Featured Application
African catfish mucus (ACM), a waste product sustainably sourced from fish production, has potential as a natural emulsifier in food emulsion formulations and the cosmetic industry.
Abstract
Mucus, a waste product produced when African catfish undergoes stress, has lubricating effects and could be a potential emulsifier. Emulsions are thermodynamically unstable; researchers have documented synthetic bio-polymers as emulsifiers, but its sustainability is in question. This research aims to establish some physicochemical properties of African catfish mucus (ACM) and its effect in soya milk emulsions. A Zetasizer and Turbiscan were used to measure stability, morphology was determined with Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), while functional groups in ACM and ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions were determined using Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier Transform Infra-red spectroscopy. ACM is a stable hydrogel with negatively charged (−36.2 mV) loosely bound electrons with polar and non-polar portions. ACM concentrations of 1, 3, and 5 g w/w stabilized soya milk emulsions after 180 min of storage. The spectra of stabilized emulsion revealed interactions with soya milk droplets. ACM encapsulated the stabilized emulsion and conferred a kind of cohesive interaction and stability. Turbiscan revealed that the mucin formed strong cohesive connections with stabilized emulsions and the mucin exhibited adhesive properties. ACM is an excellent natural emulsifier with mucoadhesive properties as it encapsulates soya milk to enhance stability.
1. Introduction
Fish skin mucus, a waste product, is a substance produced when the fish undergoes stress. Mucus obtained from fish has anti-microbial and lubricating properties; and contains proteins, sugars and nucleic acid [1,2,3]. The disposal of this mucus has raised economic and environmental concerns for the fish industry in recent times [4,5]. Researchers have regarded food security as an important subject for many years, particularly as poverty still exists in some areas globally [6]. Statistics from the United Nations Development Program in 2012 indicated that more than 25% of persons in Sub-Saharan Africa continue to be malnourished [6]. The 2030 program for sustainable development suggests the use of novel technology in adding value to agricultural products such as bread, fish, and meat [6,7]. Consequently, a primary concern of researchers has been value-addition to fish and fish products for sustainable fisheries development to curtail fish wastes [8,9]. Emulsions are systems that could change phases thermodynamically; they comprise two non-miscible liquids, commonly oil and water or milk dispersions, which destabilize over time via mechanisms such as coalescence, creaming, flocculation, phase inversion, and Ostwald ripening [10,11,12,13]. The thermodynamic change of phase of emulsions and its breakdown over time is as a result of specific gravity differences in the milk/oil globules and the aqueous phase [10,11,14]. Kinetic stability of emulsions can be achieved by using emulsifiers that allow the dispersed phase to be suspended in a continuous phase due to the intrinsic properties of the emulsifier [10,15]. Previously, synthetic bio-polymers (κ-Carrageenan), synthetic surfactants (Spans and Tweens), animal-based (egg protein, gelatin whey protein), and other surfactants (poly-glycerol esters of fatty acids and sucrose fatty acid ester) have been used as emulsifiers [15,16,17,18]. However, due to consumer preference, researchers have been motivated to use natural bio-polymers as emulsifiers instead of synthetic bio-polymers and surfactants [19]. Previous studies have reported the use of plant-based foods as emulsifiers such as Bambara groundnut flour [20,21], quillaja saponin and soy lecithin [22], lutein [23], and hydrolyzed rice glutelin and quillaja saponin [24]. Plant-based emulsifier sources are natural, but its sustainability is in question as it serves as a food ingredient. Fish skin mucus (FSM) could be a potential natural emulsifier as it is a waste product sustainably sourced from fish production. African catfish mucus (ACM) could serve as a cheaper emulsifier compared with synthetic emulsifiers since it is sourced sustainably as waste during fish processing. Furthermore, that ACM is not a food source coupled with the fact that its use would lead to a greener environment makes it a better sustainable source in comparison to synthetic emulsifier sources; however, studies on FSM as an emulsifying agent has not received much attention from researchers despite its benefits.
Studies have revealed that the analysis of spectrum, microstructure, and stability could depict the physicochemical properties of bio-polymers. Fourier Transform Infra-red (FTIR) spectroscopy has been used in the analysis of biomaterials for more than half a century [25,26,27,28,29]. In the last decade FTIR in conjunction with attenuated total reflectance (ATR) spectroscopy, has been used to determine the structure of bio-polymers [26,30,31]. The technique is now used to express highly automated sub-cellular investigations for examining spectra of bio-systems and chemical changes at a molecular level that can be used to predict detailed information on the structural and functional groups in a biopolymer [32,33,34]. Also, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has been used to investigate the microstructure of bio-polymers because it produces highly magnified images [35,36,37]. However, the literature on the physicochemical properties of FSM such as functional groups, microstructure, and stability has been limited. Furthermore, a detailed investigation of the microstructural, functional groups and stability of ACM has been scarce.
The authors have reported that fish contributes to an intake of 19% animal protein for Africans and also contributes micronutrients and long-chain key polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) [38,39]. Also, authors have reported that catfish sourced from aquaculture and the wild are consumed in Africa, Asia and other parts of the world [40,41,42,43]. In the same vein, fiber-rich soy milk a plant-based protein has been used in bioproducts due to its low-cost, safe and easy storage parameters [44]. Animal and plant-based adhesives such as milk proteins, starch, and tree gums, are ecofriendly, adhere effectively with other materials, are safe and can be sustainably sourced [44,45]. In the past animal and plant-based adhesives were steadily replaced by synthetic adhesives because they were more expensive but due to consumer demand for natural products focus has shifted to bioadhesives that are sustainably sourced [45]. Also, food scientists have suggested the use of fish slime as emulsifiers based on the fact that they are consumed for its animal protein, micronutrients, and long-chain key PUFAs; for instance, hagfish, which includes its slime, is part of the diet in Japan and Korea [46,47]. Consequently, authors have reported that fish slime has the likelihood of being used as emulsifiers in food-grade emulsions [1,47,48].
There are documented research findings on the use of mucus obtained from hagfish as an emulsifier [1,2,47]. The FSM a postharvest waste product has both lubricating properties and anti-microbial properties but researchers have focused mainly on its anti-microbial action [49,50]. Similarly, Ref [49,51] revealed that the FSM of freshwater fishes such as estuarine catfish, African catfish, and tilapia have bactericidal properties due to the presence of anti-microbial peptides [52,53]. Hence, ACM could be a potential emulsifier. Despite the lubricating and anti-microbial benefits of ACM, the literature on its physicochemical properties and its effect on the stability of emulsions is scarce.
The South African fishing industry is currently plagued with under-use of wastes from fish that could add value to the industry. Therefore, the objective of this work was to characterize selected physicochemical properties of ACM and investigate the effectiveness of ACM in stabilizing soya milk emulsions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Commercial brands of soya milk were procured from a neighborhood hypermarket and ACM was used as an emulsion stabilizer.
2.2. Methods
ACM was collected using an adaptation of a method developed by [54]. Before acquiring ACM, the African catfish was made insensitive using 100 mg per liter methanesulfonate [55]. The insensitive African catfish were blotted dry on a dissection tray and a fish stimulation gadget (HPG1, Velleman Instruments, 18 V, 80 Hz) was used to enhance mucus discharge aseptically from mucus glands by placing the gadget on the ventral lateral section of the catfish [2,51]. ACM secreted was stabilized in medium-chain triglycerides oil, as described by [1,50,56]. The insensitive African catfish were conveyed to a recuperation bath after the ACM was collected. The retained ACM was freeze-dried; a portion of the freeze-dried ACM was dissolved in Milli Q Water and used for zeta potential, morphology, and stability tests while the freeze-dried ACM was used to acquire wavelength peaks. Sampling was done using the reviewed South African National Standard for the care and use of laboratory animals for scientific purposes [57].
2.3. Emulsion Formulation
The hydrophobic dispersed state used was commercial brands of soya milk procured from a neighborhood hypermarket and was not purified further. Soya milk emulsions were formulated from a dispersed state comprised of soya milk and a continuous state comprising of freeze-dried ACM dispersion using a method developed by [40]. Freeze-dried ACM diffusions of known amounts were formulated by adding precise quantities of freeze-dried ACM (1, 3 and 5 g (w/w)) in specific amounts of Milli Q Water (ACM dispersions). Soya milk (10, 30, 50, 75 mL (w/w)) were added into the ACM dispersions to attain different ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsion concentrations. The precise quantities of freeze-dried ACM in Milli Q Water and measured quantities of soya milk were homogenized with the aid of an Ultra Turrax T-25 homogenizer (KA®-Werke GmbH & Co. KG IKA, Germany) at 11,000 rpm for 10 min [40]. The temperature was controlled using a thermal ice jacket at 20 ± 1 °C.
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Particle Size Analysis
TEM was used to investigate the microstructure of ACM and soya milk emulsions stabilized by ACM using modifications of a method described by [58]. The microstructure of ACM and soya milk emulsions stabilized by ACM was investigated using an FEI/Tecnai T20 TEM with a high-resolution camera and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) system using modifications of methods described by [58,59]. An accelerating voltage of 200 kV was used in investigating the ACM dispersion and each emulsion sample. One droplet of each sample dispersion was transferred over the surface of the carbon-coated copper grid, negatively spotted with a 2% (w/w) solution of uranyl acetate and then dried at room temperature [58,59]. Digital image analysis was used to determine the particle size. The TEM images were acquired using the FEI/Tecnai T20 TEM and a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera size of 2048 × 2048 (Gatan UK Milton Park Innovation Centre Abingdon OX14 4RY United Kingdom Gatan, USA) [58,59]. The images at 50 and 100 nm were taken to quantify the particle size of each soya milk globule and its distribution in each emulsion sample using the method described by [60]. The particle size distribution of ACM-stabilized emulsions was elucidated by calculating Sauter mean diameter (D(3,2)) using Equation (1) while the standard deviation i.e., value of the width of the milk goblets distribution in the ACM-stabilized emulsion was calculated using Equation (2). The average droplet size is given by Equation (3) where ni is the number of goblets in each size class, di is the particle diameter, ∑ni is the total number of droplets, and dn is average droplet size [61].
2.5. Zeta Potential and Particle Size Measurement
The electrical charge was investigated with the aid of a particle electrophoresis Nano series ZS instrument (Zetasizer Nano-ZS, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK) by determining the electrophoretic mobility of the droplets using a capillary electrophoresis cell. The particle size was measured using the principle of direct light scattering with the aid of a particle electrophoresis Nano series (Zetasizer Nano-ZS, Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK). The ACM dispersion electrical charge and the particle size of soya milk emulsion stabilized with ACM were analyzed in three replicates.
2.6. Absorption Bands Analysis
Infra-red spectra of ACM were gathered with a Perkin Elmer universal total reflectance-Fourier Transform Infra-Red spectrum II spectrometer (UATR-FTIR, Llantrisant, Wales, UK), run with spectrum software as described by [62]. Wavelength bands were collected in the region of 4000–400 cm−1 to categorize the functional groups in the ACM [62].
2.7. Stability Studies
The Turbiscan MA 2000 (Formulaction, Toulouse, France) was used to evaluate the stability of the ACM soya milk stabilized emulsions as described by [40]. ACM dispersions and ACM stabilized emulsions of about 7 mL was measured into a Turbiscan tube (65 mm length) and measurements were taken. The measurement involved scanning each dispersion and emulsion along with its height for 3 h at 30 min intervals [21]. The backscattering (BS) and transmission curve acquired provided the BS and transmission flux percentage in relation to the instrument’s internal standard as a function of the height of the sample. To study the effect of ACM on the stability of ACM-stabilized emulsions multiple scans were analyzed using the principle of Multiple Light Scattering in both Transmission (T) and Backscattering (BS) mode.
2.8. Data Analysis
GraphPad Prism version 5.00 for Windows, GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA, was used for data analysis. The results were subject to Two-way analysis of variance after Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and as mean ± standard error for the backscattering flux percentage and particle size as a function of stability. The coefficient of determination (R2) was used to assess the goodness-of-fit and predict the response that had more impact on stability.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Appearance of Unmagnified Freeze-Dried ACM
Unmagnified freeze-dried ACM was found to be greyish with a powdery appearance as shown in Figure 1a.

Figure 1.
Structural characteristics of (a) unmagnified ACM; (b) ACM at 0.2 microns; (c) ACM-stabilized 30 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsion at 100 nm with thread-like fibers; (d) ACM-stabilized 30 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsion at 100 nm; (e) ACM-stabilized 50 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsion at 50 nm; (f) ACM-stabilized 50 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsion at 100 nm.
3.2. Structural Characteristics of Freeze-Dried ACM in Milli-Q Water
Freeze-dried African catfish slime in Milli Q Water formed a gel aggregate of fibrous material. Figure 1b shows the photographic image of dispersion of freeze-dried ACM, and TEM images of ACM at 0.2 microns. Structure studies with the transmission electron microscope revealed that the ACM dispersion is spherical in shape and forms aggregate networking into gel fibers as revealed The images obtained at 0.2 microns show some air bubbles which become enmeshed when the ACM was homogenized in Milli-Q Water. The particle size of ACM measured under TEM analysis and Zetasizer was 73–80 nm. The freeze-dried ACM, Figure 1b was found to entrap the Milli Q Water and form a dilute hydrogel that was adhesive [2,47]. The TEM image of ACM in Milli Q Water Figure 1b show intermediate filaments which entrap Milli Q Water to form an elastic gel-like stable structure [35,63]. The results obtained from structural investigations of ACM in Milli Q Water using TEM is in agreement with results obtained in TEM investigations of Atlantic and Pacific hagfish mucus as reported by other authors [35,63].
3.3. Structural Characteristics of ACM-Stabilized Soya Milk Emulsion
TEM imaging of soya milk emulsion stabilized with ACM was investigated with concentrations of 30 mL and 50 mL (w/w) soya milk to 3 g and 5 g concentrations of ACM. Figure 1c,d depict the TEM images of 30 mL soya milk emulsion stabilized with 3 g African catfish. The images show the encapsulation of the soya milk dispersion by the ACM to form a cohesive aggregate structure. Figure 1e,f show the TEM images of 50 mL soya milk emulsion stabilized with 1 g African catfish with similar encapsulation. The particle size measured from TEM analysis for 30 mL (w/w) Soya milk emulsion stabilized with 3 g ACM was 112–125 nm while that for 50 mL (w/w) was between 173–180 nm. Figure 1c,d show TEM images of 30 mL soya milk emulsion stabilized with 3 g ACM (w/w). The images show that aggregates of thread-like filamentous fibers of ACM encapsulate the soya milk emulsion leading to the bridging and flocculation of the soya milk emulsion. The particle size of emulsions stabilized with a higher concentration of ACM was lower than the particle size of emulsion stabilized with a lower concentration of ACM this might be a result of constant time and homogenization speeds used in formulating the emulsions. The TEM images of 30 mL and 50 mL soya milk emulsion stabilized with ACM (Figure 1c–f) showed similar encapsulation. It can be inferred that the TEM images obtained for both emulsions showed that the soya milk dispersion was encapsulated by the ACM to form a cohesive aggregate raw structure. Thus, it can be postulated that encapsulation of the soya milk stabilized emulsion could be a result of the ACM potential to adhere to the soya milk emulsions’ droplets which induces a kind of cohesive interaction and confers stability as suggested by [2].
3.4. Functional Group Characteristics of Freeze-Dried ACM
Several authors have reported that Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier transform infra-red (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy is a good tool to determine the functional groups of bio-polymers [26,30,31]. The ATR-FTIR spectra of freeze-dried ACM showing the wavelength peaks in the range 4000–400 cm−1 with the focal functional group are presented in Figure 2a. Table 1 also shows the focal functional groups in freeze-dried ACM. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy was employed in analyzing the functional groups of unprocessed ACM (Table 1 and Figure 2a). Twelve vital absorption peaks were observed from the spectrum of ACM (Table 1). The peaks at 3301 and 3080 cm−1 were designated to stretching vibrations of hydroxyl groups of hydrophilic amino and defined aromatic overtone that may be due to aromatic amino acids [64,65]. The peak at 2958 cm−1 could be attributed to CH2, asymmetric stretch for bio-polymers such as glycoprotein or mucus [66,67]. The peak at 2924 cm−1 could be attributed to the C–H symmetric and anti-symmetric stretching vibrations in CH2 ascribed to pyranose rings which point to aliphatic (–CH) chains in the slime [32]. The peaks at 1634 and 1539 cm−1 could be as a result of amide stretch, from ß-sheets absorption bands (Amide I bands) and aromatic C=C bending or C=C stretch in the ring (Amide II) [64,65]. The peak at 1414 cm−1 represents a C–O of carboxyl group accepting zero or one H-bond or O–H (alcohols) bend while the peak at 1136 cm−1 could represent anti-symmetric C–O–C glycoside bond, C–O strong bond stretch [29,68]. The peak at 1040 cm−1 is ascribed to a primary amine, stretching, secondary R-carbon of amino acids for glycoprotein or mucus while the peak at 867 cm−1 represents C–H out of plane bending [66,69,70]. In addition, the peaks at 626 cm−1 are attributed to C–H vibrating bends in RC=CH sites while peaks at 524 cm−1 are linked to S–S disulfide stretch in bio-polymers with proteins and collagen [69,71,72].
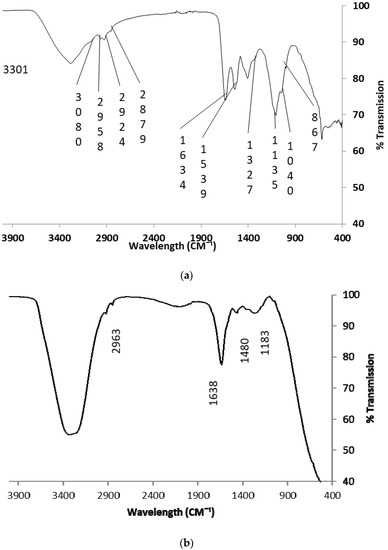
Figure 2.
ATR-FTIR spectra of (a) raw freeze-dried ACM; (b) ACM-stabilized emulsion.

Table 1.
Functional groups of raw African catfish mucus.
The presence of amide A (N–H) stretching vibration found at around 3301 cm−1, amide I at 1634 cm−1 and Amide II near 1539 cm−1 in ACM suggests the presence of α helix with ß- turns. The authors have. reported that although, Amide I, II, and III bands could be used to affirm protein secondary structure, FTIR investigations of amide I give better results as it is most responsive to changes in conformation and establish the presence of peptide bonds [27]. The peak of amide I occurs as a result of stretching vibration of C–O bonds and N–H bending while C–H stretching vibration is responsible for the Amide II band [27,70]. In the same way, studies by other authors revealed that amide I bands were found in the range 1600–1700 cm−1 with bands that show C–O stretching vibrations of protein-peptide bonds which is consistent with the results obtained in the ACM [28]. The distinctive absorption bands of 3301 cm−1, 1634 cm−1 and 1539 cm−1 in the ACM designates the presence of peptide bonds [28,64,65,70].
ACM also showed wavelength peaks of 1136 cm−1, which suggested the possibility of anti-symmetric glycoside bond, C–O strong bond stretch [29,68,70,73] investigated the physicochemical characteristics of glycoprotein present in green algae and suggested that asymmetric stretch of bonds with intense bands around 1130 cm−1 could be used to identify glycosidic linkages. Furthermore, FTIR analysis of brown algae polysaccharides indicated peaks around 1135 cm−1 which are characteristics of vibrational stretches of the glycosidic C–O group of bio-polymers. The authors stated further that broad peaks in the range 1120–1270 cm−1 pointed to S=O stretch in sulphate groups for molecular branches of alginic acid or fucoidan [29,70]. Hence, the wavelength peak of 1136 cm−1 recorded in the spectra of raw FTIR spectra of ACM could be attributed to the anti-symmetric glycoside bond. Several authors have established that the presence of the glycosidic bond in glycoproteins is the reason a glycan can covalently attach to polypeptide side-chains and form stable structures that are suitable for biological processes [74,75,76]. It can be inferred that the raw FTIR spectrum of ACM probably has glycosidic linkages similar to other glycoproteins.
3.5. Functional Group Characteristics of ACM-Stabilized Soya Milk Emulsion
The ATR-FTIR spectra of soya milk emulsion stabilized with freeze-dried ACM showing the wavelength peaks in the range 4000–400 cm−1 with the focal functional groups shown in Figure 2b. Also Table 2 gives the wavelength peak changes noted in ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions. The shift in the amide I at 3336 cm−1 is similar to the stretching vibrations of hydroxyl groups of hydrophilic amino in the spectra of raw ACM however; the peak is much wider and profound (Table 2). This might result from interactions between the hydroxyl groups of hydrophilic amino of ACM and the soya milk. Similarly, the peak at 2924 cm−1 in ACM which was ascribed to CH2 symmetric and anti-symmetric stretching vibrations shifted to a peak 2963 cm−1 in the ATR-FTIR spectra of soya milk emulsion stabilized with freeze-dried ACM (Table 2). In addition, shifts were observed for amide I at 1638 cm−1, C–O of carboxyl COO group accepting zero or one H-bond at 1480 cm−1 and anti-symmetric C–O–C glycoside bond, C–O strong bond stretch at 1183 cm−1 (Table 2). This phenomenon was described by [32] in the study of changes in the chemical composition of aloe vera and snail mucus composite scaffold using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. The higher wavelength bands for functional groups of amide A, amide I, C–O of carboxyl, COO group accepting zero or one H-bond, CH2 symmetric and anti-symmetric stretching vibrations and anti-symmetric C–O–C glycoside bond observed in the spectra of ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions (Figure 3 and Table 2) might suggest a type of bonding that leads to a stable structure. This is consistent with results observed in TEM images of ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsion (Figure 1c–f).

Table 2.
Interactions observed in the functional groups ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsion.
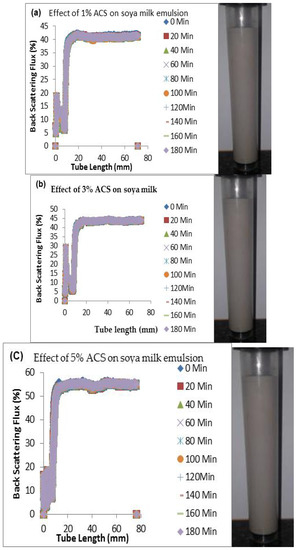
Figure 3.
Changes in stability of ACM-stabilized 50 mL (w/w soya milk emulsions (a) 1 g w/w; (b) 3 g w/w; (c) 5 g w/w African catfish mucus.
3.6. Stability of Freeze-Dried African Catfish Mucus in Milli-Q Water Using Zeta Potential
Zeta potential is a vital tool that could be used to evaluate if an emulsifier can stabilize dispersions or emulsions. It depicts the potential charge in the boundary double layer at the droplet boundary of the continuous and dispersed phases [77,78]. The absolute zeta potential of freeze-dried ACM in Milli Q Water was found to be −36.2 mV at a pH of 7.83. This data showed that sufficient repulsion exists between the droplets of the African Catfish mucins and Milli Q Water to keep particles away from each other. Published works propose that a dispersion becomes stable if its zeta potential is more than ±30 mV [78,79,80]. Stability is a result of static electrical repulsive forces between the particles hence the dispersion does not form aggregates because the absolute zeta potential is greater than 30 mV [60,78].
3.7. Stability of ACM-Stabilized Soya Milk Emulsions
Table 3 compares the particle sizes of the nine different combinations of ACM soya milk stabilized emulsions in terms of the Sauter mean diameter (D(3,2)) and its standard deviation. In the same vein, the results of higher concentrations of soya milk (75 mL) were not reported because according to [1] hagfish mucus entraps large volumes of water. Although the results for higher soya milk content was not presented in Table 3, results shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 supports this claim that ACM-stabilized emulsions containing 10 mL, 30, mL, 50mL and 75 mL soya milk were stable. The analysis of ACM-stabilized emulsions containing 75 mL soya milk was discontinued because the homogenized mixture contained low volumes of water (20, 22, and 24 mL w/w). The results obtained for the particle size from TEM imaging studies were similar to the particle size measured with the Zetasizer. The authors have established that the lower the particle size the more stable an emulsion becomes [21,40]. An increase in ACM concentration led to a decrease in D(3,2) of soya milk droplets for ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions containing 50 mL soya milk (Table 3). The results obtained showed that ACM-stabilized emulsions with 50 mL w/w soya milk performed better than emulsions with 10 and 30 mL w/w soya milk (Table 3). The D(3,2) of the three emulsions containing 50 mL soya milk stabilized with ACM concentrations 1, 3, and 5 g were 179.2, 176.1 and 172.9 nm respectively (Table 3). The smallest D(3,2) was found in the emulsion stabilized with. 5 g ACM for 10, 30 and 50 mL soya milk (Table 3) and it can be inferred that it is the most physically stable emulsion as a result of particle size and D(3,2) [21]. These observed results agree with stability results as a function of backscattering % flux in Figure 3. This occurrence might be a result of the decrease in diffusion time of ACM to the soya milk oil droplet surfaces, as well as, the formation of thicker adsorption layer which were influenced by an increase in ACM concentration in the continuous phase. This phenomenon results in less coalescence when mixing and sustains emulsion stability [21,61].

Table 3.
Effect of ACM on the stability of soya milk emulsions.
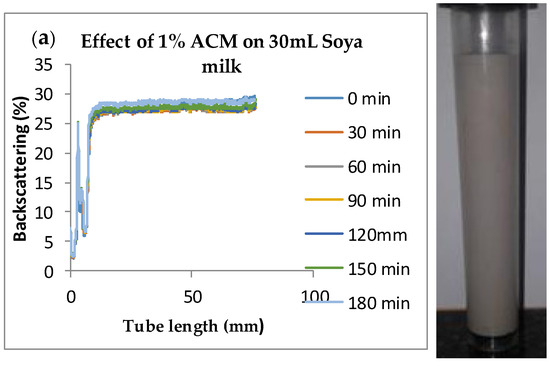
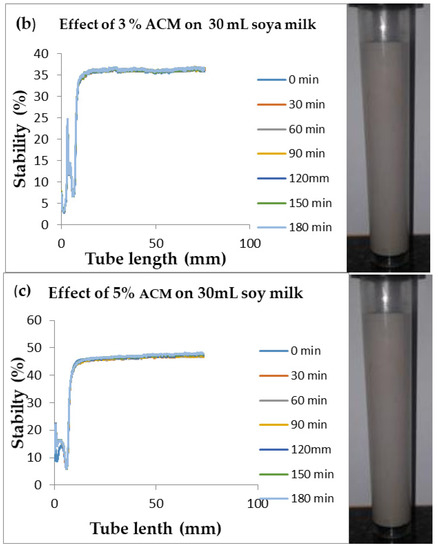
Figure 4.
Changes in stability of ACM-stabilized 30 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsions (a) 1 g w/w; (b) 3 g w/w; (c) 5 g w/w African catfish mucus.
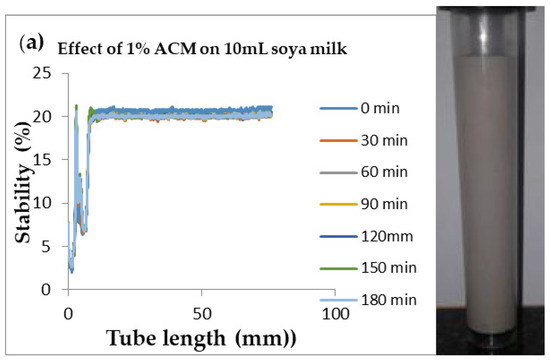
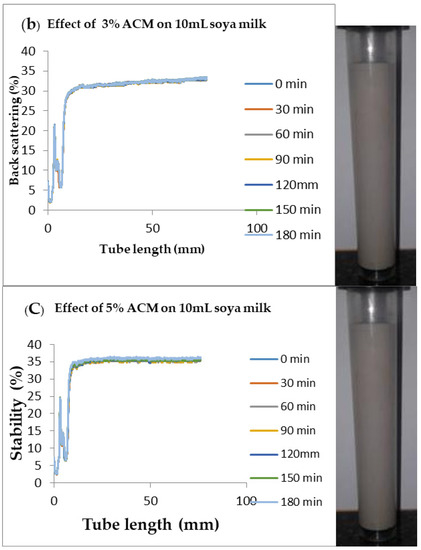
Figure 5.
Changes in stability of ACM-stabilized 10 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsions (a) 1 g w/w; (b) 3 g w/w; (c) 5 g w/w African catfish mucus.
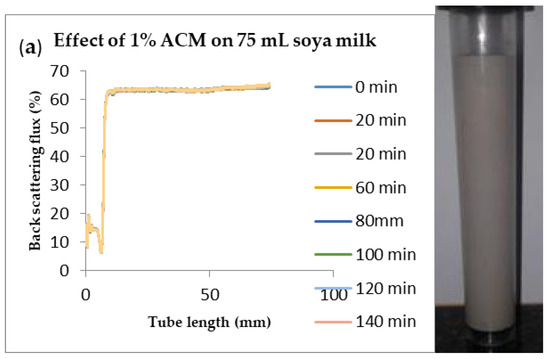
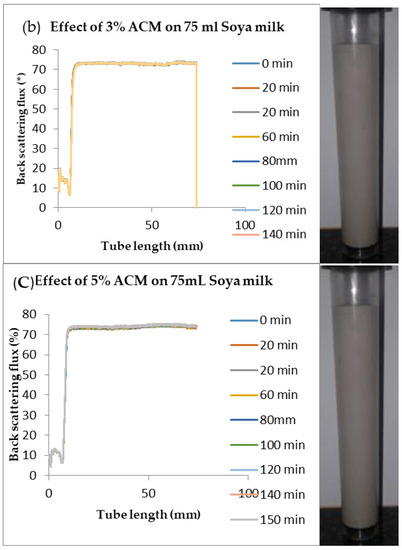
Figure 6.
Changes in stability of ACM-stabilized 75 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsions (a) 1 g w/w; (b) 3 g w/w; (c) 5 g w/w African catfish mucus.
The impact of ACM concentration on the particle size of an emulsion can also be revealed by changes in the particle size distribution of the emulsion as a function of the width of the distribution. Several authors have computed the width of distribution i.e., standard deviation as a variance of the mean diameter of droplets in the diffuse state [10,61]. Table 3 presents the changes in the standard deviation of values of the particle size, dependent upon the ACM amount used to stabilize the emulsion. An increase in ACM concentration led to a decrease in the standard deviation of all emulsions investigated i.e., mean droplets diameter deviation decreased as ACM concentration increased. Hence the impact of changes in ACM concentration on the standard deviation is similar to the impact of changes in ACM concentration on Sauter mean diameter versus (Table 1). These results are consistent with the results obtained in published works [21,61].
Changes in backscattering flux percentage (BS %) as a function of tube length of emulsion containing 50 mL (w/w) soya milk stabilized with (a) 1 g w/w (b) 3 g w/w (c) 5 g w/w ACM after 180 min were investigated as depicted in Figure 3. Similarly, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 shows the changes in backscattering flux percentage (BS %) as a function of tube length of emulsion containing 30 mL, 10 mL and 75 mL (w/w) soya milk stabilized with (a) 1 g w/w (b) 3 g w/w (c) 5 g w/w ACM after 180 min. Also Figure 7 was included to show Instability in homogenized soya milk and Milli Q Water for 10, 30, 50 and 75 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsions. Emulsion stability alludes to an emulsions’ capacity to withstand changes in its physicochemical characteristics through time [60]. Due to all ACM-stabilized emulsions’ turbid appearance through scans, an analysis of the distinct backscattering (BS) characteristics of ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions as a function of tube magnitude were carried out to ascertain the stability of the system at room temperature (20 °C). The BS characteristics and matching particle size for each concentration are presented in Figure 3. The initial average BS flux percentage for ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions was 41.39%, 43.75%, and 55.34% respectively for emulsions stabilized with 1, 3 and 5 g w/w ACM concentrations. It was observed that the BS flux percentage of all emulsions investigated depended greatly on the concentration of ACM [21,60]. The results of lower concentrations of soya milk were not reported because studies on hagfish slime stabilized soya milk showed that small quantities of hagfish slime was able to stabilize soya milk emulsions [2,40]. Also, the results of higher concentrations of soya milk (75% mL) were not reported because according to [1] hagfish mucus entraps large volumes of water. Hence, this study only investigated the effect of ACM concentrations on 50 mL w/w soya milk emulsions. Literature studies have established relationships between the BS flux % and particle size for soy stabilized emulsions [40]. Studies have shown that the BS flux % depicts the arrangement of molecules before it becomes unstable hence a high percentage in BS flux % infers a more stable structure [21].
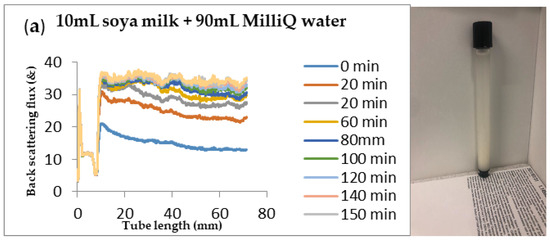
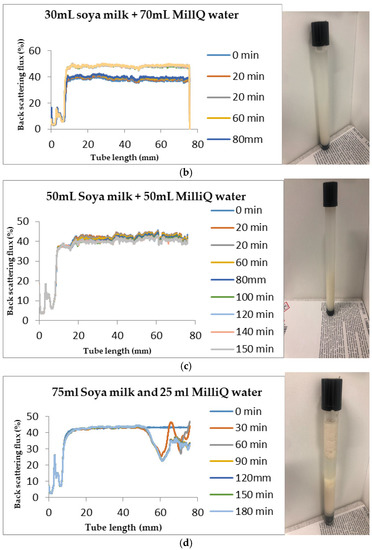
Figure 7.
Instability in homogenized soya milk and Milli Q Water for (a) 10 mL (b) 30 mL (c) 50 mL and (d) 75 mL (w/w) soya milk emulsions.
In Figure 3 the tube length is plotted on the x-axis while the BS flux percentage is plotted on the y-axis. It shows that all three emulsions conformed to similar disintegration modes but, scans did not ideally align as slightly lower percentages in BS flux % were noted along the tube. The observed slightly lower percentages in BS flux % as emulsions disintegrate when particles aggregate could be because of kinetic instability. This observed phenomenon is consistent with reports by [81] who established that flocculation resulted in the disintegration of rice glutelin stabilized emulsions destabilized by flocculation [24]. In all the three ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions, a peak was observed within the 0–20 mm range, followed by a stable phase within the 20–40 mm range, then a slight lowering within the 40–60 mm range and a final stage of rest within the 60–80 mm range. All the ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions formed a cohesive network which suggests that the ACM stabilizes emulsions through a different entrapment interaction as described by [2]. for hagfish mucus stabilized soya milk emulsions. The results also suggest that the ACM has the potential to stabilize emulsions even with low concentrations and form a cohesive interactive network as described by [2]. The authors stated that little amounts of hagfish mucus were able to stabilize soya milk emulsions as a result of a different entrapment interaction called mucoadhesion [2]. The average initial BS flux % of 55.34% exhibited by the ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions showed that higher concentrations of ACM could lead to better stability as suggested by [40]. Also, to better understand the stability kinetics of ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions, an evaluation of differences in BS flux % within the 20–40 mm range over time was conducted using one-way ANOVA as depicted in Table 2. The selected data points on BS flux % within the 20–40 mm range over time was compared with particle size to decipher the best-fit predictor of stability in ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions.
The effect of ACM on the stability of soya milk emulsions using one-way ANOVA on initial BS flux (%), and D(3,2) (nm) is presented in Table 2. The goodness-of-fit was assessed using the coefficient of determination (R2) to establish which effect was more significant in the response to stability between particle size and BS flux %. One-way ANOVA subsequent to Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons (BMC) test was performed using GraphPad Prism version 5.00 for Windows to evaluate whether the initial BS flux (%) or the D(3,2) as a function of particle size (nm) better explained the stability characteristics of the ACM soya milk stabilized emulsions. A significant difference (p < 0.05) was established on all three ACM soya milk stabilized emulsions with respect to BS flux % and particle size at pH range 7.85–7.95. The F statistic of BS flux % was 5078 while the F statistic of particle size was 27. The result implied that the means in both responses i.e., BS flux % and particle size significantly responded to concentrations of ACM but the response of BS flux % was more significant than that of particle size as a function of Sauter mean diameter. This establishes that we can reject the null hypothesis that ACM concentrations would not affect or enhance the stability of ACM soya milk emulsions. The adjusted p-value was calculated for both responses to establish the most significant response. The adjusted p-value obtained for BS flux % using the BMC test was <0.0001 for all ACM concentrations (1, 3 and 5 g w/w). However, the adjusted p-value obtained for particle size using the BMC test was 0.024, <0.001 and 0.024 respectively for ACM concentrations (1, 3 and 5 g w/w). This result showed that the BS flux % was a better response factor in comparison to particle size. A similar trend was followed with the R2 statistic with the values 0.9994 and 0.9000 for BS flux % and particle size, respectively. The results show that data obtained from BS flux % closely fit the regression line by about 94% while the data for particle size was 90% fit. These results show that data from both the BS flux % and the particle sizes explains the variance of the response around its means. In addition, both responses are good predictors of stability of an emulsion. The result that BS flux % and the particle sizes are good predictors of the stability of an emulsion is consistent with the results obtained by other authors [40,46]. However, although both responses are good predictors of the stability of an emulsion, the BS flux % response with adjusted p-value < 0.0001, F statistic of 5078, and R2 statistic 0.9994 better explains the stability characteristics of the ACM soya milk stabilized emulsion.
3.8. Mucoadhesive Property of African Catfish Mucus
Even though automated and rheological analysis have been used to depict that bio-polymers could be mucoadhesive, studies have revealed that the analysis of spectrum and image analysis could be used to establish the bio-adhesive properties of mucus-based bio-polymers [66,82,83]. TEM imaging results of ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsions revealed a form of entrapment by which the mucins in the African catfish entrapped and adhered to the droplets of the soya milk emulsion to confer stability on the ACM-stabilized soya milk emulsion by forming aggregates. Researchers have investigated the aggregation effect of saliva mucus on food emulsions stabilized with protein from whey protein isolate (WPI), b-lacto-lactoglobulin (b-lg), b-casein, and Tween 20 with mucus obtained from humans and pigs using light microscopy [84]. The authors reported that aggregation was irreversible with emulsions stabilized with Tween 20 and undiluted saliva from humans and pigs. However, saliva from humans and pigs coupled with 20:1 dilutions recorded reversible aggregations on emulsions i.e., diluted saliva did not aggregate emulsions because it did not contain mucins. The authors proposed that aggregation was due to the presence of glycoproteins in the mucin because protein is a major part of mucins in saliva. However, irreversible aggregations occurred for WPI- and b-lg-stabilized emulsions even with 20:1 diluted saliva emulsions while reversible aggregations occurred for WPI- and b-lg-stabilized emulsions stabilized with undiluted saliva [84]. The authors suggested that undiluted saliva had a different mechanism for aggregating emulsions and hypothesized that mucin a key protein in saliva accounted for the observed aggregation, but also noted that other salivary components influenced the aggregation. This phenomenon was also observed when [1] investigated the mucoadhesive properties of hagfish mucin aggregated soya milk. Consequently, authors have established that fish, humans, and pig mucin have bio-adhesive properties [1]. Literature has established that mucin interacts strongly with lectins, as lectins selectively adhere to cells and forms precipitates with glycopeptides [2]. The authors [2] elucidated that this phenomenon occurred because soybean lectins adhere to hagfish mucin and conferred cohesive stability on hagfish mucus stabilized soya milk emulsions [2]. It can be suggested that the aggregation of the soya milk emulsion is as a result of adhesion between the mucins in African catfish with the soya milk which could be as a result of strong cohesive bonds formed and could confer adhesive properties on the African catfish mucilage as suggested by [2].
4. Conclusions
ACM could be a potential natural emulsifier as it is a waste product sustainably sourced from fish production and its usage could lead to a greener environment. Due to consumer preference for natural products, ACM could serve as a cheaper emulsifier compared with synthetic emulsifiers. ACM, as an emulsifier, provides specific dispersion and stability characteristics for emulsions. The increase in ACM concentration led to a reduction of Sauter mean diameter of dispersed soya milk droplets and narrowed the range of particle size distribution. ACM is a stable material with negatively charged (−36.2 mV) loosely bound electrons with polar and non-polar portions. The application of low-concentration 1 g, 3 g, and 5 g w/w of ACM led to stabilized soya milk emulsions. The results from TEM, zeta potential, FTIR, particle size, and BS flux % analysis showed that ACM is a good natural emulsifier with mucoadhesive properties as it encapsulates soya milk to enhance stability. A significant difference (p < 0.05) was established on all three ACM soya milk-stabilized emulsions with respect to BS flux % and particle size. The ANOVA studies show that although both particle size and BS flux % responses are good predictors of stability of an emulsion, the BS flux % response better explains the stability characteristics of the emulsion.
5. Patents
This work is being considered for intellectual property rights by the Technology Transfer Office, Cape Peninsula University of Technology.
Author Contributions
A.J.O.O., D.I.I.-O., and V.A.J. designed the experiment; A.J.O.O. performed the characterization and stability experiments and drafted the manuscript; D.I.I.-O. and V.A.J. contributed research materials and provided necessary inputs for the revision of the manuscript as research advisors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Cape Peninsula University of Technology (CPUT) through the university research fund (URF) program.
Acknowledgments
A.O. Oluwole acknowledges the grant provided by the Cape Peninsula University of Technology, for his doctoral studies, and the staff development support received from Agricultural Research Council of Nigeria.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Böcker, L.; Ruühs, P.A.; Böni, L.; Fischer, P.; Kuster, S. Fiber-enforced hydrogels: Hagfish slime stabilized with biopolymers including κ-carrageenan. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Böni, L.; Fischer, P.; Böcker, L.; Kuster, S.; Rühs, P.A. Hagfish slime and mucin flow properties and their implications for defense. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter, M.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Biological and ecological roles of external fish mucus: A review. Fishes 2018, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Terova, G.; Simó-Mirabet, P.; Rimoldi, S.; Folkedal, O.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Olsen, R.E.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Skin mucus of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Protein mapping and regulation in chronically stressed fish. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadir, T.; Çelebi, H.; Simsek, I.; Tulun, S. Antibiotic applications in fish farms and environmental problems. Turk. J. Eng. 2019, 3, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Conceição, P.; Levine, S.; Lipton, M.; Warren-Rodríguez, A. Toward a food secure future: Ensuring food security for sustainable human development in Sub-Saharan Africa. Food Policy 2016, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikström, F.; Verghese, K.; Auras, R.; Olsson, A.; Williams, H.; Wever, R.; Grönman, K.; Kvalvåg Pettersen, M.; Møller, H.; Soukka, R. Packaging strategies that save food: A research agenda for 2030. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Arthur, R.; Norbury, H.; Allison, E.H.; Beveridge, M.; Bush, S.; Campling, L.; Leschen, W.; Little, D.; Squires, D. Contribution of fisheries and aquaculture to food security and poverty reduction: Assessing the current evidence. World Dev. 2016, 79, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.R.; Newton, R.W.; Tlusty, M.; Little, D.C. The rise of aquaculture by-products: Increasing food production, value, and sustainability through strategic utilisation. Mar. Policy 2018, 90, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Kelly, A.L.; Miao, S. Emulsion-based encapsulation and delivery systems for polyphenols. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Jafari, S.M. Improving emulsion formation, stability and performance using mixed emulsifiers: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 251, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, A.P.; Hung, Y.-C.; Adhikari, K. Optimization of Emulsifier and Stabilizer Concentrations in a Model Peanut-Based Beverage System: A Mixture Design Approach. Foods 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadros, T.F. Interfacial Phenomena and Colloid Stability: Industrial Applications; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.-J.; Dong, M.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Ren, J.-N.; Pan, S.-Y.; Fan, G. Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release. Molecules 2016, 21, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Effect of emulsifiers on the preparation of food-grade oil-in-water emulsions using a straight-through extrusion filter. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2002, 104, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.P.; Nakajima, M. Effect of polyglycerol esters of fatty acids on physicochemical properties and stability of β-carotene nanodispersions prepared by emulsification/evaporation method. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralova, I.; Sjöblom, J. Surfactants used in food industry: A review. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2009, 30, 1363–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural emulsifiers—Biosurfactants, phospholipids, biopolymers, and colloidal particles: Molecular and physicochemical basis of functional performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasinu, E.G.; Ikhu-Omoregbe, D.I.; Jideani, V.A. Influence of selected physicochemical factors on the stability of emulsions stabilized by Bambara groundnut flour and starch. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7048–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphosa, Y.; Jideani, V.A.; Adeyi, O. Effect of soluble dietary fibres from Bambara groundnut varieties on the stability of orange oil beverage emulsion. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2017, 9, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Formulation of food emulsions using natural emulsifiers: Utilization of quillaja saponin and soy lecithin to fabricate liquid coffee whiteners. J. Food Eng. 2017, 209, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, F.; Weiss, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Lutein-enriched emulsion-based delivery systems: Influence of emulsifiers and antioxidants on physical and chemical stability. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Q.; McClements, D.J. Enhancing the formation and stability of emulsions using mixed natural emulsifiers: Hydrolyzed rice glutelin and quillaja saponin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba)-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.; Amado, A.M.; Critchley, A.T.; Van de Velde, F.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J. Identification of selected seaweed polysaccharides (phycocolloids) by vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman). Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassford, S.E.; Byrne, B.; Kazarian, S.G. Recent applications of ATR FTIR spectroscopy and imaging to proteins. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba)-Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarroukh, R.; Goormaghtigh, E.; Ruysschaert, J.-M.; Raussens, V. ATR-FTIR: A “rejuvenated” tool to investigate amyloid proteins. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba)-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2328–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.; Sanjeewa, K.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Lee, W.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, E.-A.; Gunasekara, U.; Abeytunga, D.; Nanayakkara, C.; de Silva, E. FTIR characterization and antioxidant activity of water soluble crude polysaccharides of Sri Lankan marine algae. Algae 2017, 32, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniszewska, E.; Malek, K.; Baranska, M. Rapid approach to analyze biochemical variation in rat organs by ATR FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, L.; Rencoret, J.; Maliger, V.R.; Rackemann, D.W.; Harrison, M.D.; Gutiérrez, A.; del Riéo, J.C.; Doherty, W.O. Structural characteristics of bagasse furfural residue and its lignin component. An NMR, Py-GC/MS, and FTIR study. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4846–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, D.E.L.; do Amaral Sobral, P.J. Characterization of gelatin/chitosan scaffold blended with aloe vera and snail mucus for biomedical purpose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Hannoufa, A.; Christensen, D.; Shi, H.; Prates, L.; Yu, P. Molecular Structural Changes in Alfalfa Detected by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy in Response to Silencing of TT8 and HB12 Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Yan, X.; Peng, Q.; Yu, P. Using vibrational ATR-FTIR spectroscopy with chemometrics to reveal faba CHO molecular spectral profile and CHO nutritional features in ruminant systems. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 214, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fudge, D.S.; Schorno, S. The hagfish gland thread cell: A fiber-producing cell involved in predator defense. Cells 2016, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drapala, K.P.; Mulvihill, D.M.; O’Mahony, J.A. A review of the analytical approaches used for studying the structure, interactions and stability of emulsions in nutritional beverage systems. Food Struct. 2018, 16, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielke, C.; Stradner, A.; Nilsson, L. Characterization of cereal β-glucan extracts: Conformation and structural aspects. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Barange, M.; Subasinghe, R.; Pinstrup-Andersen, P.; Merino, G.; Hemre, G.-I.; Williams, M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050–Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.; Tran, N.; Pethiyagoda, S.; Crissman, C.C.; Sulser, T.B.; Phillips, M.J. Prospects and challenges of fish for food security in Africa. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, O.; Ikhu-Omoregbe, D.; Jideani, V. Emulsion stability and steady shear characteristics of concentrated oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by gelatinized bambara groundnut flour. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 4995–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbekpornu, H.; Yeboah, D.; Pappoe, A.; Ennin, J.E.; Oyih, M. The State of Farm Raised Catfish Consumption in Ghana: A Case of the Ashanti Region. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-K.; Nam, J. The determinants of live fish consumption frequency in South Korea. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiero, K.; Meulenbroek, P.; Drexler, S.; Dagne, A.; Akoll, P.; Odong, R.; Kaunda-Arara, B.; Waidbacher, H. The contribution of fish to food and nutrition security in Eastern Africa: Emerging trends and future outlooks. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Chia, L.-S.; Pauls, K.P. Protein-Based Bioproducts. In Plant Bioproducts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 143–175. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Wang, G. Milk protein polymer and its application in environmentally safe adhesives. Polymers 2016, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.E.; Rowe, S.; Lotze, H.K. Expansion of hagfish fisheries in Atlantic Canada and worldwide. Fish. Res. 2015, 161, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böni, L.; Rühs, P.A.; Windhab, E.J.; Fischer, P.; Kuster, S. Gelation of soy milk with hagfish exudate creates a flocculated and fibrous emulsion-and particle gel. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuster, S.; Böni, L.J.; Fischer, P.; Rühs, P.A.; Windhab, E.J. About hagfish, effective hydrogels and protein fiber enriched Tofu—An overview from our published work. In Proceedings of the General Information about Hagfish for Nestlé PTC Singen, Singen, Germany, 19 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Elavarasi, K.; Ranjini, S.; Rajagopal, T.; Rameshkumar, G.; Ponmanickam, P. Bactericidal proteins of skin mucus and skin extracts from fresh water fishes, Clarias batrachus and Tilapia mossambicus. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 37, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuartero, M.; del Mar Collado-González, M.; Baños, F.G.D.; Cuesta, A.; Moriñigo, M.Á.; Esteban, M.Á. Terminal carbohydrates abundance, immune related enzymes, bactericidal activity and physico-chemical parameters of the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup) skin mucus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 60, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobinath, R.A.C.; Ravichandran, S. Antimicrobial peptide from the epidermal mucus of some estuarine cat fishes. World App. Sci. J. 2011, 12, 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Tyor, A.K.; Kumari, S. Biochemical characterization and antibacterial properties of fish skin mucus of fresh water fish, hypophthalmichthys nobilis. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan, G.; Mohan, K.; Vinoth, J.; Ravi, V. Biotic potential of mucus extracts of giant mudskipper Periophthalmodon schlosseri (Pallas, 1770) from Pichavaram, southeast coast of India. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2019, 80, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, N.W.; Firth, K.J.; Wang, A.; Burka, J.F.; Johnson, S.C. Changes in hydrolytic enzyme activities of naive Atlantic salmon Salmo salar skin mucus due to infection with the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis and cortisol implantation. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 41, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Cuesta, A.; Arizcun, M.; Meseguer, J.; Esteban, M.A. Comparative skin mucus and serum humoral defence mechanisms in the teleost gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2014, 36, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, J.; Winegard, T.; O’Donnell, M.; Yancey, P.; Fudge, D.S. Stabilization and swelling of hagfish slime mucin vesicles. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- SABS. South African National Standard: The Care and the Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes, SANS 10386:2008; SABS South African Bureau of Standards: Groenkloof, Pretoria, South Africa, 2008.
- Kasiri, N.; Fathi, M. Production of cellulose nanocrystals from pistachio shells and their application for stabilizing Pickering emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Jun, S.; Kim, I.; Jin, S.M.; Kim, J.G.; Shin, T.J.; Lee, E. Stepwise Drug-Release Behavior of Onion-Like Vesicles Generated from Emulsification-Induced Assembly of Semicrystalline Polymer Amphiphiles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4570–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto de Castro, C.A.; Vieira, S.I.; Lourenço, M.J.; Murshed, S. Understanding Stability, Measurements, and Mechanisms of Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluids. J. Nanofluids 2017, 6, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokić, L.; Krstonošić, V.; Nikolić, I. Physicochemical characteristics and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by OSA starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zide, D.; Fatoki, O.; Oputu, O.; Opeolu, B.; Nelana, S.; Olatunji, O. Zeolite ‘adsorption’capacities in aqueous acidic media; The role of acid choice and quantification method on ciprofloxacin removal. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 255, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böni, L.J.; Zurflüh, R.; Widmer, M.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J.; Rühs, P.A.; Kuster, S. Hagfish slime exudate stabilization and its effect on slime formation and functionality. Biol. Open 2017, 6, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, I.P.; Steiner, C.; Schmutzler, M.; Wilcox, M.D.; Veldhuis, G.J.; Pearson, J.P.; Huck, C.W.; Salvenmoser, W.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Mucus permeating carriers: Formulation and characterization of highly densely charged nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 97, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapella, C.; Rizzo, R.; Gallo, S.; Alogna, A.; Bortolotti, D.; Casciano, F.; Zauli, G.; Secchiero, P.; Voltan, R. HelixComplex snail mucus exhibits pro-survival, proliferative and pro-migration effects on mammalian fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Smart, J.D.; Nevell, T.G.; Ewen, R.J.; Eaton, P.J.; Tsibouklis, J. Mucin/poly (acrylic acid) interactions: A spectroscopic investigation of mucoadhesion. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reneeta, N.P.; Thiyonila, B.; Aathmanathan, V.S.; Ramya, T.; Chandrasekar, P.; Subramanian, N.; Prajapati, V.K.; Krishnan, M. Encapsulation and Systemic Delivery of 5-Fluorouracil Conjugated with Silkworm Pupa Derived Protein Nanoparticles for Experimental Lymphoma Cancer. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizi, L.; McArdle, P.; Ektefan, M.; Chiniforoshan, H. Synthesis, crystal structure, spectroscopic and biological properties of mixed ligand complexes of cadmium (II), cobalt (II) and manganese (II) valproate with 1, 10-phenanthroline and imidazole. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 439, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Revathi, A.; Gunasekaran, G. Studies on anticancer, haemolytic activity and chemical composition of crude epidermal mucus of fish Mugil cephalus. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2016, 4, 438–443. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, A.; Jones, K.; Lewis, K.; Jones, S.; Lewis, P. Detection of Lewis antigen structural change by FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.G.; Holeiter, M.; Brauchle, E.; Layland, S.L.; Lu, Y.; Deb, A.; Pandit, A.; Nsair, A.; Schenke-Layland, K. Exogenous miR-29B delivery through a hyaluronan-based injectable system yields functional maintenance of the infarcted myocardium. Tissue Eng. Part A 2018, 24, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, N.; Kendall, C.; Shepherd, N.; Crow, P.; Barr, H. Near-infrared Raman spectroscopy for the classification of epithelial pre-cancers and cancers. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2002, 33, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F.; Sousa, R.A.; Reis, R.L. Extraction and physico-chemical characterization of a versatile biodegradable polysaccharide obtained from green algae. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Schnaar, R.L.; Schauer, R. Sialic acids and other nonulosonic acids. In Essentials of Glycobiology [Internet], 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lamriben, L.; Graham, J.B.; Adams, B.M.; Hebert, D.N. N-Glycan-based ER Molecular Chaperone and Protein Quality Control System: The Calnexin Binding Cycle. Traffic 2016, 17, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhong, G.; Cai, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, X. Rapid and efficient separation of glycoprotein using pH double-responsive imprinted magnetic microsphere. Talanta 2017, 169, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, A.M.; Tan, K.W.; Tan, C.P.; Nyam, K.L. Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed oil-in-water Pickering nanoemulsions stabilised by mixture of sodium caseinate, Tween 20 and β-cyclodextrin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Lin, D.; Liu, D.; Yang, X. Emulsions stabilized by nanofibers from bacterial cellulose: New potential food-grade Pickering emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankhla, A.; Sharma, R.; Yadav, R.S.; Kashyap, D.; Kothari, S.; Kachhwaha, S. Biosynthesis and characterization of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles–an emphasis of zeta potential behavior due to capping. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 170, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkena, B.; Vasudevan, S. Understanding aqueous dispersibility of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide through p K a measurements. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Luo, L.; Liu, C.; McClements, D.J. Utilization of anionic polysaccharides to improve the stability of rice glutelin emulsions: Impact of polysaccharide type, pH, salt, and temperature. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaldawi, M. Chemical and Physical Strategies Promoting Nanoparticle Permeation Through Intestinal Mucus Barrier. Ph.D. Thesis, Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdizadeh Barzoki, Z.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mortazavian, E.; Akbar Moosavi-Movahedi, A.; Rafiee Tehrani, M. Formulation, in vitro evaluation and kinetic analysis of chitosan–gelatin bilayer muco-adhesive buccal patches of insulin nanoparticles. J. Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingerhoeds, M.H.; Blijdenstein, T.B.; Zoet, F.D.; van Aken, G.A. Emulsion flocculation induced by saliva and mucin. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).