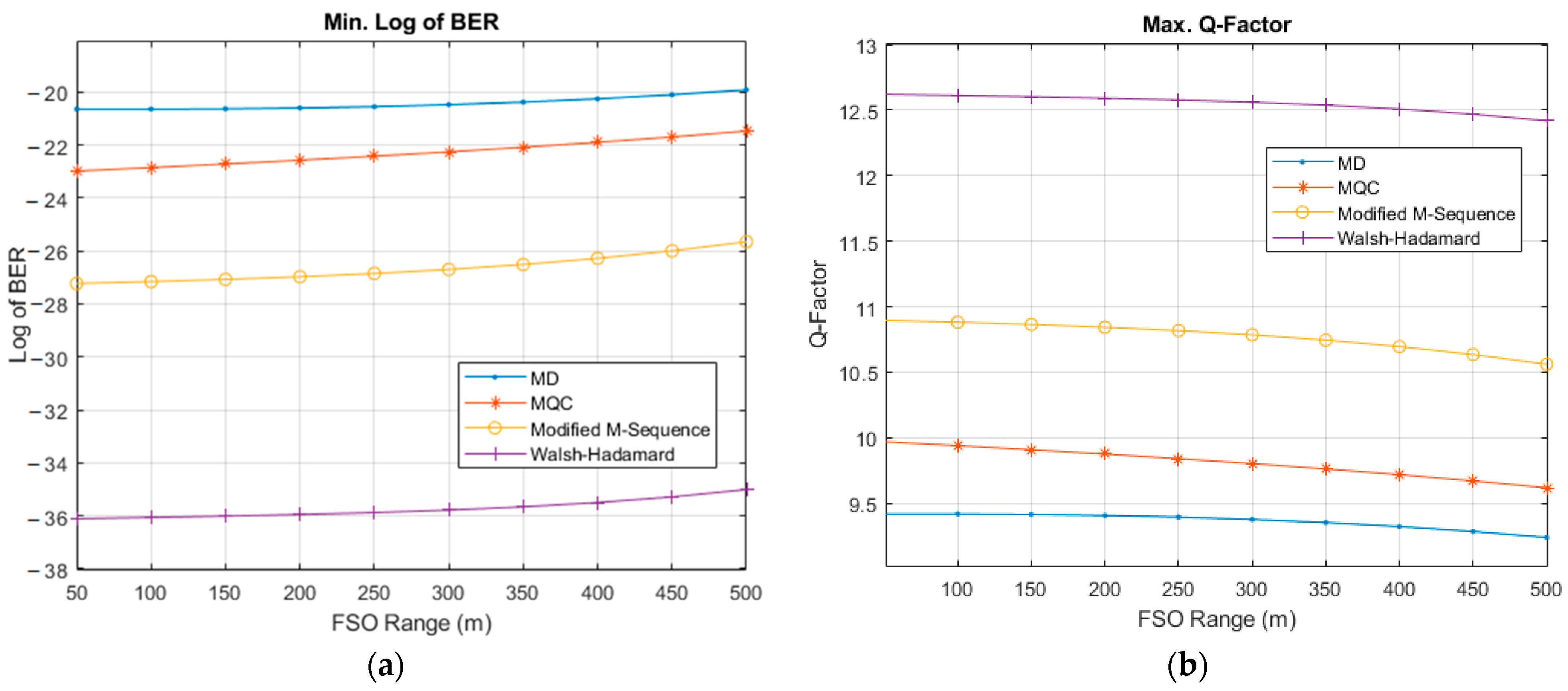
| User No. | Signature Sequence | Data Bit | Transmitted Optical Polarized Signal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | V | |||
| #1 | 10111000 | 0 | λ1 λ3 λ4 λ5 | λ2 λ6 λ7 λ8 |
| 1 | λ2 λ6 λ7 λ8 | λ1 λ3 λ4 λ5 | ||
| #2 | 01110010 | 0 | λ2 λ3 λ4 λ7 | λ1 λ5 λ6 λ8 |
| 1 | λ1 λ5 λ6 λ8 | λ2 λ3 λ4 λ7 | ||
| #3 | 11100100 | 0 | λ1 λ2 λ3 λ6 | λ4 λ5 λ7 λ8 |
| 1 | λ4 λ5 λ7 λ8 | λ1 λ2 λ3 λ6 | ||
| #4 | 11001010 | 0 | λ1 λ2 λ5 λ7 | λ3 λ4 λ6 λ8 |
| 1 | λ3 λ4 λ6 λ8 | λ1 λ2 λ5 λ7 | ||
| #5 | 10010110 | 0 | λ1 λ4 λ6 λ7 | λ2 λ3 λ5 λ8 |
| 1 | λ2 λ3 λ5 λ8 | λ1 λ4 λ6 λ7 | ||
| #6 | 00101110 | 0 | λ3 λ5 λ6 λ7 | λ1 λ2 λ4 λ8 |
| 1 | λ1 λ2 λ4 λ8 | λ3 λ5 λ6 λ7 | ||
| #7 | 01011100 | 0 | λ2 λ4 λ5 λ6 | λ1 λ3 λ7 λ8 |
| 1 | λ1 λ3 λ7 λ8 | λ2 λ4 λ5 λ6 | ||
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Global | Bit rate | 109 bits/s |
| Sample rate | 64.1010 Hz | |
| Number of samples | 4096 | |
| Sensitivity | −100 dBm | |
| CW laser | Linewidth | 10 MHz |
| Power | 0 dBm | |
| Azimuth | 45 deg | |
| Noise threshold | −100 dB | |
| Frequency | 1546…1568 nm (λ1…λ12) | |
| Electrical bias | Bias | 1 |
| Electrical gain | Gain | 0.5 |
| Phase modulator | Phase deviation | 180 degrees |
| FSO channel | Range | 50–500 m |
| Transmitter aperture diameter | 5 cm | |
| Receiver aperture diameter | 20 cm | |
| Beam divergence | 2 mrad | |
| Uniform FBG | Bandwidth | 125 GHz |
| Reflectivity | 0.99 | |
| Noise threshold | −100 dB | |
| Avalanche photodetector | Gain | 3 |
| Responsivity | 1 A/W | |
| Ionization ratio | 0.9 | |
| Dark current | 10 nA | |
| Sample rate | 32.1011 Hz | |
| Thermal power density | 10−22 W/Hz | |
| Weather Conditions | Precipitation | Visibility (m) | Attenuation (dB/km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light fog | Stormy | 770 | 18.3 |
| Very light fog | Intense rainy | 1900 | 6.9 |
| Light mist | Average rain | 2800 | 4.6 |
| Very light mist | Light rain | 5900 | 2 |
| Clean air | Drizzle | 18,100 | 0.6 |
| Code | Signature Code |
|---|---|
| MD | |
| MQC | |
| Modified M-Sequence | |
| Walsh-Hadamard |
| Weather Condition | Code | Min. Log of BER (a.u.) | Max. Q-Factor (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intense Rainy | MD | 1.9466 | 0.48296 |
| MQC | 2.7031 | 0.63817 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 3.9077 | 0.8524 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 3.2771 | 0.6095 | |
| Stormy | MD | 8.9661 | 2.48757 |
| MQC | 9.0417 | 2.33693 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 15.9262 | 4.0917 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 18.8968 | 4.07411 |
| Weather Condition | Code | Min. Log of BER (a.u.) | Max. Q-Factor (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intense Rainy | MD | 2.5724 | 0.64368 |
| MQC | 3.2382 | 0.76975 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 5.1366 | 1.13579 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 4.8101 | 0.9055 | |
| Stormy | MD | 10.5638 | 3.02852 |
| MQC | 10.6674 | 2.8358 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 17.96109 | 4.80502 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 22.0608 | 4.96498 |
| Weather Condition | Code | Min. Log of BER (a.u.) | Max. Q-Factor (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Turbulence | MD | 0.7285 | 0.17811 |
| MQC | 1.5086 | 0.35096 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 1.5746 | 0.3357 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 1.1005 | 0.2018 | |
| Medium Turbulence | MD | 1.0025 | 0.24587 |
| MQC | 1.767 | 0.41239 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 2.1138 | 0.4531 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 1.8359 | 0.3382 | |
| Intense Turbulence | MD | 3.7143 | 0.94502 |
| MQC | 4.0829 | 0.98137 | |
| Modified M-Sequence | 7.2407 | 1.6425 | |
| Walsh-Hadamard | 8.5379 | 1.6617 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijanto, E.; Huang, C.-M. Design of Bipolar Optical Code-Division Multiple-Access Techniques Using Phase Modulator for Polarization Coding in Wireless Optical Communication. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135955
Wijanto E, Huang C-M. Design of Bipolar Optical Code-Division Multiple-Access Techniques Using Phase Modulator for Polarization Coding in Wireless Optical Communication. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(13):5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135955
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijanto, Eddy, and Chun-Ming Huang. 2021. "Design of Bipolar Optical Code-Division Multiple-Access Techniques Using Phase Modulator for Polarization Coding in Wireless Optical Communication" Applied Sciences 11, no. 13: 5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135955
APA StyleWijanto, E., & Huang, C.-M. (2021). Design of Bipolar Optical Code-Division Multiple-Access Techniques Using Phase Modulator for Polarization Coding in Wireless Optical Communication. Applied Sciences, 11(13), 5955. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11135955







