A Membership-Fusing Model for Characterizing the Shift of Methanogen Community in a Three-Stage Sludge-Treatment Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
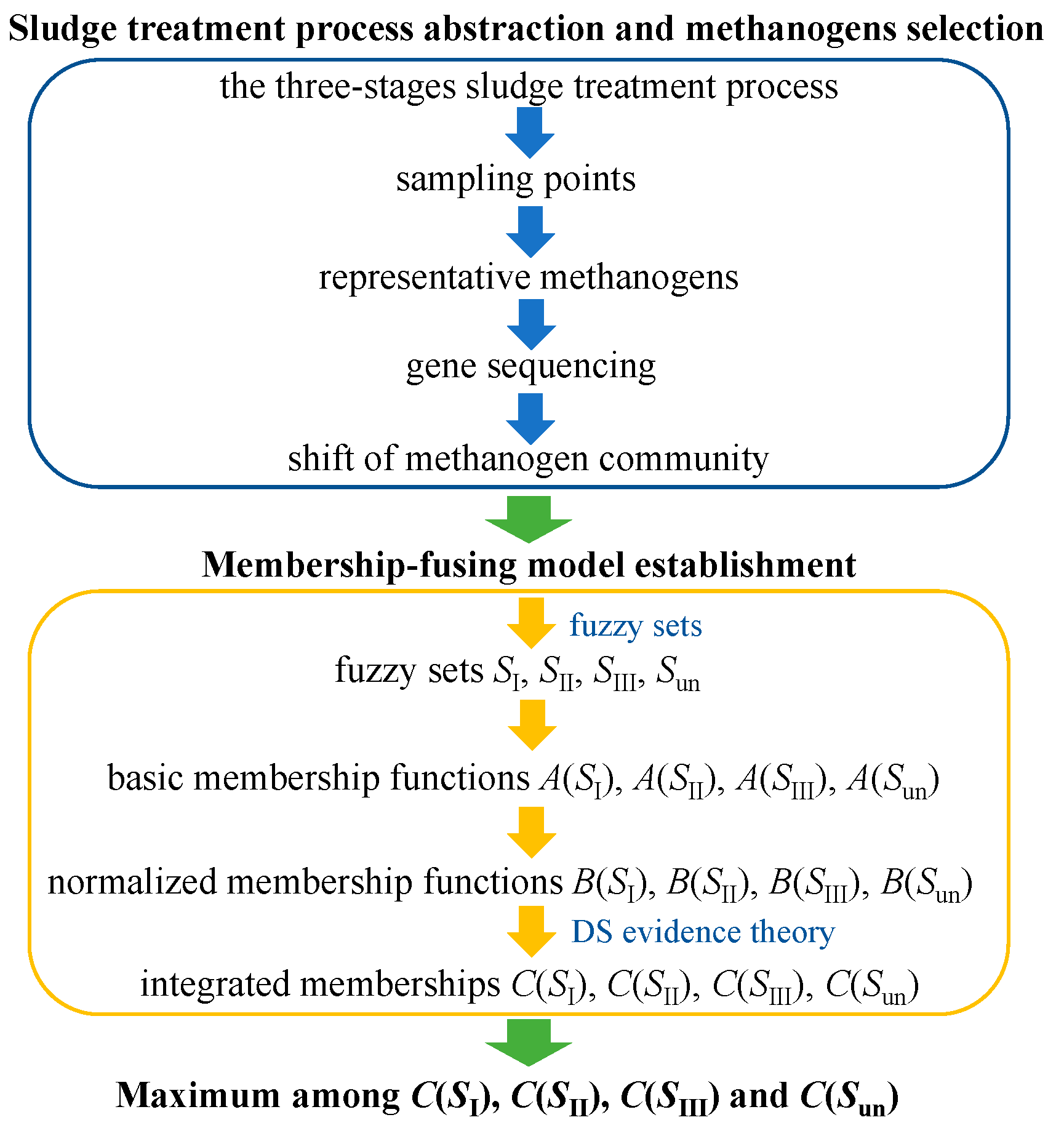
2. Membership-Fusing Model of Sludge-Treatment Process
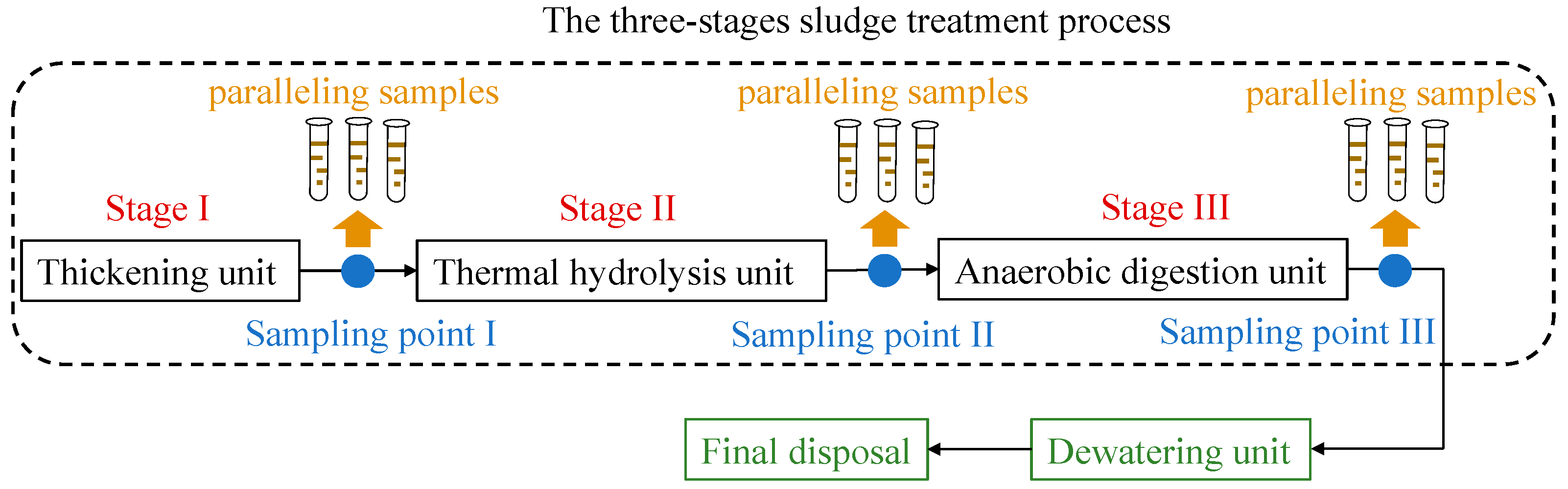
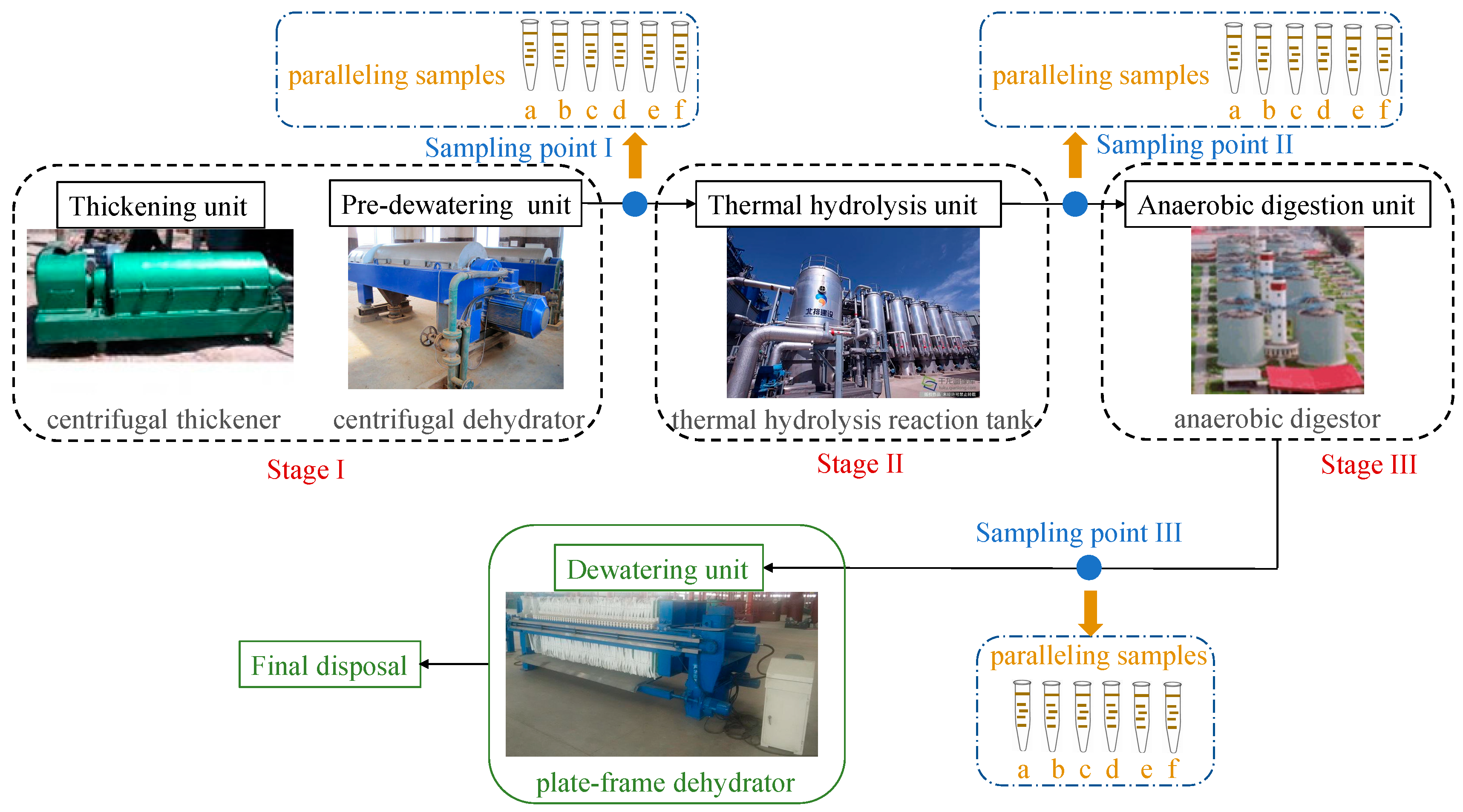
2.1. Sludge-Treatment Process and Representative Methanogen
2.2. Membership-Fusing Model
3. Experiment and Parameter Setup
3.1. Sampling Scheme
3.2. High-throughput Sequencing Technology
3.2.1. DNA Extraction
3.2.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification, Sequencing, Quantification
3.2.3. Sequence Analysis
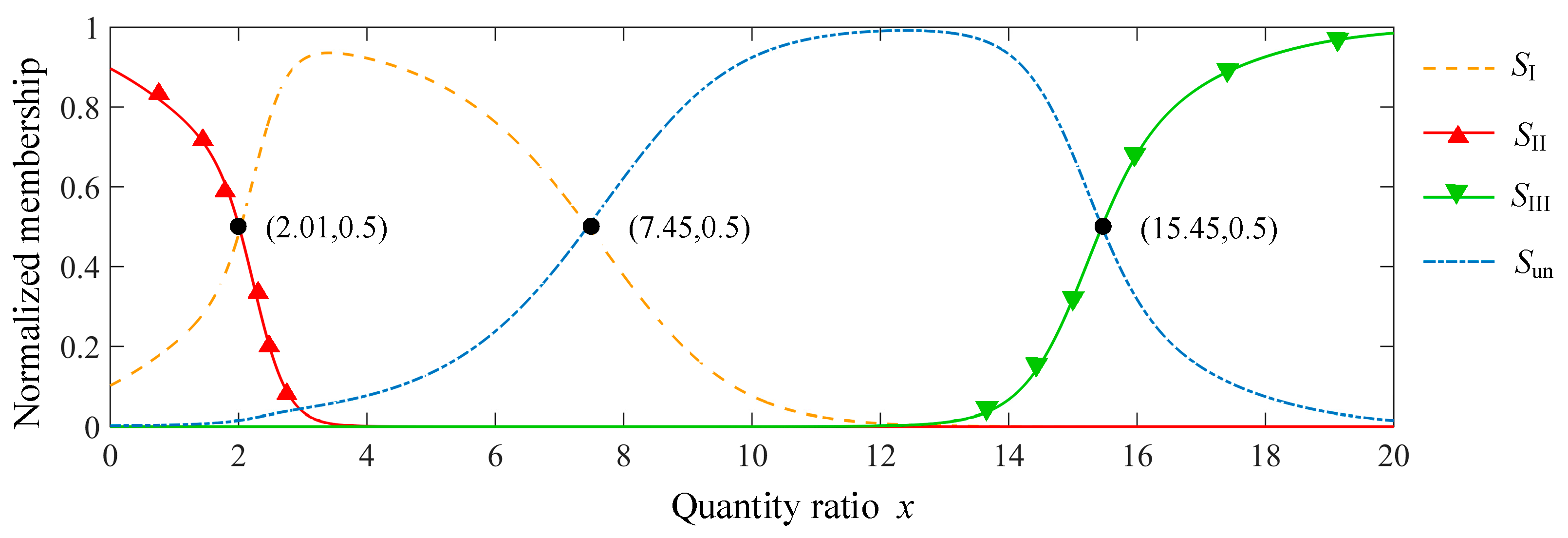
3.3. Model Parameter
4. Results and Discussion
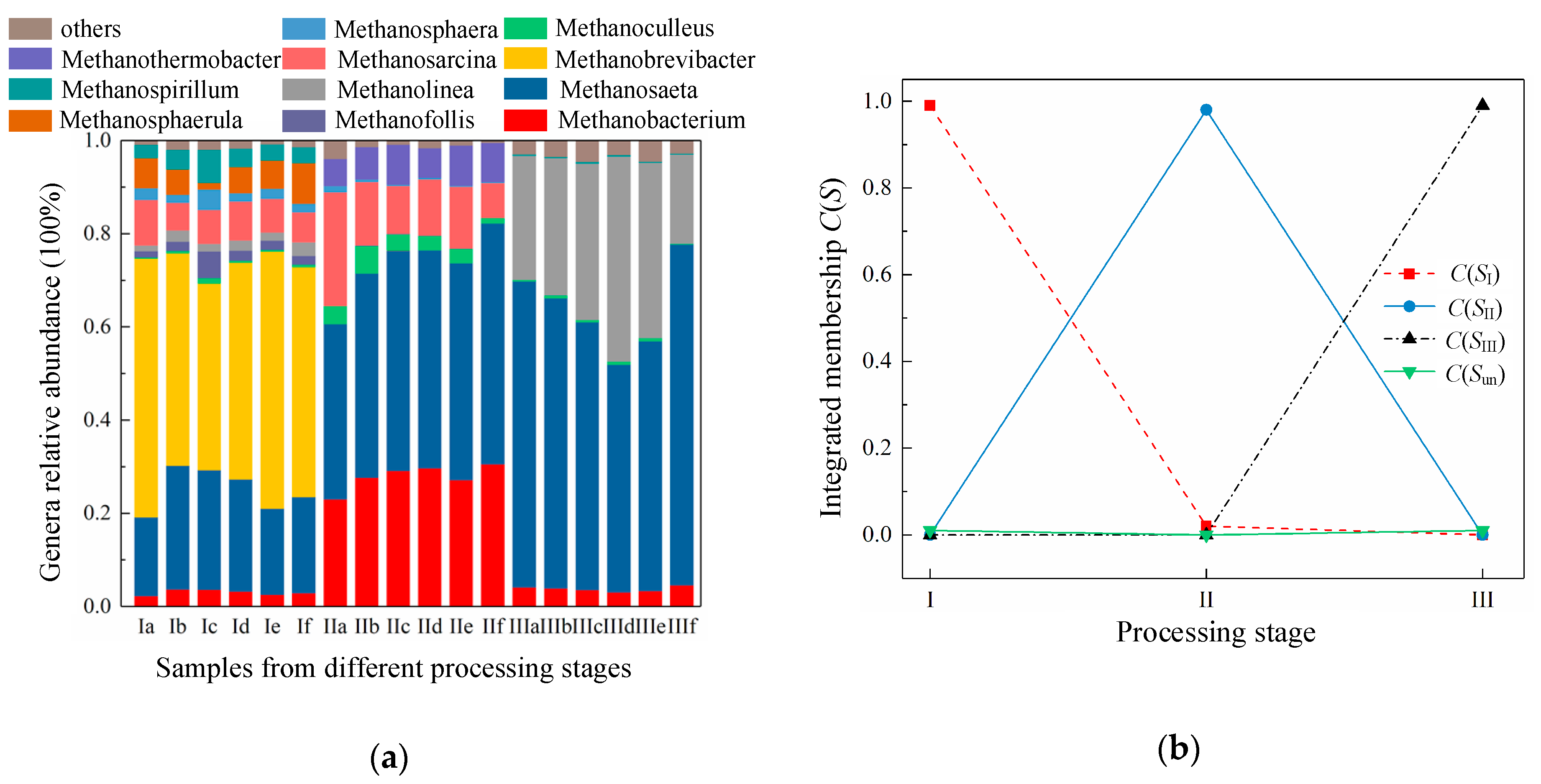
4.1. Variation of Membership of Different Stage
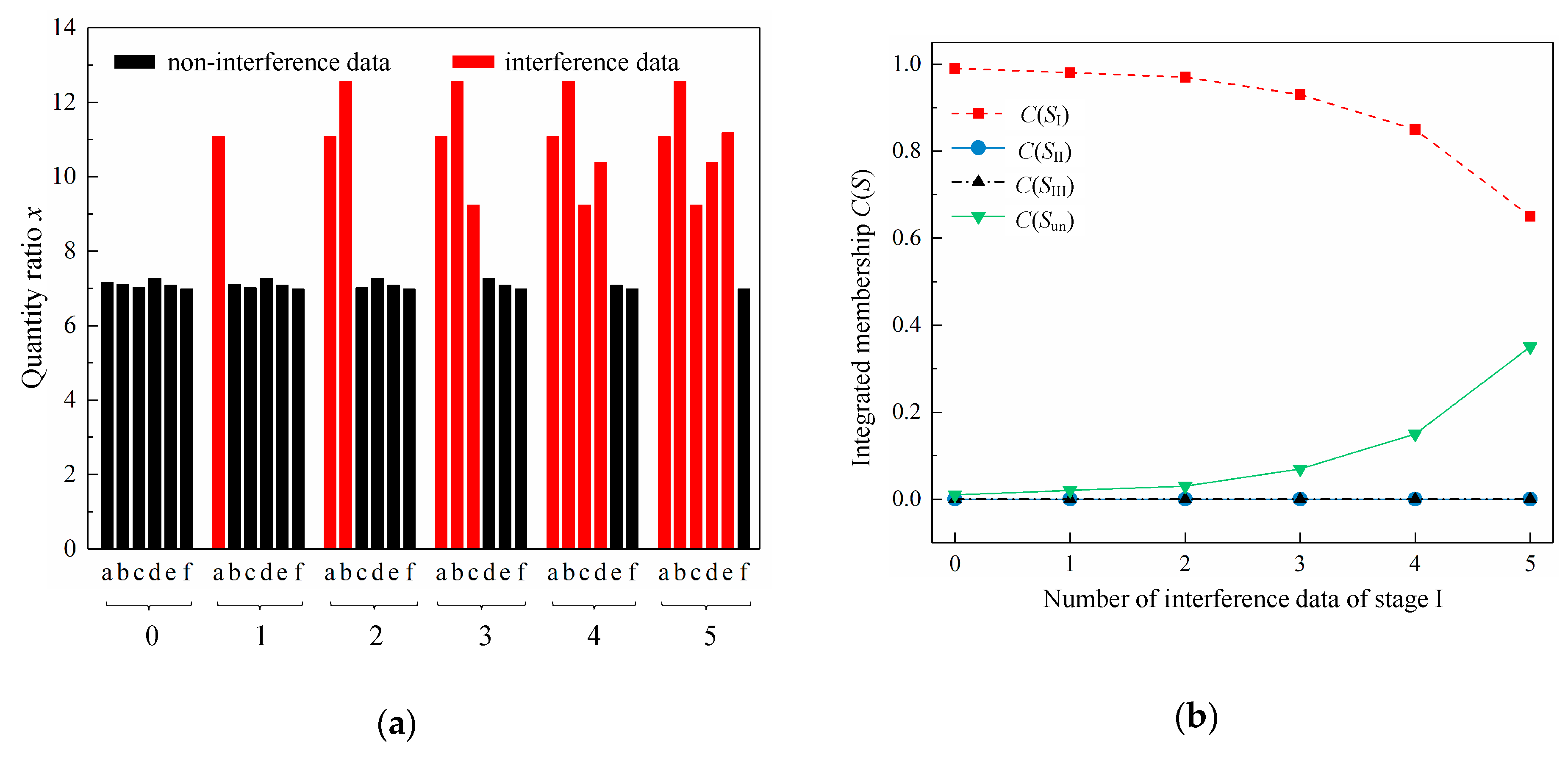
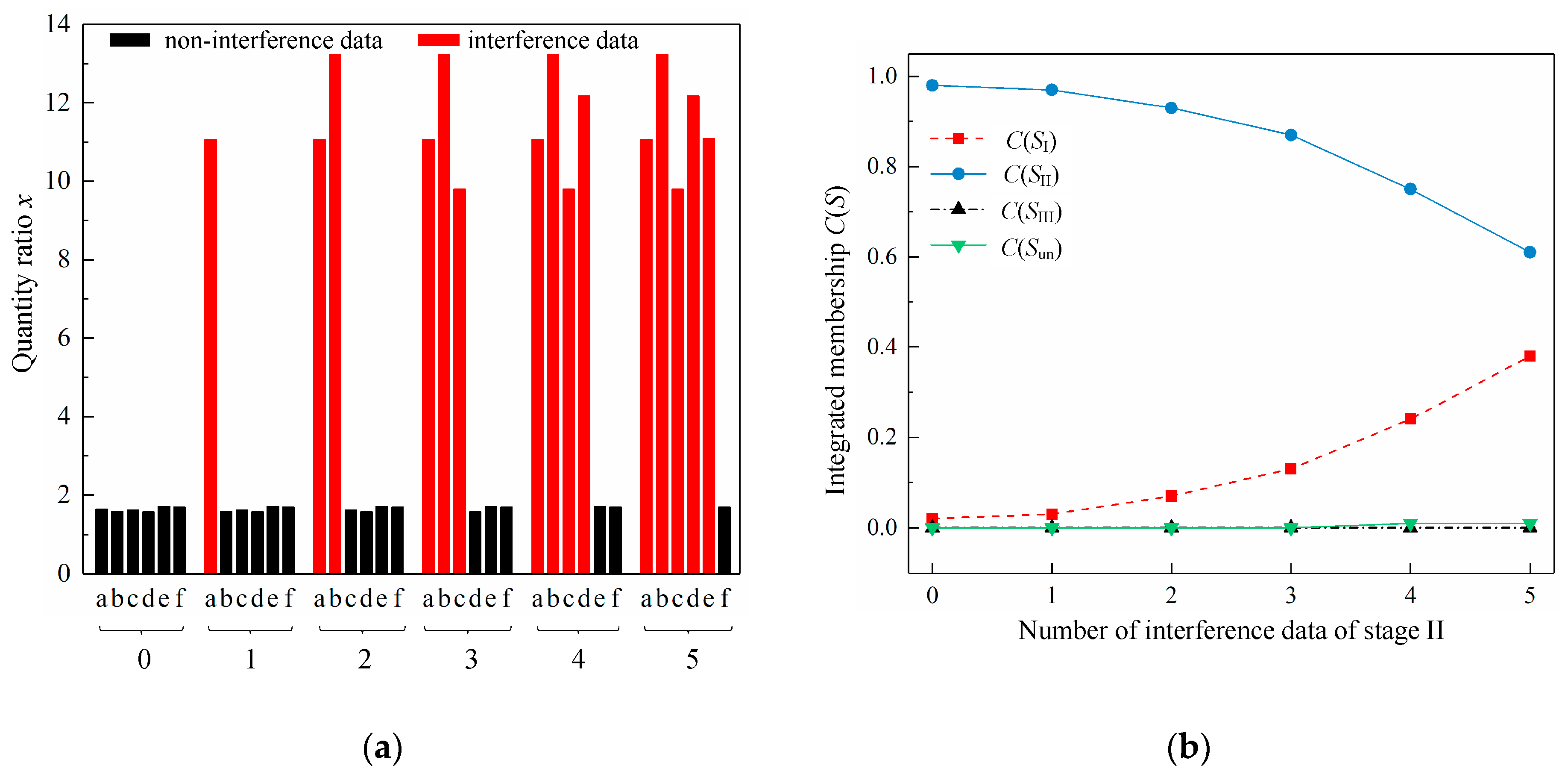
4.2. Variation of Membership with Different Number of Interference Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. Current state of sludge production, management, treatment, and disposal in China. Water Res. 2015, 78, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, Q.; Matsumoto, S.; Maeda, T.; Ogawa, H.I. Isolation, identification of sludge-lysing strain and its utilization in thermophilic aerobic digestion for waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2475–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadier, A.; Simayi, Y.; Abdeshahian, P.; Azman, N.F.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Kalil, M.S. A comprehensive review of microbial electrolysis cells (MEC) reactor designs and configurations for sustainable hydrogen gas production. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batstone, D.J.; Virdis, B. The role of anaerobic digestion in the emerging energy economy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Cho, S.-K.; Lee, J.; Hwang, K.; Chung, J.; Jang, H.-N.; Shin, S.G. Performance and Microbial Community Dynamics in Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge: Impact of Immigration. Energies 2019, 12, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samadder, S.R. Performance evaluation of anaerobic digestion technology for energy recovery from organic fraction of municipal solid waste: A review. Energy 2020, 197, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejerizo, G.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Maus, I.; Wibberg, D.; Winkler, A.; Off, S.; Pühler, A.; Scherer, P.; Schlüter, A. Genome sequence of Methanobacterium congolense strain Buetzberg, a hydrogenotrophic, methanogenic archaeon, isolated from a mesophilic industrial-scale biogas plant utilizing bio-waste. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 247, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, A.S.; Stensel, H.D.; Ferguson, J.F. The Growth Kinetics and Competition Between Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta in Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2005, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, S.F.; Stuckey, D.C. Integrated model of the production of soluble microbial products (SMP) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in anaerobic chemostats during transient conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 38, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacławek, S.; Grübel, K.; Silvestri, D.; Padil, V.V.T.; Wacławek, M.; Černík, M.; Varma, R.S. Disintegration of Wastewater Activated Sludge (WAS) for Improved Biogas Production. Energies 2018, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrońska, I.; Cybulska, K. Quantity and Quality of Biogas Produced from the Poultry Sludge Optimized by Filamentous Fungi. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2018, 25, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grübel, K.; Machnicka, A.; Wacławek, S. Impact of Alkalization of Surplus Activated Sludge on Biogas Production. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2013, 20, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Polanco, D.; Tatsumi, H. Optimum energy integration of thermal hydrolysis through pinch analysis. Renew. Energy 2016, 96, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, U.; Machenbach, I.; Weisz, N.; Solheim, O.E. Enhanced stabilisation of sewage sludge through thermal Hydrolysis—Three years of experience with full scale plant. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitamo, T.M.; Treu, L.; Boldrin, A.; Sartori, C.; Angelidaki, I.; Scheutz, C. Microbial population dynamics in urban organic waste anaerobic co-digestion with mixed sludge during a change in feedstock composition and different hydraulic retention times. Water Res. 2017, 118, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.A.; Wickham, R.; Nguyen, L.N.; Phan, H.V.; Galway, B.; Bustamante, H.; Nghiem, L.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Bustamante, H. Impact of anaerobic co-digestion between sewage sludge and carbon-rich organic waste on microbial community resilience. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balch, W.E.; Fox, G.E.; Magrum, L.J.; Woese, C.R.; Wolfe, R.S. Methanogens: A re-evaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol. Rev. 1979, 43, 260–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, B.; Scherer, P. The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach-Wiśniewska, A.; Ciesielski, S.; Bacza, T.; Pieczykolan, M.; Ziembinska-Buczynska, A. Microbial community composition and methanogens’ biodiversity during a temperature shift in a methane fermentation chamber. Environ. Technol. 2018, 40, 3252–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.B.; Wilson, D.B. Why Are Ruminal Cellulolytic Bacteria Unable to Digest Cellulose at Low pH? J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romsaiyud, A.; Songkasiri, W.; Nopharatana, A.; Chaiprasert, P. Combination effect of pH and acetate on enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; McAdam, E.; Zhang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Longhurst, P. Ammonia inhibition and toxicity in anaerobic digestion: A critical review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.T.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Luo, X.Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of straw on microbial community composition and degradation efficiency of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sludge digester. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 7973–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.; Yulisa, A.; Hwang, S. Microbial community structure in full scale anaerobic mono-and co-digesters treating food waste and animal waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Li, A.; Zhang, L.; Li, R.; Yang, T.; Xing, W. Mechanism of process imbalance of long-term anaerobic digestion of food waste and role of trace elements in maintaining anaerobic process stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valo, A.; Carrere, H.; Delgenes, J.P. Thermal, chemical and thermo-chemical pre-treatment of waste activated sludge for anaerobic digestion. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graja, S.; Chauzy, J.; Fernandes, P.; Patria, L.; Cretenot, D. Reduction of sludge production from WWTP using thermal pretreatment and enhanced anaerobic methanisation. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougrier, C.; Delgenès, J.P.; Carrere, H. Combination of Thermal Treatments and Anaerobic Digestion to Reduce Sewage Sludge Quantity and Improve Biogas Yield. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2006, 84, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fdz-Polanco, M.; Velazquez, R.; Pérez-Elvira, S.I.; Casas, C.; del Barrio, D.; Cantero, F.J.; Rodríguez, P.; Panizo, L.; Serrat, J.; Rouge, P.; et al. Continuous thermal hydrolysis and energy integration in sludge anaerobic digestion plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, W.P.F. Thermal hydrolysis for sewage treatment: A critical review. Water Res. 2016, 104, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerholm, M.; Castillo, M.; Andersson, A.C.; Nilsen, P.J.; Schnürer, A. Effects of thermal hydrolytic pre-treatment on biogas process efficiency and microbial community structure in industrial- and laboratory-scale digesters. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh, L. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas, G.; Diamantis, D.E.; Kalozoumis, P.; Iakovidis, D. Uncertainty-Aware Visual Perception System for Outdoor Navigation of the Visually Challenged. Sensors 2020, 20, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Niu, D. Application of Fuzzy and Rough Sets to Environmental Zonation for Concrete Durability: A Case Study of Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Deng, Y.; Hu, Y. DS-VIKOR: A new multi-criteria decision-making method for supplier selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 21, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, J. A Novel Evidence Conflict Measurement for Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Based on the Evidence Distance and Evidence Angle. Sensors 2020, 20, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wachemo, A.C.; Yuan, H.; Korai, R.M.; Li, X. Improving methane content and yield from rice straw by adding extra hydrogen into a two-stage anaerobic digestion system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumdhitiahutsawakul, L.; Jirachaisakdeacha, D.; Pholchan, P.; Pathom-aree, W.; Bovonsombut, S. Use of the PCR-DGGE technique to determine the microbial community in anaerobic activated sludges from biogas plants. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2019, 46, 444–455. [Google Scholar]
- Mccarty, P.L.; Smith, D.P. Anaerobic wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1986, 20, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, R. Holographic dark energy from nonadditive entropy: Cosmological perturbations and observational constraints. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.; Snyderman, N.; Verbeke, J. Analytical error bars and RSD for neutron multiplicity counting. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2018, 903, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titkanloo, H.N.; Keramati, A.; Fekri, R. Proposing a new model to aggregate ratings in multi-source feedback approach based on the evidence theory. Soft Comput. 2019, 24, 9479–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luton, P.E.; Wayne, J.M.; Sharp, R.J.; Riley, P.W. The mcrA gene as an alternative to 16S rRNA in the phylogenetic analysis of methanogen populations in landfill b bThe GenBank accession numbers for the mcrA sequences reported in this paper are AF414034–AF414051 (see Figure 2) and AF414007–AF414033 (environmental isolates in Figure 3). Microbiology 2002, 148, 3521–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liebner, S.; Alawi, M.; Ebenhöh, O.; Wagner, D. Taxonomic database, and cut-off value for processing mcrA gene 454 pyrosequencing data by MOTHUR. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 103, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, K.; Ren, G.; Pu, C.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, A. mcrA sequencing reveals the role of basophilic methanogens in a cathodic methanogenic community. Water Res. 2018, 136, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlovski, A.; Alric, M.; Brugère, J.-F. A putative new order of methanogenic Archaea inhabiting the human gut, as revealed by molecular analyses of the mcrA gene. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, L.; Li, H.; Yao, H. A Membership-Fusing Model for Characterizing the Shift of Methanogen Community in a Three-Stage Sludge-Treatment Process. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124274
Cai L, Li H, Yao H. A Membership-Fusing Model for Characterizing the Shift of Methanogen Community in a Three-Stage Sludge-Treatment Process. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(12):4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124274
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Linna, Hongyang Li, and Hong Yao. 2020. "A Membership-Fusing Model for Characterizing the Shift of Methanogen Community in a Three-Stage Sludge-Treatment Process" Applied Sciences 10, no. 12: 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124274
APA StyleCai, L., Li, H., & Yao, H. (2020). A Membership-Fusing Model for Characterizing the Shift of Methanogen Community in a Three-Stage Sludge-Treatment Process. Applied Sciences, 10(12), 4274. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124274



