Abstract
The pineal gland is an endocrine gland whose main function is the biosynthesis and secretion of melatonin, a hormone responsible for regulating circadian rhythms, e.g., the sleep/wake cycle. Due to its exceptionally high vascularization and its location outside the blood–brain barrier, the pineal gland may accumulate significant amounts of calcium and fluoride, making it the most fluoride-saturated organ of the human body. Both the calcification and accumulation of fluoride may result in melatonin deficiency.
1. Introduction
The effect of fluoride on the human body is characterized by a very narrow margin of safety, which means that even relatively low concentrations may cause various adverse or even toxic effects [1,2,3,4,5]. The risk naturally increases with the intensity and duration of the exposure, with long-term exposure resulting in chronic poisoning [6,7]. One of the defense mechanisms protecting the body against the effects of fluoride toxicity seems to be its deposition in calcified tissues [2]. The most important role is played by hard tissues; bones; and teeth [2,8,9,10], in which fluoride accumulates in the form of fluorohydroxylapatite and fluoroapatite, replacing hydroxyl ions in the hydroxylapatite structure [11,12]. These processes may occur at any point in life, starting as early as in the prenatal period [13,14,15], and their effects are observed even in the skeletons and dentition of archaeological excavations from the times when exposure to fluorine compounds was incomparably lower to modern times [16,17,18]. Significantly, the deposition of fluoride in hard tissues may have its own adverse effects. The symptoms of excessive fluoride accumulation in bones and teeth are known and well documented, classified as skeletal fluorosis and dental fluorosis, respectively [19,20,21,22,23,24]. In addition to deposition in hard tissues, fluoride may also be found in calcification areas in soft tissues such as the aorta [25,26,27,28,29], coronary arteries [30,31], placenta [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41], tendons [42,43,44], or cartilage [42,45,46]. In these cases, however, this accumulation may not be classified as a defense mechanism triggered by an excessive exposure to fluoride. Unlike in hard tissues, calcium accumulation in soft tissues is never a physiological phenomenon and almost always leads to some undesirable effects, e.g., complications in pregnancy [47,48]. This indicates that the saturation of soft tissues with fluoride is a natural consequence of their calcification. On the other hand, fluoride itself may stimulate the formation of calcification foci in the soft tissues [27,49], which suggests that fluoride accumulation is the primary phenomenon in calcification. Yet, regardless of the exact mechanisms, concentration of fluoride in the bloodstream, and thus the risk of adverse effects in the body, is reduced as fluoride accumulates in the soft tissues. Obviously, the exceptions to this are the fluoride-accumulating soft tissues; for example, extensive deposits of calcium fluoride in the placenta may impair blood flow through this organ and thus impair fetal nutrition [32,33,50,51].
One of the most interesting soft tissues able to accumulate fluoride is the pineal gland [1,52,53,54,55]. However, while knowledge of the calcification of this organ dates back to the 17th century [56], the first reports on its accumulation of fluoride appeared only in the mid-1990s [54].
2. Pineal Gland—Anatomy and Physiology
In humans, the pineal gland is a neuroendocrine gland weighing about 150 mg [57]. The organ, part of the epithalamus, is located between the colliculi superiores of the lamina tecti, at the back of the posterior wall of the third brain ventricle [58] (Figure 1). The pineal gland is characterized by a very rich network of blood vessels, which ensures blood flow of 4 mL/min/g, second only to the blood supply to the kidneys [58,59,60]. Another unique anatomical feature of the gland is its location outside the blood–brain barrier [58,59]. Therefore, unlike most other brain structures, the pineal gland has open access to blood and all of its components. Extremely rich vascularization and no significant restrictions in transport from the bloodstream make it possible for the pineal gland to accumulate significant amounts of various substances, mainly, calcium [58,61,62,63,64,65,66]; microelements such as cobalt, zinc, and selenium [67]; and fluoride [52,53,54].
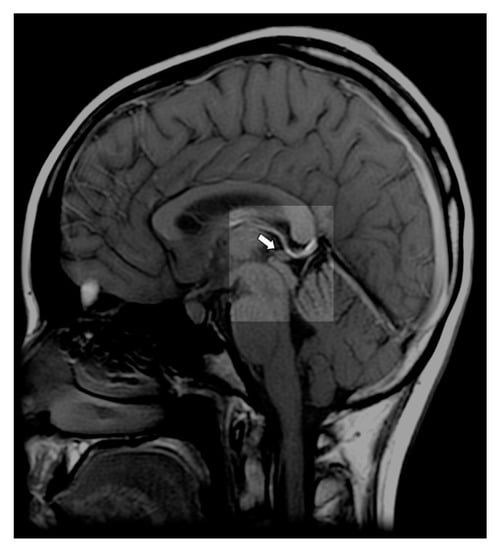
Figure 1.
T1-weighted midline sagittal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with an arrow pointing to a normal pineal gland (case courtesy of Assoc Prof Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 10767).
The basic function of the pineal gland is the production and secretion of melatonin [58,64], a hormone found in all vertebrates [60], including humans, which regulates circadian rhythms such as the sleep–wake cycle [64] (Figure 2). It is also a strong antioxidant [68,69,70] and an anti-inflammatory agent [71,72]. Although melatonin can be synthesized in almost all organs and tissues, including skin [73], intestines [74], bone marrow [75], testicles [76], ovaries [77], or the placenta [78], the proper biological response is regulated by the pineal hormone [64].
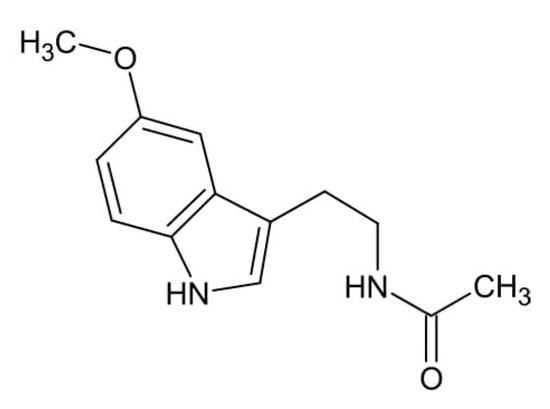
Figure 2.
Chemical structure of melatonin.
Biosynthesis of melatonin (Figure 3) occurs in pinealocytes, which constitute about 95% of the pineal gland’s volume [79]. The remaining part of the organ consists of astrocytes, microglia, vascular endothelial cells, and nerve fibers [79,80]. The precursor of melatonin is tryptophan [58], and most of the hormone is produced during sleep [81]. Its plasma concentration reaches its maximum between 2 and 3 o’clock in the morning (80–150 pg/mL) [82]. The mechanism conditioning this effect is initiated by reducing the activity of the suprachiasmatic nuclei, which occurs at night. The effect is the activation of postganglionic sympathetic fibers and the release of norepinephrine from their nerve endings. This neurotransmitter stimulates β-adrenergic receptors, inducing activation of the adenylate cyclase-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) system. As a result of the increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) concentration in pinealocyte cytosol, the activity of serotonin N-acetyltransferase increases, which leads to the stimulation of melatonin synthesis [83,84].

Figure 3.
Biosynthesis of melatonin.
3. Calcium Accumulation in the Pineal Gland
Calcium accumulates in the pineal gland in the apatite structure, similar to that found in bones and teeth [63,85,86], and as calcium carbonate (calcite) [87]. The process is initiated in childhood [88], and even in newborns [89,90], so some scientists see it as a physiological phenomenon [64]. It is, however, difficult to agree with such a conviction in the face of ample evidence showing the relationship between pineal calcification and various pathological states. This includes mental illnesses and disorders [91,92,93], neurodegenerative disorders [94,95], primary brain tumors [96], ischemic stroke [97], migraine [98], and sleep disorders [99]. The accumulation of calcium in the pineal gland is also related to aging processes [100] (Figure 4).
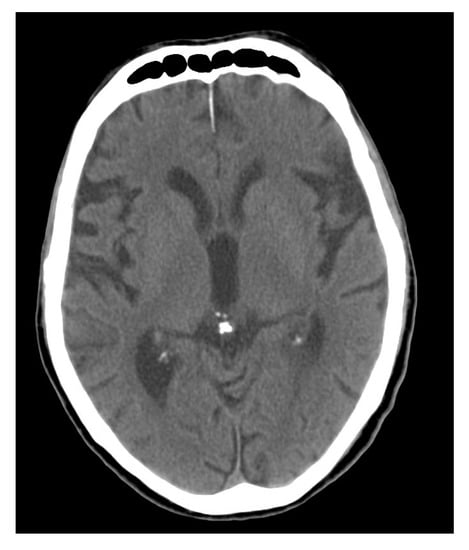
Figure 4.
Computer tomography (CT) scan through the brain with calcification of the pineal gland (case courtesy of Radswiki, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 11770).
In the study in adolescents and adults, Kunz et al. [61] demonstrated an inverse correlation between the degree of pinealocyte calcification and pinealocyte count. Although there was no significant correlation between gland calcification and plasma melatonin concentration, it was noted that the reduction in pinealocyte count caused by calcification was accompanied by a reduction in melatonin synthesis. Hence, the conclusion that pineal gland calcification has an indirect effect on the production and secretion of this hormone. These observations were confirmed by Liebrich et al. [101], who, using magnetic resonance imaging, showed a positive correlation between the size of the uncalcified part of the pineal gland and the concentration of melatonin in saliva.
According to some authors, the concentration of melatonin in the cerebrospinal fluid plays a decisive role in the regulation of circadian rhythms, while plasma hormone concentrations are of little importance in exerting biological effects in this respect [102,103]. As pineal calcification results in the reduction of melatonin concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid, its relation to diseases of the central nervous system becomes understandable. The pathomechanism of this relationship is to reduce the antioxidant effects of melatonin, which favors neuronal damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS) and, thus, to accelerate the development of neurodegenerative changes [64,70]. For example, it has been found that the concentration of melatonin in the cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer’s disease is only 20% of that recorded in healthy individuals [104].
4. Fluoride Accumulation in the Pineal Gland and Its Consequences
Both calcified and calcium-free areas of the pineal gland undergo mineralization and accumulate, among other things, magnesium, iron, manganese, zinc, strontium, or copper [105]. However, it was not until the 1990s that it was discovered that the foci of calcification within the gland may be accompanied by extremely high concentrations of fluoride for soft tissue [54]. In 2001, Luke [52] first published the results of fluoride concentration measurements in pineal glands taken from human corpses. The mean concentration was 297 mg F/kg of wet weight (ww), but the range of recorded values was very wide (14 mg/kg–875 mg/kg ww). It is not difficult to notice that they are similar or even higher than those observed in bones and teeth and many times exceed the concentrations observed in other soft tissues (e.g., in muscles, they are about 1 mg F/kg ww). After converting these values into dry weight (dw), we obtain concentrations of 1485 + 1285 mg F/kg dw. Although these data come from older individuals (studies were conducted on a group of deceased people aged 70 to 100 years), this does not disprove the idea that the pineal gland may be considered the most fluoride-saturated organ of the human body. It has been observed that the fluoride content in pineal gland apatite is higher than in any other natural apatite and may even reach 21000 mg/kg [52,53].
The results of Luke’s research also revealed a strong positive correlation between calcium and fluoride concentrations (r = 0.73, p < 0.02) [52]. Ten or so years later this observation was confirmed, albeit not for the full range of fluoride concentrations. Tharnpanich et al. [53] demonstrated that a statistically significant correlation occurs only when the fluoride concentration exceeds 50 mg/kg of fresh gland tissue. They recorded the values of these concentrations, which ranged anywhere from 0 mg F/kg ww to 831 mg F/kg ww (mean 75.5 + 228 mg F/kg ww). This suggests that the accumulation of fluoride in the pineal gland is rather a secondary phenomenon to the primary calcification of this organ and at some point the relation between them reaches the status of a very strong positive correlation (r = 0.915, p < 0.001). It is also worth noting that pineal glands in the study by Tharnpanich et al. [53] were collected from deceased persons aged 33 to 91 years (mean 67 years), who had inhabited an area with low fluoride contamination, which is a strong argument for the idea that a smaller or larger accumulation of fluoride in the gland occurs even when the organism is not exposed to particularly large amounts of fluorine compounds in the environment.
Regardless of how accumulation of fluoride in the pineal gland takes place, whether this is primary or secondary to calcification, the most important issue is the effects of this phenomenon. It is obvious that they will primarily concern the physiological function of the gland.
Assuming the preferential accumulation of fluoride in the pineal gland and the related possible risk of toxic effects, Malin et al. [11] have recently published a study on the processes of sleep regulation among older adults in the United States. They tried to answer the question of whether chronic exposure to low doses of fluoride has an effect on sleep patterns and daytime sleepiness in the studied population. The study investigated adolescents aged 16–19 years (mean = 17 years), who had declared that they had no sleeping disorders, who were exposed to low doses of fluoride (mean concentration in drinking water = 0.39 mg/L), and who had low concentrations of fluoride in plasma (mean = 0.35 μmol/L). Higher water fluoride levels were connected with higher odds of participants reporting snorting, gasping, or apnea, while sleeping at night. Additionally, adolescents who lived in areas with higher fluoride levels in tap water experienced more frequent daytime sleepiness. The authors [11] were of the opinion that fluoride exposure may contribute to increased pineal gland calcification and subsequent decreases in nighttime melatonin production that contribute to sleep disturbances.
For obvious reasons, there are very few reports on the accumulation of fluoride in the pineal gland and its effect on the functionality of the organ in humans. Therefore, it is worth noting the studies carried out in both experimental and free-living animals.
In the pineal glands taken from the common merganser (Mergus merganser), Kalisińska et al. [1] recorded very high fluoride contents (mean > 1000 mg/kg dw), which even exceed the concentrations observed in the bones of these birds. Such a high concentration of fluoride in the gland is explained by the incompleteness of the blood–brain barrier in birds, which facilitates the penetration of various substances into the central nervous system.
Mrvelj and Womble [79] conducted a study to determine the effect of fluoride removal from the diet of aged rats (over 26 months of age) on the pineal cell structure and to compare the results with rats receiving fluoride with food (control). It was observed that in animals deprived of fluoride for 8 weeks, the number of pinealocytes was higher than in control animals, which suggests a harmful effect of fluoride contained in the diet on pineal morphology and thus on the production and secretion of melatonin.
In turn, studies conducted by Bharti and Srivastava [106,107] in rats showed the beneficial effect of melatonin and pineal proteins on fluoride-induced oxidative stress, which is one of the best known effects of fluoride on the body [108,109]. The animals were exposed to different doses of fluoride and melatonin and proteins obtained from buffalo pineal (Bubalus bubalis). The severity of oxidative stress was measured by the degree of activity of antioxidative enzymes: superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione reductase (GR), as well as the concentration of reduced glutathione (GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the brains of the animals [6]. The antioxidant system parameters were markedly improved by the intake of melatonin and pineal proteins; in the latter case, the beneficial effect was even stronger. The action consisted of increased activity of antioxidant enzymes, increased GSH concentration, and decreased MDA concentration. All these parameters were adversely affected in the group of animals receiving fluoride only (decreased activity of enzymes and GSH concentration and increased MDA concentration, which is a marker of increased oxidative stress), painting a very disturbing picture of the effects of fluoride accumulation in the pineal gland. Since it is known that fluoride reduces the production and secretion of melatonin [79], a substance which reduces the oxidative stress induced by them [107], the accumulation of fluoride in the pineal gland may be a significant factor in enhancing the effects of reactive oxygen species, with all potential adverse consequences.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that the concentrations of fluoride in the pineal gland at the magnitude of several dozen or even several hundred mg/kg ww, revealed in the studies by Luke [52] and Tharnpanich et al. [53], may show inhibitory activity on melatonin synthesis pathway enzymes. Fluoride having this effect has been known for a long time in relation to many enzymes [108,110]. Thus, it cannot be excluded that the restriction of melatonin synthesis associated with pinealocyte calcification may be caused not only by a decrease in the number of active pinealocytes but also by the direct influence of fluoride accumulated in the gland on enzymatic activity. This issue undoubtedly needs to be clarified in the future.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally in this article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kalisińska, E.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Łanocha, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Królaczyk, K.; Wilk, A.; Kavetska, K.; Budis, H.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D. Fluoride concentrations in the pineal gland, brain and bone of goosander (Mergus merganser) and its prey in Odra River estuary in Poland . Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanduti, D.; Sterbenk, P.; Artnik, B. Fluoride: A review of use and effects on health. Mater. Sociomed. 2016, 28, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupnicka, P.; Kojder, K.; Metryka, E.; Kapczuk, P.; Jeżewski, D.; Gutowska, I.; Goschorska, M.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Morphine-element interactions—The influence of selected chemical elements on neural pathways associated with addiction. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 60, 126495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.L.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y.; Grandjean, P. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 10, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, K.; Łukomska, A.; Maciejewska, D.; Jakubczyk, K.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Chlubek, D.; Wąsik, A.; Gutowska, I. The influence of fluorine on the disturbances of homeostasis in the central nervous system. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 177, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Jiao, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Association between water fluoride and the level of children’s intelligence: A dose-response meta-analysis. Public Health 2018, 154, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Saha, B. Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2013, 39, 2881–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palczewska-Komsa, M.; Barczak, K.; Kotwas, A.; Sikora, M.; Chlubek, D.; Buczkowska-Radlińska, J. Fluoride concentration in dentin of human permanent teeth. Fluoride 2019, 52, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Waszkiel, D.; Opalko, K.; Łagocka, R.; Chlubek, D. Fluoride and magnesium content in superficial enamel layers of teeth with erosions. Fluoride 2004, 37, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Buzalaf, M.A.; Whitford, G.M. Fluoride metabolism. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2011, 22, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malin, A.J.; Bose, S.; Busgang, S.A.; Gennings, C.; Thorpy, M.; Wright, R.O.; Wright, R.J.; Arora, M. Fluoride exposure and sleep patterns among older adolescents in the United States: A cross-sectional study of NHANES 2015–2016. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ten Cate, J.M.; Featherstone, J.D. Mechanistic aspects of the interactions between fluoride and dental enamel. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1991, 2, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrzyński, S.; Machoy, Z. Fluoride incorporation into fetal bone. Fluoride 1994, 27, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrzyński, S.; Chlubek, D.; Mikulski, T.; Machoy, Z. The use of microdensitometric examinations for evaluating the influence of fluorine on bone mineralization in fetus. Pol. Przegl. Radiol. 1994, 58, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mokrzyński, S.; Chlubek, D.; Machoy, Z.; Samujło, D. Fluoride in the organism of mother and fetus. II. Fluoride cumulation in the organism of fetus. Ginekol. Pol. 1994, 65, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sikora, M.; Kwiatkowska, B.; Chlubek, D. Fluoride content in superficial enamel layers of human teeth from archeological excavations. Fluoride 2014, 47, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Noceń, I.; Dąbkowska, E.; Żyluk, B.; Machoy, Z.; Kwiatkowska, B. Fluoride accumulation in human skulls in relation to chronological age. Fluoride 1996, 29, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Sikora, M.; Kwiatkowska, B.; Gronkiewicz, S. Determinations of mineral composition in superficial enamel layers of human teeth from archeological excavations by means of enamel biopsy. Biul. Magnezol. 2001, 6, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, M.M.; Lakhkar, B.B.; Patil, S.S. Course of fluorosis. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, M.N.; Anil, N.S. A comparative study of dental fluorosis and non-skeletal manifestations of fluorosis in areas with different water fluoride concentrations in rural Kolar. J. Family Med. Prim. Care. 2018, 7, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Rajapakse, P.S.; Jayawardhane, W.M.; Lokubandara, A.; Gamage, R.; Dasanayake, A.P.; Goonaratna, C. High prevalence of dental fluorosis among schoolchildren in three villages in Vavuniya District: An observational study. Ceylon Med. J. 2017, 62, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewavithana, P.B.; Jayawardhane, W.M.; Gamage, R.; Goonaratna, C. Skeletal fluorosis in Vavuniya District: An observational study. Ceylon Med. J. 2018, 63, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, M.; Riahi, H.; Maatallah, K.; Ferjani, H.; Bouaziz, M.C.; Ladeb, M.F. Skeletal fluorosis: Don’t miss the diagnosis! Skeletal Radiol. 2020, 49, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoba, T.; Fejerskov, O. Dental fluorosis: Chemistry and biology. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldbott, G.L. Fluoride and calcium levels in the aorta. Exeprientia 1966, 22, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipkin, I.; Zucas, S.M.; Lavender, D.R.; Fullmer, H.M.; Schiffmann, E.; Corcoran, B.A. Fluoride and calcification of rat aorta. Calcif. Tissue Res. 1970, 6, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susheela, A.K.; Kharb, P. Aortic calcification in chronic fluoride poisoning: Biochemical and electronmicroscopic evidence. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1990, 53, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiz, F.; Morbelli, S.; Bauckneht, M.; Piccardo, A.; Ferrarazzo, G.; Nieri, A.; Artom, N.; Cabria, M.; Marini, C.; Canepa, M.; et al. Correlation between thoracic aorta 18F-natrium fluoride uptake and cardiovascular risk. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, Y.; Hammarström, L. Autoradiographic localization of fluoride and calcium deposition in the atherosclerotic aorta of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Gerontology 1964, 9, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Berenji, G.R.; Shaba, W.F.; Tafti, B.; Yevdayev, E.; Dadparvar, S. Association of vascular fluoride uptake with vascular calcification and coronary artery disease. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2012, 33, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dilsizian, V. Targeted PET/CT imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques: Microcalcification with sodium fluoride and inflammation with fluorodeoxyglucose. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2013, 15, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlubek, D.; Poręba, R.; Machaliński, B. Fluoride and calcium distribution in human placenta. Fluoride 1998, 31, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Rzeuski, R. Toxic effects of fluorine compounds on the fetus and their effect on the course of pregnancy. Ginekol. Pol. 1996, 67, 141–418. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.W.; Taves, D.R. Fluoride concentrations in human placenta and maternal and cord blood. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1974, 119, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurumurthy, S.M.; Mohanty, S.; Vyakaranam, S.; Bhongir, A.V.; Rao, P. Transplacental transport of fluoride, calcium and magnesium. Natl. J. Integr. Res. Med. 2011, 2, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gurumurthy, S.M.; Mohanty, S.; Rao, P. Role of placenta to combat fluorosis (in fetus) in endemic fluorosis area. Natl. J. Integr. Res. Med. 2010, 1, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Machoy, Z.; Samujło, D. Fluoride concentration in human placenta in the region of fluorine industrial emissions. Bromat. Chem. Toksykol. 1997, 30, 299–302. [Google Scholar]
- Feltman, R.; Kosel, G. Prenatal ingestion of fluorides and their transfer to the fetus. Science 1955, 122, 560–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlubek, D.; Machoy, Z. Role of placenta in fluoride metabolism. Ginekol. Pol. 1991, 42, 568–572. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D. Some aspects of prenatal fluoride metabolism in humans. Studies performed during the perinatal period. Ann. Acad. Med. Stetin. 1996, 42 (Suppl. S31), 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Zawierta, J.; Kaźmierczyk, A.; Kramek, J.; Olszewska, M.; Stachowska, E. Effect of different fluoride ion concentrations on malondialdehyde (MDA) formation in the mitochondrial fraction of human placental cells. Bromat. Chem. Toksykol. 1999, 32, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kot, K.; Ciosek, Ż.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Ziętek, P.; Karaczun, G.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Kalisińska, E.; Chlubek, D. Fluoride concentrations in cartilage, spongy bone, anterior cruciate ligament, meniscus, and infrapatellar fat pad of patients undergoing primary knee joint arthroplasty. Fluoride 2017, 50, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Giachini, M.; Pierleoni, F. Fluoride toxicity. Minerva Stomatol. 2004, 53, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fordyce, F.M.; Vrana, K.; Zhovinsky, E.; Povoroznuk, V.; Toth, G.; Hope, B.C.; Iljinsky, U.; Baker, J. A health risk assessment for fluoride in Central Europe. Environ. Geochem. Health 2007, 29, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Kot, K.; Ziętek, P.; Karaczun, M.; Gutowska, I.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Grzeszczak, K.; Sikora, M.; Chlubek, D. Fluoride concentration in synovial fluid, bone marrow, and cartilage in patients with osteoarthritis. Fluoride 2018, 51, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Dołęgowska, B.; Machoy, Z.; Chlubek, D. Changes in the content of zinc and fluoride during growth of the femur in chicken. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2003, 91, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Moshfeghi, M.; Moshfeghi, S.; Mohammadi, N.; Zarean, E.; Jahangiri, N. Is preterm placental calcification related to adverse maternal and foetal outcome? J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 37, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.; Higgins, M.; Zombori, G.; Ryan, J.; McAuliffe, F.M. Computerized assessment of placental calcification post-ultrasound: A novel software tool. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 41, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kong, L.; Zhao, H.; Dong, R.; Li, J.; Jia, Z.; Ji, N.; Deng, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, J. Thoracic ossification of ligamentum flavum caused by skeletal fluorosis. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlubek, D.; Mokrzyński, S.; Machoy, Z.; Samujło, D.; Węgrzynowski, J. Fluoride concentration in mother and fetus. I. Placental transport of fluorides. Ginekol. Pol. 1994, 65, 611–615. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Mokrzyński, S.; Machoy, Z.; Olszewska, M. Fluorides in the body of mother and in the fetus. III. Fluorides in amniotic fluid. Ginekol Pol. 1995, 66, 614–617. [Google Scholar]
- Luke, J. Fluoride deposition in the aged human pineal gland. Caries Res. 2001, 35, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharnpanich, T.; Johns, J.; Subongkot, S.; Johns, N.P.; Kitkhuandee, A.; Toomsan, Y.; Luengpailin, S. Association between high pineal fluoride content and pineal calcification in a low fluoride area. Fluoride 2016, 49, 472–484. [Google Scholar]
- Luke, J. The Effect of Fluoride on the Physiology of the Pineal Gland. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Surrey, Guildford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Fluoride in Drinking Water: A Scientific Review of EPAs Standards; Advisors of the Nation on Science Engineering and Medicine; Committee on Fluoride in Drinking Water; Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology; The National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 262–263. [Google Scholar]
- Del Rio-Hortega, P. Cytology and cellular pathology of the nervous system. In Pineal Gland; Penfield, W., Ed.; Hoeber: New York, NY, USA, 1932; pp. 637–703. [Google Scholar]
- Golan, J.; Torres, K.; Staśkiewicz, G.J.; Opielak, G.; Maciejewski, R. Morphometric parameters of the human pineal gland in relation to age, body weight and height. Folia Morphol. 2002, 61, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Macchi, M.M.; Bruce, J.N. Human pineal physiology and functional significance of melatonin. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 25, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, J. Melatonin and the Mammalian Pineal Gland, 1st ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1995; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Fuentes-Broto, L.; Paredes, S.D.; Reiter, R.J. Significance and application of melatonin in the regulation of brown adipose tissue metabolism. Relation to human obesity. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 167–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, D.; Schmitz, S.; Mahlberg, R.; Mohr, A.; Stöter, C.; Wolf, K.J.; Herrmann, W.M. A new concept for melatonin deficit: On pineal calcification and melatonin excretion. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 21, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlberg, R.; Kienast, T.; Hödel, S.; Heidenreich, J.O.; Schmitz, S.; Kunz, D. Degree of pineal calcification (DOC) is associated with polysomnographic sleep measures in primary insomnia patients. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Rahmani, B.; Gandhi, J.; Seyam, O.; Joshi, G.; Reid, I.; Smith, N.L.; Waltzer, W.C.; Khan, S.A. Revisiting the pineal gland: A review of calcification, masses, precocious puberty, and melatonin functions. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.-X.; Xu, B.; Zhou, X.; Reiter, R.J. Calcification, melatonin production, aging, associated health consequences and rejuvenation of the pineal gland. Molecules 2018, 23, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiroğlu, Y.; Çalli, C.; Karabulut, N.; Oncel, C. Intracranial calcifications on CT. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 16, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, A.M. Atlas of Normal Imaging Variations of the Brain, Skull, and Craniocervical Vasculature; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Demmel, U.; Höck, A.; Kasperek, K.; Feinendegen, L.E. Trace element concentration in the human pineal body. Activation analysis of cobalt, iron, rubidium, selenium, zinc, antimony and cesium. Sci. Total Environ. 1982, 24, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.-X.; Sainz, R.M.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.; Qin, I. Melatonin as an antioxidant: Under promises but over delivers. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J. Oxidative damage in the central nervous system: Protection by melatonin. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 359–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; BaHammam, A.S.; Brown, G.M.; Spence, D.W.; Bharti, W.K.; Kaur, C.; Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P. Melatonin antioxidative defense: Therapeutical implications for aging and neurodegenerative processes. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 267–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, L.; Xu, Y.; Luo, D.; Ren, Q.; Wu, S.; Sun, C. Melatonin alleviates inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through inhibiting NF-κB/GSDMD signal in mice adipose tissue. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin and brain inflammaging. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 127–128, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Semak, I.; Kim, T.K.; Janjetovic, Z.; Slominski, R.M.; Zmijewski, J.W. Melatonin, mitochondria, and the skin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3913–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Boga, J.A.; Tan, D.-X.; Davis, J.M.; Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, S.J.; Brzozowski, T. The photoperiod, circadian regulation and chronodisruption: The requisite interplay between the suprachiasmatic nuclei and the pineal and gut melatonin. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2011, 62, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, A.; Conconi, S.; Hertens, E.; Skwarlo-Sonta, K.; Markowska, M.; Maestroni, J.M. Evidence for melatonin synthesis in mouse and human bone marrow cells. J. Pineal Res. 2000, 28, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijmes, M.; Pedraza, R.; Valladares, I. Melatonin in the rat testis: Evidence for local synthesis. Steroids 1996, 61, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.T.; Ishizuka, B.; Kudo, Y.; Fusama, S.; Amemiya, A.; Sumi, Y. Detection of melatonin and serotonin N-acetyltransferase and hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase activities in rat ovary. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1997, 136, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.; Lacasse, A.-A.; Lanoix, D.; Sagrillo-Fagundes, L.; Boulard, V.; Vaillancourt, C. Placental melatonin system is present throughout pregnancy and regulates villous trophoblast differentiation. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrvelj, A.; Womble, M.D. Fluoride-free diet stimulates pineal growth in aged male rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020. (In press) [CrossRef]
- Ibañez Rodriguez, M.P.; Noctor, S.C.; Muñoz, E.M. Cellular basis of pineal gland development: Emerging role of microglia as phenotype regulator. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia Garcia, J.; Muñoz Hovos, A.; Molina Carballo, A.; Fernández Garcia, J.M.; Narbona López, E.; Uberos Fernández, J. Puberty and melatonin. An. Esp. Pediatr. 2002, 57, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewy, A.J.; Cutler, N.L.; Sack, R.L. The endogenous melatonin profile as a marker for circadian phase position. J. Biol. Rhythms 1999, 14, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmaoui, B.; Touitou, Y. Reproducibility of the circadian rhythms of serum cortisol and melatonin in healthy subjects: A study of three different 24-h cycles over six weeks. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Someren, E.; Nagtegaal, E. Improving melatonin circadian phase estimates. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchi, G.V.G. Physical, chemical, and mineralogical characterization of carbonatehydroxyapatite concretions of the human pineal gland. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1993, 49, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabie, C.P.; Wallace, M.M. Optical, physical and chemical properties of pineal gland calcifications. Calcif. Tissue Res. 1974, 16, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baconnier, S.; Lang, S.B.; Polomska, M.; Hilczer, B.; Berkovic, G.; Meshulam, G. Calcite microcrystals in the pineal gland of the human brain: First physical and chemical studies. Bioelectromagnetics 2002, 23, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.J.; Anderson, G.D. Physiologic calcification of the pineal gland in children on computed tomography: Prevalence, observer reliability and association with choroid plexus calcification. Acad. Radiol. 2006, 13, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, P.; Helmke, K. Age-related incidence of pineal gland calcification in children: A roentgenological study of 1044 skull films and a review of the literature. J. Pineal Res. 1987, 4, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maślińska, D.; Laure-Kamionowska, M.; Deręgowski, K.; Maśliński, S. Association of mast cells with calcification in the human pineal gland. Folia Neuropathol. 2010, 48, 276–282. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.R.; Sandyk, R. Experimental models of schizophrenia. Int. J. Neurosci. 1991, 58, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandyk, R.; Kay, S.R. Abnormal EEG and calcification of the pineal gland in schizophrenia. Int. J. Neurosci. 1992, 62, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandyk, R.; Pardeshi, R. The relationship between ECT nonresponsiveness and calcification of the pineal gland in bipolar patients. Int. J. Neurosci. 1990, 54, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, R.P.; Luxenberg, J.S.; Koss, E.A. A quantitative study of intracranial calcification in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1990, 2, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlberg, L.; Walther, S.; Kalus, P.; Bohner, G.; Haedel, S.; Reischies, F.M.; Kuhl, K.P.; Hellweg, R.; Kunz, D. Pineal calcification in Alzheimer’s disease: An in vivo study using computed tomography. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuntapakul, S.; Kitkhuandee, A.; Kanpittaya, J.; Johns, J.; Johns, N.P. Pineal calcification is associated with pediatric primary brain tumor. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 12, e405–e410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitkhuandee, A.; Sawanyawisuth, K.; Johns, N.P.; Kanpittaya, J.; Johns, J. Pineal calcification is associated with symptomatic cerebral infarction. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozlece, H.K.; Akyuz, O.; Huseyinoglu, N.; Aydin, S.; Can, S.; Serim, V.A. Is there a correlation between the pineal gland calcification and migraine? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 3861–3864. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kunz, D.; Bes, F.; Schlattmann, P.; Herrmann, W.M. On pineal calcification and its relation to subjective sleep perception: A hypothesis-driven pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 1998, 82, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, R.; Kodaka, T.; Sano, T. Preliminary report on the correlation among pineal concretions, prostatic calculi and age in human adult males. Anat. Sci. Int. 2003, 78, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebrich, L.S.; Schredl, M.; Findeisen, P.; Groden, C.; Bumb, J.M.; Nölte, I.S. Morphology and function: MR pineal volume and melatonin level in human saliva are correlated. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J. CSF generation by pineal gland results in a robust melatonin circadian rhythm in the third ventricle as a unique light/dark signal. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 86, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Kim, S.J.; Cruz, M.H.C. Delivery of pineal melatonin to the brain and SCN: Role of canaliculi, cerebrospinal fluid, tanycytes and Virchow-Robin perivascular spaces. Brain Struct. Funct. 2014, 219, 1873–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-N.; Liu, R.-Y.; Kamphorst, W.; Hofman, M.A.; Swaab, D.F. Early neuropathological Alzheimer’s changes in aged individuals are accompanied by decreased cerebrospinal fluid melatonin levels. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michotte, Y.; Lowenthal, A.; Knaepen, L.; Colland, M.; Massart, D.L. A morphological and chemical study of calcification of the pineal gland. J. Neurol. 1977, 215, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, V.K.; Srivastava, R.S. Effect of pineal proteins at different dose level on fluoride-induced changes in plasma biochemicals and blood antioxidants enzymes in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 141, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, V.K.; Srivastava, R.S. Fluoride-induced oxidative stress in rat’s brain and its amelioration by buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) pineal proteins and melatonin. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 130, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlubek, D. Fluoride and oxidative stress. Fluoride 2003, 36, 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Rzeuski, R.; Chlubek, D.; Machoy, Z. Interactions between fluoride and biological free radical reactions. Fluoride 1998, 31, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Chlubek, D.; Machoy, Z. Significance of the effect of fluorine dose on enzymes activity in in vivo and in vitro studies. Bromat. Chem. Toksykol. 1989, 22, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).