Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications
Abstract
1. Introduction
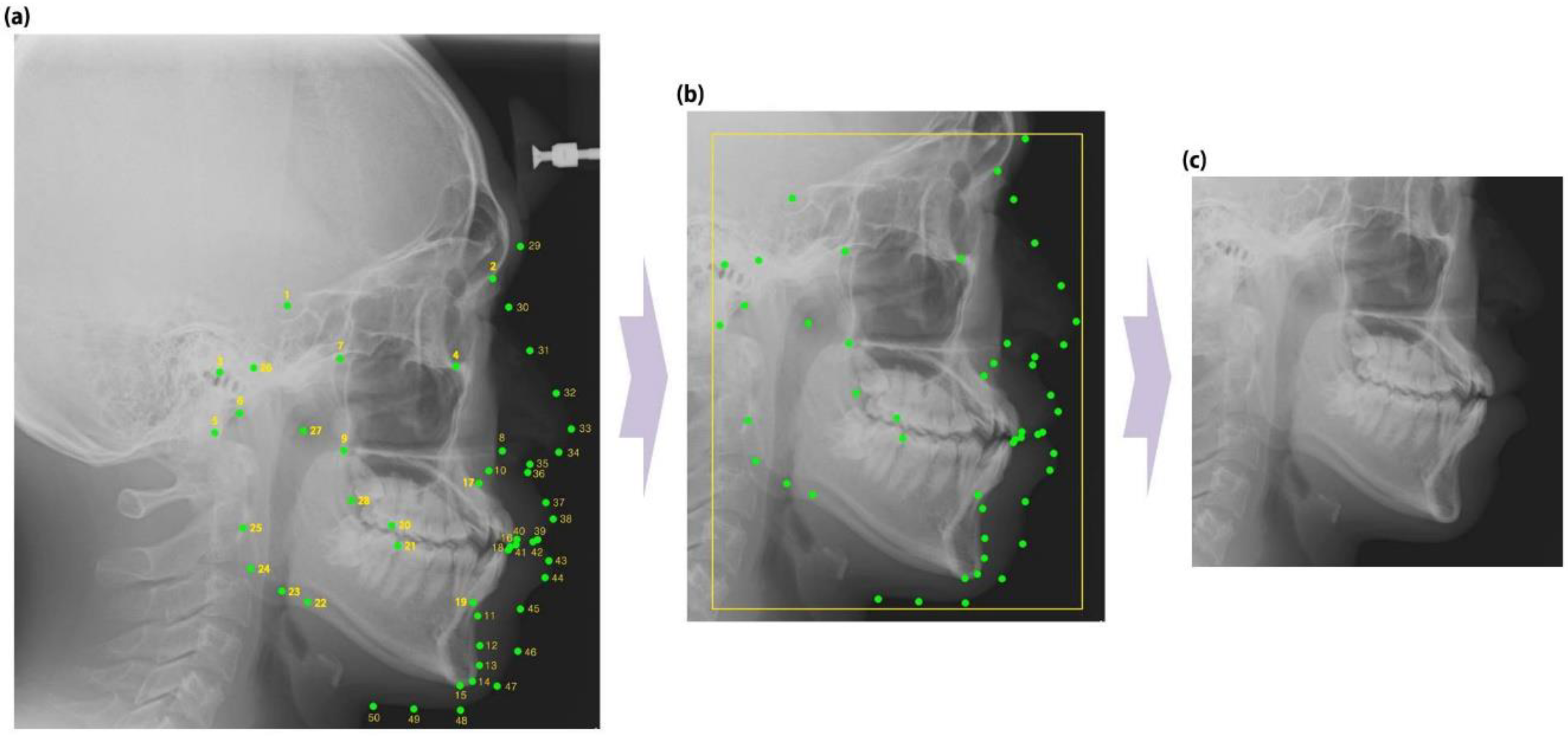
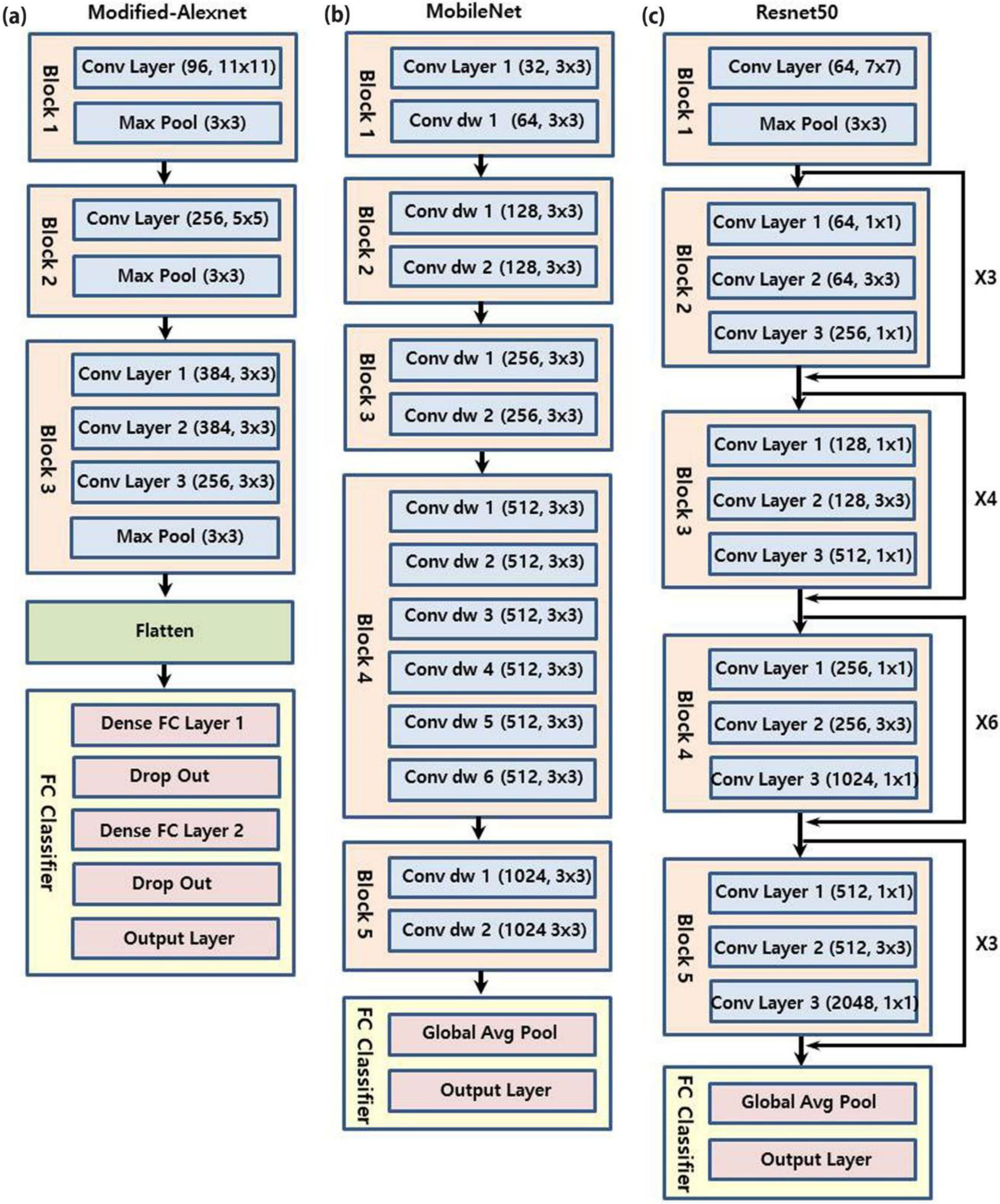
2. Materials and Methods
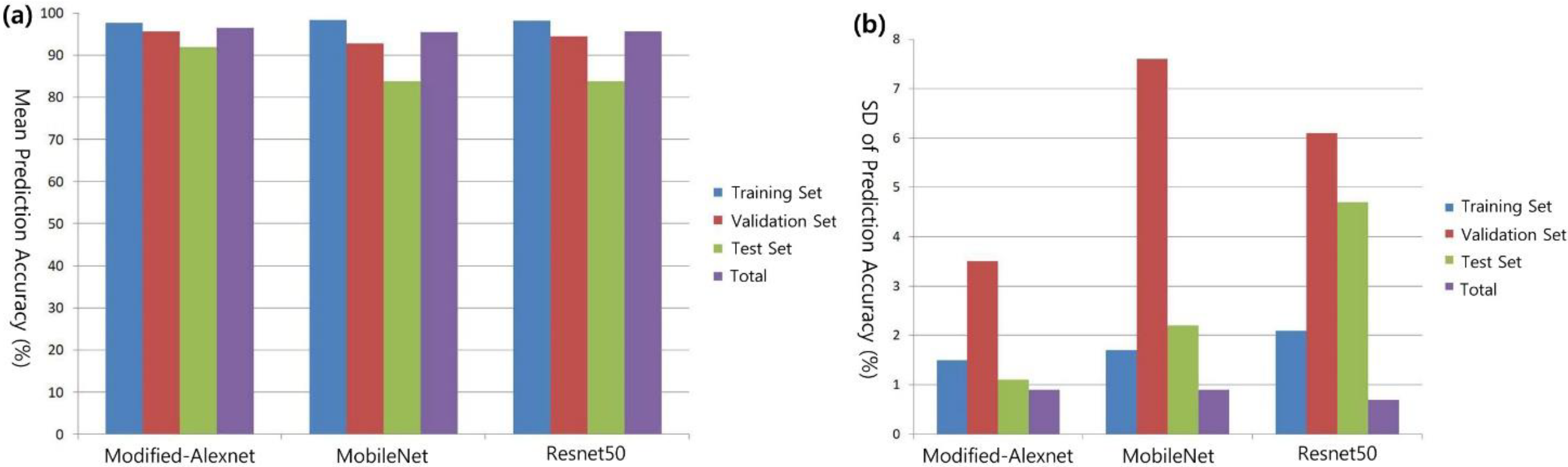
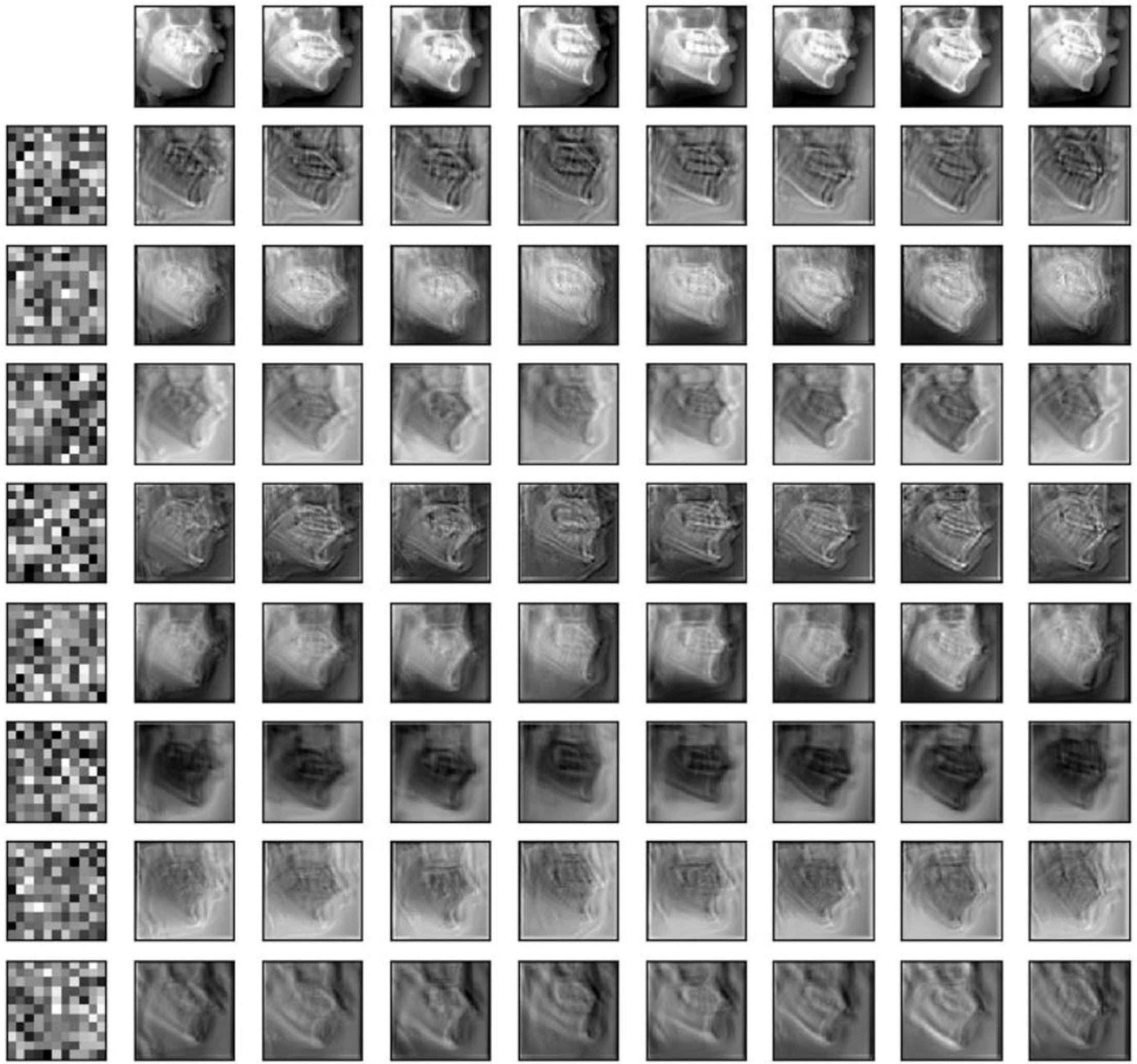
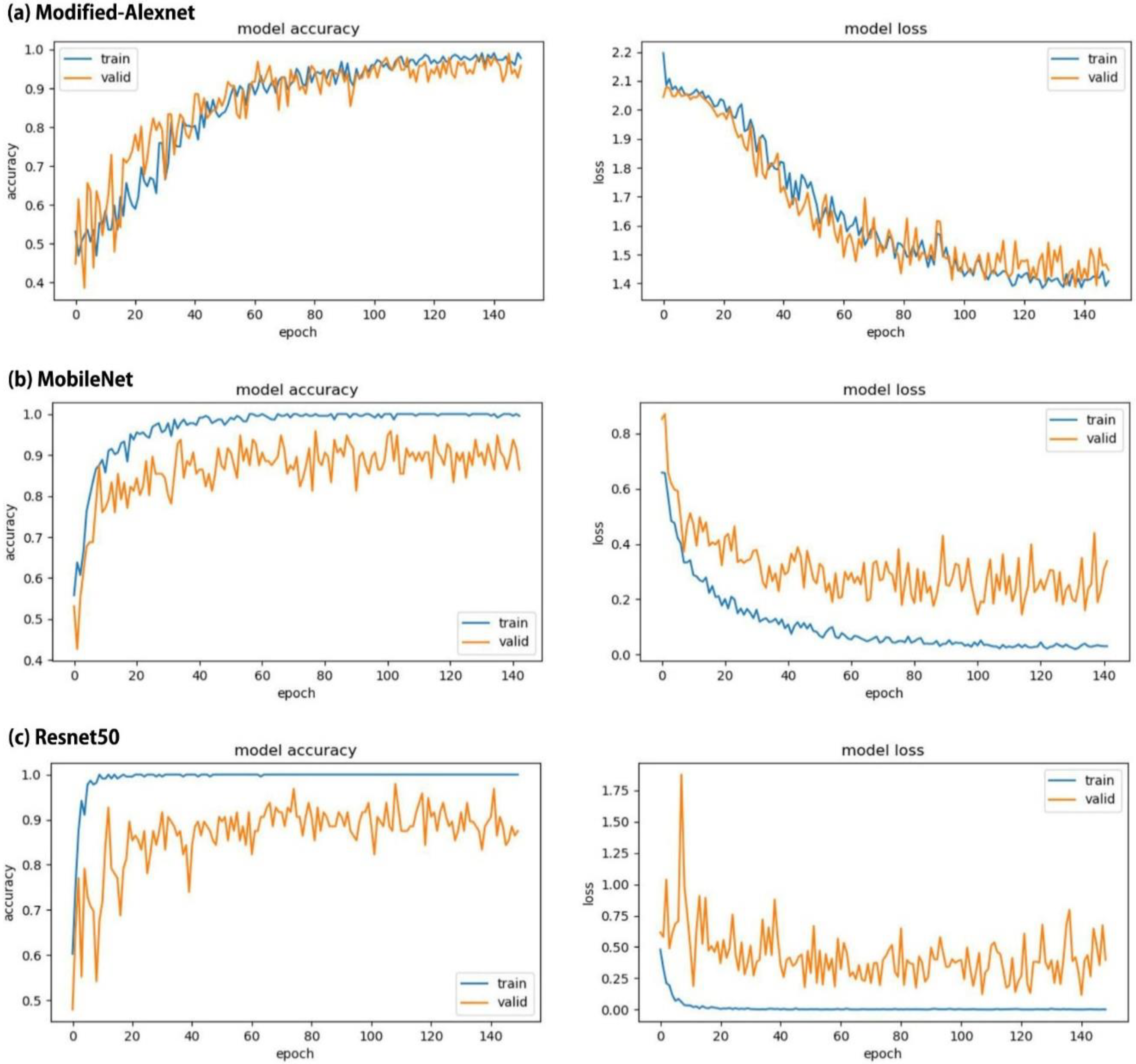
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.W.; Sarver, D.M. Contemporary Orthodontics, 5th ed.; Mosby: St Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Veiszenbacher, E.; Wang, J.; Davis, M.; Waite, P.D.; Borbely, P.; Kau, C.H. Virtual surgical planning: Balancing esthetics, practicality, and anticipated stability in a complex Class III patient. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geramy, A.; Sheikhzadeh, S.; Jalali, Y.F.; Nazarifar, A.M. Anthropometric Facial Changes After Orthognathic Surgery and Their Relation With Oral Health Related Quality of Life. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.P.; Kaban, L.B.; Masoud, M.I. Orthognathic Surgery and Orthodontics: Inadequate Planning Leading to Complications or Unfavorable Results. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin, D.L. The orthodontic examination. Angle Orthod. 1990, 60, 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz, J.; Stewart, K.; Ghoneima, A. Evaluation of two-dimensional lateral cephalometric radiographs and three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography superimpositions: A comparative study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 48, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosudprasit, A.; Haghi, A.; Allareddy, V.; Masoud, M.I. Diagnosis and treatment planning of orthodontic patients with 3-dimensional dentofacial records. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Yin, D.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Xu, T. Automated 2-D cephalometric analysis on X-ray images by a model-based approach. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Perillo, M.; Beideman, R.; Shofer, F. Effect of landmark identification on cephalometric measurements: Guidelines for cephalometric analyses. Clin. Orthod. Res. 2000, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.W. Variation of the sella-nasion plane and its effect on SNA and SNB. J. Oral Surg. 1976, 34, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, D.; Gao, L. A CNN-SVM combined model for pattern recognition of knee motion using mechanomyography signals. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 42, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arandjelovic, R.; Gronat, P.; Torii, A.; Pajdla, T.; Sivic, J. NetVLAD: CNN Architecture for Weakly Supervised Place Recognition. IEEE. Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1437–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, S.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Qian, W.; Yao, Y.; Sun, J. Deep CNN models for pulmonary nodule classification: Model modification, model integration, and transfer learning. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadea, M.F.; Pileggi, G.; Zaffino, P.; Salome, P.; Catana, C.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Amato, F.; Seco, J. Deep Convolution Neural Network (DCNN) Multiplane Approach to Synthetic CT Generation From MR images-Application in Brain Proton Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Chaudhari, P.; Varghese, K. Runtime Programmable and Memory Bandwidth Optimized FPGA-Based Coprocessor for Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE. Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 2018, 29, 5922–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.J.; Park, J.B. History and application of artificial neural networks in dentistry. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Dudley, J.T. Deep learning for healthcare: Review, opportunities and challenges. Brief Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N.; Choi, S.H. Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Dent. 2018, 77, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Huang, C.T.; Hsieh, M.C.; Li, C.H.; Chang, S.W.; Li, W.C.; Vandaele, R.; Maree, R.; Jodogne, S.; Geurts, P.; et al. Evaluation and Comparison of Anatomical Landmark Detection Methods for Cephalometric X-Ray Images: A Grand Challenge. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, E.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Deng, H.; Wu, Y.; Megalooikonomou, V.; Gable, B.; Ling, H. Automatic Dent-landmark detection in 3-D CBCT dental volumes. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; Volume 2011, pp. 6204–6207. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.-K.; Kim, T.-W. New approach for the diagnosis of extractions with neural network machine learning. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 149, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kong, D.; Tang, T.; Su, D.; Yang, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y. Orthodontic Treatment Planning based on Artificial Neural Networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 1, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Esesn, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.; Asari, V.K. The history began from alexnet: A comprehensive survey on deep learning approaches. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01164. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Large-scale machine learning with stochastic gradient descent. In Proceedings of the COMPSTAT’2010, Paris, France, 22–27 August 2010; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.; Hu, J. A K-fold Averaging Cross-validation Procedure. J. Nonparametr. Stat. 2015, 27, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.02391. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-S.; Jung, S.-K.; Ryu, J.-J.; Shin, S.-W.; Choi, J. Evaluation of Transfer Learning with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Screening Osteoporosis in Dental Panoramic Radiographs. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.W.; Park, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.J. Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: Part 2-Might it be better than human? Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michele, A.; Colin, V.; Santika, D.D. Mobilenet convolutional neural networks and support vector machines for palmprint recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 157, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.I.; Jung, S.K.; Baek, S.H.; Lim, W.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Yang, I.H.; Kim, T.W. Artificial Intelligent Model With Neural Network Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Orthodontic Treatment | Orthognathic Surgery | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 159 | 174 | 333 |
| Number of females/males | 88/71 | 93/81 | 181/152 |
| Mean age (SD) | 22.7 (5.8) | 23.4 (4.9) | 23.1 (5.1) |
| Model | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified-Alexnet | 0.969 (±0.019) | 0.919 (±0.030) | 0.852 (±0.041) | 0.973 (±0.017) |
| MobileNet | 0.908 (±0.032) | 0.838 (±0.429) | 0.761 (±0.051) | 0.931 (±0.028) |
| Resnet50 | 0.923 (±0.030) | 0.838 (±0.429) | 0.750 (±0.052) | 0.944 (±0.025) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-S.; Ryu, J.-J.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, D.-Y.; Jung, S.-K. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124
Lee K-S, Ryu J-J, Jang HS, Lee D-Y, Jung S-K. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(6):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ki-Sun, Jae-Jun Ryu, Hyon Seok Jang, Dong-Yul Lee, and Seok-Ki Jung. 2020. "Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications" Applied Sciences 10, no. 6: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124
APA StyleLee, K.-S., Ryu, J.-J., Jang, H. S., Lee, D.-Y., & Jung, S.-K. (2020). Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Based Analysis of Cephalometric Radiographs for Differential Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery Indications. Applied Sciences, 10(6), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10062124







