An Italian Innovative Small-Scale Approach to Promote the Conscious Consumption of Healthy Food
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
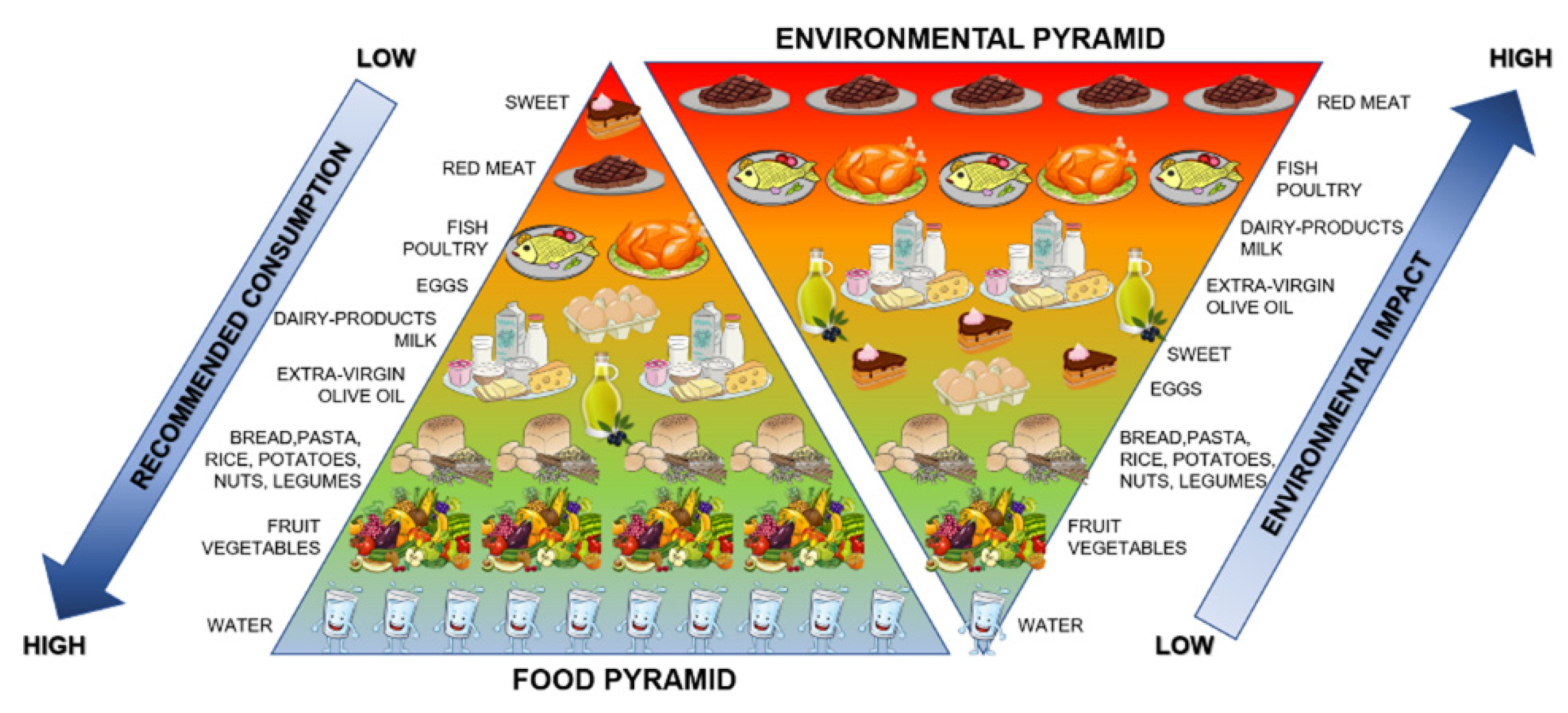
2.1. Description of SANI General Approach
2.2. Evaluation of Specific Nutritional Molecules and Chemical Food Contaminants in Selected Products
2.3. Assessment of the Environmental Impact in Selected Products
2.4. Identification of Health Claims and Development of SANI Labels
2.5. Determination of Customer Shopping Habits
2.6. SANI Approach Communication, Dissemination and Marketing Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions and Implications
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature 2014, 515, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas Garciá-Dorado, S.; Cornselsen, L.; Smith, R.; Walls, H. Economic globalization, nutrition and health: A review of quantitative evidence. Global. Health 2019, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, M.J.; Van Dael, P.; Eggersdorfer, M. The Role of Nutrients in Reducing the Risk for Noncommunicable Diseases during Aging. Nutrients 2019, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavan, C.R.; Noor, R.A.; Golden, C.D.; Juma, C.; Fawzi, W. Sustainable food systems for optimal planetary health. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 111, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.A.; Springmann, M.; Hill, J.; Tilman, D. Multiple health and environmental impacts of foods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23357–23362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitiello, V.; Germani, A.; Capuzzo Dolcetta, E.; Donini, L.M.; del Balzo, V. The new modern mediterranean diet italian pyramid. Ann. Ig. 2016, 28, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, R.; Cacciabaudo, F.; Damiano, G.; Palumbo, V.D.; Gioviale, M.C.; Bellavia, M.; Tomasello, G.; Lo Monte, A.I. The mediterranean diet: A history of health. Iran. J. Public Health 2013, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Fresán, U.; Bes-rastrollo, M.; Marventano, S.; Galvano, F. Environmental impact of dietary choices: Role of the mediterranean and other dietary patterns in an Italian cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lăcătușu, C.M.; Grigorescu, E.D.; Floria, M.; Onofriescu, A.; Mihai, B.M. The mediterranean diet: From an environment-driven food culture to an emerging medical prescription. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruini, L.F.; Ciati, R.; Pratesi, C.A.; Marino, M.; Principato, L.; Vannuzzi, E. Working toward Healthy and Sustainable Diets: The “Double Pyramid Model” Developed by the Barilla Center for Food and Nutrition to Raise Awareness about the Environmental and Nutritional Impact of Foods. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnowski, A.; Finley, J.; Hess, J.M.; Ingram, J.; Miller, G.; Peters, C. Toward Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttriss, J.; Stanner, S.; McKevith, B.; Nugent, A.P.; Kelly, C.; Phillips, F.; Theobald, H.E. Successful ways to modify food choice: Lessons from the literature. Nutr. Bull. 2004, 29, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Crawford, C.; Ly, L. Human food choice and nutritional interventions. Nutr. Bull. 2013, 38, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, S.J.; Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C.; Chatzisarantis, N.L.D. Food choice and nutrition: A social psychological perspective. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8712–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. An umbrella review of systematic reviews on food choice and nutrition published between 2017 and-2019. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunneram, Y.; Jeewon, R. Determinants of eating habits among older adults. Prog. Nutr. 2015, 17, 274–283. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.A.M.; Thorndike, A.N.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Van Horn, L.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Foraker, R.; Spees, C. Innovation to Create a Healthy and Sustainable Food System: A Science Advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, L.; Cordeiro-Netto, O.; Oweis, T.; Ringler, C.; Schreiner, B.; Varghese, S. The High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security HLPE; Technical Report for Nutrition and Food Systems: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, M.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Glass, T.A.; Caballero, B.; Brancati, F.L. Neighborhood characteristics and availability of healthy foods in Baltimore. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2008, 35, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, D.F.M.; Belon, A.P.; Marín-León, L.; Do Nascimento Jacinto de Souza, B.F.; Pérez-Escamilla, R.; Segall-Corrêa, A.M. Comparing food environment and food purchase in areas with low and high prevalence of obesity: Data from a mapping, in-store audit, and population-based survey. Cad. Saude Publica 2019, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, K.; Yaroch, A.L. Strategies for increasing fruit and vegetable intake in grocery stores and communities: Policy, pricing, and environmental change. Prev. Med. Baltim. 2004, 39, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visioli, F.; Franco, M.; Toledo, E.; Luchsinger, J.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Olive oil and prevention of chronic diseases: Summary of an International conference. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.B.; Shashank, A.; Gasevic, D.; Schuurman, N.; Poirier, P.; Teo, K.; Rangarajan, S.; Yusuf, S.; Lear, S.A. The Local Food Environment and Obesity: Evidence from Three Cities. Obesity 2020, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.S.; Ghosh, D.; Page, M.; Wolff, M.; McMinimee, K.; Zhang, M. What role do local grocery stores play in urban food environments? A case study of Hartford-Connecticut. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cueto, F.J.A.; Olsen, A. The Multifaceted Dimensions of Food Choice and Nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, I.; Di Tomo, P.; Di Pietro, N.; Mandatori, D.; Pipino, C.; Formoso, G.; Napolitano, A.; Palumbo, A.; Pandolfi, A. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Marine Ovothiol A in an In Vitro Model of Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Hyperglycemia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tomo, P.; Canali, R.; Ciavardelli, D.; Di Silvestre, S.; De Marco, A.; Giardinelli, A.; Pipino, C.; Di Pietro, N.; Virgili, F.; Pandolfi, A. β-Carotene and lycopene affect endothelial response to TNF-α reducing nitro-oxidative stress and interaction with monocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, N.; Di Tomo, P.; Pandofi, A. Carotenoids in cardiovascular disease prevention. JSM Atheroscler 2016, 1, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Ucci, M.; Di Tomo, P.; Tritschler, F.; Cordone, V.G.P.; Lanuti, P.; Bologna, G.; Di Silvestre, S.; Di Pietro, N.; Pipino, C.; Mandatori, D.; et al. Anti-inflammatory Role of Carotenoids in Endothelial Cells Derived from Umbilical Cord of Women Affected by Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignani, A.G.; Ciaccheri, L.; Ottevaere, H.; Thienpont, H.; Conte, L.; Marega, M.; Cichelli, A.; Attilio, C.; Cimato, A. Visible and near-infrared absorption spectroscopy by an integrating sphere and optical fibers for quantifying and discriminating the adulteration of extra virgin olive oil from Tuscany. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Boccio, P.; Rossi, C.; di Ioia, M.; Cicalini, I.; Sacchetta, P.; Pieragostino, D. Integration of metabolomics and proteomics in multiple sclerosis: From biomarkers discovery to personalized medicine. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberatore, L.; Procida, G.; D’Alessandro, N.; Cichelli, A. Solid-phase extraction and gas chromatographic analysis of phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichelli, A.; Riciputi, Y.; Cerretani, L.; Caboni, M.F.; d’Alessandro, N. Glycidols Esters, 2-Chloropropane-1,3-Diols, and 3-Chloropropane-1,2-Diols Contents in Real Olive Oil Samples and their Relation with Diacylglycerols. JAOCS, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2020, 97, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadangi, F.; Azzi, A. Vitamin E—The Next 100 Years. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, W. Dietary Polyphenols—Important Non-Nutrients in the Prevention of Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases. A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Carlo, M.; Fusella, G.C.; Pepe, A.; Sergi, M.; Di Martino, M.; Mascini, M.; Martino, G.; Cichelli, A.; Di Natale, C.; Compagnone, D. Novel oligopeptides based e-nose for food quality control: Application to extra-virgin olive samples. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crop. Foods 2014, 6, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, J. Determination of bound 2,3-epoxy-1-propanol (glycidol) and bound monochloropropanediol (MCPD) in refined oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, S.; Appel, K.E.; Lampen, A. Toxicology, occurrence and risk characterisation of the chloropropanols in food: 2-Monochloro-1,3-propanediol, 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol and 2,3-dichloro-1-propanol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwagerman, R.; Overman, P. A novel method for the automatic sample preparation and analysis of 3-MCPD-, 2-MCPD-, and glycidylesters in edible oils and fats. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattara, C.; Salomone, R.; Cichelli, A. Carbon footprint of extra virgin olive oil: A comparative and driver analysis of different production processes in Centre Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattara, C.; Russo, C.; Antrodicchia, V.; Cichelli, A. Carbon footprint as an instrument for enhancing food quality: Overview of the wine, olive oil and cereals sectors. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Parliament & Council Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 of the European Parliament and the of the Council on nutrition and health claims made on foods. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 404, 9–25.
- Cheng, W.W.; Liu, G.Q.; Wang, L.Q.; Liu, Z.S. Glycidyl Fatty Acid Esters in Refined Edible Oils: A Review on Formation, Occurrence, Analysis, and Elimination Methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, S.; Begley, T.H.; Diachenko, G.W. Occurrence of 3-MCPD and glycidyl esters in edible oils in the United States. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 2081–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerretani, L.; Giuliani, A.; Maggio, R.M.; Bendini, A.; Toschi, T.G.; Cichelli, A. Rapid FTIR determination of water, phenolics and antioxidant activity of olive oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, F.; Falcone, G.; Stillitano, T.; De Luca, A.I.; Gulisano, G.; Mistretta, M.; Strano, A. Life cycle assessment of olive oil: A case study in southern Italy. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.; Barbanera, M.; Lascaro, E. Assessment of carbon footprint and energy performance of the extra virgin olive oil chain in Umbria, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Borghi, A.; Gallo, M.; Strazza, C.; Del Borghi, M. An evaluation of environmental sustainability in the food industry through Life Cycle Assessment: The case study of tomato products supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 78, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, G.; Ridoutt, B.; Bellotti, B. Carbon and water footprint tradeoffs in fresh tomato production. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 32, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhart, M.; Penker, M.; Schmid, E. Sustainable local food production and consumption: Challenges for implementation and research. Outlook Agric. 2009, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Wolf, J.; Corvalán, C.; Neville, T.; Bos, R.; Neira, M. Diseases due to unhealthy environments: An updated estimate of the global burden of disease attributable to environmental determinants of health. J. Public Health 2017, 39, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, A.; Vecchio, R. Organic Farming and Sustainability in Food Choices: An Analysis of Consumer Preference in Southern Italy. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.A.C.; Lesser, L.I.L. I HHS Public Access. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson Blight, K. Can Asylum Seeking Be ‘Managed’ Ethically? In Public Health Ethics: Cases Spanning the Globe; Barrett, D.H., Bolan, G., Dawson, A., Ortmann, L., PAHO, C.S., Eds.; Springer: Gewerbestr, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vo-Nguyen, B.Q.; Kong, H.Y. Symbol Error Rate expression for decode-and-forward relaying using generalized selection combining over Rayleigh fading channels. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2009, E92-B, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyomard, H.; Darcy-Vrillon, B.; Esnouf, C.; Marin, M.; Russel, M.; Guillou, M. Eating patterns and food systems: Critical knowledge requirements for policy design and implementation. Agric. Food Secur. 2012, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egnell, M.; Ducrot, P.; Touvier, M.; Allès, B.; Hercberg, S.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Julia, C. Objective understanding of Nutri-Score Front-Of-Package nutrition label according to individual characteristics of subjects: Comparisons with other format labels. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmon, N.; Vieux, F.; Maillot, M.; Volatier, J.L.; Martin, A. Nutrient profiles discriminate between foods according to their contribution to nutritionally adequate diets: A validation study using linear programming and the SAIN, LIM system. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostaghel, R.; Oghazi, P. Elderly and technology tools: A fuzzyset qualitative comparative analysis. Qual. Quant. 2017, 51, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| PRODUCT | Vitamin E | Polyphenols | β-Carotene | Lycopene | 2-MCDP 3-MCDP Glycidol | CO2eq/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVOO | 229.5 mg/kg | 360 mg/kg | --- | --- | absence | 1.2 kg |
| Tomato sauce | 1.14 mg/100 g | --- | 0.12 mg/100 g | 7.57 mg/100 g | absence | 1.3 kg |
| 1. Are you …? | A) Female |
| B) Male | |
| 2. What is your occupation? | A) A professional |
| B) An employee | |
| C) An entrepreneur | |
| D) Other | |
| 3. Age | A) 25–30 |
| B) 31–40 | |
| C) 41–50 | |
| D) 51–60 | |
| E) 61–70 | |
| F) Other | |
| 4. What do you think about natural products? | A) I think they are good for my health |
| B) I think I should consume them or use them every day | |
| C) I think it is okay if I consume them or use them occasionally | |
| D) I think industrial products convince me more | |
| E) Other | |
| 5. What does natural food mean to you? | A) Whole food, without any human intervention |
| B) Organic food | |
| D) Natural, thus you can trust it | |
| E) A new way to sell products | |
| F) Other | |
| 6. What would you do to live in a state of wellness? | A) I would go to a beauty center |
| B) I would go to a gym | |
| C) I would go on holiday in a farmhouse or in a spa | |
| D) I would use natural products for my diet and/or my esthetic | |
| E) Other |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Formoso, G.; Pipino, C.; Baldassarre, M.P.A.; Del Boccio, P.; Zucchelli, M.; D’Alessandro, N.; Tonucci, L.; Cichelli, A.; Pandolfi, A.; Di Pietro, N. An Italian Innovative Small-Scale Approach to Promote the Conscious Consumption of Healthy Food. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165678
Formoso G, Pipino C, Baldassarre MPA, Del Boccio P, Zucchelli M, D’Alessandro N, Tonucci L, Cichelli A, Pandolfi A, Di Pietro N. An Italian Innovative Small-Scale Approach to Promote the Conscious Consumption of Healthy Food. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(16):5678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165678
Chicago/Turabian StyleFormoso, Gloria, Caterina Pipino, Maria Pompea Antonia Baldassarre, Piero Del Boccio, Mirco Zucchelli, Nicola D’Alessandro, Lucia Tonucci, Angelo Cichelli, Assunta Pandolfi, and Natalia Di Pietro. 2020. "An Italian Innovative Small-Scale Approach to Promote the Conscious Consumption of Healthy Food" Applied Sciences 10, no. 16: 5678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165678
APA StyleFormoso, G., Pipino, C., Baldassarre, M. P. A., Del Boccio, P., Zucchelli, M., D’Alessandro, N., Tonucci, L., Cichelli, A., Pandolfi, A., & Di Pietro, N. (2020). An Italian Innovative Small-Scale Approach to Promote the Conscious Consumption of Healthy Food. Applied Sciences, 10(16), 5678. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165678












