Abstract
Nowadays, active packaging plays a key role in the food sector, improving the safety and quality of food and, at the same time, extending its shelf life. The aim of the study was to evaluate the efficacy that an active absorbent pad has in limiting microbial growth during the shelf-life of fresh bovine meat. The experiment was carried out on 50 slices of eye of round (semitendinosus muscle) of an adult bovine, packaged in two different packs, one containing the conventional pad (C: Control group) and the other containing the active pad (PAD group). The analyses, performed at 0, 3 and 6 days of refrigeration storage (4 °C), concerned the pH, color, total volatile basic nitrogen (TVBN) and microbiological parameters. The packaging with the active pad had no noticeable effect on the pH, but with regard to the color coordinates, the meat at day 6 was lighter than the control group (p < 0.01). The innovative pad was able to delay the growth of all the microorganisms investigated, but only at day 3 (p < 0.05 to p < 0.001) compared to the control group. Furthermore, the TVBN values were lower than the control ones at both the third (p = 0.036) and sixth (p < 0.01) day of analysis. All samples were negative for coagulase positive staphylococci, L. monocytogenes, and Salmonella spp. In conclusion, following a preliminary examination, the packaging with the active pad was potentially effective in delaying microbial growth and it positively affected the color and TVBN of beef meat.
1. Introduction
The acceptability of fresh meat is not only due to its nutritional and dietetic properties, but also to food safety aspect that may be affected by different factors such as the hygienic conditions of the equipment and the premises where carcasses and meat cuts are handled, storage conditions and packaging methods [1].
In general, regardless of the possibility of developing foodborne disease for the consumer, high microbial contamination, particularly of spoilage bacteria, negatively affects the shelf life, quality and sensorial meat properties [2].
Therefore, packaging manufacturers respond to the producers’ need to preserve food, especially highly perishable food such as fresh meat, from contamination and alteration during commercialization, while at the same time meeting the consumers’ demand to buy safe and high quality food [3,4,5]. In recent years however, the concept of quality and safety on the part of the consumer has undergone a profound evolution. In general, awareness of the risks associated with food consumption and the importance of healthy eating has increased. Thus, particular attention is being paid to high quality food, low processed, additive-free and with adequate shelf life, able to satisfy the consumer’s expectations and current market needs [6,7].
For these reasons, the new challenges to improve the sustainability of the meat supply chain, by ensuring fresher, safer and higher quality products, lies in the development of new packaging solutions to increase the shelf life of the meat by improving the microbiological profile (contrasting microbial development or decreasing it) [8,9].
From an analysis of the literature, many packaging options exist to date for the preservation of meat, which can control the microbial growth and can extend the shelf life of food products [10,11]. The most widespread and known solution is modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) which limits bacterial development and vacuum packed (VP) which, as a result, inhibits the development of aerobic spoilage microorganisms [10].
Among the different types of packaging there are also the active packaging varieties, defined by the EU Regulation No. 450/2009 as “active materials and articles” intended to extend the shelf-life or to maintain or improve the condition of packaged food; they are designed to deliberately incorporate components that would release or absorb substances into or from the packaged food or the environment surrounding the food.
For these reasons, in recent times, researchers have focused on the study and development of new active packaging which is able to improve the quality and safety of food products, particularly in meat and meat products, through the inclusion of different active substances.
Many studies have focused on the direct incorporation of antimicrobial substances into the packaging film or into an absorbent pad/sachet [12], or through the coating of the packaging themselves, in a manner that the antimicrobial agents could be released gradually into the food and modulate microbial growth, with the aim to extend the product shelf life [13].
Several researchers have also evaluated the immobilization of antimicrobial agents to polymers or the direct use of polycationic polymers such as chitosan and poly-l-lysine and lysozime with inherent antimicrobial action [14], because the amines present in the polymers interact with the cell wall of the bacteria causing their death [15].
Furthermore, in addition to a high number of antimicrobial agents being tested, including ethanol [16], carbon dioxide [17] and silver ions [18], attention has also been given to the incorporation of natural substances or essential oils such as rosemary extract [19], thyme extract [20], garlic [21], oregano and lemongrass extract [22].
In this context, the study aimed at evaluating the efficacy of an active absorbent pad in limiting microbial growth during the shelf-life of fresh beef meat.
The uniqueness of this active pad, which sets it apart from others tested in previous studies, is that its mechanism of action is expressed through a physical-mechanical action and not through the incorporation of antibacterial or natural substances.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Active Absorbent Pad
The active absorbent pad was developed and supplied by ANT Advanced Nonwovens Technologies s.r.l.—Deatex group (Milan, Italy).
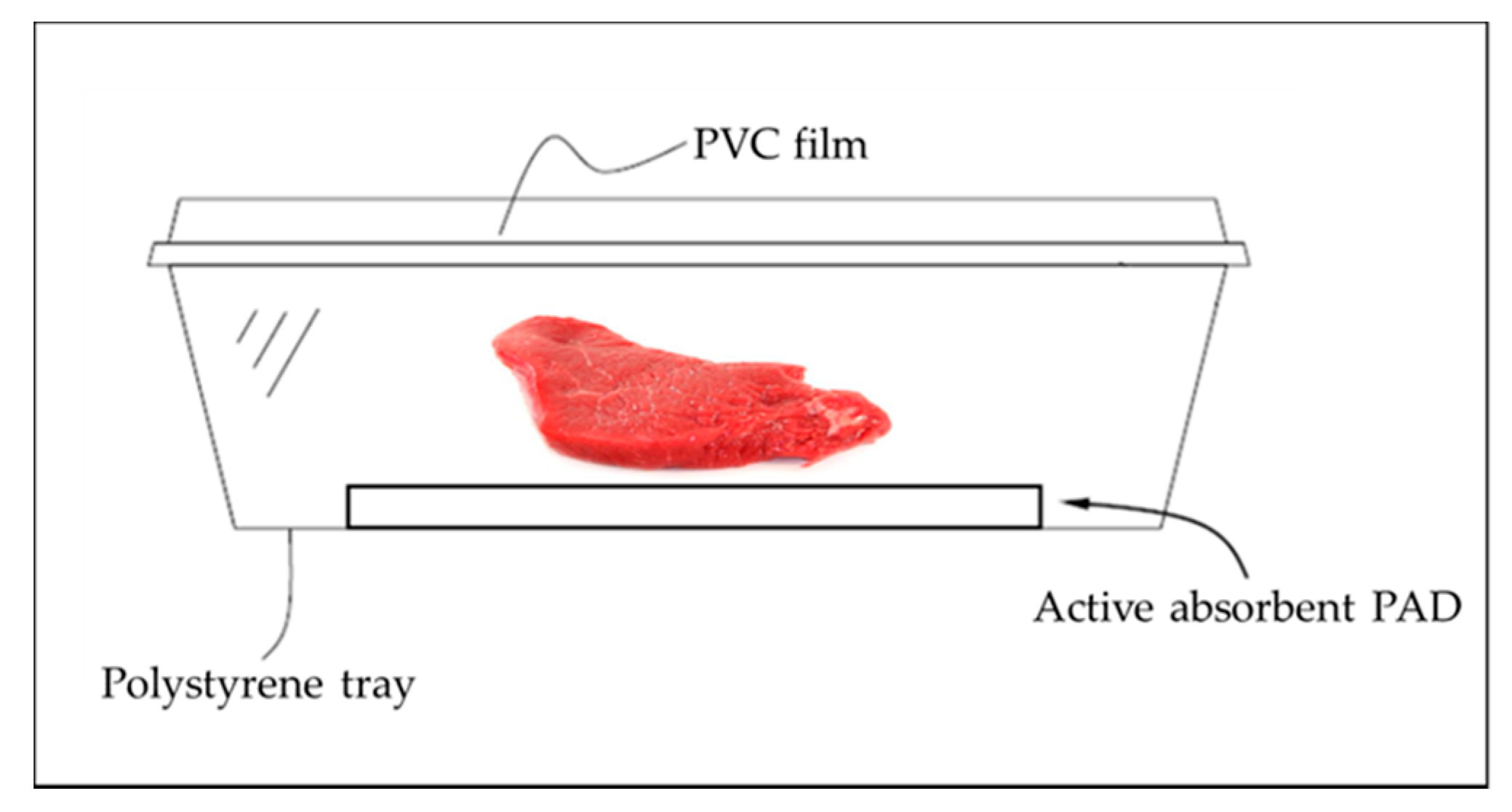
In order to evaluate the efficacy of the pad during the shelf life of the meat, it was placed on the base of the trays and it was suitable for storage and food contact (Figure 1). The pad size was 7.5 × 15 cm.
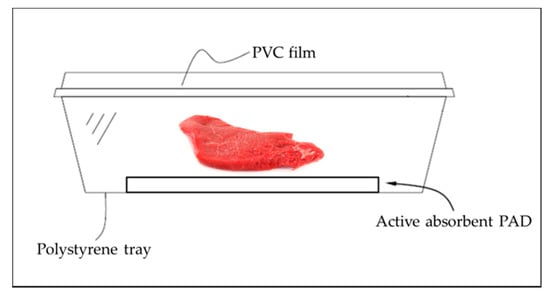
Figure 1.
Conformation of the packages where the meat slices were storage.
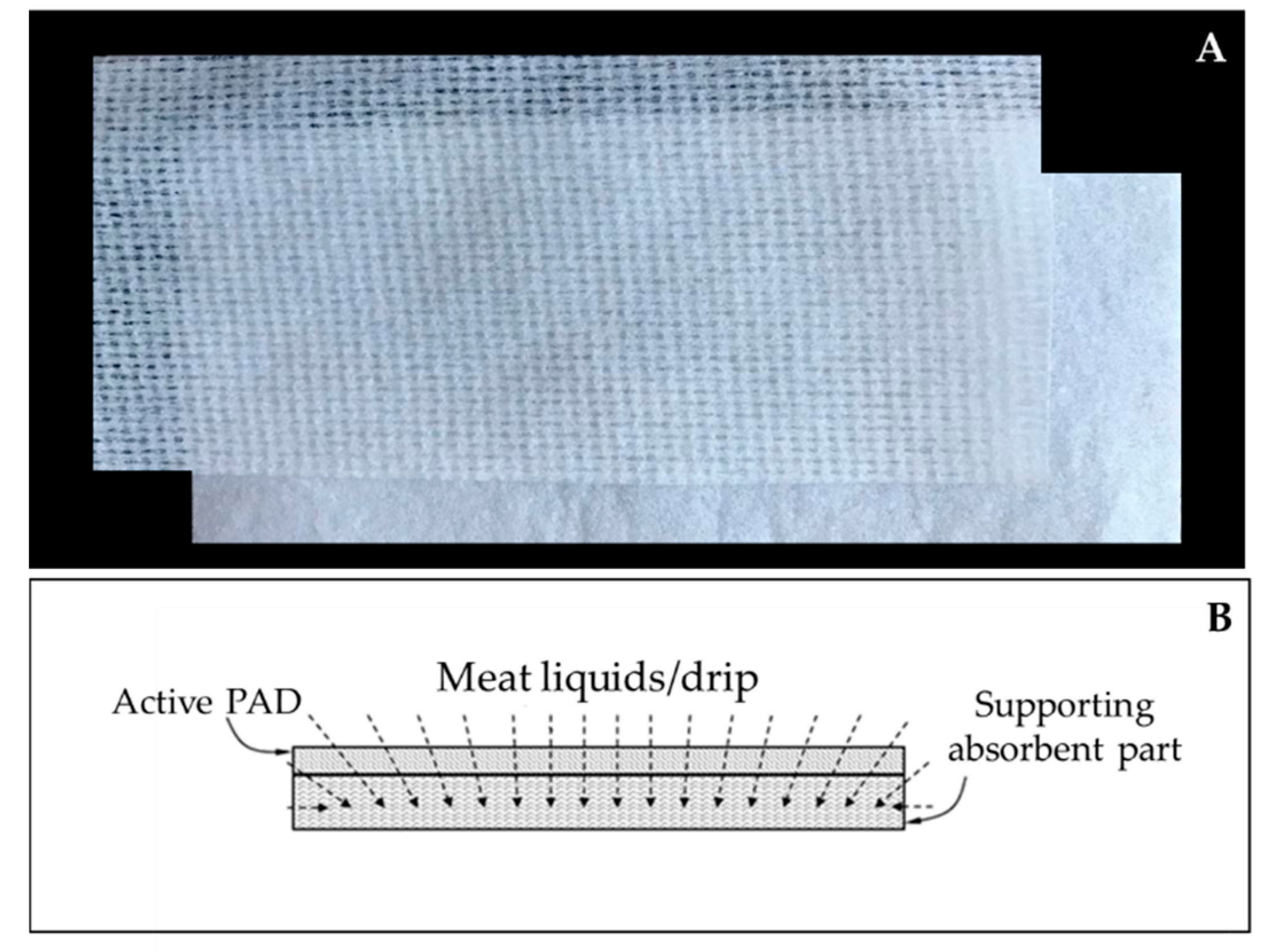
The active absorbent pad is made of two parts: the absorbing part, which is anchored to the base of the package composed of non-woven fabric, and the active part, which includes a polymeric cationic agent, in direct contact with the meat, capable of generating an attraction effect on the bacterial cell wall (Figure 2). To assume these specific characteristics, the active pad is soaked in an additive mixture comprising of 30% to 50% of a polymeric cationic agent by weight of the total weight, 10% to 20% of a base by weight of the total weight and 1% to 10% of auxiliary substances by weight of the total weight.
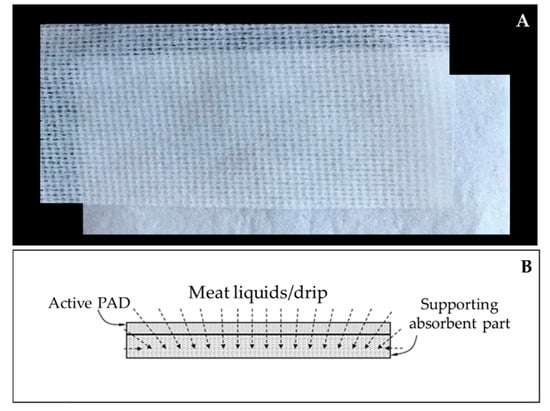
Figure 2.
Active absorbent pad (A) and scheme of the pad architecture (B).
The active pad part (Figure 2) has a filtering component and has been configured to be crossed by any meat liquids as reported in Figure 2 (dotted arrows), all this is designed to exercise both a partially absorbent effect for liquids or drips, and a blocking effect for bacteria so as to catch them before they reach the absorbent part thanks to its cationic properties. The innovative pad analyzed in this study, is compliant with Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food. Moreover, it does not fall within the definition of a biocidal, provided by Regulation (EC) No. 528/2012, as its mechanism of action is physical-mechanical.
2.2. Sample Preparation
Fifty slices of eye of round cut (semitendinosus muscle) of an adult bovine of over 24 months of age, born, reared and slaughtered in Italy, with 20 days of ageing, were purchased from a local butcher (Perugia, Italy). The slices were specially cut with a slicer to obtain a constant thickness of 4 mm and immediately brought, in a refrigerated bag, to the Food Inspection laboratory at the Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Perugia (Italy). Once arrived, 10 samples were immediately analyzed (day 0), while the remaining slices were individually packed in an oxygen-permeable package consisting of an expanded polystyrene tray wrapped in PVC film, containing two different absorbent pads: conventional pads (C group) and modified pads (PAD group). The packages were stored in dark conditions at 4 ± 1 °C and analyzed after 3 and 6 days of storage.
2.3. Chemical–Physical Parameters
The pH was measured in triplicate with a pH meter equipped with an insertion electrode (Crison pH25, Crison, Barcelona, Spain), by grinding 2 g of each meat sample with 20 mL of MilliQ water. Lightness (L*), redness (a*) and yellowness (b*) color coordinates were evaluated on the surface of each slice at three different points using a CR400 Minolta chromameter (Minolta, Osaka, Japan), with a light source of D65 calibrated before measurement with a standard white tile (CIE, 1976). The concentration of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVBN) was quantified using a VELP Marka model UDK 139 instrument (Velp Scientifica, Usmate, Milan, Italy), by alkalization of 10 g of sample with 2 g of sodium and subsequent steam distillation and titration with 0.01 N hydrochloric acid. At the beginning of the trial, protein (method 992.15), fat (method 960.30), moisture (method 950.46) and ash (method 923.03) quantification of the meat was performed according to the AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 2000).
2.4. Microbiological Analyses
A portion of 25 g was aseptically collected from each slice of meat and deposited in a stomacher bag containing 225 mL of buffered peptone water (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK). After a 1 min homogenization in the Stomacher 400 apparatus (Stomacher 400 circulator; Seward Ltd., Norfolk, UK), serial dilutions with a physiological solution were prepared and used for the following microbiological analyses: Total viable count (TVC) with plate count agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) inoculated by inclusion and incubated at 30 °C for 48 h; Pseudomonas spp. on Pseudomonas Agar Base (Biolife Italiana s.r.l., Milan, Italy) with CFC Peseudomonas supplement (Biolife Italiana s.r.l., Milan, Italy), incubated at 25 °C for 48 h; Brocothrix thermosphacta using STAA agar base (Biolife Italiana s.r.l., Milan, Italy) added with STAA selective supplement (Biolife Italiana s.r.l., Milan, Italy), incubated at 22 °C for 48 h; lactic acid bacteria (LAB) were counted by inoculating, for Lactobacillus spp., de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar (Biolife Italiana s.r.l., Milan, Italy) anaerobically incubated at 37 °C for 48 h and for Lactococcus spp., M17 Agar (Biolife Italiana s.r.l., Milan, Italy) incubated at 37 °C for 48 h.
The enumeration of coagulase positive staphylococci, total coliforms and Enterobacteriaceae were carried out by employing Petrifilm (3M, St. Paul, MN, USA), according to AFNOR 3M 01/09-04/03 A, AFNOR 3M 01/2-09/89 A and AFNOR 3M 01/06-09/97, respectively. Besides, the research on Salmonella spp. and L. monocytogenes was assessed in compliance with UNI EN ISO 6579-1:2017 and AFNOR BRD 07/04- 09/98, respectively. The analyses were performed in duplicate and the results are expressed as Log CFU/g.
2.5. Data Analysis
Linear mixed model procedures were used to evaluate the effects of the group and sampling time on microbiological, chemical and physical parameters. The models evaluated the effect of the groups (2 levels: control and PAD groups), storage time (2 levels: 3 and 6 days), and their interaction. The values at T0 were included as covariates in each model. Diagnostic graphics were used to check assumptions and outliers. Pairwise comparisons were performed using the least significant difference. P values from Wald chi-square tests were reported. Results are expressed as estimated marginal means ± standard error (SE) while row data are presented in figures.
The total color difference (ΔE) was calculated between groups and between different storage times, as previously reported [23,24]:
The 95% confidence interval (CI) was reported for each storage time and a score of 2.3 was used as a threshold for human noticeable difference. Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS Statistics version 25 (IBM, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Statistical significance occurred when p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
The TVBN values increased in all samples (p < 0.001) but with significant differences between groups at all storage times. Indeed, the pad showed lower values than the control both after 3 (16.8 ± 0.1 and 16.4 mg/100 g ± 0.1 for C and PAD group, respectively; p = 0.036) and 6 days (19.2 ± 0.1 and 18.1 mg/100 g ± 0.1 for C and PAD group, respectively; p < 0.001) of storage. Overall, the initial pH (5.54 ± 0.01) decreased after 3 days (5.46 ± 0.01) and then increased until 5.57 ± 0.01 after 6 days of storage (p < 0.001). At day 3, the pad had higher values compared to the control group (p = 0.004) but the differences were no longer significant after 6 days of storage (p = 0.354; Table 1).

Table 1.
Effect of packaging on the physical parameters of the meat during storage.
During the storage of fresh meat, the pH generally follows a similar trend, with values that tend to increase as the shelf life progresses. This is associated with the presence of nitrogen compounds that are generated during storage following the degradation of proteins by certain microbial species, in particular Gram-negative bacteria [25].
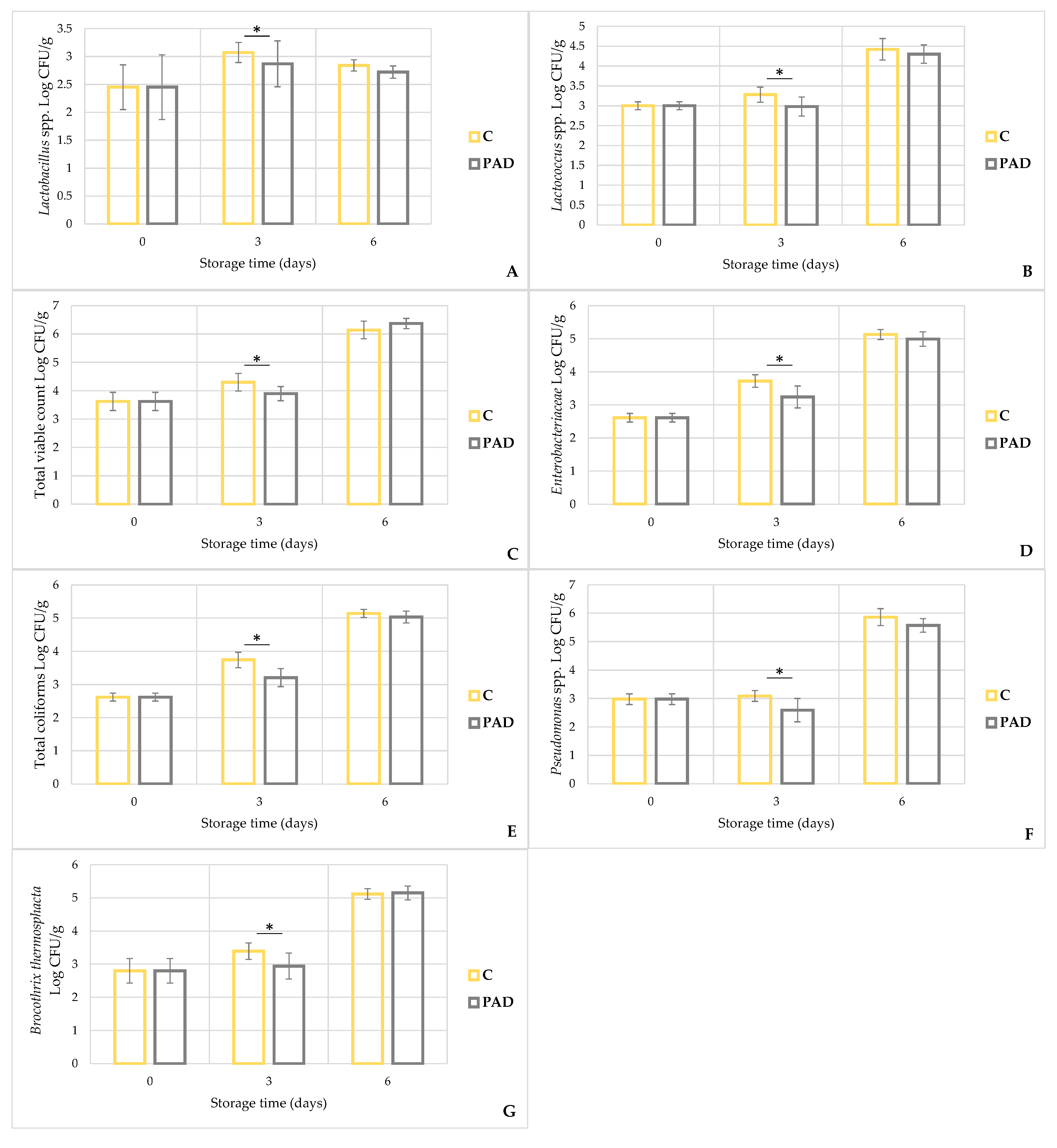
In our study, however, we observed an initial pH reduction (day 3) in the control group, which could be explained by a slight acidification induced by lactic acid bacteria. These microorganisms are normally present on meat and their metabolism leads to lactic acid production [26]. Therefore, if the ratio between basic compounds and acids is in favor of the latter, the pH will tend to decrease. This analysis is consistent with the microbial counts detected, where at day 3, Lactobacilli and Lactococci had higher concentrations in the control samples than in the meat packaged with active pad (Figure 3A,B).
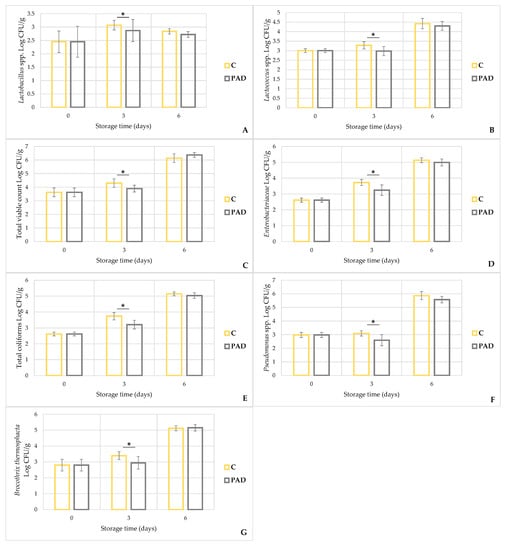
Figure 3.
Trend of microbial development during storage in control (C) and PAD group. Lactobacillus spp. (A), Lactococcus spp. (B), total viable count (C), Enterobacteriaceae (D), total coliforms (E), Pseudomonas spp. (F) and Brocotrhix thermosphacta (G). The bar graphs show mean ± standard deviation. *: p < 0.05.
The color parameters L*, a*, and b* reduced over time in both groups (p < 0.001) but significant differences between groups were found only for L*. In particular, pad samples showed higher L* values than the control at day 6 of storage (p < 0.001; Table 1).
Color alteration is one of the aspects that limits the preservation of meat the most, as well as conditioning the consumer’s preference at the time of purchase [27,28]. It is therefore essential that during retail display, the color deteriorates as little as possible. Color changes are mainly related to the oxidation of the protein (transformation of red oximioglobin to brown methyoglobin) and lipid components and the two processes are closely correlated [29]. For these reasons, the meat industry tries to limit these processes through the incorporation of additives (where current regulations allow it) or through the development and use of active packaging, with consequent shelf life extension and increase in the attractiveness of the packaged product to consumers [30,31,32].
With reference to our study, meat packaged with the active pad remained lighter over time compared to the control group, presumably as a consequence of the different chemical composition of the two pads used. This could result in a different perception of color by the human eye. Indeed, according to the ΔE values, color differences between groups can be noticed after 6 days of storage (Table 2).

Table 2.
Color differences (ΔE) between groups and between storage time.
Then, analyzing the ΔE values over time, it emerged that the meat color remained stable until day 3 (D0–D3), but changed at day 6 (D0–D6) regardless of the packaging. However, at the end of the storage period, the color differences compared to the beginning were particularly evident in the control group.
3.2. Microbiological Analyses
The microbial population present in fresh meat at the time of packaging is extremely varied and depends on the hygienic characteristics of the previous processing phases [31]. In our study, all samples were negative for coagulase positive staphylococci, Listeria monocytigenes, and Salmonella spp., and the initial microbial loads ranged from 2.5 ± 0.2 Log CFU/g for Lactobacillus spp. to 3.6 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g for the total viable count. After 6 days, a significant effect of storage time was found for all microorganisms evaluated, with an increase in overall bacterial counts over time (p < 0.01). In fact, all bacteria had concentrations greater than 4 Log, with the exception of Lactobacilli (2.8 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g).
During storage, both temperature and packaging type are able to exercise selective pressure—with different consequences—on the bacterial replication rate and, therefore, on the related growth curves, regardless of the type of meat [33,34,35]. For example, in aerobic conditions, spoilage bacteria are mainly represented by Pseudomonas spp. [36], while in the absence of oxygen, facultative anaerobic bacteria such as lactic acid bacteria and Brochotrix thermosphacta are predominant [37]. In the current work, with the same oxygen and refrigeration conditions, the packaging influenced the growth trend and all bacteria showed a significant effect in response to the group and/or of the group–time interaction (p < 0.05). In particular, after 3 days of storage, the control group showed higher concentrations in total viable count (+0.4 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p = 0.003; Figure 3C), Lactobacillus spp. (+0.2 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p = 0.028; Figure 3A), Lactococcus spp. (+0.3 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p = 0.014; Figure 3B), Enterobacteriaceae (+0.5 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p < 0.001; Figure 3D), total coliforms (+0.5 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p < 0.001; Figure 3E), Pseudomonas spp. (+0.5 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p < 0.002; Figure 3F), and Brochothrix thermosphacta (+0.4 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g; p = 0.002; Figure 3G) than the PAD group. At the end of the storage period (D6), all microbial counts, except for TVC and Brochothrix thermosphacta, continued to be lower in the PAD group, but these differences were no longer significant. Therefore, the antimicrobial effect exerted by the active pad seems to have been exhausted in the second part of storage, allowing all microorganisms to reach similar counts as the control group at day 6.
It is possible that the capturing action of the pad, which is physical-mechanical and not bactericidal, may have been effective only up to a certain microbial load, beyond which the bacteria were released again on the meat surface.
However, analyzing in percentage terms, the differences in concentrations detected at day 3, the growth rate of total coliform, Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas spp. and Brocotrhix thermosphacta was influenced more by the active pad, with count reductions of 20.2%, 18.4%, 16.8% and 16.1%, respectively, while TVC, Lactobacilli and Lactococci were less affected (reduction of 11%, 10% and 8.2%, respectively). This different growth trend under the same conservation conditions could be relevant, considering that only a fraction of the initial microbial population is effectively involved in the deterioration process [37]. In particular, Brocotrhix thermosphacta and Pseudomonas spp. are recognized to be spoilage related. Previous studies have shown that some members of the Pseudomonaceae family, characterized by a strong proteolytic activity, are frequently isolated from aerobically spoiled meat stored at refrigeration temperature [38].
Therefore, from a first analysis of microbial trends recorded in the current work, it is not possible to understand the actual changes in microbial ecology that occurred in the samples tested. Today, despite numerous studies, there is still much uncertainty on the evolution of species and bacterial strains in the presence of specific inhibiting factors used in packaging and, therefore, on the consequent development of altering phenomena [33]. Silva et al. [39] tested the efficacy of an absorbent pad containing pinosylvin inclusion complexes for the control of chicken meat spoilage bacteria, obtaining a reduction in lactic acid bacteria, psychrotrophic and total viable counts, but not in pseudomonads levels, after seven days of refrigerated storage. Ren et al. [40] have investigated the effectiveness of the antimicrobial action exerted by of N-halamine, 1-chloro-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-4-imidazolidinone loaded absorbent pads in raw beef. The results showed a reduction in total aerobic bacteria, Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas spp. and lactic acid bacteria. Furthermore, the authors pointed out that to obtain a better result it would be useful to combine the treated pad with vacuum packaging. Similarly, Fernandez et al. [15] evaluated the antibacterial ability of a silver-loaded absorbent pad (1%) during storage of beef meat in MAP. The pad was effective at lowering microbial contamination of exuded fluids by an average of 1 log CFU/g for total aerobic bacteria, Pseudomonas spp., Enterobacteriaceae and LAB, even though the latter were less sensitive.
In general, new packaging technologies are able to: (i) improve food safety and quality, (ii) increase the attractiveness of the packaged product to retailers and consumers [41] and at the same time have the potential to (iii) reduce the environmental impact and food waste. However, only some of these active packaging technologies are applicable for fresh meat and meat products [19,31,42,43,44,45]. In particular, the addition of active compounds in the packaging can modify the sensory characteristics of the meat [41] compared to packaging that uses a mechanical action, such as the one tested in this study. On the other hand, the antibacterial effectiveness at different levels of contamination needs to be further investigated and may represent a limit for the practical application of this technology.
4. Conclusions
The active pad tested in this study was observed to be effective in limiting the growth of bacteria commonly present in fresh meat, but only up until a certain period of storage. In particular, increased antimicrobial efficiency was reported for those microorganisms which are known to be involved in altering processes and this adds value to our results. Finally, the positive effects obtained in regard to meat color and the reduction in TVBN values at the end of the observation period, highlight the better condition of the meat packaged with the active pad. The encouraging results obtained in this preliminary study need further investigation in order to understand whether the interaction between the active pad and the microorganisms, can determine an effective extension of the shelf life.
5. Patents
Principi, A. and Merlotti, S. (2020). “Italian Patent application No. 102020000019345—Vaschetta per alimenti comprendente un articolo cattura batteri”.
The complete disclosure could be forward to readers but under NDA agreement only.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M.B., M.C. and D.M.; methodology, M.C., D.M. and L.M.; formal analysis, M.C., D.M. and L.M.; investigation, M.C. and D.M.; resources, M.C. and D.M.; data curation, M.C., D.M. and L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.C. and D.M.; writing—review and editing, M.C., D.M.; visualization, C.M.B., M.C., D.M., L.M., R.B. and D.R.; supervision, C.M.B., M.C., D.M. and L.M.; project administration, M.C. and D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Margherita Angelucci for the English revision.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sheridan, J.J. Sources of Contamination During Slaughter. J. Food Saf. 1998, 18, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, S.; Lues, J.F.R.; Buys, E.M.; Venter, P. Bacterial populations associated with meat from the deboning room of a high throughput red meat abattoir. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, K.K.; Singh, S.; Lee, Y.S. A pyrogallol-coated modified LDPE film as an oxygen scavenging film for active packaging materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, Y.S. Phase change materials for advanced cooling packaging. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Lee, Y.S. Characteristics of moisture-absorbing film impregnated with synthesized attapulgite with acrylamide and its effect on the quality of seasoned laver during storage. J. Food Eng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, K.K.; Singh, S.; Lee, Y.S. Antimicrobial and improved barrier properties of natural phenolic compound-coated polymeric films for active packaging applications. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gaikwad, K.K.; Lee, M.; Lee, Y.S. Temperature sensitive smart packaging for monitoring the shelf life of fresh beef. J. Food Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, B.W.B.; Kerry, J.P.; Hopkins, D.L. Meat packaging solutions to current industry challenges: A review. Meat Sci. 2018, 144, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Martino, P.A.; Cagnardi, P.; Celano, G.; Tedesco, D.; Castrica, M.; Balzaretti, C.; Chiesa, L.M. Feasibility of biodegradable based packaging used for red meat storage during shelf-life: A pilot study. Food Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopacka, J.; Półtorak, A.; Wierzbicka, A. Effect of MAP, vacuum skin-pack and combined packaging methods on physicochemical properties of beef steaks stored up to 12 days. Meat Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillin, K.W. Where is MAP Going? A review and future potential of modified atmosphere packaging for meat. Meat Sci. 2008, 90, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoni, C.G.; Espitia, P.J.P.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; McHugh, T.H. Trends in antimicrobial food packaging systems: Emitting sachets and absorbent pads. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahvenainen, R. Novel Food Packaging Techniques; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; ISBN 9781855736757. [Google Scholar]
- Appendini, P.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Review of antimicrobial food packaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.; Doyle, R.J.; Rosenberg, M. Mechanism of enhancement of microbial cell hydrophobicity by cationic polymers. J. Bacteriol. 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daifas, D.P.; Smith, J.P.; Tarte, I.; Blanchfield, B.; Austin, J.W. Effect of ethanol vapor on growth and toxin production by Clostridium botulinum in a high moisture bakery product. J. Food Saf. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Marcelino, F.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.; Estevinho, L.; Bento, A.; Pereira, J.A. Phenolic compounds and antimicrobial activity of olive (Olea europaea L. Cv. Cobrançosa) leaves. Molecules 2007, 12, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.; Picouet, P.; Lloret, E. Reduction of the spoilage-related microflora in absorbent pads by silver nanotechnology during modified atmosphere packaging of beef meat. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 2263–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Stratakos, A.C. Application of modified atmosphere packaging and active/smart technologies to red meat and poultry: A review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1423–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Patel, D.; Kim, J.E.; Min, S.C. Retardation of Listeria monocytogenes growth in mozzarella cheese using antimicrobial sachets containing rosemary oil and thyme oil. J. Food Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Optimizing the use of garlic oil as antimicrobial agent on fresh-cut tomato through a controlled release system. J. Food Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.A.A.; Soares, N.D.F.F.; Polito, T.D.O.S.; Sousa, M.M.D.; Silva, D.F.P. Sachês antimicrobianos em pós-colheita de manga. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G. Digital Color Imaging Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781420041484. [Google Scholar]
- Castrica, M.; Menchetti, L.; Balzaretti, C.M.; Branciari, R.; Ranucci, D.; Cotozzolo, E.; Vigo, D.; Curone, G.; Brecchia, G.; Miraglia, D. Impact of dietary supplementation with goji berries (lycium barbarum) on microbiological quality, physico-chemical, and sensory characteristics of rabbit meat. Foods 2020, 9, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; García-López, M.L.; Santos, J.A.; Otero, A. Development of the aerobic spoilage flora of chilled rabbit meat. Meat Sci. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Ghaly, A.E. Meat spoilage mechanisms and preservation techniques: A critical review. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustman, C.; Cassens, R.G. The biochemical basis for discoloration in fresh meat: A review. J. Muscle Foods 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyamkondan, S.; Jayas, D.S.; Holley, R.A. Review of centralized packaging systems for distribution of retail-ready meet. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renerre, M. Oxidative processes and myoglobin. In Antioxidants in Muscle Foods: Nutritional Strategies to Improve Quality; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-471-31454-4. [Google Scholar]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Tsitsika, E.V.; Panagiotaki, P. Implementation of quality control methods (physicochemical, microbiological and sensory) in conjunction with multivariate analysis towards fish authenticity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Holley, R.A. Antimicrobial and antioxidative strategies to reduce pathogens and extend the shelf life of fresh red meats. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.P. Instrumental assessment of the sensory quality of meat, poultry and fish. Instrum. Assess. Food Sens. Qual. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F.; Nychas, G.J.E. Spoilage microbiota associated to the storage of raw meat in different conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Stamatiou, A.; Skandamis, P.; Nychas, G.J.E. Development of a microbial model for the combined effect of temperature and pH on spoilage of ground meat, and validation of the model under dynamic temperature conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Skandamis, P.N.; Tassou, C.C.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Meat spoilage during distribution. Meat Sci. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corry, J.E.L. Spoilage organisms of red meat and poultry. In Microbiological Analysis of Red Meat, Poultry and Eggs: A Volume in Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 9781845690595. [Google Scholar]
- Nychas, G.J.E.; Skandamis, P.N. Fresh meat spoilage and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP). In Improving the Safety of Fresh Meat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Nederlanden, 2005; ISBN 9781855739550. [Google Scholar]
- Ercolini, D.; Casaburi, A.; Nasi, A.; Ferrocino, I.; Di Monaco, R.; Ferranti, P.; Mauriello, G.; Villani, F. Different molecular types of Pseudomonas fragi have the same overall behaviour as meat spoilers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Domingues, F.C.; Nerín, C. Control microbial growth on fresh chicken meat using pinosylvin inclusion complexes based packaging absorbent pads. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Qiao, M.; Huang, T.S.; Weese, J.; Ren, X. Efficacy of N-halamine compound on reduction of microorganisms in absorbent food pads of raw beef. Food Control 2018, 84, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Warner, R.D.; Johnson, S.K. Active and intelligent packaging in meat industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, V. Bioactive packaging technologies for extended shelf life of meat-based products. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, J.P.; O’Grady, M.N.; Hogan, S.A. Past, current and potential utilisation of active and intelligent packaging systems for meat and muscle-based products: A review. Meat Sci. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintavalla, S.; Vicini, L. Antimicrobial food packaging in meat industry. Meat Sci. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, C.E.; Marcos, B. Active and intelligent packaging systems for a modern society. Meat Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).