Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm as Optimal Feature Selection for Power Quality Disturbance Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Power Quality Disturbance Signals
3. Feature Extraction
3.1. Wavelet Transform
3.2. Multi-Resolution Analysis
3.3. Feature Vector Arrangement
4. Probabilistic Neural Network as a Classifier
5. Proposed Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm for Optimal Feature Selection
5.1. Salp Swarm Algorithm
5.2. Proposed Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm
5.2.1. Proposed Approaches for a Modification of Salp Movement
5.2.2. Proposed Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Optimal Number of Selected Features for the Proposed Classification System
6.2. PQD Classification Accuracy Using the Adaptive SSA
6.3. Classification Pergormance under a Noisy Environment
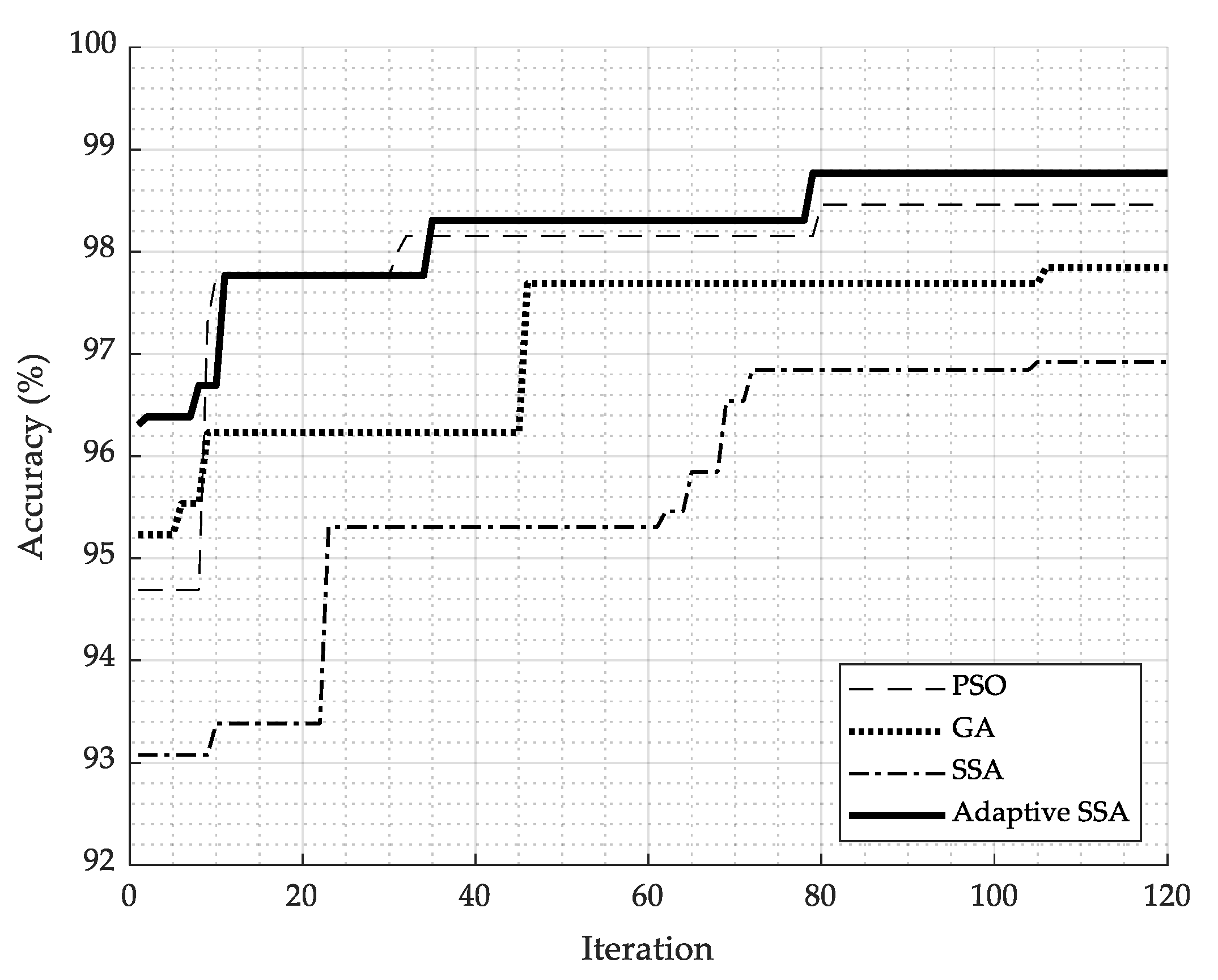
6.4. Convergence Rate
6.5. Classification Performance Based on the Real Dataset
6.6. Comparison of Classification Performance to the Existing Works
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kandananond, K. Forecasting electricity demand in Thailand with an artificial neural network approach. Energies 2011, 4, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithapon, C.; Ghosh, P.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Chatthaworn, R. Optimization of electric vehicle charging scheduling in urban village networks considering energy arbitrage and distribution cost. Energies 2020, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaboot, N.; Srithapon, C.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. Increasing benefits in high PV penetration distribution system by using battery enegy storage and capacitor placement based on salp swarm algorithm. Energies 2019, 12, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithapon, C.; Fuangfoo, P.; Ghosh, P.K.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Chatthaworn, R. Surrogate-Assisted multi-objective probabilistic optimal power flow for distribution network with photovoltaic generation and electric vehicles. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34395–34414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonluk, P.; Khunkitti, S.; Fuangfoo, P.; Siritaratiwat, A. Optimal siting and sizing of battery energy storage: Case study seventh feeder at Nakhon Phanom substation in Thailand. Energies 2021, 14, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonluk, P.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Fuangfoo, P.; Khunkitti, S. Optimal siting and sizing of battery energy storage systems for distribution network of distribution system operators. Batteries 2020, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaboot, N.; Chatthaworn, R.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Surawanitkun, C.; Khunkitti, P. Increasing PV penetration level in low voltage distribution system using optimal installation and operation of battery energy storage. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 1641911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, W.G.; El-Hawary, M.E. Power quality evaluation in smart grids considering modern distortion in electric power systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Recommended Practice for Monitoring Electric Power Quality; 1159-2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019.
- CENELEC-EN 50160-Voltage Characteristics of Electricity Supplied by Public Electricity Networks. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/13493775/EN50160 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- IEC 61000-4-30:2015 RLV. IEC Webstore. Electromagnetic Compatibility, EMC, Smart City. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/22270 (accessed on 3 December 2020).
- Gazzana, D.S.; Ferreira, G.D.; Bretas, A.S.; Bettiol, A.L.; Carniato, A.; Passos, L.F.N.; Ferreira, A.H.; Silva, J.E.M. An integrated technique for fault location and section identification in distribution systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2014, 115, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, S.; Farsa, A.R.; Ghaffarzadeh, N. Identification of optimal features for fast and accurate classification of power quality disturbances. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2018, 116, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.K.; Mohanty, A.; Panigrahi, T. Power quality analysis in solar PV integrated microgrid using independent component analysis and support vector machine. Optik 2019, 180, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Fontova, A.; Torrens, P.C.; Bosch, R. Power quality disturbances assessment during unintentional islanding scenarios. A contribution to voltage sag studies. Energies 2019, 12, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Tang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yao, W. An automatic identification framework for complex power quality disturbances based on multi-fusion convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Che, Y. Power quality disturbance classification based on dwt and multilayer perceptron extreme learning machine. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, H.S.; Dash, P.K.; Biswal, B. Power quality time series data mining using S-transform and fuzzy expert system. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2010, 10, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados-Lieberman, D.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J.; Osornio-Rios, R.A. A Hilbert transform-based smart sensor for detection, classification, and quantification of power quality disturbances. Sensors 2013, 13, 5507–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, M.; Dash, P.K. Detection and characterization of multiple power quality disturbances with a fast S-transform and decision tree based classifier. Digit. Signal Process. A Rev. J. 2013, 23, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoos, A.A.; Khorshidian Mianaei, P.; Rayatpanah Ghadikolaei, M. Combined VMD-SVM based feature selection method for classification of power quality events. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2016, 38, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevitha, S.R.S.; Mabel, M.C. Novel optimization parameters of power quality disturbances using novel bio-inspired algorithms: A comparative approach. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 42, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu, S.; Saraç, Z. Classification of power quality disturbances by 2D-Riesz transform, multi-objective grey wolf optimizer and machine learning methods. Digit. Signal Process. A Rev. J. 2020, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhar Samanta, I.; Rout, P.K.; Mishra, S. An optimal extreme learning-based classification method for power quality events using fractional Fourier transform. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 4979–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, O.; Rioual, P.; Meunier, M. Detection and measurement of power quality disturbances using wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2000, 15, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, F.; Baños, R.; Alcayde, A.; Montoya, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Power quality: Scientific collaboration networks and research trends. Energies 2018, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.H.; Zanghi, R.; Fortes, M.Z.; Sotelo, G.G.; Silva, R.B.M.; Souza, J.C.S.; Guimarães, C.H.C.; Gomes, S. A survey on intelligent system application to fault diagnosis in electric power system transmission lines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 136, 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, P.; Madhira, S.T.S.; Ul Haque, A.; Meng, J.; Pineda, R.L. Forecasting power output of solar photovoltaic system using wavelet transform and artificial intelligence techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2012, 12, 332–337. [Google Scholar]
- Gunal, S.; Gerek, O.N.; Ece, D.G.; Edizkan, R. The search for optimal feature set in power quality event classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 10266–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, S.; Yildirim, S.; Poyraz, M. Energy and entropy-based feature extraction for locating fault on transmission lines by using neural network and wavelet packet decomposition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2008, 34, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshmand, R.; Enshaee, A. Detection and classification of single and combined power quality disturbances using fuzzy systems oriented by particle swarm optimization algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizjak, B.; Planinšič, P. Classification of power disturbances using fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 12th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference EPE-PEMC 2006, Portoroz, Slovenia, 30 August–1 September 2006; pp. 1356–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.H.; Tseng, Y.F. A novel analytic method of power quality using extension genetic algorithm and wavelet transform. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 12491–12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Rodríguez, J.C.; Torres, F.J.; Borrás, M.D. Hybrid machine learning models for classifying power quality disturbances: A comparative study. Energies 2020, 13, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Zhang, S.; Cai, G.; Xu, D. Power quality disturbances recognition based on a multiresolution generalized S-transform and a PSO-improved decision tree. Energies 2015, 8, 549–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Bhende, C.N.; Panigrahi, B.K. Detection and classification of power quality disturbances using S-transform and probabilistic neural network. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2008, 23, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedero, I.; León, C.; Ropero, J.; García, A.; Elena, J.M.; Montaño, J.C. Classification of electrical disturbances in real time using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhende, C.N.; Mishra, S.; Panigrahi, B.K. Detection and classification of power quality disturbances using S-transform and modular neural network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Shen, Y.X. Optimal feature selection for power-quality disturbances classification. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26, 2342–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Peng, H.; Cai, G.; Chen, J. Power quality disturbances feature selection and recognition using optimal multi-resolution fast S-Transform and CART algorithm. Energies 2016, 9, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Singh, S.N. Optimal feature selection via NSGA-II for power quality disturbances classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Dash, P.K.; Panigrahi, B.K. Power quality disturbance classification using fuzzy C-Means algorithm and adaptive particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erişti, H.; Yıldırım, Ö.; Erişti, B.; Demir, Y. Optimal feature selection for classification of the power quality events using wavelet transform and least squares support vector machines. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 49, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahila, R.; Sadasivam, V.; Manimala, K. An integrated PSO for parameter determination and feature selection of ELM and its application in classification of power system disturbances. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 32, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorti, T.; Dash, P.K. Multiclass power quality events classification using variational mode decomposition with fast reduced kernel extreme learning machine-based feature selection. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2018, 12, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhu, T.; Pan, G.; Chen, S.; Zhong, Q.; Wei, Y. Power quality disturbance recognition using VMD-based feature extraction and heuristic feature selection. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, H.; Vahidi, B.; Naghizadeh, R.A.; Hosseinian, S.H. Power quality disturbance classification using a statistical and wavelet-based Hidden Markov model with Dempster-Shafer algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 47, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-D.; Sian, H.-W.; Wang, M.-H.; Liao, R.-M. Application of extension neural network with discrete wavelet transform and Parseval’s theorem for power quality analysis. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarweh, J.; Mustaklem, R.; Saleem, A.; Mohamed, O. The application of discrete wavelet transform to classification of power transmission system faults. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Jordan International Joint Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, JEEIT 2019, Amman, Jordan, 9–11 April 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Aker, E.; Othman, M.L.; Veerasamy, V.; Aris, I.B.; Wahab, N.I.A.; Hizam, H. Fault detection and classification of shunt compensated transmission line using discrete wavelet transform and naive bayes classifier. Energies 2020, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, S.; Mohanty, S. Localization and classification of power quality disturbances using maximal overlap discrete wavelet transform and data mining based classifiers. IFAC PapersOnLine 2016, 49, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- César, D.G.; Valdomiro, V.G.; Gabriel, O.P. Automatic power quality disturbances detection and classification based on discrete wavelet transform and artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/PES Transmission & Distribution Conference and Exposition, Caracas, Venezuela, 15–18 August 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erişti, H.; Demir, Y. A new algorithm for automatic classification of power quality events based on wavelet transform and SVM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4094–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamchuen, S.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Fuangfoo, P.; Suthisopapan, P.; Khunkitti, P. High-Accuracy power quality disturbance classification using the adaptive ABC-PSO as optimal feature selection algorithm. Energies 2021, 14, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decanini, J.G.M.S.; Tonelli-Neto, M.S.; Malange, F.C.V.; Minussi, C.R. Detection and classification of voltage disturbances using a Fuzzy-ARTMAP-wavelet network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanirajan, P.; Suresh Kumar, V. Wavelet-Based power quality disturbances detection and classification using RBFNN and fuzzy logic. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 17, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Abubakar, M.; Liu, H.; Hussain, F. Power quality disturbance monitoring and classification based on improved PCA and convolution neural network for wind-grid distribution systems. Energies 2019, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Xu, D.; Liu, X.; Lin, L. Power quality disturbances classification based on S-transform and probabilistic neural network. Neurocomputing 2012, 98, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.R.; Ray, P.K.; Kishor, N.; Panigrahi, B.K. Classification of disturbances in hybrid DG system using modular PNN and SVM. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 44, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Połap, D.; Capizzi, G.; Sciuto, G.L.; Kośmider, L.; Frankiewicz, K. Small lung nodules detection based on local variance analysis and probabilistic neural network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, M.R.G.; Somu, N.; Kirthivasan, K.; Sriram, V.S.S. A Hypergraph and arithmetic residue-based probabilistic neural network for classification in intrusion detection systems. Neural Netw. 2017, 92, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chaovalitwongse, W.A. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization algorithm with local search for multimodal functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Shi, Z. MPSO: Modified particle swarm optimization and its applications. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2018, 41, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp swarm algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Li, C.Y. Adaptive levy-assisted salp swarm algorithm: Analysis and optimization case studies. Math. Comput. Simul. 2021, 181, 380–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Shehab, M.; Alshinwan, M.; Alabool, H. Salp swarm algorithm: A comprehensive survey. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 11195–11215. [Google Scholar]
- Kandiri, A.; Sartipi, F.; Kioumarsi, M. Predicting compressive strength of concrete containing recycled aggregate using modified ann with different optimization algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, H.; Habib, M.; Almomani, I.; Eshtay, M.; Aljarah, I. Optimizing extreme learning machines using chains of salps for efficient android ransomware detection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Cai, W.; Yang, S.; Cheng, X.; Frank, I. Renyi’s entropy based multilevel thresholding using a novel meta-heuristics algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Alghamdi, T.; Khan, Z.; Fatima, A.; Abid, S.; Khalid, A.; Javaid, N. Enhanced evolutionary sizing algorithms for optimal sizing of a stand-alone PV-WT-battery hybrid system. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PQube—Live World Map of Power Quality. Available online: http://map.pqube.com/ (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Biswal, B.; Mishra, S. Power signal disturbance identification and classification using a modified frequency slice wavelet transform. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2014, 8, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Biswal, M.; Mishra, S.; Jalaja, R. Automatic classification of power quality events using balanced neural tree. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Dash, P.K.; Mishra, S. A hybrid ant colony optimization technique for power signal pattern classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 6368–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achlerkar, P.D.; Samantaray, S.R.; Sabarimalai Manikandan, M. Variational mode decomposition and decision tree based detection and classification of power quality disturbances in grid-connected distributed generation system. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3122–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar, S.A.; Waghmare, L.M. Integrated DWT-FFT approach for detection and classification of power quality disturbances. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 61, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.K.; Mohanty, S.R.; Kishor, N.; Catalao, J.P.S. Optimal feature and decision tree-based classification of power quality disturbances in distributed generation systems. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Label | Disturbance Classes | Mathematic Equations | Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Pure sine | ||
| C2 | Sag | ||
| C3 | Swell | ||
| C4 | Interruption | ||
| C5 | Harmonic | ||
| C6 | Impulsive transient | ||
| C7 | Oscillatory transient | ||
| C8 | Flicker | ||
| C9 | Notch | ||
| C10 | Spikes | ||
| C11 | Sag with harmonic | ||
| C12 | Swell with harmonic | ||
| C13 | Interruption with harmonic |
| Parameter | Statistical Equation | Parameter | Statistical Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | RMS | ||
| Entropy | Range | ||
| Standard deviation | Log-energy entropy | ||
| Mean | Crest factor | ||
| Kurtosis | Form factor | ||
| Skewness |
| Feature Vector |
|---|
| Number of Feature Data | Feature Selected | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37 | 65.62 |
| 2 | 72 21 | 75.30 |
| 3 | 36 1 14 | 92.15 |
| 4 | 7 16 20 14 | 94.77 |
| 5 | 18 37 14 8 7 | 95.62 |
| 6 | 2 40 5 16 7 58 | 97.31 |
| 7 | 40 6 7 17 16 82 14 | 98.23 |
| 8 | 32 7 10 16 40 21 9 19 | 97.31 |
| 9 | 70 18 10 4 17 2 85 41 9 | 97.08 |
| 10 | 2 10 7 2 6 99 40 6 5 16 | 97.62 |
| 11 | 51 7 40 16 11 4 39 6 12 4 12 | 97.77 |
| 12 | 41 38 43 27 40 9 29 7 16 47 26 18 | 98.77 |
| 13 | 54 7 63 38 40 54 19 13 24 17 22 57 18 | 97.92 |
| Iteration | Selected Features | Classification Accuracy (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75 | 7 | 8 | 14 | 1 | 11 | 90 | 8 | 15 | 49 | 16 | 3 | 10 | 92.15 |
| 76 | 7 | 92 | 9 | 18 | 17 | 33 | 15 | 30 | 28 | 8 | 89 | 14 | 92.00 |
| 77 | 9 | 70 | 27 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 38 | 20 | 17 | 5 | 52 | 7 | 78.46 |
| 78 | 20 | 31 | 14 | 49 | 44 | 12 | 31 | 16 | 9 | 3 | 35 | 4 | 94.31 |
| 79 | 41 | 38 | 43 | 27 | 40 | 9 | 29 | 7 | 16 | 47 | 26 | 18 | 98.77 |
| 80 | 24 | 22 | 29 | 13 | 24 | 6 | 12 | 4 | 11 | 25 | 9 | 6 | 89.00 |
| 81 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 7 | 12 | 4 | 22 | 13 | 15 | 10 | 9 | 3 | 93.23 |
| 82 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 12 | 51 | 90 | 5 | 88.38 |
| 83 | 8 | 6 | 43 | 3 | 4 | 13 | 4 | 10 | 8 | 25 | 26 | 2 | 79.46 |
| Type of PQD | Classification Accuracy (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Type (Energy) | 1 Type (Entropy) | 1 Type (Kurtosis | 3 Types (Energy, Entropy, S.D.) | 5 Types (Energy, Entropy, S.D., Mean, Kurtosis) | All Types | Adaptive SSA | |
| Pure sine | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sag | 73 | 76 | 77 | 86 | 96 | 98 | 96 |
| Swell | 82 | 89 | 56 | 95 | 98 | 99 | 98 |
| Interruption | 81 | 96 | 60 | 96 | 100 | 99 | 100 |
| Harmonic | 97 | 100 | 99 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Sag with harmonic | 59 | 66 | 72 | 81 | 89 | 78 | 93 |
| Swell with harmonic | 86 | 94 | 68 | 95 | 98 | 96 | 97 |
| Interruption with harmonic | 67 | 93 | 97 | 93 | 99 | 93 | 100 |
| Flicker | 72 | 84 | 99 | 92 | 99 | 100 | 100 |
| Oscillatory transient | 75 | 92 | 97 | 97 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Impulsive transient | 74 | 85 | 100 | 90 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Periodic notch | 100 | 53 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 77 | 100 |
| Spike | 47 | 73 | 26 | 61 | 77 | 87 | 100 |
| Overall accuracy | 77.92 | 84.69 | 80.85 | 91.23 | 96.61 | 94.38 | 98.77 |
| Noise Magnitude | Classification Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Features | PSO | GA | SSA | Adaptive SSA | |
| Without noise | 94.38 | 98.46 | 97.85 | 96.85 | 98.77 |
| 10 dB | 55.26 | 72.31 | 69.38 | 60.55 | 72.86 |
| 20 dB | 74.89 | 88.43 | 77.85 | 81.17 | 89.11 |
| 30 dB | 87.20 | 93.60 | 92.38 | 89.66 | 93.91 |
| 40 dB | 90.03 | 94.46 | 89.85 | 90.52 | 94.95 |
| 50 dB | 91.45 | 95.94 | 96.31 | 91.63 | 96.37 |
| Feature Selection Algorithms | Overall Accuracy (%) | Required Iterations |
|---|---|---|
| PSO | 98.46 | 80 |
| GA | 97.85 | 106 |
| SSA | 96.85 | 105 |
| Adaptive SSA | 98.77 | 79 |
| Signal Type | Classification Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| Pure sine | 97.5 |
| Sag | 100 |
| Swell | 100 |
| Interruption | 95 |
| Harmonic | 100 |
| Overall accuracy | 98.5 |
| Reference | Number of PQD Types | Feature Extraction Type | Classification Technique | Optimal Feature Selection Algorithm | Overall Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | 5 | DWT | LS-SVM | k-means +Apriori algorithm | 98.88 |
| [72] | 8 | Modified frequency slice wavelet | PNN | 97.70 | |
| [73] | 8 | Hilbert–Huang transform | NN | 97.90 | |
| [74] | 9 | Time-time transform | Decision tree | Ant Colony Optimization | 95.97 |
| [42] | 9 | ST | Fuzzy C-means | Adaptive PSO | 96.33 |
| [21] | 9 | ST + VMD | SVM | Sequential forward selection | 99.66 |
| [75] | 9 | VDM | Decision tree | 98.56 | |
| [44] | 10 | DWT | extreme learning machine | PSO | 97.60 |
| [76] | 10 | DWT + FFT | Threshold | 90.04 | |
| [46] | 13 | VMD | OVR-SVM | Permutation Entropy+ Fisher Score | 97.6 |
| [77] | 13 | hyperbolic S-transform | Decision tree | GA | 99.5 |
| [45] | 15 | VDM | Fast reduced kernel extreme learning machine | Fischer linear discriminant analysis | 98.82 |
| This work | 13 | WT | PNN | Adaptive SSA | 98.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chamchuen, S.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Fuangfoo, P.; Suthisopapan, P.; Khunkitti, P. Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm as Optimal Feature Selection for Power Quality Disturbance Classification. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5670. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125670
Chamchuen S, Siritaratiwat A, Fuangfoo P, Suthisopapan P, Khunkitti P. Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm as Optimal Feature Selection for Power Quality Disturbance Classification. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(12):5670. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125670
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamchuen, Supanat, Apirat Siritaratiwat, Pradit Fuangfoo, Puripong Suthisopapan, and Pirat Khunkitti. 2021. "Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm as Optimal Feature Selection for Power Quality Disturbance Classification" Applied Sciences 11, no. 12: 5670. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125670
APA StyleChamchuen, S., Siritaratiwat, A., Fuangfoo, P., Suthisopapan, P., & Khunkitti, P. (2021). Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm as Optimal Feature Selection for Power Quality Disturbance Classification. Applied Sciences, 11(12), 5670. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11125670






