Laboratory Performance Evaluation of Hot-Mix Asphalt Mixtures with Different Design Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design
3. Materials
3.1. Asphalt Binder
3.2. Aggregates
3.3. Specimen Preparation
4. Test Procedures
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. High-Temperature Performance
5.2. Low-Temperature Performance
5.3. Fatigue Performance
5.4. Dynamic Modulus
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jenks, C.W.; Jencks, C.F.; Harrigan, E.T.; Adcock, M.; Delaney, E.P.; Freer, H. NCHRP Report 673: A Manual for Design of Hot Mix Asphalt with Commentary; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Sun, L.J.; Luo, D. Design Process of Asphalt Mixture Incorporating Compaction Effort Variable. J. Mater. Civil Eng. (accepted; in press).
- Khosla, N.P.; Ayyala, D. A performance-based evaluation of Superpave design gyrations for high traffic surface mixes. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 104, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qarouach, S. An Investigation of the Effect of Ndesign Values on Performance of Superpave Mixtures; Master of Science, North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Giunta, M.; Pisano, A.A. One-dimensional visco-elastoplastic constitutive model for asphalt concrete. Multidiscip. Model Mater. Struct. 2006, 2, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diefenderfer, S.D.; Bowers, B.F. Initial Approach to Performance (Balanced) Mix Design: The Virginia Experience. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.W.; Bonaquist, R.F. Volumetric Requirements for Superpave Mix Design (Vol. 567); Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Team, W.F. Performance of Coarse-Graded Mixes at Westrack–Premature Rutting; Report No. FHWA-RD-99-134; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Haddock, J.; Pan, C.; Feng, A.; White, T.D. Effect of gradation on asphalt mixture performance. Transp. Res. Rec. 1999, 1681, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.B.; Pais, J.C.; Prates, M.; Barros, R.; Langlois, P.; Leclerc, A.M. Effect of aggregate gradation on fatigue life of asphalt concrete mixes. Transp. Res. Rec. 1998, 1630, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyalaa, D.; Qarouacha, S.; Khoslaa, N.P.; Tayebalia, A.A. An Investigation of Ndesign Values for Superpave Surface Mixtures. In Asphalt Paving Technology 2014: Volume 83; Journal of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015; p. 345. [Google Scholar]
- Prowell, B.D.; Brown, E.R. Superpave Mix Design: Verifying Gyration Levels in the Ndesign Table (Vol. 573); Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Communications of China. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; JTGE20-2011; China Communication Press (in Chinese): Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Sun, L.J.; Liu, L.P. Performance-based Design of Hard Asphalt Mixtures Based on Different Compaction Effort Variable. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J. Structural Behavior Study for Asphalt Pavements; China Communications: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Huang, B.; Xu, Z. Uniaxial penetration testing for shear resistance of hot-mix asphalt mixtures. Transp. Res. Rec. 2006, 1970, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, L. Development and calibration of shear-based rutting model for asphalt concrete layers. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2017, 18, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Communications of China. Specifications for Design of Highway Asphalt Pavement: JTG D50-2017; China Communication Press (in Chinese): Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO, T321-03. Standard Method of Test for Determining the Fatigue Life of Compacted Hot-Mix Asphalt (HMA) Subjected to Repeated Flexural Bending; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO): Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- AASHTO, T342-11. Standard Method of Test for Determining Dynamic Modulus of Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA); American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO): Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
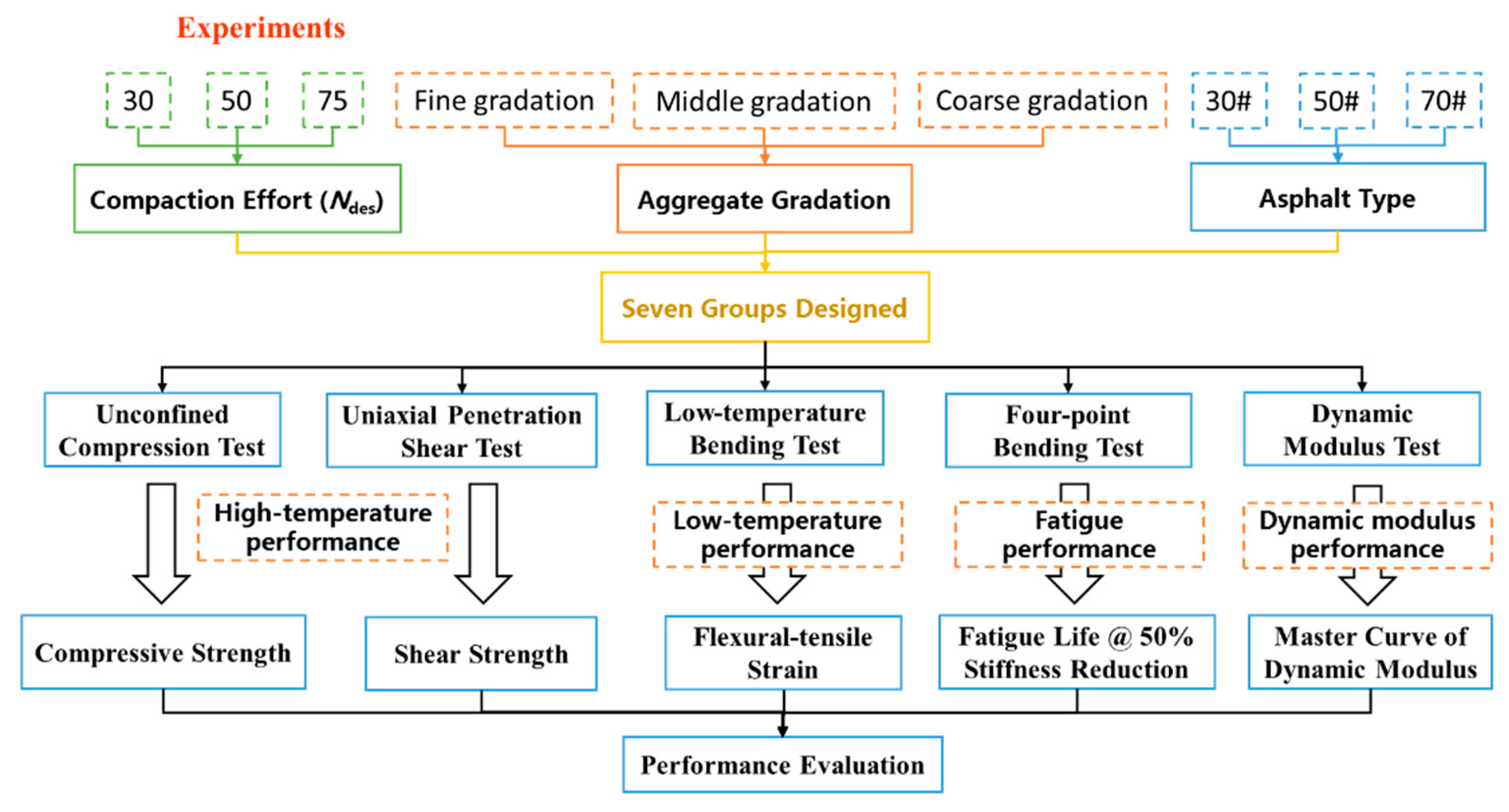

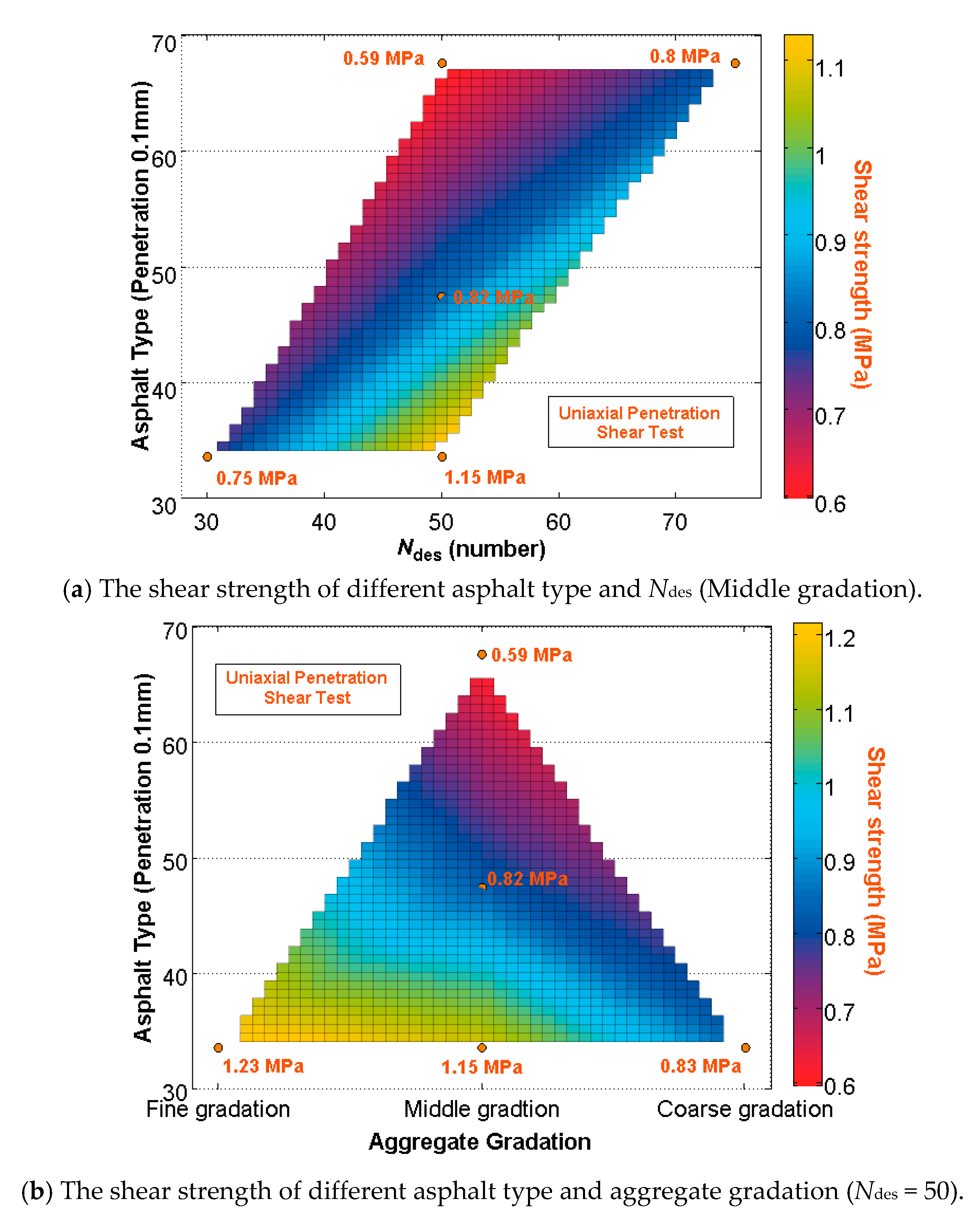

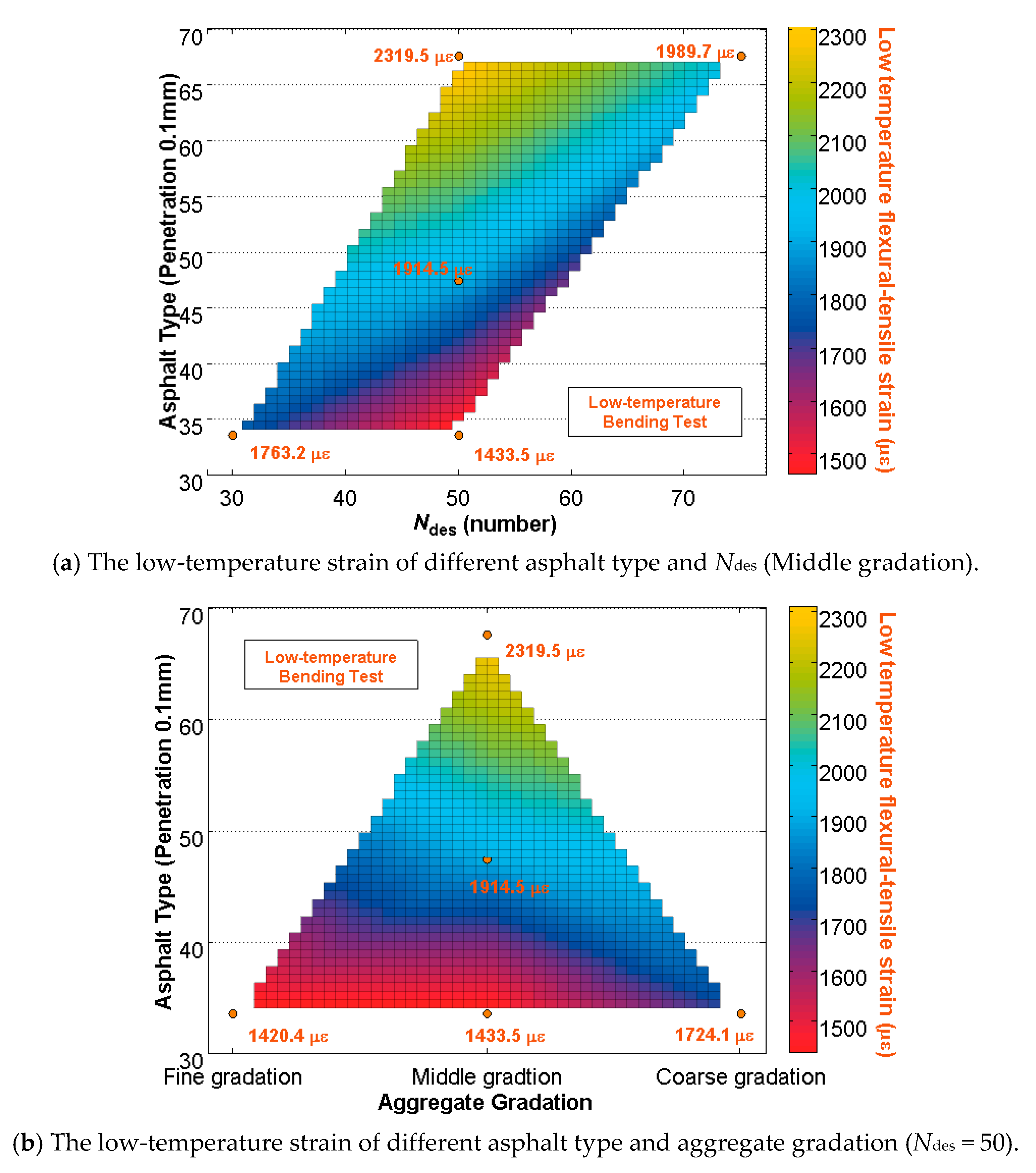
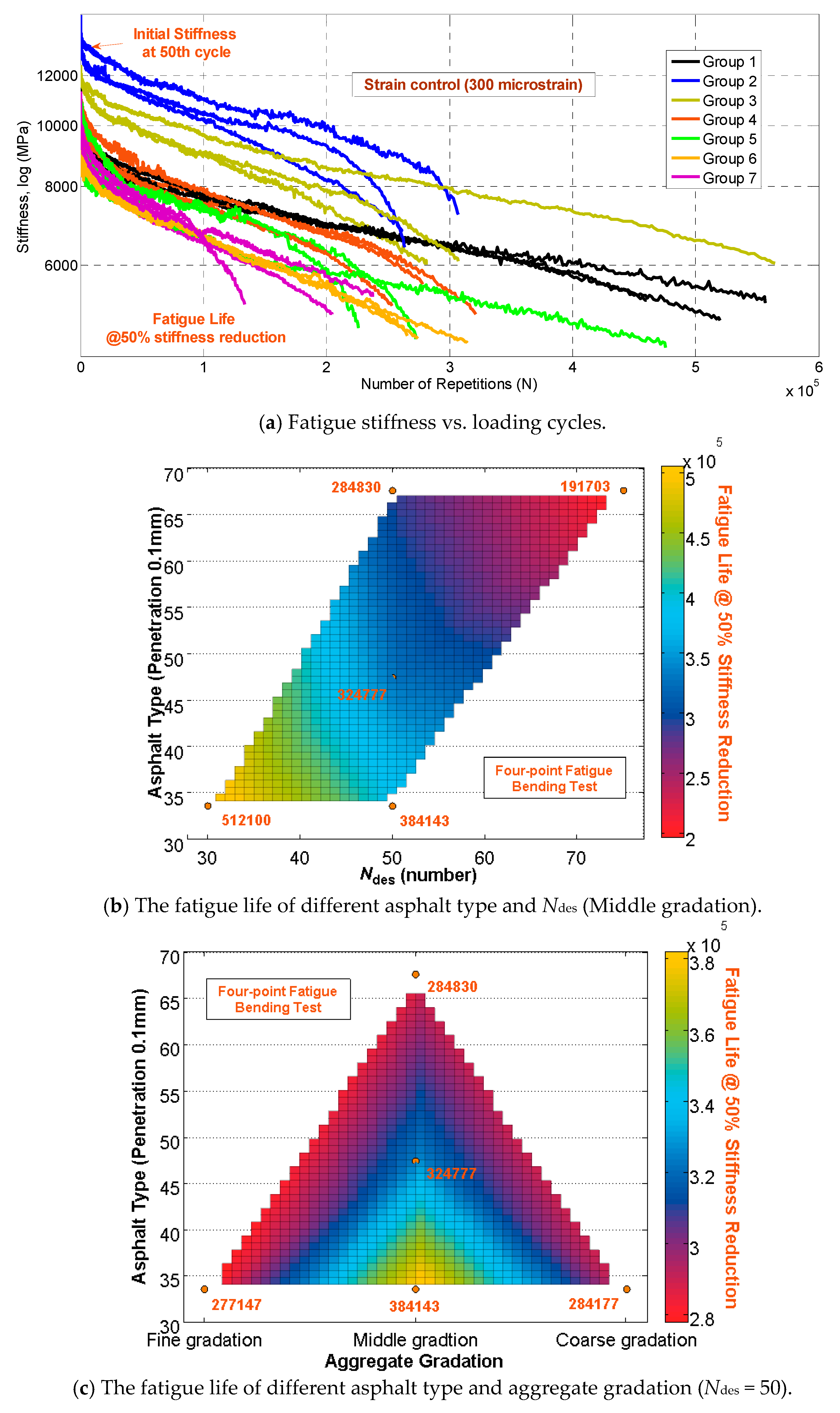
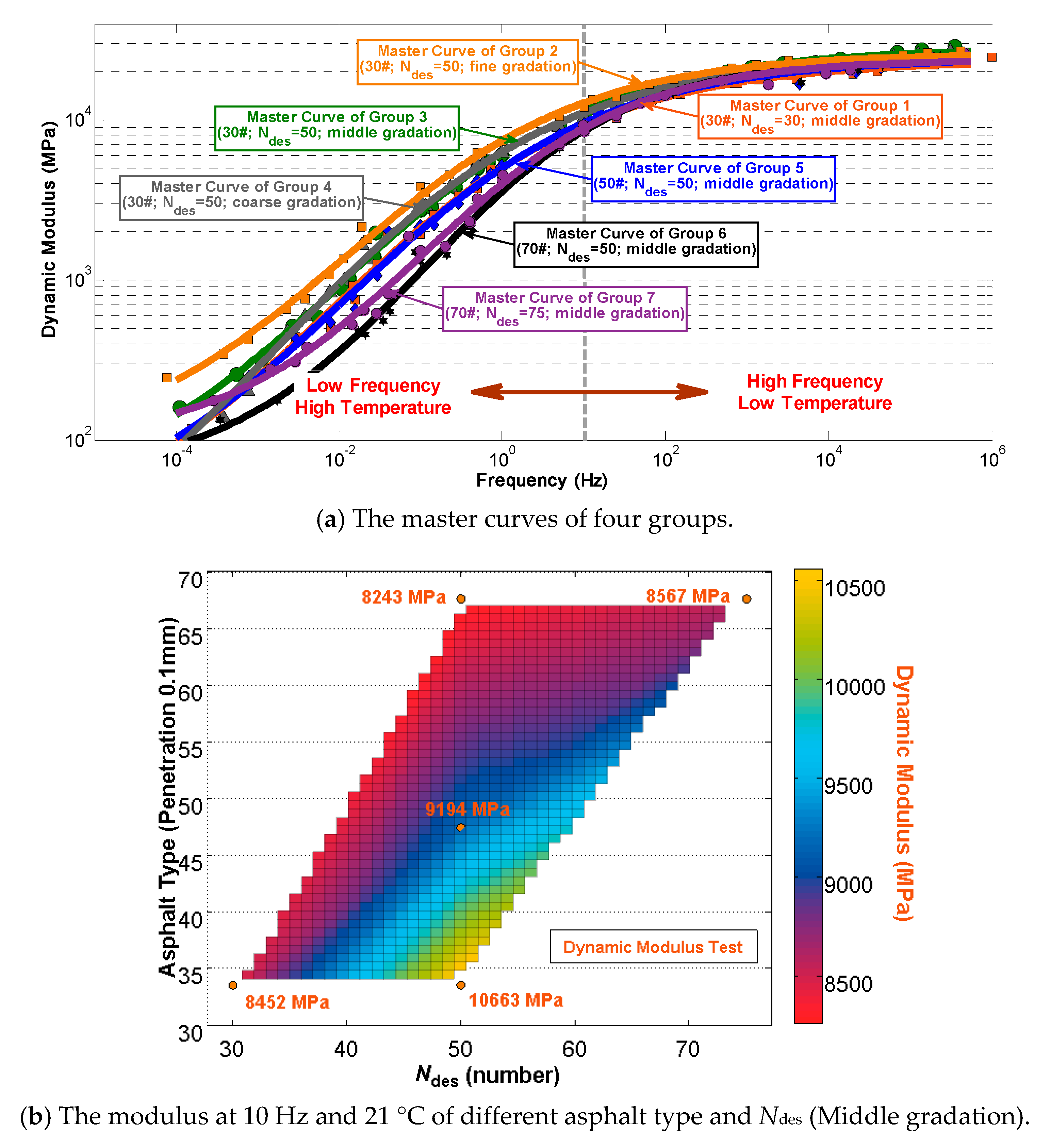
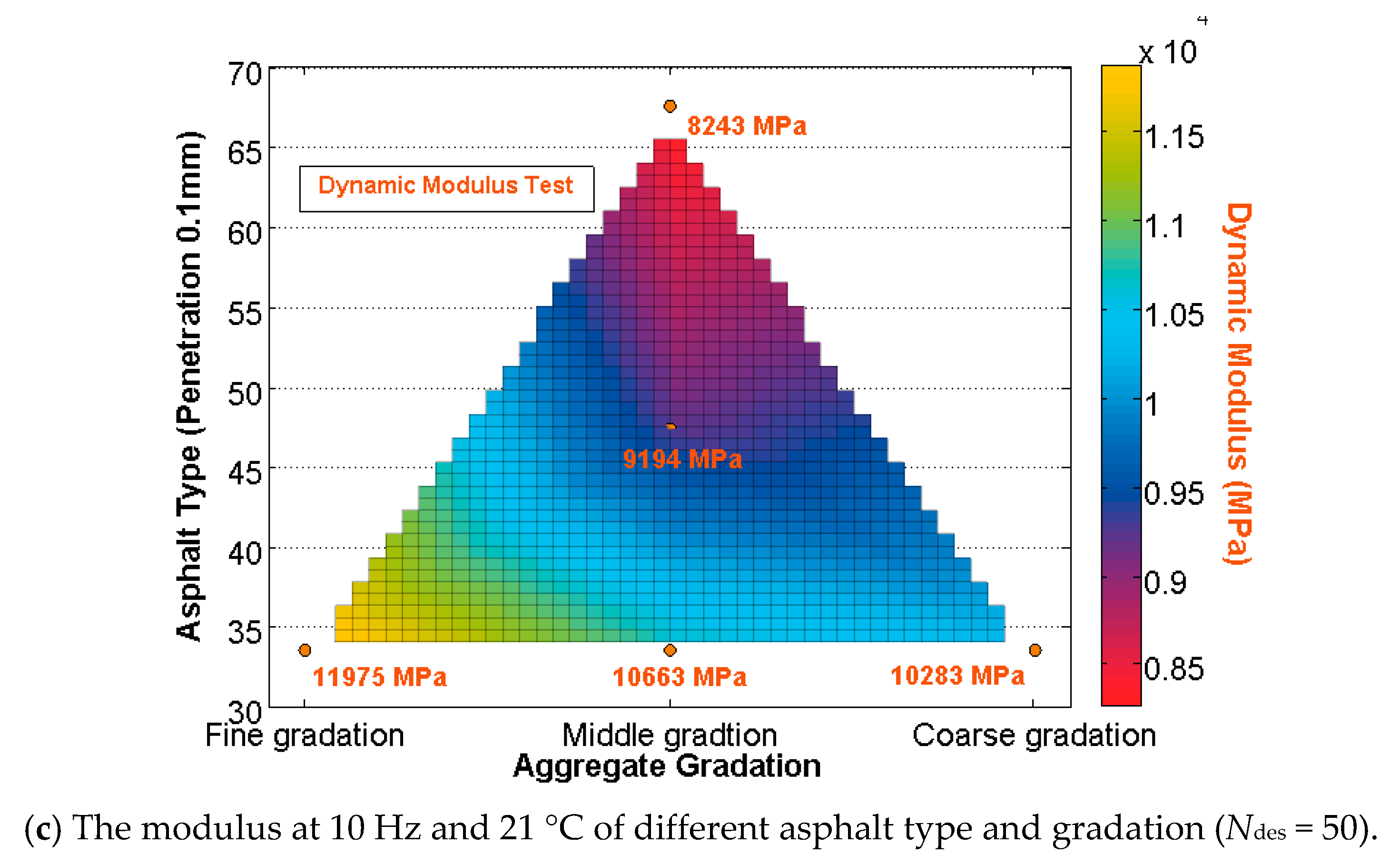
| Experiment | Design Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregate Gradation | Ndes (numbers) | Asphalt Type | |
| Group 1 | Middle gradation | 30 | 30# |
| Group 2 | Fine gradation | 50 | 30# |
| Group 3 | Middle gradation | 50 | 30# |
| Group 4 | Coarse gradation | 50 | 30# |
| Group 5 | Middle gradation | 50 | 50# |
| Group 6 | Middle gradation | 50 | 70# |
| Group 7 | Middle gradation | 75 | 70# |
| Aggregate Gradation | Sieve Size | 19 | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 |
| Fine Gradation | 100 | 97.5 | 93.5 | 84.1 | 66.6 | 38.9 | 22.9 | 18.4 | 11.4 | 8.6 | 6.4 | |
| Middle Gradation | 100 | 95.8 | 89.2 | 73.6 | 48.0 | 28.2 | 17.2 | 14.1 | 9.3 | 7.2 | 5.6 | |
| Coarse Gradation | 100 | 95.0 | 87.0 | 68.3 | 38.7 | 22.9 | 14.3 | 11.9 | 8.1 | 6.5 | 5.1 | |
| Aggregate Property | Sieve Size | 10–15 | 3–5 | 0–3 | Mineral | |||||||
| Bulk Specific Gravity | 2.696 | 2.756 | 2.776 | 2.752 | ||||||||
| Crushing Stone Value = 22.8% | Los Angeles Abrasion = 16.2% | Flat and Elongated Particle Content = 16.4% | ||||||||||
| Experiment | Asphalt Content (%) | Air Void (%) | Density (g/cm3) | VMA (%) | VFA (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | (30#; Ndes = 30; middle gradation) | 5.70 | 3.8 | 2.432 | 16.5 | 77.0 |
| Group 2 | (30#; Ndes = 50; fine gradation) | 5.50 | 3.7 | 2.446 | 16.1 | 76.9 |
| Group 3 | (30#; Ndes = 50; middle gradation) | 5.40 | 3.9 | 2.460 | 16.1 | 76.0 |
| Group 4 | (30#; Ndes = 50; coarse gradation) | 5.70 | 4.1 | 2.421 | 16.7 | 75.7 |
| Group 5 | (50#; Ndes = 50; middle gradation) | 5.30 | 3.7 | 2.455 | 15.7 | 76.4 |
| Group 6 | (70#; Ndes = 50; middle gradation) | 5.25 | 4.4 | 2.416 | 16.1 | 72.4 |
| Group 7 | (70#; Ndes = 75; middle gradation) | 4.90 | 4.5 | 2.437 | 15.5 | 71.1 |
| Experiments | UCT | UPST | LTBT | 4PBT | UCMT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Group 2 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Group 3 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Group 4 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Group 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Group 6 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Group 7 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Cheng, H. Laboratory Performance Evaluation of Hot-Mix Asphalt Mixtures with Different Design Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093038
Zhang Y, Sun L, Cheng H. Laboratory Performance Evaluation of Hot-Mix Asphalt Mixtures with Different Design Parameters. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(9):3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093038
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yining, Lijun Sun, and Huailei Cheng. 2020. "Laboratory Performance Evaluation of Hot-Mix Asphalt Mixtures with Different Design Parameters" Applied Sciences 10, no. 9: 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093038
APA StyleZhang, Y., Sun, L., & Cheng, H. (2020). Laboratory Performance Evaluation of Hot-Mix Asphalt Mixtures with Different Design Parameters. Applied Sciences, 10(9), 3038. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10093038




