Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Plasma Treatment on Quality of Selected Spices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.1.1. Treated Material
2.1.2. Culture Preparation
2.1.3. Culture Preparation
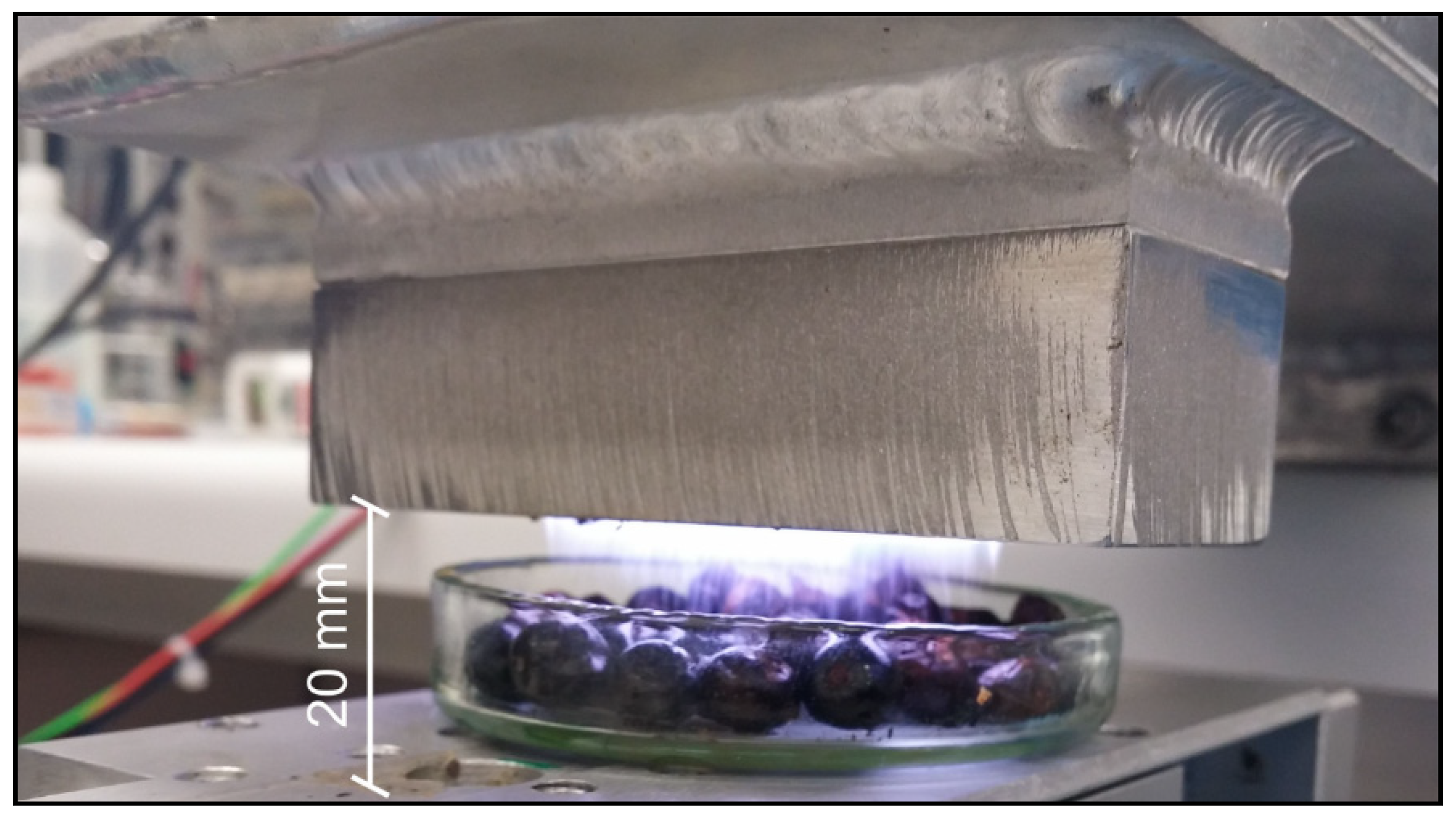
2.2. Plasma Sources and Plasma Treatment
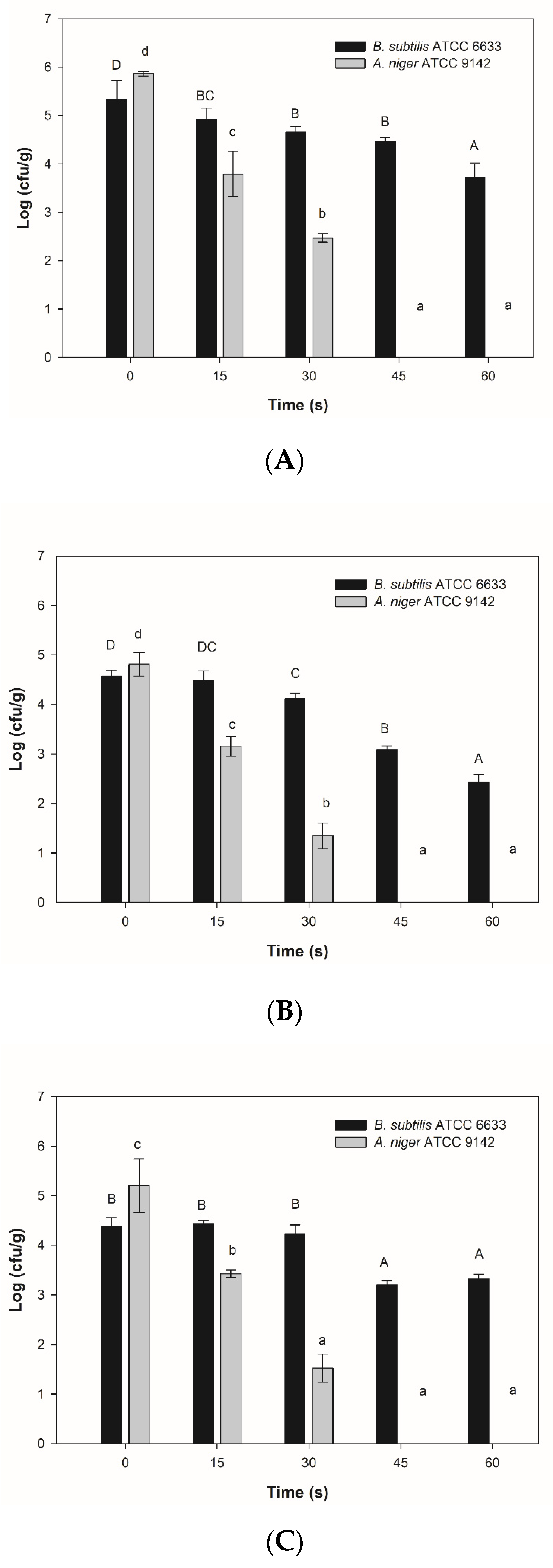
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
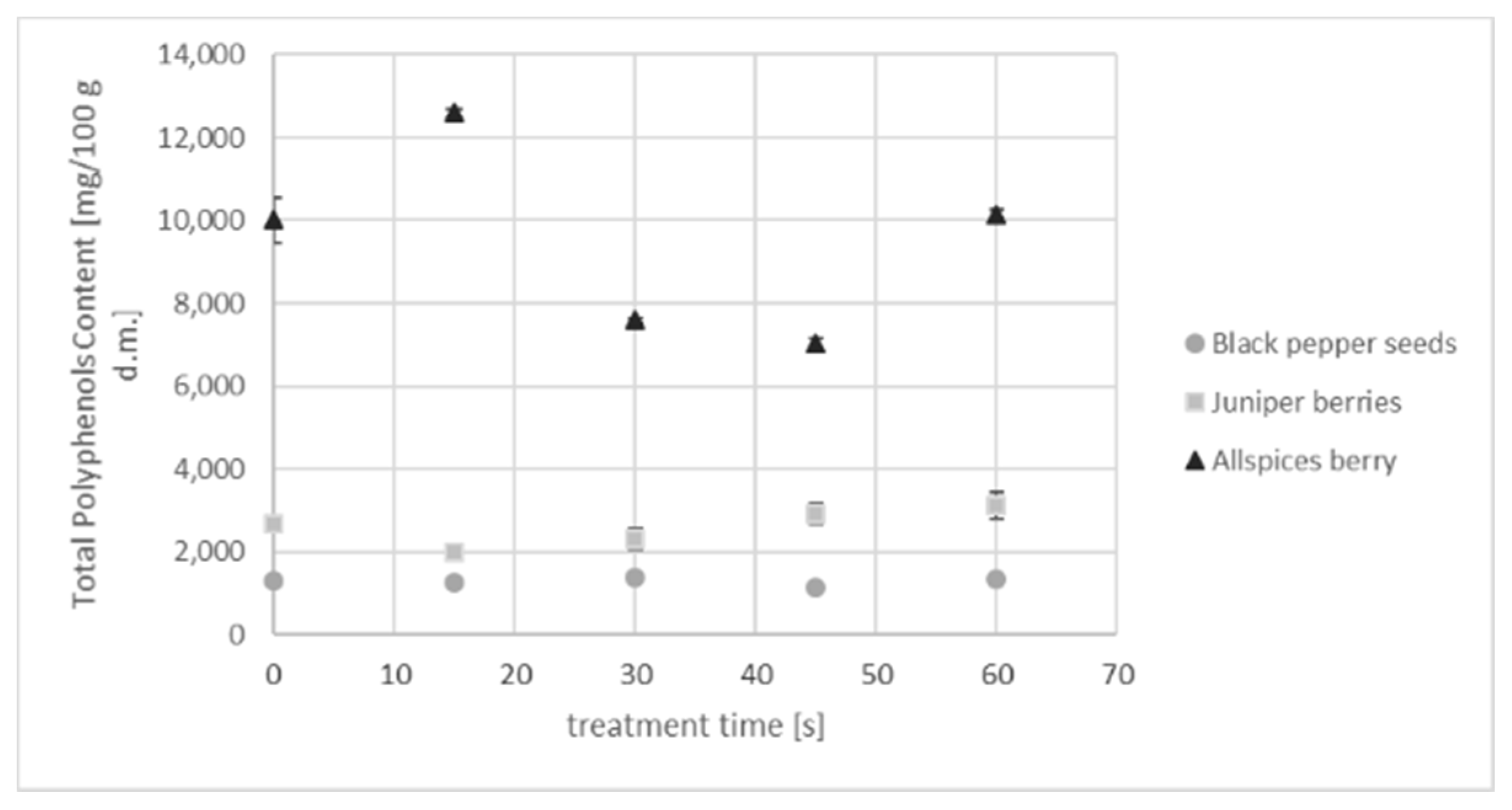
2.4. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Piperine Content in Black Pepper
2.7. Color Measurement
2.8. Water Activity
2.9. Dry Matter Content
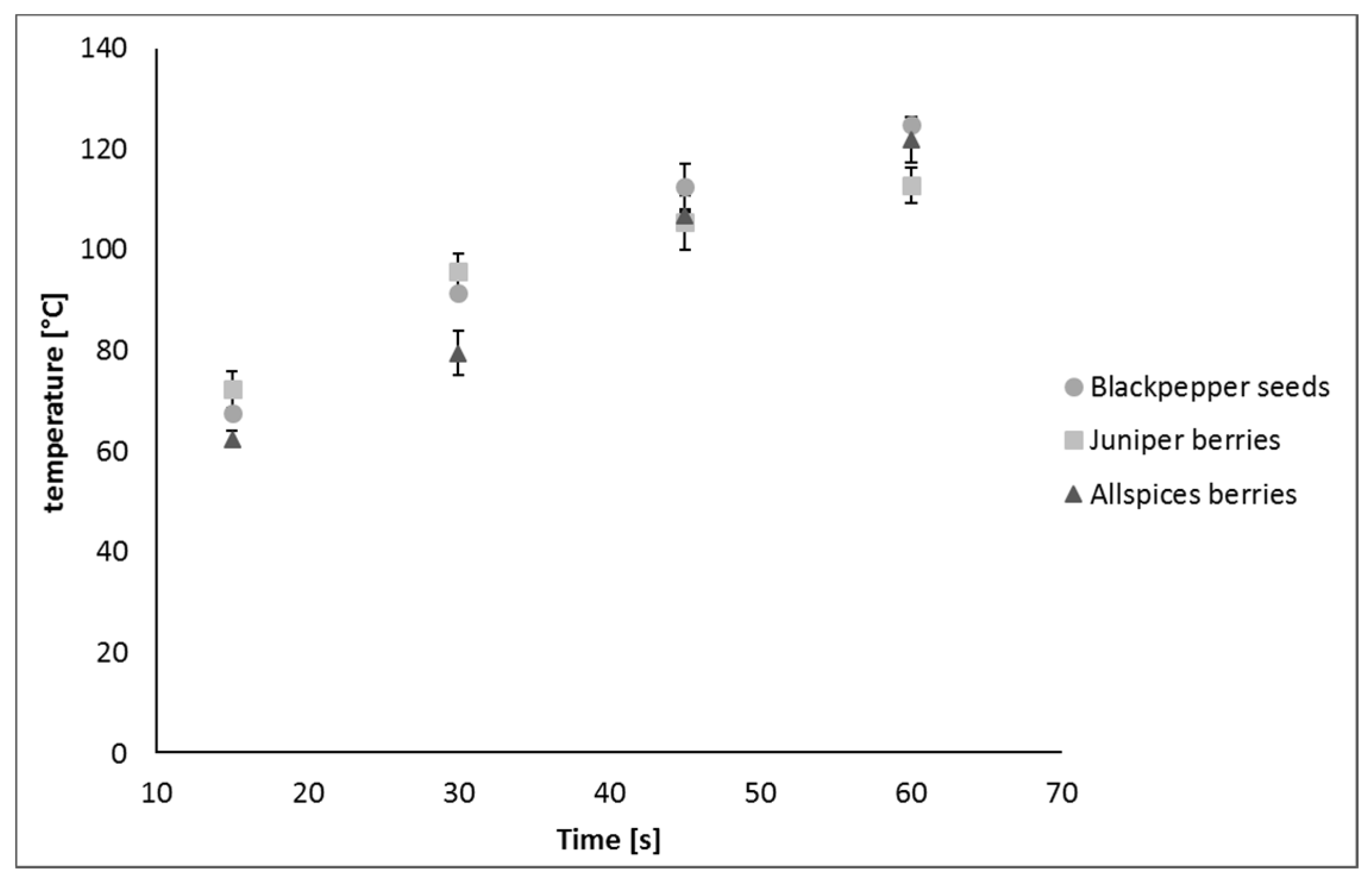
2.10. Temperature Measurements
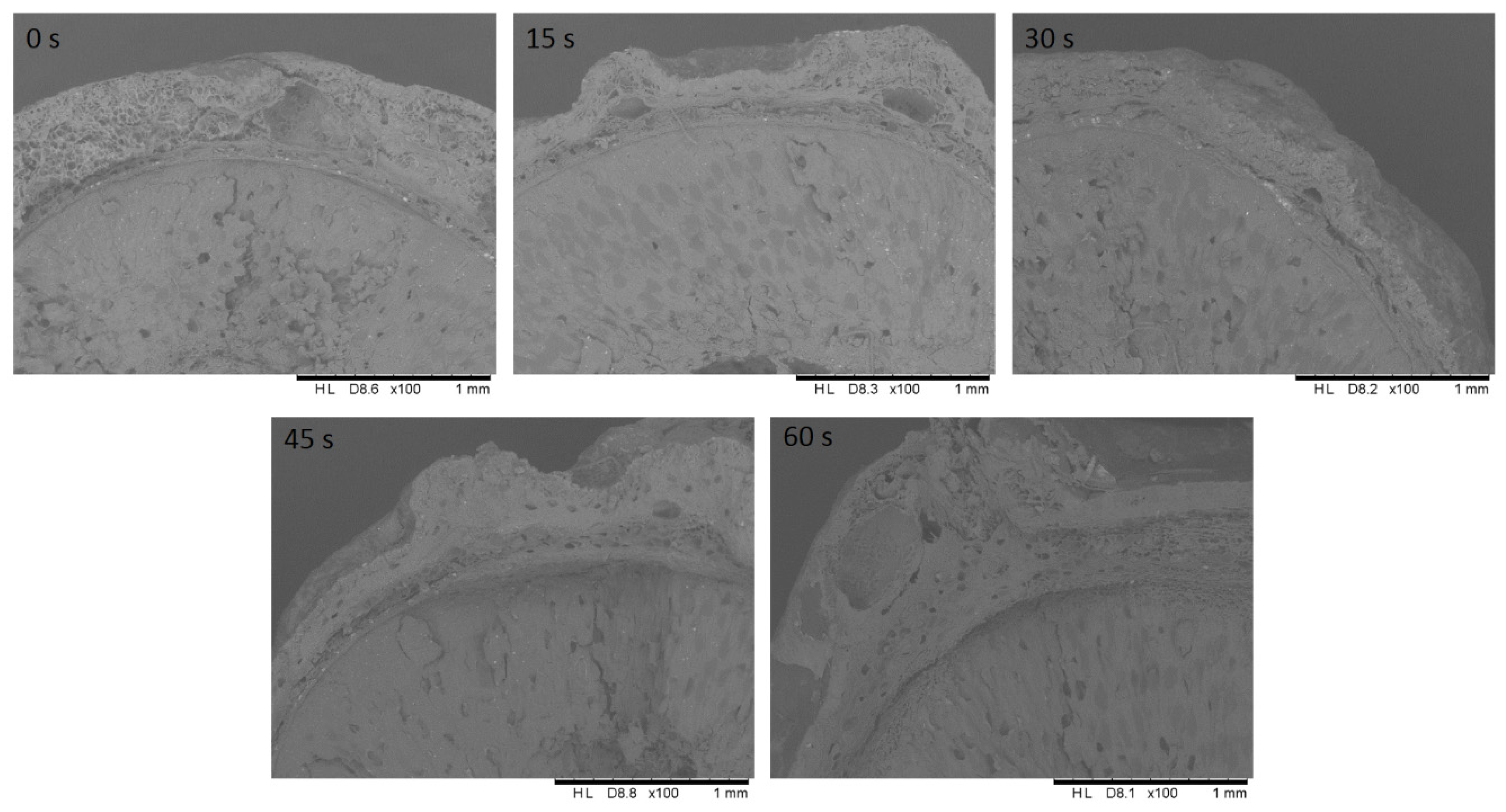
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Imaging
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dry Matter Content and Water Activity
3.2. Microorganism Growth
3.3. Color
3.4. Total Polyphenolc Content and Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Morphology Analysis
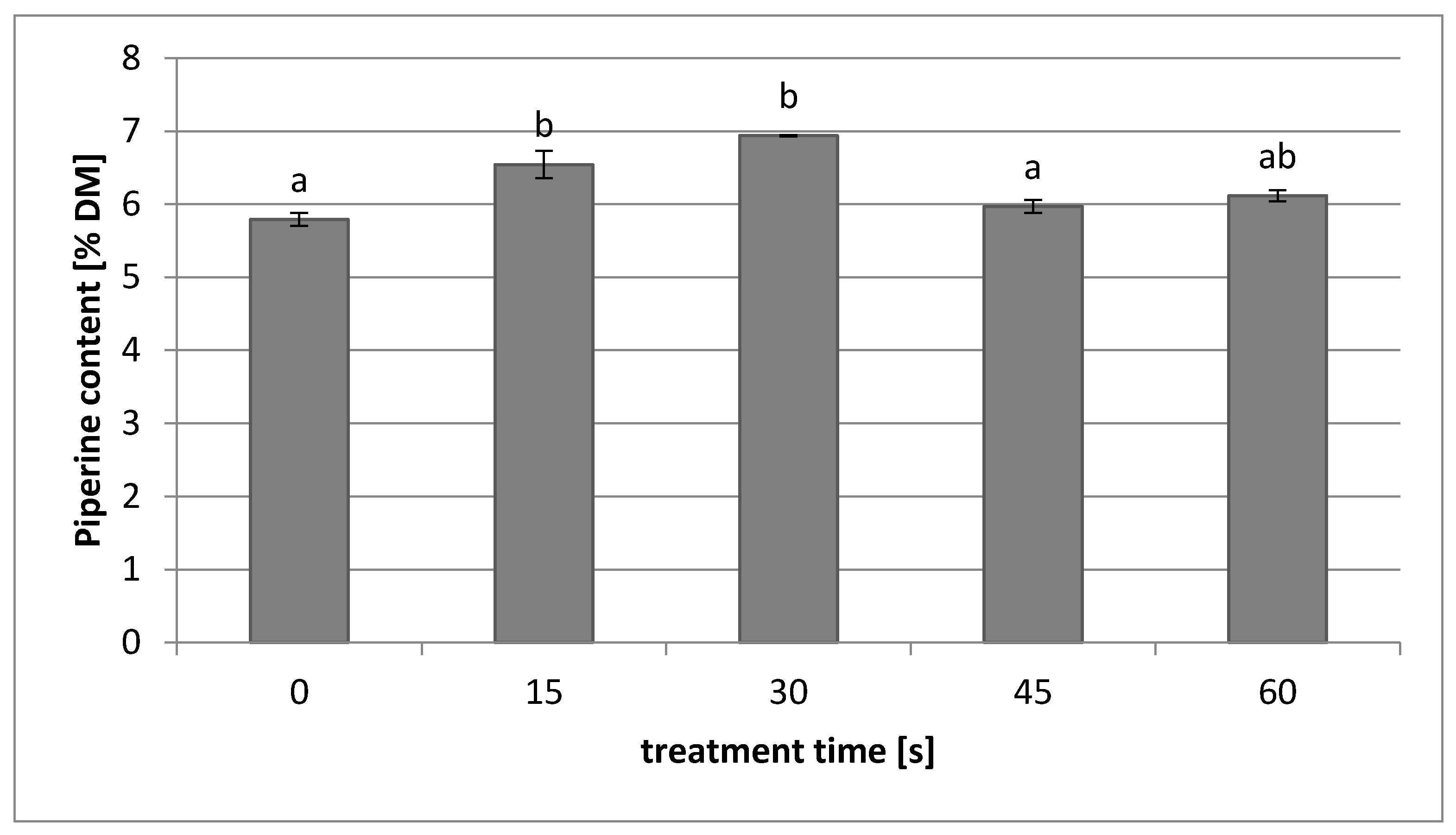
3.6. Piperine Content in Black Pepper Seeds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kebede, B.; Grauwet, T.; Mutsokoti, L.; Palmers, S.; Vervoort, L.; Hendrickx, M.; Van Loey, A. Comparing the impact of high pressure high temperature and thermal sterilization on the volatile fingerprint of onion, potato, pumpkin and red beet. Food Res. Int. 2014, 56, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, A.; Sandaka, P.G. Heat transfer analysis of canned food sterilization in a still retort. J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Coates, G.A. Effect of thermal pasteurization on Valencia orange juice color and pigments. LWT 2003, 36, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Coates, G. Thermal Pasteurization Effects on Color of Red Grapefruit Juices. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberian, H.; Hamidi Esfahani, Z.; Abbasi, S. Effect of conventional and ohmic pasteurization on some bioactive components of aloe vera gel juice. Iran. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 34, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Marszałek, K.; Mitek, M.; Skąpska, S. The effect of thermal pasteurization and high pressure processing at cold and mild temperatures on the chemical composition, microbial and enzyme activity in strawberry purée. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 27, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Terefe, N.S.; Buckow, R.; Knorr, D.; Orlien, V. New opportunities and perspectives of high pressure treatment to improve health and safety attributes of foods. A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Parniakov, O.; Pereira, S.A.; Wiktor, A.; Grimi, N.; Boussetta, N.; Saraiva, J.; Raso, J.; Martín-Belloso, O.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D.; et al. Current applications and new opportunities for the use of pulsed electric fields in food science and industry. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 773–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemat, F.; HumMa, Z.; Khan, M. Applications of ultrasound in food technology: Processing, preservation and extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataro, G.; Munoz, A.; Palgan, I.; Noci, F.; Ferrari, G.; Lyng, J. Bacterial inactivation in fruit juices using a continuous flow Pulsed Light (PL) system. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemira, B.A. Cold Plasma Decontamination of Foods *. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroussi, M. Low Temperature Plasma-Based Sterilization: Overview and State-of-the-Art. Plasma Process. Polym. 2005, 2, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowsky, B.; Schluter, O.; Knorr, D. Interactions of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasmawith Solid and Liquid Food Systems: A Review. Food Eng. Rev. 2015, 2, 82–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisan, M.; Barbeau, J.; Moreau, S.; Pelletier, J.; Tabrizian, M.; Yahia, L. Low-temperature sterilization using gas plasmas: A review of the experiments and an analysis of the inactivation mechanisms. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 226, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puač, N.; Gherardi, M.; Shiratani, M. Plasma agriculture: A rapidly emerging field. Plasma Process. Polym. 2017, 15, 1700174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovich, I.V.; Baalrud, S.D.; Bogaerts, A.; Bruggeman, P.J.; Cappelli, M.; Colombo, V.; Czarnetzki, U.; Ebert, U.; Eden, J.G.; Favia, P.; et al. The 2017 Plasma Roadmap: Low temperature plasma science and technology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 323001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktor, A.; Śledź, M.; Nowacka, M.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. Possible applications of low-temperature (cold) plasma in food technology. ŻYWNOŚĆ. Nauka. Technol. 2013, 90, 5–14. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Misra, N.; Tiwari, B.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Cullen, P.J. Nonthermal Plasma Inactivation of Food-Borne Pathogens. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrycak, B.; Czylkowski, D.; Miotk, R.; Dors, M.; Jasiński, M.; Mizeraczyk, J. Application of atmospheric pressure microwave plasma source for hydrogen production from ethanol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14184–14190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patange, A.; Boehm, D.; Ziuzina, D.; Cullen, P.J.; Gilmore, B.; Bourke, P.; Zuizina, D. High voltage atmospheric cold air plasma control of bacterial biofilms on fresh produce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 293, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasiński, M.; Dors, M.; Mizeraczyk, J. Destruction of Freon HFC-134a Using a Nozzleless Microwave Plasma Source. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2009, 29, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuji, T.; Urayama, T.; Fujii, S.; Mungkung, N.; Akatsuka, H. Temperature behavior of atmospheric-pressure non-equilibrium microwave discharge plasma jets for poly(ethylene naptharate)-surface processing. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2008, 202, 5289–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czylkowski, D.; Hrycak, B.; Jasinski, M.; Dors, M.; Mizeraczyk, J. Atmospheric pressure microwave microplasma microorganism deactivation. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2013, 234, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizeraczyk, J.; Dors, M.; Jasiński, M.; Hrycak, B.; Czylkowski, D. Atmospheric pressure low-power microwave microplasma source for deactivation of microorganisms. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 61, 24309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowska, H.; Czylkowski, D.; Hrycak, B.; Jasiński, M. Characterization of a novel microwave plasma sheet source operated at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2018, 27, 085008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Steffes, B.; Pompl, R.; Jamitzky, F.; Bunk, W.; Ramrath, K.; Georgi, M.; Stolz, W.; Schmidt, H.-U.; Urayama, T.; et al. Characterization of Microwave Plasma Torch for Decontamination. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Takatori, K.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Kim, I.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Han, D.-W.; Chung, K.-H.; Hyun, S.O.; Park, J.-C. Degradation of mycotoxins using microwave-induced argon plasma at atmospheric pressure. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2007, 201, 5733–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhling, A.; Durek, J.; Schnabel, U.; Ehlbeck, J.; Bolling, J.; Schlüter, O. Indirect plasma treatment of fresh pork: Decontamination efficiency and effects on quality attributes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, C.; Reineke, K.; Ehlbeck, J.; Knorr, D.; Schlüter, O.K. Decontamination of whole black pepper using different cold atmospheric pressure plasma applications. Food Control 2015, 55, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, M.; Goch, M.; Mizeraczyk, J. Plasma Device for Treatment of Surface. PL 215139 B1, 31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jasinski, M.; Mizeraczyk, J. Plasma sheet generated by microwave discharge at atmospheric pressure. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 39, 2136–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizeraczyk, J.; Jasiński, M.; Nowakowska, H.; Dors, M. Studies of atmospheric-pressure microwave plasmas used for gas processing. Nukleonika 2012, 57, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Newerli-Guz, J. The antioxidant properties of Spice—Example Black pepper Piper Nigrum L. Bromatol. Chem. Toksykol. 2012, XLV, 887–891. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kříž, P.; Petr, B.; Zbynek, H.; Jaromir, K.; Pavel, O.; Petr, S.; Miroslav, D.; Bartos, P.; Havelka, Z.; Kadlec, J.; et al. Influence of Plasma Treatment in Open Air on Mycotoxin Content and Grain Nutriments. Plasma Med. 2015, 5, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selcuk, M.; Oksuz, L.; Basaran, P. Decontamination of grains and legumes infected with Aspergillus spp. and Penicillum spp. by cold plasma treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5104–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, D.-U.; Min, S.C. Microbial decontamination of red pepper powder by cold plasma. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purevdorj, D.; Igura, N.; Hayakawa, I.; Ariyada, O. Inactivation of Escherichia coli by microwave induced low temperature argon plasma treatments. J. Food Eng. 2002, 53, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Park, B.J.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, I.-S.; Hyun, S.O.; Chung, K.-H.; Park, J.-C. Sterilization of Escherichia coli and MRSA using microwave-induced argon plasma at atmospheric pressure. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 193, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, M.; Foerster, J.; Schnabel, U.; Knorr, D.; Ehlbeck, J.; Herppich, W.; Schlüter, O. Direct non-thermal plasma treatment for the sanitation of fresh corn salad leaves: Evaluation of physical and physiological effects and antimicrobial efficacy. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 84, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, F.; Stratakos, A.C.; Koidis, A.; Berardinelli, A.; Cevoli, C.; Ragni, L.; Mancusi, R.; Manfreda, G.; Trevisani, M. Atmospheric cold plasma process for vegetable leaf decontamination: A feasibility study on radicchio (red chicory, Cichorium intybus L.). Food Control 2016, 60, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzina, D.; Patil, S.; Cullen, P.J.; Keener, K.; Bourke, P. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Listeria monocytogenes inoculated on fresh produce. Food Microbiol. 2014, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handorf, O.; Below, H.; Schnabel, U.; Riedel, K.; Ehlbeck, J. Investigation of the chemical composition of plasma-treated water by MidiPLexc and its antimicrobial effect on L. monocytogenes and Pseudomonas fluorescens monospecies suspension cultures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 305204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki, W.; Tatol, M. Color difference ΔE–a survey. Mach. Graph. Vis. 2011, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Zhong, C.-S.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Yang, X.-H.; Deng, L.-Z.; Wang, J.; Xiao, H.-W. Cold plasma pretreatment enhances drying kinetics and quality attributes of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Food Eng. 2019, 241, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, A.; Niemira, B.A.; Gurtler, J.B.; Fan, X.; Sites, J.; Boyd, G.; Chen, T.H.-H. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of aerobic microorganisms on blueberries and effects on quality attributes. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangapani, C.; O’Toole, G.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Atmospheric cold plasma dissipation efficiency of agrochemicals on blueberries. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, M.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Min, S.C. Mandarin preservation by microwave-powered cold plasma treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 39, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktor, A.; Śledź, M.; Nowacka, M.; Rybak, K.; Chudoba, T.; Lojkowski, W.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. The impact of pulsed electric field treatment on selected bioactive compound content and color of plant tissue. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 30, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappi, S.; Ramazzina, I.; Rizzi, F.; Sacchetti, G.; Ragni, L.; Rocculi, P. Effect of Plasma Exposure Time on the Polyphenolic Profile and Antioxidant Activity of Fresh-Cut Apples. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Influence of Plasma Treatment on the Polyphenols of Food Products—A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Roh, S.H.; Min, S.C. Inactivation of Potato Polyphenol Oxidase Using Microwave Cold Plasma Treatment. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülçin, I. The antioxidant and radical scavenging activities of black pepper (Piper nigrum) seeds. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flögel, A.; Kim, D.-O.; Chung, S.-J.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Comparison of ABTS/DPPH assays to measure antioxidant capacity in popular antioxidant-rich US foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvecká, V.; Mošovská, S.; Mikulajová, A.; Valík, Ľ.; Zahoranová, A. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma decontamination of allspice berries and effect on qualitative characteristics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newerli-Guz, J.; Śmiechowska, M. Ocena zawartości piperyny w czarnym pieprzu ziarnistym piper nigrum L. Bromatol. Chem. Toksykol. 2009, 42, 827–830. [Google Scholar]




| Material | Time [s] | L* | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black pepper seeds | 0 | 16.81 ± 0.39 a | 2.43 ± 0.22 a | 3.85 ± 0.26 a | 0 |
| 15 | 15.55 ± 0.41 b | 3.04 ± 0.31 b | 5.4 ± 0.75 b | 4.04 | |
| 30 | 15.06 ± 0.42 b | 3.3 ± 0.24 b | 6.04 ± 0.32 b | 7.28 | |
| 45 | 15.24 ± 0.40 b | 3.15 ± 0.24 b | 5.86 ± 0.40 b | 6.13 | |
| 60 | 14.92 ± 0.41 b | 3.14 ± 0.29 b | 5.86 ± 0.34 b | 6.42 | |
| Juniper berries | 0 | 15.57 ± 0.59 A | 3.57 ± 0.38 A | 4.11 ± 0.88 A B | 0 |
| 15 | 13.4 ± 0.73 C D | 4.45 ± 0.42 B C | 5.37 ± 0.83 B C | 4.52 | |
| 30 | 12.64 ± 1.02 B C | 4.42 ± 0.6 B C | 4.1 ± 0.70 A | 3.66 | |
| 45 | 14.17 ± 1.0 D | 4.96 ± 0.09 C | 5.88 ± 0.55 C | 6.45 | |
| 60 | 11.84 ± 0.78 B | 4.15 ± 0.56 A B | 3.92 ± 0.65 A | 4.1 | |
| Allspices berries | 0 | 23.84 ± 0.63 [A] [B] | 6.28 ± 0.25 [A] | 10.64 ± 0.53 [A] | 0 |
| 15 | 23.28 ± 0.41 [A] | 6.96 ± 0.15 [B] | 12.06 ± 0.33 [B] [C] | 3.02 | |
| 30 | 23.76 ± 0.27 [A] [B] | 7.06 ± 0.21 [B] | 12.49 ± 0.33 [C] | 4.09 | |
| 45 | 22.31 ± 0.7 [C] | 6.74 ± 0.27 [B] | 11.49 ± 0.66 [A] [B] | 2.46 | |
| 60 | 24.24 ± 0.65 [B] | 6.98 ± 0.23 [B] | 12.94 ± 0.72 [C] | 6.18 |
| Sample | Treatment Time [s] | Antioxidant Activity [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABTS | DPPH | ||
| Black pepper seeds | 0 | 47.03 ± 1.71 a | 45.91 ± 1.75 a |
| 15 | 40.51 ± 0.45 b | 42.19 ± 1.86 a b | |
| 30 | 51.15 ± 0.87 c | 42.77 ± 0.41 a b | |
| 45 | 48.14 ± 0.62 a | 41.53 ± 1.14 b | |
| 60 | 57.60 ± 1.50 e | 48.61 ± 2.27 a | |
| Juniper berries | 0 | 30.00 ± 2.61 A | 32.91 ± 0.80 A |
| 15 | 28.08 ± 2.28 A | 26.16 ± 1.39 B | |
| 30 | 29.23 ± 0.44 A | 28.76 ± 0.50 B | |
| 45 | 33.08 ± 1.31 B | 39.03 ± 1.69 C | |
| 60 | 35.77 ± 0.33 B | 42.69 ± 1.09 C | |
| Allspices berries | 0 | 30.57 ± 1.85 [A] | 32.47 ± 1.29 [A] |
| 15 | 40.83 ± 0.72 [B] | 47.97 ± 0.20 [B] | |
| 30 | 24.02 ± 0.62 [C] | 23.42 ± 3.17 [C] | |
| 45 | 24.75 ± 0.62 [C] | 24.47 ± 0.30 [C] | |
| 60 | 36.17 ± 1.96 [D] | 40.53 ± 2.58 [D] | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiktor, A.; Hrycak, B.; Jasiński, M.; Rybak, K.; Kieliszek, M.; Kraśniewska, K.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Plasma Treatment on Quality of Selected Spices. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196815
Wiktor A, Hrycak B, Jasiński M, Rybak K, Kieliszek M, Kraśniewska K, Witrowa-Rajchert D. Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Plasma Treatment on Quality of Selected Spices. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(19):6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196815
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiktor, Artur, Bartosz Hrycak, Mariusz Jasiński, Katarzyna Rybak, Marek Kieliszek, Karolina Kraśniewska, and Dorota Witrowa-Rajchert. 2020. "Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Plasma Treatment on Quality of Selected Spices" Applied Sciences 10, no. 19: 6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196815
APA StyleWiktor, A., Hrycak, B., Jasiński, M., Rybak, K., Kieliszek, M., Kraśniewska, K., & Witrowa-Rajchert, D. (2020). Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Microwave Plasma Treatment on Quality of Selected Spices. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196815








