Impacts of Killing Process on the Nutrient Content, Product Stability and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meals
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Killing Procedures and Processing
2.2. Microbial Analysis
2.3. Chemical Compositions and Physicochemical Properties
2.3.1. Chemical Compositions
2.3.2. PH and Color
2.4. Enzymatic and Non-Enzyme Browning Reaction
2.4.1. Enzymatic Browning Reaction
2.4.2. Non-Enzymatic Browning Reaction
2.5. Protein Oxidation
2.6. Fat Acidity
2.7. Storage Trail
2.7.1. Lipid Oxidation
2.7.2. In Vitro Digestibility
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Analysis in BSF Larvae after Killing
3.2. Chemical Composition and Physicochemical Parameters of BSF Larvae Meal
3.3. Lipid Peroxidation of BSF after Killing
3.4. In Vitro Digestibility of BSF Larvae Meal
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Killing Method on Microbial Load
4.2. Impacts of Killing Methods on Chemical Composition and Physicochemical Properties
4.2.1. Proximate Compositions
4.2.2. Physicochemical Properties
4.3. Impacts of Killing Methods on In Vitro Digestibility
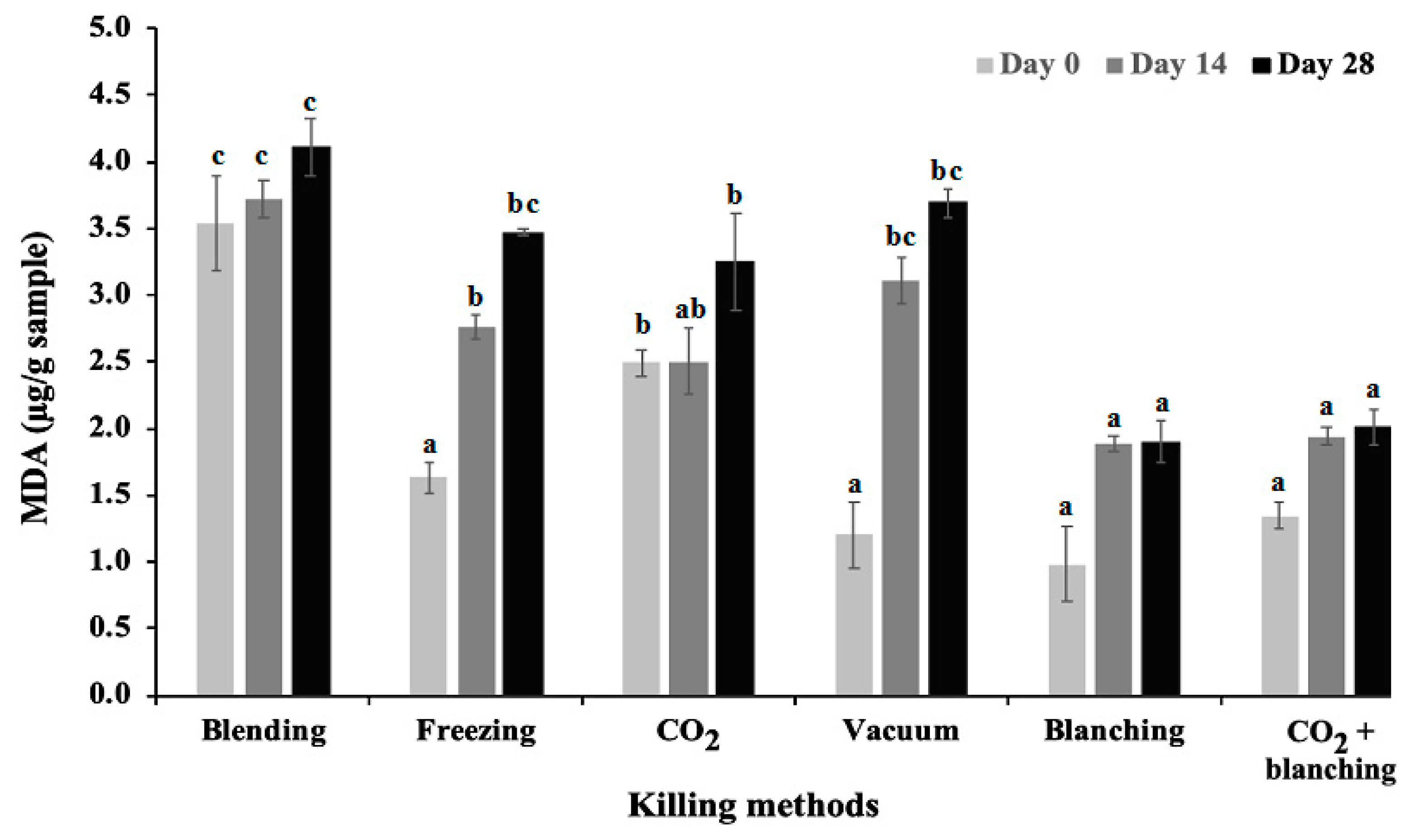
4.4. Impacts of Killing Methods on Storage Trail (Lipid Oxidation Content)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Makkar, H.P.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Biasato, I.; Dabbou, S.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F. Animals Fed Insect-Based Diets: State-of-the-Art on Digestibility, Performance and Product Quality. Animals 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Amato, M.; Biasato, I.; Chiesa, S.; Gasco, L. The Potential Role of Insects as Feed: A Multi-Perspective Review. Animals 2019, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancarosa, I.; Liland, N.S.; Biemans, D.; Araujo, P.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Amlund, H.; Lock, E.-J. Uptake of heavy metals and arsenic in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae grown on seaweed-enriched media. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 98, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniers, J.; Graham, R. Effect of protein and carbohydrate feed concentrations on the growth and composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2019, 5, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, V.; Marseglia, A.; Sorci, A.; Bonzanini, F.; Lolli, V.; Maistrello, L.; Sforza, S. Influence of the killing method of the black soldier fly on its lipid composition. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, J.; Deschamps, M.-H.; Saucier, L.; Lebeuf, Y.; Doyen, A.; Vandenberg, G.W. Effects of Killing Methods on Lipid Oxidation, Colour and Microbial Load of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae. Animals 2019, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leni, G.; Caligiani, A.; Sforza, S. Killing method affects the browning and the quality of the protein fraction of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae: A metabolomics and proteomic insight. Food Res. Int. 2019, 115, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montevecchi, G.; Zanasi, L.; Masino, F.; Maistrello, L.; Antonelli, A. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.): Effect on the fat integrity using different approaches to the killing of the prepupae. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjerris, M.; Gamborg, C.; Röcklinsberg, H. Ethical aspects of insect production for food and feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2016, 2, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis of. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 148. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, F. Catalytic properties of tyrosinase from potato and edible fungi. Biotechnology 2006, 5, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.-Y.; Shue, Y.-S.; Chang, H.-M. Antioxidative activity of roasted and defatted peanut kernels. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, M.; Heinonen, M.; Ollilainen, V.; Toldrá, F.; Estévez, M. Analysis of protein carbonyls in meat products by using the DNPH-method, fluorescence spectroscopy and liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation–mass spectrometry (LC–ESI–MS). Meat Sci. 2009, 83, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Boil. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- AACC International. Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; Method 02–01.02. Fat acidity-General method. Approved October 3, 1984; re-approved November 3, 1999; revised 2009; Available online: https://methods.aaccnet.org/summaries/02-01-02.aspx (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Fletouris, D.J.; Papageorgiou, G.E.; Vassilopoulos, V.N.; Mantis, A.J.; Trakatellis, A.G. Rapid, Sensitive, and Specific Thiobarbituric Acid Method for Measuring Lipid Peroxidation in Animal Tissue, Food, and Feedstuff Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Park, C.S.; Kim, B.G. Effects of an enzyme complex on in vitro dry matter digestibility of feed ingredients for pigs. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansuwan, K.; Kovitvadhi, S.; Thongprajukaew, K.; Ozorio, R.O.D.A.; Somsueb, P. Microwave irradiation and pelleting method affected feed chemical composition and growth performance and feed utilization of sex-reversed Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquac. Res. 2016, 48, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovitvadhi, A.; Chundang, P.; Thongprajukaew, K.; Tirawattanawanich, C.; Srikachar, S.; Chotimanothum, B. Potential of Insect Meals as Protein Sources for Meat-Type Ducks Based on In Vitro Digestibility. Animals 2019, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Package MASS. Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 17 October 2012).
- Clark, M.A.; Eaton, D.C. Effect of CO2 on neurons of the house cricket, acheta domestica. J. Neurobiol. 1983, 14, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynants, E.; Frooninckx, L.; Crauwels, S.; Verreth, C.; De Smet, J.; Sandrock, C.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Van Schelt, J.; Depraetere, S.; Lievens, B.; et al. Assessing the Microbiota of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Reared on Organic Waste Streams on Four Different Locations at Laboratory and Large Scale. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 77, 913–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives. Animal Feed Quality Control ACT B.E.2558; Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016. Available online: http://afvc.dld.go.th (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Minister of Justice. Division 27: Low-Acid Foods Packaged in Hermetically Sealed; Containers (B.27.001); Food and Drug Regulations, Government of Canada, Minister of Justice: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2019. Available online: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Erdoğdu, F.; Balaban, M.O.; Otwell, W.; Garrido, L. Cook-related yield loss for pacific white (Penaeus vannamei) shrimp previously treated with phosphates: Effects of shrimp size and internal temperature distribution. J. Food Eng. 2004, 64, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.H.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Fogliano, V.; Renzone, G.; Scaloni, A.; Vincken, J.-P. Involvement of phenoloxidase in browning during grinding of Tenebrio molitor larvae. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, R.H.; Vincken, J.-P.; Arts, N.J.; Fogliano, V.; Janssen, R.H. Effect of endogenous phenoloxidase on protein solubility and digestibility after processing of Tenebrio molitor, Alphitobius diaperinus and Hermetia illucens. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.H.; Canelli, G.; Sanders, M.G.; Bakx, E.J.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Fogliano, V.; Vincken, J.-P. Iron-polyphenol complexes cause blackening upon grinding Hermetia illucens (black soldier fly) larvae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David-Birman, T.; Raften, G.; Lesmes, U. Effects of thermal treatments on the colloidal properties, antioxidant capacity and in-vitro proteolytic degradation of cricket flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, R.; Braca, A.; Mulas, G.; Sanna, R.; Spada, S.; Serra, G.; Fadda, M.L.; Roggio, T.; Uzzau, S.; Anedda, R. Effect of freezing and drying processes on the molecular traits of edible yellow mealworm. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 48, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.J. Freezing processed foods. In Managing Frozen Foods; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2000; p. 304. [Google Scholar]
- Barden, L.; Decker, E.A. Lipid Oxidation in Low-moisture Food: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 56, 2467–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Martinez, C.; Cervantes, E.; Ke, P.J. Recommended method for testing the objective rancidity development in fish based on TBARS formation. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 1089, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wazir, H.; Chay, S.Y.; Zarei, M.; Hussin, F.S.; Mustapha, N.A.; Ibadullah, W.Z.W.; Saari, N. Effects of Storage Time and Temperature on Lipid Oxidation and Protein Co-Oxidation of Low-Moisture Shredded Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyer, A.; Özalp, B.; Dalmış, Ü.; Bilgin, V. Effects of freezing temperature and duration of frozen storage on lipid and protein oxidation in chicken meat. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiencheu, B.; Womeni, H.M.; Linder, M.; Mbiapo, F.T.; Villeneuve, P.; Fanni, J.; Parmentier, M. Changes of lipids in insect (Rhynchophorus phoenicis) during cooking and storage. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 115, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, S.; Van Der Borght, M.; Callens, A.; Van Campenhout, L. Suitability of microwave drying for mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) as alternative to freeze drying: Impact on nutritional quality and colour. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Microorganism | Killing Methods | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Asphyxiation | Heat | ||||
| Blending | Freezing | CO2 | Vacuum | Blanching | CO2 Plus Blanching | |
| TVC (CFU/g sample) | 4.1 × 1010 | 1.6 × 1010 | 4.8 × 1010 | 3.5 × 1010 | 7.7 × 109 | 7.2 × 109 |
| Acinetobacter sp. | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Bacillus cereus | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Bacillus spp. | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Enterobacter cloacae | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Escherichia coli | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Proteus mirabilis | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Salmonella sp. | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Parameters | Killing Methods | SEM | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Asphyxiation | Heat | ||||||
| Blending | Freezing | CO2 | Vacuum | Blanching | CO2 Plus Blanching | |||
| Proximate composition | ||||||||
| Dry matter (%FM) | 95.7 ab | 96.6 c | 96.1 bc | 95.5 a | 97.4 d | 97.2 d | 0.181 | 0.001 |
| Crude ash (%DM) | 7.29 | 7.30 | 7.50 | 7.44 | 7.04 | 6.90 | 0.068 | 0.47 |
| Ether extract (%DM) | 25.7 a | 27.3 ab | 28.1 b | 29.1 b | 28.1 b | 28.4 b | 0.331 | 0.001 |
| Crude protein (%DM) | 39.3 a | 44.9 b | 46.8 b | 52.5 c | 46.3 b | 44.6 b | 0.990 | 0.001 |
| Crude fiber (%DM) | 10.2 | 9.22 | 9.29 | 9.51 | 9.66 | 9.77 | 0.116 | 0.12 |
| NFE (%DM) | 17.5 d | 11.4 c | 8.28 b | 2.69 a | 8.95 bc | 10.3 bc | 1.074 | 0.001 |
| Physicochemical properties | ||||||||
| pH value | 6.14 a | 6.48 c | 6.43 bc | 6.36 b | 7.31 d | 7.47 e | 0.128 | 0.001 |
| Browning reaction | ||||||||
| Enzymatic (U) | 2.65 d | 0.83 b | 1.53 c | 1.52 c | ND a | ND a | 0.246 | 0.001 |
| Non-enzymatic (BI) | 1.27 d | 0.65 b | 0.59 b | 0.79 c | 0.17 a | 0.15 a | 0.094 | 0.001 |
| Color | ||||||||
| L* (Lightness) | 40.2 a | 41.4 b | 41.3 b | 41.4 b | 41.7 c | 41.7 c | 0.043 | 0.001 |
| a* (Redness) | 0.23 d | 0.08 b | 0.04 a | 0.09 b | 0.23 d | 0.14 c | 0.018 | 0.001 |
| b* (Yellowness) | 0.80 c | 0.47 b | 0.43 a | 0.48 b | 0.85 d | 0.80 c | 0.043 | 0.001 |
| Hue | 1.30 a | 1.41 b | 1.49 c | 1.40 b | 1.31 a | 1.41 b | 0.016 | 0.001 |
| Chroma | 0.83 c | 0.48 b | 0.43 a | 0.49 b | 0.88 d | 0.81 c | 0.046 | 0.001 |
| Fat acidity | 84.9 c | 13.9 b | 10.4 b | 12.2 b | 0.77 a | 0.55 a | 7.527 | 0.001 |
| Protein oxidation | 0.81 bc | 1.03 c | 0.42 a | 0.51 ab | 0.60 ab | 0.71 ab | 0.060 | 0.01 |
| In Vitro Digestibility | Killing Methods | SEM | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Asphyxiation | Heat | ||||||
| Blending | Freezing | CO2 | Vacuum | Blanching | CO2 Plus Blanching | |||
| Supernatant | ||||||||
| IVCD | 19.5 d | 13.2 c | 8.42 b | 11.2 bc | 2.54 a | 1.87 a | 1.521 | 0.001 |
| IVPD | 122 a | 112 a | 124 a | 129 a | 133 a | 166 b | 5.374 | 0.04 |
| Sediment (%) | ||||||||
| Dry matter | 53.3 a | 59.4 b | 57.1 ab | 61.0 b | 56.1 ab | 59.8 b | 0.868 | 0.04 |
| Crude protein | 31.3 a | 48.9 b | 53.1 b | 54.8 b | 52.9 b | 51.9 b | 2.094 | 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhen, Y.; Chundang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Vongsangnak, W.; Pruksakorn, C.; Kovitvadhi, A. Impacts of Killing Process on the Nutrient Content, Product Stability and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10176099
Zhen Y, Chundang P, Zhang Y, Wang M, Vongsangnak W, Pruksakorn C, Kovitvadhi A. Impacts of Killing Process on the Nutrient Content, Product Stability and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meals. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(17):6099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10176099
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhen, Yongkang, Pipatpong Chundang, Yu Zhang, Mengzhi Wang, Wanwipa Vongsangnak, Chantima Pruksakorn, and Attawit Kovitvadhi. 2020. "Impacts of Killing Process on the Nutrient Content, Product Stability and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meals" Applied Sciences 10, no. 17: 6099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10176099
APA StyleZhen, Y., Chundang, P., Zhang, Y., Wang, M., Vongsangnak, W., Pruksakorn, C., & Kovitvadhi, A. (2020). Impacts of Killing Process on the Nutrient Content, Product Stability and In Vitro Digestibility of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meals. Applied Sciences, 10(17), 6099. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10176099









