Abstract
Short-term load forecast (STLF) plays an important role in power system operations. This paper proposes a spline bases-assisted Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for STLF with a semi-parametric model being adopted to determine the suitable spline bases for constructing the RNN model. To reduce the exposure to real-time uncertainties, interpolation is achieved by an adapted mean adjustment and exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) scheme for finer time interval forecast adjustment. To circumvent the effects of forecasted apparent temperature bias, the forecasted temperatures issued by the weather bureau are adjusted using the average of the forecast errors over the preceding 28 days. The proposed RNN model is trained using 15-min interval load data from the Taiwan Power Company (TPC) and has been used by system operators since 2019. Forecast results show that the spline bases-assisted RNN-STLF method accurately predicts the short-term variations in power demand over the studied time period. The proposed real-time short-term load calibration scheme can help accommodate unexpected changes in load patterns and shows great potential for real-time applications.
1. Introduction
Short Term Load Forecasting (STLF) can be used to obtain the most economical way to commit power generation sources while fulfilling policies requirements, ensuring reliability and meeting the security, environmental, and equipment constraints of the power system [1].
The daily load profile generally follows cyclic and seasonal patterns related to both the climate and human activities, and is intrinsically a univariate time series. Many general forecasting methods based on regression or time-series models can be used for load forecasting (e.g., a semi-parametric additive model [2] or an autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) [3]). These methods assume, however, a linear relationship between the observed and future time series. This assumption makes them less effective for time series with significant nonlinear characteristics, such as those associated with energy demand. Chen et al. [4] considers a more complicated time series model with a functional trend curve to improve the forecast results.
Due to their nonlinear fitting ability, machine learning techniques have been applied to many forecasting problems. The Artificial Neural Network (ANN) [5] is a typical machine learning method. ANNs learn regularities and patterns automatically from past recorded data and produce generalized results with the ability to be self-adaptive. Feed forward Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) [6,7] and Generalized Regression Neural Network (GRNN) [8] are among numerous ANN-based STLF techniques used in many control centers [9,10]. A systematic review on the techniques of electricity demand forecasting methods is available [11]. This overview includes regression, time series analysis, ANN, support vector machines and certain bottom-up approaches.
Load demand time series are nonlinear and non-stationary, with time-dependent dynamic behaviors. Thus, in our view, the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) is a more suitable model for this purpose, as it can consider the temporal context in the feedback connections and as it has a nonlinear property [12]. Several RNN models for STLF have been proposed. In [13], system net load profiles are modeled by RNNs as the outputs of dynamic systems influenced by weather, time and other environmental factors. A pooling-based deep RNN for household load forecasts is proposed in [14], where the focus is to provide more suitable training samples to the network.
Besides the cyclic patterns, the load demand is also affected by several exogenous variables, including the prevailing weather conditions, the calendar effect, and the general randomness inherent in individual’s behaviors. With climate change and the increase of behind-the-meter renewable integrations, it is challenging to effectively integrate the various exogenous variables into the STLF model and provide accurate load forecasts. In [15], an ensemble of radial basis function neural networks (RBFNNs) is proposed where exogenous features and features extracted from load series, through long short-term memory (LSTM) networks and multi-resolution wavelet transforms in various timescales, are used to train the RBFNNs. While in [16], a hybrid algorithm that combines similar day selection, empirical mode decomposition, and LSTM neural networks to construct a prediction model for STLF.
This study develops a RNN-based short-term (i.e., over the next few hours, the next day, or the next week) load forecast model for the Taiwan Power Company (TPC) system. It is implemented through a semi-parametric regression framework to catch general daily demand behaviors. The STLF method uses the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso) regression [17] and an adaptive Lasso [18] to select suitable variables. It includes multi-resolution basis functions [19] and cubic B-spline basis functions in the RNN model, in order to catch useful patterns, reduce the overfitting problem, and increase the forecast accuracy. An intuitive approach for calibrating the temperature forecasts is also adopted to account for the trend of past temperature forecast errors.
To accommodate real-time operation purposes and deal with any unexpected changes in system net load, a real-time short-term load adjustment tool is also developed. An interpolation technique [20] based on the historical load values over the previous 15 min and their differences with the current STLF values is employed to achieve a real-time forecast adaptation in which the load forecast is updated every 5 min, for real time operation applications.
The main contribution of this work is to develop a systematic procedure to combine the methodologies of statistical modeling and machine learning in two consecutive stages, so as to provide accurate forecasts of the load demand. To address overfitting in the forecast model used in the statistical modelling stage, the important and effective factors are identified by means of a variable selection procedure, together with an error-reducing calibration of the forecasted temperature using a suitable non-linear transformation. RNN machine learning models are then constructed, to capture the uncertainties of the complex and non-linear load patterns. The procedure for real-time short-term load demand adjustment further enhances the real-time forecast accuracy. As a result of this improved forecasting, the system operator can begin earlier preparations to reduce the impact of net load intermittency, particularly in systems with higher renewable penetration.
2. Methodology
The proposed RNN-based STLF procedure, with selected bases through a semi-parametric model and a real-time load forecast adjustment scheme, is shown in Figure 1. In the first stage, forecasts of daily load patterns up to the next seven days are obtained using the apparent temperatures predicted by the Taiwan Central Weather Bureau (TCWB). In the second stage, based on past-forecasted results, real-time adapted forecasting load sequences are generated through the interpolation method using real-time adaptation and an exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA). Figure 1 presents the data flow of the proposed RNN-based model.
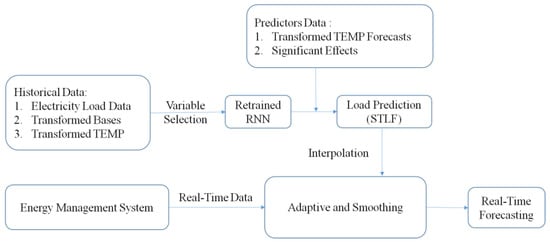
Figure 1.
Proposed spline-bases assisted Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) for Short Term Load Forecasting (STLF) and
2.1. Apparent Temperature
The system net-loads are greatly affected by external factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed and seasonal events that change over time. The apparent temperature index [21] equivalent to the temperature felt is used to evaluate its effect upon the load. The apparent temperature is defined as:
where is the temperature in Celsius, , e is the pressure in hPa, V is the wind speed in m/sec, and RH is the relative humidity in percent. The apparent temperature for the next 48 h (with a 3 h resolution) is provided by the TCWB. Throughout this work, references to “temperature” refer to the apparent temperature.
Different regions have different weather patterns. The total system load is a combination of the loads from the north, central, south and east regions of Taiwan (whose average load proportions are 38%, 28%, 33% and 1%, respectively). Since the goal is to forecast the total system load, the temperatures of the four regions are merged into one value by taking the weighted average of their temperatures with weights equal to their load proportions; namely:
where corresponds to the north, central, south and east regions respectively, is the temperature in the ith region and is the proportion of regional load in system total energy demand.
2.2. Spline Basis Functions
To catch the general behaviors of the daily load patterns, we consider the class of multi-resolution basis functions proposed by Tzeng and Huang [19], which are ordered in the direction of increasing resolution detail, with the number of bases, K, being chosen to be large enough to represent the general 24-h patterns. On the other hand, due to the fact that the daily load patterns may change rapidly between the peak and off-peak periods, we also include the cubic B-spline basis functions to accommodate load patterns that change substantially within relatively short periods of time. Two sets of bases functions are used: (1). the multi-resolution bases defined on n control points and (2). the B-spline bases of order d, with knots at . Details about the spline basis functions can be found in [19].
2.3. Semi-Parametric Model
A semi-parametric (SPM) model is adopted for STLF under the framework of additive models [22], by a suitable combination of the two aforementioned sets of spline basis functions, together with the nonlinear function of the temperature.
Now let the sequence of daily load random vectors at time t be , , with y(t,s) denoting the load at time t and local time grid location (control point)
The model for STLF is assumed to have the following form:
where represents the mean function of the logarithm of the daily load , and is the corresponding random error at time and period , assuming that with being the covariance matrix of the random error vector at time t. In the case of an independent error at time t and assuming , the time series errors sequence may yield a different covariance matrix estimate.
Specific patterns of the response variable (i.e., the system net load) of the model for forecasts are described below, under the following explanatory variables.
- It is observed that there are patterns depicted by the intra-daily, intra-weekly, peak and off-peak effects to be modeled by the multi-resolution and cubic B-spline bases.
- It is clear that the temperature significantly affects the load pattern. The weighted average of the temperature at different periods each day, and similarly the daily highest and lowest and the weighted average of temperatures in the different regions, are included as important predictors.
- The interaction effects of the period with the day type within each week are also crucial.
To accommodate these three effects, and also the temperature effect, let the mean function at time t and point s be given by:
with:
- 1
- intra-weekly effect
- 2
- intra-daily effect
- 3
- interaction effect among the intra-daily and intra-weekly
- 4
- apparent temperature effect
To model the intra-daily effect, we use a combination of the first 24 multi-resolution bases for 96 control points with and 96 cubic B-spline bases with knots at .
Similarly, the intra-weekly effect is modeled by 7 cubic B-spline bases with knots at .
The interaction effects among the intra-daily and intra-weekly are modeled by the products of the corresponding intra-daily and intra-weekly bases functions, namely: , .
A detailed description of the spline bases functions is provided in Appendix A. The corresponding SPM is a linear combination of the above basis functions. The explicit expression of the model is given in Appendix B.
2.4. Model Bases Selection
Many standard estimators can be improved by shrinkage methods, such as ridge regression [23] and Lasso regression. This study adopts Lasso regression to obtain sparse solutions from the model bases selection.
In a Lasso regression, the value of the parameter controls both the size and the number of coefficients. Cross-validation is a resampling technique which can find a parameter value that ensures a proper balance between bias and variance. In this case, cross-validation considers the best tuning parameter value to be the one that minimizes the estimated test error rate of the forecasting results. More details about the Lasso estimate and adaptive Lasso can be found in [17,18].
2.5. Temperature Forecast Adjustment
Currently, TCWB provides three-hour temperature forecasts for the present day (D-day), the next day (D + 1), and the maximum and minimum temperature forecasts for the days (D + 2) to (D + 7).
- Calibration of temperature forecasts
To calibrate the day-ahead temperature forecasts at the eight time points provided by TCWB before D-day (the first day that the temperature forecasts are to be calibrated), the errors between the historical apparent temperatures , and the recorded day-ahead temperature forecasts of the 28 days before D-day, , are used for the calibration. Define both the historical and the forecasted mean temperatures of the 28 days before D-day as respectively, where :
For D-day, let the error between the mean temperatures and the calibrated temperature forecasts be, respectively:
The calibrations and (D + 1)-day’s eight temperature forecast time points can be found similarly. Note that samples from historical days with unusual temperature pattern are treated as outliers and thus deleted beforehand.
- 2.
- Refined temperature forecasts
As we need to make load forecasts at 15-min intervals, we first interpolate the provided three-hour forecast data into a 15-min resolution, which will lead to smaller biases versus the real 15-min interval temperatures. We use the well-established Cubic Hermite interpolation method [20] and present that interpolation formula below.
Let the sequence be a partition of the interval , and let , be the corresponding data points. The local grid spacing is , and the slope of the piecewise linear interpolant between the data points is .
The cubic Hermite interpolant polynomial defined for is:
where
Then the interpolant method produces as its output a sequence of temperature forecasts at 15-min intervals.
- 3.
- Transformed temperature forecasts
It is noted that the effect of temperature to the load is nonlinear as shown in Figure 2 and upon examination it is observed that the load is approximately linearly related to the logistic sigmoid transformation of the temperature through
where represents the location of the reflection from concave upward to concave downward, represents the scale parameter controlling slope changes.
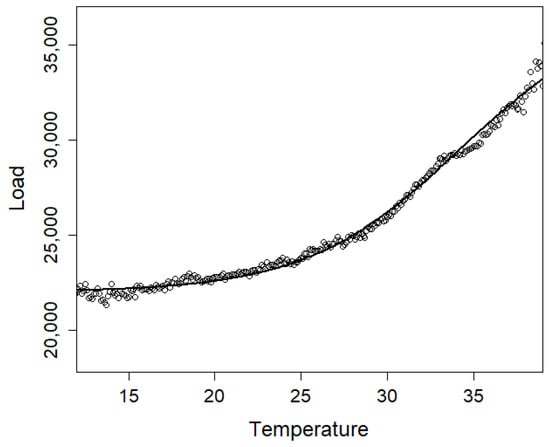
Figure 2.
The scatterplot of temperature and load.
2.6. Recurrent Neural Network with Selected Bases
RNN introduces loops in the network and allow internal connections among hidden units to enable exploration of the temporal relationships among the data [24]. The RNN structure with selected model bases taken from the resulting SPM described above is presented in the following.
- General Structure of RNN
Each of the RNN layers uses a loop to iterate over the time steps of the sequence. An RNN with a single hidden layer is illustrated below.
The input training data is the adaptive lasso estimator effects, it is given as:
The mapping of the output can be represented as:
where , t = 1,..., T, are the activation functions, u is the input weight for, w is the input weight for , where both are the same for all time points t, and where b is a parameter in the model representing the bias of the hidden layer and the output layer. The RNN uses the hidden state at time step t to memorize the network. When t = 1, an RNN is the same as an ANN.
Consider a RNN model with k multilayer perceptrons, where in the ith hidden layer there are m neurons and the time step is T. Then the ith layer vector for these m neurons in the (i−1)th layer at time t is expressed as: which can be obtained through the following equation:
where , , are the transition and input weight matrices. The mapping of the output can be represented as:
where V is output weight matrices and is a parameter in the model representing the bias of the hidden layer and the output layer.
With suitable choices for the parameters, such as the number of layers k, number of neurons in each layer m, and time steps of a sequence T, the RNN is expected to perform better than a more general model structure considering time effects in the neural network framework for STLF problems. We build an RNN model with k multilayer perceptrons in Python using the tensorflow library.
- 2.
- Configuration Architecture
The RNN training process is heavily influenced by the choice of hyper parameters: sequence size, number of hidden layers and number of nodes per hidden layer. Efforts were made to search for a hyper parameter space to test different parameter combinations most suitable for TPC system. The experiment was conducted using standard RNN network to provide a best set of hyper-parameters. The results shown in Table 1 indicate that the best number of hyper-parameters units is 14, Layers is 3, and Time steps is 4.

Table 1.
Performance accuracy of various RNN architectures.
Figure 3 shows the structure of the RNN used in this work, where the input are values obtained from the selected model bases in the SPM model.
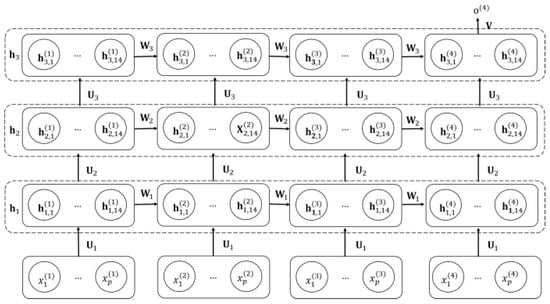
Figure 3.
The structure of an RNN (Time Steps 4, Units 14 and Layers 3).
2.7. Real-Time Adapted Forecasting
The increasing use of renewable power sources has produced an increase in intermittency and a ramping in the net load profile that requires additional control efforts to maintain frequency quality. For a complete treatment for STLF, we also provide a real-time adaptive STLF procedure to help system operators with a detailed view into the real-time power system condition, so as to aid in their decision making. A quasi-real time RNN-based forecasting model () with the objective of providing short-term load forecasts is described below.
- Load Forecasts Interpolation
In the first stage, the STLF results are interpolated to be a sequence with values in every 5-min period. The Cubic Hermite interpolation method is used to produce the load forecasts at 5-min intervals. This real time load data at 5-min intervals is then used in the second step to adaptively adjust the forecasting results.
- 2.
- Adaptive Load Forecasting
The correction value is the average difference between the actual and the forecasted load values in the past 15-min interval. In other words, it is the average of the three differences of the actual and forecasted load values calculated at 5-min intervals.
- 3.
- Exponentially Weighted Average
Finally, we use the EWMA to smooth the correction result. The exponential smoothing is given by the formula:
where is the ith corrected value.
3. Test Results
TPC system load data from January 2012 to December 2019 are used for testing the proposed method. The load data used here is the net load (the power served by all generators minus the TPC’s pumped storage load). The days in each year are divided into two classes: general days and special days. Special days refer to exceptional days that have their own load patterns (e.g., holidays, days experiencing a typhoon, etc.). General days refer to either typical working days or weekends. The main goal of this study is to provide STLF method for general days.
3.1. Training Data Selection
For the future day loads to be predicted, the training samples are chosen from historical days with a similar load pattern. The input-target pairs are the historical temperature (predicted and actual) and load data recorded during the corresponding days in the previous 28 days (4 weeks), together with the 6 weeks around the same period of the previous year and the predicted temperatures of the future days from TCWB. To select a subset of model bases as predictors for estimating the future day loads, a training set that has 70 daily loads and temperature data corresponding to the time period shown in Figure 4 is used. The forecasting process begins every morning at 9:00 a.m. to forecast demand up to next 7 days with 15 min resolution. The test results obtained when applying the method to forecast the load in year 2018–2019 are presented. STLF performance indices, such as the mean absolute mean error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), absolute performance error (APE) and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), are used to evaluate the forecasting accuracy of the model used [25].
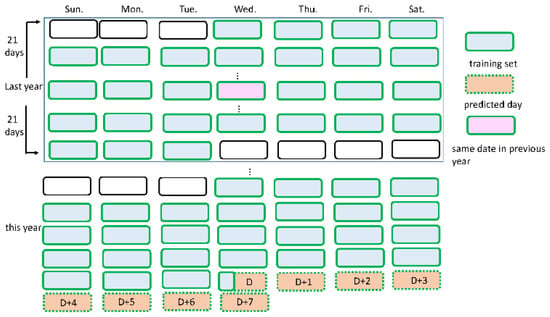
Figure 4.
The training set used for model training.
3.2. Comparison of Test Results Obtained from the Semi-Parametric Model and the RNN Model
The MAE, RMSE and MAPE of the accuracies of the load forecasts for every month from 2018–2019 are provided. The forecasting accuracies for the two models based on the historical temperatures serve as a baseline for comparison. In Table 2 the corresponding (D + 1)-day monthly MAE, RMSE and MAPE of the two models with historical temperatures are given in details. It can be seen that with the actual temperature, both models have good accuracies on the (D + 1)-day forecasts and the performances of the RNN model is especially outstanding on most of the months from 2018–2019 with annual averages of MAPE at 2.03, 1.70 respectively.

Table 2.
Comparisons of the Model Performances of the next (D + 1)-day Forecasting Accuracies of the SPM and RNN Models with Historical Temperatures.
3.3. Forecasts with Temperature Calibration
The actual temperature data indicate that temperature forecasting biases increase rapidly with large values (around 3 degrees). Figure 5 presents the MAPE time plots of two STLF models using original and adjusted temperature forecasts as inputs. From Figure 5 and Table 3, it can be seen that, after calibrating the forecasted temperature through bias correction based on the previous 28 days’ temperature forecasting biases, the forecasting accuracies are significantly improved.
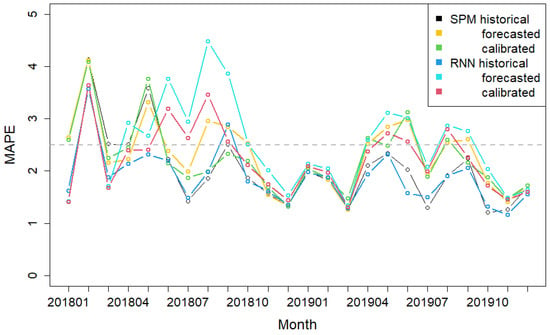
Figure 5.
The mean absolute percentage errors (MAPEs) of semi-parametric (SPM) and RNN models with the historical, forecasted and calibrated temperatures for the (D + 1)-day daily load patterns.

Table 3.
Performance Comparisons on mean absolute percentage errors (MAPEs) of semi-parametric (SPM) and RNN Models with the Historical, Forecasted and Calibrated Temperatures, for the next (D + 1)-day Load Patterns.
3.4. Real-Time Forecast Performance
The monthly performance comparisons for 2018 on the MAPE of the real-time D-day forecast for the next 6 h are given in Table 4. As the table shows, the annual averages of the MAPE for the RNN-based model are below 1%.

Table 4.
Performance Evaluation on MAPE of the Real-Time D-day Forecast Over the Next 6 Hours.
Figure 6 shows the performance of the model for a typical day of the studied period, June 22. As can be seen, the real time load pattern and the forecasting load pattern of the RNN model have similar trend patterns, but the forecasted curve is much lower. With the adjusted model, , however, the forecast accuracy improves significantly, obtaining an average error of 0.567% across the entire day.
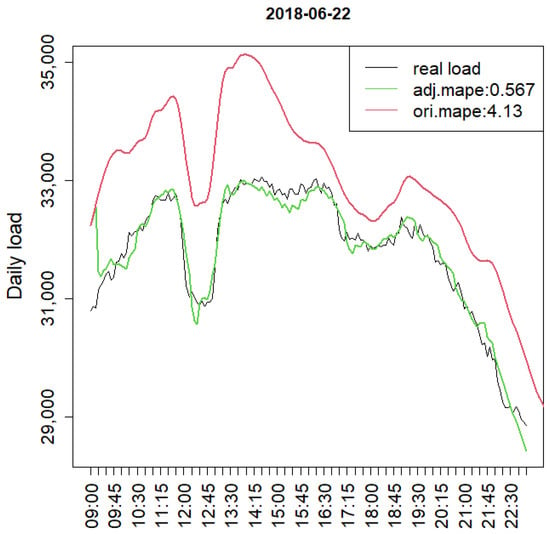
Figure 6.
Actual Load and Forecasts for 22 June 2018 by the RTLF and RNN Models, with 5 min Intervals.
3.5. Comparison of ANN, MIX, SPM and RNN Model Performance
In this sub-section, performance of different STLF methods are compared, including a two-stage Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model and an STLF model developed previously by TPC with special attention being given to the adjustments of the peak and nadir load forecasts [26], and a mixed model (MIX) with a weighted average of the ANN and against our basic RNN without Lasso variable selection or temperature calibration, where the weights are inversely proportional to the MAPEs of the previous day.
The performances of the next (D + 1)-day monthly MAPEs for these four forecasting models are presented in Table 5, for the year 2018. As the table shows, each model has its own advantages and disadvantages in daily load profile and max/min load forecasts. For example, the RNN model has the best overall yearly average performance for monthly MAPEs: 2.34 for the daily loads and 2.23 for daily peak loads. The SPM model, however, performs the best for nadir loads, with an average monthly MAPE of 2.18.

Table 5.
Performance Comparisons of the Monthly MAPE (Daily Load Average, Peak Load and Nadir Load) for the (D + 1)-day Forecasts with the Artificial Neural Network (ANN), mixed model (MIX), SPM and RNN Models.
The RNN performance is the best in the spring seasons and fairly good in the winter, when daily load patterns are stable. The SPM performance is the best in the summer season when the weather varies more. The MIX model has its best accuracy in the winter season. The ANN does very well in February and August, when there is the most uncertainty in the load pattern. Both the ANN and MIX models have large biases in June, however, especially for days adjacent to special days.
In more closely examining the daily MAPEs of the four models, we find that there are only 2 days for which all four models have MAPEs greater than 4, thus failing to catch the real load patterns: the day before Chinese New Year’s Eve in February and the “nine in one” election day in November. Figure 7 shows the actual and (D + 1)-day forecasts for the four models made on the previous D-day of these two days. All four models have similar forecasts with large biases to the real load on these two days. This indicates that these two days should be considered as special days in the future, so as to avoid large biases being included in the training samples for future forecasts, thereby helping improving the biases, particularly in February, for the SPM and RNN models.
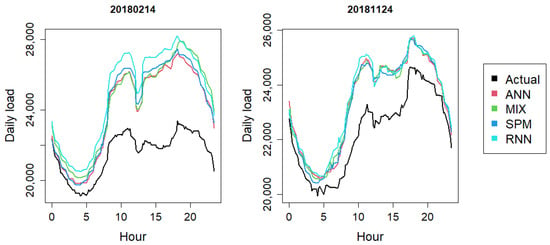
Figure 7.
Actual Load and (D + 1)-day Forecasts for 14 February and 24 November 2018 by the ANN (Artificial Neural Network), Mixed, SPM and RNN Models Made on the Previous D-Day.
Figure 8 presents the boxplots of daily MAPEs in 2018, after deleting the two days mentioned above. The performances of SPM and RNN are shown to be generally more robust, with fewer extremely large MAPEs. Figure 9 provides two subfigures with the actual and forecasted loads in two of the days where both ANN and MIX have large biased forecasts.
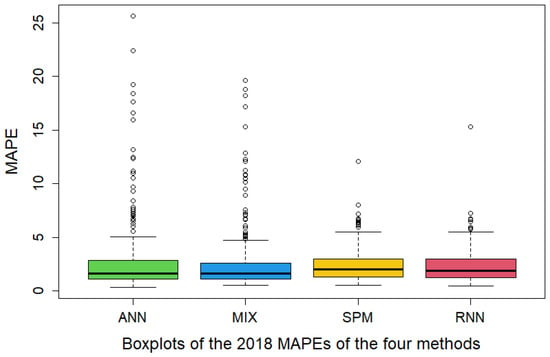
Figure 8.
Performance Comparisons of the Daily MAPEs for (D + 1)-day Forecasts with the ANN, Mixed, Semi-Parametric and RNN Models.
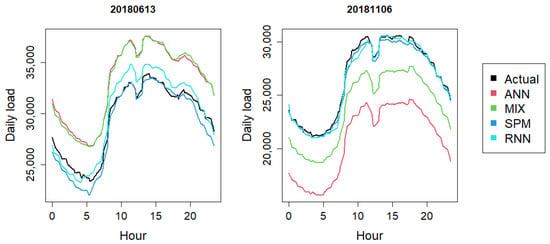
Figure 9.
Actual Load and (D + 1)-day Forecasts for 13 June and 16 November 2018 by the ANN, Mixed, SPM and RNN Models Made on the Previous D-day.
One of those days is 13 June 2018, where the MIX and ANN have similar daily forecasts, while the SPM and RNN perform reasonably well. The other day is 11 June 2018, where the MIX model is slightly better than the ANN, with smaller biases.
Another indication that the four models complement each other well is that only about 5% of forecasting days have MAPEs greater than 2.5 for all four models. This 5% compares to the 18% of days where the MAPEs of both ANN and MIX are both greater than 2.5, and the 14% of days where this is true for both SPM and RNN–a reduction of more than 9% in these cases. Among those days where all four models had large errors, about two thirds had explainable unexpected circumstances that caused the forecasting errors, such as TPC executing electric demand bidding, extreme weather conditions, or special events.
A new model can, in fact, be created by using an optimal weighted average of the ANN, SPM and RNN forecasts as such a hybrid model might further reduce the forecasting errors with proper time-varying weightings. How to choose appropriate optimal weights is a topic worthy of further investigation.
3.6. Performances of the (D + 2) to (D + 7) Day Forecasting Accuracies of the RNN Models
Figure 10 presents the monthly averages of the (D + 2)-day to (D + 7)-day forecasting MAPEs of the RNN models with forecasting temperatures from 2018–2019. Note that the seasonal patterns appear in both years, and, as they are the (D + 2)-day to (D + 7)-day forecasts, the higher MAPEs due to longer-range forecasts are to be expected.
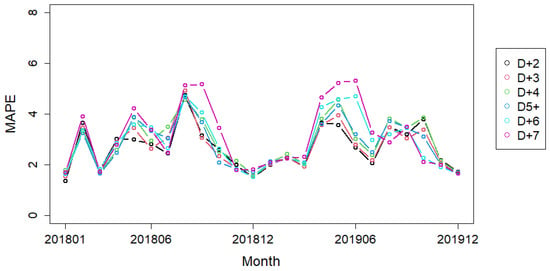
Figure 10.
The Model Performance of Monthly MAPEs on the Days (D + 2) to (D + 7), for the RNN Model.
4. Conclusions
An STLF method using a semi-parametric model and RNN with selected bases is presented. This tool has been adopted by TPC Operation Department for daily operation purposes since 2019. Due to the weather characteristics in Taiwan, test results indicate that STLF is especially challenging at season transitions: from spring to summer and from summer to autumn. The main advantage of an RNN-based STLF proposed here is that with the calibrated forecasted temperatures and features extracted from the load series, through ensembles of B-spline and multi-resolution bases after statistical variable selection approach, it can avoid the overfitting problems in the deep learning stage and adapt to these weather changing patterns earlier than other methods. Noticeable improvements of the MAPEs in 2019 for the RNN model with calibrating temperatures as compared with other methods are observed. However, the intra-day load forecasts are sometimes far off due to unexpected meteorologic factors. The real-time adaptive load forecasts for the next one hour with every 5-min interval and helps the system operator to adjust the ancillary service requirement to meet the electricity demand changes. In [15,16], both have used LSTM as the deep learning methodology; we have also tried the LSTM model, where results for the STLF show that the improvements on the accuracies of the forecasts are limited and the model is more complicated and takes much more time to compute, which is not that feasible for daily use in practice. In [16], a similar-days selection procedure is adopted, which is worthy of more studies to see the advantages and shortcomings of this approach for our dataset with fast changing weather patterns. Besides the techniques presented, an optimal model averaging various load forecasting models is a topic for further investigation, as is how to extend the training samples to special day load forecasts.
Author Contributions
T.-L.Y. has assisted in data analysis, programming, validation of result, and writing original draft. D.-S.J., S.-Y.H., Y.-Y.H. have contributed to programming and data analysis. H.-C.Y. has contributed to data curation and supervise the research study. M.-N.L.H. and C.-N.L. supervise the research study, and assistance in project administration, formal analysis and have reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Taiwan Power Company under contract No. TPC-546-4841-0405 and TPC-546-4840-0706.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Spline Bases Functions
Appendix A.1. Multi-Resolution Bases
The proposed class of basis functions in Tzeng and Huang [19] is developed using thin-plate splines (TPS). As presented in Tzeng and Huang [19], for given data observed at n distinct control points , a TPS function f(s) can be obtained by minimizing
where
is a smoothness penalty, and is a tuning parameter.
The multi-resolution spline basis functions , are defined in Tzeng and Huang [19] for the knot points , to have the following expression
where x = (1,s)’, , with and is the matrix with the (i,j)th element is the kth column of V, Vdiag () V’ is the eigen-decomposition of QQ’ with and
Appendix A.2. Cubic B-Spline Bases
B-splines are a clean, flexible way of making long splines with arbitrary order continuity. B-splines of order d are connected piecewise polynomial functions of degree d−1 defined over a grid of knots . The B-spline bases for all orders d, , may be defined through Cox-deBoor recurrence formula. A spline curve of order d, built from a linear combination of cubic B-spline basis functions , can be expressed as
where
and
with d = 4 corresponding to the cubic B-spline basis function. Note that are non-zero only for s in interval [.
Appendix B. Semi-Parametric Model
The mean function for the semi-parametric model mentioned above, at time of day t and daily time control point s, is given by
where
and are unknown coefficients to be estimated.
References
- Gross, G.; Galiana, F.D. Short-term load forecasting. Proc. IEEE 1987, 75, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Hyndman, R.J. Short-term load forecasting based on a semi-parametric additive model. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 27, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juberias, G.; Yunta, R.; Moreno, J.G.; Mendivil, C.A. A new ARIMA model for hourly load forecasting. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Transmission and Distribution Conference (Cat. No. 99CH36333), New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–16 April 1999; pp. 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Koch, T.; Xu, X. Regularized Partially Functional Autoregressive Model. 2019. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3482262 (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Vagropoulos, S.I.; Kardakos, E.G.; Simoglou, C.K.; Bakirtzis, A.G.; Catalão, J.P. Artificial neural network-based methodology for short-term electric load scenario generation. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Intelligent System Application to Power Systems (ISAP), Porto, Portugal, 11–16 September 2015; 2015; Volume 12, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kazeminejad, M.; Dehghan, M.; Motamadinejad, M.B.; Rastegar, H. A new short term load forecasting using multilayer perceptron. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Information and Automation, Colombo, Sri Lanka, 15–19 May 2006; pp. 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Humeau, S.; Wijaya, T.K.; Vasirani, M.; Aberer, K. Electricity load forecasting for residential customers: Exploiting aggregation and correlation between households. In Proceedings of the 2013 Sustainable Internet and ICT for Sustainability (SustainIT), Palermo, Italy, 30–31 October 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Cheng, X. Application of the generalized regression neural network in short-term load forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Xi’an, China, 27–29 May 2011; pp. 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.; Cardeira, C.; Calado, J.M.F. The daily and hourly energy consumption and load forecasting using artificial neural network method: A case study using a set of 93 households in Portugal. Energy Procedia 2014, 62, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lusis, P.; Khalilpour, K.R.; Andrew, L.; Liebman, A. Short-term residential load forecasting: Impact of calendar effects and forecast granularity. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, C.; Rezgui, Y.; Mourshed, M. Electrical load forecasting models: A critical systematic review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 35, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.M.; Maiorino, E.; Kampffmeyer, M.C.; Rizzi, A.; Jenssen, R. Recurrent Neural Networks for Short-Term Load Forecasting: An Overview and Comparative Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vermaak, J.; Botha, E.C. Recurrent neural networks for short-term load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1998, 13, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, M.; Li, R. Deep learning for household load forecasting-A novel pooling deep RNN. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 5271–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.; Yang, Y.; Pan, K.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.L.H.L.; Ng, W.W.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, T.; Shahidehpour, M.; et al. Multi-view neural network ensemble for short and mid-term load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yuan, J.; Chen, L. Short-Term Load Forecasting Using EMD-LSTM Neural Networks with a Xgboost Algorithm for Feature Importance Evaluation. Energies 2017, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H. The adaptive Lasso and its oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2006, 101, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzeng, S.; Huang, H.C. Resolution adaptive fixed rank kriging. Technometrics 2018, 60, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, J.M. Accurate monotonicity preserving cubic interpolation. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 1983, 4, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steadman, R.G. A universal scale of apparent temperature. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1984, 23, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hoerl, A.E. Applications of Ridge Analysis to regression Problems. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1962, 58, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Botchkarev, A. Performance metrics (error measures) in machine learning regression, forecasting and prognostics: Properties and typology. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.03006. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, Y.Y.; Tung, T.T.; Yeh, H.C.; Lu, C.N. Two-stage artificial network model for short-term load forecasting. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).